Abstract
Marine fungi can metabolize structurally diverse active components, and have become an important source of drug lead molecules. In the present study, the chemical investigation on the EtOAc extract of the fermentation broth of the marine-derived fungus Trametes sp. ZYX-Z-16 led to the isolation of eight meroterpenoids (1–8), including two undescribed ones, together with ten ergostane steroid analogues (9–18). The structures of two new spiromeroterpenoids, asnovolin H (1) and asnovolin I (2), were determined based on 1D, 2D NMR, and HRESIMS spectroscopic data along with ECD spectra calculations. All compounds were tested for antibacterial and α-glucosidase inhibitory activity. Among them, compound 12 showed definite antibacterial activities against Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 6538 (MIC 32 μg/mL) and Bacillus subtilis ATCC 6633 (MIC 16 μg/mL). In addition, compounds 9 and 10 showed superior inhibitory activity, with IC50 values of 104.1 and 111.3 μM, respectively, to the positive control acarbose (304.6 μM).
1. Introduction
The ocean has a unique and complex ecological environment with low temperature, high temperature, high pressure, high salinity, no light, and low oxygen. The rapidly increasing number of marine natural products (MNPs) with structural novelty and high biological activities each year has greatly stimulated the interest of researchers [1,2]. In recent years, the metabolites of marine microorganisms have become one of the research hotspots of scholars at home and abroad [3]. Marine fungi form different metabolic pathways and adaptation mechanisms in the peculiar marine environment and can produce natural secondary metabolites with unique chemical structures [4]. A great deal of work on mining the active secondary metabolites from marine-derived fungi has been performed. The main types of these metabolites contained alkaloids [5,6], anthraquinones [7], terpenes [8,9,10], polyketones [11], macrolides [12], isocoumarins [13], and sterols [14]. These different types of compounds show diverse biological activities, including antibacterial [15], antifungal [16], antioxidant [17], cytotoxic [8,18], anti-inflammatory [19], enzyme inhibition [20], antituberculosis [21], neuroprotection [22], and antiproliferative [23] activities.
The genus Trametes of fungi is distinguished by a white aerial mycelia. In the present day, researchers have mainly focused on the biodegradable enzymes [24,25] and polysaccharides with cytotoxic activity [26,27] in the macrofungi species of genus Trametes such as T. versicolor and T. robiniophila. The active secondary metabolites from the microfungi species of genus Trametes relatively lack studies. In the course of our ongoing search for structurally new and biologically active metabolites from marine-derived fungi, the fungus Trametes sp. ZYX-Z-16, isolated from conch snails in Silver Island, Xisha, South Sea, China, and presenting complex metabolite profiles revealed by high-pressure liquid chromatogram, attracted our attention. Subsequent chemical investigation on the EtOAc extract of the fermentation broth of this fungus led to the identification of eight meroterpenoids (1–8), including two new spiromeroterpenoids, asnovolin H (1) and asnovolin I (2), together with ten ergostane steroid analogues (9–18) (Figure 1). Herein, the isolation, structural elucidation, and bioassays, including antibacterial, antifungal, and α-glucosidase inhibitory activities, of these compounds are described.
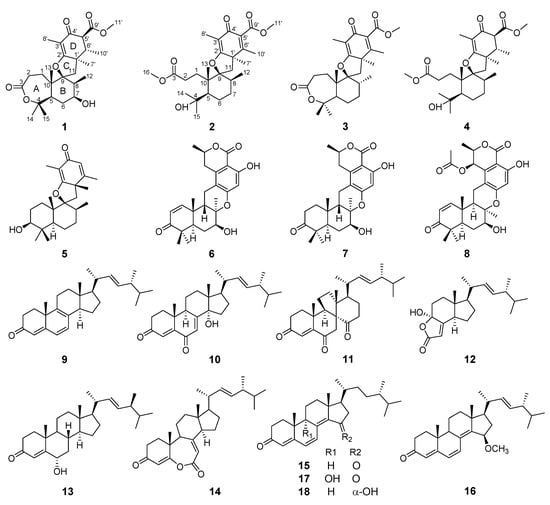
Figure 1.
The structures of compounds 1–18.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Structural Elucidation of Compounds
Compound 1 was isolated as a yellow powder, and the molecular formula was determined as C26H38O7 on the basis of HRESIMS ion peak at m/z [M + Na]+ 485.2528 (calcd. 485.2510 for C26H38NaO7) and 13C NMR data, suggesting eight degrees of unsaturation. The IR spectrum revealed the presence of hydroxyl group (3475 cm−1), double bond (1637 cm−1), ester carbonyls (1686 cm−1), and ketone carbonyl (1735 cm−1). The 1H NMR spectral data (Table 1) of 1 revealed the signals for seven methyls (δH 1.03, 1.14, 1.25, 1.40, 1.50, 1.52, and 1.72), one methoxy (δH 3.74), and oxygen-bearing methine (δH 3.95). The 13C NMR and DEPT (Table 1) spectra presented 26 carbon signals for eight methyls, four methylenes, five methines (one oxygenated at δC 69.6), and nine nonprotonated carbons (two olefinic at δC 183.4 and 110.2, two oxygenated, one ketone at δC 195.8, and two ester carbonyls at δC 177.9, 173.3). Three carbonyls and one double bond account for four degrees of unsaturation, indicating that four rings (A–D) are presented in compound 1. Careful comparison of the above-mentioned NMR data of 1 with those of asnovolin A [28] revealed that they had the same spiromeroterpenoid skeleton. The only difference between them was that the methylene at C-7 (δC 24.4) in asnovolin A was oxidized to hydroxylated methine (δC 69.6) in 1, which was confirmed by key HMBC correlations (Figure 2) from H3-12 (δH 1.14) and H2-6 (δH 1.87/1.78) to C-7, and the sequential 1H–1H COSY cross peaks of H2-6/H-7/H-8. The other key HMBC and 1H–1H COSY correlations of 1, as shown in Figure 2, further corroborated the structure of 1, as shown in Figure 1.

