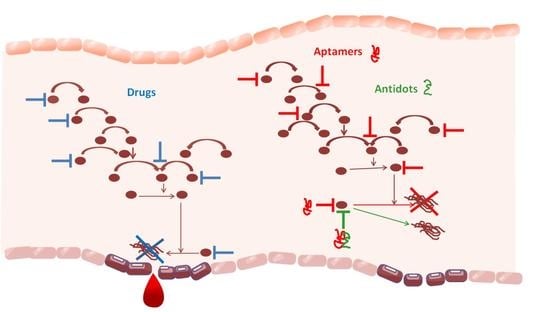
Aptamers Regulating the Hemostasis System
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Aptamers to Blood Coagulation Factors
2.1. Aptamer to FXII/XIIa
2.2. Aptamers to FXI/XIa
2.3. Aptamers to FX/Xa
2.4. Aptamer to FIXa
2.5. Aptamers to VII/VIIa
2.6. Aptamers to II/IIa (Prothrombin/Thrombin)
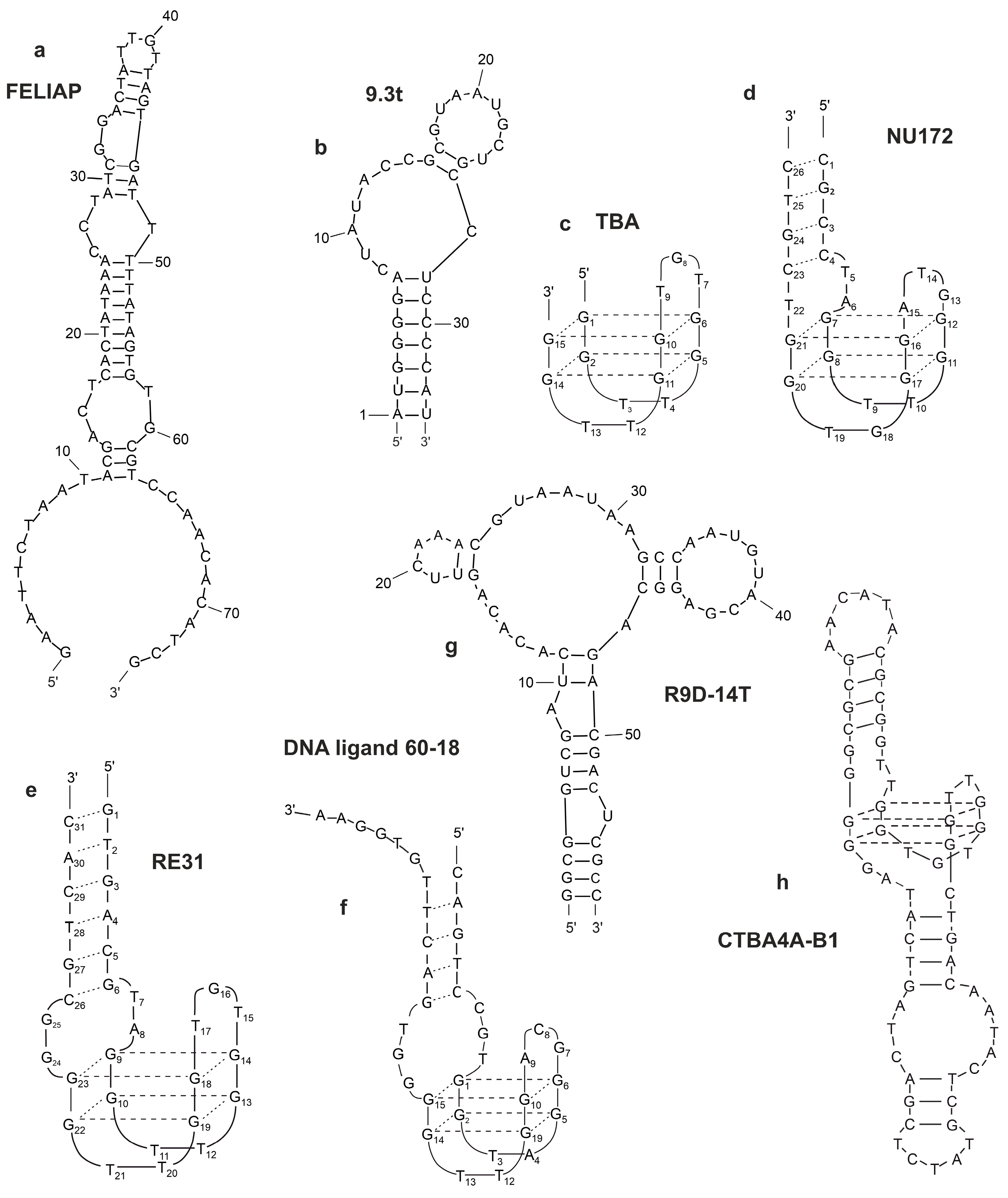
2.6.1. Thrombin-Binding Aptamer (TBA)
2.6.2. NU172
2.6.3. RE31
2.6.4. ThAD
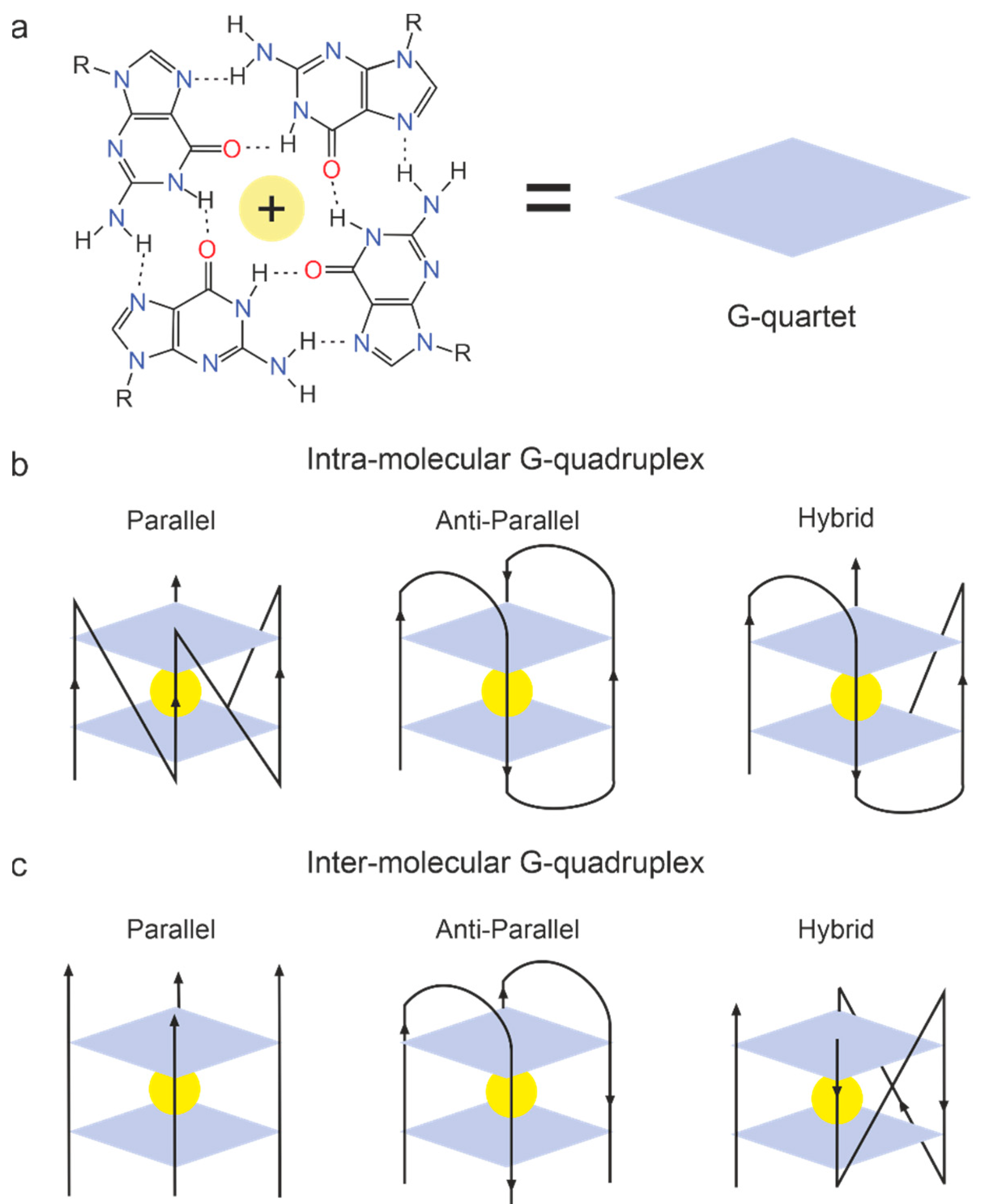
2.6.5. G-Quadruplex Aptamers to Thrombin
2.7. Aptamers to Pre-Kallikrein/Kallikrein
2.8. Aptamers to von Willebrand Factor
2.9. Aptamers to Activated Protein C
2.10. Aptamers to Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor 1
2.11. Aptamer to Tissue Factor Pathway Inhibitor
3. Prospects for Selection of Aptamers to Platelet Adhesion Receptors
4. Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Otite, F.O.; Khandelwal, P.; Malik, A.M.; Chaturvedi, S.; Sacco, R.L.; Romano, J.G. Ten-Year Temporal Trends in Medical Complications After Acute Intracerebral Hemorrhage in the United States. Stroke 2017, 48, 596–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sposato, L.A.; Hilz, M.J.; Aspberg, S.; Murthy, S.B.; Bahit, M.C.; Hsieh, C.-Y.; Sheppard, M.N.; Scheitz, J.F. Post-Stroke Cardiovascular Complications and Neurogenic Cardiac Injury. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 76, 2768–2785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffman, H.; Jalal, M.S.; Furst, T.; Chin, L.S. The Obesity Paradox in Spontaneous Intracerebral Hemorrhage: Results from a Retrospective Analysis of the Nationwide Inpatient Sample. J. Neurocrit. Care 2020, 32, 765–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uzunhan, T.A.; Aydinli, N.; Çalişkan, M.; Tatli, B.; Özmen, M. Short-term neurological outcomes in ischemic and hemorrhagic pediatric stroke. Pediatr. Int. 2019, 61, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulivi, L.; Squitieri, M.; Cohen, H.; Cowley, P.; Werring, D.J. Cerebral Venous Thrombosis: A Practical Guide. Pract. Neurol. 2020, 20, 356–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ataullakhanov, F.I.; Rumyantsev, A.G. New Insights into the Blood Clotting. Russ. J. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2018, 5, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Belyaev, A.; Dunster, J.; Gibbins, J.; Panteleev, M.; Volpert, V. Modeling thrombosis in silico: Frontiers, challenges, unresolved problems and milestones. Phys. Life Rev. 2018, 26–27, 57–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaPelusa, A.; Dave, H.D. Physiology, Hemostasis. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, R. Physiology, Coagulation Cascade: Inherited Disorders, and the Molecular Phenomenon of Alterations in Hemostasis. J. Clin. Haematol. 