High-Throughput Metabolic Soft-Spot Identification in Liver Microsomes by LC/UV/MS: Application of a Single Variable Incubation Time Approach
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
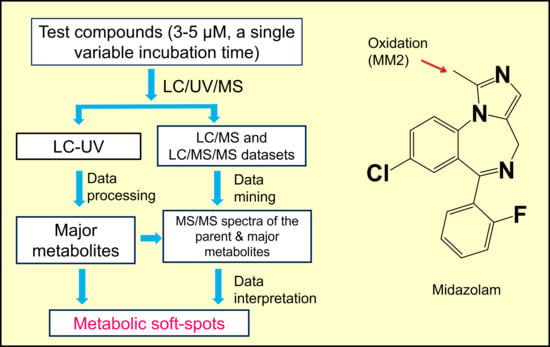
2.1. Workflow of MSSID Assay
2.2. Metabolic stability of Test Compounds
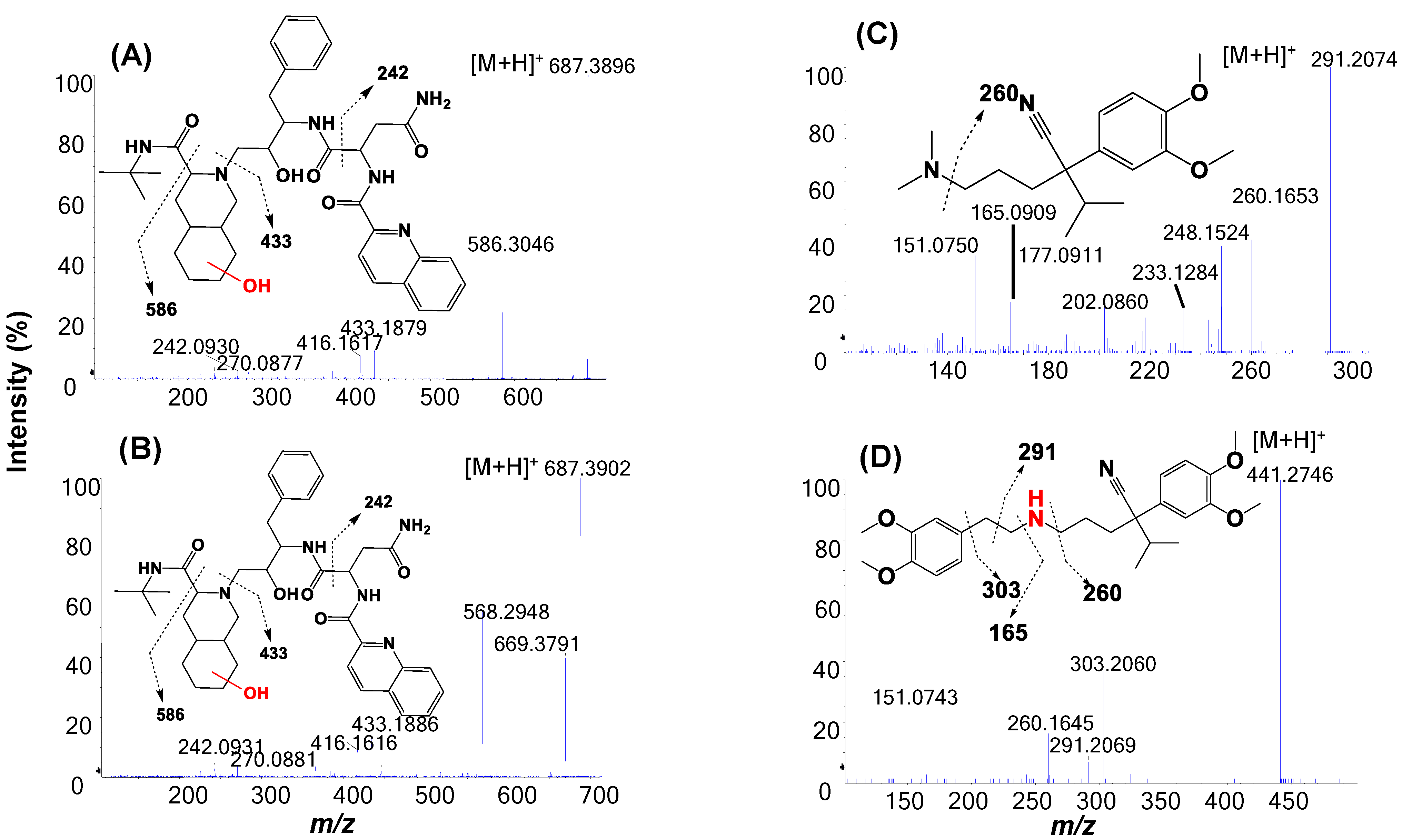
2.3. Metabolic Soft-Spot Determination Using LC/UV/Q-TOF
2.4. Metabolic Soft Spot Determination by LC/UV/Qtrap
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals and Reagents
4.2. Determination of Metabolic Stability in HLM
4.3. Determination of Metabolic Soft Spots in HLM Using LC/UV/HRMS
4.4. Determination of Metabolic Soft-Spots in HLM Using LC/UV/Qtrap
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Zhang, Z.; Tang, W. Drug metabolism in drug discovery and development. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2018, 8, 721–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, R.E. High-throughput screening in drug metabolism and pharmacokinetic support of drug discovery. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2000, 40, 133–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korfmacher, W.A.; Palmer, C.A.; Nardo, C.; Dunn-Meynell, K.; Grotz, D.; Cox, K.; Lin, C.C.; Elicone, C.; Liu, C.; Duchoslav, E. Development of an automated mass spectrometry system for the quantitative analysis of liver microsomal incubation samples: A tool for rapid screening of new compounds for metabolic stability, Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 1999, 13, 901–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, P.; Kerns, E.; Nguyen, D.-T.; Obach, R.S.; Wang, A.Q.; Zakharov, A.; McKew, J.; Simeonov, A.; Hop, C.E.; Xu, X. An automated high-throughput metabolic stability assay using an integrated high-resolution accurate mass method and automated data analysis software. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2016, 44, 1653–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, A.P.; Lu, C.; Brent, J.A.; Pham, C.; Fackett, A.; Ruegg, C.E.; Silber, P.M. Cryopreserved human hepatocytes: Characterization of drug-metabolizing activities and applications in higher throughput screening assays for hepatotoxicity, metabolic stability, and drug–drug interaction potential. Chem. Biol. Interact. 