Applications of Deep Eutectic Solvents in Sample Preparation and Extraction of Organic Molecules
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Synthesis and Properties of Deep Eutectic Solvents
2.1. Synthesis of Deep Eutectic Solvents
2.2. Properties of Deep Eutectic Solvents
3. Extraction of Organic Compounds
3.1. Pesticides, Fungicides and Herbicides
3.2. Flavonoids, Phenolic and Other Bioactive Compounds
3.3. Pharmaceutical Compounds and Preservatives
3.4. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons, Volatile Organic Compounds and Pollutants
3.5. Polysaccharides, Pigments and Terpenes
3.6. Other Organic Compounds
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Armenta, S.; Garrigues, S.; Esteve-Turrillas, F.A.; de la Guardia, M. Green extraction techniques in green analytical chemistry. Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 116, 248–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plastiras, O.E.; Andreasidou, E.; Samanidou, V. Microextraction techniques with deep eutectic solvents. Molecules 2020, 25, 6026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paiva, A.; Craveiro, R.; Aroso, I.; Martins, M.; Reis, R.L.; Duarte, A.R.C. Natural deep eutectic solvents—Solvents for the 21st century. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 1063–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, S.C.; Fernandes, J.O. Extraction techniques with deep eutectic solvents. Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 105, 225–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espino, M.; Fernandez, M.D.; Gomez, F.J.V.; Silva, M.F. Natural designer solvents for greening analytical chemistry. Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 76, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanda, H.; Dai, Y.T.; Wilson, E.G.; Verpoorte, R.; Choi, Y.H. Green solvents from ionic liquids and deep eutectic solvents to natural deep eutectic solvents. Comptes Rendus Chim. 2018, 21, 628–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florindo, C.; Branco, L.C.; Marrucho, I.M. Quest for green-solvent design: From hydrophilic to hydrophobic (Deep) eutectic solvents. ChemSusChem 2019, 12, 1549–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, B.; Zhang, H.; Row, K.H. Application of deep eutectic solvents in the extraction and separation of target compounds from various samples. J. Sep. Sci. 2015, 38, 1053–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kissoudi, M.; Samanidou, V. Recent advances in applications of ionic liquids in miniaturized microextraction techniques. Molecules 2018, 23, 1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pena-Pereira, F.; Namiesnik, J. Ionic liquids and deep eutectic mixtures: Sustainable solvents for extraction processes. ChemSusChem 2014, 7, 1784–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, A.; Santos, A.; Tojo, J.; Rodriguez, A. Toxicity and biodegradability of imidazolium ionic liquids. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 151, 268–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berthod, A.; Ruiz-Angel, M.J.; Carda-Broch, S. Recent advances on ionic liquid uses in separation techniques. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1559, 2–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, E.L.; Abbott, A.P.; Ryder, K.S. Deep Eutectic Solvents (DESs) and their applications. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 11060–11082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A.P.; Capper, G.; Davies, D.L.; Munro, H.L.; Rasheed, R.K.; Tambyrajah, V. Preparation of novel, moisture-stable, Lewis-acidic ionic liquids containing quaternary ammonium salts with functional side chains. Chem. Commun. 2001, 2001, 2010–2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shishov, A.; Bulatov, A.; Locatelli, M.; Carradori, S.; Andruch, V. Application of deep eutectic solvents in analytical chemistry. A review. Microchem. J. 2017, 135, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.T.; van Spronsen, J.; Witkamp, G.J.; Verpoorte, R.; Choi, Y.H. Natural deep eutectic solvents as new potential media for green technology. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 766, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, B.B.; Spittle, S.; Chen, B.; Poe, D.; Zhang, Y.; Klein, J.M.; Horton, A.; Adhikari, L.; Zelovich, T.; Doherty, B.W.; et al. Deep eutectic solvents: A review of fundamentals and applications. Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 1232–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.T.; van Spronsen, J.; Witkamp, G.J.; Verpoorte, R.; Choi, Y.H. Ionic liquids and deep eutectic solvents in natural products research: Mixtures of solids as extraction solvents. J. Nat. Prod. 2013, 76, 2162–2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; An, Y.; Row, K.H. Emerging applications of (micro) extraction phase from hydrophilic to hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents: Opportunities and trends. Trends Anal. Chem. 2021, 136, 116187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Osch, D.; Dietz Chjt van Spronsen, J.; Kroon, M.C.; Gallucci, F.; Annaland, M.V.; Tuinier, R. A search for natural hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents based on natural components. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 2933–2942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zdanowicz, M.; Wilpiszewska, K.; Spychaj, T. Deep eutectic solvents for polysaccharides processing. A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 200, 361–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makos, P.; Slupek, E.; Gebicki, J. Hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents in microextraction techniques-A review. Microchem. J. 2020, 152, 104384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwamena, A.K. Recent advances in hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents for extraction. Separations 2019, 6, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana-Mayor, A.; Rodriguez-Ramos, R.; Herrera-Herrera, A.V.; Socas-Rodriguez, B.; Rodriguez-Delgado, M.A. Deep eutectic solvents. The new generation of green solvents in analytical chemistry. Trends Anal. Chem. 2021, 134, 116108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z. Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents and Their Applications in Biotechnology. In Application of Ionic Liquids in Biotechnology; Itoh, T., Koo, Y.M., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 31–59. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.N.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.P.; Liu, W. Application of deep eutectic solvents in food analysis: A review. Molecules 2019, 24, 4594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.T.; Pei, D.; Yu, P.L.; Wei, J.T.; Wang, N.L.; Di, D.L.; Liu, Y.W. Aqueous two-phase systems based on deep eutectic solvents and their application in green separation processes. J. Sep. Sci. 2020, 43, 348–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.N.; Liu, Y.M.; Wang, Z.T.; Yang, L.; Liu, H.W. Development and applications of deep eutectic solvent derived functional materials in chromatographic separation. J. Sep. Sci. 2021, 44, 1098–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, B.K.; Row, K.H. Recent developments in deep eutectic solvents in chemical sciences. Mon. Chem. 2013, 144, 1427–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A.P.; Boothby, D.; Capper, G.; Davies, D.L.; Rasheed, R.K. Deep eutectic solvents formed between choline chloride and carboxylic acids: Versatile alternatives to ionic liquids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 9142–9147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sereshti, H.; Jamshidi, F.; Nouri, N.; Nodeh, H.R. Hyphenated dispersive solid- and liquid-phase microextraction technique based on a hydrophobic deep eutectic solvent: Application for trace analysis of pesticides in fruit juices. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2020, 100, 2534–2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.H.; Vigier, K.D.; Royer, S.; Jerome, F. Deep eutectic solvents: Syntheses, properties and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 7108–7146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbott, A.P.; Capper, G.; Davies, D.L.; Rasheed, R.K.; Tambyrajah, V. Novel solvent properties of choline chloride/urea mixtures. Chem. Commun. 2003, 39, 70–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Florindo, C.; Oliveira, F.S.; Rebelo, L.P.N.; Fernandes, A.M.; Marrucho, I.M. Insights into the synthesis and properties of deep eutectic solvents based on cholinium chloride and carboxylic acids. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 2416–2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.; Hu, X.T.; Wang, J.W.; Cheng, H.Y.; Chen, L.F.; Qi, Z.W. Overview of acidic deep eutectic solvents on synthesis, properties and applications. Green Energy Environ. 2020, 5, 8–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Liu, M.J.; Wang, Q.; Du, H.Z.; Zhang, L.W. Deep Eutectic solvent-based microwave-assisted method for extraction of hydrophilic and hydrophobic components from radix salviae miltiorrhizae. Molecules 2016, 21, 1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Y.T.; Witkamp, G.J.; Verpoorte, R.; Choi, Y.H. Tailoring properties of natural deep eutectic solvents with water to facilitate their applications. Food Chem. 2015, 187, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skulcova, A.; Russ, A.; Jablonsky, M.; Sima, J. The pH behavior of seventeen deep eutectic solvents. Bioresources 2018, 13, 5042–5051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Achkar, T.; Greige-Gerges, H.; Fourmentin, S. Basics and properties of deep eutectic solvents: A review. Environ. Chem. 2021, 19, 3397–3408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Friesen, J.B.; McAlpine, J.B.; Lankin, D.C.; Chen, S.N.; Pauli, G.F. Natural deep eutectic solvents: Properties, applications, and perspectives. J. Nat. Prod. 2018, 81, 679–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abolghasemi, M.M.; Piryaei, M.; Imani, R.M. Deep eutectic solvents as extraction phase in head-space single-drop microextraction for determination of pesticides in fruit juice and vegetable samples. Microchem. J. 2020, 158, 105041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farajzadeh, M.A.; Abbaspour, M.; Kazemian, R. Synthesis of a green high density deep eutectic solvent and its application in microextraction of seven widely used pesticides from honey. J. Chromatogr. A 2019, 1603, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farajzadeh, M.A.; Hojghan, A.S.; Mogaddam, M.R.A. Development of a new temperature-controlled liquid phase microextraction using deep eutectic solvent for extraction and preconcentration of diazinon, metalaxyl, bromopropylate, oxadiazon, and fenazaquin pesticides from fruit juice and vegetable samples followed by gas chromatography-flame ionization detection. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2018, 66, 90–97. [Google Scholar]
- Florindo, C.; Branco, L.C.; Marrucho, I.M. Development of hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents for extraction of pesticides from aqueous environments. Fluid Phase Equilib. 2017, 448, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouyban, A.; Farajzadeh, M.A.; Mogaddam, M.R.A. In matrix formation of deep eutectic solvent used in liquid phase extraction coupled with solidification of organic droplets dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction; application in determination of some pesticides in milk samples. Talanta 2020, 206, 120169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musarurwa, H.; Tavengwa, N.T. Deep eutectic solvent-based dispersive liquid-liquid micro-extraction of pesticides in food samples. Food Chem. 2021, 342, 127943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemati, M.; Farajzadeh, M.A.; Mohebbi, A.; Khodadadeian, F.; Mogaddam, M.R.A. Development of a stir bar sorptive extraction method coupled to solidification of floating droplets dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction based on deep eutectic solvents for the extraction of acidic pesticides from tomato samples. J. Sep. Sci. 2020, 43, 1119–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemati, M.; Tuzen, M.; Farazajdeh, M.A.; Kaya, S.; Mogaddam, M.R.A. Development of dispersive solid-liquid extraction method based on organic polymers followed by deep eutectic solvents elution; application in extraction of some pesticides from milk samples prior to their determination by HPLC-MS/MS. Anal. Chim. Acta 2022, 1199, 339570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.H.; Zhang, Y.H.; Zhao, Q.Y.; Chen, A.H.; Jiao, B.N. Ultrasound-assisted dispersive liquid-phase microextraction by solidifying L-menthol-decanoic acid hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents for detection of five fungicides in fruit juices and tea drinks. J. Sep. Sci. 2021, 44, 3870–3882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torbati, M.; Farajzadeh, M.A.; Mogaddam, M.R.A. Deep eutectic solvent based homogeneous liquid-liquid extraction coupled with in-syringe dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction performed in narrow tube; application in extraction and preconcentration of some herbicides from tea. J. Sep. Sci. 2019, 42, 1768–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skarpalezos, D.; Detsi, A. Deep eutectic solvents as extraction media for valuable flavonoids from natural sources. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.H.; Verpoorte, R. Green solvents for the extraction of bioactive compounds from natural products using ionic liquids and deep eutectic solvents. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2019, 26, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanovic, M.; Razborsek, M.I.; Kolar, M. Innovative extraction techniques using deep eutectic solvents and analytical methods for the isolation and characterization of natural bioactive compounds from plant material. Plants 2020, 9, 1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Socas-Rodriguez, B.; Torres-Cornejo, M.V.; Alvarez-Rivera, G.; Mendiola, J.A. Deep eutectic solvents for the extraction of bioactive compounds from natural sources and agricultural by-products. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 4897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakhle, L.; Kfoury, M.; Mallard, I.; Landy, D.; Greige-Gerges, H. Microextraction of bioactive compounds using deep eutectic solvents: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2021, 19, 3747–3759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, W.T.; Tian, M.L.; Row, K.H. Evaluation of alcohol-based deep eutectic solvent in extraction and determination of flavonoids with response surface methodology optimization. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1285, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nam, M.W.; Zhao, J.; Lee, M.S.; Jeong, J.H.; Lee, J. Enhanced extraction of bioactive natural products using tailor-made deep eutectic solvents: Application to flavonoid extraction from Flos sophorae. Green Chem. 2015, 17, 1718–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajkacz, S.; Adamek, J. Evaluation of new natural deep eutectic solvents for the extraction of isoflavones from soy products. Talanta 2017, 168, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Z.R.; Zhao, J.; Duan, H.X.; Guan, Y.Y.; Zhao, L.S. Green and efficient extraction of four bioactive flavonoids from Pollen Typhae by ultrasound-assisted deep eutectic solvents extraction. J. Pharm. Biomed. 