Table 1.
1H (500 MHz) and 13C NMR (125 MHz) data of compounds 1 (in MeOD) and 2 (in CDCl3).
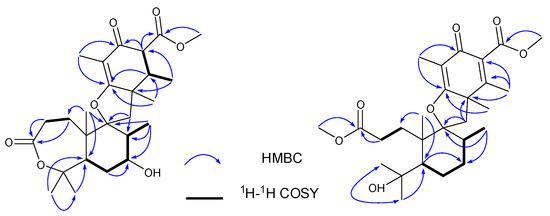
Figure 2.
Key HMBC (H→C) and COSY (↔) correlations of 1 and 2.
The relative structure of 1 was established from the analysis of ROESY data (Figure 3) and its similar NMR data with that of asnovolin A. The ROE cross peaks of H-5/H-7/H-11β/H-8/H-6’, H-5/H2-11, H-1α/H-11α, and H3-12/H3-13 were observed, suggesting that H-5, H-7, H-8, H-1α, and H2-11 resided on the same side of the A/B ring and H3-12/H3-13 were located at the opposite face of the A/B ring. The ROE correlations of H-1α/H-11β/H3-7′/H-5′ and H-8/H-11β/H-6′ indicated that the two sets of protons were located at the two sides of the C/D ring, respectively (Figure 3). In order to further confirm the relative configuration of the A/B ring and the C/D ring, an NMR chemical shifts calculation for the two diastereomers, (5R,7S,8S,9S,10S,1′R,5′S,6′S)-1 and (5R,7S,8S,9S,10S,1′S,5′R,6′R)-1, was performed. The 13C and 1H NMR data of (5R,7S,8S,9S,10S,1′R,5′S,6′S)-1 fitted with the experimental data better than (5R,7S,8S,9S,10S,1′S,5′R,6′R)-1 based on the correlation coefficient (R2), mean absolute error (MAE), and corrected mean absolute error (CMAE) parameters (Figure 4). In addition, DP4 + analysis also predicted (5R,7S,8S,9S,10S,1′R,5′S,6′S)-1 as the most likely structure of 1, with 100% DP4+ probability (all data). Thus, the relative configuration was assigned as 5R*,7S*,8S*,9S*,10S*, 1′R*, 5′S*,6′S*, as shown in Figure 1. The absolute configurations of 1 were determined by the electronic circular dichroism (ECD) calculation. As shown in Figure 4, the ECD spectra of 1 displayed one positive ECD cotton effect around 270 nm and one negative ECD cotton effect around 302 nm, which were closely similar to those of asnovolin A [28]. The comparison of experimental and calculated ECD curves (Figure 5) of 1 established its absolute configuration as 5R, 7S, 8S, 9S, 10S, 1′R, 5′S, 6′S. The structure of 1 was therefore defined as 7-hydroxy-asnovolin A and named asnovolin H.
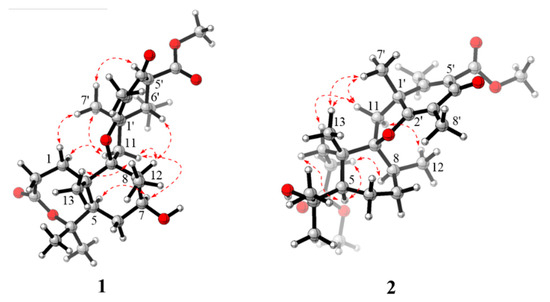
Figure 3.
Key ROESY (red dashed arrows) correlations of compounds 1 and 2.
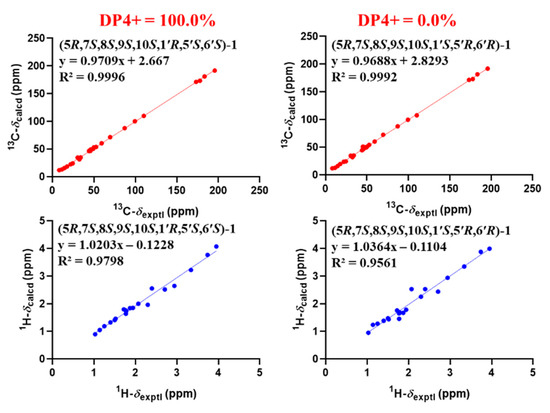
Figure 4.
Linear regression analysis between experimental and calculated 13C and 1H NMR chemical shifts of diastereomers of (5R,7S,8S,9S,10S,1′R,5′S,6′S)-1 (left) and (5R,7S,8S,9S,10S,1′S,5′R,6′R)-1 (right).
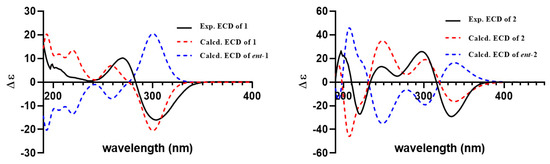
Figure 5.
The experimental and calculated ECD spectra for 1 and 2 (σ = 0.30 eV, UV shift = 0 nm).