1999, 121, 17–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, H.S.; Griffin, M.; Houston, J.B. Evaluation of cryopreserved human hepatocytes as an alternative in vitro system to microsomes for the prediction of metabolic clearance. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2007, 35, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richardson, S.J.; Bai, A.; Kulkarni, A.A.; Moghaddam, M.F. Efficiency in drug discovery: Liver S9 fraction assay as a screen for metabolic stability. Drug Metab. Lett. 2016, 10, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halladay, J.S.; Wong, S.; Jaffer, S.M.; Sinhababu, A.K.; Khojasteh-Bakht, S.C. Metabolic stability screen for drug discovery using cassette analysis and column switching. Drug Metab. Lett. 2007, 1, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kieltyka, K.; Zhang, J.; Li, S.; Vath, M.; Baglieri, C.; Ferraro, C.; Zvyaga, T.A.; Drexler, D.M.; Weller, H.N.; Shou, W.Z. A high-throughput bioanalytical platform using automated infusion for tandem mass spectrometric method optimization and its application in a metabolic stability screen. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2009, 23, 1579–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Wang, J.; Tan, L.; Bui, J.; Gjerstad, E.; McMillan, K.; Zhang, W. In vitro ADME profiling using high-throughput rapidfire mass spectrometry: Cytochrome p450 inhibition and metabolic stability assays. J. Biomol. Screen. 2012, 17, 761–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trunzer, M.; Faller, B.; Zimmerlin, A. Metabolic soft spot identification and compound optimization in early discovery phases using MetaSite and LC-MS/MS validation. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferlenghi, F.; Giorgio, C.; Incerti, M.; Guidetti, L.; Chiodelli, P.; Rusnati, M.; Tognolini, M.; Vacondio, F.; Mor, M.; Lodola, A. Metabolic soft spot and pharmacokinetics: Functionalization of C-3 position of an Eph–ephrin antagonist featuring a bile acid core as an effective strategy to obtain oral bioavailability in mice. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 15, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padilha, E.C.; Shah, P.; Rai, G.; Xu, X. NOX2 inhibitor GSK2795039 metabolite identification towards drug optimization. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2021, 201, 114102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiller, P.R.; Yu, S.; Castro-Perez, J.; Fillgrove, K.L.; Baillie, T.A. High-throughput, accurate mass liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry on a quadrupole time-of-flight system as a ‘first-line’approach for metabolite identification studies. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2008, 22, 1053–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamora, I.; Fontaine, F.; Serra, B.; Plasencia, G. High-throughput, computer assisted, specific MetID. A revolution for drug discovery. Drug Discov. Today Technol. 2013, 10, e199–e205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortishire-Smith, R.J.; O'Connor, D.; Castro-Perez, J.M.; Kirby, J. Accelerated throughput metabolic route screening in early drug discovery using high-resolution liquid chromatography/quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry and automated data analysis. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. Int. J. Devoted Rapid Dissem. Minute Res. Mass Spectrom. 2005, 19, 2659–2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrona, M.; Mauriala, T.; Bateman, K.P.; Mortishire-Smith, R.J.; O’Connor, D. ‘All-in-one’analysis for metabolite identification using liquid chromatography/hybrid quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry with collision energy switching. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2005, 19, 2597–2602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grubb, M.F.; Humphreys, W.G.; Josephs, J.L. A semi-automated method for the integrated evaluation of half-life and metabolic soft spots of discovery compounds. Bioanalysis 2012, 4, 1747–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiva, A.A.; Klakouski, C.; Li, S.; Johnson, B.M.; Shu, Y.