Abstract
Marine fungi Aspergillus sp. is an important source of natural active lead compounds with biological and chemical diversity, of which sesquiterpenoids are an extremely important class of bioactive secondary metabolites. In this paper, we review the sources, chemical structures, bioactivity, biosynthesis, and druggability evaluation of sesquiterpenoids discovered from marine fungi Aspergillus sp. since 2008. The Aspergillus species involved include mainly Aspergillus fumigatus, Aspergillus versicolor, Aspergillus flavus, Aspergillus ustus, Aspergillus sydowii, and so on, which originate from sponges, marine sediments, algae, mangroves, and corals. In recent years, 268 sesquiterpenoids were isolated from secondary metabolites of marine Aspergillus sp., 131 of which displayed bioactivities such as antitumor, antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, and enzyme inhibitory activity. Furthermore, the main types of active sesquiterpenoids are bisabolanes, followed by drimanes, nitrobenzoyl, etc. Therefore, these novel sesquiterpenoids will provide a large number of potential lead compounds for the development of marine drugs.
1. Introduction
More than 70% area of the earth is covered by oceans, which is the largest known habitat for life. The marine environment is characterized by high salinity, high pressure, low oxygen, low temperature, darkness, scarce nutrients, etc. To adapt to the special environment and obtain advantages in the competition of limited resources, marine microorganisms could produce novel secondary metabolites with unique structures and potent biological activities during evolution [1,2]. Rich marine microorganisms, mainly derived from marine actinomycetes and marine fungi, are ubiquitous in the natural environment [3]. Diverse active natural products exist in endophytic fungi from the marine environment, which can be the resources for new lead compounds [4,5].
Aspergillus is a typical filamentous fungus, which is divided mainly into Aspergillus fumigatus, Aspergillus versicolor, Aspergillus flavus, Aspergillus ustus, Aspergillus sydowii, and so on [6]. Fumiquinazolines were isolated by Numata from marine Aspergillus sp. for the first time in 1992, which opened the door to the study of the metabolites of marine Aspergillus [7]. Recent studies have found that many organic compounds with unique structures, which showed a lot of physiological activities, were found in marine Aspergillus sp., including terpenoids, alkaloids, and polyketones [8]. Sesquiterpenoids, the most abundant among all the terpenoids skeletons, exhibit excellent biological activities, such as cytotoxicity, antibacterial, antifungal, antiviral, anti-inflammatory, and enzyme inhibitory activity, and have aroused widespread interest of many scholars [9,10]. This paper attempts to review the sources, bioactivities, biosynthesis, and other studies of sesquiterpenoids discovered from marine fungi Aspergillus sp. in the last 15 years.
2. Characteristics of Sesquiterpenoids from Marine Aspergillus sp.
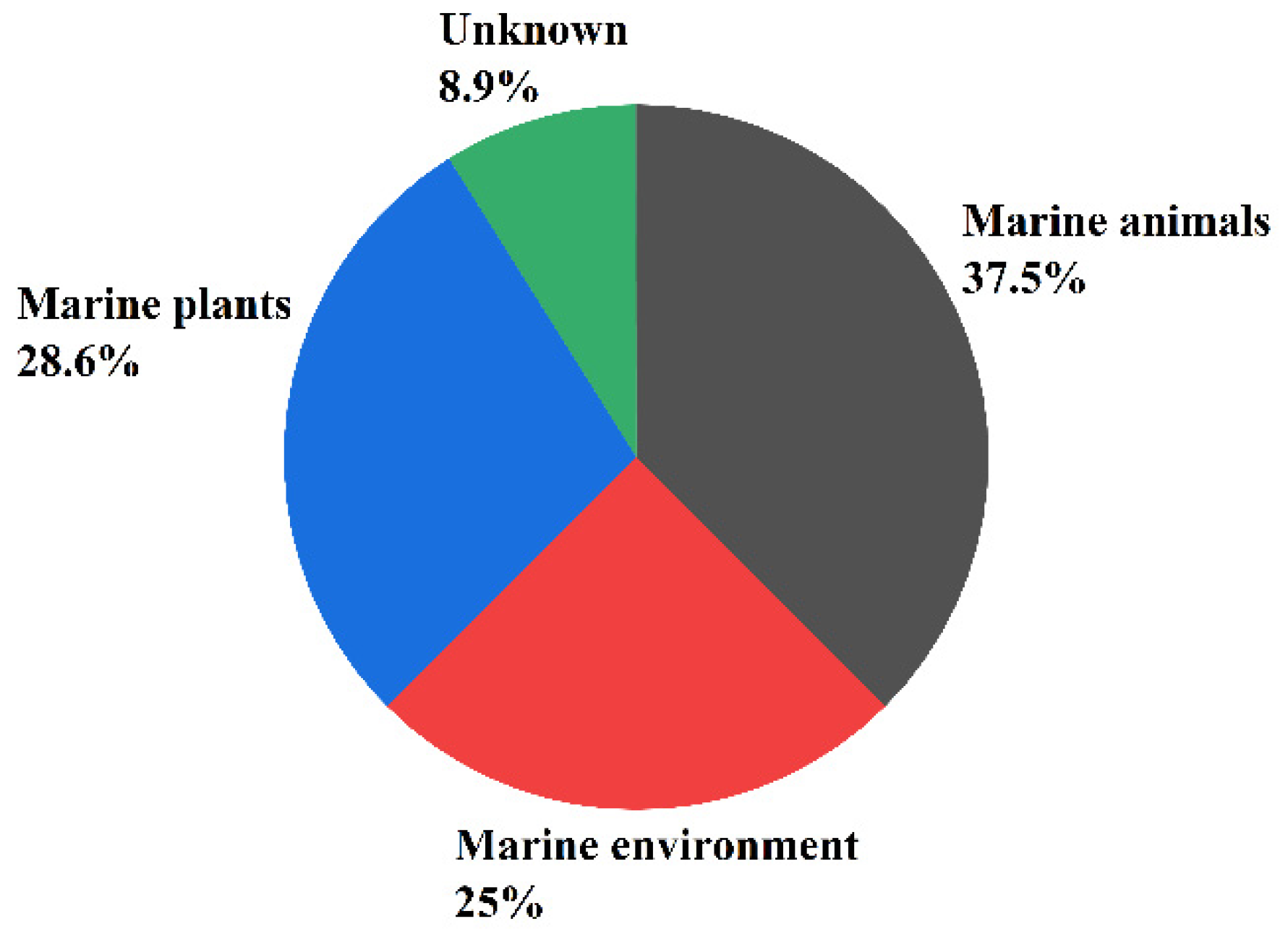
Secondary metabolites of marine fungi have become one of the most active subfields of natural pharmaceutical discovery [11]. Sesquiterpenoids are an extremely important class of secondary metabolites and have been associated with a wide variety biological activities [12]. Approximately 268 sesquiterpenoids isolated from 56 strains of marine fungi are reviewed in this work. Furthermore, research has found that 37.5% of the sesquiterpenoid compounds came from marine animals (sponges, 21.4% and corals, 8.9%), 28.6% from marine plants (algae, 16.1% and mangroves, 12.5%), and the remaining compounds from the marine environment (21.4% from marine sediments and 1.8% from seawater), and 8.9% from unknown sources (see Figure 1).
