PINK1/Parkin-Mediated Mitophagy Partially Protects against Inorganic Arsenic-Induced Hepatic Macrophage Polarization in Acute Arsenic-Exposed Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Inorganic Arsenic Up-Regulates Expression of Hepatic Macrophage Phenotypic Molecules and Chemokines in Mice
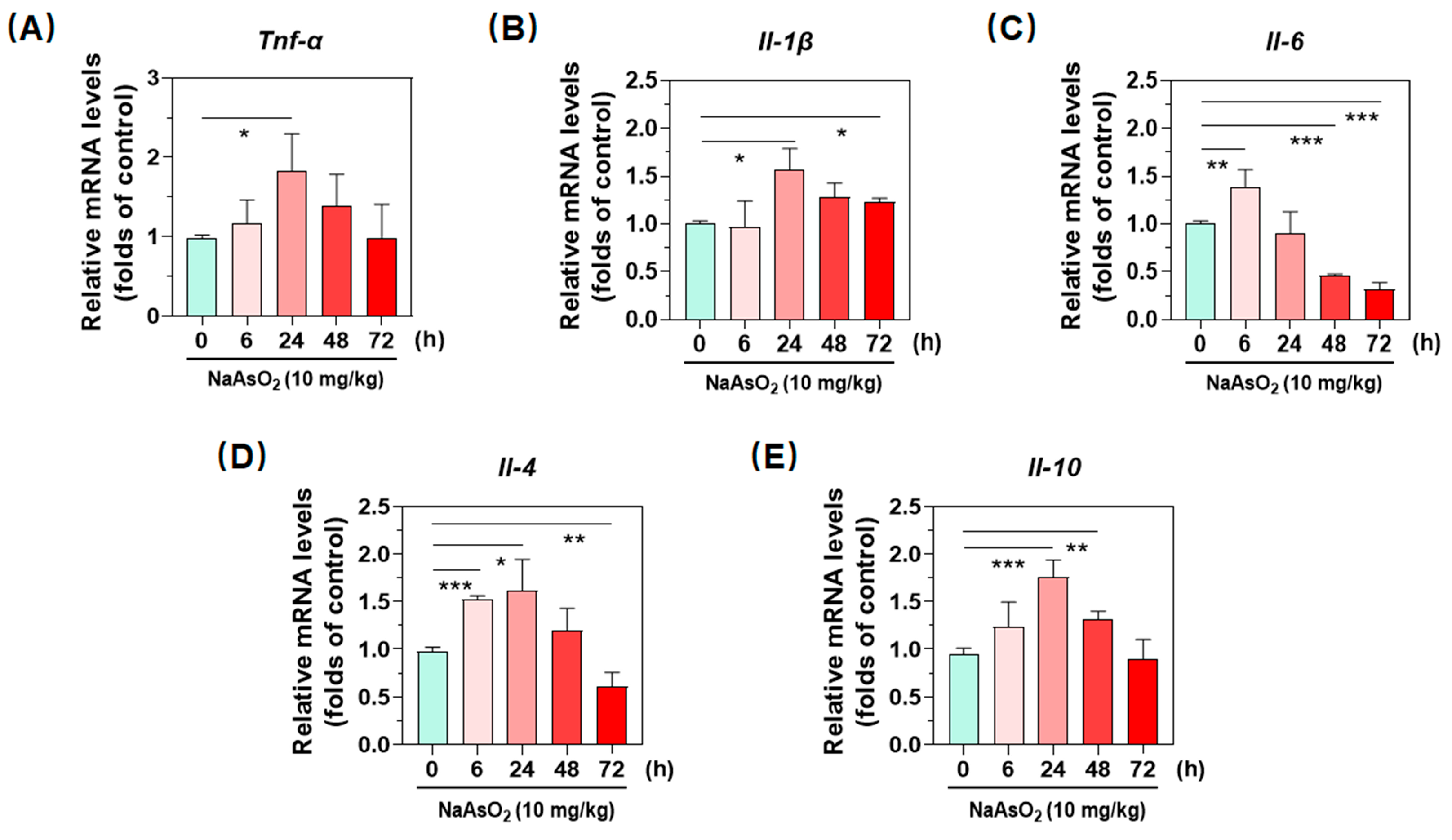
2.2. Inorganic Arsenic Induces Gene Expression of Hepatic Inflammatory Cytokines in Mice
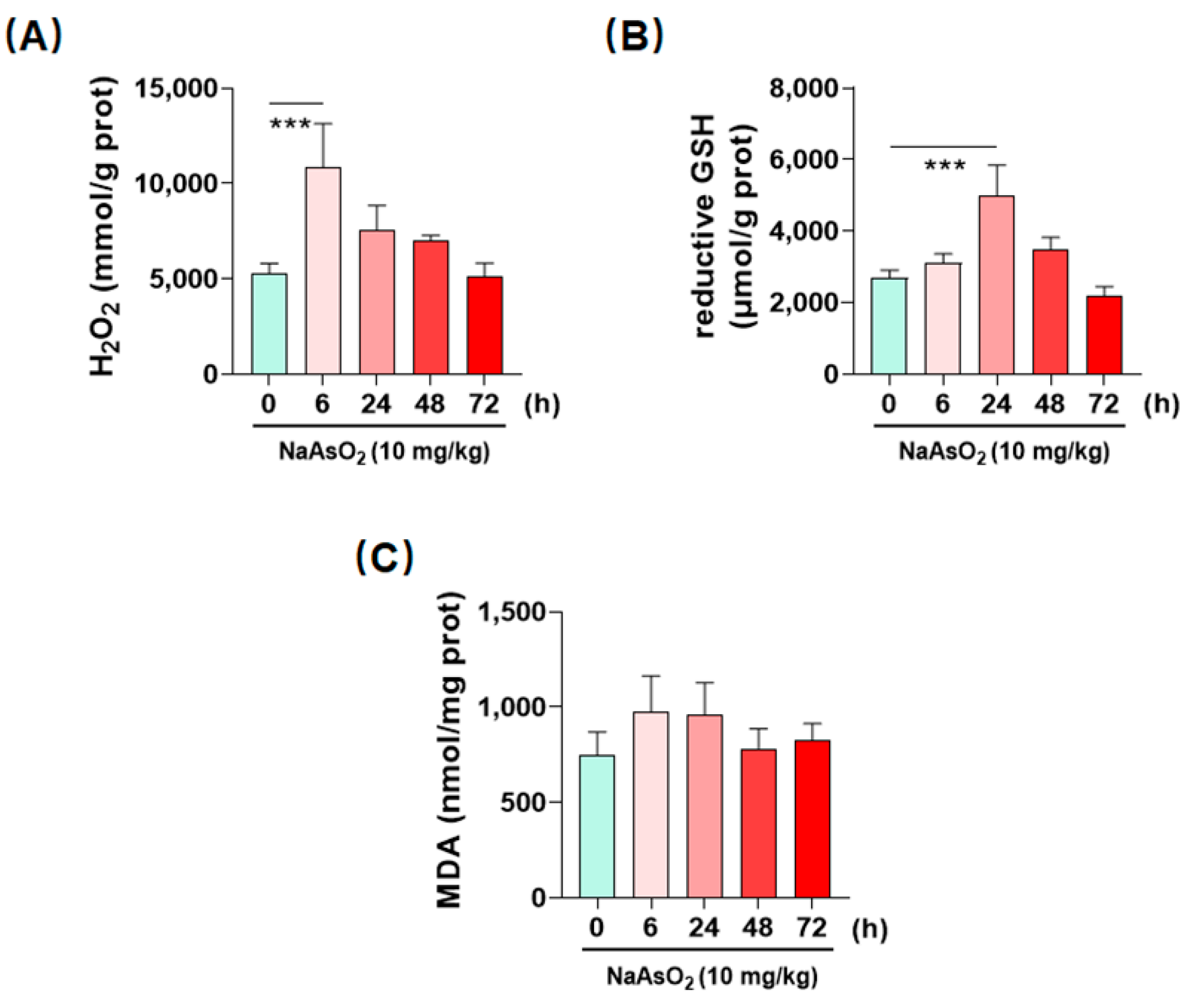
2.3. Inorganic Arsenic Induces Hepatic Redox Imbalance in Mice
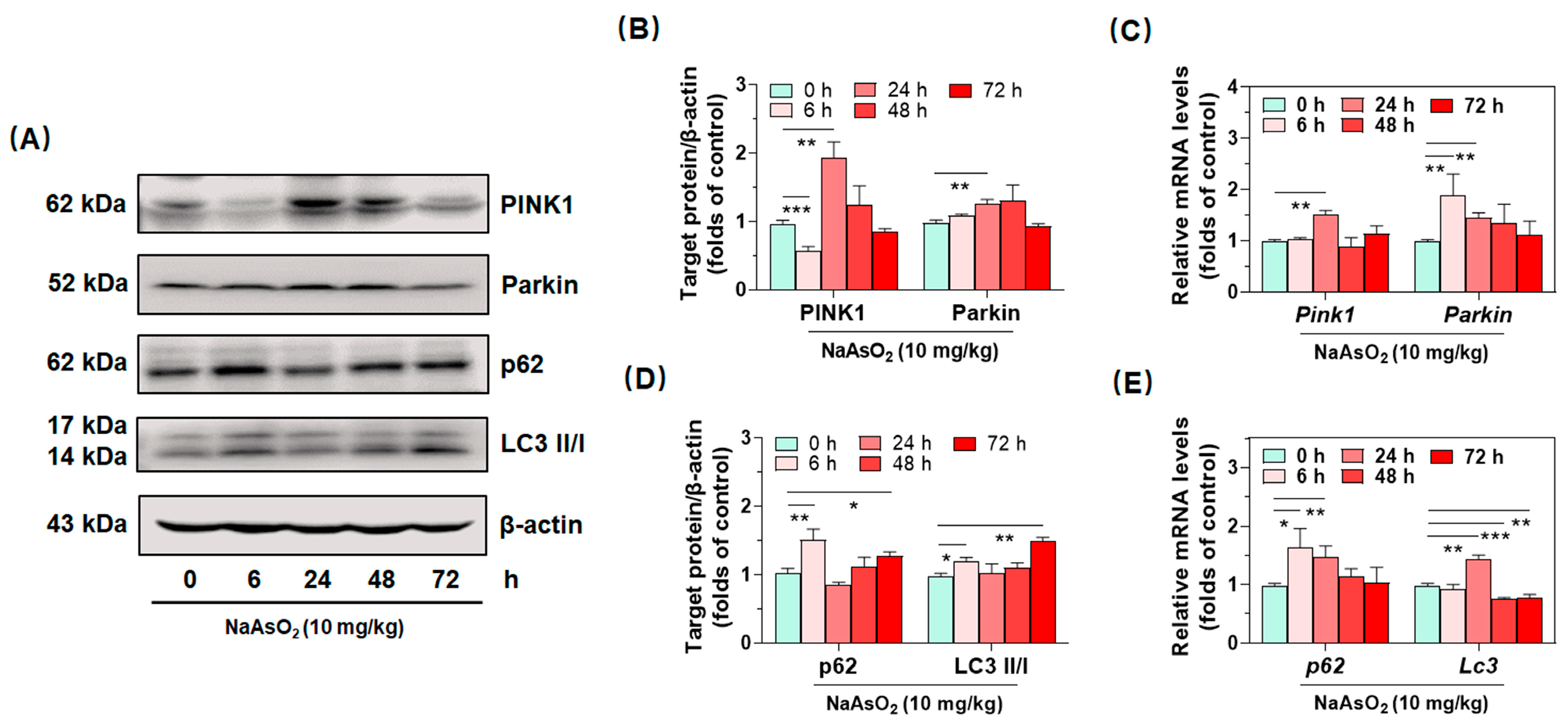
2.4. Inorganic Arsenic Activates PINK1/Parkin-Mediated Mitophagy in the Livers of Acute Arsenic-Exposed Mice
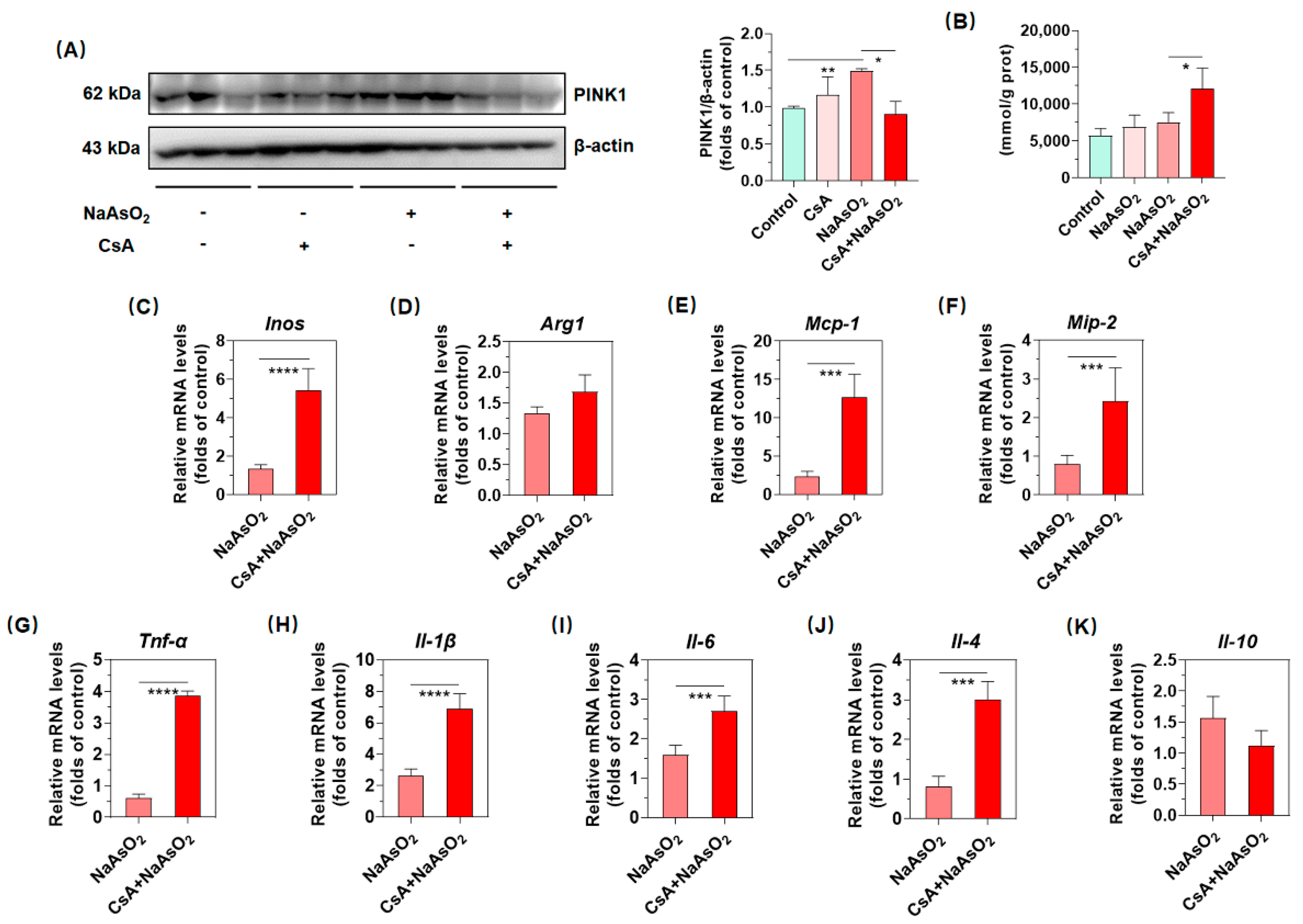
2.5. PINK1/Parkin-Mediated Mitophagy Resists Arsenic-Induced Gene Expression of Inflammatory Cytokines in Liver
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals and Experimental Procedures
4.2. Western Blot Analysis
4.3. Total RNA Isolation and Real-Time qPCR Analysis
4.4. Analysis of H2O2 Content in Liver
4.5. Analysis of GSH Levels in Liver
4.6. Analysis of MDA Levels in Liver
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Chen, Q.Y.; Costa, M. Arsenic: A Global Environmental Challenge. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2021, 61, 47–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palma-Lara, I.; Martinez-Castillo, M.; Quintana-Perez, J.C.; Arellano-Mendoza, M.G.; Tamay-Cach, F.; Valenzuela-Limon, O.L.; Garcia-Montalvo, E.A.; Hernandez-Zavala, A. Arsenic exposure: A public health problem leading to several cancers. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2020, 110, 104539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Guo, C.; Jiang, H.; Han, B.; Wang, X.; Li, S.; Lv, Y.; Lv, Z.; Zhu, Y. Inflammation response after the cessation of chronic arsenic exposure and post-treatment of natural astaxanthin in liver: Potential role of cytokine-mediated cell-cell interactions. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 9252–9262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez, B.G.; Tsai, M.S.; Baratta, J.L.; Longmuir, K.J.; Robertson, R.T. Characterization of Kupffer cells in livers of developing mice. Comp. Hepatol. 2011, 10, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, L.; He, S.; Mao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Cai, Y.; Li, S. Effect of Hepatic Macrophage Polarization and Apoptosis on Liver Ischemia and Reperfusion Injury During Liver Transplantation. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Hu, X.; Shen, Q.; Xing, D. Mitochondria-specific drug release and reactive oxygen species burst induced by polyprodrug nanoreactors can enhance chemotherapy. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dan Dunn, J.; Alvarez, L.A.; Zhang, X.; Soldati, T. Reactive oxygen species and mitochondria: A nexus of cellular homeostasis. Redox Biol. 2015, 6, 472–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deretic, V.; Saitoh, T.; Akira, S. Autophagy in infection, inflammation and immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 722–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palikaras, K.; Lionaki, E.; Tavernarakis, N. Mechanisms of mitophagy in cellular homeostasis, physiology and pathology. Nat. Cell Biol. 2018, 20, 1013–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, N.; Li, L.; Chen, S.; Wang, T. PINK1-dependent phosphorylation of PINK1 and Parkin is essential for mitochondrial quality control. Cell Death Dis. 2016, 7, e2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rath, M.; Muller, I.; Kropf, P.; Closs, E.I.; Munder, M. Metabolism via Arginase or Nitric Oxide Synthase: Two Competing Arginine Pathways in Macrophages. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baeck, C.; Wehr, A.; Karlmark, K.R.; Heymann, F.; Vucur, M.; Gassler, N.; Huss, S.; Klussmann, S.; Eulberg, D.; Luedde, T.; et al. Pharmacological inhibition of the chemokine CCL2 (MCP-1) diminishes liver macrophage infiltration and steatohepatitis in chronic hepatic injury. Gut 2012, 61, 416–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, J.; Muniroh, M.; Nandakumar, A.; Tsuji, M.; Koriyama, C.; Yamamoto, M. Inorganic mercury-induced MIP-2 expression is suppressed by N-acetyl-L-cysteine in RAW264.7 macrophages. Biomed. Rep. 2020, 12, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reczek, C.R.; Chandel, N.S. ROS-dependent signal transduction. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2015, 33, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ursini, F.; Maiorino, M. Lipid peroxidation and ferroptosis: The role of GSH and GPx4. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2020, 152, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsikas, D. Assessment of lipid peroxidation by measuring malondialdehyde (MDA) and relatives in biological samples: Analytical and biological challenges. Anal. Biochem. 2017, 524, 13–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.N.; Padman, B.S.; Lazarou, M. Deciphering the Molecular Signals of PINK1/Parkin Mitophagy. Trends Cell Biol. 2016, 26, 733–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Racanelli, V.; Rehermann, B. The liver as an immunological organ. Hepatology 2006, 43 (Suppl. S1), S54–S62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dou, L.; Shi, X.; He, X.; Gao, Y. Macrophage Phenotype and Function in Liver Disorder. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 3112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ley, K. M1 Means Kill; M2 Means Heal. J. Immunol. 