Compound 2 was isolated as a colorless amorphous solid and possessed a molecular formula C27H40O7 with eight degrees of unsaturation deduced from its HRESIMS ion peak at m/z 499.2695 [M + Na]+ and 13C NMR data. The IR spectrum also revealed the absorptions 3486 cm−1 for hydroxyl group, 1736 cm−1 for ketone carbonyl, and 1633 cm−1 for double bonds. The 1H NMR spectrum of 2 exhibited signals indicative of nine methyl groups (δH 0.61,1.36, 1.37, 1.43, 1.59, 1.77, 2.06, 3.69, and 3.84), including two methoxy groups (Table 1). The 13C NMR and DEPT (Table 1) spectra presented 27 carbon signals for nine methyls, five methylenes, two methines, and eleven nonprotonated carbonyls (four olefinic, two oxygenated, and three carbonyls). Three carbonyl (δC 184.2, 174.2, and 167.6) and two double bonds (δC 179.6, 107.9, 155.2, and 132.4) account for five degrees of unsaturation, indicating that three rings are present in 2. The NMR spectra of 2 resembled those of asnovolin C (4) [28], except for the presence of a double bond at C-5’ (δC 132.4) and C-6’ (δC 155.2) in 2 replacing two corresponding sp3 methine in asnovolin C. The relative configuration of 2 was determined to be the same as that of asnovolin C on the basis of their similar 1D NMR data and detailed ROESY data analysis of 2 (Figure 3). The ROE correlations of H-5/H2-2/H-8 are indicative of α orientation for these protons. The ROE correlations of H3-12/H-11β, and H-1/H-11α/H-7′ and H3-13 suggested that the two sets of protons were located at the different sides of the C/D ring. The ECD spectra of 2 revealed positive ECD Cotton effects around 246 nm and 298 nm, and one negative ECD Cotton effect around 220 nm and 315 nm, which fitted the calculated ECD curve (Figure 5) of 2 and established its absolute configurations as 5R, 8S, 9S, 10S, 1′R. Therefore, compound 2 was identified and named asnovolin I.
The structures of known compounds, including five meroterpenoids (3–8) and ten ergostane steroids (9–18), were identified as asnovolin C 5′6′-dehydro hydrogen (3) [28] and asnovolin C (4) [28], chermesin A(5) [29], chrodrimanin E (6) [30], chrodrimanin H (7) [30], thailandolide B (8) [31], ergosta-4,6,8,22E-tetraene-3-one (9) [32], 14α-hydroxyergosta-4,7,22E-triene-3,6-dione (10) [33], dankasterones A (11) [34], 4α-hydroxy-17-methylincisterol (12) [35], ergosta-6α-hydroxy-4,22E-dien-3-one (13) [36], fortisterol (14) [37], gymnasterone (15) [38], 15β-methoxy-ergosta-4,6,8(14),22E-tetraene-3-one (16) [38], ganodermaside C (17) [39], and ganodermaside A (18) [40] by comparing their NMR data to the previously reported data.
Meroterpenoids are a class of natural products derived from mixed biosynthetic origin, with a terpenoid as one of the structural components [41]. Here, the isolated meroterpenoids (1–8) from this fungus were divided into two groups. One group was spiromeroterpenoids (1–5), with a spiro carbon at (C-9) through an oxygen atom. The other group was meroterpenoids (6–8) with 6/6/6/6/6 pentacyclic ring framework, which was often found in fungal metabolites [42]. Only 11 spiromeroterpenoid analogues have been reported from fungal metabolites, including asnovolins A–G [28], chermesins A–D [29], and novofumigatonin [43]. Two undescribed spiromeroterpenoids, asnovolins H and I, from marine-derived fungus Trametes sp. ZYX-Z-16 would further enriched the understanding of structural diversity of this type of spiromeroterpenoids.
2.2. Bioassays of Compounds
2.2.1. α-Glucosidase and Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitory Activity
Compounds 9 and 10 showed superior α-glucosidase inhibitory activity with IC50 values of 104.1 µM and 111.3 µM, respectively, to that of positive control acarbose (304.6 µM). The remaining sixteen compounds (1–8 and 11–18) did not show remarkable inhibitory activities (IC50 > 200 µM) against α-glucosidase. In addition, none of these compounds showed inhibitory activity against acetylcholinesterase (IC50 > 200 µM).
2.2.2. Antibacterial Activity
The inhibitory activity of all compounds against four bacteria (Staphylococcus aureus ATCC6538, Bacillus subtilis ATCC 6633, Escherichia coli ATCC 25922, and Listeria monocytogenes ATCC 1911) was evaluated using the 96-well microtiter plates method. The results showed that compound 5 has weak inhibitory activity against S. aureus (MIC = 128 µg/mL), while it is worth noting that compound 12 has good inhibitory activity against S. aureus (MIC = 32 µg/mL) and B. subtilis (MIC = 16 µg/mL). The remaining sixteen compounds (1–4, 6–11, and 13–18) did not show remarkable antibacterial activities (MIC > 128 µg/mL) against S. aureus and B. subtilis. In this assay, none of these compounds showed inhibitory activity against E. coli ATCC 25922 and L. monocytogenes ATCC 1911 (MIC > 128 µg/mL).
2.2.3. Antifungal Activity
The inhibitory activities of all compounds against five phytopathogenic fungi (Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. cubense, Fusarium spp., Peronophythora litchii, Colletotrichum gloeosporioides, and Hylocereus undatus) were evaluated using the broth microdilution method. Unfortunately, none of the compounds showed definite inhibitory activity.
