Salvianolic Acid B Strikes Back: New Evidence in the Modulation of Expression and Activity of Matrix Metalloproteinase 9 in MDA-MB-231 Human Breast Cancer Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
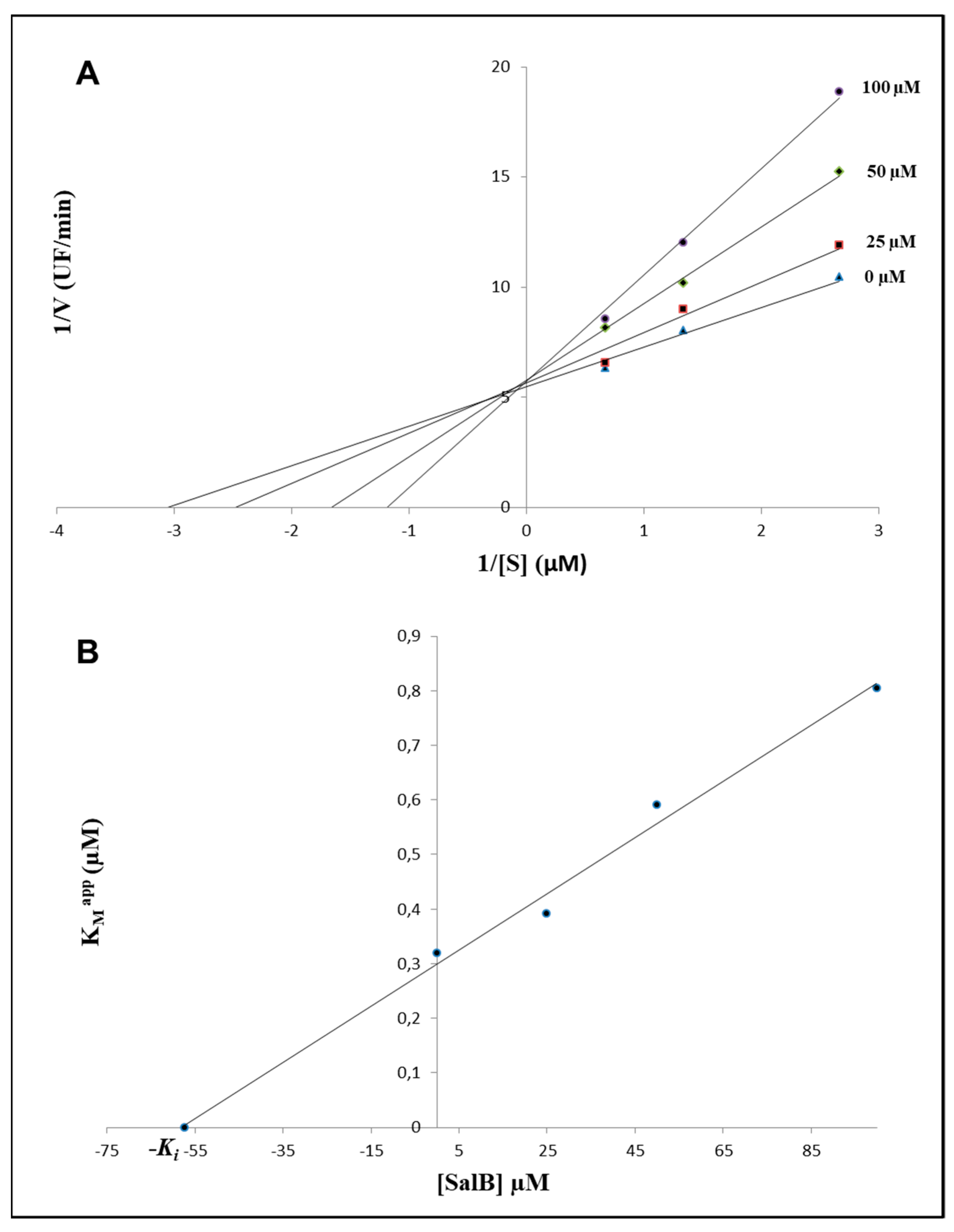
2.1. In Silico Evaluations and In Vitro Analysis of the Interaction between Salvianolic Acid B and MMP-9
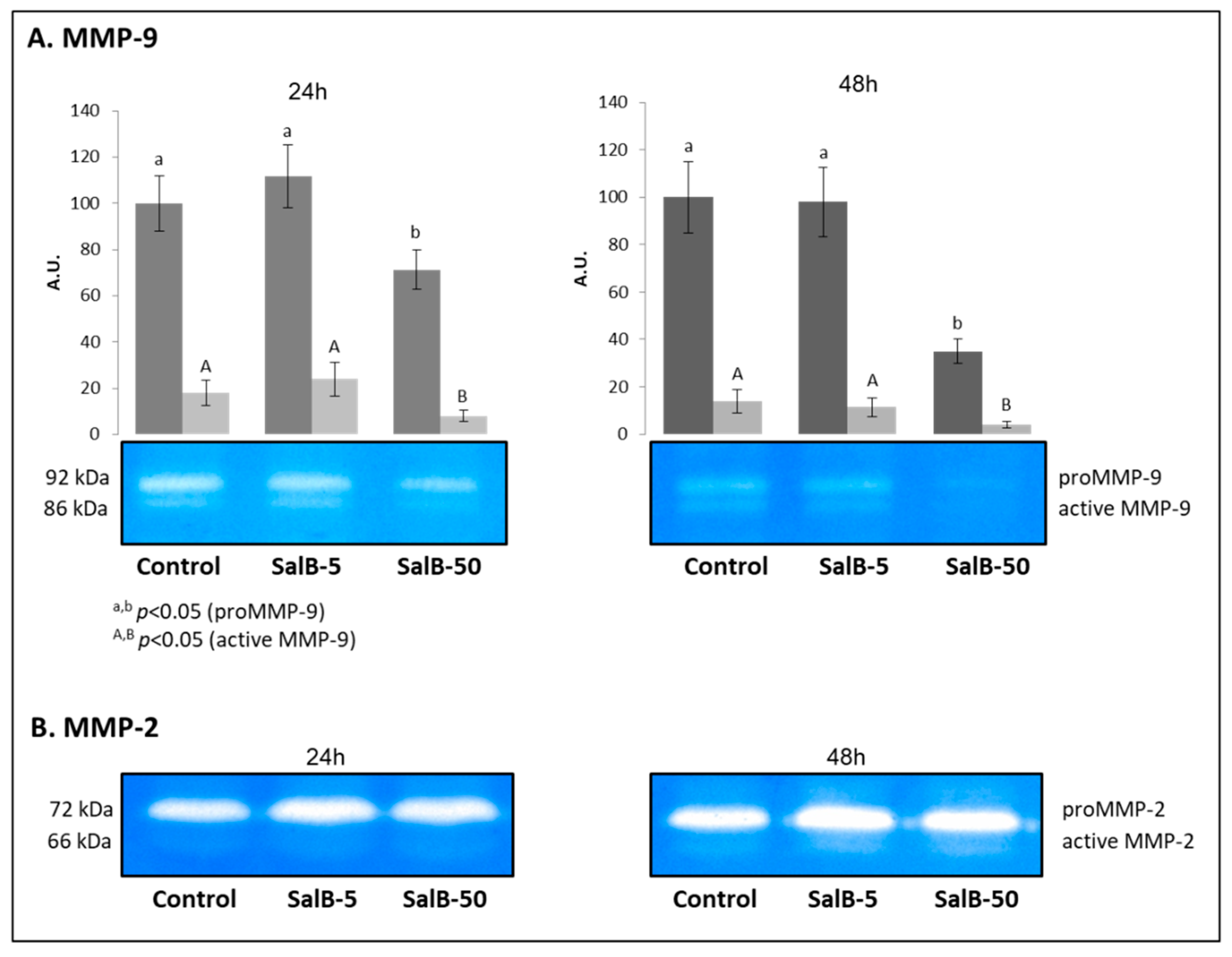
2.2. Evaluation of Gelatinolytic Activity in MDA-MB-231 Cells
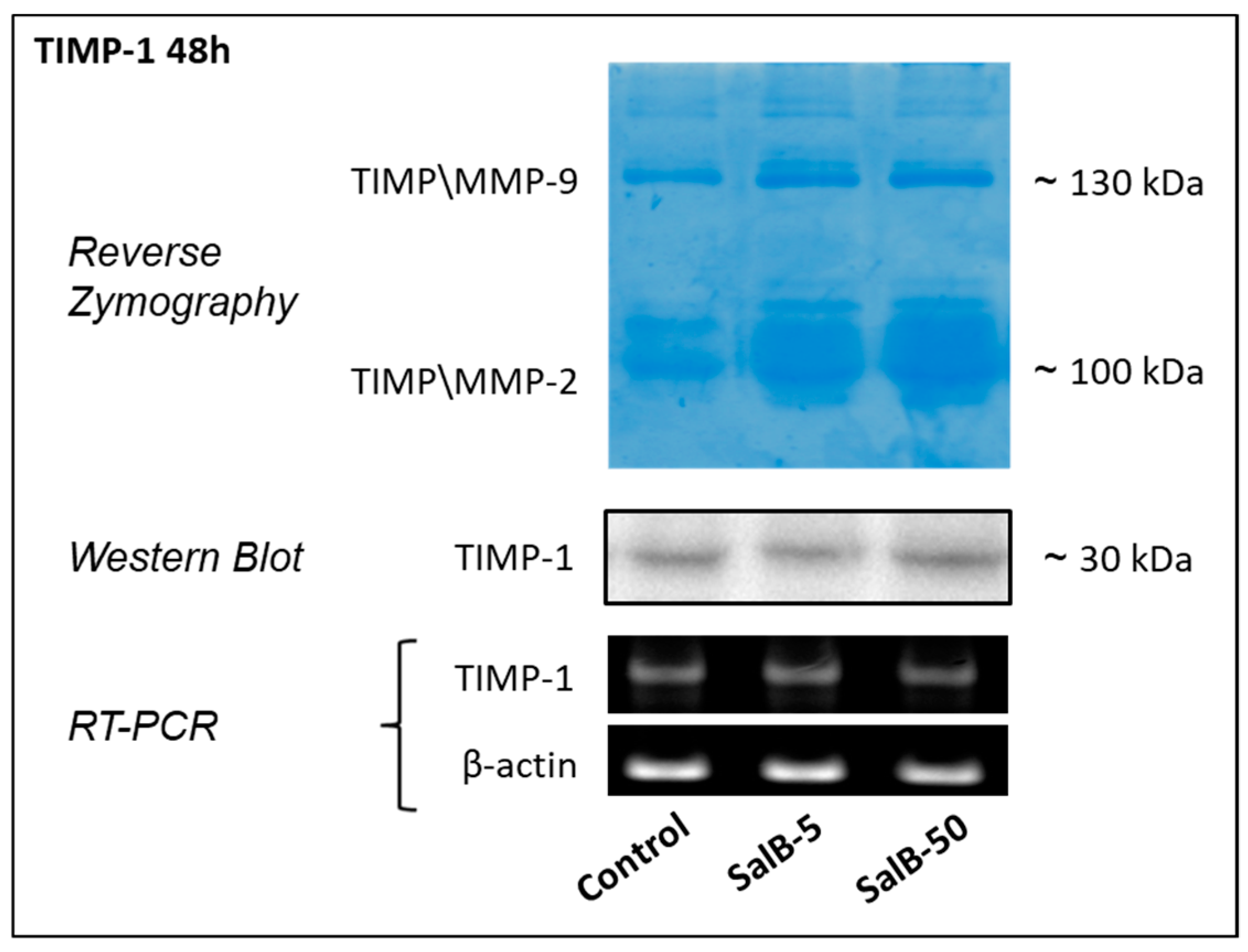
2.3. Salvianolic Acid B Had no Effects on TIMP-1 Expression in MDA-MB-231 Cells
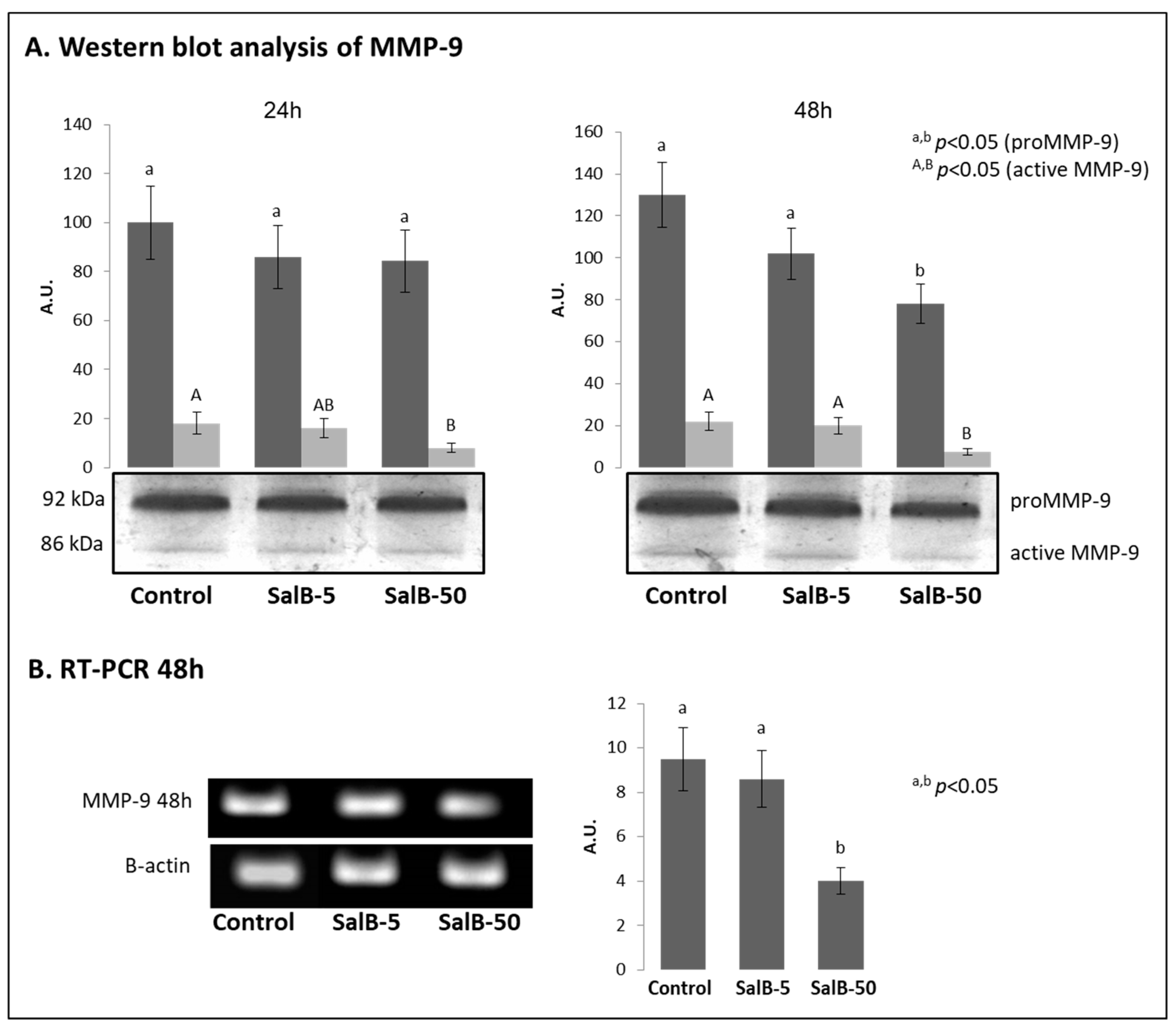
2.4. MMP-9 Expression Was Affected in Treated MDA-MB-231 Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents
4.2. ADME Analysis and Modelling of the Enzyme-Inhibitor Interaction
4.3. Fluorometric Inhibition Assay of MMP-9 Activity
4.4. Identification of the Experimental Conditions and Cell Culture
4.5. Evaluation of Gelatinases Activity by Zymography and Determination of TIMPs Expression by Reverse Zymography
4.6. Western Blotting Analysis of MMP-9 and TIMP-1
4.7. RNA Purification and Reverse Transcriptase Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR)
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nagase, H.; Visse, R.; Murphy, G. Structure and function of matrix metalloproteinases and TIMPs. Cardiovasc. Res. 2006, 69, 562–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brew, K.; Dinakarpandian, D.; Nagase, H. Tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases: Evolution, structure and function. Biochim. et Biophys. Acta (BBA) Protein Struct. Mol. Enzym. 2000, 1477, 267–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, T.; Bischoff, R. Physiology and pathophysiology of matrix metalloproteases. Amino Acids 2011, 41, 271–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamenkovic, I. Matrix metalloproteinases in tumor invasion and metastasis. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2000, 10, 415–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merdad, A.; Karim, S.; Schulten, H.J.; Dallol, A.; Buhmeida, A.; Al-Thubaity, F.; Gari, M.A.; Chaudhary, A.G.; Abuzenadah, A.M.; Al-Qahtani, M.H. Expression of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) in primary human breast cancer: MMP-9 as a potential biomarker for cancer invasion and metastasis. Anticancer. Res. 2014, 34, 1355–1366. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Giusti, I.; D’Ascenzo, S.; Millimaggi, D.; Taraboletti, G.; Carta, G.; Franceschini, N.; Pavan, A.; Dolo, V. Cathepsin B mediates the pH-dependent proinvasive activity of tumor-shed microvesicles. Neoplasia 2008, 10, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nissinen, L.; Kähäri, V.M. Matrix metalloproteinases in inflammation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta, Gen. Subj. 2014, 1840, 2571–2580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; Celenza, G.; Boggess, B.; Blasé, J.; Shi, Q.; Toth, M.; Margarida Bernardo, M.; Wolter, W.R.; Suckow, M.A.; Hesek, D.; et al. A Potent Gelatinase Inhibitor with Anti-Tumor-Invasive Activity and its Metabolic Disposition. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2009, 73, 189–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobsen, J.A.; Jourden, J.L.M.; Miller, M.T.; Cohen, S.M. To bind zinc or not to bind zinc: An examination of innovative approaches to improved metalloproteinase inhibition. Biochim. Biophys. Acta, Mol. Cell Res. 2010, 1803, 72–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ianni, A.; Celenza, G.; Franceschini, N. Oxaprozin: A new hope in the modulation of matrix metalloproteinase 9 activity. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2019, 93, 811–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huneif, M.A.; Alqahtani, S.M.; Abdulwahab, A.; Almedhesh, S.A.; Mahnashi, M.H.; Riaz, M.; Ur-Rahman, N.; Jan, M.S.; Ullah, F.; Aasim, M.; et al. α-Glucosidase, α-Amylase and Antioxidant Evaluations of Isolated Bioactives from Wild Strawberry. Molecules 2022, 27, 3444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Joufi, F.A.; Jan, M.; Zahoor, M.; Nazir, N.; Naz, S.; Talha, M.; Sadiq, A.; Nawaz, A.; Khan, F.A. Anabasis articulata (Forssk.) Moq: A Good Source of Phytochemicals with Antibacterial, Antioxidant, and Antidiabetic Potential. Molecules 2022, 27, 3526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majid, M.; Farhan, A.; Asad, M.I.; Khan, M.R.; Hassan, S.S.U.; Haq, I.U.; Bungau, S. An Extensive Pharmacological Evaluation of New Anti-Cancer Triterpenoid (Nummularic Acid) from Ipomoea batatas through In Vitro, In Silico, and In Vivo Studies. Molecules 2022, 27, 2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ende, C.; Gebhardt, R. Inhibition of matrix metalloproteinase-2 and-9 activities by selected flavonoids. Planta Med. 2004, 70, 1006–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rice-Evans, C. Flavonoids and isoflavones: Absorption, metabolism, and bioactivity. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2004, 7, 827–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.Q. Salvia miltiorrhiza: Chemical and pharmacological review of a medicinal plant. J. Med. Plants Res. 2010, 4, 2813–2820. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, G.R.; Zhang, H.M.; Ye, T.X.; Xiang, Z.J.; Yuan, Y.J.; Guo, Z.X.; Zhao, L.B. Characterization of the radical scavenging and antioxidant activities of danshensu and salvianolic acid B. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2008, 46, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.S.; Wang, S.Q. Salvianolic acid B from Salvia miltiorrhiza inhibits tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α)-induced MMP-2 upregulation in human aortic smooth muscle cells via suppression of NAD(P)H oxidase-derived reactive oxygen species. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2006, 41, 138–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.; Chen, J.; Xu, L.; Gao, Z.; Deng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xu, F.; Shen, X.; Guo, D.A. Salvianolic acid B functioned as a competitive inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinase-9 and efficiently prevented cardiac remodeling. BMC Pharmacol. 2010, 10, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, F.; Chen, J.; Shen, X.; Deng, Y.; Xu, L.; Yin, J.; Chen, H.; Teng, F.; Liu, X.; et al. Matrix metalloproteinase-9 induces cardiac fibroblast migration, collagen and cytokine secretion: Inhibition by salvianolic acid B from Salvia miltiorrhiza. Phytomedicine 2011, 19, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, W.; Zhou, Y.; Ling, Z.Q.; Xie, G.; Pang, X.; Wang, P.; Gu, X. Antitumor properties of Salvianolic acid B against triple-negative and hormone receptor-positive breast cancer cells via ceramide-mediated apoptosis. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 36331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Katary, M.A.; Abdelsayed, R.; Alhashim, A.; Abdelhasib, M.; Elmarakby, A.A. Salvianolic acid B slows the progression of breast cancer cell growth via enhancement of apoptosis and reduction of oxidative stress, inflammation, and angiogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varma, M.V.; Sateesh, K.; Panchagnula, R. Functional role of P-glycoprotein in limiting intestinal absorption of drugs: Contribution of passive permeability to P-glycoprotein mediated efflux transport. Mol. Pharm. 