2017, 199, 2191–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, D.I.; Kim, M.R.; Jeong, H.Y.; Jeong, H.C.; Jeong, M.H.; Yoon, S.H.; Kim, Y.S.; Ahn, Y. Mesenchymal stem cells reciprocally regulate the M1/M2 balance in mouse bone marrow-derived macrophages. Exp. Mol. Med. 2014, 46, e70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogun, M.; Ozcan, A.; Karaman, M.; Merhan, O.; Ozen, H.; Kukurt, A.; Karapehlivan, M. Oleuropein ameliorates arsenic induced oxidative stress in mice. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2016, 36, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, J.; Xiao, T.; Wei, S.; Sun, J.; Zou, Z.; Shi, M.; Sun, Q.; Dai, X.; Wu, L.; Li, J.; et al. miR-21-regulated M2 polarization of macrophage is involved in arsenicosis-induced hepatic fibrosis through the activation of hepatic stellate cells. J. Cell Physiol. 2021, 236, 6025–6041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Liu, J.; Waalkes, M.P.; Cheng, M.L.; Li, L.; Li, C.X.; Yang, Q. High dietary fat exacerbates arsenic-induced liver fibrosis in mice. Exp. Biol. Med. 2008, 233, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacy, P.; Stow, J.L. Cytokine release from innate immune cells: Association with diverse membrane trafficking pathways. Blood 2011, 118, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Narazaki, M.; Kishimoto, T. IL-6 in inflammation, immunity, and disease. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2014, 6, a016295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Lopez, E.; Zhong, Z.; Stubelius, A.; Sweeney, S.R.; Booshehri, L.M.; Antonucci, L.; Liu-Bryan, R.; Lodi, A.; Terkeltaub, R.; Lacal, J.C.; et al. Choline Uptake and Metabolism Modulate Macrophage IL-1beta and IL-18 Production. Cell Metab. 2019, 29, 1350–1362.