Semisynthesis and Pesticidal Activities of Novel Cholesterol Ester Derivatives Containing Cinnamic Acid-like Fragments
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis of Compounds 2a and 2b
2.2. Synthesis of Compounds 3a and 3b
2.3. Synthesis of Compounds 4a and 4b
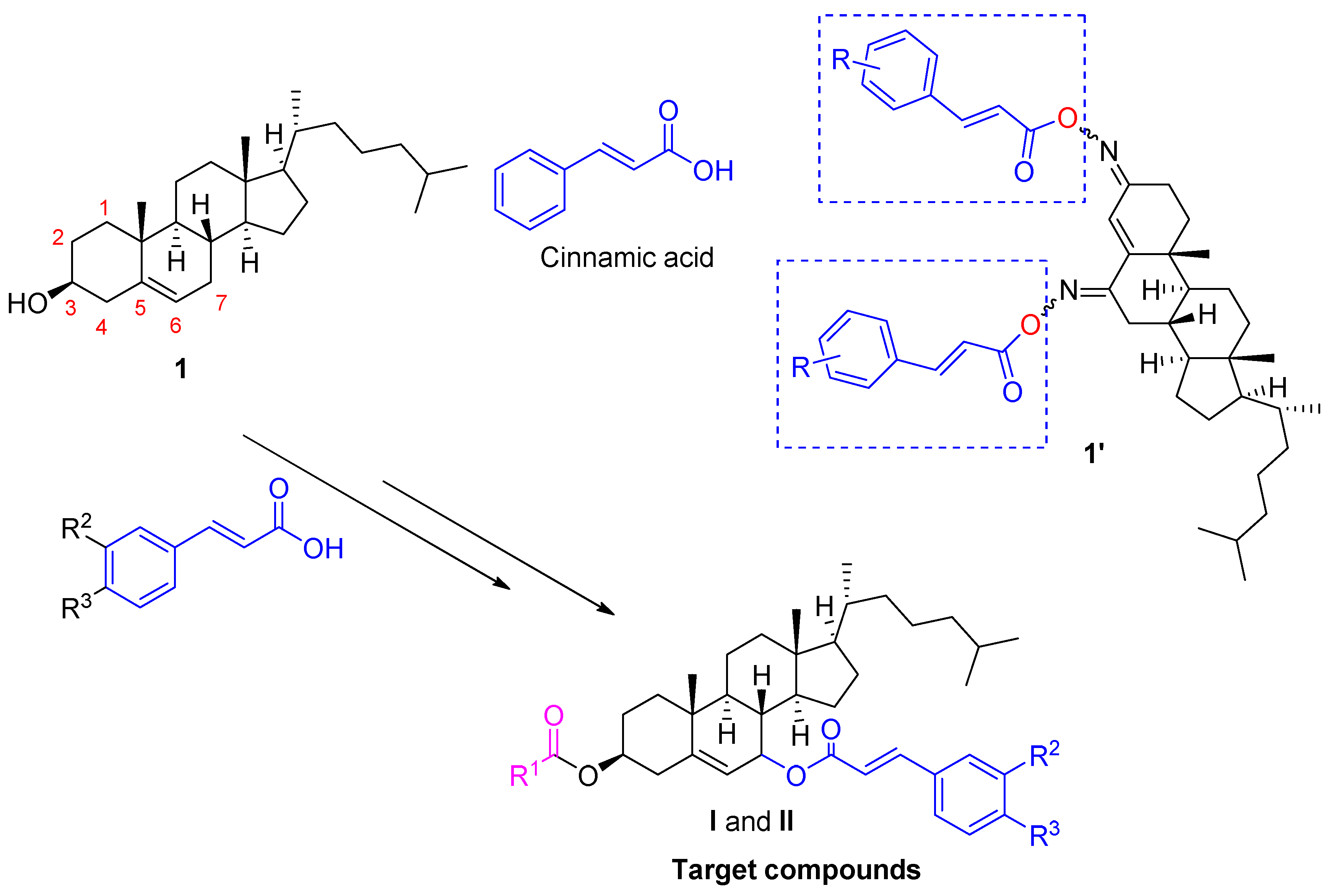
2.4. General Procedure for Synthesis of Target Compounds I(a–i)–II(a–i)
2.5. Biological Assay
2.5.1. Insecticidal Activity of Compounds I(a–i)–II(a–i) against M. separata
2.5.2. Insecticidal Activity of Compounds I(a–i)–II(a–i) against P. xylostella
3. Results and Discussion
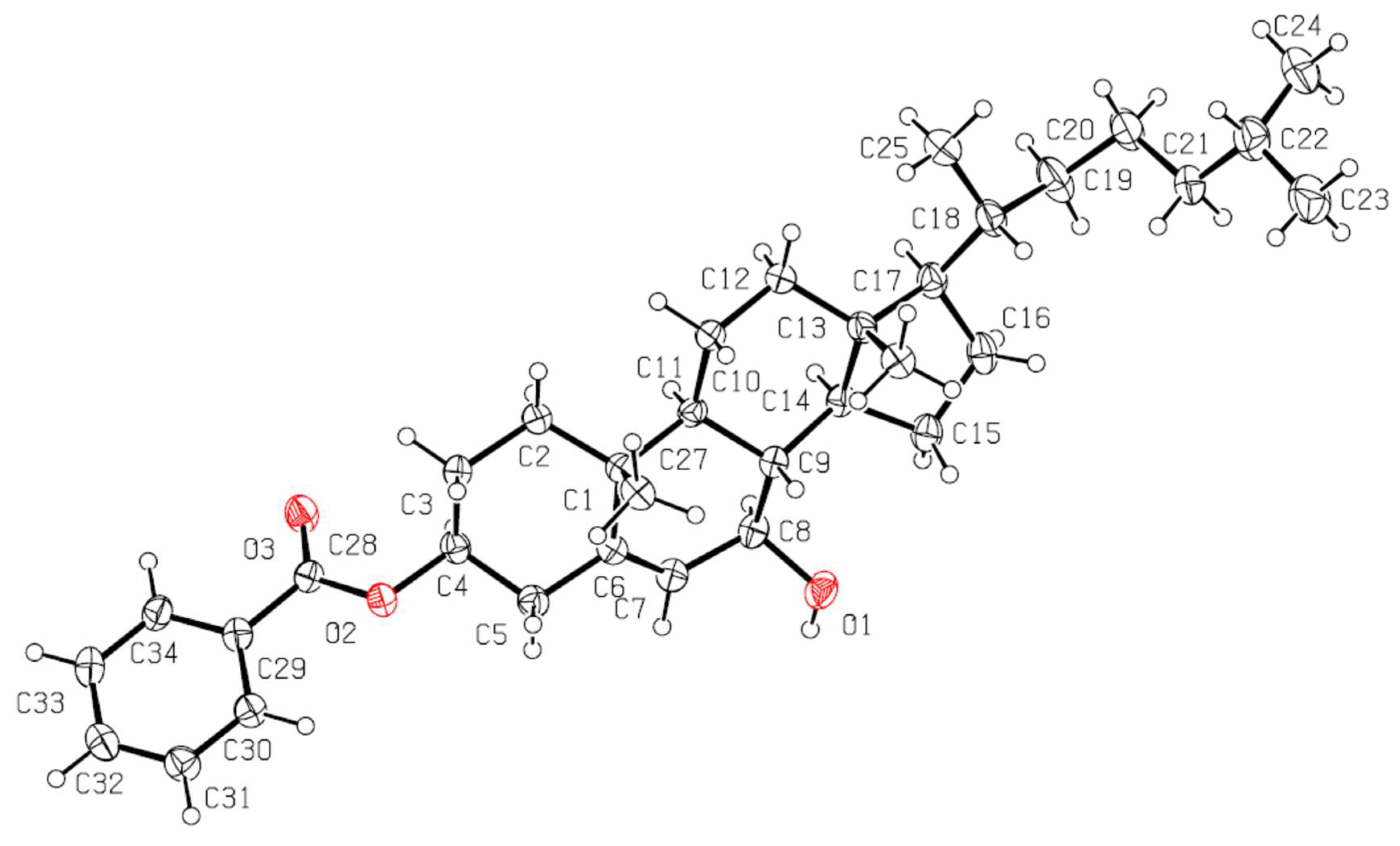
3.1. Chemistry
3.2. Insecticidal Activities
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Cui, J.; Lin, Q.; Gan, C.; Yao, Q.; Su, W.; Huang, Y. Synthesis and cytotoxic activity of some 4,6-diaza-A,B-dihomo-steroid bilactams. Steroids 2014, 79, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choteau, F.; Durand, G.; Ranchon-Cole, I.; Cercy, C.; Pucci, B. Cholesterol-based α-phenyl-N-tert-butyl nitrone derivatives as antioxidants against light-induced retinal degeneration. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 7405–7409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, P.; Ghosh, A.; Mandal, A.; Sultana, S.S.; Dey, S.; Pal, C. Oxysterols: Synthesis and anti-leishmanial activities. Steroids 2016, 107, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; Wang, H.; Hao, M.; Wang, Z.; Lv, M. Semisynthesis of conjugates from matrine/cholesterol with piperic acid/piperic acids-like as insecticidal and aphicidal agents. Heterocycles 2022, 104, 1323–1333. [Google Scholar]
- Banday, M.R.; Farshori, N.N.; Ahmad, A.; Khan, A.U.; Rauf, A. Synthesis and characterization of novel fatty acid analogs of cholesterol: In vitro antimicrobial activity. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 45, 1459–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Shao, Y.; Zhi, X.; Huan, Q.; Yu, X.; Yao, X.; Xu, H. Semisynthesis and quantitative structure-activity relationship (QSAR) study of some cholesterol-based hydrazone derivatives as insecticidal agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 4806–4812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Lv, M.; Hao, M.; Li, T.; Zhang, S.; Xu, H. Natural-product-based pesticides: Semisynthesis, structural elucidation, and evaluation of new cholesterol-matrine conjugates as pesticidal agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2021, 