-Z.; Josephs, J.; Zvyaga, T.; Zamora, I.; Shou, W.Z. Development, optimization and implementation of a centralized metabolic soft spot assay. Bioanalysis 2017, 9, 541–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauriala, T.; Chauret, N.; Oballa, R.; Nicoll-Griffith, D.A.; Bateman, K.P. A strategy for identification of drug metabolites from dried blood spots using triple-quadrupole/linear ion trap hybrid mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2005, 19, 1984–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Wang, F.; Li, Q.; Zhu, M.; Du, A.; Tang, W.; Chen, W. Amlodipine metabolism in human liver microsomes and roles of CYP3A4/5 in the dihydropyridine dehydrogenation. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2014, 42, 245–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, S.; Chowdhury, S.K. Application of LC–high-resolution MS with ‘intelligent’ data mining tools for screening reactive drug metabolites. Bioanalysis 2012, 4, 501–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, M.; Zhang, H.; Humphreys, W.G. Drug metabolite profiling and identification by high-resolution mass spectrometry. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 25419–25425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Cheng, Z.; Zhang, K.; Jiang, H.; Zhu, M. An integrated approach for profiling oxidative metabolites and glutathione adducts using liquid chromatography coupled with ultraviolet detection and triple quadrupole-linear ion trap mass spectrometry. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2016, 129, 482–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, D.; Ray, K.; Zhu, M. Mass defect filter technique and its applications to drug metabolite identification by high-resolution mass spectrometry. J. Mass Spectrom. 2009, 44, 999–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, M.; Ma, L.; Duchoslav, E.; Zhu, M. Rapid screening and characterization of drug metabolites using multiple ion monitoring dependent product ion scan and postacquisition data mining on a hybrid triple quadrupole-linear ion trap mass spectrometer. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2009, 23, 1683–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, M.; Ma, L.; Humphreys, W.G.; Zhu, M. Rapid screening and characterization of drug metabolites using a multiple ion monitoring–dependent MS/MS acquisition method on a hybrid triple quadrupole-linear ion trap mass spectrometer. J. Mass Spectrom. 2008, 43, 1364–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abernethy, D.R.; Wainer, I.W.; Anacleto, A.I. Verapamil metabolite exposure in older and younger men during steady-state oral verapamil administration. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2000, 28, 760–765. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, M.; Zhao, W.; Jimenez, H.; Zhang, D.; Yeola, S.; Dai, R.; Vachharajani, N.; Mitroka, J. Cytochrome P450 3A-mediated metabolism of buspirone in human liver microsomes. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2005, 33, 500–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moody, J.D.; Freeman, J.P.; Fu, P.P.; Cerniglia, C.E. Biotransformation of mirtazapine by Cunninghamella elegans. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2002, 30, 1274–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eagling, V.; Profit, L.; Back, D. Inhibition of the CYP3A4-mediated metabolism and P-glycoprotein-mediated transport of the HIV-1 protease inhibitor saquinavir by grapefruit juice components. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1999, 48, 543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thurman, E.M.; Ferrer, I. Liquid chromatography/quadrupole-time-of-flight mass spectrometry with metabolic profiling of human urine as a tool for environmental analysis of dextromethorphan. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1259, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mäenpää, J.; Hall, S.D.; Ring, B.J.; Strom, S.C.; Wrighton, S.A. Human cytochrome P450 3A (CYP3A) mediated midazolam metabolism: The effect of assay conditions and regioselective stimulation by alpha-naphthoflavone, terfenadine and testosterone. Pharmacogenetics 1998, 8, 137–155. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- He, P.; Greenblatt, D.J.; von Moltke, L.L. Factors influencing midazolam hydroxylation activity in human liver microsomes. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2006, 34, 1198–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-Q.; Björkman, A.; Andersson, T.B.; Ridderström, M.; Masimirembwa, C.M. Amodiaquine Clearance and Its Metabolism toN-Desethylamodiaquine Is Mediated by CYP2C8: A New High Affinity and Turnover Enzyme-Specific Probe Substrate. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2002, 300, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, Q.; Peterman, S.; Szewc, M.A.; Ma, L.; Cui, D.; Humphreys, W.G.; Zhu, M. An integrated method for metabolite detection and identification using a linear ion trap/Orbitrap mass spectrometer and multiple data processing techniques: Application to indinavir metabolite detection. J. Mass Spectrom. 2008, 43, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.C.; Shou, W.Z.; Mai, T.T.; Jiang, X.Y. Complete profiling and characterization of in vitro nefazodone metabolites using two different tandem mass spectrometric platforms. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2007, 21, 4001–4008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.C.; Gohdes, M.A.; Shou, W.Z. ‘N-in-one’strategy for metabolite identification using a liquid chromatography/hybrid triple quadrupole linear ion trap instrument using multiple dependent product ion scans triggered with full mass scan. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2007, 21, 1421–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shou, W.Z.; Magis, L.; Li, A.C.; Naidong, W.; Bryant, M.S. A novel approach to perform metabolite screening during the quantitative LC–MS/MS analyses of in vitro metabolic stability samples using a hybrid triple-quadrupole linear ion trap mass spectrometer. J. Mass Spectrom. 2005, 40, 1347–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Deng, S.; Obach, R.S. A simple liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method to determine relative plasma exposures of drug metabolites across species for metabolite safety assessments. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2010, 38, 2147–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.C.; Alton, D.; Bryant, M.S.; Shou, W.Z. Simultaneously quantifying parent drugs and screening for metabolites in plasma pharmacokinetic samples using selected reaction monitoring information-dependent acquisition on a QTrap instrument. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2005, 19, 1943–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, B.; Ma, L.; Nelson, S.D.; Zhu, M. High-throughput screening and characterization of reactive metabolites using polarity switching of hybrid triple quadrupole linear ion trap mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 1788–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, S.; Chowdhury, S.K.; Alton, K.B. Application of mass spectrometry for metabolite identification. Curr. Drug Metab. 2006, 7, 503–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prakash, C.; Shaffer, C.L.; Nedderman, A. Analytical strategies for identifying drug metabolites. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2007, 26, 340–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
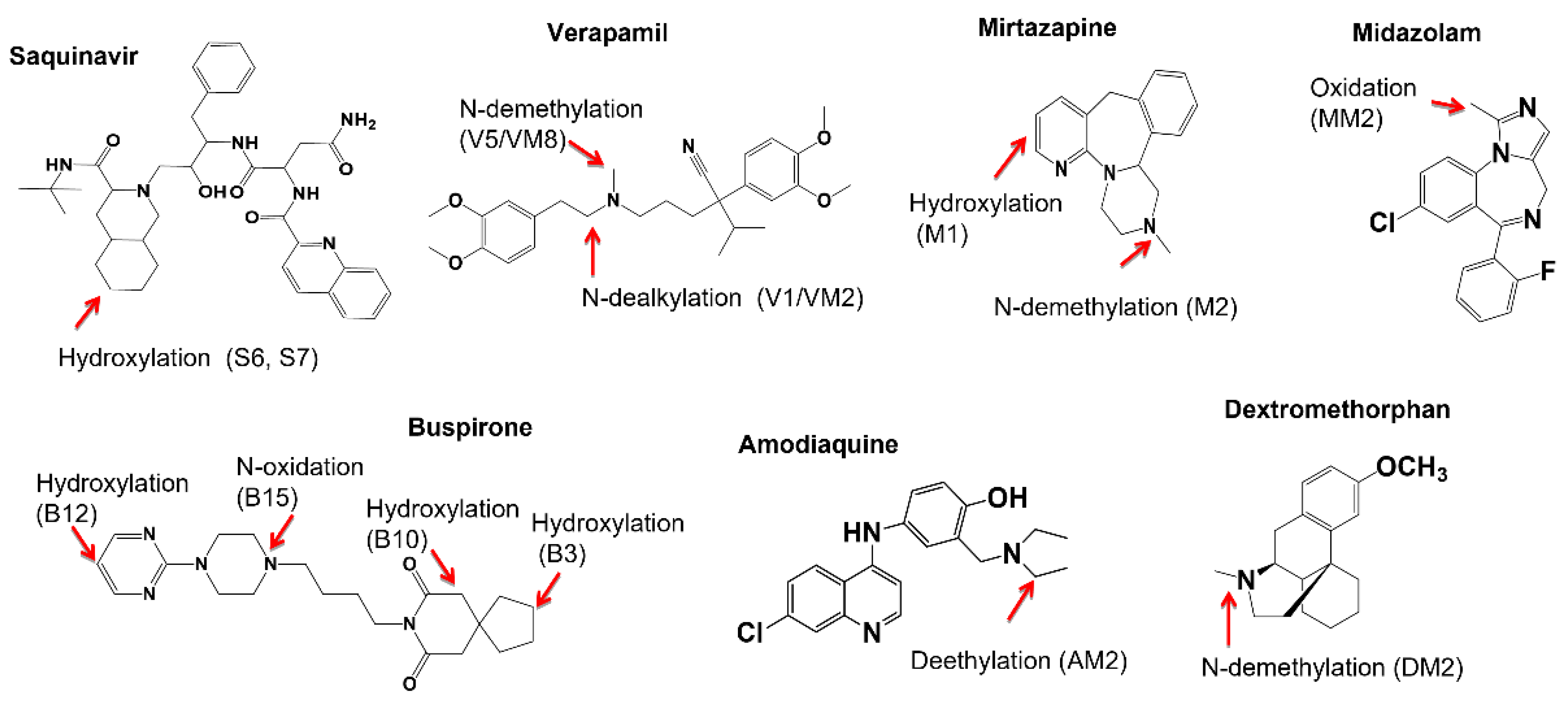
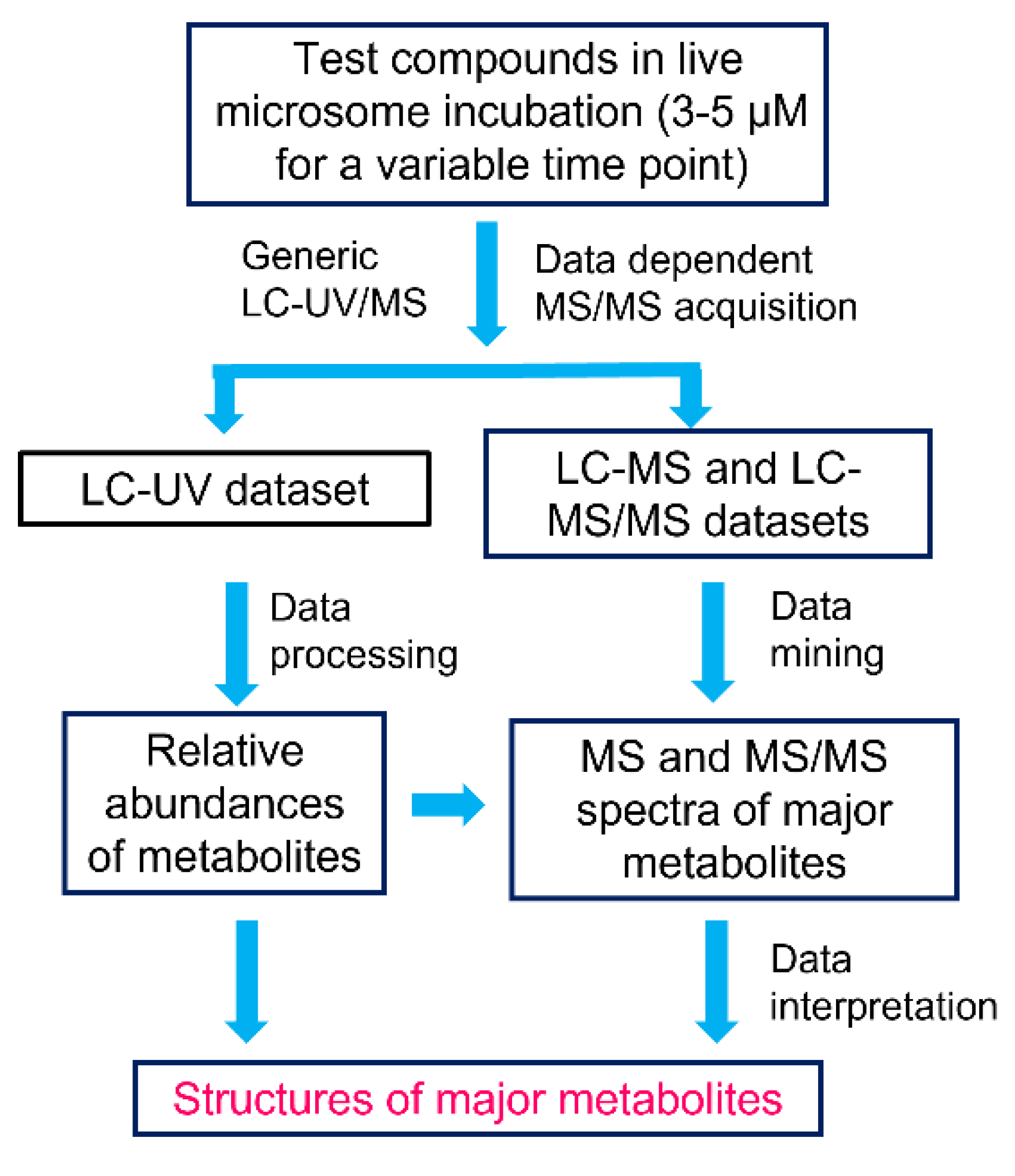


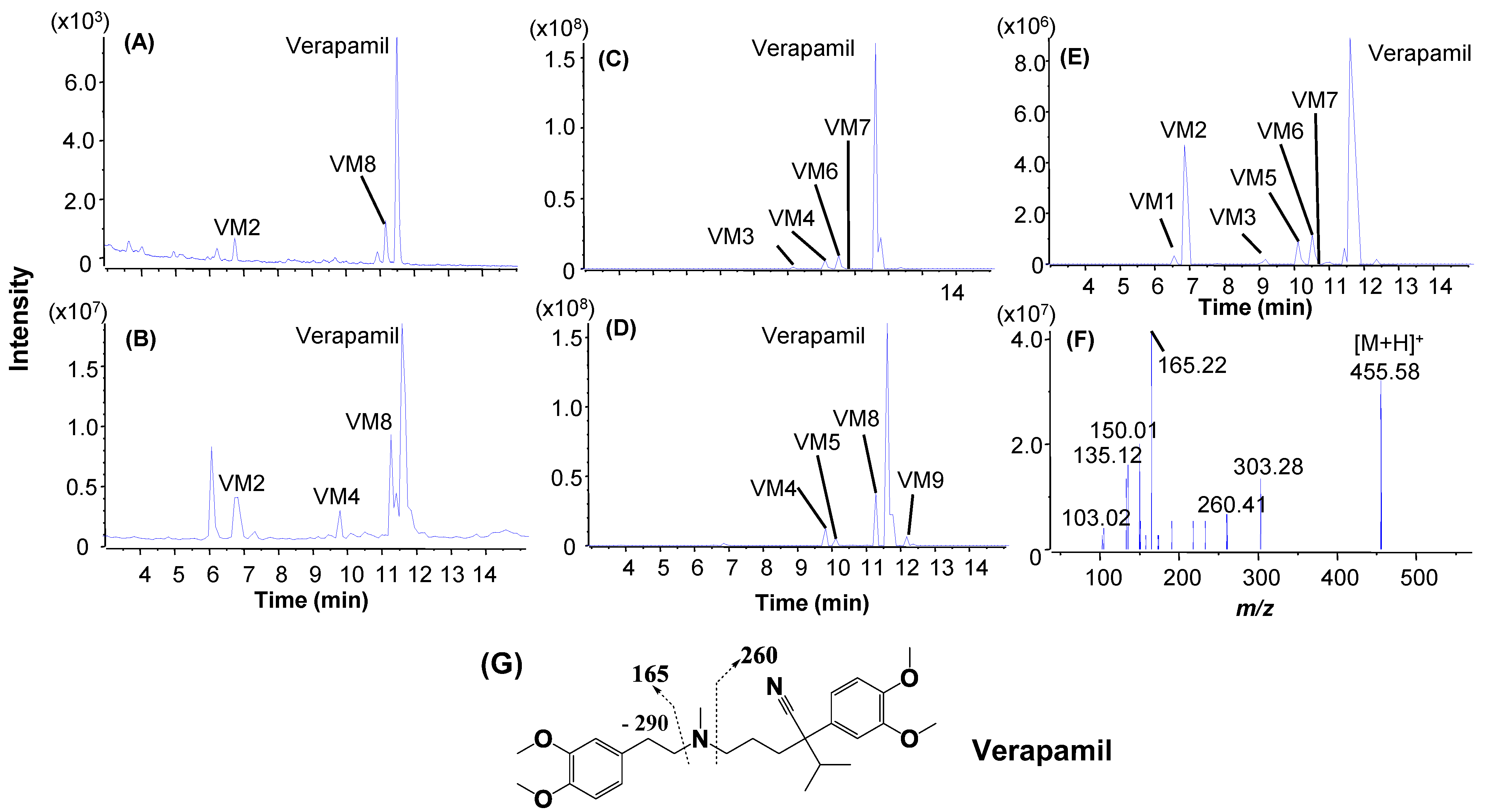
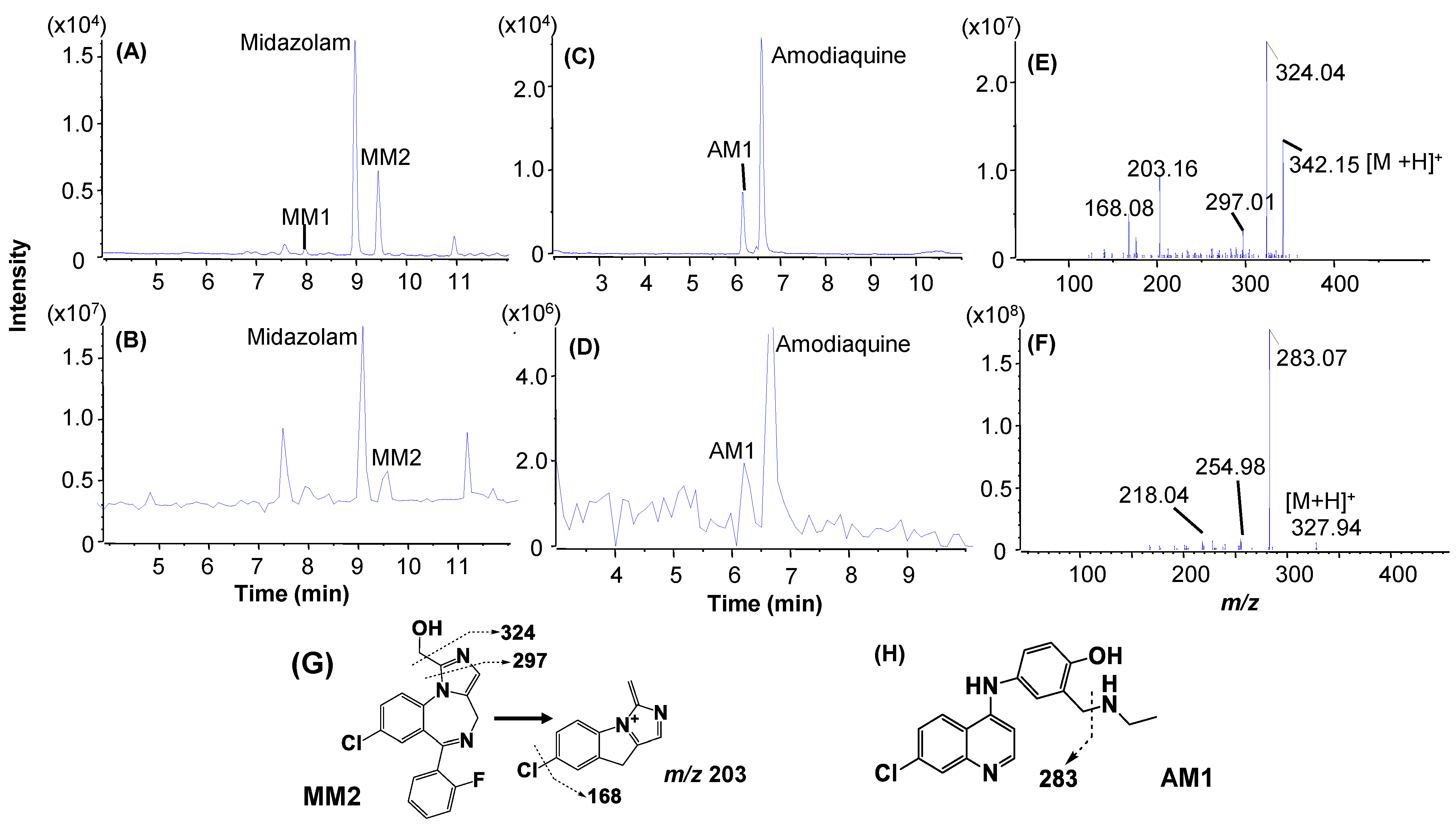
| Compound(T1/2) a | Incubation Conditions | The Parent Drugs (Relative Abundances) | Major Metabolites and (Relative Abundances b) | Minor or Trace Metabolites c |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Analyzed using LC/UV/Triple TOF | ||||
| Saquinavir a (2.6 min) | 5 μM, 4 min | Saquinavir (58%) | Mono-oxidation: S6 (11.6%), S7 (12.8%). | Di-oxidation: S1, S3, S8, S9; Mono-oxidation: S4, S5, S10. |
| Verapamil a (6.9 min) | 5 μM, 8 min | Verapamil (79.3%) | N-dealkylation: V1 (6.1%); N-demethylation: V5 (14.7%); | O-demethylation: V2, V3; Mono-oxidation: V4. |
| Mitazapine d (165 min) | 3 μM, 60 min | Mitazapine (74.2%) | Momo-oxidation: M1 (10.7%); N-demethylation: M2 (8.1%); N-oxidation: M3 (5.0%). | Mono-oxidation: M4; Ketone formation: M5. |
| Buspirone d (7.6 min) | 3 μM, 8 min | Buspirone (59.1%) | Mono-oxidation: B3 (12.1%), B10 (16.5%), B12 (5.2%), B15 (7.1%). | N-dealkylation: B1 e. Mono oxidation: B4, B7; Di-oxidation: B2, B5, B6, B8, B9, B11, B14; Desaturation: B13. |