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Santra, A.; Lahiri, S.; Guha Mazumder, D.N. Implications of oxidative stress and hepatic cytokine (TNF-alpha and IL-6) response in the pathogenesis of hepatic collagenesis in chronic arsenic toxicity. Toxicol. Appl. Pharm. 2005, 204, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liang, Y.; Zheng, B.; Chu, L.; Ma, D.; Wang, H.; Chu, X.; Zhang, J. Protective Effects of Crocetin on Arsenic Trioxide-Induced Hepatic Injury: Involvement of Suppression in Oxidative Stress and Inflammation Through Activation of Nrf2 Signaling Pathway in Rats. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2020, 14, 1921–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deckers, J.; Branco Madeira, F.; Hammad, H. Innate immune cells in asthma. Trends Immunol. 2013, 34, 540–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Liu, Y.; Wang, D.; Zhu, K.; Zou, Z.; Zhang, A. Imbalanced inflammatory response in subchronic arsenic-induced liver injury and the protective effects of Ginkgo biloba extract in rats: Potential role of cytokines mediated cell-cell interactions. Environ. Toxicol. 2021, 36, 2073–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, A.; Islam, M.S.; Tony, S.R.; Siddique, A.E.; Mondal, V.; Hosen, Z.; Islam, Z.; Hossain, M.I.; Rahman, M.; Anjum, A.; et al. T helper 2-driven immune dysfunction in chronic arsenic-exposed individuals and its link to the features of allergic asthma. Toxicol. Appl. Pharm. 2021, 420, 115532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diebold, L.; Chandel, N.S. Mitochondrial ROS regulation of proliferating cells. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2016, 100, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodaghi-Namileh, V.; Sepand, M.R.; Omidi, A.; Aghsami, M.; Seyednejad, S.A.; Kasirzadeh, S.; Sabzevari, O. Acetyl-l-carnitine attenuates arsenic-induced liver injury by abrogation of mitochondrial dysfunction, inflammation, and apoptosis in rats. Environ. Toxicol. Pharm. 