50, 128350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, C.R.; Garber, D.W.; Anantharamaiah, G.M. Anti-inflammatory and cholesterol-reducing properties of apolipoprotein mimetics: A review. J. Lipid Res. 2014, 55, 2007–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, B.; Land, H. Anticancer activity of the cholesterol exporter ABCA1 gene. Cell Rep. 2012, 2, 580–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laka, K.; Makgoo, L.; Mbita, Z. Cholesterol-lowering phytochemicals: Targeting the mevalonate pathway for anticancer interventions. Front Genet. 2022, 13, 841639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurup, A.; Kumar, A.V.; Rao, M.N.A. Antiinflammatory activity of cinnamic acids. Die Pharm. 1989, 44, 870. [Google Scholar]
- Godoy, M.E.; Rotelli, A.; Pelzer, L.; Tonn, C.E. Antiinflammatory activity of cinnamic acid esters. Molecules 2000, 5, 547–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Lan, Q.; Liu, N.N. Larvicidal activity of mosquito sterol carrier protein-2 inhibitors to the insecticide-resistant mosquito Culex quinquefasciatus (Diptera: Culicidae). J. Med. Entomol. 2009, 46, 1430–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Lv, M.; Xu, H. Construction of new oxime esters of cholesterol containing piperic acid-like fragments as insecticidal agents against Aphis citricola Van der Goot (Homoptera: Aphididae) and Plutella xylostella Linnaeus (Lepidoptera: Plutellidae). Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2022, 62, 128634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heckel, D.G. Insecticide resistance after silent spring. Science 2012, 337, 1612–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Lv, M.; Yu, X.; Xu, H. Application of sustainable natural bioresources in crop protection: Insight into a podophyllotoxin-derived botanical pesticide for regulating insect vestigial wing of Mythimna separata Walker. ACS Sust. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 3945–3954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Li, T.; Shan, X.; Lu, R.; Hao, M.; Lv, M.; Sun, Z.; Xu, H. High value-added use of citrus industrial wastes in agriculture: Semisynthesis and anti-tobacco mosaic virus/insecticidal activities of ester derivatives of limonin modified in the B ring. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 12241–12251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Liu, Y.; Hua, X.W.; Wu, C.C.; Zhou, S.; Wang, B.L.; Li, Z.M. Synthesis of osthole derivatives with grignard geagents and their larvicidal activities on mosquitoes. Chin. J. Chem. 2015, 33, 1353–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Yu, M.; Lv, M.; Xu, H. Synthesis of 2′(2′,6′)-(di)halogenoisoxazolopodophyllic acids-based amides derived from a naturally occurring lignan podophyllotoxin and their acaricidal activity. Heterocycles 2018, 97, 541–549. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, X.; Che, Z.; Xu, H. Recent advances in the chemistry and biology of podophyllotoxins. Chem. Eur. J. 2017, 23, 4467–4526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, H. Recent progress in the chemistry and biology of limonoids. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 35191–35220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Ma, Y.; Xiong, L.; Li, Z. Synthesis and insecticidal activity of novel N-pyridylpyrazole carbonyl thioureas. Chin. J. Chem. 2012, 30, 815–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.R.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, H.S.; Yoo, J.K. Some biochemical evidence on the selective insecticide toxicity between the two aphids, Aphis citricola and Myzus rnalisuctus (Homoptera: Phididae), and their predator, Harmonia axyridis (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). J. Asia-Pacif. Entomol. 2002, 5, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Zhang, K.; Lv, M.; Hao, M. Construction of cholesterol oxime ether derivatives containing isoxazoline/isoxazole fragments and their agricultural bioactive properties/control efficiency. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 8098–8109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Compound | Corrected Final Mortality Rate (Mean ± SE, %) a |
|---|---|
| 1 | 21.2 ± 2.7 |
| 2a | 45.4 ± 4.8 |
| 2b | 28.1 ± 2.7 |
| 3a | 42.4 ± 2.7 |
| 3b | 31.2 ± 2.7 |
| 4a | 39.3 ± 2.7 |
| 4b | 34.3 ± 4.8 |
| Ia | 33.3 ± 2.7 |
| Ib | 36.3 ± 4.8 |
| Ic | 27.2 ± 4.8 |
| Id | 48.4 ± 2.7 |
| Ie | 39.3 ± 2.7 |
| If | 39.3 ± 2.7 |
| Ig | 51.5 ± 2.7 |
| Ih | 30.3 ± 2.7 |
| Ii | 42.4 ± 2.7 |
| IIa | 25.0 ± 4.8 |
| IIb | 31.2 ± 2.7 |
| IIc | 28.1 ± 2.7 |
| IId | 37.5 ± 5.5 |
| IIe | 25.0 ± 4.8 |
| IIf | 34.3 ± 4.8 |
| IIg | 46.8 ± 2.7 |
| IIh | 31.2 ± 2.7 |
| IIi | 28.1 ± 2.7 |
| rotenone | 87.8 ± 2.7 |
| Compound | Corrected Mortality Rate (Mean ± SE, %) a | |
|---|---|---|
| 24 h | 48 h | |
| 1 | 6.8 ± 2.2 | 18.6 ± 2.2 |
| 2a | 13.6 ± 2.2 | 23.2 ± 0 |
| 2b | 15.5 ± 2.2 | 20.4 ± 2.2 |