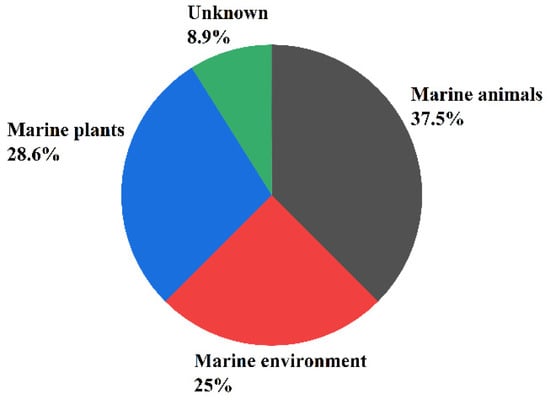
Figure 1.
The main sources of the sesquiterpene-rich marine fungi.
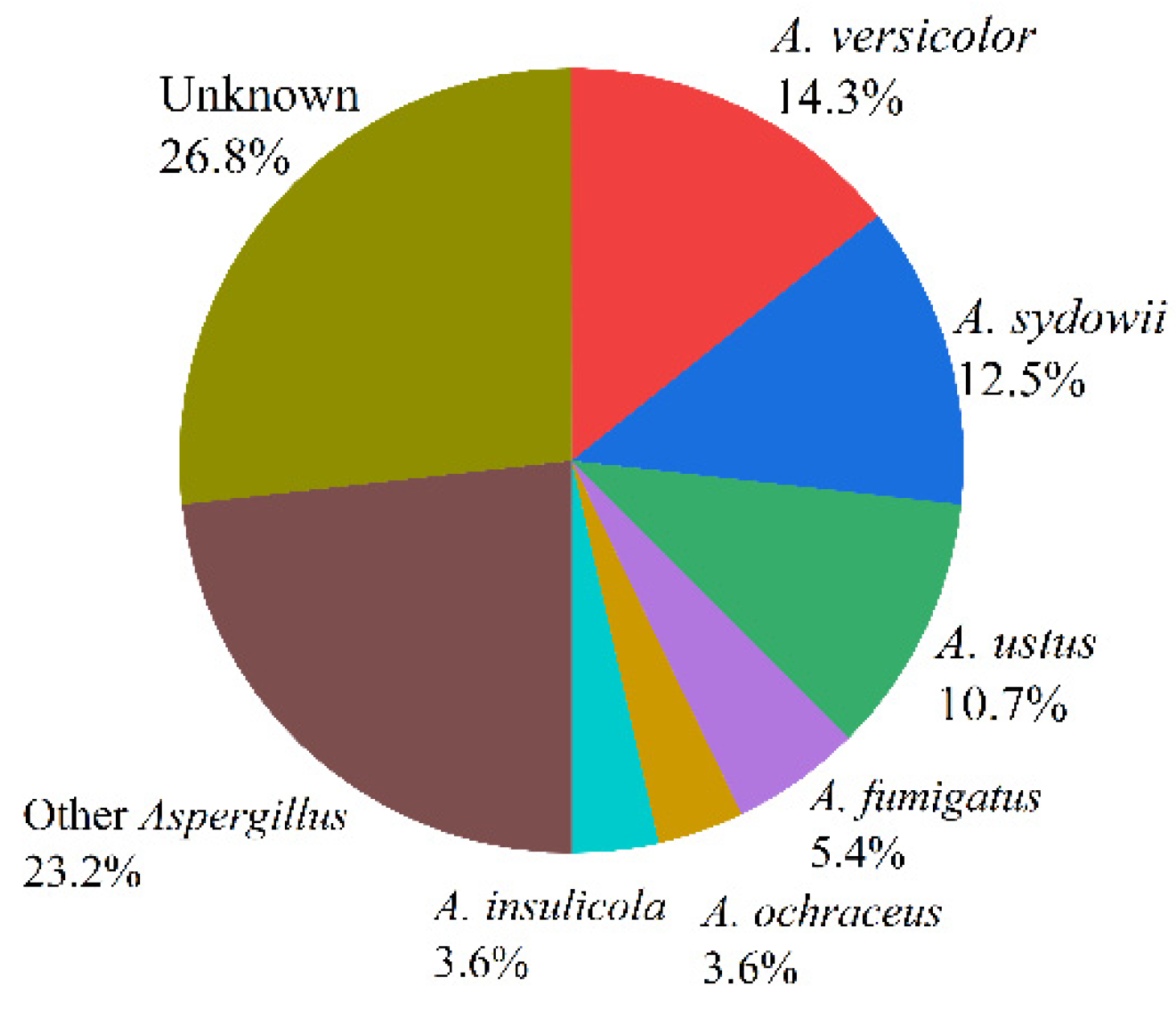
Marine fungus Aspergillus is a huge community that occupies a great proportion in the fungus family, which is widely distributed in marine plants, marine organisms, marine sediments, and other environments. According to incomplete statistics, there were more than 180 species of fungus Aspergillus, such as Aspergillus fumigatus, Aspergillus flavus, Aspergillus terreus, and Aspergillus versicolor [13]. The proportions of the 56 species (Table 1) reviewed in this paper are as follows: Aspergillus versicolor (14.3%), Aspergillus sydowii (12.5%), Aspergillus ustus (10.7%), Aspergillus fumigatus (5.4%), Aspergillus insulicola (3.6%), Aspergillus ochraceus (3.6%), Aspergillus carneus (3.6%), Aspergillus terreus (3.6%), Aspergillus flavus (3.6%), Aspergillus flavipes (3.6%), and Aspergillus unknown (26.8%) (see Figure 2).