2021, 2, 62–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solari, F.; Varacallo, M. Low Molecular Weight Heparin (LMWH). In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan, A.M.; Prasad, V.N.; Fidelis, N. Drugs Used in Thromboembolic Disorders: An Insight into Their Mechanisms. Asian J. Cardiol. Res. 2019, 2, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Kuchinka, J.; Willems, C.; Telyshev, D.V.; Groth, T. Control of Blood Coagulation by Hemocompatible Material Surfaces—A Review. Bioengineering 2021, 8, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elango, K.; Javaid, A.; Khetarpal, B.; Ramalingam, S.; Kolandaivel, K.; Gunasekaran, K.; Ahsan, C. The Effects of Warfarin and Direct Oral Anticoagulants on Systemic Vascular Calcification: A Review. Cells 2021, 10, 773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nwangwa, E.K.; Anachuna, K.M.; Ekhoye, E.; Chijiokwu-Agbonifo, E. Deteriorating Hemostatic Functions of Adult Female Wistar Rats Mediated by Activities of Non-Steroidal AntiInflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)—Piroxicam and Vitamin E. Niger. J. Physiol. Sci. 2018, 33, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ricciotti, E.; Laudanski, K.; FitzGerald, G.A. Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs and Glucocorticoids in COVID-19. Adv. Biol. Regul. 2021, 81, 100818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nimjee, S.M.; White, R.R.; Becker, R.C.; Sullenger, B.A. Aptamers as Therapeutics. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2017, 57, 61–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellington, A.D.; Szostak, J.W. In Vitro Selection of RNA Molecules That Bind Specific Ligands. Nature 1990, 346, 818–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, H.; Bruno, J.G.; Kumar, A.; Sharma, T.K. Aptamers in the Therapeutics and Diagnostics Pipelines. Theranostics 2018, 8, 4016–4032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Chen, Z.; Liu, D.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, Z.-K.; Lu, A.; Zhang, B.-T.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, G. Structural Biology for the Molecular Insight between Aptamers and Target Proteins. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodruff, R.S.; Xu, Y.; Layzer, J.; Wu, W.; Ogletree, M.L.; Sullenger, B.A. Inhibiting the intrinsic pathway of coagulation with a factor XII-targeting RNA aptamer. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2013, 11, 1364–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundaram, P.; Kurniawan, H.; Byrne, M.E.; Wower, J. Therapeutic RNA aptamers in clinical trials. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 48, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacevic, K.D.; Gilbert, J.C.; Jilma, B. Pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics and safety of aptamers. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2018, 134, 36–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holbrook, A.; Schulman, S.; Witt, D.M.; Vandvik, P.O.; Fish, J.; Kovacs, M.J.; Svensson, P.J.; Veenstra, D.L.; Crowther, M.; Guyatt, G.H. Evidence-Based Management of Anticoagulant Therapy: Antithrombotic Therapy and Prevention of Thrombosis, 9th ed: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines. Chest 2012, 141, e152S–e184S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodruff, R.; Ivanov, I.; Verhamme, I.; Sun, M.