| 3a | 15.9 ± 2.2 | 25.5 ± 2.2 |
| 3b | 11.1 ± 2.2 | 22.7 ± 2.2 |
| 4a | 22.2 ± 2.2 | 29.5 ± 2.2 |
| 4b | 17.7 ± 2.2 | 25.0 ± 3.8 |
| Ia | 22.2 ± 2.2 | 31.8 ± 3.8 |
| Ib | 11.1 ± 2.2 | 25.0 ± 3.8 |
| Ic | 13.3 ± 0 | 22.7 ± 2.2 |
| Id | 24.4 ± 2.2 | 38.6 ± 3.8 |
| Ie | 8.9 ± 2.2 | 29.5 ± 2.2 |
| If | 20.0 ± 0 | 36.3 ± 2.2 |
| Ig | 26.6 ± 3.8 | 40.9 ± 2.2 |
| Ih | 15.5 ± 2.2 | 27.2 ± 2.2 |
| Ii | 17.7 ± 2.2 | 34.0 ± 2.2 |
| IIa | 15.9 ± 2.2 | 27.9 ± 2.2 |
| IIb | 20.0 ± 3.8 | 36.3 ± 2.2 |
| IIc | 13.3 ± 3.8 | 20.4 ± 2.2 |
| IId | 15.9 ± 2.2 | 25.5 ± 2.2 |
| IIe | 22.2 ± 2.2 | 34.0 ± 2.2 |
| IIf | 25.0 ± 3.8 | 44.1 ± 3.8 |
| IIg | 20.4 ± 2.2 | 34.8 ± 4.4 |
| IIh | 11.3 ± 0 | 18.6 ± 2.2 |
| IIi | 20.4 ± 2.2 | 41.8 ± 2.2 |
| β-cypermethrin | 56.8 ± 2.2 | 97.6 ± 2.2 |
| Compound | Linear Regression Equation | LC50 (mg/mL) | Confidence Interval 95% (mg/mL) | r |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Y = −0.816 + 1.738 X | 2.946 | 2.293–3.923 | 0.992 |
| Ig | Y = −0.253 + 1.308 X | 1.560 | 1.136–2.329 | 0.989 |
| IIf | Y = –0.201 + 1.405 X | 1.390 | 1.021–1.982 | 0.997 |
| IIi | Y = −0.239 + 1.339 X | 1.508 | 1.095–2.232 | 0.998 |
| β-cypermethrin | Y = 1.583 + 2.054 X | 0.170 | 0.132–0.211 | 0.989 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, R.; Xu, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, S.; Wang, H.; Xu, H.; Lv, M. Semisynthesis and Pesticidal Activities of Novel Cholesterol Ester Derivatives Containing Cinnamic Acid-like Fragments. Molecules 2022, 27, 8437. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27238437
Lu R, Xu J, Wang Z, Zhang S, Wang H, Xu H, Lv M. Semisynthesis and Pesticidal Activities of Novel Cholesterol Ester Derivatives Containing Cinnamic Acid-like Fragments. Molecules. 2022; 27(23):8437. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27238437
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Rongfei, Jianwei Xu, Zhen Wang, Shaoyong Zhang, Hailong Wang, Hui Xu, and Min Lv. 2022. "Semisynthesis and Pesticidal Activities of Novel Cholesterol Ester Derivatives Containing Cinnamic Acid-like Fragments" Molecules 27, no. 23: 8437. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27238437
APA StyleLu, R., Xu, J., Wang, Z., Zhang, S., Wang, H., Xu, H., & Lv, M. (2022). Semisynthesis and Pesticidal Activities of Novel Cholesterol Ester Derivatives Containing Cinnamic Acid-like Fragments. Molecules, 27(23), 8437. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27238437