Table 1.
List of sesquiterpenoids isolated from marine fungi Aspergillus sp. with potential biological activity.
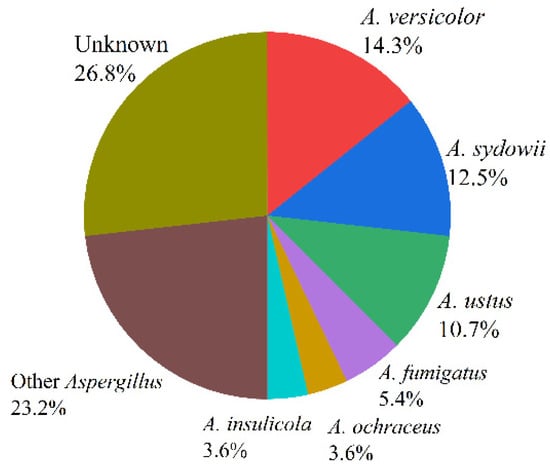
Figure 2.
The proportions of marine fungi reviewed in this paper.
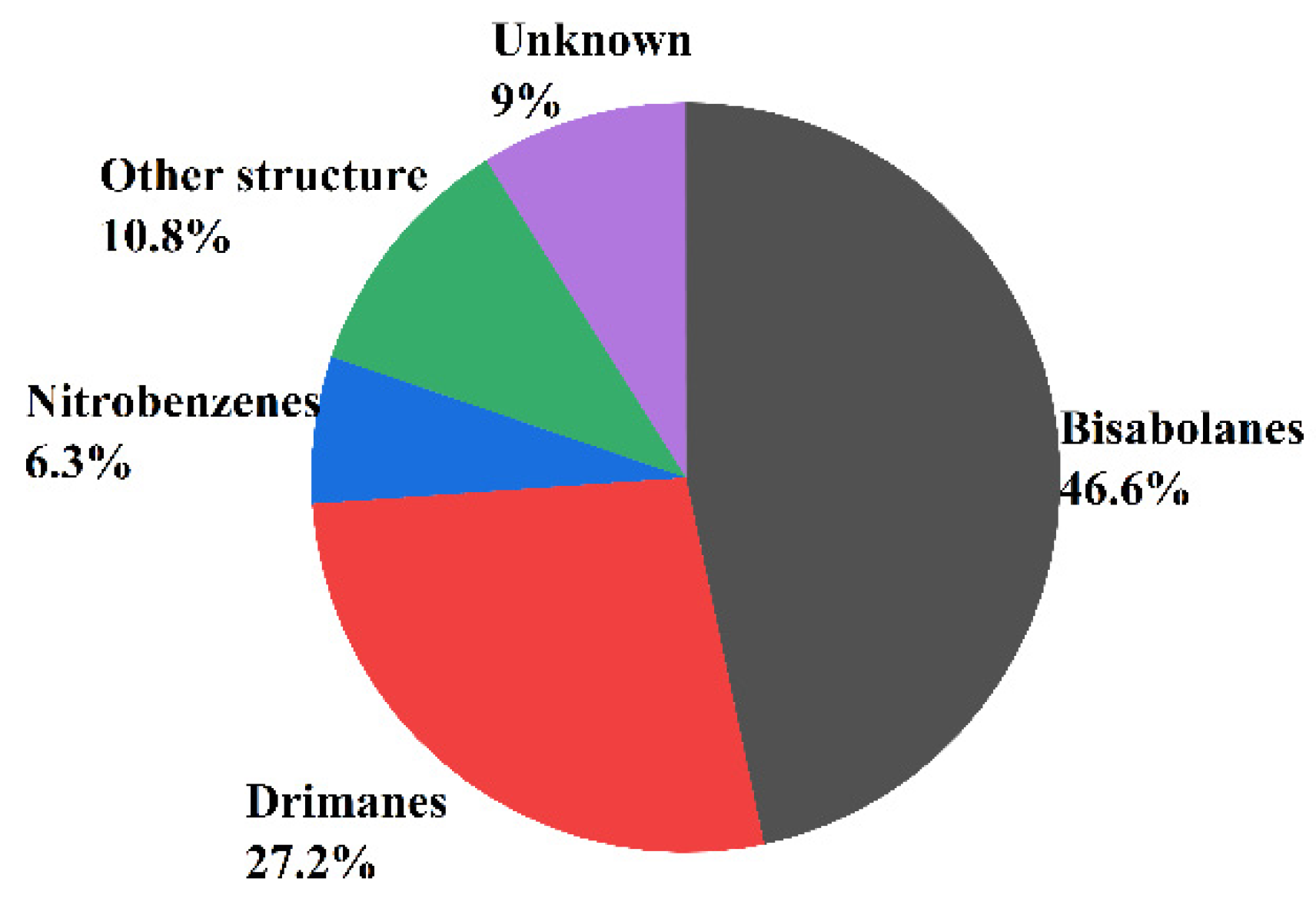
In recent years, more and more sesquiterpenoids were found in marine fungi Aspergillus, which consisted of the molecular skeleton structure with three isoprene units and contains 15 carbon atoms [56]. In addition, the number and skeleton types of sesquiterpenoids are the most abundant among all the terpenoids. According to the number of carbon rings, sesquiterpenoids can be divided into acyclic sesquiterpenes, monocyclic sesquiterpenoids, bicyclic sesquiterpenoids, tricyclic sesquiterpenoids, tetracyclic sesquiterpenoids, etc., [57]. Acyclic sesquiterpenes are also known as chain sesquiterpenes but rarely reported in fungi. The monocyclic sesquiterpenes referred mainly to bisabolanes, humaranes, and cybrodins, while the bicyclic sesquiterpenes consist mainly of drimanes, lacticinanes, and eudesmanes. This paper finds that the main types of sesquiterpenoids isolated from marine fungi Aspergillus were bisabolanes (46.6%), drimanes (27.2%), nitrobenzenes (6.3%), and unknown structure (9%) (see Figure 3).