-F.; Gailani, D.; Sullenger, B. Generation and characterization of aptamers targeting factor XIa. Thromb. Res. 2017, 156, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Zaman, K.; Fortenberry, Y. Overview of the Therapeutic Potential of Aptamers Targeting Coagulation Factors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donkor, D.; Bhakta, V.; Eltringham-Smith, L.J.; Stafford, A.R.; Weitz, J.I.; Sheffield, W.P. Selection and characterization of a DNA aptamer inhibiting coagulation factor XIa. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buddai, S.K.; Layzer, J.M.; Lu, G.; Rusconi, C.P.; Sullenger, B.A.; Monroe, D.; Krishnaswamy, S. An Anticoagulant RNA Aptamer That Inhibits Proteinase-Cofactor Interactions within Prothrombinase. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 5212–5223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soule, E.E.; Bompiani, K.M.; Woodruff, R.S.; Sullenger, B.A. Targeting Two Coagulation Cascade Proteases with a Bivalent Aptamer Yields a Potent and Antidote-Controllable Anticoagulant. Nucleic Acid Ther. 2016, 26, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunaratne, R.; Kumar, S.; Frederiksen, J.W.; Stayrook, S.; Lohrmann, J.L.; Perry, K.; Bompiani, K.M.; Chabata, C.V.; Thalji, N.K.; Ho, M.D.; et al. Combination of aptamer and drug for reversible anticoagulation in cardiopulmonary bypass. Nat. Biotechnol. 2018, 36, 606–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, A.; Pitoc, G.A.; Ganson, N.J.; Layzer, J.M.; Hershfield, M.S.; Tarantal, A.F.; Sullenger, B.A. Anti-PEG Antibodies Inhibit the Anticoagulant Activity of PEGylated Aptamers. Cell Chem. Biol. 2019, 26, 634–644.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusconi, C.P.; Yeh, A.; Lyerly, H.K.; Lawson, J.H.; Sullenger, B.A. Blocking the Initiation of Coagulation by RNA Aptamers to Factor VIIa. Thromb. Haemost. 2000, 84, 841–848. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Layzer, J.M.; Sullenger, B.A. Simultaneous Generation of Aptamers to Multiple Gamma-Carboxyglutamic Acid Proteins from a Focused Aptamer Library Using DeSELEX and Convergent Selection. Oligonucleotides 2007, 17, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, J.; Freitag, D.; Mayer, G.; Pötzsch, B. Anticoagulant characteristics of HD1-22, a bivalent aptamer that specifically inhibits thrombin and prothrombinase. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2008, 6, 2105–2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, R.; Rusconi, C.P.; Scardino, E.; Wolberg, A.S.; Lawson, J.H.; Hoffman, M.; A Sullenger, B. Generation of Species Cross-reactive Aptamers Using “Toggle” SELEX. Mol. Ther. 2001, 4, 567–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bompiani, K.M.; Monroe, D.M.; Church, F.C.; Sullenger, B.A. A High Affinity, Antidote-Controllable Prothrombin and Thrombin-Binding RNA Aptamer Inhibits Thrombin Generation and Thrombin Activity. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2012, 10, 870–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimjee, S.M.; Povsic, T.J.; Sullenger, B.A.; Becker, R.C. Translation and Clinical Development of Antithrombotic Aptamers. Nucleic Acid Ther. 2016, 26, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burrell, K.-A.S.; Layzer, J.; Sullenger, B.A. A kallikrein-targeting RNA aptamer inhibits the intrinsic pathway of coagulation and reduces bradykinin release. