New MgFeAl-LDH Catalysts for Claisen–Schmidt Condensation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
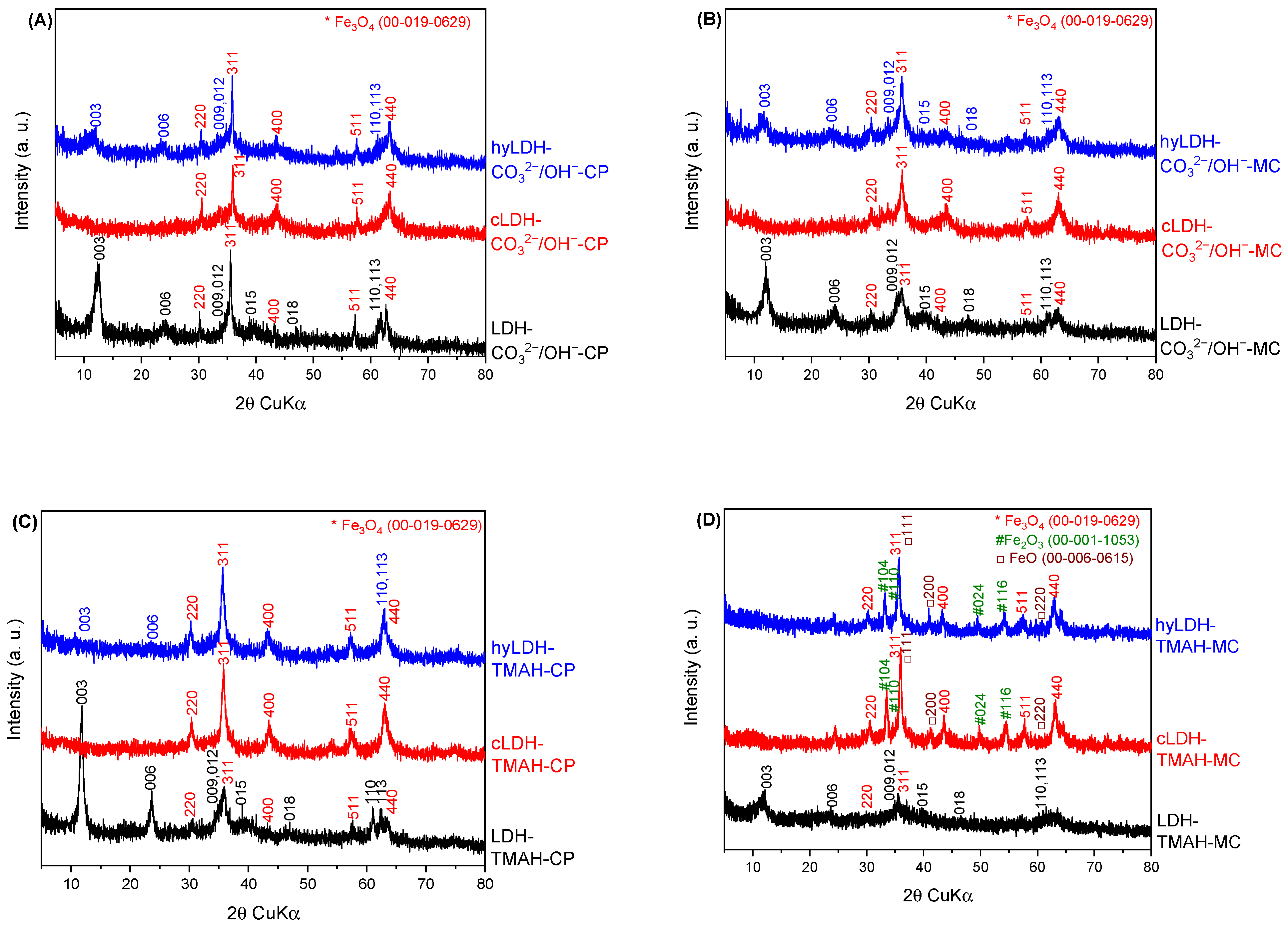
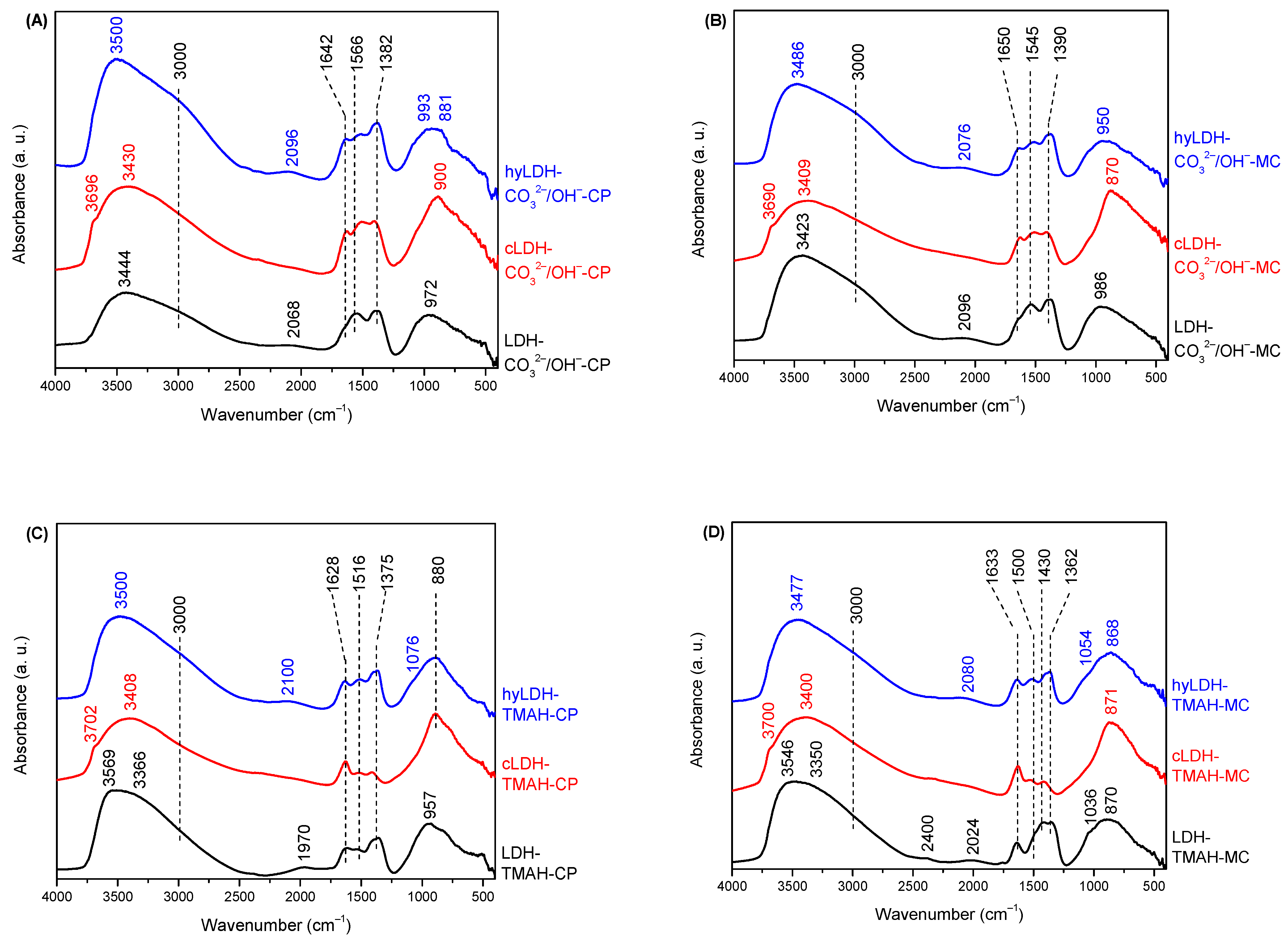
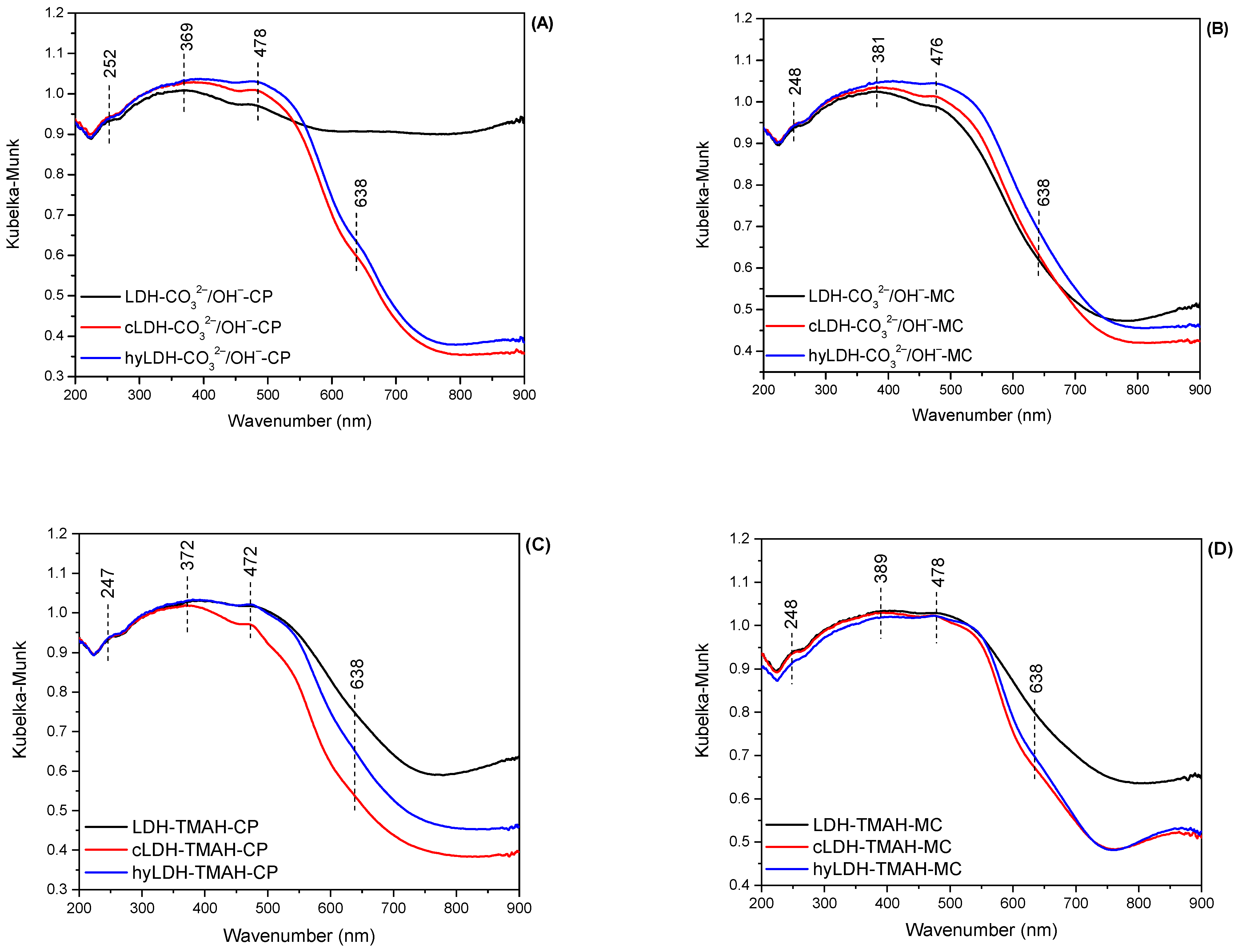
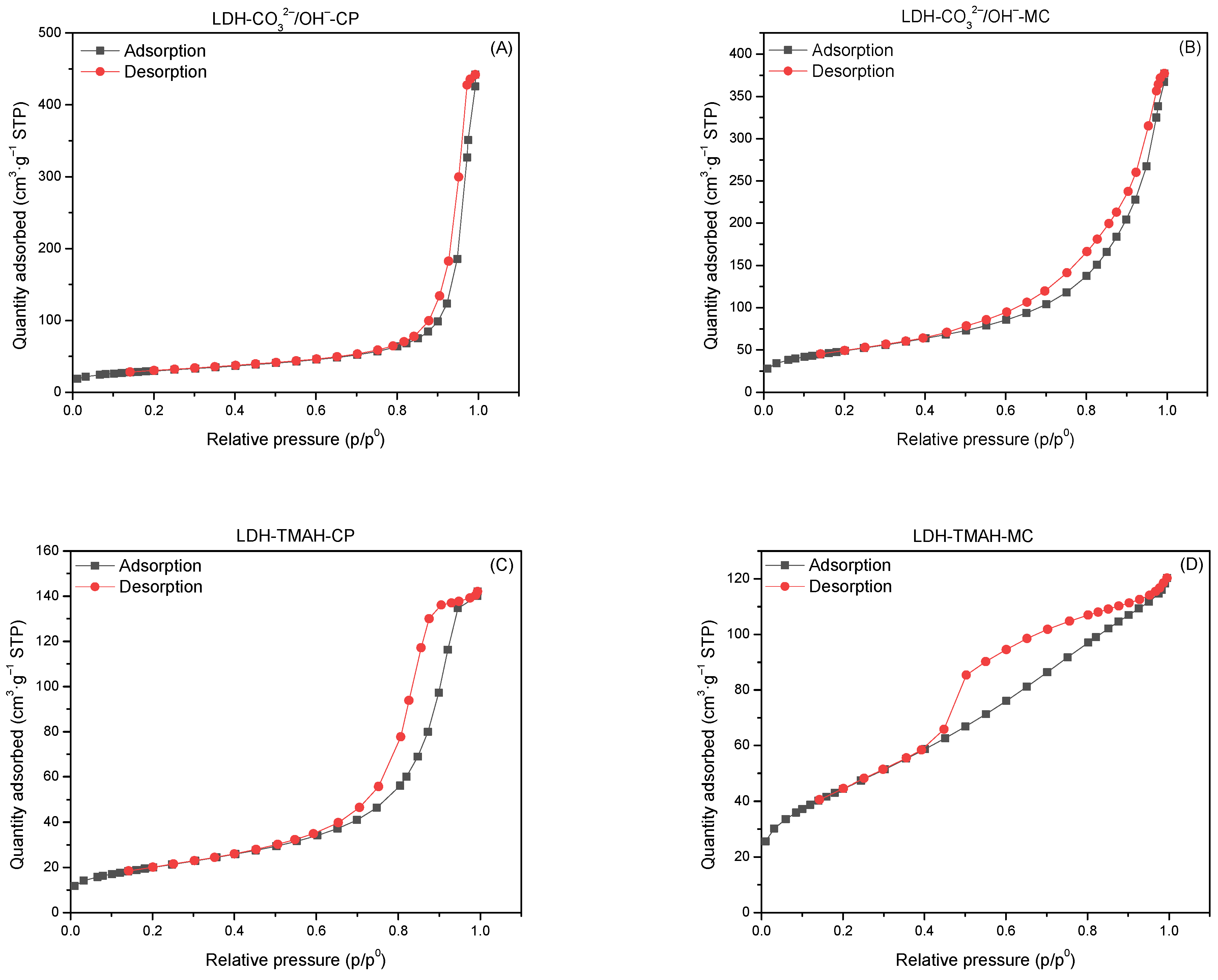
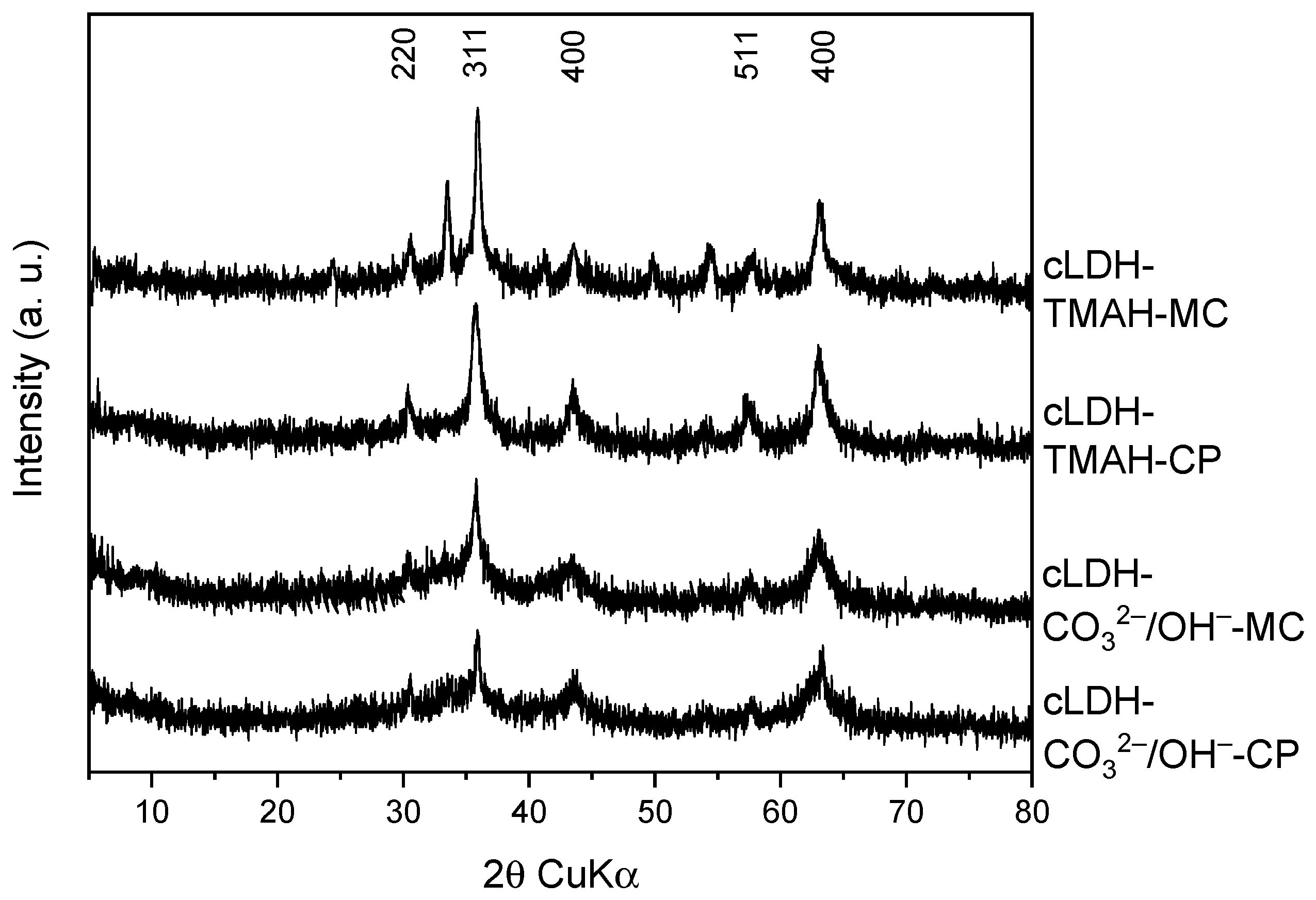
2.1. Characterization of Catalysts
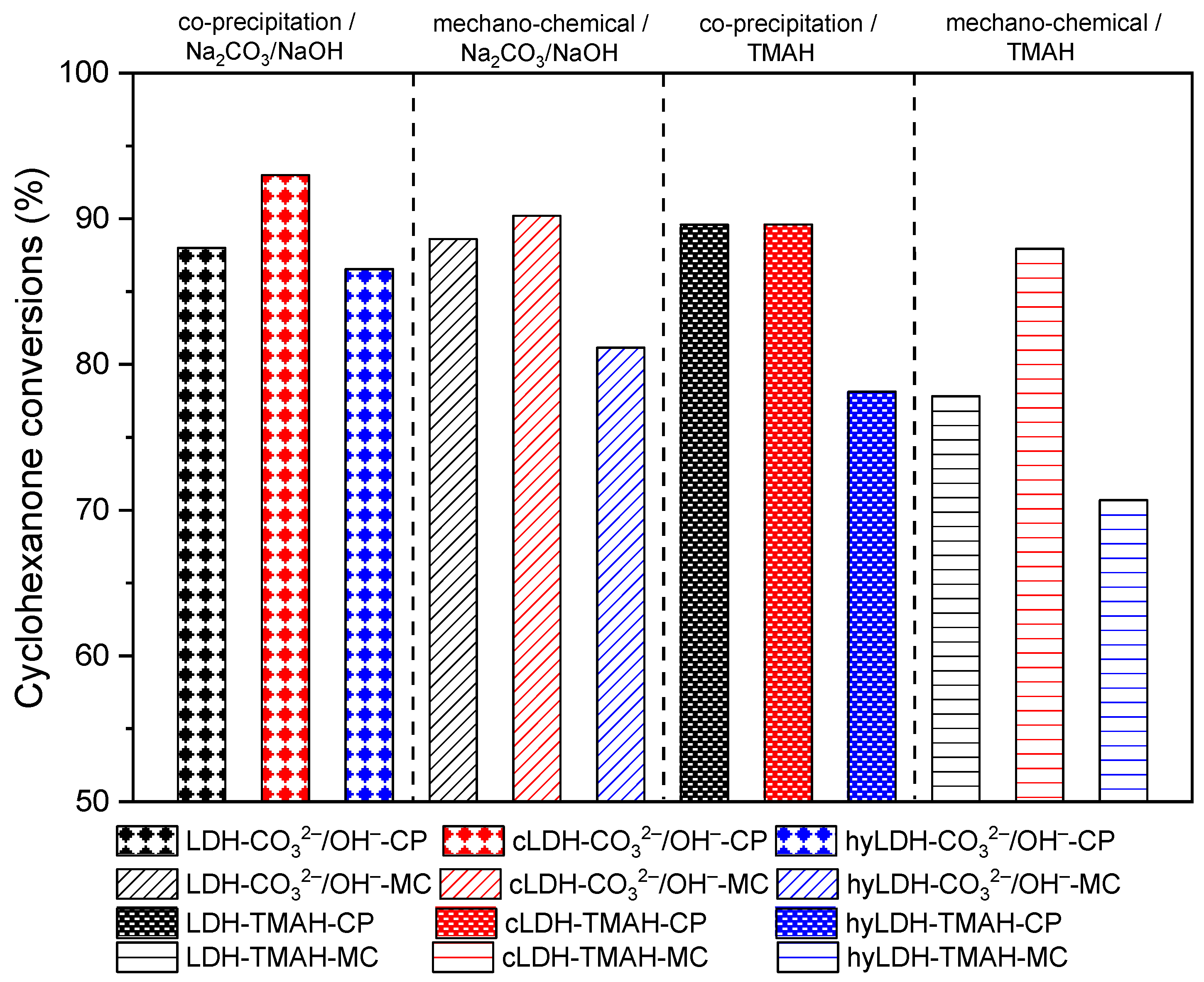
2.2. Catalytic Activity
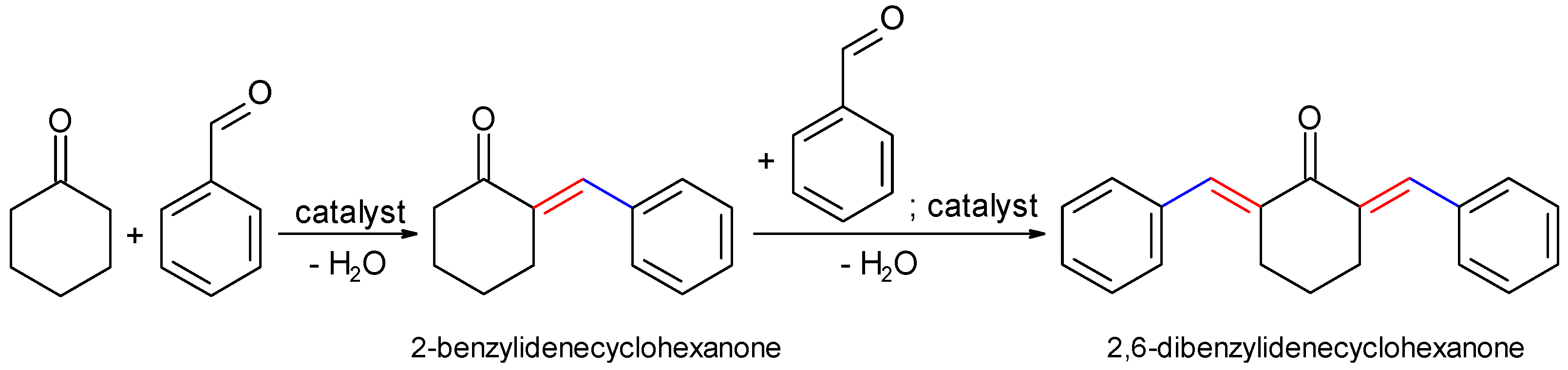