Meroterpenoids are the main characteristic class of natural products generated by this fungus. Those spiromeroterpenoids with a spiro carbon at (C-9) through an oxygen atom were reported to show bioactivities of suppression of fibronectin expression [28] and antibacterial activity [29]. The other type of meroterpenoids with 6/6/6/6/6 pentacyclic ring framework showed various bioactivities, including insecticidal activity [30,44], lipid droplet formation inhibition [45], protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B inhibitory activity [46], and antiviral activity [42,47]. From the above bioassays of all the isolated meroterpenoids, only compound 5 showed definite inhibitory activity against Staphylococcus aureus ATCC6538. None of the meroterpenoids with 6/6/6/6/6 pentacyclic ring framework had good biological activity in the present experiment.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Experimental Procedures
NMR spectra were recorded on Bruker AV-500 and Bruker AV-600 spectrometers (Bruker, Bremen, Germany) with TMS as an internal standard and the peak signals of MeOD (δC/H 49.0/3.31) and CDCl3 (δC/H 77.16/7.26) as reference. The mass spectrometric (HRESIMS) data were acquired using an API QSTAR Pulsar mass spectrometer (Bruker, Bremen, Germany) and an AB SCIEX Trip TOF 5600+ mass spectrometer (SCIEX, Framingham, MA, USA). Optical rotations were measured with a JASCO P-1020 digital polarimeter (Jasco, Tokyo, Japan). IR spectra were recorded on a Shimadzu UV2550 spectrophotometer (Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan). UV spectra and ECD data were collected using a JASCO J-715 spectropolarimeter (Jasco, Tokyo, Japan). Semipreparative HPLC was carried out using an ODS column (YMC-pack ODS-A, 10 × 250 mm, 5 µm, 4 mL/min, YMC, Kyoto, Japan). Column chromatography was carried out on silica gel (SiO2, 200–300 mesh, Qingdao Marine Chemical Inc., Qingdao, Shandong, China), and Sephadex LH-20 (green herbs, Beijing, China) and Rp-C18 (20–45 µm; Fuji Silysia Chemical Ltd., Durham, NC, USA) were used for column chromatography.
3.2. Fungal Material
The fungus strain Trametes sp. ZYX-Z-16 with white mycelium was isolated from an unidentified sea snail collected from Silver Island, Xisha, South Sea, China, in May 2021. After grinding, the sample (1 g) was diluted to 10−2 g/mL with sterile H2O, 100 μL of which was spread on a PDA medium plate containing chloramphenicol as bacterial inhibitor. A single colony was identified according to its morphological characteristics and ITS4 gene sequences (GenBank accession no. ON386187, see Supplementary Materials). A reference culture of Trametes sp. ZYX-Z-16 was deposited in our laboratory and maintained at −80 °C.
3.3. Fermentation, Extraction, and Isolation
The marine fungus Trametes sp. ZYX-Z-16 was cultured in the medium which contained 20 g/L malt, 20 g/L Mannitol, 10 g/L glucose, sodium glutamate 10 g, 3 g/L yeast extract, 1 g/L corn steep liquor, 0.5 g/L KH2PO4, 0.3 g/L MgSO4·7H2O, 10 g/L sea salt, and 1 L H2O at pH 6.5. Fungal mycelia were cut and transferred aseptically to 1 L Erlenmeyer flasks, each adding 300 mL of sterilized liquid medium. The flasks were incubated at room temperature (about 27 °C~34 °C) for 30 days.
The whole culture broth (50 L) was harvested and filtered to yield the mycelium cake and liquid broth. The mycelium cake was extracted by tissue crusher using EtOAc for three times. The EtOAc solution was evaporated under reduced pressure. A total of 135 g EtOAc extract was obtained. The extract was extracted between petroleum ether and 90% methanol (1:1) to remove the oil. The secondary metabolites extract (38 g) was subjected to a silica gel VLC column, eluting with a stepwise gradient of petroleum ether–EtOAc (10:1, 8:1, 6:1, 4:1, 2:1, 1:1, 1:2, 0:1, v/v) to yield eight subfractions (Fr. 1–Fr. 8) based on HPLC and TLC.
