Composite Hydrogel Microspheres Encapsulating Hollow Mesoporous Imprinted Nanoparticles for Selective Capture and Separation of 2′-Deoxyadenosine
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Materials
2.2. Characterization
2.3. Synthesis of Polystyrene (PS)
2.4. Synthesis of Hollow Mesoporous Silicon Spheres with Large Pores (MHSs)
2.5. Synthesis of MIPs (MMHSs) Based on MHSs
2.6. Synthesis of MMHS-Encapsulated Hybrid Hydrogel Microspheres (MMHSGs)
2.7. Batch Mode Absorption Experiments
2.8. Regeneration Tests
2.9. Actual Sample Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
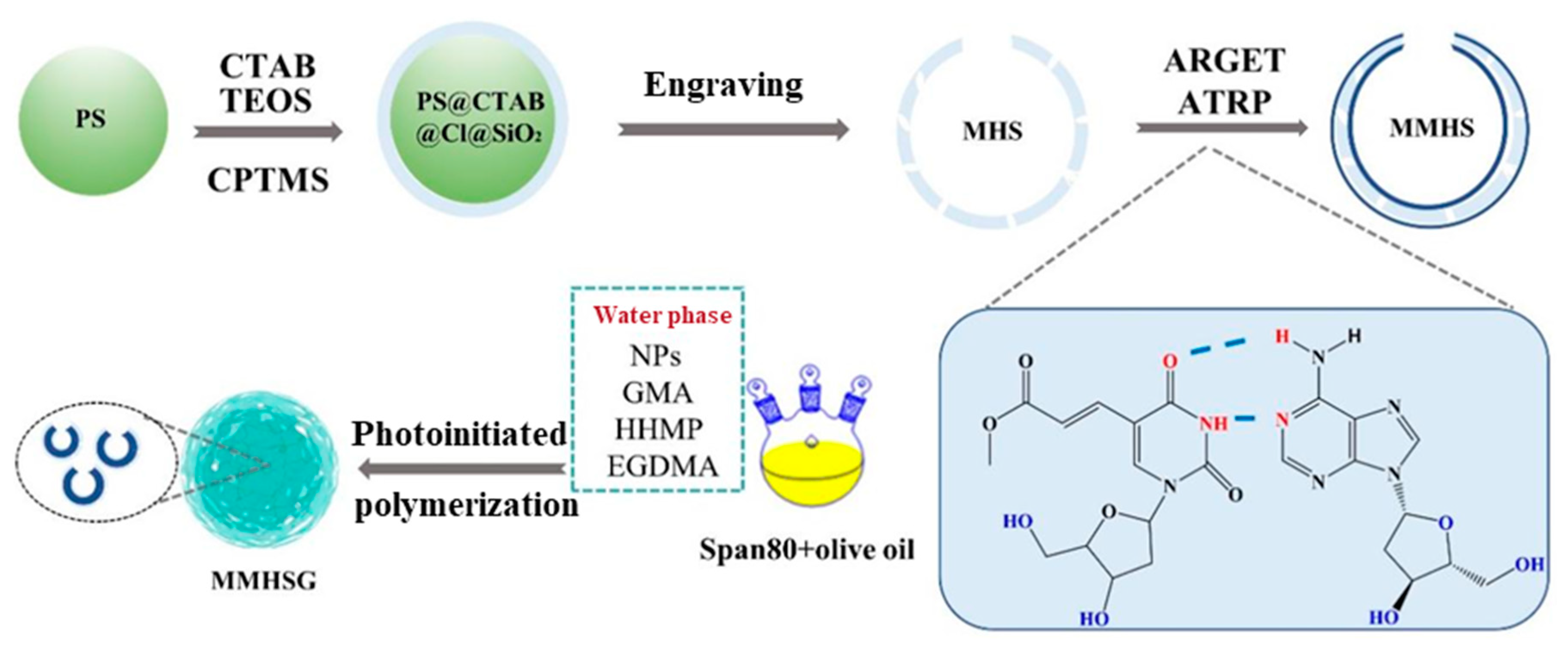
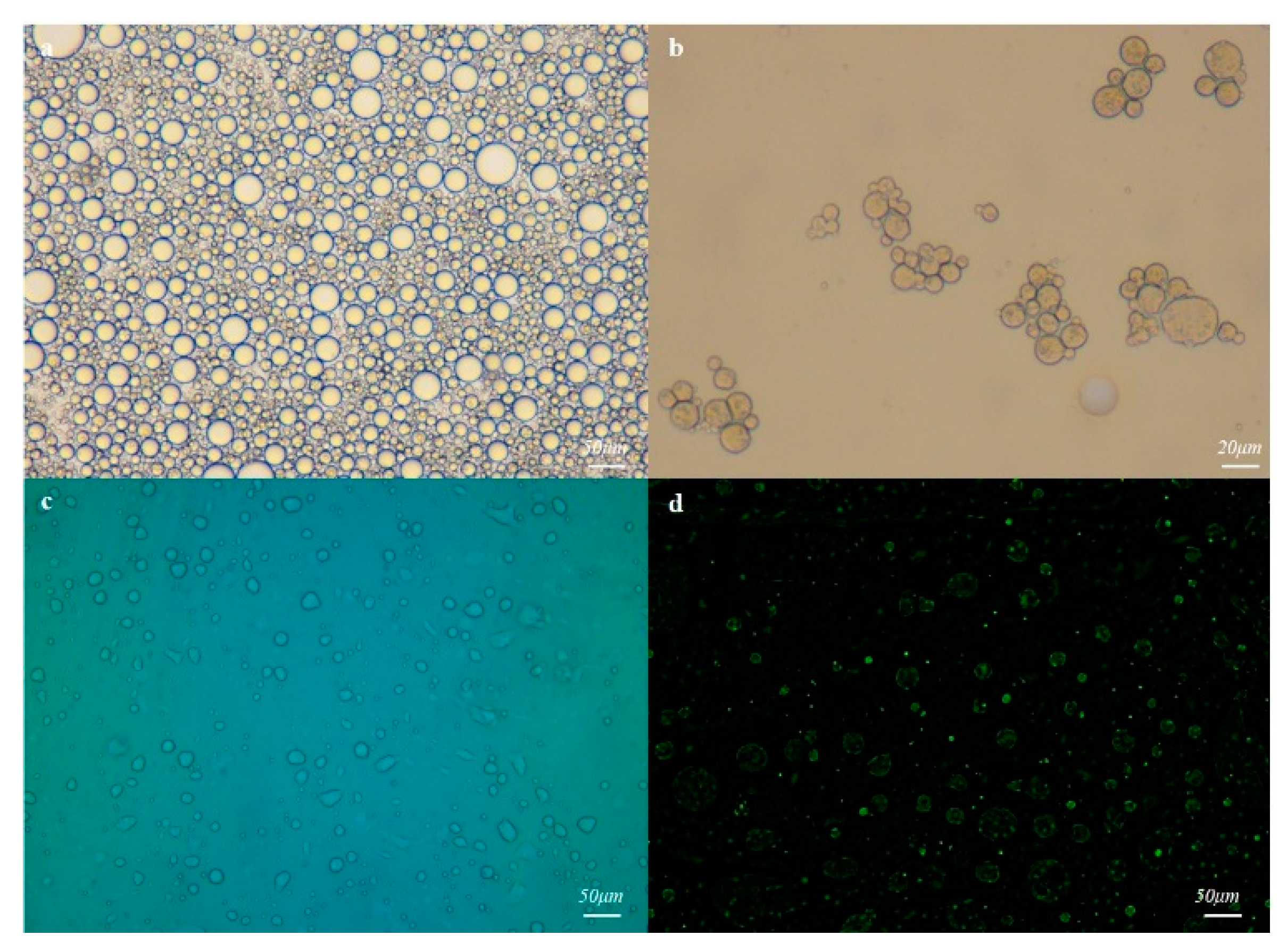
3.1. Preparation and Recognition Mechanism of MMHSG
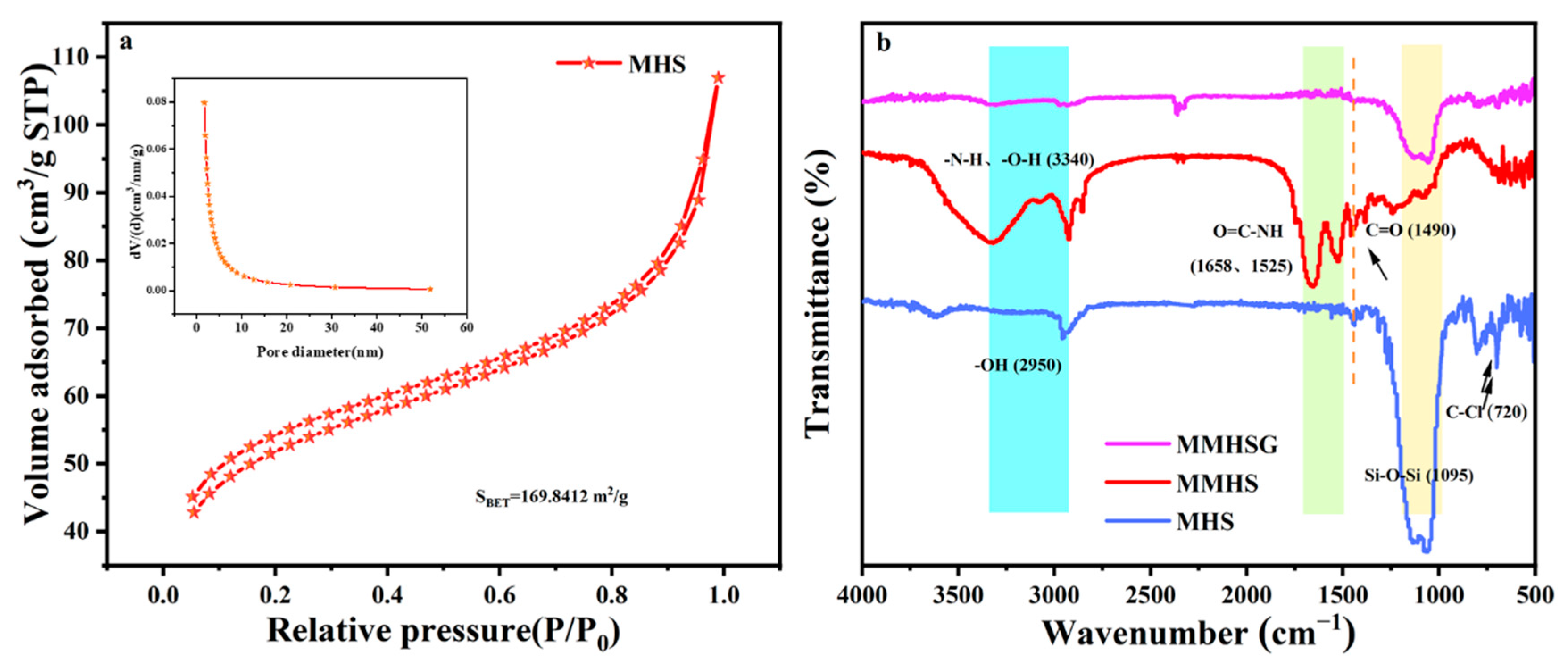
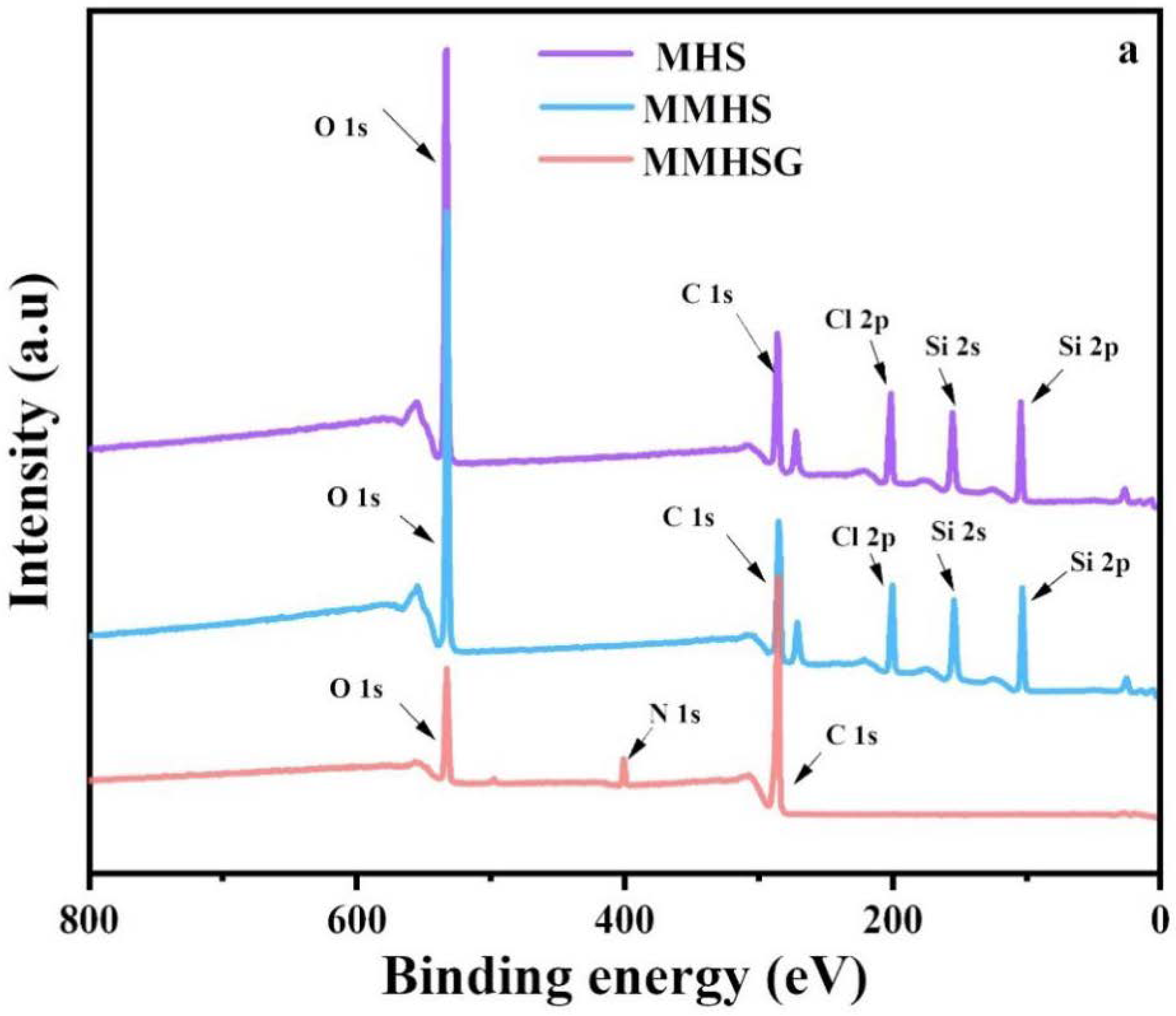
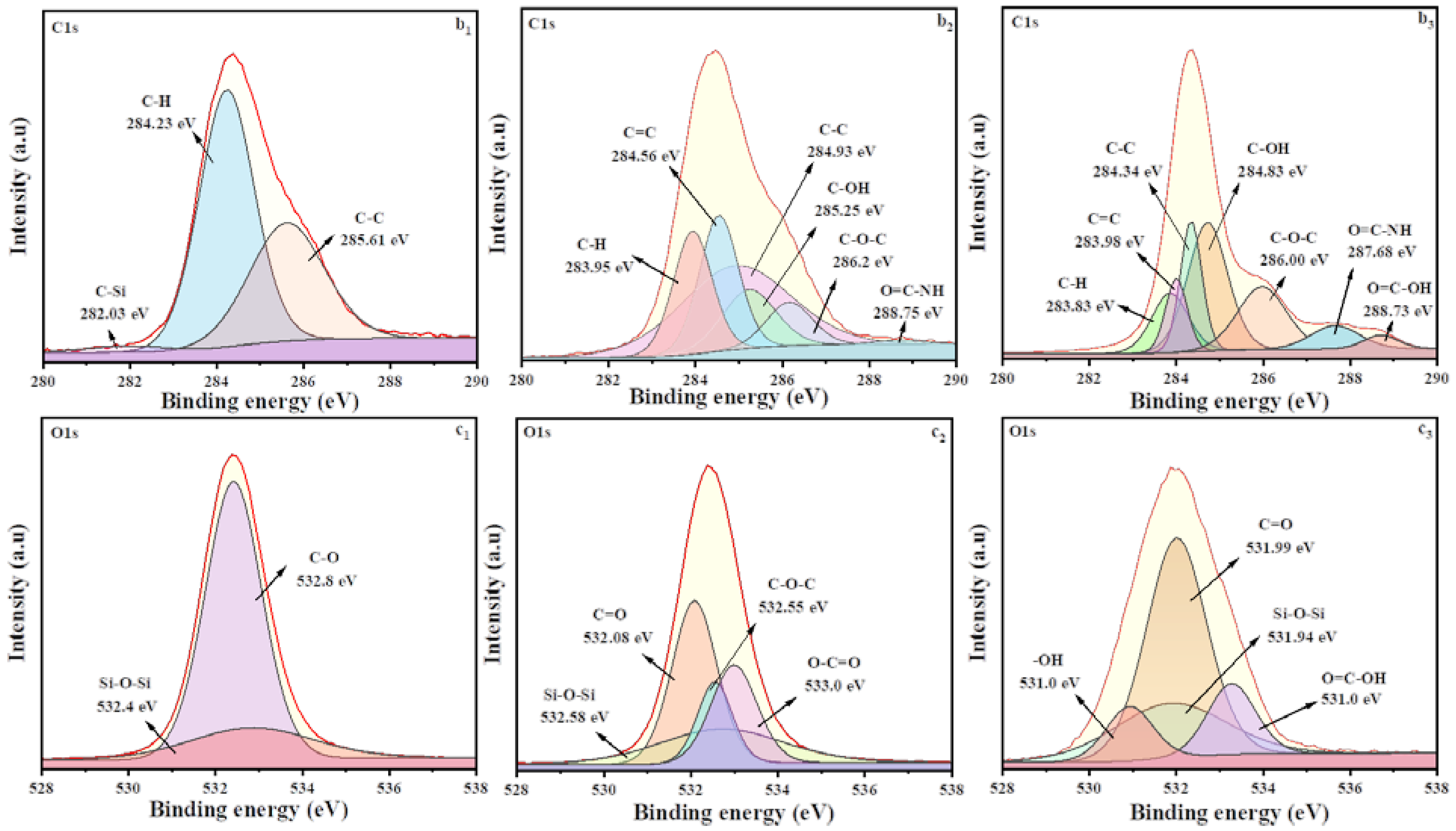
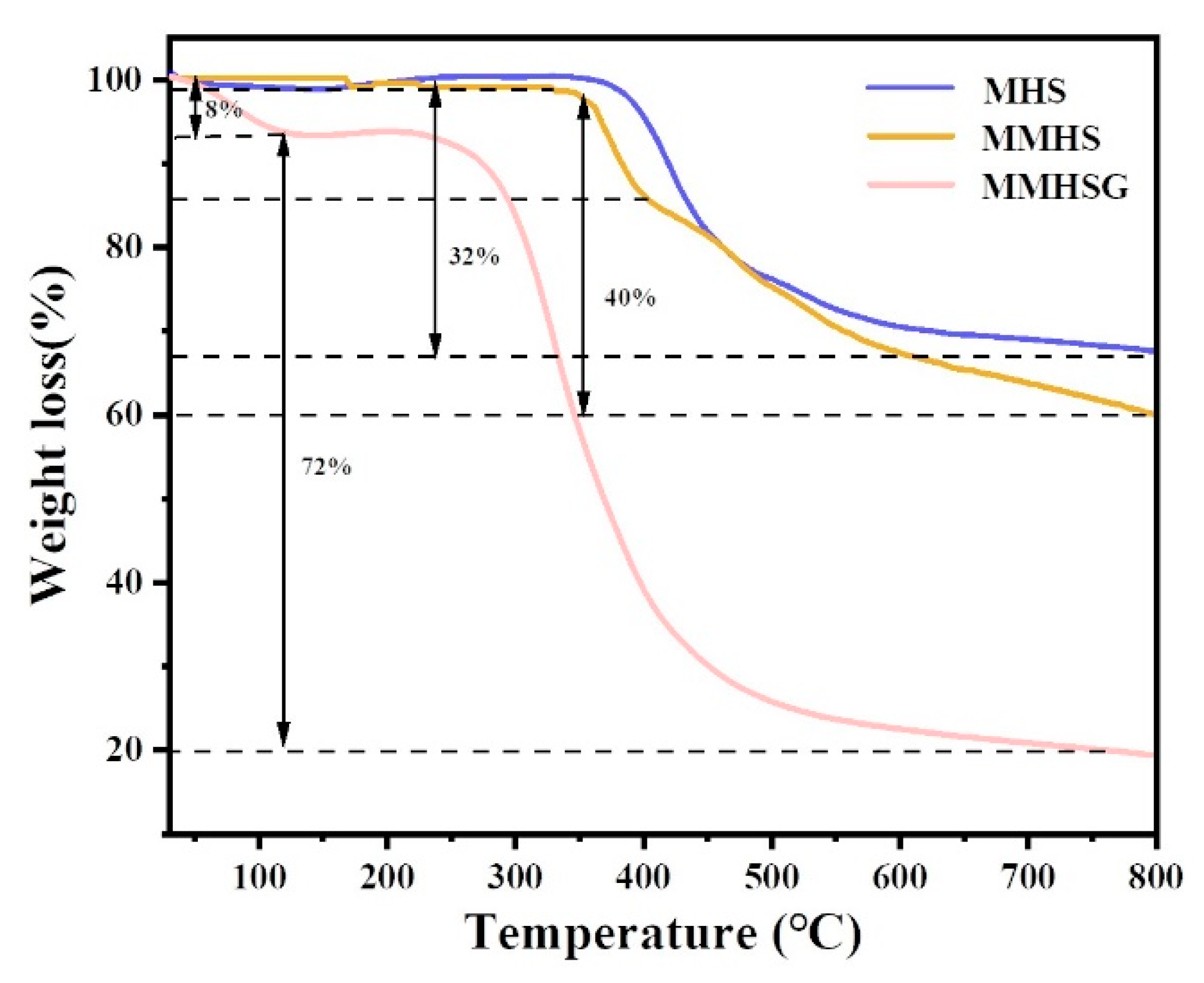
3.2. Characterization of MMHSs and MMHSGs
3.3. Analysis of the Adsorption Kinetic Performance of MMHSG and NMHSG on dA
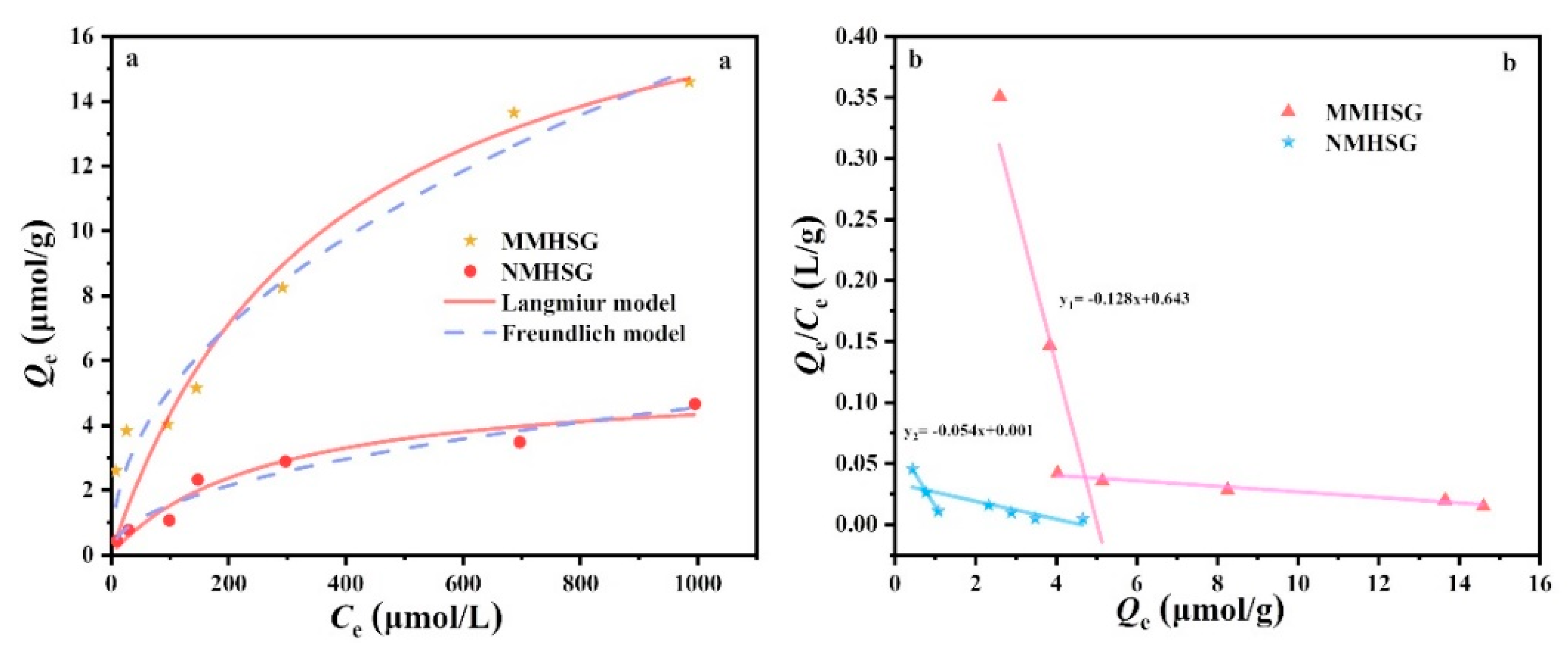
3.4. Adsorption Isotherm Analysis of dA by MMHSG and NMHSG
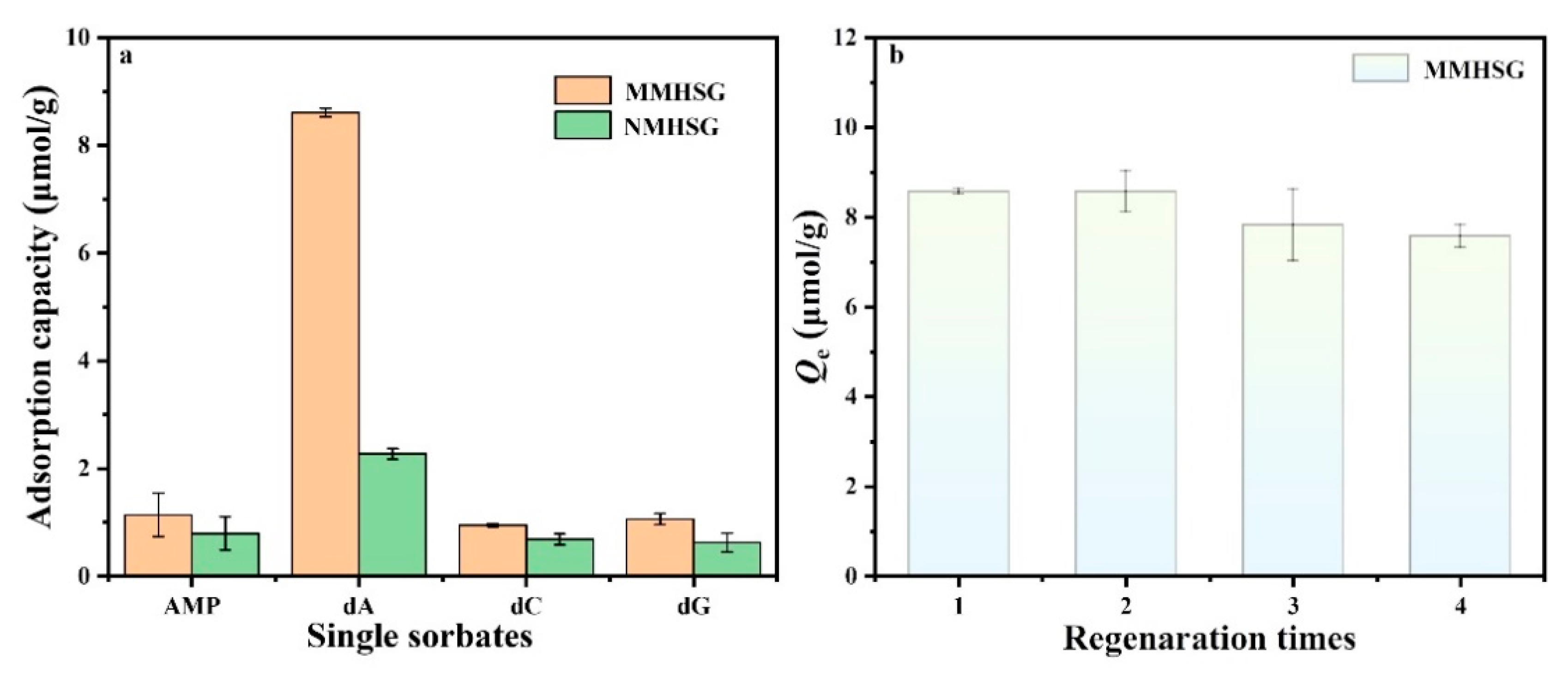
3.5. Adsorption Selectivity and Regeneration of MMHSG
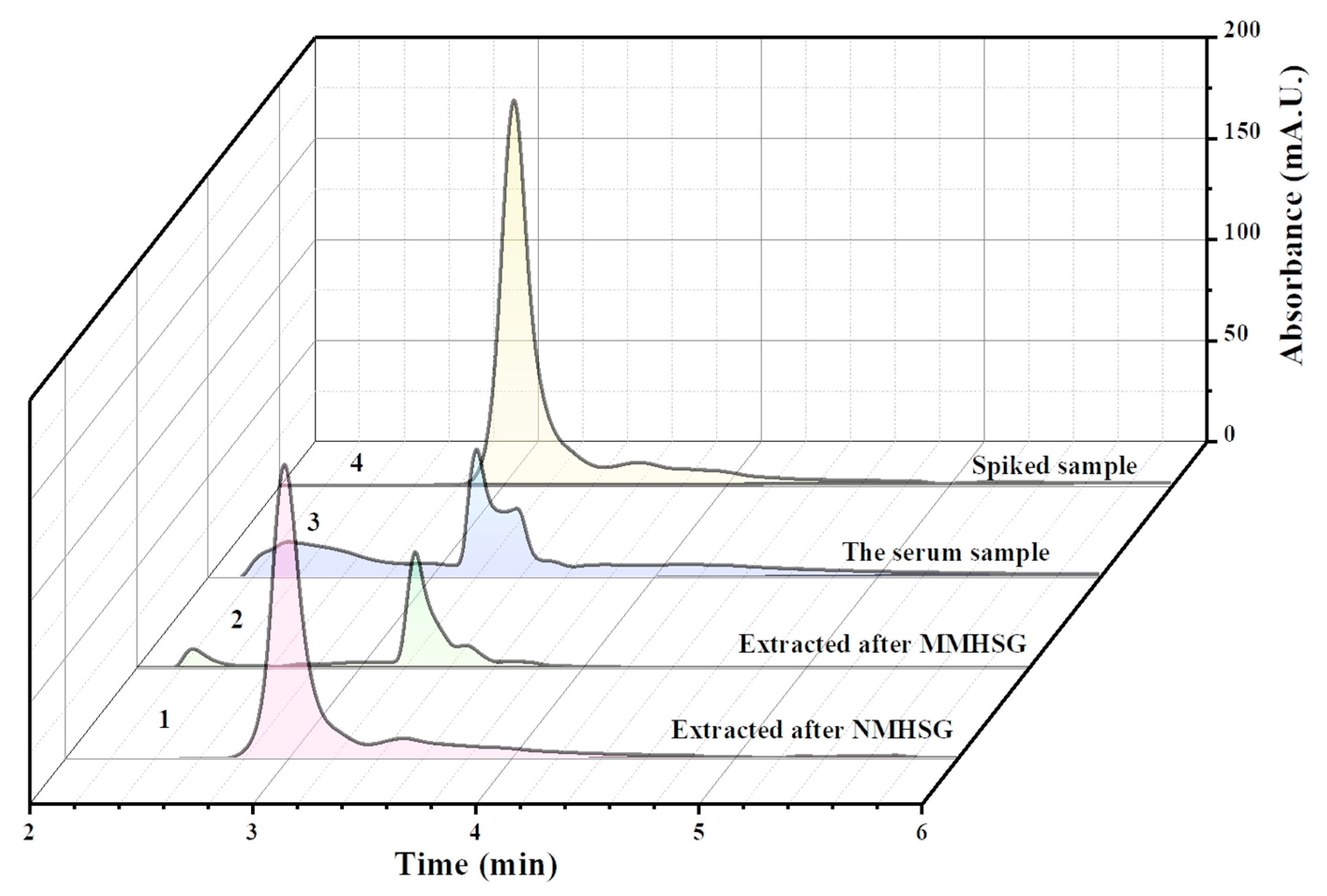
3.6. Analysis of Actual Samples
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Levy, M.; Griswold, K.E.; Ellington, A.D. Direct Selection of Trans-Acting Ligase Ribozymes by in Vitro Compartmentalization. RNA 2005, 11, 1555–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Li, X.; Yin, D.; Li, D.; Bie, Z.; Liu, Z. Dual-Template Docking Oriented Molecular Imprinting: A Facile Strategy for Highly Efficient Imprinting within Mesoporous Materials. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 10929–10932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsui, J.; Higashi, M.; Takeuchi, T. Molecularly Imprinted Polymer as 9-Ethyladenine Receptor Having a Porphyrin-Based Recognition Center. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122, 5218–5219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drzazgowska, J.; Schmid, B.; Süssmuth, R.D.; Altintas, Z. Self-Assembled Monolayer Epitope Bridges for Molecular Imprinting and Cancer Biomarker Sensing. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 4798–4806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Jiang, M.; Zou, L.; Shi, D.; Mei, S.; Zhu, Y.; Shi, Y.; Dai, K.; Lu, B. Selective Solid-Phase Extraction of Bisphenol A Using Molecularly Imprinted Polymers and Its Application to Biological and Environmental Samples. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2006, 385, 780–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Sheng, N.; Zhu, R.; Wei, F.; Cai, Z.; Zhai, M.; Du, S.; Hu, Q. Preparation of Dummy Template Imprinted Polymers at Surface of Silica Microparticles for the Selective Extraction of Trace Bisphenol A from Water Samples. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 179, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bicak, T.C.; Cormack, P.A.G.; Walker, C. Synthesis of Uniform Polymer Microspheres with “Living” Character Using Ppm Levels of Copper Catalyst: ARGET Atom Transfer Radical Precipitation Polymerisation. React. Funct. Polym. 2021, 163, 104891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaihinger, D.; Landfester, K.; Kräuter, I.; Brunner, H.; Tovar, G.E.M. Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Nanospheres as Synthetic Affinity Receptors Obtained by Miniemulsion Polymerisation. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2002, 203, 1965–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, T.; Gao, X.-D.; Wang, P.; Wang, Y.; Lin, Y.-F.; Hu, X.-Z.; Hao, Q.-L.; Zhou, Y.-K.; Mei, S.-R. Determination of Trace Tetracycline Antibiotics in Foodstuffs by Liquid Chromatography--Tandem Mass Spectrometry Coupled with Selective Molecular-Imprinted Solid-Phase Extraction. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2009, 393, 2009–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, D.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, M.; Xie, C.; Guan, G.; Wang, D. A Surface Functional Monomer-Directing Strategy for Highly Dense Imprinting of TNT at Surface of Silica Nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 7859–7866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cumbo, A.; Lorber, B.; Corvini, P.F.-X.; Meier, W.; Shahgaldian, P. A Synthetic Nanomaterial for Virus Recognition Produced by Surface Imprinting. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, C.; Long, Y.; Pan, J.; Li, K.; Liu, F. Molecularly Imprinted Silica Prepared with Immiscible Ionic Liquid as Solvent and Porogen for Selective Recognition of Testosterone. Talanta 2008, 74, 1126–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, X.; He, X.; Liu, Z. Molecularly Imprinted Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Specific Extraction and Efficient Identification of Amadori Compounds. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1019, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Wang, L.; He, X.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, L. A Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-Coated Nanocomposite of Magnetic Nanoparticles for Estrone Recognition. Talanta 2009, 78, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; He, Y.; He, X.; Li, W.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Y. BSA-Imprinted Synthetic Receptor for Reversible Template Recognition. J. Sep. Sci. 2009, 32, 1981–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Liu, B.; Wang, Z.; Gao, D.; Guan, G.; Zhang, Z. Molecular Imprinting at Walls of Silica Nanotubes for TNT Recognition. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 437–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Jiang, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, P. Efficient Synthesis of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers with Enzyme Inhibition Potency by the Controlled Surface Imprinting Approach. ACS Macro. Lett. 2013, 2, 566–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boonpangrak, S.; Whitcombe, M.J.; Prachayasittikul, V.; Mosbach, K.; Ye, L. Preparation of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers Using Nitroxide-Mediated Living Radical Polymerization. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2006, 22, 349–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, Z.; Li, W.; Tang, Y.; Elzatahry, A.; Lu, G.; Zhao, D. Mesoporous Organosilica Hollow Nanoparticles: Synthesis and Applications. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1707612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosquera, J.; Szyszko, B.; Ho, S.K.Y.; Nitschke, J.R. Sequence-Selective Encapsulation and Protection of Long Peptides by a Self-Assembled FeII8L6 Cubic Cage. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Yang, Y.; Geng, J.; Gu, Z.; Zou, J.; Yu, C. Electron Tomography: A Unique Tool Solving Intricate Hollow Nanostructures. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1801564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, N.; Jayawardana, K.W.; Chen, X.; Yan, M. One-Step Synthesis of Amine-Functionalized Hollow Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles as Efficient Antibacterial and Anticancer Materials. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 1040–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, W.; Wang, J.; Lee, S.-J.; Dong, F.; Park, S.S.; Ha, C.-S. A General PH-Responsive Supramolecular Nanovalve Based on Mesoporous Organosilica Hollow Nanospheres. Chem. A Eur. J. 2010, 16, 8641–8646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Qiao, S.Z.; Liu, H.; Chen, J.; Orpe, A.; Zhao, D.; Lu, G.Q. Extension of the Stöber Method to the Preparation of Monodisperse Resorcinol—Formaldehyde Resin Polymer and Carbon Spheres. Angew. Chem. 2011, 123, 6069–6073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Tian, H.; Wang, C.; Xu, S. Designing and Controlling the Morphology of Spherical Molecularly Imprinted Polymers. Mater. Adv. 2020, 1, 2182–2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosari, M.; Borgna, A.; Zeng, H.C. Transformation of Stöber Silica Spheres to Hollow Nanocatalysts. ChemNanoMat 2020, 6, 889–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.; Shi, C.; Wang, T.; Li, X.; Ma, J. Recent Progress in Hollow Silica: Template Synthesis, Morphologies and Applications. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2016, 227, 121–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Wang, B.; Dai, J.; Dai, X.; Hang, H.; Ou, H.; Yan, Y. Selective Recognition of 2, 4, 5-Trichlorophenol by Temperature Responsive and Magnetic Molecularly Imprinted Polymers Based on Halloysite Nanotubes. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 3360–3369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, G.-L.; Jiang, N.; Maharjan, S.; Yin, Y.-X.; Chai, R.-R.; Cao, X.; Yang, J.-Z.; Miri, A.K.; Hassan, S.; Zhang, Y.S. Aqueous Two-Phase Emulsion Bioink-Enabled 3D Bioprinting of Porous Hydrogels. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1805460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Q.; Gao, F.; Zeng, Z.; Yang, J.; Wu, M.; Gao, C.; Cheng, D.; Pan, H.; Liu, W.; Ruan, C. Coaxial Scale-up Printing of Diameter-Tunable Biohybrid Hydrogel Microtubes with High Strength, Perfusability, and Endothelialization. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2001485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Yu, Q.; Wen, J.; Li, C.; Guo, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, N. Ultrafast and Highly Selective Uranium Extraction from Seawater by Hydrogel-like Spidroin-Based Protein Fiber. Angew. Chem. 2019, 131, 11911–11916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marciano, J.S.; Ferreira, R.R.; de Souza, A.G.; Barbosa, R.F.S.; de Moura Junior, A.J.; Rosa, D.S. Biodegradable Gelatin Composite Hydrogels Filled with Cellulose for Chromium (VI) Adsorption from Contaminated Water. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 181, 112–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Wang, J.; Han, Y.; Luo, X.; Tang, W.; Yue, T.; Li, Z. Robust MOF Film of Self-Rearranged UiO-66-NO2 Anchored on Gelatin Hydrogel via Simple Thermal-Treatment for Efficient Pb (II) Removal in Water and Apple Juice. Food Control 2021, 130, 108409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Sun, W.; Song, X.; Ji, H.; Yang, Y.; Sun, S.; Zhao, W.; Zhao, C. Precipitated Droplets In-Situ Cross-Linking Polymerization towards Hydrogel Beads for Ultrahigh Removal of Positively Charged Toxins. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 238, 116497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fijneman, A.J.; Högblom, J.; Palmlöf, M.; de With, G.; Persson, M.; Friedrich, H. Multiscale Colloidal Assembly of Silica Nanoparticles into Microspheres with Tunable Mesopores. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2002725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seong, Y.-J.; Lin, G.; Kim, B.J.; Kim, H.-E.; Kim, S.; Jeong, S.-H. Hyaluronic Acid-Based Hybrid Hydrogel Microspheres with Enhanced Structural Stability and High Injectability. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 13834–13844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, J.; Wang, D.; Wang, D.; Xu, F.; Duan, R.; Zhang, D.; Fan, J.; Dong, B. Visible-Light-Driven Water-Fueled Ecofriendly Micromotors Based on Iron Phthalocyanine for Highly Efficient Organic Pollutant Degradation. Langmuir 2019, 36, 6930–6937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, D.S.; Lee, Y.; Ryu, H.A.; Jang, Y.; Lee, K.