2.2.1. Claisen–Schmidt Condensation
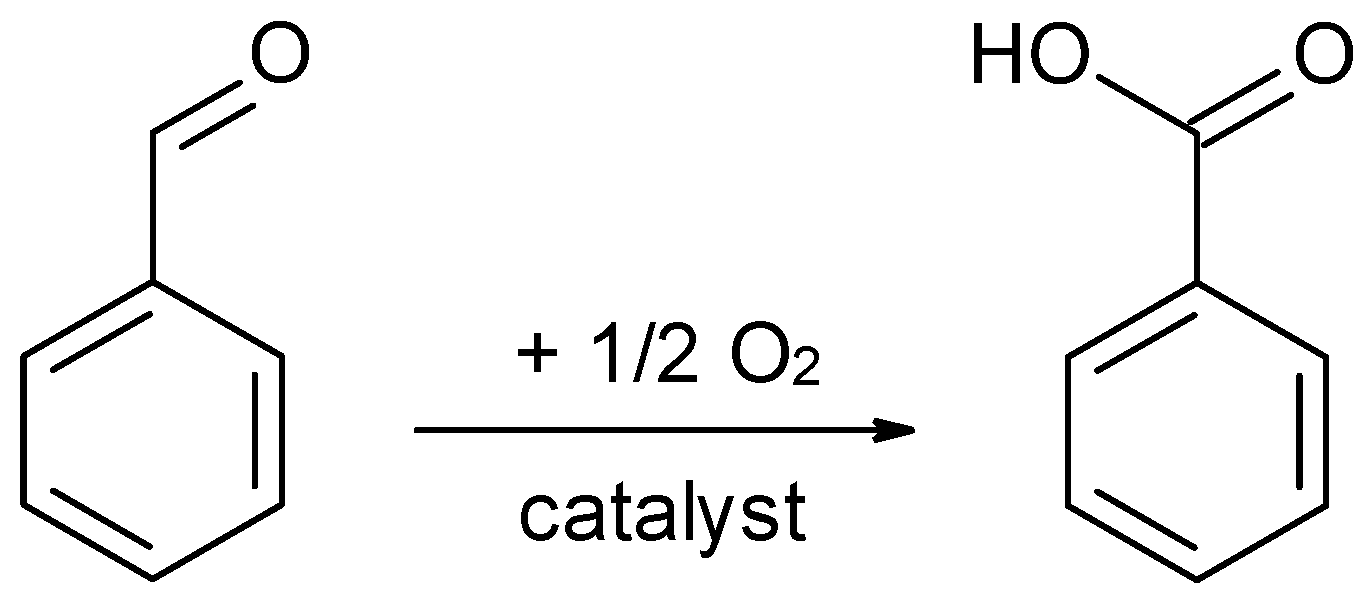
2.2.2. Benzaldehyde Oxidation as Possible Side Reaction
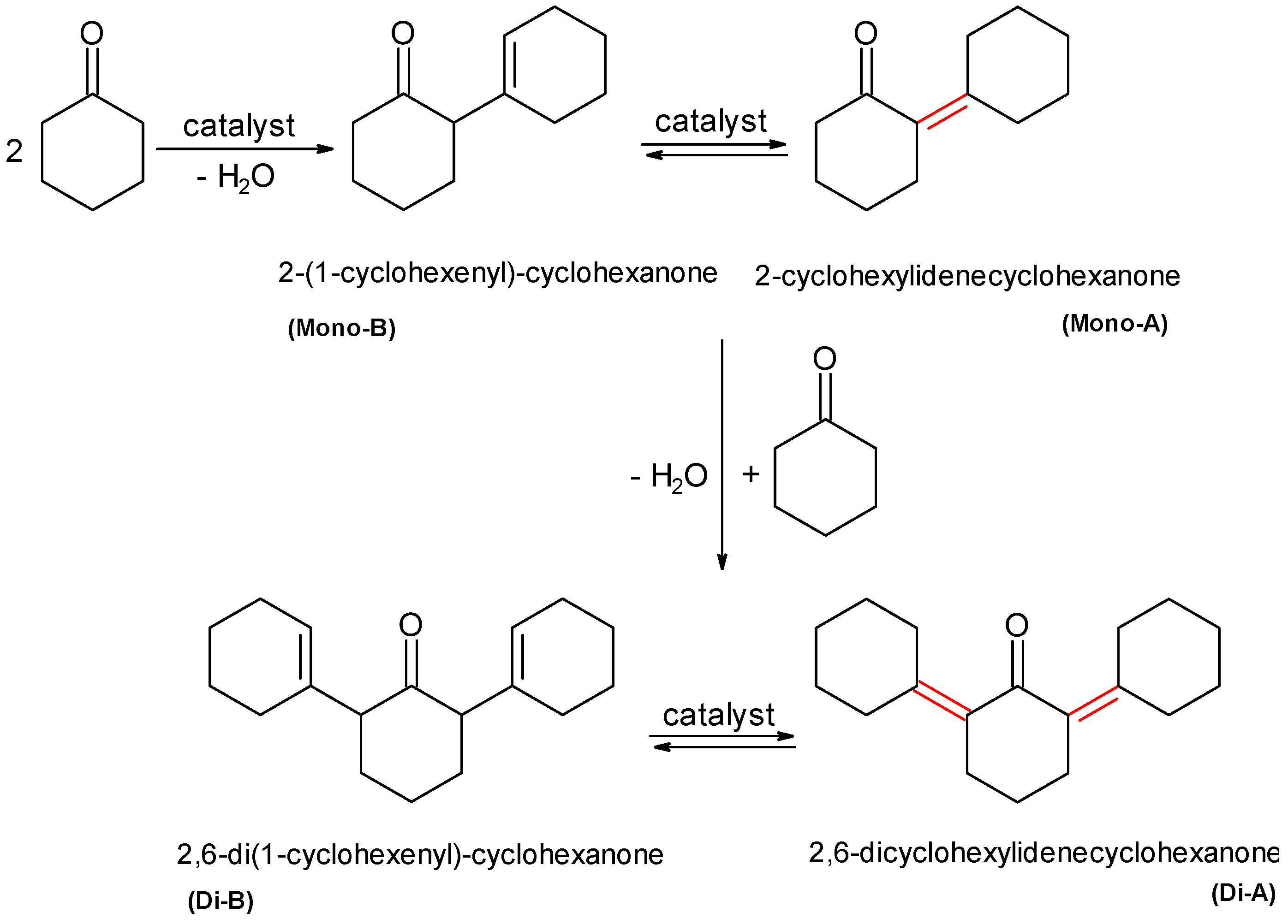
2.2.3. Self-Cyclohexanone Condensation as Possible Side Reaction
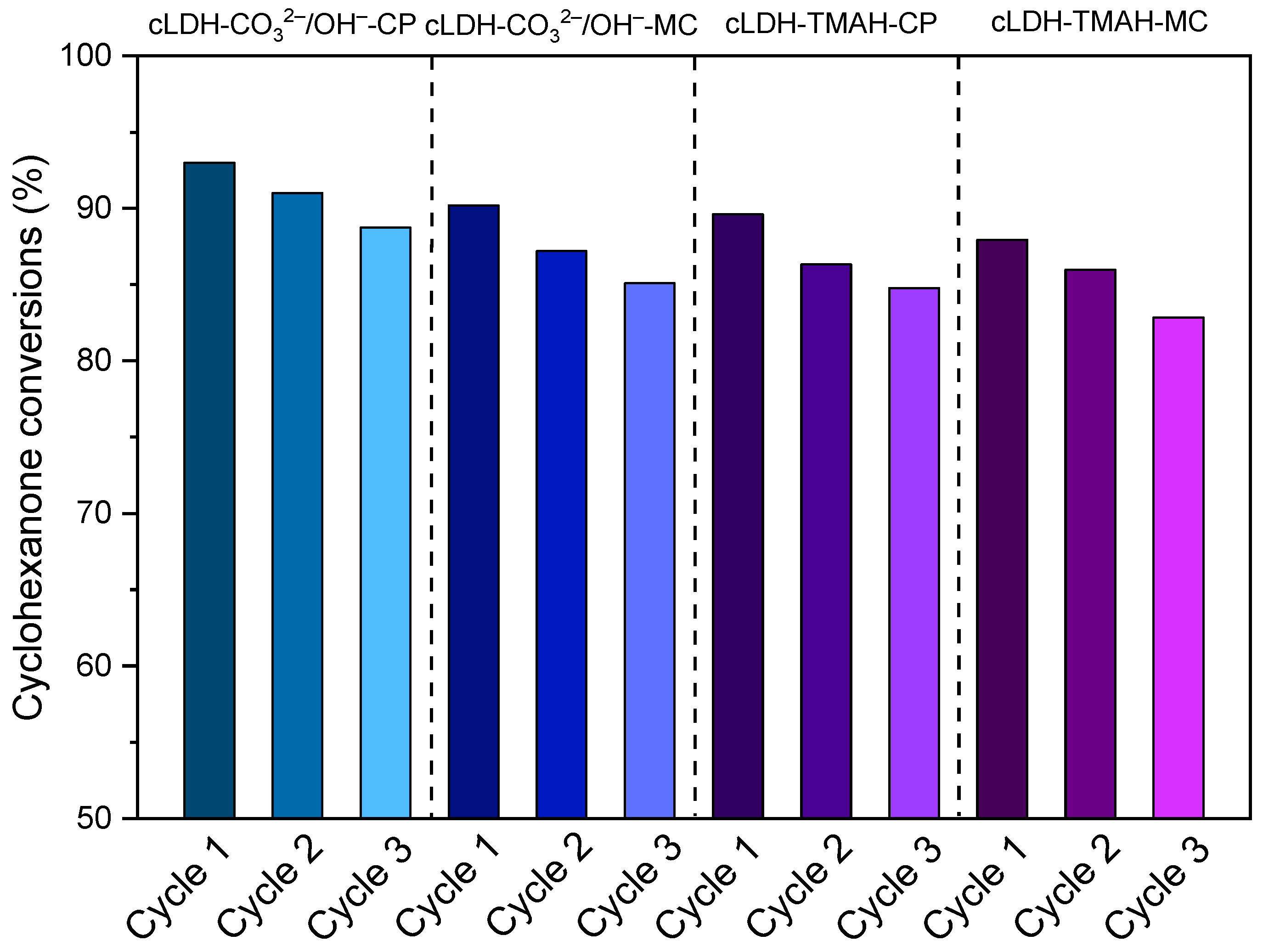
2.3. Catalyst Reusability
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Catalyst Preparation
3.2. Catalyst Characterization
3.3. Catalytic Tests
