Emerging Direct Targeting β-Catenin Agents
Abstract
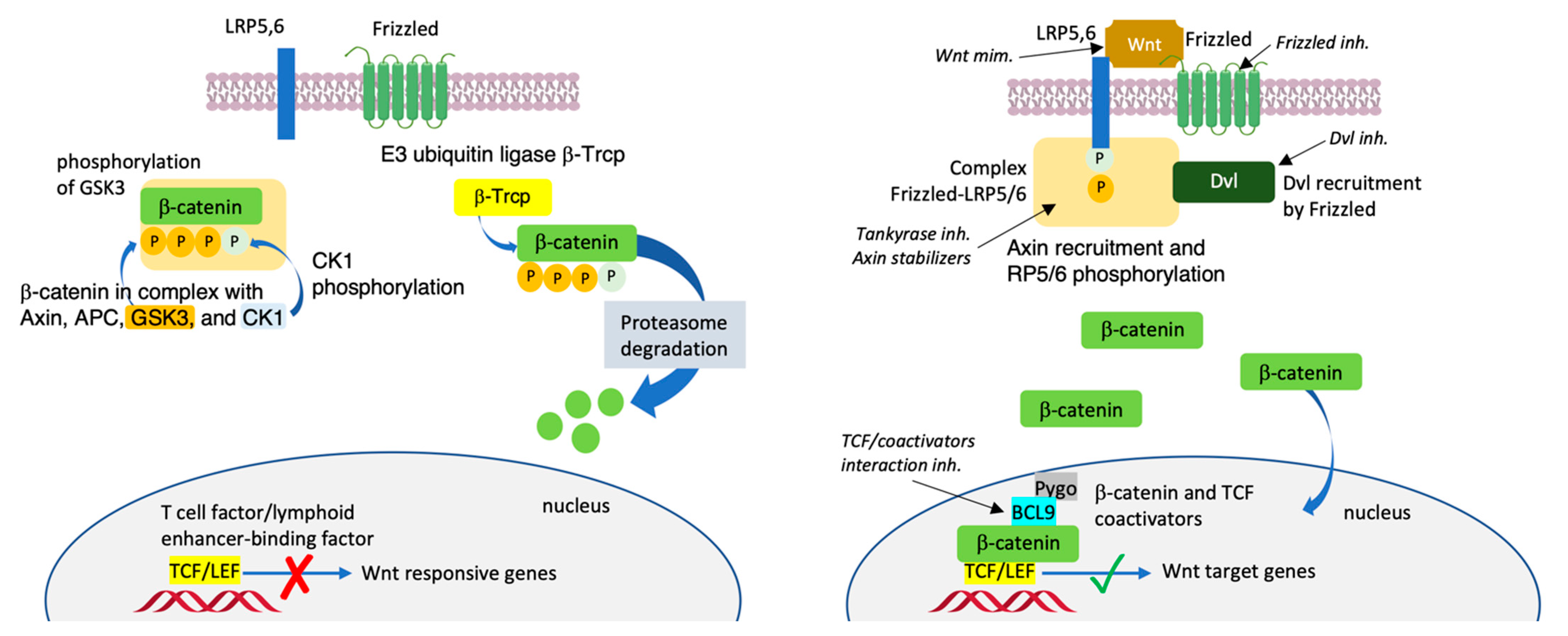
1. Introduction
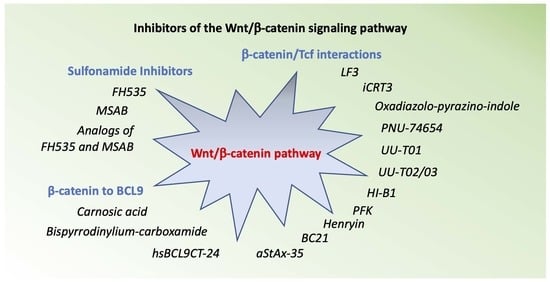
2. Inhibitors the Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway
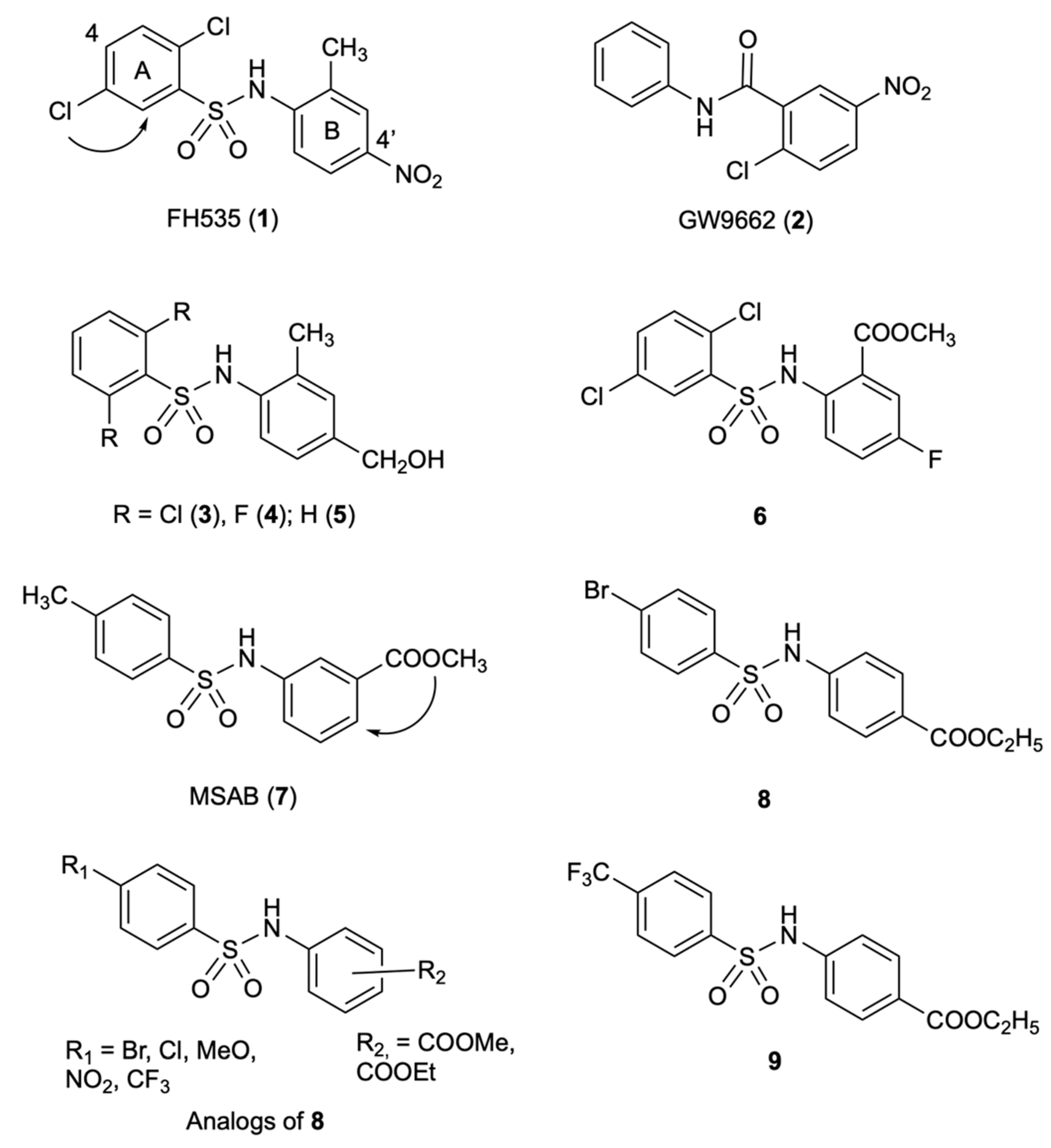
2.1. FH535
2.2. Analogs of FH535
2.3. MSAB
2.4. Analogs of MSAB
3. Inhibitors of β-Catenin /Tcf Interactions
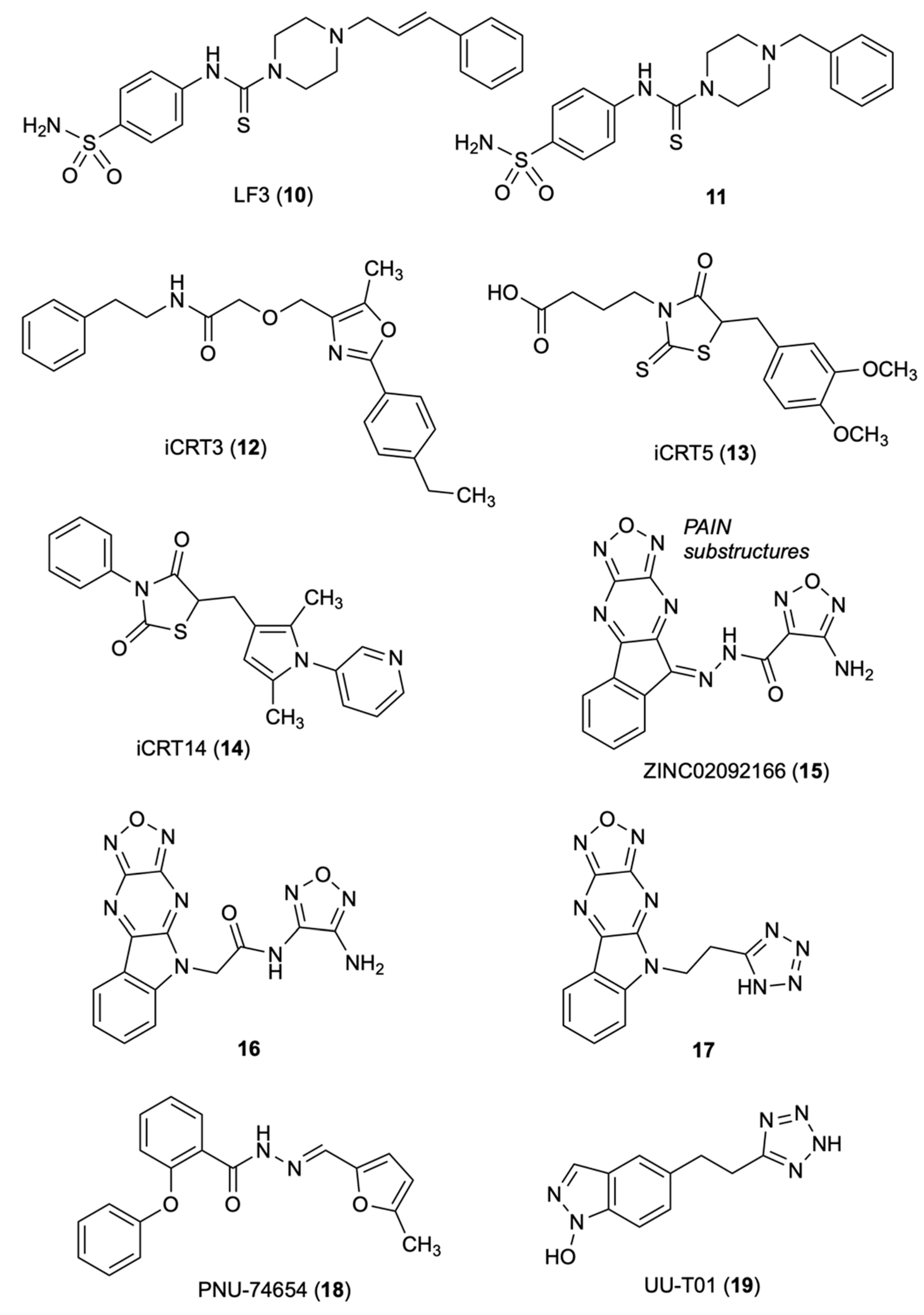
3.1. LF3
3.2. iCRT3
3.3. Oxadiazolo-Pyrazino-Indole
3.4. PNU-74654
3.5. UU-T01
3.6. UU-T02/03
3.7. HI-B1
3.8. PFK Compounds
3.9. Henryin
3.10. BC21
3.11. aStAx-35
4. Inhibitors of β-Catenin to BCL9
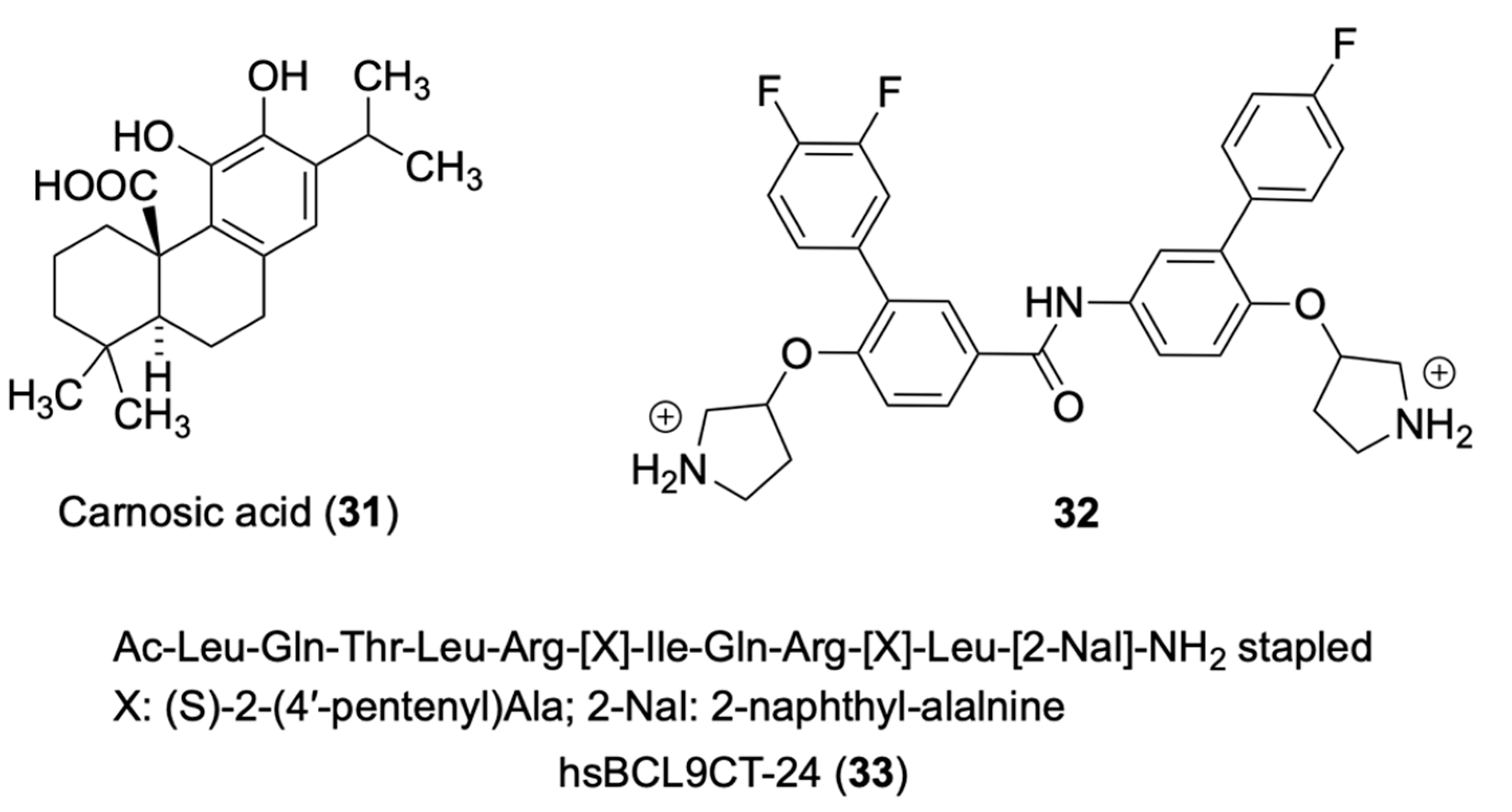
4.1. Carnosic Acid
4.2. Bispyrrodinylium-Carboxamide
4.3. hsBCL9CT-24
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Valenta, T.; Hausmann, G.; Basler, K. The many faces and functions of ß-catenin. EMBO J. 2012, 31, 2714–2736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito-Diaz, K.; Chen, T.W.; Wang, X.; Thorne, C.A.; Wallace, H.A.; Page-McCaw, A.; Lee, E. The way Wnt works: Components and mechanism. Growth Factors 2013, 31, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clevers, H.; Nusse, R. Wnt/β-catenin signaling and disease. Cell 2012, 149, 1192–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clevers, H.; Loh, K.M.; Nusse, R. Stem cell signaling. An integral program for tissue renewal and regeneration: Wnt signaling and stem cell control. Science 2014, 346, 1248012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nusse, R.; Clevers, H. Wnt/β-catenin signaling, disease, and emerging therapeutic modalities. Cell 2017, 169, 985–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubinfeld, B.; Albert, I.; Porfiri, E.; Fiol, C.; Munemitsu, S.; Polakis, P. Binding of GSK3β to the APC-β-catenin complex and regulation of complex assembly. Science 1996, 272, 1023–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hecht, A.; Vleminckx, K.; Stemmler, M.P.; van Roy, F.; Kernier, R. The p300/CBP acetyltransferases function as transcriptional coactivators of β-catenin in vertebrates. EMBO J. 2000, 19, 1839–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brack, A.S.; Murphy-Seiler, F.; Hanifi, J.; Deka, J.; Eyckerman, S.; Keller, C.; Aguet, M.; Rando, T.A. BCL9 is an essential component of canonical Wnt