2018, 58, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Aboud, D.; Baty, R.S.; Alsharif, K.F.; Hassan, K.E.; Zhery, A.S.; Habotta, O.A.; Elmahallawy, E.K.; Amin, H.K.; Abdel Moneim, A.E.; Kassab, R.B. Protective efficacy of thymoquinone or ebselen separately against arsenic-induced hepatotoxicity in rat. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021, 28, 6195–6206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadian, M.; Mianabadi, M.; Zargari, M.; Karimpour, A.; Khalafi, M.; Amiri, F.T. Effects of Olive Oil supplementation on Sodium Arsenate-induced Hepatotoxicity in Mice. Int. J. Prev. Med. 2018, 9, 59. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Shen, J.; Ran, Z. Emerging views of mitophagy in immunity and autoimmune diseases. Autophagy 2020, 16, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Tang, Y.; Lu, J.; Zhang, W.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Ma, G.; Jiang, P.; Zhang, W. PINK1-mediated mitophagy protects against hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury by restraining NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2020, 160, 871–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durcan, T.M.; Fon, E.A. The three ‘P’s of mitophagy: PARKIN, PINK1, and post-translational modifications. Genes Dev. 2015, 29, 989–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oka, T.; Hikoso, S.; Yamaguchi, O.; Taneike, M.; Takeda, T.; Tamai, T.; Oyabu, J.; Murakawa, T.; Nakayama, H.; Nishida, K.; et al. Mitochondrial DNA that escapes from autophagy causes inflammation and heart failure. Nature 2012, 485, 251–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sliter, D.A.; Martinez, J.; Hao, L.; Chen, X.; Sun, N.; Fischer, T.D.; Burman, J.L.