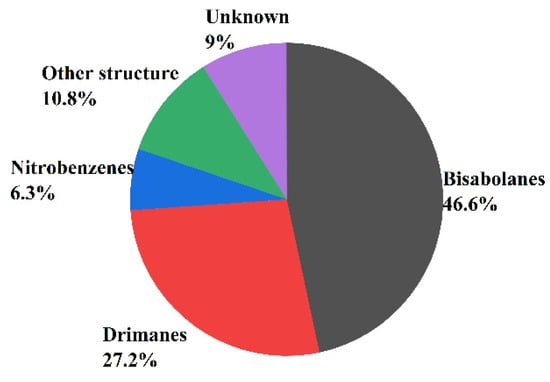
Figure 3.
The main types of sesquiterpenoids isolated from Aspergillus sp.
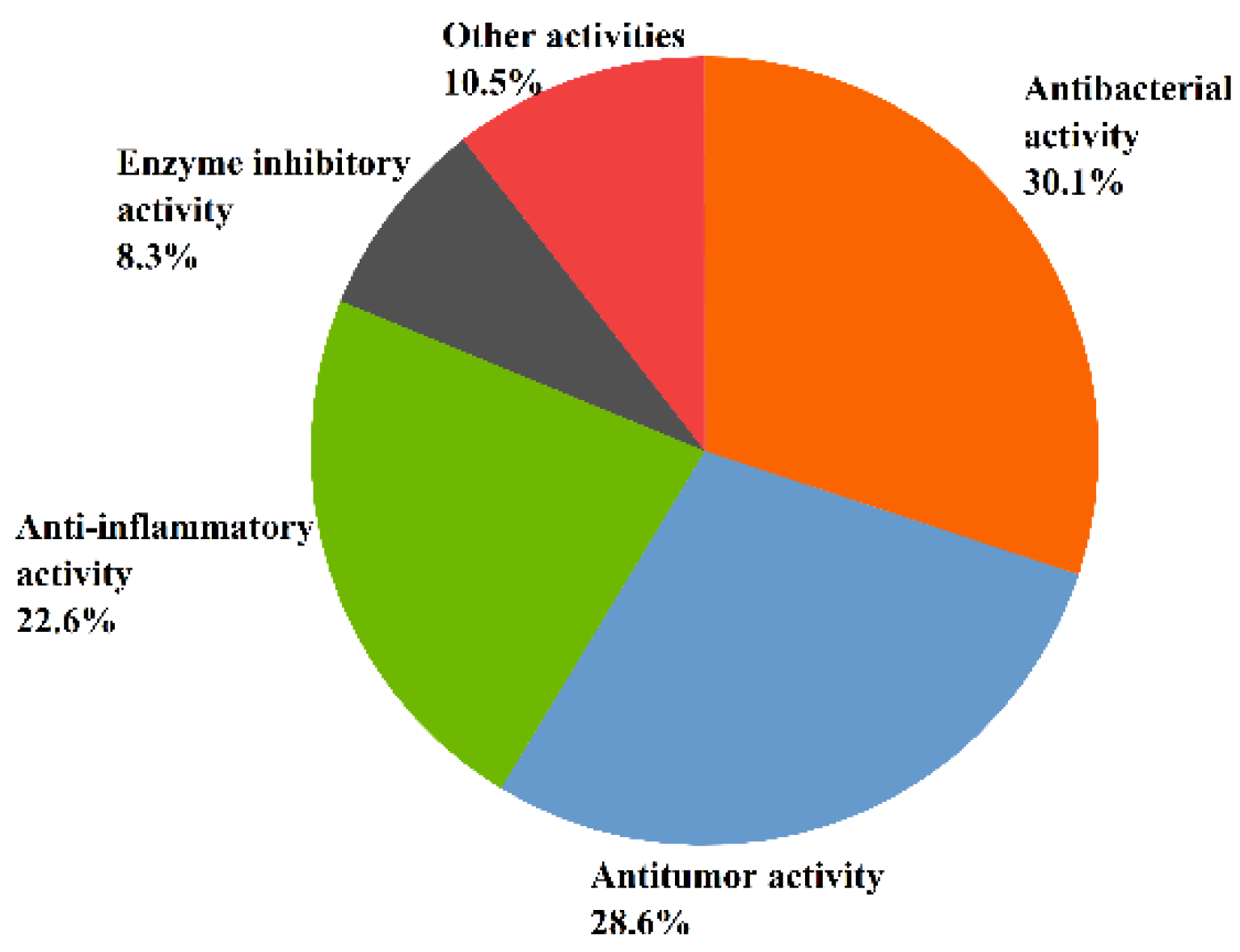
Recent studies have indicated that the metabolic pathway of marine fungi—that results in the production of a number of secondary metabolites with various chemical structures and specific physiological activities—is very different from that of terrestrial fungi [37]. This article concludes that 131 of the 268 sesquiterpenoids isolated from marine fungi Aspergillus have significant biological activities. Moreover, the structure types of inactive sesquiterpenoids are mostly bisabolanes and drimanes [58,59,60,61,62]. The relatively large number of sesquiterpenoids shows a variety of biological activities such as antitumor, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, enzyme inhibitory, antioxidant, antiviral, and other activities. Overall, 30.5% of sesquiterpenoids exhibited antibacterial activity, followed by antitumor activity (29%), anti-inflammatory activity (22.9%), enzyme inhibitory activity (8.4%), and other activities (10.7%) (see Figure 4).
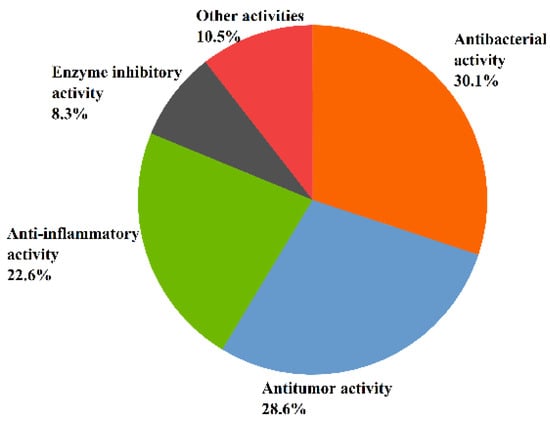
Figure 4.
The bioactivity of sesquiterpenoids from Aspergillus sp.