| Analyzed using LC/UV/Qtrap | ||||
| Midazolam a (3.3 min) | 3 μM, 2 min | Midazolam (69.0%) | Mono-oxidation: MM2 (29.0%) | Hydroxylation: MM1 |
| Dextromethorphan a (24.0 min) | 3 μM, 30 min | Dextromethorphan (75.5%) | Demethylation: DM1/DM2 (33.0%). | N-demethylation: DM4Hydroxylation: DM3, DM5 |
| Amodiaquine (1.3 min) a | 3 μM, 1 min | Amodiaquine (77.0%) | Deethylation: AM1 (26.5%) | Not detected |
| Verapamila (6.9 min) | 3 μM, 4 min | Verapamil (72.1%) | N-dealkylation: VM2 (8.9%);N-demethylation: VM8 (19.0%) | N-dealkylation+ N-demethylation + hydroxylation: VM1; N-dealkylation: VM3. O-demethylation + hydroxylation: VM4, VM9; N-demethylation + O-demethylation: VM5, VM7; O-demethylation: VM6, VM11; Hydroxylation: VM10, VM13; N-demethylation: VM12 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, Y.; Chen, G.; Zhang, K.; Chen, C.; Chen, W.; Zhu, M.; Jiang, H. High-Throughput Metabolic Soft-Spot Identification in Liver Microsomes by LC/UV/MS: Application of a Single Variable Incubation Time Approach. Molecules 2022, 27, 8058. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27228058
Zhu Y, Chen G, Zhang K, Chen C, Chen W, Zhu M, Jiang H. High-Throughput Metabolic Soft-Spot Identification in Liver Microsomes by LC/UV/MS: Application of a Single Variable Incubation Time Approach. Molecules. 2022; 27(22):8058. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27228058
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Yanlin, Guiying Chen, Kerong Zhang, Chang Chen, Weiqing Chen, Mingshe Zhu, and Hongliang Jiang. 2022. "High-Throughput Metabolic Soft-Spot Identification in Liver Microsomes by LC/UV/MS: Application of a Single Variable Incubation Time Approach" Molecules 27, no. 22: 8058. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27228058
APA StyleZhu, Y., Chen, G., Zhang, K., Chen, C., Chen, W., Zhu, M., & Jiang, H. (2022). High-Throughput Metabolic Soft-Spot Identification in Liver Microsomes by LC/UV/MS: Application of a Single Variable Incubation Time Approach. Molecules, 27(22), 8058. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27228058