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2017, 15, 1807–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacevic, K.D.; Buchtele, N.; Schoergenhofer, C.; Derhaschnig, U.; Gelbenegger, G.; Brostjan, C.; Zhu, S.; Gilbert, J.C.; Jilma, B. The Aptamer BT200 Effectively Inhibits von Willebrand Factor (VWF) Dependent Platelet Function after Stimulated VWF Release by Desmopressin or Endotoxin. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 11180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacevic, K.D.; Greisenegger, S.; Langer, A.; Gelbenegger, G.; Buchtele, N.; Pabinger, I.; Petroczi, K.; Zhu, S.; Gilbert, J.C.; Jilma, B. The Aptamer BT200 Blocks von Willebrand Factor and Platelet Function in Blood of Stroke Patients. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 3092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markus, H.S.; McCollum, C.; Imray, C.; Goulder, M.A.; Gilbert, J.; King, A. The von Willebrand Inhibitor ARC1779 Reduces Cerebral Embolization After Carotid Endarterectomy: A Randomized Trial. Stroke 2011, 42, 2149–2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siller-Matula, J.M.; Merhi, Y.; Tanguay, J.-F.; Duerschmied, D.; Wagner, D.D.; McGinness, K.E.; Pendergrast, P.S.; Chung, J.-K.; Tian, X.; Schaub, R.G.; et al. ARC15105 Is a Potent Antagonist of Von Willebrand Factor Mediated Platelet Activation and Adhesion. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2012, 32, 902–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Gilbert, J.C.; Hatala, P.; Harvey, W.; Liang, Z.; Gao, S.; Kang, D.; Jilma, B. The development and characterization of a long acting anti-thrombotic von Willebrand factor (VWF) aptamer. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 18, 1113–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, R.C.; Sexton, T.; Smyth, S. COVID-19 and biomarkers of thrombosis: Focus on von Willebrand factor and extracellular vesicles. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2021, 52, 1010–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oney, S.; Nimjee, S.; Layzer, J.; Que-Gewirth, N.; Ginsburg, D.; Becker, R.; Arepally, G.; Sullenger, B. Antidote-Controlled Platelet Inhibition Targeting von Willebrand Factor with Aptamers. Oligonucleotides 2007, 17, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nimjee, S.M.; Dornbos, D.; Pitoc, G.A.; Wheeler, D.G.; Layzer, J.M.; Venetos, N.; Huttinger, A.; Talentino, S.E.; Musgrave, N.J.; Moody, H.; et al. Preclinical Development of a vWF Aptamer to Limit Thrombosis and Engender Arterial Recanalization of Occluded Vessels. Mol. Ther. 2019, 27, 1228–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsunaga, K.-I.; Kimoto, M.; Hirao, I. High-Affinity DNA Aptamer Generation Targeting von Willebrand Factor A1-Domain by Genetic Alphabet Expansion for Systematic Evolution of Ligands by Exponential Enrichment Using Two Types of Libraries Composed of Five Different Bases. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 324–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamedani, N.S.; Rühl, H.; Zimmermann, J.J.; Heiseler, T.; Oldenburg, J.; Mayer, G.; Pötzsch, B.; Müller, J. In Vitro Evaluation of Aptamer-Based Reversible Inhibition of Anticoagulant Activated Protein C as a Novel Supportive Hemostatic Approach. Nucleic Acid Ther. 2016, 26, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamedani, N.S.; Müller, J.; Tolle, F.; Rühl, H.; Pezeshkpoor, B.; Liphardt, K.; Oldenburg, J.; Mayer, G.; Pötzsch, B. Selective Modulation of the Protease Activated Protein C Using Exosite Inhibiting Aptamers. Nucleic Acid Ther. 2020, 30, 276–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gal, S.W.; Amontov, S.; Urvil, P.T.; Vishnuvardhan, D.; Nishikawa, F.; Kumar, P.K.R.; Nishikawa, S. Selection of a RNA Aptamer That Binds to Human Activated Protein C and Inhibits Its Protease Function. Eur. J. Biochem. 1998, 252, 553–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, N.Z.; Gopinath, S.C. Potential blood clotting factors and anticoagulants. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2016, 84, 356–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortenberry, Y.M.; Brandal, S.M.; Carpentier, G.; Hemani, M.; Pathak, A.P. Intracellular Expression of PAI-1 Specific Aptamers Alters Breast Cancer Cell Migration, Invasion and Angiogenesis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0164288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandal, S.; Blake, C.M.; Sullenger, B.A.; Fortenberry, Y.M. Effects of Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor-1–Specific RNA Aptamers on Cell Adhesion, Motility, and Tube Formation. Nucleic Acid Ther. 2011, 21, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madsen, J.B.; Dupont, D.; Andersen, T.B.; Nielsen, A.F.; Sang, L.; Brix, D.M.; Jensen, J.K.; Broos, T.; Hendrickx, M.L.V.; Christensen, A.; et al. RNA Aptamers as Conformational Probes and Regulatory Agents for Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor-1. Biochemistry 2010, 49, 4103–4115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damare, J.; Brandal, S.; Fortenberry, Y.M. Inhibition of PAI-1 Antiproteolytic Activity Against tPA by RNA Aptamers. Nucleic Acid Ther. 2014, 24, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elokdah, H.; Abou-Gharbia, M.; Hennan, J.K.; McFarlane, G.; Mugford, C.P.; Krishnamurthy, G.; Crandall, D.L. Tiplaxtinin, a Novel, Orally Efficacious Inhibitor of Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor-1: Design, Synthesis, and Preclinical Characterization. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 47, 3491–3494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McFadyen, J.D.; Schaff, M.; Peter, K. Current and future antiplatelet therapies: Emphasis on preserving haemostasis. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2018, 15, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullenger, B.; Woodruff, R.; Monroe, D.M. Potent Anticoagulant Aptamer Directed against Factor IXa Blocks Macromolecular Substrate Interaction. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 12779–12786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, M.G.; Purdy, D.A.; Rossi, J.S.; Grinfeld, L.R.; Myles, S.K.; Aberle, L.H.; Greenbaum, A.B.; Fry, E.; Chan, M.Y.; Tonkens, R.M.; et al. First Clinical Application of an Actively Reversible Direct Factor IXa Inhibitor as an Anticoagulation Strategy in Patients Undergoing Percutaneous Coronary Intervention. Circulation 2010, 122, 614–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vavalle, J.P.; Rusconi, C.P.; Zelenkofske, S.; Wargin, W.A.; Alexander, J.H.; Becker, R.C. A phase 1 ascending dose study of a subcutaneously administered factor IXa inhibitor and its active control agent. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2012, 10, 1303–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, C.R.; Bonadonna, D.; Otto, J.C.; McDaniel, C.G.; Chabata, C.V.; Kuchibhatla, M.; Frederiksen, J.; Layzer, J.M.; Arepally, G.M.; Sullenger, B.A.; et al. Aptamer-based factor IXa inhibition preserves hemostasis and prevents thrombosis in a piglet model of ECMO. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2021, 27, 524–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, B.L. The Association of Direct Thrombin Inhibitor Anticoagulants with Cardiac Thromboses. Chest 2015, 147, 21–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zavyalova, E.; Ustinov, N.; Golovin, A.; Pavlova, G.; Kopylov, A. G-Quadruplex Aptamers to Human Thrombin Versus Other Direct Thrombin Inhibitors: The Focus on Mechanism of Action and Drug Efficiency as Anticoagulants. Curr. Med. Chem. 2016, 23, 2230–2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roxo, C.; Kotkowiak, W.; Pasternak, A. G-Quadruplex-Forming Aptamers—Characteristics, Applications, and Perspectives. Molecules 2019, 24, 3781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Platella, C.; Riccardi, C.; Montesarchio, D.; Roviello, G.N.; Musumeci, D. G-quadruplex-based aptamers against protein targets in therapy and diagnostics. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Gen. Subj. 2017, 1861, 1429–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovačič, M.; Podbevšek, P.; Tateishi-Karimata, H.; Takahashi, S.; Sugimoto, N.; Plavec, J. Thrombin binding aptamer G-quadruplex stabilized by pyrene-modified nucleotides. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, 3975–3986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotkowiak, W.; Pasternak, A. Beyond G-Quadruplexes—The Effect of Junction with Additional Structural Motifs on Aptamers Properties. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venczel, E.A.; Sen, D. Parallel and Antiparallel G-DNA Structures from a Complex Telomeric Sequence. Biochemistry 1993, 32, 6220–6228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riccardi, C.; Meyer, A.; Vasseur, J.-J.; Cavasso, D.; Krauss, I.R.; Paduano, L.; Morvan, F.; Montesarchio, D. Design, Synthesis and Characterization of Cyclic NU172 Analogues: A Biophysical and Biological Insight. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakui, K.; Yoshitomi, T.; Yamaguchi, A.; Tsuchida, M.; Saito, S.; Shibukawa, M.; Furusho, H.; Yoshimoto, K. Rapidly Neutralizable and Highly Anticoagulant Thrombin-Binding DNA Aptamer Discovered by MACE SELEX. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2019, 16, 348–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Rossi, J. Aptamers as Targeted Therapeutics: Current Potential and Challenges. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2017, 16, 181–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musumeci, D.; Platella, C.; Riccardi, C.; Moccia, F.; Montesarchio, D. Fluorescence Sensing Using DNA Aptamers in Cancer Research and Clinical Diagnostics. Cancers 2017, 9, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Qi, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, F.; Yan, H. DNA-Nanoscaffold-Assisted Selection of Femtomolar Bivalent Human A-Thrombin Aptamers with Potent Anticoagulant Activity. ChemBioChem 2019, 20, 2494–2503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdary, P. Inhibition of Tissue Factor Pathway Inhibitor (TFPI) as a Treatment for Haemophilia: Rationale with Focus on Concizumab. Drugs 2018, 78, 881–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dockal, M.; Pachlinger, R.; Hartmann, R.; Knappe, S.; Sorensen, B.; Wong, W.Y.; Conlan, M.; Cecerle, M.; Ewenstein, B.M.; Ehrlich, H.J.; et al. Biological Explanation of Clinically Observed Elevation of TFPI Plasma Levels After Treatment with TFPI-Antagonistic Aptamer BAX 499. Blood 2012, 120, 1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tummala, R.; Rai, M.P. Glycoprotein IIb/IIIa Inhibitors. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]

| Selection No. | Target | Aptamer/Antidote | Mechanism of Action/Disease/Side Effects of the Antidote | Drug/Antidote | Mechanism of Action/Disease/Side Effects of the Antidote |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2.1 | FXII/XIIa | R4cXII-1t/ antidote—oligonucleotide [20,21,22] | Inhibits XI cleavage by XIIa, autoactivation of XII/prevention of thromboembolic disease | Heparin/ antidote—protamine [23] | Inhibits XII/acute coronary syndrome; deep-vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism; indwelling central and peripheral venous catheters; cerebral vascular diseases, strokes/hypotension, pulmonary edema, pulmonary vasoconstriction, pulmonary hypertension, anaphylaxis |
| 2.2 | FXI/XIa | 12,7; 11,16 FELIAP/antidote—oligonucleotide [24,25,26] | Inhibits XI cleavage by XIa/prevention of thromboembolic disease | Etamsylate/ heparin/ antidote—protamine | Multifunctional hemostatic action/deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, acute coronary syndrome, percutaneous, coronary intervention, cerebral vascular diseases and strokes/hypotension, pulmonary edema, pulmonary vasoconstriction, pulmonary hypertension, anaphylaxis |
| 2.3 | FX/Xa | RNA IIF7t; RNABA4 [27,28] | Blocks FXa/FVa assembly/prevention of thromboembolic disease | Rivaroxaban/[29] heparin/ antidote—protamine | Direct inhibitor Xa/deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, acute coronary syndrome, percutaneous, coronary intervention, cerebral vascular diseases and strokes/hypotension, pulmonary edema, pulmonary vasoconstriction, pulmonary hypertension, anaphylaxis |
| 2.4. | FIX/IXa | REG1; REG2 DTRI-178 9.3t; RB006/antidote—oligonucleotide [16,25,26,30] | Inhibits X cleavage by IXa/ acute coronary syndrome; percutaneous coronary intervention | Heparin/ antidote—protamine | Direct inhibitor FIX/deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, acute coronary syndrome, percutaneous, coronary intervention, cerebral vascular diseases and strokes/hypotension, pulmonary edema, pulmonary vasoconstriction, pulmonary hypertension, anaphylaxis |