3. Bioactivity of Sesquiterpenoids from Aspergillus sp.
3.1. Antibacterial Activity
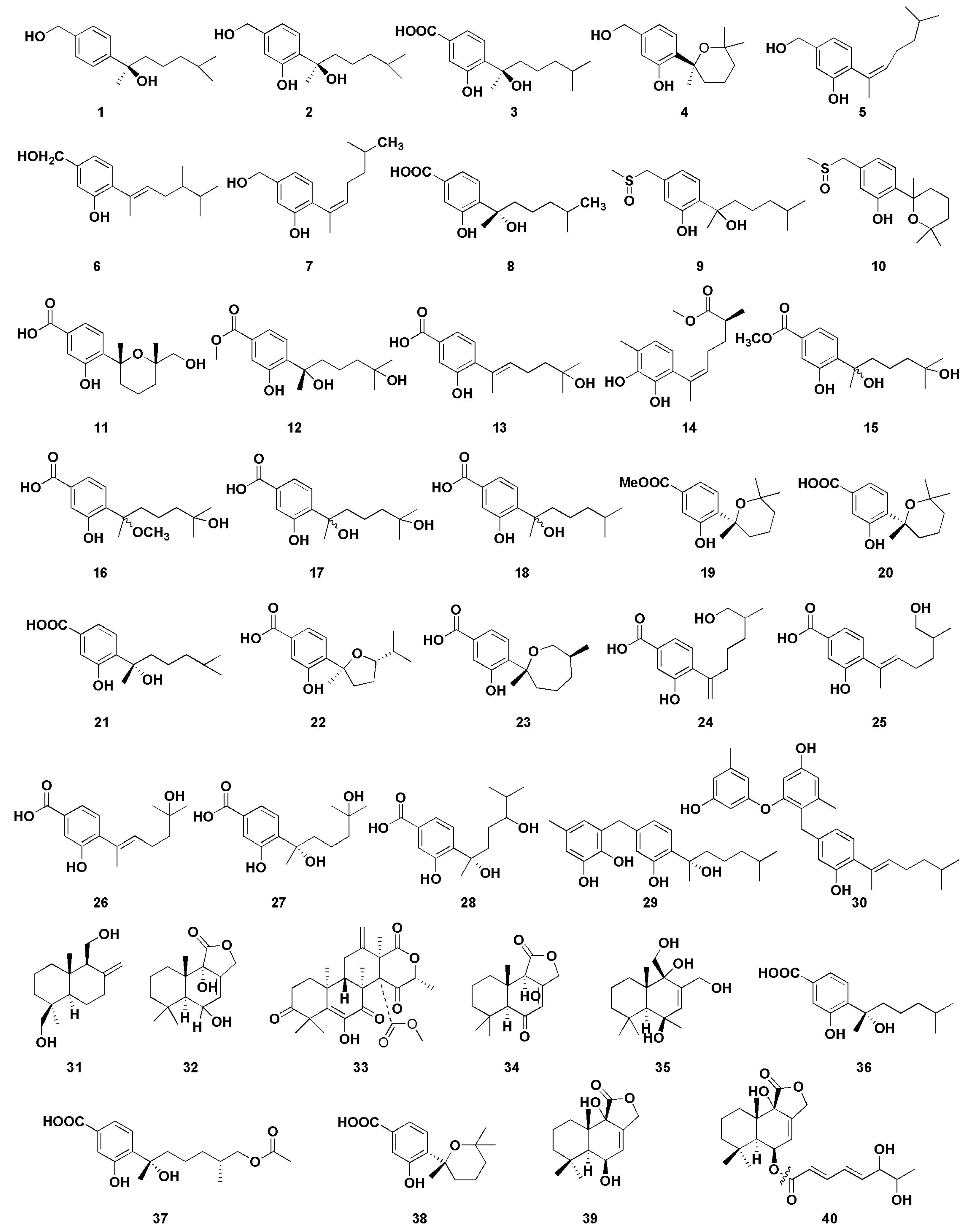
In recent years, inappropriate and irrational use of antibiotics provides favorable conditions for resistant microorganisms to emerge and spread, which has become a global public health problem [63]. Therefore, it is urgent to develop new antibiotics with new structures and significant biological activities. To that end, the secondary metabolites of microorganisms in the marine environment are a great source for new antibacterial agents screening and much attention has been attracted to the relevant studies. This section covers 40 bioactive sesquiterpenoids (Figure 5) with antibacterial activity described to date from marine-derived Aspergillus sp.
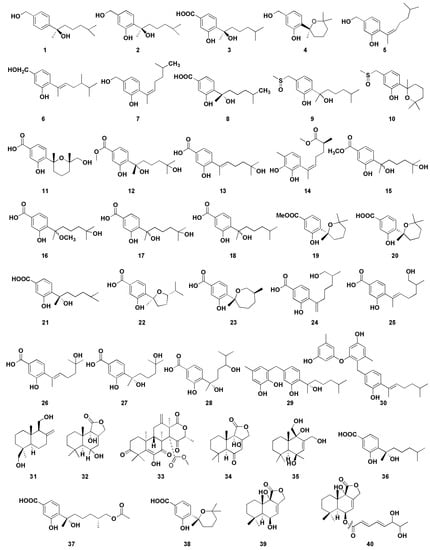
Figure 5.
Chemical structures of antimicrobial compounds (1–40).
Li et al. [14] isolated four new and one known bisabolane-type sesquiterpenoid from secondary metabolites of Aspergillus sp. from sponge. Compounds 1–5 showed different antibacterial activity against six pathogenic bacteria and two marine bacteria, and compounds 2 and 4 showed selective antibacterial activity. Compound 2 had strong inhibitory effects on Staphylococcus albus and Micrococcus tetragenus, with minimum inhibiting concentrations (MIC) values of 5.00 and 1.25 µM, respectively. The MIC values of compound 4 with S. albus and Bacillus subtilis were 5.00 µM and 2.50 µM, respectively. Notably, compound 1 represents the rare example of a bisabolane-type sesquiterpenoid with a 1, 4-disubstituted benzene ring isolated from marine organisms. Compounds 2 and 3 were the enantiomers of (+)-sydonol and (+)-sydonic acid, respectively. This fact suggests that fungi isolated from different marine organisms may produce different stereochemisty compounds. Furthermore, there were three sesquiterpenoids, 6–8, from the sponge-associated fungus Aspergillus sydowii ZSDS1-F6, which has certain antibacterial activities; among them, compound 6 and 7 displayed antibacterial activities against Klebsiella pneumonia, with MIC values of 21.4 and 10.7µM, respectively [15]. In addition, compound 6 showed moderate antibacterial activity against Aeromonas hydrophila (MIC, 4.3 µM), while compound 8 showed moderate antibacterial activity against Enterococcus faecalis (MIC, 18.8 µM). Chen et al. [16] isolated two phenolic bisabolane sesquiterpenoids (PBS) compounds (9–10) from Aspergillus flavipes 297, including a pair of new enantiomers (±)-flavilane A (9). However, compounds 9 and 10 represent the rare PBS-containing methylsulfinyl group and showed selective antibacterial activities against several pathogenic bacteria; their MIC values were 2–64 μg/mL. Furthermore, compound 10 exhibited mild antifungal activity against plant pathogenic fungus Valsa mari.