-M.; Choi, Y.; Choi, W.J.; Lee, M.; Park, K.M.; Park, K.D.; et al. Cell Recruiting Chemokine-Loaded Sprayable Gelatin Hydrogel Dressings for Diabetic Wound Healing. Acta Biomater. 2016, 38, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bode, F.; da Silva, M.A.; Drake, A.F.; Ross-Murphy, S.B.; Dreiss, C.A. Enzymatically Cross-Linked Tilapia Gelatin Hydrogels: Physical, Chemical, and Hybrid Networks. Biomacromolecules 2011, 12, 3741–3752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo, M.T.; Harley, B.A.C. Perivascular Signals Alter Global Gene Expression Profile of Glioblastoma and Response to Temozolomide in a Gelatin Hydrogel. Biomaterials 2019, 198, 122–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Jin, M.; Chen, Y.; Teng, L.; Qi, D.; Ren, L. Air-In-Water Emulsion Solely Stabilized by Gelatin Methacryloyl and Templating for Macroporous Nanocomposite Hydrogels. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2019, 220, 1800500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wu, X.; Hou, X.; Su, X.; Chu, Q.; Fahruddin, N.; Zhao, J.X. Shape-Tunable Hollow Silica Nanomaterials Based on a Soft-Templating Method and Their Application as a Drug Carrier. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 21921–21930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Liu, J.; Chen, X.; Ma, X.; Guo, D.; Li, Z.; Pan, J. Janus Silica Nanosheets-Based MMIPs Platform for Synergetic Selective Capture and Fast Separation of 2′-Deoxyadenosine: Two Different Components Segmented on the Surface of One Object. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 369, 793–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Tian, Q.; Boyjoo, Y.; Hou, G.; Shi, X.; Liu, J. Synthesis of Colloidal Mesoporous Silica Spheres with Large Through-Holes on the Shell. Langmuir 2019, 36, 6984–6993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Zou, H.; Chen, S.; Xue, N.; Yang, H. Janus Mesoporous Silica Nanosheets with Perpendicular Mesochannels: Affording Highly Accessible Reaction Interfaces for Enhanced Biphasic Catalysis. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 10455–10458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, M.; Li, P.; Sheng, N.; Liu, L.; Pan, H.; Wang, C.; Cai, L.; Ma, Y. Sialic Acid-Targeted Nanovectors with Phenylboronic Acid-Grafted Polyethylenimine Robustly Enhance SiRNA-Based Cancer Therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 9565–9576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Zhang, H.; Wei, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, J.; Dong, L.; Li, E.; Ruhlmann, L.; et al. Catalytic Emulsion Based on Janus Nanosheets for Ultra-Deep Desulfurization. Chem. A Eur. J. 2017, 23, 1920–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Wu, Y.; Shen, Y.; Zhou, C.; Li, Y.-F.; He, R.-R.; Liu, M. Enhanced Therapeutic Efficacy of Doxorubicin for Breast Cancer Using Chitosan Oligosaccharide-Modified Halloysite Nanotubes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 26578–26590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Tian, X.; Pan, J. One-Step Double Emulsion via Amphiphilic SeN Supramolecular Interactions: Towards Porous Multi-Cavity Beads for Efficient Recovery Lithium from Brine. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 266, 118540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Wang, P.; Song, Y.; Li, H.; Luo, J.; Pan, J. Hybrid Hydrogel Microspheres Loading Single-Hole Hollow Imprinted Particles for Fast and Selective Uptake of 2′-Deoxyadenosine. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 287, 120472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Wang, P.; Tian, X.; Sun, W.; Pan, J. Imprinted Polymer Beads Featuring Both Predefined Multiple-Point Interaction and Accessible Binding Sites for Precise Recognition of 2′-Deoxyadenosine. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 302, 122048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Liu, J.; Ma, Y.; Tang, J.; Yang, K.; Liu, Z.; Pan, J. Mosaic-Inspired Magnetic Alginate Composite Sorbents Derived from Coalesce of Two Emulsion Droplets for Selective Recognition of 2′-Deoxyadenosine. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 394, 124931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Adsorbent | Pseudo-First-Order Kinetic Model | Pseudo-Second-Order Kinetic Model | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nonlinear | Nonlinear | ||||||||