3.3.1. Claisen–Schmidt Condensation
3.3.2. The Aldol Cyclohexanone Self-Condensation
3.3.3. Benzaldehyde Oxidation
3.4. Catalyst Recycling
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Cavani, F.; Trifirò, F.; Vaccari, A. Hydrotalcite-type anionic clays: Preparation, properties and applications. Catal. Today 1991, 11, 173–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo-Suárez, J.J.; Páez-Mozo, E.A.; Oyama, S.T. Review of the synthesis of layered double hydroxides: A thermodynamic approach. Quim. Nova 2004, 27, 601–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelescu, E.; Pavel, O.; Bîrjega, R.; Zăvoianu, R.; Costentin, G.; Che, M. Solid base catalysts obtained from hydrotalcite precursors, for Knoevenagel synthesis of cinamic acid and coumarin derivatives. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2006, 308, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teodorescu, F.; Slabu, A.; Pavel, O.; Zăvoianu, R. A comparative study on the catalytic activity of ZnAl, NiAl, and CoAl mixed oxides derived from LDH obtained by mechanochemical method in the synthesis of 2-methylpyrazine. Catal. Commun. 2020, 133, 105829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bröcker, F.J.; Kainer, L. German Patent 2.024.282 (1970), to BASF AG, and UK Patent 1.342.020 (1971), to BASF AG.