signaling that mediates the differentiation of myogenic progenitors during muscle regeneration. Dev. Biol. 2009, 335, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantù, C.; Zimmerli, D.; Hausmann, G.; Valenta, T.; Moor, A.; Aguet, M.; Basler, K. Pax6-dependent, but β-catenin-independent, function of Bcl9 proteins in mouse lens development. Genes Develop. 2014, 28, 1879–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotolloshi, R.; Gajda, M.; Grimm, M.-O.; Steinbach, D. Wnt/β-catenin signalling and its cofactor BCL9L have an oncogenic effect in bladder cancer cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwab, K.R.; Patterson, T.L.; Hartman, H.A.; Song, N.; Lang, R.A.; Lin, X.; Potter, S.S. Pygo1 and Pygo2 roles in Wnt signaling in mammalian kidney development. BMC Biol. 2007, 5, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, D.J. Wnt signaling pathway in non-small cell lung cancer. J. Nat. Cancer Inst. 2014, 106, djt356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, A.H.; Weis, W.I. The structure of the β-catenin/E-cadherin complex and the molecular basis of diverse ligand recognition by β-catenin. Cell 2001, 105, 391–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, S.; Hua, F.; Hu, Z.-W. The regulation of β-catenin activity and function in cancer: Therapeutic opportunities. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 33972–33989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, X. Targeting the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in cancer. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 13, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Li, Z.; Ji, H. Direct targeting of β-catenin in the wnt signaling pathway: Current progress and perspectives. Med. Res. Rev. 2021, 41, 2109–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Xiao, Q.; Xiao, J.; Niu, C.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, Z.; Shu, G.; Yin, G. Wnt/β-catenin signalling: Function, biological mechanisms, and therapeutic opportunities. Signal Trans. Targ. Ther. 2022, 7, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handeli, S.; Simon, J.A. A small-molecule inhibitor of Tcf/β-catenin signaling down-regulates PPARγ and PPARδ activities. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2008, 7, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansson, E.A.; Are, A.; Greicius, G.; Petterson, S. The Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway targets PPARg activity in colon cancer cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 1460–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, T.C.; Chan, T.A.; Vogelstein, B.; Kinzler, K.W. PPARy is an APC-regulated target of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Cell 1999, 99, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leesnitzer, L.M.; Parks, D.J.; Bledsoe, R.K.; Cobb, J.E.; Collins, J.L.; Consler, T.G.; Davis, R.G.; Hull-Ryde, E.A.; Lenhard, J.M.; Patel, L.; et al. Functional consequences of cysteine modification in the ligand binding sites of peroxisome proliferator activated receptors by GW9662. Biochemistry 2002, 41, 6640–6650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kril, L.M.; Vilchez, V.; Jiang, J.; Turcios, L.; Chen, C.; Sviripa, V.M.; Zhang, W.; Liu, C.; Spear, B.; Watt, D.S.; et al. N-aryl benzenesulfonamide inhibitors of [3H]-thymidine incorporation and β-catenin signaling in human hepatocyte-derived Huh-7 carcinoma cells. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 25, 3897–3899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Hwang, S.-Y.; Deng, X.; Byun, S.; Lee, C.; Lee, S.-J.; Suh, H.; Zhang, J.; Kang, Q.; Zhang, T.; Westover, K.D.; et al. Direct targeting of β-catenin by a small molecule stimulates proteasomal degradation and suppresses oncogenic Wnt/β-catenin signalin. Cell Rep. 2016, 16, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Magno, L.; Di Pastena, F.; Puxeddu, M.; La Regina, G.; Coluccia, A.; Ciogli, A.; Manetto, S.; Maroder, M.; Canettieri, G.; Silvestri, R.; et al. Sulfonamide inhibitors of β-catenin signaling as anticancer agents with different output on c-MYC. ChemMedChem 2020, 15, 2264–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coluccia, A.; La Regina, G.; Naccarato, V.; Nalli, M.; Orlando, V.; Biagioni, S.; De Angelis, M.L.; Baiocchi, M.; Gautier, C.; Gianni, S.; et al. Drug design and synthesis of first in class PDZ1 targeting NHERF1 inhibitors as anticancer agents. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2019, 10, 499–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farrell, A.S.; Sears, R.C. MYC degradation. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2014, 4, a014365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabay, M.; Li, Y.; Felsher, D.W. MYC activation is a hallmark of cancer initiation and maintenance. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2014, 4, a014241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Zhu, Q.; Neuenschwander, M.; Specker, E.; Wulf-Goldenberg, A.; Weis, W.I.; von Kries, J.P.; Birchmeier, W. A small-molecule antagonist of the β-catenin/TCF4 interaction blocks the self-renewal of cancer stem cells and suppresses tumorigenesis. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 891–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisurek, M.; Rupp, B.; Wichard, J.; Neuenschwander, M.; von Kries, J.P.; Frank, R.; Rademann, J.; Kühne, R. Design of chemical libraries with potentially bioactive molecules applying a maximum common substructure concept. Mol. Divers. 2010, 14, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäfer, F.; Seip, N.; Maertens, B.; Block, H.; Kubicek, J. Purification of GST-tagged proteins. Methods Enzymol. 2015, 559, 127–139. [Google Scholar]
- Lipinski, C.A.; Lombardo, F.; Dominy, B.W.; Feeney, P.J. Experimental and computational approaches to estimate solubility and permeability in drug discovery and development settings. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2001, 46, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Kries, J.P.; Winbeck, G.; Asbrand, C.; Schwarz-Romond, T.; Sochnikova, N.; Dell’Oro, A.; Behrens, J.; Birchmeier, W. Hot spots in beta-catenin for interactions with LEF-1, conductin and APC. Nat. Struct. Biol. 2000, 7, 800–807. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hulsken, J.; Birchmeier, W.; Behrens, J. E-cadherin and APC compete for the interaction with beta-catenin and the cytoskeleton. J. Cell Biol. 1994, 127, 2061–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birchmeier, W.; Behrens, J. Cadherin expression in carcinomas: Role in the formation of cell junctions and the prevention of invasiveness. Biochim. Biophys Acta 1994, 1198, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukacs, R.U.; Memarzadeh, S.; Wu, H.; Witte, O.N. Bmi-1 is a crucial regulator of prostate stem cell self-renewal and malignant transformation. Cell Stem Cell 2010, 7, 682–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonsalves, F.C.; Kleina, K.; Carson, B.B.; Katz, S.; Ekas, L.A.; Evans, S.; Nagourney, R.; Cardozo, T.; Brown, A.M.C.; DasGuptaa, R. An RNAi-Based chemical genetic screen identifies three small-molecule inhibitors of the Wnt/wingless signaling pathway. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 5954–5963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omer, C.A.; Miller, P.J.; Diehl, R.E.; Kral, A. MIdentification of Tcf4 residues involved inhigh-affinity beta-catenin binding. Bioch. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1999, 256, 584–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, T.A.; Weaver, C.; Mao, F.; Kimelman, D.; Xu, W. Crystal structure of a beta-catenin/Tcf complex. Cell 2000, 103, 885–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, H.; Zuo, Y.; Farmer, S.R. Functional interaction between peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma and beta-catenin. Mol. Cell Biol. 2006, 26, 5827–5837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepourcelet, M.; Chen, Y.-N.P.; France, D.S.; Wang, H.; Crews, P.; Petersen, F.; Bruseo, C.; Wood, A.W.; Shivdasani, R.A. Small-Molecule antagonists of the oncogenic Tcf/beta-catenin protein complex. Cancer Cell 2004, 5, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guedat, P.; Jacq, X.; Colland, F.; Daviet, L.; Formstecher, E.; Rain, J.-C.; Colombo, M. Preparation of Tetracyclic Compounds as Cysteine Proteases Inhibitors. U.S. Patent 7,875,613-B2, 25 January 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Catrow, J.L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Ji, H. Discovery of selective small-molecule inhibitors for the β- catenin/T-cell factor protein-protein interaction through the optimization of the acyl hydrazone moiety. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 4678–4692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Huang, Z.; Yu, B.; Ji, H. New homogeneous highthroughput assays for inhibitors of β-catenin/Tcf protein−protein interactions. Anal. Biochem. 2012, 424, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Che, J.; King, F.J.; Zhou, B.; Zhou, Y. Chemical and biolog ical properties of frequent screening hits. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2012, 52, 913–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trosset, J.-Y.; Dalvit, C.; Knapp, S.; Fasolini, M.; Veronesi, M.; Mantegani, S.; Gianellini, L.M.; Catana, C.; Sundström, M.; Stouten, P.F.W.; et al. Inhibition of protein-protein interactions: The discovery of druglike β-catenin inhibitors by combining virtual and biophysical screening. Proteins 2006, 64, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.L.; Liu, D.; Zhang, Z.J.; Shan, S.; Han, X.; Srinivasula, S.M.; Croce, C.M.; Alnemri, E.S.; Huang, Z. Structure-based discovery of an organic compound that binds Bcl-2 protein and induces apoptosis of tumor cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 7124–7129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalvit, C.; Fogliatto, G.P.; Stewart, A.; Veronesi, M.; Stockman, B. WaterLOGSY as a method for primary NMR screening: Practical aspects and range of applicability. J. Biomol. NMR 2001, 21, 349–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalvit, C.; Fasolini, M.; Flocco, M.; Knapp, S.; Pevarello, P.; Veronesi, M. NMR-Based screening with competition water-ligand observed via gradient spectroscopy experiments: Detection of high-affinity ligands. J. Med. Chem. 2002, 45, 2610–2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, M.; Dillard, D.R.; Ji, H. Rational design of small-molecule inhibitors for β-catenin/T-cell factor protein-protein interactions by bioisostere replacement. ACS Chem. Biol. 2013, 8, 524–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poy, F.; Lepourcelet, M.; Shivdasani, R.A.; Eck, M.J. Structure of a human Tcf4-à-catenin complex. Nat. Struct. Biol. 2001, 8, 1053–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, T.A.; Ferkey, D.M.; Mao, F.; Kimelman, D.; Xu, W. Tcf4 can specifically recognize à-catenin using alternative conformations. Nat. Struct. Biol. 2001, 8, 1048–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Zhang, M.; Burton, S.D.; Katsakhyan, L.N.; Ji, H. Targeting the Tcf4 G13ANDE17 binding site to selectively disrupt β-catenin/T-cell factor protein-protein interactions. ACS Chem. Biol. 2014, 9, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, S.H.; Lim, D.Y.; Reddy, K.; Malakhova, M.; Liu, F.; Wang, T.; Song, M.; Chen, H.; Bae, K.B.; Ryu, J.; et al. A small molecule inhibitor