Aromatic bisabolene-type sesquiterpenoids 11–13 were isolated from the marine fungus Aspergillus versicolor SD-330 in the deep-sea sediments [17]. Compounds 11 and 12 had significant inhibitory activities against A. hydrophilia, Escherichia coli, Edwardsiella tarda, and Vibrio harveyi, with MIC values ranging from 2.0 to 8.0 μg/mL. Moreover, compound 13 had significant inhibitory activity against E. coli (MIC value was 1.0 μg/mL), which was better than the positive control chloramphenicol (MIC value was 2.0 μg/mL). A new aromatic bisabolene-type sesquiterpenoid (14) was discovered in Aspergillus sydowii SW9, whose absolute configuration is (S). Compound 14 had significant inhibitory effect on E. coli, and its MIC value was 2.0 µg/mL, which was similar to that of positive control chloramphenicol (MIC 2.0 µg/mL). Compound 14 also exhibited potent activity against S. pneumonise, with an MIC value of 4.0 µg/mL [18]. Wang et al. [19] obtained four sesquiterpenoids 15–18 with antibacterial activity from marine Aspergillus versicolor SD-330. Compounds 15 and 16 showed significant antibacterial activity against E. coli, E. trada, V. harveyi, and Vibrio parahaemolyticus, and the MIC values were less than or equal to 8.0 µg/mL. However, compound 17 exhibited significant antibacterial effect on E. coli with MIC value of 1.0 µg/mL, which was more potent than that of positive control chloramphenicol (MIC 2.0 µg/mL). Moreover, compound 17 showed strong inhibitory activity against A. hydrophilia, E. tarda, Vibrio anguillarum, and V. harveyi, each with MIC value of 4.0 µg/mL. Compound 17 showed a stronger antibacterial activity than compounds 15 and 16, suggesting that C-15 carboxyl group methyl ester or the methylated C-7 hydroxyl group could reduce their antibacterial activity.
Wei et al. isolated three phenolic bisabolane-type sesquiterpenoids compounds 19–21 from Aspergillus sp., which is the first report of natural metabolites from marine fungus Aspergillus from gorgonian Dichotella gemmacea [20]. All of them exhibited weak antibacterial activity against Staphylococcus aureus, with the diameters of inhibition zones of 11, 7, and 5 mm at 100 μg/mL, respectively. Seven phenolic bisabolane sesquiterpenoids 22–28 were obtained from the endophytic fungus Aspergillus sp. xy02 from a Thai mangrove Xylocarpus moluccensis [21] and displayed moderate inhibitory activities against S. aureus, with IC50 values ranging from 31.5 to 41.9 μM. Two new phenolic bisabolane sequiterpenes, asperchondols A (29) and asperchondols B (30), were obtained from the sponge-derived fungus Aspergillus sp. and showed antibacterial activity against S. aureus, with the MICs of 50 and 25 μM, respectively [22]. Furthermore, structure–activity relationship found that the coexistence of phenolic bisabolane sesquiterpene and diphenyl ether moieties seems to be very important since the hybrid 30 was more active than phenolic bisabolane sesquiterpenoid 29 and phenyl esters.
A series of phenolic bisabolane-type sesquiterpenoids have been discovered from different marine invertebrates such as sponges [64] and gorgonians [65] in the last century. In addition, such compounds were also found in bacterium CNH-741 and fungus CNC-979 isolated from marine sediments [66]. These results indicate that the real producers of these compounds from marine invertebrates, sponges, and corals may be constituents of microorganisms. Albican-11,14-diol (31) is a sesquiterpene compound isolated from the cultures of the endophytic fungus Aspergillus versicolor, which is isolated from marine green alga Codium fragile [23]. The diameters of inhibition zones of compound 31 against E. coli and S. aureus were 7 and 10.3 mm, respectively, at the concentration of 30 μg/disk. Fang et al. isolated a drimane-type sesquiterpenoid (32) and three unknown-type sesquiterpenoids (33–35) from the algicolos fungus Aspergillus sp. RR-YLW-12, which exhibited little inhibitory activity against four marine-derived pathogenic bacteria, V. anguillarum, V. harveyi, V. parahaemolytics, and Vibrio splendidus [24]. Zheng et al. isolated and purified three bisabolane sesquiterpenes 36–38 from the fermentation products of Aspergillus versicolor ZJ-2008015, which were obtained from a soft coral Sarcophyton sp. [25]. The results showed that compounds 36–38 exhibited potent antibacterial activity with MICs of 5.3, 6.4, and 5.4 μM against S. albus and 2.6, 6.4, and 5.4 μM against S. aureus, respectively. Cohen et al. [26] isolated two drimane sesquiterpenes (39–40) from the sponge-derived fungus Aspergillus insuetus (OY-207), which exhibited anti-fungal activity against Neurospora crassa, with the MICs of 140 and 242 μM, respectively.