Fraction 2 (4.2 g) was further separated into four subfractions, 2.1–2.4, by reversed phase silica gel (ODS) using stepwise gradient elution with MeOH–H2O (40–100%). Subfraction 2.3 (452 mg) was subjected to HPLC over ODS (MeOH/H2O, 80:20, v/v) to give compound 9 (tR 48 min, 13.1 mg). Fraction 3 (0.8 g) was further separated into six subfractions, 3.1–3.6, by ODS column using stepwise gradient elution with MeOH–H2O (30–100%). Subfraction 3.3 (92 mg) was further subjected to HPLC purification using ODS column (MeOH/H2O, 90:10, v/v) to obtain compounds 11 (tR 15 min, 4 mg), 14 (tR 25 min, 4.6 mg), and 15 (tR 38 min, 1.9 mg). Subfraction 3.4 (70 mg) was further subjected to semipreparative HPLC using ODS column (MeOH/H2O, 85:15, v/v) to yield compounds 10 (tR 22 min, 1.9 mg) and 12 (tR 30 min, 2.7 mg). Fraction 4 (2.8 g) was further purified and afford seven subfractions, 4.1–4.7, by ODS using stepwise gradient elution with MeOH–H2O (30–100%). Subfraction 4.4 (56 mg) was further subjected to HPLC purification using ODS column (MeCN/H2O, 80:20, v/v) to yield compounds 17 (tR 25 min, 1.5 mg) and 18 (tR 38 min, 3.5 mg). Subfraction 4.7 (486mg) was further subjected to HPLC purification using ODS column (MeOH/H2O, 90:10, v/v) to afford compounds 13 (tR 36 min, 2.0 mg) and 16 (tR 48 min, 2.3 mg). Fraction 5 (0.6 g) was further separated into two subfractions, 5.1–5.2, by reversed phase silica gel (ODS) using stepwise gradient elution with MeOH–H2O (40–100%). Subfraction 5.2 (119 mg) was subjected to HPLC over ODS (50% MeCN/H2O, v/v) to give compounds 6 (tR 25 min, 3.0 mg) and 8 (tR 28 min, 5.0 mg). Fraction 7 (2.6 g) was further separated into seven subfractions, 7.1–7.7, by reversed phase silica gel (ODS) using stepwise gradient elution with MeOH–H2O (10–100%). Subfractions 7.5 (233 mg) and 7.6 (169 mg) were further subjected to HPLC purification using ODS column (MeCN/H2O, 45:55, v/v) to yield compounds 2 (tR 15 min, 2.6 mg), 3 (tR 18 min, 2.1 mg), and 4 (tR 25 min, 2.8 mg). Subfraction 7.7 (350 mg) was chromatographed on a silica gel column with elution of petroleum ether–EtOAc (2.7:1) to give compound 5 (2.1 mg). Compound 7 (tR 43 min, 4.2 mg) was isolated from subfraction 7.3 by HPLC purification using ODS column (MeCN/H2O, 40:60, v/v). Fraction 8 (2.5 g) was further separated into three subfractions, 8.1–8.3, by reversed phase silica gel (ODS) using stepwise gradient elution with MeOH–H2O (10–100%). Subfraction 8.2 (74 mg) was further subjected to HPLC purification using ODS column (MeCN/H2O, 30:70, v/v) to yield compound 1 (tR 27 min, 8.0 mg).
Asnovolin H (1): Yellow amorphous powder; [α]25D –122.0° (c 0.1, MeOH); UV (MeOH) λmax (logε) 266 (3.19), 226 (2.43), 205 (2.51) nm; IR (KBr) νmax cm−1 3425, 1735, 1686, 1637, 1410, 1028; ECD (MeOH) λmax (∆ε): 205 (6.65), 270 (11.91), 303 (–18.63) nm; 1H and 13C NMR data, see Table 1; HRESIMS m/z [M+Na]+ 485.2528 (calcd. 485.2510 for C26H38NaO7).
Asnovolin I (2): colorless, amorphous solid; [α]25D –8.0° (c 0.1, MeOH); UV (MeOH) λmax (log ε) 304 (2.51), 272 (2.14), 246 (2.77), 235 (2.74), 220 (2.83) nm; IR (KBr) νmax cm−1 3486, 1736, 1633, 1412, 1096; ECD (MeOH) λmax (∆ε): 197 (7.57), 220 (–7.78), 247 (3.80), 267 (1.46), 298 (7.46), 334 (–8.40) nm; 1H and 13C NMR data, see Table 1; HRESIMS m/z [M+Na]+ 499.2695 (calcd. 499.2666 for C27H40NaO7).
3.4. Bioassay of Enzyme Inhibition, Antibacterial, and Antifungal Activity
All the compounds were evaluated for their inhibitory effects against α-glucosidase using p-NPG as the substrate, referring to the previous method [48] with acarbose and genistein as the positive control, as well as against acetylcholinesterase using AICI as the substrate, referring to the previous method [49] with Tacrine as the positive control.
Four bacteria (Staphylococcus aureus ATCC6538, Bacillus subtilis ATCC 6633, Escherichia coli ATCC 25922, and Listeria monocytogenes ATCC 1911) were used for antibacterial evaluation for all compounds, referring to the previous method [50] with ampicillin as a positive control. The bacteria inhibitory activity of all compounds was observed after 12 h in a constant temperature incubator at 37 °C. Five phytopathogens (Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. cubense, Fusarium spp., Peronophythora litchii, Colletotrichum gloeosporioides, and Hylocereus undatus) were used for antifungal evaluation for all compounds, referring to the previous broth microdilution method [51] with carbendazim as a positive control. The fungal inhibitory activity of all compounds was observed after 48 h in a constant temperature incubator at 28 °C. The MIC value was defined as the lowest concentration of the test compound at which the microorganism did not demonstrate visible growth. Each test was performed in triplicate.
3.5. Computation Section
Conformational search was performed using the iMTD-GC method imbedded in Crest program [52]. Density functional theory calculations were performed using the Gaussian 16 package [53]. The conformers within 5 kcal/mol were optimized at B3LYP/6-31G(d) in gas phase and the conformers with population over 1% were kept. Then, these conformers were further reoptimized at B3LYP/6-311G(d) with IEFPCM solvent model, and frequency analyses of all optimized conformers were also performed at the same level of theory to exclude imaginary frequencies. NMR shielding tensors were calculated with the GIAO method [54] at mPW1PW91/6-31+G(d,p) level with IEFPCM solvent model in methanol. The shielding constants were converted into chemical shifts by referencing to TMS at 0 ppm (δcal = σTMS – σcal), where the σTMS (the shielding constant of TMS) was calculated at the same level. For each candidate, the parameters a and b of the linear regression δcal = aδexp + b; the correlation coefficient, R2; the mean absolute error (MAE), defined as Σn |δcal – δexp|/n; and the corrected mean absolute error, CMAE, defined as Σn |δcorr–δexp|/n, where δcorr = (δcal – b)/a, were calculated. DP4+ probability analysis was performed using the shielding tensors [55]. ECD spectra were calculated by the TDDFT methodology at the B3LYP/TZVP, utilizing IEFPCM in methanol. ECD spectra were simulated using SpecDis 1.71 [56].