| Qae,e (μmol·g−1) | Qbe,c (μmol·g−1) | k1 (min−1) | R2 | Qce,c (μmol·g−1) | k2 × 10−3 (g·μmol−1·min−1) | R2 | h (μmol·g−1 min−1) | t1/2 (min) | |
| MMHSG | 8.615 | 8.48 | 0.042 | 0.99 | 10.39 | 4.19 | 0.99 | 0.45 | 22.86 |
| NMHSG | 2.665 | 2.55 | 0.035 | 0.98 | 3.23 | 10.51 | 0.98 | 0.11 | 29.48 |
| Adsorbent | Linear | Linear | |||||||
| k1 (min−1) | Qe (μmol·g−1) | R2 | k2 × 10−3 (g·μmol−1·min−1) | Qe (μmol·g−1) | R2 | ||||
| MMHSG | 0.035 | 8.141 | 0.99 | 3.58 | 10.648 | 0.99 | |||
| NMHSG | 0.024 | 2.385 | 0.97 | 10.85 | 2.639 | 0.95 | |||
| Adsorbent | Langmuir Isotherm | Freundlich Isotherm | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qm (μmol·g−1) | KL (L·μg−1) | RL | R2 | KF (μmol·g−1) (L·μmol)−1/n | 1/n | R2 | |
| MMHSG | 20.22 | 0.0027 | 0.948 | 0.91 | 0.58 | 0.47 | 0.96 |
| NMHSG | 5.44 | 0.0038 | 0.979 | 0.94 | 0.47 | 0.47 | 0.95 |
| Adsorbent | High-Affinity Binding Sites | Low-Affinity Binding Sites | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ka (μmol·L−1) | Nmax (μmol·g−1) | ka (μmol·L−1) | Nmax (μmol·g−1) | |
| MMHSG | 442.27 | 21.6 | 7.81 | 4.54 |
| NMHSG | 136.99 | 4.54 | 18.52 | 1.26 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, L.; Zhou, M.; Pan, J. Composite Hydrogel Microspheres Encapsulating Hollow Mesoporous Imprinted Nanoparticles for Selective Capture and Separation of 2′-Deoxyadenosine. Molecules 2022, 27, 7444. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27217444
Liu L, Zhou M, Pan J. Composite Hydrogel Microspheres Encapsulating Hollow Mesoporous Imprinted Nanoparticles for Selective Capture and Separation of 2′-Deoxyadenosine. Molecules. 2022; 27(21):7444. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27217444
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Lu, Mengdie Zhou, and Jianming Pan. 2022. "Composite Hydrogel Microspheres Encapsulating Hollow Mesoporous Imprinted Nanoparticles for Selective Capture and Separation of 2′-Deoxyadenosine" Molecules 27, no. 21: 7444. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27217444
APA StyleLiu, L., Zhou, M., & Pan, J. (2022). Composite Hydrogel Microspheres Encapsulating Hollow Mesoporous Imprinted Nanoparticles for Selective Capture and Separation of 2′-Deoxyadenosine. Molecules, 27(21), 7444. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27217444