2018, 161, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.Y.; Li, G.Z.; Chen, B.Q.; Zhu, T.; Row, K.H. Evaluating ternary deep eutectic solvents as novel media for extraction of flavonoids from Ginkgo biloba. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2017, 52, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.Y.; Wang, M.; Zhang, K.L.; Fu, Q.F.; Wang, L.J.; Gao, M.J.; Xia, Z.N.; Gao, D.E. Extraction and determination of bioactive flavonoids from Abelmoschus manihot (Linn.) Medicus flowers using deep eutectic solvents coupled with high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Sep. Sci. 2019, 42, 2044–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Row, K.H. Application of natural deep eutectic solvents in the extraction of quercetin from vegetables. Molecules 2019, 24, 2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, L.; Dou, L.L.; Guo, L.; Li, P.; Liu, E.H. Comprehensive evaluation of deep eutectic solvents in extraction of bioactive natural products. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 2405–2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radosevic, K.; Curko, N.; Srcek, V.G.; Bubalo, M.C.; Tomasevic, M.; Ganic, K.K.; Redovnikovic, I.R. Natural deep eutectic solvents as beneficial extractants for enhancement of plant extracts bioactivity. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 73, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Row, K.H. Optimized extraction of bioactive compounds from Herba Artemisiae Scopariae with ionic liquids and deep eutectic solvents. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2017, 40, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, D.T.; Pauletto, R.; Cavalheiro, S.D.; Bochi, V.C.; Rodrigues, E.; Weber, J.; da Silva, C.D.; Morisso, F.D.; Barcia, M.T.; Emanuelli, T. Natural deep eutectic solvents as a biocompatible tool for the extraction of blueberry anthocyanins. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2020, 89, 103470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosiljkov, T.; Dujmic, F.; Bubalo, M.C.; Hribar, J.; Vidrih, R.; Brncic, M.; Zlatic, E.; Redounikavic, I.R.; Jokic, S. Natural deep eutectic solvents and ultrasound-assisted extraction: Green approaches for extraction of wine lees anthocyanins. Food Bioprod. Process. 2017, 102, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.T.; Rozema, E.; Verpoorte, R.; Choi, Y.H. Application of natural deep eutectic solvents to the extraction of anthocyanins from Catharanthus roseus with high extractability and stability replacing conventional organic solvents. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1434, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruesgas-Ramon, M.; Figueroa-Espinoza, M.C.; Durand, E. Application of Deep Eutectic Solvents (DES) for phenolic compounds extraction: Overview, challenges, and opportunities. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 3591–3601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redha, A.A. Review on extraction of phenolic compounds from natural sources using green deep eutectic solvents. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 878–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.T.; Witkamp, G.J.; Verpoorte, R.; Choi, Y.H. Natural deep eutectic solvents as a new extraction media for phenolic metabolites in carthamus tinctorius L. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 6272–6278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bubalo, M.C.; Curko, N.; Tomasevic, M.; Ganic, K.K.; Redovnikovic, I.R. Green extraction of grape skin phenolics by using deep eutectic solvents. Food Chem. 2016, 200, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, A.; Rodriguez-Juan, E.; Rodriguez-Gutierrez, G.; Rios, J.J.; Fernandez-Bolanos, J. Extraction of phenolic compounds from virgin olive oil by deep eutectic solvents (DESs). Food Chem. 2016, 197, 554–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanioti, S.; Tzia, C. Extraction of phenolic compounds from olive pomace by using natural deep eutectic solvents and innovative extraction techniques. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2018, 48, 228–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shishov, A.; Volodina, N.; Gagarionova, S.; Shilovskikh, V.; Bulatov, A. A rotating disk sorptive extraction based on hydrophilic deep eutectic solvent formation. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1141, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, M.A.; Muhammad, G.; Khan, M.N.; Mofijur, M.; Lv, Y.K.; Xiong, W.L.; Xu, J.L. Choline chloride-based deep eutectic solvents as green extractants for the isolation of phenolic compounds from biomass. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 309, 127445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozturk, B.; Parkinson, C.; Gonzalez-Miquel, M. Extraction of polyphenolic antioxidants from orange peel waste using deep eutectic solvents. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 206, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, M.D.; Espino, M.; Gomez, F.J.V.; Silva, M.F. Novel approaches mediated by tailor-made green solvents for the extraction of phenolic compounds from agro-food industrial by-products. Food Chem. 2018, 239, 671–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Kantar, S.; Rajha, H.N.; Boussetta, N.; Vorobiev, E.; Maroun, R.G.; Louka, N. Green extraction of polyphenols from grapefruit peels using high voltage electrical discharges, deep eutectic solvents and aqueous glycerol. Food Chem. 2019, 295, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.Z.; Wang, D.; Belwal, T.; Xu, Y.Q.; Li, L.; Luo, Z.S. Sonication-synergistic natural deep eutectic solvent as a green and efficient approach for extraction of phenolic compounds from peels of Carya cathayensis Sarg. Food Chem. 2021, 355, 129577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherif, M.M.; Grigorakis, S.; Halahlah, A.; Loupassaki, S.; Makris, D.P. High-efficiency extraction of phenolics from wheat waste biomass (Bran) by combining deep eutectic solvent, ultrasound-assisted pretreatment and thermal treatment. Environ. Process. 2020, 7, 845–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Feng, F.; Jiang, J.; Qiao, Y.; Wu, T.; Voglmeir, J.; Chen, Z.G. Green and efficient extraction of rutin from tartary buckwheat hull by using natural deep eutectic solvents. Food Chem. 2017, 221, 1400–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bubalo, M.C.; Vidovic, S.; Redovnikovic, I.R.; Jokic, S. New perspective in extraction of plant biologically active compounds by green solvents. Food Bioprod. Process. 2018, 109, 52–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakirtzi, C.; Triantafyllidou, K.; Makris, D.P. Novel lactic acid-based natural deep eutectic solvents: Efficiency in the ultrasound-assisted extraction of antioxidant polyphenols from common native Greek medicinal plants. J. Appl. Res. Med. Aromat. Plants 2016, 3, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Duan, M.H.; Yao, X.H.; Zhang, Y.H.; Zhao, C.J.; Zu, Y.G.; Fu, Y.J. Green extraction of five target phenolic acids from Lonicerae japonicae Flos with deep eutectic solvent. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2016, 157, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.Z.; Cui, Q.; Wang, L.T.; Meng, Y.; Yu, L.; Li, Y.Y.; Fu, Y.J. A green and integrated strategy for enhanced phenolic compounds extraction from mulberry (Morus alba L.) leaves by deep eutectic solvent. Microchem. J. 2020, 154, 104598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.E.; Tang, B.; Row, K.H. Application of deep eutectic solvents as additives in ultrasonic extraction of two phenolic acids from herba artemisiae scopariae. Anal. Lett. 2014, 47, 1476–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.J.; Zhang, H.; Yu, H.M.; Guo, S.H.; Chen, D.W. Deep eutectic solvent as a green solvent for enhanced extraction of narirutin, naringin, hesperidin and neohesperidin from Aurantii Fructus. Phytochem. Anal. 2019, 30, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oktaviyanti, N.D.; Kartini; Mun’im, A. Application and optimization of ultrasound-assisted deep eutectic solvent for the extraction of new skin-lightening cosmetic materials from Ixora javanica flower. Heliyon 2019, 5, e02950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontes, P.V.D.; Shiwaku, I.A.; Maximo, G.J.; Batista, E.A.C. Choline chloride-based deep eutectic solvents as potential solvent for extraction of phenolic compounds from olive leaves: Extraction optimization and solvent characterization. Food Chem. 2021, 352, 129346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogaddam, M.R.A.; Farajzadeh, M.A.; Tuzen, M.; Jouyban, A.; Khandaghi, J. Organic solvent-free elevated temperature liquid-liquid extraction combined with a new switchable deep eutectic solvent-based dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction of three phenolic antioxidants from oil samples. Microchem. J. 2021, 168, 106433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.Y.; Liu, Y.Z.; Hu, F.J.; Ren, H.W.; Duan, E.H. Amino Acid-based natural deep eutectic solvents for extraction of phenolic compounds from aqueous environments. Processes 2021, 9, 1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.L.; Tang, W.Y.; Tang, B.K.; Han, D.D.; Row, K.H.; Zhu, T. Pipette-tip solid-phase extraction based on deep eutectic solvent modified graphene for the determination of sulfamerazine in river water. J. Sep. Sci. 2017, 40, 1887–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogan, B.; Elik, A.; Altunay, N. Determination of paracetamol in synthetic urea and pharmaceutical samples by shaker-assisted deep eutectic solvent microextraction and spectrophotometry. Microchem. J. 2020, 154, 104645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.Z.; Zhu, T.; Row, K.H. Deep eutectic solvents for the purification of chloromycetin and thiamphenicol from milk. J. Sep. Sci. 2017, 40, 625–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouyban, A.; Farajzadeh, M.A.; Khodadadeian, F.; Khoubnasabjafari, M.; Mogaddam, M.R.A. Development of a deep eutectic solvent-based ultrasound-assisted homogenous liquid-liquid microextraction method for simultaneous extraction of daclatasvir and sofosbuvir from urine samples. J. Pharm. Biomed. 