- Jin, W.; Lee, D.; Jeon, Y.; Park, D.-H. Biocompatible Hydrotalcite Nanohybrids for Medical Functions. Minerals 2020, 10, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulibarri, M.; Pavlovic, I.; Hermosín, M.; Cornejo, J. Hydrotalcite-like compounds as potential sorbents of phenols from water. Appl. Clay Sci. 1995, 10, 131–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaoka, T.; Abe, M.; Tsuji, M. Synthesis of Cu–Al hydrotalcite like compound and its ion exchange property. Mater. Res. Bull. 1989, 24, 1183–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaillot, D.; Bennici, S.; Brendlé, J. Layered double hydroxides and LDH-derived materials in chosen environmental applications: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 24375–24405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, V.N.; Pham, T.H.T.; Chanthavong, M.; Do, T.H.; Nguyen, T.H.L.; Nguyen, Q.D.; Tran, T.K.N. Enhanced Photocatalytic Degradation of Rhodamine-B under Led Light Using CuZnAl Hydrotalcite Synthesized by Co-Precipitation Technique. Inorganics 2022, 10, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Ven, L.; van Gemert, M.; Batenburg, L.; Keern, J.; Gielgens, L.; Koster, T.; Fischer, H. On the action of hydrotalcite-like clay materials as stabilizers in polyvinylchloride. Appl. Clay Sci. 2000, 17, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, C.; Dong, B.; Raza, A.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, Y. Corrosion inhibition of layered double hydroxides for metal-based systems. Nano Mater. Sci. 2020, 3, 47–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tichit, D.; Coq, B. Catalysis by Hydrotalcites and Related Materials. CATTECH 2003, 7, 206–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Zhou, J.; Fan, Y.; Zhan, Y.; Chen, C.; Li, D.; Jiang, L. Mg–Al hydrotalcite-supported Pd catalyst for low-temperature CO oxidation: Effect of Pdn+ species and surface hydroxyl groups. Dalton Trans. 2018, 47, 14938–14944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, L.; Huang, H.; Niederberger, M. Layered cobalt hydrotalcite as an advanced lithium-ion anode material with high capacity and rate capability. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 21264–21269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trujillano, R.; González-García, I.; Morato, A.; Rives, V. Controlling the Synthesis Conditions for Tuning the Properties of Hydrotalcite-Like Materials at the Nano Scale. ChemEngineering 2018, 2, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, S.; Fan, M.; DaCosta, H.F.M.; Russell, A.G.; Berchtold, K.A.; Dubey, M.K. Chapter 10–CO2 Sorption. In Coal Gasification and Its Applications; Bell, D.A., Towler, B.F., Fan, M., Eds.; William Andrew Publishing: Norwich, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 293–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, R.D. Revised effective ionic radii and systematic studies of interatomic distances in halides and chalcogenides. Acta Cryst. 1976, A32, 751–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardhayanti, L.I.; Santosa, S.J. Synthesis of Magnetite-Mg/Al Hydrotalcite and Its Application as Adsorbent for Navy Blue and Yellow F3G Dyes. Procedia Eng. 2016, 148, 1380–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centi, G.; Perathoner, S. Behaviour of SOx-traps derived from ternary Cu/Mg/Al hydrotalcite materials. Catal. Today 2007, 127, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, N.N.; Das, R. Synthesis, characterization and activation of quaternary layered double hydroxides for the one-pot synthesis of methyl isobutyl ketone. React. Kinet. Mech. Catal. 2010, 99, 397–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, C.A.; Dias, P.M.; Ferreira, A.M.D.C.; Constantino, V.R. Mg–Al hydrotalcite-like compounds containing iron-phthalocyanine complex: Effect of aluminum substitution on the complex adsorption features and catalytic activity. Appl. Clay Sci. 2005, 28, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jana, S.K.; Kubota, Y.; Tatsumi, T. Cobalt-substituted polyoxometalate pillared hydrotalcite: Synthesis and catalysis in liquid-phase oxidation of cyclohexanol with molecular oxygen. J. Catal. 2008, 255, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Kirkpatrick, R.J. Organic anions in layered double hydroxides: An experimental investigation of citrate hydrotalcite. Am. Min. 2007, 92, 397–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jana, A.; Roy, O.; Ravuru, S.S.; De, S. Tuning of graphene oxide intercalation in magnesium aluminium layered double hydroxide and their immobilization in polyacrylonitrile beads by single step mussel inspired phase inversion: A super adsorbent for lead. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 391, 123587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, M.F.; Rocha, I.M.; Figueiredo, J.L.; Freire, C.; Pereira, M.F.R. CoMn-LDH@carbon nanotube composites: Bifunctional electrocatalysts for oxygen reactions. Catal. Today 2018, 301, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, M.; Cai, R.; Ren, J.; Chen, J.; Qi, L.; Long, X.; Yang, S. Conductive Polymer Intercalation Tunes Charge Transfer and Sorption–Desorption Properties of LDH Enabling Efficient Alkaline Water Oxidation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 37063–37070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, J.; Zhang, Q.; Li, X.; He, X.; Song, S. Mechanochemical approaches to synthesize layered double hydroxides: A review. Appl. Clay Sci. 2015, 119, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavel, O.; Zăvoianu, R.; Bîrjega, R.; Angelescu, E.; Pârvulescu, V. Mechanochemical versus co-precipitated synthesized lanthanum-doped layered materials for olefin oxidation. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2017, 542, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavel, O.D.; Stamate, A.-E.; Zăvoianu, R.; Bucur, I.C.; Bîrjega, R.; Angelescu, E.; Pârvulescu, V.I. Mechano-chemical versus co-precipitation for the preparation of Y-modified LDHs for cyclohexene oxidation and Claisen-Schmidt condensations. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2020, 605, 117797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavel, O.D.; Stamate, A.