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Narendra, D.P.; et al. Parkin and PINK1 mitigate STING-induced inflammation. Nature 2018, 561, 258–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, W.; Duan, X.; Chen, J.; Guo, Y.; Yang, S.; Sun, G.; Li, B. Imbalanced immune responses involving inflammatory molecules and immune-related pathways in the lung of acute and subchronic arsenic-exposed mice. Environ. Res. 2017, 159, 381–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Duan, X.; Dong, D.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Li, W.; Chen, J.; Sun, G.; Li, B. Tissue-specific distributions of inorganic arsenic and its methylated metabolites, especially in cerebral cortex, cerebellum and hippocampus of mice after a single oral administration of arsenite. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2017, 43, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Gene Name | Primer Sequence (5′–3′) | Amplicon Size (bp) |
|---|---|---|
| Accession Number | ||
| iNOS | ACCCCTGTGTTCCACCAGGAGATGTTGAA | 189 |
| (NM_001313922.1) | TGAAGCCATGACCTTTCGCATTAGCATGG | |
| Arg1 | CTCCAAGCCAAAGTCCTTAGAG | 185 |
| (NM_007482.3) | AGGAGCTGTCATTAGGGACATC | |
| Mcp-1 | TGAGTAGGCTGGAGAGCTACAA | 123 |
| (NM_053647.1) | ATGTCTGGACCCATTCCTTC | |
| Mip-2 | CCCCAAAGGGATGAGAAGTTC | 323 |
| (NM_053647.1) | GGCTTGTCACTCGAATTTTGAGA | |
| Tnf-α | CCCCAAAGGGATGAGAAGTTC | 101 |
| (NM_013693) | GGCTTGTCACTCGAATTTTGAGA | |
| Il-1β | TGACCTGGGCTGTCCTGATG | 160 |
| (NM_008361) | GGTGCTCATGTCCTCATCCTG | |
| Il-6 | CTGCAAGAGACTTCCATCCAG | 131 |
| (NM_031168) | AGTGGTATAGACAGGTCTGTTGG | |
| Il-4 | GGTCTCAACCCCCAGCTAGT | 102 |
| (NM_021283) | GCCGATGATCTCTCTCAAGTGAT | |
| Il-10 | GGGGCCAGTACAGCCGGGAA | 101 |
| (NM_010548) | CTGGCTGAAGGCAGTCCGCA | |
| Pink1 | CACACTGTTCCTCGTTATGAAGA | 157 |
| (NM_036164400.1) | CTTGAGATCCCGATGGGCAAT | |
| Parkin | TCTTCCAGTGTAACCACCGTC | 115 |