4. Conclusions
The metabolites from marine fungi have extensive biological and pharmacological activities and have been an important source of drug lead molecules. The chemical investigation of the marine fungus Trametes sp. ZYX-Z-16 led to the isolation of eight meroterpenoids (1–8), including two undescribed spiro-ones, asnovolins H (1) and I (2), together with eight ergostane steroids (9–18). The bioassay of enzyme inhibition assay showed that two ergostane steroids (9 and 10) revealed definite inhibition against α-glucosidase with IC50 values of 104.1 μM and 111.3 μM, respectively. The result of antibacterial assay showed that an ergostane steroid (12) has obvious inhibitory effect on Staphylococcus aureus ATCC6538 (MIC 32 μg/mL) and Bacillus subtilis ATCC6633 (16 μg/mL). This study further deepens the understanding of the structural diversity of meroterpenoids of marine fungi, enriches the marine natural product database, and provides theoretical information for the subsequent utilization and development of marine natural product resources.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information about ITS1 gene sequences of Trametes sp. ZYX-Z-16, 1D, 2D NMR, IR, and HRESIMS data can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/molecules27248782/s1.
Author Contributions
Z.R.: Wrote the manuscript and isolated compounds. L.Y.: Structural elucidation and revised the manuscript. Q.M.: Fungus isolation. Q.X.: Activity test. H.D.: Method adviser. K.S.: Revised the manuscript. Y.Z.: Theory and orientation adviser. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was financially supported by Natural Science Foundation of Hainan Province (821RC643), Financial Fund of the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs, P.R. of China (NFZX2021), and China Agriculture Research System of MOF and MARA (CARS-21).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the members of the analytical group of the Institute of Tropical Bioscience and Biotechnology, Chinese Academy of Tropical Agricultural Sciences, for spectral measurements.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Sample Availability
Samples of the compounds are available from the authors.
References
- Wang, H.N.; Sun, S.S.; Liu, M.Z.; Yan, M.C.; Zhang, Z. Natural bioactive compounds from marine fungi (2017–2020). J. Asian. Nat. Prod. Res. 2021, 24, 203–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carroll, A.R.; Copp, B.R.; Davis, R.A.; Keyzers, R.A.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2022, 39, 1122–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blunt, J.W.; Copp, B.R.; Keyzers, R.A.; Munro, M.H.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2017, 34, 235–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Lu, H.; Lan, J.; Ahammad, K.H.; Cao, S.G. A review: Halogenated compounds from marine fungi. Molecules 2021, 26, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.S.; Yang, L.; Kong, F.D.; Zhao, J.H.; Yao, L.; Yuchi, Z.G.; Ma, Q.Y.; Xie, Q.Y.; Zhou, L.M.; Guo, M.F.; et al. Three new quinazoline-containing indole alkaloids from the marine-derived fungus Aspergillus sp. HNMF114. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 680879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, F.D.; Zhang, S.L.; Zhou, S.Q.; Ma, Q.Y.; Xie, Q.Y.; Chen, J.P.; Li, J.H.; Zhou, L.M.; Yuan, J.Z.; Zhong, H.; et al. Quinazoline-containing indole alkaloids from the marine-derived fungus Aspergillus sp. HNMF114. J. Nat. Prod. 2019, 82, 3456–3463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Zhou, L.M.; Kong, F.D.; Ma, Q.Y.; Xie, Q.Y.; Li, J.H.; Dai, H.F.; Guo, L.; Zhao, Y.X. Altertoxins with quorum sensing inhibitory activities from the marine-derived fungus Cladosporium sp. KFD33. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.T.; Yang, L.; Kong, F.D.; Ma, Q.Y.; Xie, Q.Y.; Dai, H.F.; Yu, Z.F.; Zhao, Y.X. Cytotoxic indole-diterpenoids from the marine-derived fungus Penicillium sp. KFD28. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.M.; Kong, F.D.; Fan, P.; Ma, Q.Y.; Xie, Q.Y.; Li, J.H.; Zheng, H.Z.; Zheng, Z.H.; Yuan, J.Z.; Dai, H.F.; et al. Indole-diterpenoids with protein tyrosine phosphatase inhibitory activities from the marine-derived fungus Penicillium sp. KFD28. J. Nat. Prod. 2019, 82, 1030–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, F.D.; Fan, P.; Zhou, L.M.; Ma, Q.Y.; Xie, Q.Y.; Zheng, H.Z.; Zheng, Z.H.; Zhang, R.S.; Yuan, J.Z.; Dai, H.F.; et al. Penerpenes A–D, four indole terpenoids with potent protein tyrosine phosphatase inhibitory activity from the marine-derived fungus Penicillium sp. KFD28. Org. Lett. 2019, 21, 4864–4867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Kong, F.D.; Ma, Q.Y.; Xie, Q.Y.; Zhou, L.M.; Zhao, Y.X.; Guo, L. Polyketides with quorum sensing inhibitory activity from the marine-derived fungus Aspergillus sp. ZF-79. J. Asian. Nat. Prod. Res. 2019, 22, 999–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karpiński, T.M. Marine macrolides with antibacterial and/or antifungal activity. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.H.; Chen, J.Q.; Zhang, X.L.; Chen, Z.L.; Li, T.; She, Z.G.; Ding, W.J.; Li, C.Y. Four new isocoumarins and a new natural tryptamine with antifungal activities from a mangrove endophytic fungus Botryosphaeria ramosa L29. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, C.L.; Kong, F.D.; Ma, Q.Y.; Xie, Q.Y.; Yuan, J.Z.; Zhou, L.M.; Dai, H.F.; Yu, Z.F.; Zhao, Y.X. Chemical constituents of the marine-derived fungus Aspergillus sp. SCS-KFD66. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.H.; Li, X.M.; Zhang, F.Z.; Wang, Y.N.; Wang, B.G. Talascortenes A–G, highly oxygenated diterpenoid acids from the sea-anemone-derived endozoic fungus Talaromyces scorteus AS-242. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 2528–2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durães, F.; Szemerédi, N.; Kumla, D.; Pinto, M.; Kijjoa, A.; Spengler, G.; Sousa, E. Metabolites from marine-derived fungi as potential antimicrobial adjuvants. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Li, X.; Yang, K.; Li, S. Characterization of a new chitosanase from a marine Bacillus sp. and the anti-oxidant activity of its hydrolysate. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.W.; Gong, B.Q.; Yuan, J.; Li, H.J.; Mahmud, T.; Huang, Y.; Li, J.F.; Yang, D.P.; Lan, W.J. L-phenylalanine alters the privileged secondary metabolite production in the marine-derived fungus Trichoderma erinaceum F1-1. J. Nat. Prod. 2019, 83, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, I.S.; Nah, J.W.; Jeon, Y.J. Potential anti-inflammatory natural products from marine algae. Environ. Toxicol. Phar. 2016, 48, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.J.; Chen, P.N.; Li, H.J.; Mahmud, T.; Wu, D.L.; Xu, J.; Lan, W.J. Potential antidiabetic fumiquinazoline alkaloids from the marine-derived fungus Scedosporium apiospermum F41-1. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 1082–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canché Chay, C.I.; Gómez Cansino, R.; Espitia Pinzón, C.I.; Torres-Ochoa, R.O.; Martínez, R. Synthesis and anti-tuberculosis activity of the marine natural product caulerpin and its analogues. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 1757–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bălașa, A.F.; Chircov, C.; Grumezescu, A.M. Marine biocompounds for neuroprotection—A review. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shabana, S.; Lakshmi, K.R.; Satya, A.K. An updated review of secondary metabolites from marine fungi. Mini-Rev. Med. Chem. 2021, 21, 602–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyanhongo, G.S.; Gűbitz, G.; Sukyai, P.; Leitner, C.; Haltrich, D.; Ludwig, R. Oxidoreductases from Trametes spp. in biotechnology: A wealth of catalytic activity. Food. Technol. Biotech. 2007, 45, 250–268. [Google Scholar]
- Knežević, A.; Milovanović, I.; Stajić, M.; Vukojević, J. Potential of Trametes species to degrade lignin. Int. Biodeter. Biodegr. 2013, 85, 52–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Castiblanco, T.; Mejía-Giraldo, J.C.; Puertas-Mejía, M.A. Trametes genus, a source of chemical compounds with anticancer activity in human osteosarcoma: A systematic review. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 10, 121–129. [Google Scholar]
- Knežević, A.; Stajić, M.; Sofrenić, I.; Stanojković, T.; Milovanović, I.; Tešević, V.; Vukojević, J. Antioxidative, antifungal, cytotoxic and antineurodegenerative activity of selected Trametes species from Serbia. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0203064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, K.; Sato, F.; Itabashi, T.; Wachi, H.; Takeda, H.; Wakana, D.; Yaguchi, D.; Kawai, K.; Hosoe, T. Asnovolins A–G, spiromeroterpenoids isolated from the fungus Aspergillus novofumigatus, and suppression of fibronectin expression by Asnovolin E. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 2167–2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Li, X.M.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, P.; Wang, J.X.; Wang, B.G. Chermesins A–D: Meroterpenoids with a drimane-type spirosesquiterpene skeleton from the marine algal-derived endophytic fungus Penicillium chermesinum EN-480. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 806–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, H.; Oka, Y.; Kai, K.; Akiyama, K. New chrodrimanin congeners, chrodrimanins D–H, from YO-2 of Talaromyces sp. Biosci. Biotech. Bioch. 2012, 76, 1765–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dethoup, T.; Manoch, L.; Kijjoa, A.; Pinto, M.; Gales, L.; Damas, A.M.; Silva, A.M.S.; Eaton, G.; Herz, W. Merodrimanes and other constituents from Talaromyces thailandiasis. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70, 1200–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chobot, V.; Opletal, L.; Jáhodář, L.; Patel, A.V.; Dacke, C.G.; Blunden, G. Ergosta-4,6,8,22-tetraen-3-one from the edible fungus, Pleurotus ostreatus (oyster fungus). Phytochemistry 1997, 45, 1669–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.Z.; Han, K.Y.; Li, Z.H.; Feng, T.; Chen, H.P.; Liu, J.K. Cytotoxic ergosteroids from the fungus Stereum hirsutum. Phytochem. Lett. 2019, 30, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amagata, T.; Tanaka, M.; Yamada, T.; Doi, M.; Minoura, K.; Ohishi, H.; Yamori, T.; Numata, A. Variation in cytostatic constituents of a sponge-derived Gymnascella dankaliensis by manipulating the carbon source. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70, 1731–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Togashi, H.; Mizushina, Y.; Takemura, M.; Sugawara, F.; Koshino, H.; Esumi, Y.; Uzawa, J.; Kumagai, H.; Matsukage, A.; Yoshida, S.; et al. 4-hydroxy-17-methylincisterol, an inhibitor of DNA polymerase-α activity and the growth of human cancer cells in vitro. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1998, 56, 583–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.J.; Shao, C.L.; Wang, K.L.; Zhao, D.L.; Wang, Y.N.; Wang, C.Y. Secondary metabolites and their bioactivities of a soft coral-derived fungus Aspergillus versicolor (ZJ-2008015). Chin. J. Mar. Drugs 2012, 31, 7–13. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.C.; Guo, Y.W.; Song, G.Q. Fortisterol, a novel steroid with an unusual seven-membered lactone ring B from the Chinese marine sponge Biemna fortis Topsent. J. Asian. Nat. Prod. Res. 2006, 8, 485–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, L.; Liu, L.Y.; Dong, Z.J.; Li, Z.H.; Liu, J.K. Six novel steroids from culture of basidiomycete Polyporus ellisii. Nat. Product. Bioprosp. 2012, 2, 240–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Weng, Y.F.; Lu, J.; Xiang, L.; Matsuura, A.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, Q.M.; Qi, J.H. Ganodermasides C and D, two new anti-aging ergosterols from spores of the medicinal mushroom Ganoderma lucidum. Bioorgan. Med. Chem. 2011, 75, 800–803. [Google Scholar]
- Weng, Y.; Xiang, L.; Matsuura, A.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, Q.; Qi, J. Ganodermasides A and B, two novel anti-aging ergosterols from spores of a medicinal mushroom Ganoderma lucidum on yeast via UTH1 gene. Bioorgan. Med. Chem. 2010, 18, 999–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geris, R.; Simpson, T.J. Meroterpenoids produced by fungi. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2009, 26, 1063–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.B.; Li, L.Y.; Wang, W.; Che, Q.; Li, D.H.; Gu, Q.Q.; Zhu, T.J. Chrodrimanins I and J from the antarctic moss-derived fungus Penicillium funiculosum GWT2-24. J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 78, 1442–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rank, C.; Phipps, R.K.; Harris, P.; Fristrup, P.; Larsen, T.O.; Gotfredsen, C.H. Novofumigatonin, a new orthoester meroterpenoid from Aspergillus novofumigatus. Org. Lett. 2008, 10, 401–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashi, H.; Oka, Y.; Kai, K.; Akiyama, K. A new meroterpenoid, chrodrimanin C, from YO-2 of Talaromyces sp. Biosci. Biotech. Bioch. 2012, 76, 745–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, H.; Ugaki, N.; Matsuda, D.; Tomoda, H. Absolute stereochemistry of pentacecilides, new inhibitors of lipid droplet formation in mouse macrophages, produced by Penicillium cecidicola FKI-3765-1. J. Antibio. 2010, 63, 315–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, H.; Nakayama, W.; Takahashi, O.; Kirikoshi, R.; Izumikawa, Y.; Iwasaki, K.; Toraiwa, K.; Rotinsulu, H.; Wewengkang, D.; Sumilat, D.; et al. Verruculides A and B, two new protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B inhibitors from an Indonesian ascidian-derived Penicillium verruculosum. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 25, 3087–3090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, F.D.; Ma, Q.Y.; Huang, S.Z.; Wang, P.; Wang, J.F.; Zhou, L.M.; Yuan, J.Z.; Dai, H.F.; Zhao, Y.X. Chrodrimanins K–N and related meroterpenoids from the fungus Penicillium sp. SCS-KFD09 isolated from a marine worm, Sipunculus nudus. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 1039–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, R.G.; Fan, Y.H.; Ma, C.M. Identification and enrichment of α-glucosidase-inhibiting dihydrostilbene and flavonoids from Glycyrrhiza uralensis leaves. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 6565, 510–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, F.; Hou, S.C.; Xu, H.N.; Liu, Z.X.; Gao, J.F.; Li, T.; Zhou, X.G.; Hu, C. 3-Aryl-6-(4-fluorobenzyl)-7H-thiazolo[3,2-b]-1,2,4-triazin-7-one derivatives as acetylcholinesterase inhibitory: Synthesis, characterization and biological activity. Chin. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 32, 661–668. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, J.J.; Dai, B.L.; Chen, N.P.; Jin, L.X.; Jiang, F.S.; Ding, Z.S.; Qian, C.D. The anti-staphylococcus aureus activity of the phenanthrene fraction from fibrous roots of Bletilla striata. Bmc. Complem. Altern. M. 2016, 16, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.H.; Huang, R.; Miao, C.P.; Chen, Y.W. Two new steroids from an endophytic fungus Phomopsis sp. Chem. Biodivers. 2013, 10, 1276–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pracht, P.; Bohle, F.; Grimme, S. Automated exploration of the low-energy chemical space with fast quantum chemical methods. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2020, 22, 7169–7192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Petersson, G.A.; Nakatsuji, H.; et al. Gaussian 16, Revision C.01; Gaussian, Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Willoughby, P.H.; Jansma, M.J.; Hoye, T.R. A guide to small-molecule structure assignment through computation of (1H and 13C) NMR chemical shifts. Nat. Protoc. 2014, 9, 643–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimblat, N.; Zanardi, M.M.; Sarotti, A.M. Beyond DP4: An improved probability for the stereochemical assignment of isomeric compounds using quantum chemical calculations of NMR shifts. J. Org. Chem. 2015, 80, 12526–12534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruhn, T.; Schaumloffel, A.; Hemberger, Y.; Bringmann, G. SpecDis: Quantifying the comparison of calculated and experimental electronic circular dichroism spectra. Chirality 2013, 25, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).