-E.; Bacalum, E.; Cojocaru, B.; Zăvoianu, R.; Pârvulescu, V.I. Catalytic behavior of Li-Al-LDH prepared via mechanochemical and co-precipitation routes for cyanoethylation reaction. Catal. Today 2021, 366, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Li, F.; Sun, Z.; Song, Q. A highly active K/Cu-Mn-O catalyst for the removal of nitric oxide in indoor air. Indoor Built. Environ. 2019, 28, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciotta, E.; Pizzoferrato, R.; Di Vona, M.L.; Ferrari, I.V.; Richetta, M.; Varone, A. Increasing the Electrical Conductivity of Layered Double Hydroxides by Intercalation of Ionic Liquids. Mater. Sci. Forum 2018, 941, 2209–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, F.; Zhao, J.; Yang, Q.; Li, C. Nanostructured hybrid NiFeOOH/CNT electrocatalysts for oxygen evolution reaction with low overpotential. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 74536–74544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cojocaru, B.; Jurca, B.C.; Zăvoianu, R.; Bîrjega, R.; Pârvulescu, V.I.; Pavel, O.D. Tailored texture synthesized LDH catalysts in the presence of quaternary ammonium salts. Catal. Commun. 2022, 170, 106485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sels, B.F.; De Vos, D.E.; Jacobs, P.A. Hydrotalcite-like anionic clays in catalytic organic reactions. Catal. Rev. 2001, 43, 443–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, J.G. Ueber die Einwirkung von Aldehyd auf Furfurol. Ber. Dtsch. Chem. Ges. 1880, 13, 2342–2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claisen, L. Condensationen der Aldehyde mit Acetessig- und Malonsäureäther. Ber. Dtsch. Chem. Ges. 1881, 14, 345–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zăvoianu, R.; Mihăilă, S.-D.; Cojocaru, B.; Tudorache, M.; Pârvulescu, V.I.; Pavel, O.D.; Oikonomopoulos, S.; Jacobsen, E.E. An Advanced Approach for MgZnAl-LDH Catalysts Synthesis Used in Claisen-Schmidt Condensation. Catalysts 2022, 12, 759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Xu, J.; Gu, X. Modified calcium oxide as stable solid base catalyst for Aldol condensation reaction. J. Chem. Sci. 2013, 125, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, D.; Khatri, C.; Rani, A. Synthesis and characterization of novel solid base catalyst from fly ash. Fuel 2011, 90, 2083–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sluban, M.; Cojocaru, B.; Parvulescu, V.I.; Iskra, J.; Korošec, R.C.; Umek, P. Protonated titanate nanotubes as solid acid catalyst for aldol condensation. J. Catal. 2017, 346, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortezaei, Z.; Zendehdel, M.; Bodaghifard, M.A. Synthesis and characterization of functionalized NaP Zeolite@CoFe2O4 hybrid materials: A micro–meso-structure catalyst for aldol condensation. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2020, 46, 2169–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, A.F.M.M.; Ali, R.; Jahng, Y.; Kadi, A.A. A Facile Solvent Free Claisen-Schmidt Reaction: Synthesis of α,α′-bis-(Substituted-benzylidene)cycloalkanones and α,α′-bis-(Substituted-alkylidene)cycloalkanones. Molecules 2012, 17, 571–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Z.G.; Liu, J.; Zeng, P.L.; Dong, Z.B. Synthesis of α,α′-bis(Substituted Benzylidene)Ketones Catalysed by a SOCl2/EtOH reagent. J. Chem. Res. 2004, 2004, 55–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vashishtha, M.; Mishra, M.; Undre, S.; Singh, M.; Shah, D.O. Molecular mechanism of micellar catalysis of cross aldol reaction: Effect of surfactant chain length and surfactant concentration. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2015, 396, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelescu, E.; Birjega, R.; Pavel, O.D.; Che, M.; Costentin, G.; Popoiu, S. Hydrotalcites (HTs) and mesoporous mixed oxides obtained from HTs, basic solid catalysts for cyclohexanone condensation. Stud. Surf. Sci. Catal. 2005, 156, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Zeb, S.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, M.; Cui, Y.; Sun, G. Highly selective self-condensation of cyclohexanone: The distinct catalytic behaviour of HRF5015. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2020, 7, 200123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Xianmei, X.; Wu, Z.; Xie, X. Oxidation of Benzaldehyde to Benzoic Acid using Heterogenous Nial-Hydrotalcite-Like-Compounds as the Catalyst in Acetic Acid. Prog. React. Kinet. Mech. 2011, 36, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bîrjega, R.; Pavel, O.; Costentin, G.; Che, M.; Angelescu, E. Rare-earth elements modified hydrotalcites and corresponding mesoporous mixed oxides as basic solid catalysts. Appl. Catal. A: Gen. 2005, 288, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyata, S. The Syntheses of Hydrotalcite-Like Compounds and Their Structures and Physico-Chemical Properties—I: The Systems Mg2+-Al3+-NO3−, Mg2+-Al3+-Cl−, Mg2+-Al3+-ClO4−, Ni2+-Al3+-Cl− and Zn2+-Al3+-Cl−. Clays Clay Min. 1975, 23, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frost, R.L.; Cash, G.A.; Kloprogge, J. ‘Rocky Mountain leather’, sepiolite and attapulgite—an infrared emission spectroscopic study. Vib. Spectrosc. 1998, 16, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchi, A.; Apesteguía, C. Impregnation-induced memory effect of thermally activated layered double hydroxides. Appl. Clay Sci. 1998, 13, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benziger, J.B.; Larson, L. An infrared spectroscopy study of the adsorption of CO on Fe/MgO. J. Catal. 1982, 77, 550–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liu, J.; Shi, R.; Waterhouse, G.I.N.; Wen, X.; Zhang, T. Fe-Based Catalysts for the Direct Photohydrogenation of CO 2 to Value-Added Hydrocarbons. Adv. Energy Mater. 2021, 11, 2002783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Wen, N.; Cheng, J.; Deng, W.; Zhou, H.; Zhao, B. Experimental Study on SCR-C3H6 Over Cu–Fe/Al-PILC Catalysts: Catalytic Performance, Characterization, and Mechanism. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2020, 59, 14776–14788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamritski, I.; Burns, G. Infrared- and Raman-Active Phonons of Magnetite, Maghemite, and Hematite: A Computer Simulation and Spectroscopic Study. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 4965–4968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chourpa, I.; Douziech-Eyrolles, L.; Ngaboni-Okassa, L.; Fouquenet, J.-F.; Cohen-Jonathan, S.; Soucé, M.; Marchais, H.; Dubois, P. Molecular composition of iron oxide nanoparticles, precursors for magnetic drug targeting, as characterized by confocal Raman microspectroscopy. Analyst 2005, 130, 1395–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunawardana, B.; Singhal, N.; Swedlund, P. Degradation of Chlorinated Phenols by Zero Valent Iron and Bimetals of Iron: A Review. Environ. Eng. Res. 2011, 16, 187–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafiee, E.; Rahimi, F. A green approach to the synthesis of chalcones via Claisen-Schmidt condensation reaction using cesium salts of 12-tungstophosphoric acid as a reusable nanocatalyst. Mon. Chem. 2013, 144, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.-T.; Yang, W.-Z.; Chen, G.-F.; Li, T.-S. A Facile Synthesis of α,α′-bis(Substituted Benzylidene) Cycloalkanones Catalyzed by KF/Al2O3 Under Ultrasound Irradiation. Synth. Commun. 2003, 33, 2619–2625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debecker, D.P.; Gaigneaux, E.M.; Busca, G. Exploring, Tuning, and Exploiting the Basicity of Hydrotalcites for Applications in Heterogeneous Catalysis. Chem. Eur. J. 2009, 15, 3920–3935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parida, K.; Das, J. Mg/Al hydrotalcites: Preparation, characterisation and ketonisation of acetic acid. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2000, 151, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavel, O.; Zăvoianu, R.; Bîrjega, R.; Angelescu, E. The effect of ageing step elimination on the memory effect presented by Mg0.75Al0.25 hydrotalcites (HT) and their catalytic activity for cyanoethylation reaction. Catal. Commun. 2011, 12, 845–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
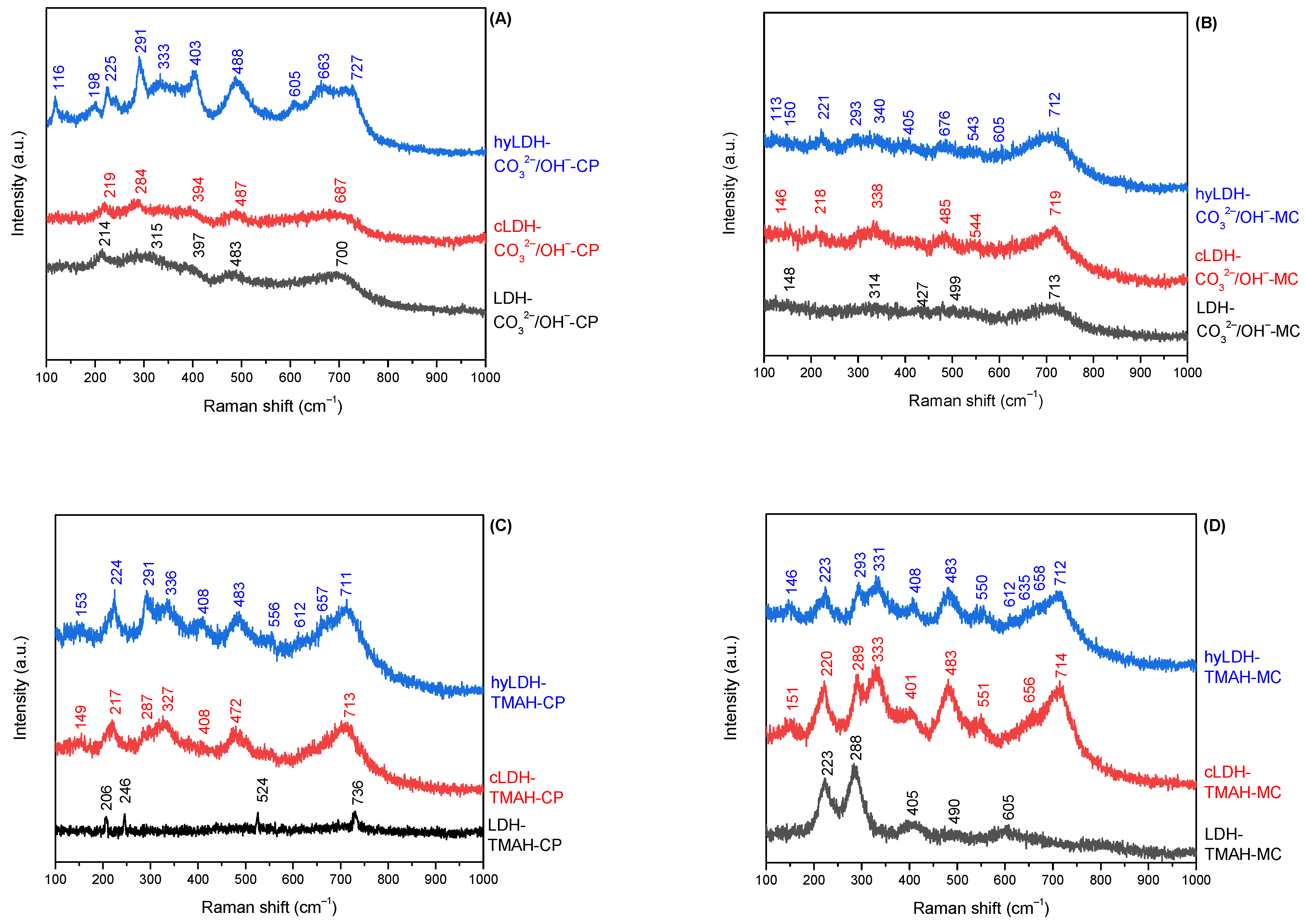



| Hydrotalcite Samples | Lattice Parameters | IFS 1 (Å) | 2θ003 (°) | I003/I006 | I003/I110 | FWHM003 | D 2 (Å) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a (Å) | c (Å) | |||||||
| LDH-CO32−/OH−-CP | 3.004 | 22.039 | 2.55 | 12.6607 | 4.30 | 2.48 | 0.3120 | 256 |
| hyLDH-CO32−/OH−-CP | 3.036 | 22.412 | 2.67 | 11.8866 | 1.70 | 1.42 | 0.2667 | 300 |
| LDH-CO32−/OH−-MC | 3.040 | 22.492 | 2.70 | 11.9400 | 3.50 | 2.80 | 0.4400 | 182 |
| hyLDH-CO32−/OH−-MC | 3.041 | 23.029 | 2.88 | 11.4720 | 1.50 | 1.17 | 0.1040 | 667 |
| LDH-TMAH-CP | 3.034 | 22.575 | 2.72 | 11.7720 | 3.73 | 4.97 | 0.7200 | 111 |
| hyLDH-TMAH-CP | 3.033 | 23.035 | 2.88 | 11.5400 | 0.57 | 0.57 | 0.1200 | 665 |
| LDH-TMAH-MC | 3.038 | 22.920 | 2.84 | 11.2666 | 1.13 | 1.38 | 0.1333 | 600 |
| hyLDH-TMAH-MC | 3.033 | 22.283 | 2.63 | 11.9000 | 0.64 | 1.00 | 0.0534 | 1296 |
| Mixed oxide samples | a (Å) | 2θ311 (°) | I311 | FWHM311 | D 3 (Å) | |||
| cLDH-CO32−/OH−-CP | 4.995 | 35.9143 | 59 | 0.2087 | 400 | |||
| cLDH-CO32−/OH−-MC | 5.025 | 35.7083 | 60 | 0.7967 | 105 | |||
| cLDH-TMAH-CP | 5.021 | 35.7333 | 95 | 0.7333 | 114 | |||
| cLDH-TMAH-MC | 4.998 | 35.9074 | 123 | 0.4709 | 177 | |||
| Samples | Surface Area (m2·g−1) | Pore Volume (cm3·g−1) | Average Pore Width (Å) | Total Number of Base Sites (mmol·g−1) 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LDH-CO32−/OH−-CP | 103 | 0.505 | 191 | 7.21 |
| cLDH-CO32−/OH−-CP | 263 | 0.831 | 127 | 7.23 |
| hyLDH-CO32−/OH−-CP | 37 | 0.199 | 209 | 7.15 |
| LDH-CO32−/OH−-MC | 170 | 0.503 | 113 | 7.14 |
| cLDH-CO32−/OH−-MC | 274 | 0.875 | 103 | 7.25 |
| hyLDH-CO32−/OH−-MC | 42 | 0.213 | 222 | 6.96 |
| LDH-TMAH-CP | 69 | 0.217 | 120 | 7.16 |
| cLDH-TMAH-CP | 223 | 0.678 | 131 | 7.20 |
| hyLDH-TMAH-CP | 101 | 0.587 | 183 | 6.88 |
| LDH-TMAH-MC | 154 | 0.177 | 43 | 6.85 |
| cLDH-TMAH-MC | 231 | 0.764 | 139 | 7.15 |
| hyLDH-TMAH-MC | 139 | 0.438 | 111 | 6.73 |
| Catalysts | Benzaldehyde Conversion (%) |
|---|---|
| blank | 31.5 |
| LDH-CO32−/OH−-CP | 0.5 |
| cLDH-CO32−/OH−-CP | 0.6 |
| hyLDH-CO32−/OH−-CP | 0.2 |
| LDH-CO32−/OH−-MC | 0.4 |
| cLDH-CO32−/OH−-MC | 4.5 |
| hyLDH-CO32−/OH−-MC | 4.5 |
| LDH-TMAH-CP | 3.4 |
| cLDH-TMAH-CP | 4.8 |
| hyLDH-TMAH-CP | 3.4 |
| LDH-TMAH-MC | 2.4 |
| cLDH-TMAH-MC | 6.0 |
| hyLDH-TMAH-MC | 3.5 |
| Catalysts | Conv. C6H10O (%) | Sel. (%) Mono-A | Sel. (%) Mono-B | Sel. (%) Di-A | Sel. (%) Di-B |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LDH-CO32−/OH−-CP | 0.8 | 60.1 | 37.8 | 1.1 | 1.0 |
| cLDH-CO32−/OH−-CP | 0.9 | 71.0 | 28.8 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| hyLDH-CO32−/OH−-CP | 0.8 | 62.2 | 37.2 | 0.5 | 0.1 |
| LDH-CO32−/OH−-MC | 0.3 | 63.3 | 36.7 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| cLDH-CO32−/OH−-MC | 0.7 | 78.5 | 21.5 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| hyLDH-CO32−/OH−-MC | 0.5 | 70.8 | 29.2 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| LDH-TMAH-CP | 1.2 | 75.6 | 13.0 | 5.5 | 5.9 |
| cLDH-TMAH-CP | 3.8 | 83.9 | 14.5 | 1.4 | 0.2 |
| hyLDH-TMAH-CP | 3.3 | 77.0 | 21.7 | 1.1 | 0.2 |
| LDH-TMAH-MC | 0.6 | 78.0 | 22.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| cLDH-TMAH-MC | 1.0 | 81.1 | 18.9 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| hyLDH-TMAH-MC | 0.9 | 80.0 | 20.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zăvoianu, R.; Tudorache, M.; Parvulescu, V.I.; Cojocaru, B.; Pavel, O.D. New MgFeAl-LDH Catalysts for Claisen–Schmidt Condensation. Molecules 2022, 27, 8391. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27238391
Zăvoianu R, Tudorache M, Parvulescu VI, Cojocaru B, Pavel OD. New MgFeAl-LDH Catalysts for Claisen–Schmidt Condensation. Molecules. 2022; 27(23):8391. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27238391
Chicago/Turabian StyleZăvoianu, Rodica, Mădălina Tudorache, Vasile I. Parvulescu, Bogdan Cojocaru, and Octavian D. Pavel. 2022. "New MgFeAl-LDH Catalysts for Claisen–Schmidt Condensation" Molecules 27, no. 23: 8391. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27238391
APA StyleZăvoianu, R., Tudorache, M., Parvulescu, V. I., Cojocaru, B., & Pavel, O. D. (2022). New MgFeAl-LDH Catalysts for Claisen–Schmidt Condensation. Molecules, 27(23), 8391. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27238391