3.2. Antitumor Activity
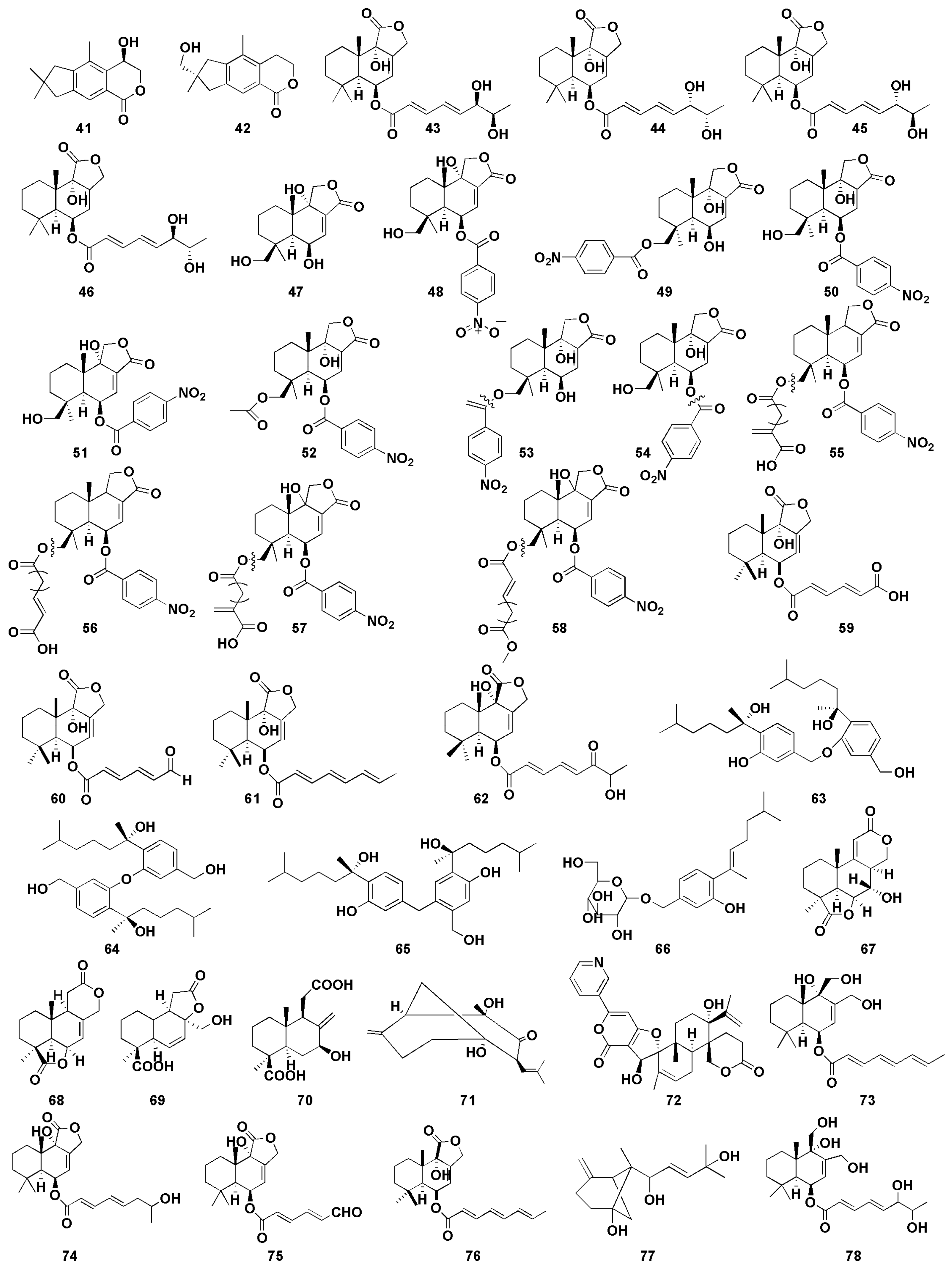
The marine environment represents a unique resource that encloses a massive chemical and biological diversity, which leads to an important source of potential antitumor drugs [67]. Among antitumor compounds, sesquiterpenes (including bisabolane, drimane, illudalane, etc.) are obtained mainly from marine fungi, including Aspergillus sp. [68,69]. Therefore, more and more researchers pay close attention to looking for effective antitumor drugs from marine Aspergillus. In recent years, there were about 38 bioactive sesquiterpenoids (Figure 6) with antitumor activity isolated from marine-derived Aspergillus sp.
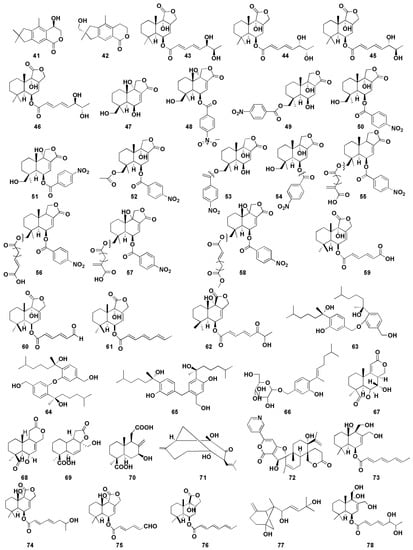
Figure 6.
Chemical structures of antitumor compounds (41–78).
Orfali et al. [27] first discovered two illudalane sesquiterpenes, asperorlactone (41) and echinolactone D (42), from marine sediment ascomycete Aspergillus oryzae, in which compound 41 has an absolute configuration of (5R). Compounds 41 and 42 showed antiproliferative activity against human lung cancer (A549), liver cancer (HepG2), and breast cancer (MCF-7) cell lines, with half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) values of asperorlactone (41) <100 µM. Furthermore, compounds 9 and 10 isolated from Aspergillus flavipes 297 exhibited promising cytotoxic effects on MKN-45 and HepG2 cells, respectively, indicating that the methylsulfinyl substituent enhanced the cytotoxicity, to a certain degree [16]. Gao et al. [28] isolated four drimane sesquiterpene esters asperienes A-D (43–46) from marine-derived fungal Aspergillus flavus CF13-11, which was the first successful isolation of two pairs of C-6′/C-7′ isoforms. Moreover, compounds 43–46 showed significant activity against four tumor cell lines (HeLa, MCF-7, MGC-803, and A549), with IC50 values of 1.4–8.3 µM. Notably, compounds 43 and 46 showed lower toxicity to normal GES-1 cells than did 44 and 45, suggesting their great potential for the development of an antitumor agent. Yurchenko et al. [29] isolated two drimane sesquiterpenes (47–48) from marine-sediment-derived fungus Aspergillus flocculosus, which exhibited potent cytotoxic effect toward mouse neuroblastoma neuro-2A and human prostate cancer 22Rv1 cells, with the IC50 values were 24.1, 4.9 µM and 31.5, 3.0 µM, respectively. It is well known that human prostate cancer 22Rv1 cells are resistant to hormone therapy because of the expression of the androgen receptor splice variants AR-V7 [70]. Therefore, the results indicated that compounds 47 and 48 could be used in the treatment of human drug-resistant prostate cancer. Fang et al. [30] isolated two nitrobenzoyl sesquiterpenoids (49–50) from the marine-derived fungus Aspergillus ochraceus Jcma1F17, which was the first time nitrobenzoyl sesquiterpenoids obtained from this fungal were reported. Both compounds displayed significant cytotoxic effects on 10 human cancer cell lines (H1975, U937, K562, BGC-823, MOLT-4, McF-7, A549, Hela, HL60, and Huh-7), with IC50 values ranging from 1.95 to 6.35 µM.