2005, 2, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Testa, B.; Kraemer, S.D. The Biochemistry of Drug Metabolism—An Introduction. Chem. Biodivers 2007, 4(3), 257–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchmair, J.; Göller, A.H.; Lang, D.; Kunze, J.; Testa, B.; Wilson, I.D.; Glen, R.C.; Schneider, G. Predicting drug metabolism: Experiment and/or computation? Nat. Rev. Drug. Discov. 2015, 14, 387–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Loo, W.T.; Sze, S.C.W.; Tong, Y. Curcumin inhibits cell proliferation of MDA-MB-231 and BT-483 breast cancer cells mediated by down-regulation of NFκB, cyclinD and MMP-1 transcription. Phytomedicine 2009, 16, 916–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.J.; Lee, I.T.; Chen, Y.H.; Lin, F.Y.; Sheu, L.M.; Ku, H.H.; Shiao, M.S.; Chen, J.W.; Chen, Y.L. Salvianolic acid B attenuates MMP-2 and MMP-9 expression in vivo in apolipoprotein-E-deficient mouse aorta and in vitro in LPS-treated human aortic smooth muscle cells. J. Cell. Biochem. 2007, 100, 372–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.P.; Zhu, D.X.; Sheng, J.T.; Chen, X.X.; Li, W.Z.; Wang, G.F.; Li, K.S.; Su, Y. Inhibition of tanshinone IIA, salvianolic acid A and salvianolic acid B on areca nut extract-induced oral submucous fibrosis in vitro. Molecules 2015, 20, 6794–6807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cayetano-Salazar, L.; Nava-Tapia, D.A.; Astudillo-Justo, K.D.; Arizmendi-Izazaga, A.; Sotelo-Leyva, C.; Herrera-Martinez, M.; Villegas-Comonfort, S.; Navarro-Tito, N. Flavonoids as regulators of TIMPs expression in cancer: Consequences, opportunities, and challenges. Life Sci. 2022, 308, 120932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, S.S.U.; Abbas, S.Q.; Ali, F.; Ishaq, M.; Bano, I.; Hassan, M.; Jin, H.Z.; Bungau, S.G. A Comprehensive in silico exploration of pharmacological properties, bioactivities, molecular docking, and anticancer potential of vieloplain F from Xylopia vielana Targeting B-Raf Kinase. Molecules 2022, 27, 917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daina, A.; Michielin, O.; Zoete, V. SwissADME: A free web tool to evaluate pharmacokinetics, drug-likeness and medicinal chemistry friendliness of small molecules. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosdidier, A.; Zoete, V.; Michielin, O. SwissDock, a protein-small molecule docking web service based on EADock DSS. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, 270–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanommeslaeghe, K.; Hatcher, E.; Acharya, C.; Kundu, S.; Zhong, S. CHARMM general force field: A force field for drug-like molecules compatible with the CHARMM all-atom additive biological force fields. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, 671–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosmann, T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: Application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J. Immunol. Met. 1983, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toth, M.; Sohail, A.; Fridman, R. Assessment of gelatinases (MMP-2 and MMP-9) by gelatin zymography. In Metastasis Research Protocols; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 121–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasband, W.S. ImageJ software; National Institutes of Health: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Hawkes, S.P.; Li, H.; Taniguchi, G.T. Zymography and reverse zymography for detecting MMPs and TIMPs. In Matrix Metalloproteinase Protocols; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ., USA, 2010; pp. 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Properties | Parameters | SalB |
|---|---|---|
| Physicochemical Properties | MW | 718.61 g/mol |
| Rotatable bonds | 14 | |
| HBA | 16 | |
| HBD | 9 | |
| Molar refractivity | 178.07 | |
| TPSA | 278.04 Å | |
| Lipophilicity (Log Po/w) | iLOGP | 2.10 |
| XLOGP3 | 3.98 | |
| WLOGP | 2.90 | |
| MLOGP | 0.25 | |
| SILICOS-IT | 2.57 | |
| Consensus estimation | 2.36 | |
| Pharmacokinetics | GI absorption | Low |
| BBB permeant | No | |
| P-gp substrate | No | |
| CYP1A2 inhibitor | No | |
| CYP2C19 inhibitor | No | |
| CYP2C9 inhibitor | No | |
| CYP2D6 inhibitor | No | |
| CYP3A4 inhibitor | No | |
| Log Kp (skin permeation) | −7.86 cm/s |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ianni, A.; Ruggeri, P.; Bellio, P.; Martino, F.; Celenza, G.; Martino, G.; Franceschini, N. Salvianolic Acid B Strikes Back: New Evidence in the Modulation of Expression and Activity of Matrix Metalloproteinase 9 in MDA-MB-231 Human Breast Cancer Cells. Molecules 2022, 27, 8514. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27238514
Ianni A, Ruggeri P, Bellio P, Martino F, Celenza G, Martino G, Franceschini N. Salvianolic Acid B Strikes Back: New Evidence in the Modulation of Expression and Activity of Matrix Metalloproteinase 9 in MDA-MB-231 Human Breast Cancer Cells. Molecules. 2022; 27(23):8514. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27238514
Chicago/Turabian StyleIanni, Andrea, Pierdomenico Ruggeri, Pierangelo Bellio, Francesco Martino, Giuseppe Celenza, Giuseppe Martino, and Nicola Franceschini. 2022. "Salvianolic Acid B Strikes Back: New Evidence in the Modulation of Expression and Activity of Matrix Metalloproteinase 9 in MDA-MB-231 Human Breast Cancer Cells" Molecules 27, no. 23: 8514. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27238514
APA StyleIanni, A., Ruggeri, P., Bellio, P., Martino, F., Celenza, G., Martino, G., & Franceschini, N. (2022). Salvianolic Acid B Strikes Back: New Evidence in the Modulation of Expression and Activity of Matrix Metalloproteinase 9 in MDA-MB-231 Human Breast Cancer Cells. Molecules, 27(23), 8514. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27238514