2021, 204, 114254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.C.; Luo, H.; Zhu, C.Y.; Li, W.J.; Wu, D.; Wu, H.W. Hydrophobic natural alcohols based deep eutectic solvents: Effective solvents for the extraction of quinine. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 275, 119112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtulbas, E.; Pekel, A.G.; Toprakci, I.; Ozcelik, G.; Bilgin, M.; Sahin, S. Hydrophobic carboxylic acid based deep eutectic solvent for the removal of diclofenac. Biomass Convers. Biorefin. 2022, 12, 2219–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahi, M.; Javadi, A.; Mogaddam, M.R.A.; Mirzaei, H.; Nemati, M. Preparation of multiwall carbon nanotube/urea-formaldehyde nanocomposite as a new sorbent in solid-phase extraction and its combination with deep eutectic solvent-based dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction for extraction of antibiotic residues in honey. J. Sep. Sci. 2021, 44, 576–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadi, N.A.; Ng, M.H.; Choo, Y.M.; Hashim, M.A.; Jayakumar, N.S. Performance of choline-based deep eutectic solvents in the extraction of tocols from crude palm oil. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2015, 92, 1709–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, B.; Shekaari, H.; Zafarani-Moattar, M.T. Selective separation of α-tocopherol using eco-friendly choline chloride—Based deep eutectic solvents (DESs) via liquid-liquid extraction. Colloids Surf. 2021, 617, 126317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Fu, X.L.; Li, Z.Z. Extraction of tocopherol from soybean oil deodorizer distillate by deep eutectic solvents. J. Oleo Sci. 2019, 68, 951–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, D.D.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Dai, E.R. A deep eutectic solvent as an extraction solvent to separate and preconcentrate parabens in water samples using in situ liquid-liquid microextraction. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2019, 30, 1203–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemi, B.; Zohrabi, P.; Dehdashtian, S. Application of green solvents as sorbent modifiers in sorptive-based extraction techniques for extraction of environmental pollutants. Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 109, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakirova, F.; Shishov, A.; Bulatov, A. Hydrolysis of triglycerides in milk to provide fatty acids as precursors in the formation of deep eutectic solvent for extraction of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Talanta 2022, 237, 122968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, J.; Yu, G.W.; Song, Z.Y.; Wang, X.J.; Li, Z.G.; She, Y.B.; Lee, M. Microwave-assisted deep eutectic solvent extraction coupled with headspace solid-phase microextraction followed by GC-MS for the analysis of volatile compounds from tobacco. Anal. Methods 2017, 9, 856–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.J.; Wang, M.S. Optimization of deep eutectic solvent-based ultrasound-assisted extraction of polysaccharides from Dioscorea opposita Thunb. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 95, 675–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, X.C.; Chu, D.P.; Zhang, J.X.; Zheng, Y.F.; Li, Y.Q. Microwave-assisted extraction, partial purification and biological activity in vitro of polysaccharides from bladder-wrack (Fucus vesiculosus) by using deep eutectic solvents. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 259, 118169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, J.G.; Chen, D.T.; Lu, Y.B. Deep eutectic solvents based ultrasonic extraction of polysaccharides from edible brown seaweed sargassum horneri. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.K.; Sharma, M.; Mondal, D.; Prasad, K. Deep eutectic solvents as efficient solvent system for the extraction of kappa-carrageenan from Kappaphycus alvarezii. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 136, 930–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.H.; Li, J.; Fu, R.Z.; Zhang, L.L.; Wang, D.Z.; Wang, S. Enhanced extraction of natural pigments from Curcuma longa L. using natural deep eutectic solvents. Ind. Crops Prod. 2019, 140, 111620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, S.S.; Pathak, A.; Rathod, V.K. Optimization and kinetic study of ultrasound assisted deep eutectic solvent based extraction: A greener route for extraction of curcuminoids from Curcuma longa. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2021, 70, 105267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aydin, F.; Yilmaz, E.; Soylak, M. Vortex assisted deep eutectic solvent (DES)-emulsification liquid-liquid microextraction of trace curcumin in food and herbal tea samples. Food Chem. 2018, 243, 442–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Tang, B.; Row, K.H. A green deep eutectic solvent-based ultrasound-assisted method to extract astaxanthin from shrimp byproducts. Anal. Lett. 2014, 47, 742–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.D.; Du, Y.G.; Xiao, Z.E.; Li, Y.; Li, B.F.; Yang, G.W. Determination of trace rhodamine B in chili oil by deep eutectic solvent extraction and an ultra high-performance liquid chromatograph equipped with a fluorescence detector. Anal. Sci. 2017, 33, 715–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, E.Z.; Yang, M.; Cao, J.; Lu, C.; Wang, J.H.; Cao, F.L. Deep eutectic solvents as green media for efficient extraction of terpene trilactones from Ginkgo biloba leaves. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2017, 40, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, D.D.; Zhang, Y.; Dai, Y.X.; Yang, S.M. Air-assisted dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction based on a new hydrophobic deep eutectic solvent for the preconcentration of benzophenone-type UV filters from aqueous samples. J. Sep. Sci. 2018, 41, 1635–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabhi, F.; Di Pietro, T.; Mutelet, F.; Sifaoui, H. Extraction of butanol and acetonitrile from aqueous solution using carboxylic acid based deep eutectic solvents. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 325, 115231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Wang, J.Q.; Zhang, Y.; Xia, Q.; Bi, W.T.; Yang, X.D.; Chen, D.D.Y. Fast environment-friendly ball mill-assisted deep eutectic solvent-based extraction of natural products. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1443, 262–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Tang, B.; Row, K. Extraction of catechin compounds from green tea with a new green solvent. Chem. Res. Chin. Univ. 2014, 30, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.P.; Wang, P.; Zheng, W.; Yu, G.W.; Li, Z.G.; She, Y.B.; Lee, M. Three-stage microwave extraction of cumin (Cuminum cyminum L.) Seed essential oil with natural deep eutectic solvents. Ind. Crops Prod. 2019, 140, 111660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.-X.; Zhang, J.-Y.; Jin, J.; Li, Z.-G.; She, Y.-B.; Lee, M.-R. Microwave-assisted natural deep eutectic solvents pretreatment followed by hydrodistillation coupled with GC-MS for analysis of essential oil from turmeric (Curcuma longa L.). J. Oleo Sci. 2021, 70, 1481–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milani, G.; Vian, M.; Cavalluzzi, M.M.; Franchini, C.; Corbo, F.; Lentini, G.; Chemat, F. Ultrasound and deep eutectic solvents: An efficient combination to tune the mechanism of steviol glycosides extraction. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2020, 69, 105255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
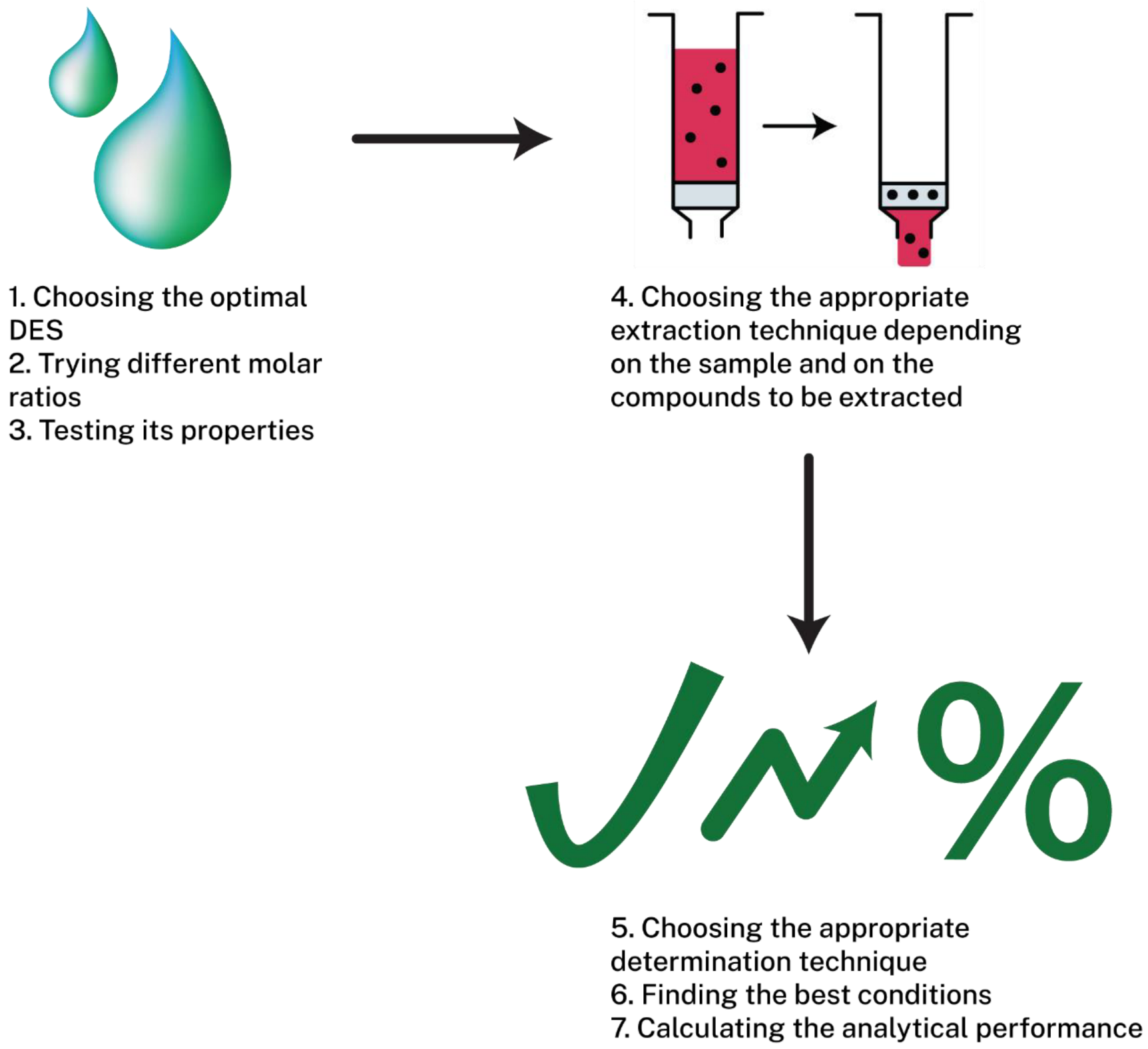
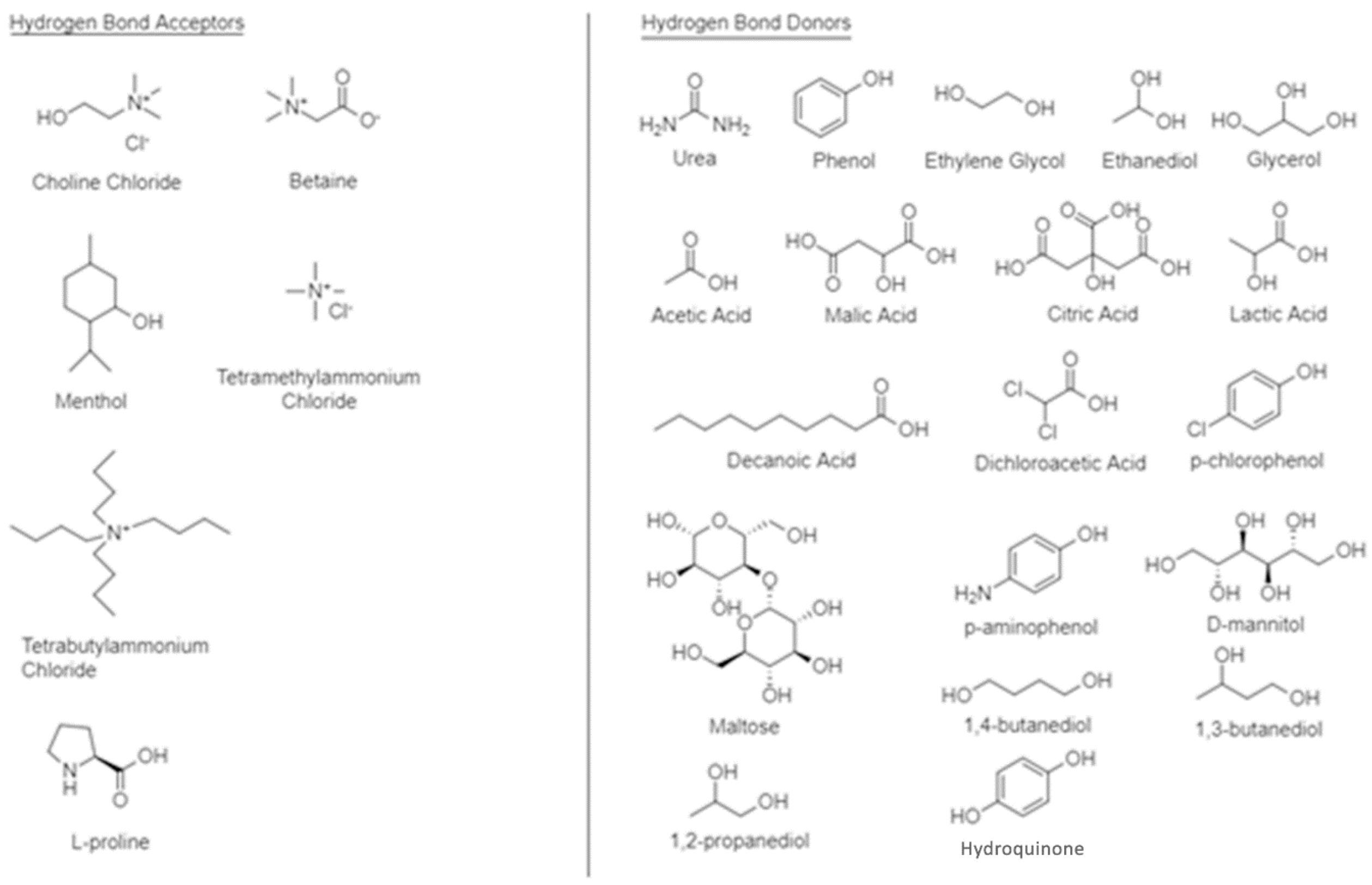
| Type | Formula | Terms |
|---|---|---|
| I | Cat+X− + zMClx | M = Zn, Sn, Ga, In, Al, Fe |
| II | Cat+X− + zMClx · yH2O | M = Cr, Cu, Fe, Ni, Co |
| III | Cat+X− + zRZ | Z = COOH, CONH2, OH |
| IV | MClx + RZ | M = Al, Zn and Z = CONH2, OH |
| Group of Compounds | DES | Molar Ratio | Extraction Technique | Recovery (%) | LOD 1 | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Triazole fungicides | ChCl: 4-chlorophenol | 1:2 | HS-SDME | 94–97 | 0.82–1.0 mg/L | [41] |
| Pesticides | Menthol: dichloroacetic acid | 1:2 | DLLME | 56–86 | 0.32–1.2 ng/g | [42] |
| Pesticides | ChCl: p-chlorophenol | 1:2 | LPME | 56–93 | 0.13–0.31 ng/mL | [43] |
| Neonicotinoid pesticides | Menthol: dodecanoic acid | 2:1 | LLE | 80 | N/R 2 | [44] |
| Pesticides | ChCl: decanoic acid | 1:2 | DLLME | 64–89 | 0.9–3.9 ng/mL | [45] |
| Acidic pesticides | ChCl: ethylene glycol | 1:2 | DLLME-SBSE | 76–90 | 7–14 ng/L | [47] |
| Pesticides | TBAC: dichloroacetic acid | 1:1 | DLLME | 81–94 | 0.09–0.27 ng/mL | [48] |
| Fungicides | Menthol: decanoic acid | 1:1 | UA-DLLME | 72–109 | 0.75–8.45 μg/mL | [49] |
| Herbicides | ChCl: butyric acid | 1:2 | LLE-DLLME | 70–89 | 2.6–8.4 ng/kg | [50] |
| Flavonoids | ChCl: 1,4-butanediol | 1:5 | UAE | N/R | 0.07, 0.09 μg/mL | [56] |
| Flavonoids | Glycerol: L-proline | 2:5 | UAE, SPE | 81–87 | N/R | [57] |
| Isoflavones | ChCl: citric acid | 1:1 | UAE | 64.7–99.2 | 0.06–0.14 μg/mL | [58] |
| Flavonoids | ChCl: 1,2-propanediol | 1:4 | UAE | 86.7–98.9 | 0.05–0.14 μg/mL | [59] |
| Flavonoids | ChCl: oxalic acid: ethylene glycol | 1:1:3 | LLE | N/R | 1.11–1.40 mg/g | [60] |
| Flavonoids | ChCl: acetic acid | 1:2 | UAE | N/R | 1.11–11.57 mg/g | [61] |
| Flavonoids | Betaine: D-mannitol | N/R | UAE | 91.7–95.8 | 0.14–0.17 μg/mL | [62] |
| Flavonoids | Different types | Diff. 3 | UAE | 93.8–107.7 | 0.14–0.22 μg/mL | [63] |
| Bioactive compounds | ChCl: malic acid | 1:1 | UAE | N/R | N/R | [64] |
| Bioactive compounds | ILs, ChCl based DES | Diff. | Reflux | N/R | N/R | [65] |
| Anthocyanins | ChCl: glycerol:citric acid | 0.5:2:0.5 | UAE | N/R | 0.02 mg/L | [66] |
| Anthocyanins | ChCl: malic acid | Diff. | UAE | N/R | 0.15–0.28 mg/L | [67] |