of the β-catenin-TCF4 interaction suppresses colorectal cancer growth in vitro and in vivo. EBioMedicine 2017, 25, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.J.; Hsu, L.S.; Shia, Y.T.; Lin, M.W.; Lin, C.M. The beta-catenin/Tcf complex as a novel target of resveratrol in the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2012, 84, 1143–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sukhdeo, K.; Mani, M.; Zhang, Y.; Dutta, J.; Yasui, H.; Rooney, M.D.; Carrasco, D.E.; Zheng, M.; He, H.; Tai, Y.-T.; et al. Targeting the β-catenin/TCF transcriptional complex in the treatment of multiple myeloma. Proc Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 7516–7521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Pu, J.; Jiang, S.; Su, J.; Kong, L.; Mao, B.; Sun, H.; Li, Y. Henryin, an ent-kaurane diterpenoid, inhibits Wnt signaling through interference with β-catenin/TCF4 interaction in colorectal cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e68525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, W.; Han, X.; Yan, M.; Xu, Y.; Dugginemi, S.; Lin, N.; Luo, G.; Michael, Y.; Han, X.; Huang, Z.; et al. Structure-Based discovery of a novel inhibitor targeting the β-catenin/Tcf4 interaction. Biochemistry 2012, 51, 724–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, G.M.; Goodsell, D.S.; Halliday, R.S.; Huey, R.; Hart, W.E.; Belew, R.K.; Olson, A.J. Automated docking using a Lamarckian genetic algorithm and an Empirical Binding Free Energy Function. J. Comput. Chem. 1998, 19, 1639–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasolini, M. Hot spots in Tcf4 for the interaction with beta-Catenin. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 21092–21098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossmann, T.N.; Yeh, J.T.; Bowman, B.R.; Chu, Q.; Moellering, R.E.; Verdine, G.L. Inhibition of oncogenic Wnt signaling through direct targeting of β-catenin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 17942–17947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De La Roche, M.; Rutherford, T.J.; Gupta, D.; Veprintsev, D.B.; Saxty, B.; Freund, S.M.; Bienz, M. An intrinsically labile α-helix abutting the BCL9- binding site of β-catenin is required for its inhibition by carnosic acid. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramps, T.; Peter, O.; Brunner, E.; Nellen, D.; Froesch, B.; Chatterjee, S.; Murone, M.; Züllig, S.; Basler, K. Wnt/wingless signaling requires BCL9/legless-mediated recruitment of pygopus to the nuclear β-catenin-TCF complex. Cell 2002, 109, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoggard, L.R.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Panic, V.; Wisniewski, J.A.; Ji, H. Rational design of selective small-molecule inhibitors for β-catenin/B-cell lymphoma 9 protein-protein interactions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 12249–12260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, M.; Jin, J.Q.; Xia, L.; Xiao, T.; Mei, S.; Wang, X.; Huang, X.; Chen, J.; Liu, M.; Chen, C.; et al. Pharmacological inhibition of β-catenin/BCL9 interaction overcomes resistance to immune checkpoint blockades by modulating Tregcells. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaau5240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Wisniewski, J.A.; Ji, H. AlphaScreen selectivity assay for β-catenin/B-cell lymphoma 9 inhibitors. Anal. Biochem. 2015, 469, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takada, K.; Zhu, D.; Bird, G.H.; Sukhdeo, K.; Zhao, J.-J.; Mani, M.; Lemieux, M.; Carrasco, D.E.; Ryan, J.; Horst, D.; et al. Targeted disruption of the BCL9/b-catenin complex inhibits oncogenic Wnt signaling. Sci. Transl. Med. 2012, 4, 148ra117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nalli, M.; Masci, D.; Urbani, A.; La Regina, G.; Silvestri, R. Emerging Direct Targeting β-Catenin Agents. Molecules 2022, 27, 7735. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27227735
Nalli M, Masci D, Urbani A, La Regina G, Silvestri R. Emerging Direct Targeting β-Catenin Agents. Molecules. 2022; 27(22):7735. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27227735
Chicago/Turabian StyleNalli, Marianna, Domiziana Masci, Andrea Urbani, Giuseppe La Regina, and Romano Silvestri. 2022. "Emerging Direct Targeting β-Catenin Agents" Molecules 27, no. 22: 7735. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27227735
APA StyleNalli, M., Masci, D., Urbani, A., La Regina, G., & Silvestri, R. (2022). Emerging Direct Targeting β-Catenin Agents. Molecules, 27(22), 7735. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27227735