| (NM_NM_016694.4) | GGCAGGGAGTAGCCAAGTT | |
| Sqstm1/p62 | GAACTCGCTATAAGTGCAGTGT | 131 |
| (NM_001290769.1) | AGAGAAGCTATCAGAGAGGTGG | |
| Map1lc3b | CGCTTGCAGCTCAATGCTAAC | 93 |
| (NM_001364358.1) | CTCGTACACTTCGGAGATGGG | |
| Gapdh | TGTGTCCGTCGTGGATCTGA | 150 |
| (NM_001289726.1) | TTGCTGTTGAAGTCGCAGGAG |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qu, G.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Guo, Y.; Li, H.; Qu, R.; Su, W.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, L.; Xu, H.; et al. PINK1/Parkin-Mediated Mitophagy Partially Protects against Inorganic Arsenic-Induced Hepatic Macrophage Polarization in Acute Arsenic-Exposed Mice. Molecules 2022, 27, 8862. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27248862
Qu G, Liu Z, Zhang J, Guo Y, Li H, Qu R, Su W, Zhang H, Zhang L, Xu H, et al. PINK1/Parkin-Mediated Mitophagy Partially Protects against Inorganic Arsenic-Induced Hepatic Macrophage Polarization in Acute Arsenic-Exposed Mice. Molecules. 2022; 27(24):8862. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27248862
Chicago/Turabian StyleQu, Gaoyang, Zi Liu, Jiaxin Zhang, Yaning Guo, Hui Li, Ruijie Qu, Wei Su, Huan Zhang, Lin Zhang, Hong Xu, and et al. 2022. "PINK1/Parkin-Mediated Mitophagy Partially Protects against Inorganic Arsenic-Induced Hepatic Macrophage Polarization in Acute Arsenic-Exposed Mice" Molecules 27, no. 24: 8862. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27248862
APA StyleQu, G., Liu, Z., Zhang, J., Guo, Y., Li, H., Qu, R., Su, W., Zhang, H., Zhang, L., Xu, H., Shen, F., Jiang, S., Liu, H., & Li, J. (2022). PINK1/Parkin-Mediated Mitophagy Partially Protects against Inorganic Arsenic-Induced Hepatic Macrophage Polarization in Acute Arsenic-Exposed Mice. Molecules, 27(24), 8862. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27248862