| 2.5. | FVII/VIIa | 16,3; 7S-1; 7S-2/antidote—oligonucleotide [31,32] | Inhibits TF/FVIIa assembly/prevention of thromboembolic disease | - | - |
| 2.6 | FII/IIa | ARC183; TBA(HD1); HD22; Tog 25; R9D-14T; RE31; M08; Nu172; R9D-14; ThAD; CTBA4A-B1/antidote—oligonucleotide [33,34,35,36] | Inhibits pro/exosite Inhibits exosite II. Inhibition of fibrin formation/prevention of thromboembolic disease | Dabigatran/ heparin/ antidote—protamine | Reversible direct thrombin inhibitor/deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, acute coronary syndrome, percutaneous, coronary intervention, cerebral vascular diseases and strokes/hypotension, pulmonary edema, pulmonary vasoconstriction, pulmonary hypertension, anaphylaxis |
| 2.7 | Pre-kallikrein/kallikrein | Kalli-T4 [37] | Inhibits pre-kallikrein cleavage by IXa/prevention of thromboembolic disease | - | - |
| 2.8 | vWF | ARC1779; ARC15105; BT100; BT200; TAGX-0004; R9.14; R9.3; DTRI-031; Rn-DsDsDs-44/antidote—oligonucleotide [38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46] | Inhibits platelet aggregation/ thrombotic microangiopathy; thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura; cerebral thromboembolism; cerebral vascular diseases and strokes; thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura | - | - |
| 2.9 | Protein C | ARC167; MS02; G-NB3 [47,48,49] | Inhibits protein C/prevention of thromboembolic disease | Warfarin [50] | Inhibits protein C synthesis/deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, prevention of embolism in patients with atrial fibrillation and mechanical prosthetic heart valves, heart disease |
| 2.10. | PAI-1 | SM-20 [51], WT-15 [52], Pionap-40, Pionap-5 [53], R10-4, R10-2 [54] | Inhibits the anti-proteolytic activity of PAI-1 | Tiplaxtinin/ | Inhibits the anti-proteolytic activity of PAI-1 [55] |
| 2.11 | TFPI | ARC19499; BAX499 [18,25,56] | Inhibits VIIa and Xa cleavage/hemophilia | Tifacogin | Tissue factor pathway inhibitor/ severe sepsis, hemophilia |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vaganov, A.A.; Taranushenko, T.E.; Luzan, N.A.; Shchugoreva, I.A.; Kolovskaya, O.S.; Artyushenko, P.V.; Zamay, T.N.; Kichkailo, A.S. Aptamers Regulating the Hemostasis System. Molecules 2022, 27, 8593. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27238593
Vaganov AA, Taranushenko TE, Luzan NA, Shchugoreva IA, Kolovskaya OS, Artyushenko PV, Zamay TN, Kichkailo AS. Aptamers Regulating the Hemostasis System. Molecules. 2022; 27(23):8593. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27238593
Chicago/Turabian StyleVaganov, Anatoly A., Tatiana E. Taranushenko, Natalia A. Luzan, Irina A. Shchugoreva, Olga S. Kolovskaya, Polina V. Artyushenko, Tatiana N. Zamay, and Anna S. Kichkailo. 2022. "Aptamers Regulating the Hemostasis System" Molecules 27, no. 23: 8593. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27238593
APA StyleVaganov, A. A., Taranushenko, T. E., Luzan, N. A., Shchugoreva, I. A., Kolovskaya, O. S., Artyushenko, P. V., Zamay, T. N., & Kichkailo, A. S. (2022). Aptamers Regulating the Hemostasis System. Molecules, 27(23), 8593. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27238593