| Anthocyanins | Lactic acid: glucose | 1:2 | Stirring | N/R | N/R | [68] |
| Phenolic metabolites | Different types | Diff. | N/R | 75–97 | N/R | [71] |
| Phenolics | ChCl: oxalic acid | 1:1 | MAE, UAE | N/R | 0.05–0.37 mg/L | [72] |
| Phenolics | ChCl: 1,2-propanediol | 1:1 | Vortex | N/R | N/R | [73] |
| Phenolics | ChCl: lactic acid | 1:2 | MAE, HUE, UAE | N/R | N/R | [74] |
| Phenolics | ChCl + phenolics | N/R | RDSE | 66–87 | 10–60 μg/L | [75] |
| Polyphenols | ChCl: ethylene glycol | 1:4 | SLE | N/R | N/R | [77] |
| Phenolics | Lactic acid: glucose | 5:1 | UAE | 86.0–109.6 | 0.6–89.1 ng/g | [78] |
| Polyphenols | Lactic acid: glucose | 5:1 | SLE | N/R | N/R | [79] |
| Phenolics | ChCl: malic acid | 1.5:1 | P-UAE | N/R | N/R | [80] |
| Phenolics | Glycerol: citric acid: glycine | Diff. | UAE | N/R | N/R | [81] |
| Flavonoids | ChCl: glycerol | 1:1 | UAE | 95 | N/R | [82] |
| Polyphenols | Lactic acid: glycine:water | 3:1:3 | UAE | N/R | N/R | [84] |
| Phenolic acids | ChCl: 1,3-butanediol | 1:6 | MAE | 79.2–86.0 | N/R | [85] |
| Phenolics | ChCl: glycerol | 1:2 | MAE | 77.8–83.8 | 0.15–0.78 μg/mL | [86] |
| Phenolics | Tetramethyl ammonuium chloride:urea | 1:4 | UAE | 97.3–100.4 | N/R | [87] |
| Flavanones | Betaine: ethanediol | 1:4 | Heated LLE | 97.0–101.6 | N/R | [88] |
| Bioactive compounds | ChCl: propylene glycol | 1:1 | UAE | N/R | N/R | [89] |
| Phenolics | ChCl: acetic acid | 1:2 | Thermo-shaking | N/R | N/R | [90] |
| Phenolics | TBAC: hydroquinone | 1:2 | LLE/DLLME | 74–89 | 0.13–0.42 ng/mL | [91] |
| Phenols | L-proline: decanoic acid | 1:4.2 | Stirring | 57–62 | N/R | [92] |
| Group of Compounds | DES | Molar Ratio | Extraction Technique | Recovery (%) | LOD 1 | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sulfonamide | ChCl: ethylene glycol | 1:2 | PT-SPE | 91.0–96.8 | 0.01 μg/mL | [93] |
| Analgetic | Betaine: oxalic acid | 1:2 | SA-DES-ME | 94.2–107.1 | 14.9 μg/L | [94] |
| Antibiotics | ChCl: glycerol | 1:2 | MIPs-SPE | 87.0–91.2 | N/R 2 | [95] |
| Antivirals | TBAC: p-aminophenol | 1:2 | LLE | 90–96 | 1.0–1.3 μg/L | [96] |
| Antimalarial | Menthol: fenchyl alcohol | 1:1 | Stirring | 101 | N/R | [97] |
| NSAID 3 | Menthol: acetic acid | Diff. 4 | LLE | 80 | N/R | [98] |
| Antibiotics | TBAC: butanol | 1:1 | SPE, DLLME | 84–99 | 0.32–0.86 ng/g | [99] |
| Tocotrienols, tocopherols | ChCl: malonic acid | 1:1 | LLE | 93.0–99.8 | N/R | [100] |
| α-tocopherols | ChCl: sucrose | 1:2 | LLE | N/R | N/R | [101] |
| α-, γ-, δ-tocopherols | ChCl: p-cresol | 1:2 | Vortex | 77.6 | N/R | [102] |
| Parabens | Menthol: decanoic acid | 2:1 | LLME | 69.1–78.5 | 0.6–0.8 mg/mL | [103] |
| PAHs | Menthol or thymol with fatty acids | Diff. | Stirring | 70–91 | 2–90 ng/kg | [105] |
| VOCs | ChCl: urea | 1:3 | MAE, HS-SPME | N/R | N/R | [106] |
| Polysaccharides | ChCl: 1,4-butanediol | N/R | UAE | N/R | N/R | [107] |
| Polysaccharides | ChCl: 1,4-butanediol | 1:5 | MAE | 91.2 | N/R | [108] |
| Polysaccharides | ChCl: 1,2-propanediol | 1:2 | UAE | N/R | N/R | [109] |
| Polysaccharides | ChCl: glycerol | 1:2 | Thermal treatment | 60.3 | N/R | [110] |
| Natural pigments | Citric acid: glucose | 1:1 | SPE | 88.5–94.4 | 0.25–0.37 mg/L | [111] |
| Curcuminoids | ChCl: lactic acid | 1:1 | UAE | N/R | N/R | [112] |
| Curcuminoids | ChCl: phenol | 1:4 | VA-LLME | 96–102 | 2.86 μg/L | [113] |
| Pigment | Different types | Diff. | UAE | N/R | N/R | [114] |
| Pigment | ChCl: ethylene glycol | Diff. | N/R | N/R | N/R | [115] |
| Terpene trilactones | Betaine: ethylene glycol | Diff. | UAE | 99.4 | N/R | [116] |
| Benzophenone-type UV filters | Menthol: decanoic acid | 1:1 | AA-DLLME | 88.8–105.9 | 0.05–0.2 ng/mL | [117] |
| Organic solvents | Menthol: capric acid | 2:1 | LLE | N/R | N/R | [118] |
| Tanshinones | ChCl: -1,3-butanediol | N/R | BMAE | 96.1–103.9 | 5–8 ng/mL | [119] |
| Catechins | Different types | Diff. | LLE | 82.7–97.0 | N/R | [120] |
| Essential oils | ChCl: L-lactic acid | 1:3 | MAE | N/R | N/R | [121] |
| Essential oils | ChCl: oxalic acid | 1:1 | MAE | N/R | N/R | [122] |
| Steviol glycosides | Tetraethylammonium chloride: ethylene glycol | 1:2 | UAE | N/R | N/R | [123] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Plastiras, O.-E.; Samanidou, V. Applications of Deep Eutectic Solvents in Sample Preparation and Extraction of Organic Molecules. Molecules 2022, 27, 7699. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27227699
Plastiras O-E, Samanidou V. Applications of Deep Eutectic Solvents in Sample Preparation and Extraction of Organic Molecules. Molecules. 2022; 27(22):7699. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27227699
Chicago/Turabian StylePlastiras, Orfeas-Evangelos, and Victoria Samanidou. 2022. "Applications of Deep Eutectic Solvents in Sample Preparation and Extraction of Organic Molecules" Molecules 27, no. 22: 7699. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27227699
APA StylePlastiras, O.-E., & Samanidou, V. (2022). Applications of Deep Eutectic Solvents in Sample Preparation and Extraction of Organic Molecules. Molecules, 27(22), 7699. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27227699