Insulicolide A (Nitrobenzoyl substituted sesquiterpene, 51) was isolated from the marine-sponge-associated endozoic fungus Aspergillus insulicola MD10-2 [31]. Compound 51 showed cytotoxic effects against human lung cancer cell line H-460, with an IC50 value of 6.9 μM. However, the cytotoxic activity of the acetylated derivatives of compound 51 decreased markedly, indicating that the double at C-7 might be involved in the cytotoxic activity. Tan et al. isolated three nitrobenzoyl sesquiterpenoids (52–54) from the marine fungus Aspergillus ochraceus Jcma 1F17 [32]. Compound 54 displayed potent cytotoxicities against three renal carcinoma ACHN, OS-RC-2, and 786-O cells lines (IC50 of 0.89–1.5 μM). The cytotoxic effects of compounds 52 and 53 on 786-O cells (IC50 of 2.3 and 4.3 μM, respectively) were exhibited more strongly than those of OS-RC-2 (IC50 5.3 and 8.2 μM) and ACHN (IC50 of 4.1 and 11 μM, respectively), suggesting that the C-9 hydroxy group may contribute more to the cytotoxic activities against renal carcinoma cells. Additionally, compound 52 showed stronger inhibitory activity at low concentration levels, compared with the positive control sorafenib, a drug approved for the treatment of primary kidney cancer (advanced renal cell carcinoma). Further investigation revealed that the cell cycle was arrested at G0/G1 phase after being treated with compound 52 at 1 μM, whereas after being treated at 2 μM for 72 h, the late apoptosis of 786-O cells were induced. Four nitrobenzoyl sesquiterpenoids (55–58) were isolated from an Antarctica-sponge-derived Aspergillus insulicola by Sun et al. [33], in which compounds 57 and 58 showed selective inhibitory activity against human pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) cell lines, whereas compounds 55 and 56 were inactive, indicating that hydroxyl groups at C-9 is essential for cytotoxicity. Furthermore, the IC50 values of compounds 57 and 58 against PDAC cell lines AsPC-1 and PANC-1 were 2.7, 4.6 μM and 2.3, 4.2 μM, respectively. Numerous studies have shown that most of nitrobenzoyl sesquiterpenes were obtained from the marine-derived fungus Aspergillus ochraceus, suggesting that Aspergillus ochraceus may be a good resource for the production of these compounds.
Liu et al. [34] found three drimane sesquiterpenoids (59–61) from marine sponge-derived fungus Aspergillus ustus, which showed cytotoxic activities against mouse lymphoma cell line L5178Y, with half maximal effective concentration (EC50) values between 0.6 and 5.3 μM. In addition, the EC50 value of compound 60 against PC12 and HeLa cells were 7.2 μM and 5.9 μM, respectively. Zhou et al. [35] isolated drimane sesquiterpenoid (62) from mangrove-derived fungus Aspergillus ustus and exhibited moderate cytotoxic effects against the mice lymphocytic leukemia P388 cell line with IC50 value of 8.7 μM. Sun et al. [36] isolated three bisabolane sesquiterpenoid dimers (63–65) from the sponge-derived fungus Aspergillus sp., and the cytotoxic activity against HePG-2 human hepatoma cell line and Caski human cervical cell line were determined in vitro. Significantly, compounds 63 and 65 with (7S) and (7′S) configuration displayed better potent cytotoxicity toward the tumor cell lines than did compound 64. The IC50 values of compound 63 and 65 were 9.31, 12.40 μM and 2.91, 10.20 μM, respectively. These results suggest that the cytotoxic activity of the compound may be weakened due to the mesomeric effect since the activity of the compounds is stereoselective. β-D-glucopyranosyl aspergillusene A (66) from the sponge-derived fungus Aspergillus sydowii J05B-7F-4 exhibited mild cytotoxicity against KB (human nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells), HepG2 (human liver cancer cells), and HCT 116 (human colon cancer cells), with IC50 values between 50 and 70 μM [37].
Deng et al. [38] found four sesquiterpenoids containing 16 carbon atoms (67–70) from the mangrove endophytic fungus Aspergillus terreus GX3-3B, of which compound 67 showed inhibitory activity against human breast cancer cells (MCF-7) and human promyelocytic leukemia cells (HL-60), with the IC50 values were 4.49 and 3.43 μM, respectively. In addition, compound 68 exhibited promising inhibitory effect on MCF-7 cells, with an IC50 value of 2.79 μM, whereas compound 70 showed potent inhibitory effect on HL-60 cells, with an IC50 value of 0.6 μM. The structure–activity relationship indicated that the presence of C or D lactone ring may be helpful for the inhibitory against the human breast cancer cell line MCF-7. Compounds 67 and 70 showed stronger activities than did compounds 68 and 69, indicating that hydroxyl group at the C-7 position could improve the cytotoxicity toward HL-60 cell.
Aspergiketone (71) is the first sesquiterpenoid derivative isolated from Aspergillus fumigatus, which exhibited obvious cytotoxicity against HL-60 and A-549 cells, with IC50 values of 12.4 and 22.1 μM, respectively [39]. Oxalicine B (72), a unique pyridino-α-pyrone sesquiterpenoid, was obtained from the sea-urchin-derived fungus Aspergillus fumigatus and exhibits moderate cytotoxicity to murine P388 leukemia cells, with IC50 of 55.9 µM [40]. Three drimane sesquiterpenes (73–75) were isolated from marine Aspergillus ustus 094102 [41], of which compounds 74 and 75 showed moderate cytotoxicity against A549 and HL-60 cells, with IC50 values of 10.5 and 9.0 µM, respectively. Moreover, compound 73 exhibited weak cytotoxic effect to A549 and HL-60 cells, with IC50 values of 20.6 and 30.0 µM, respectively. Proksch et al. found a drimane sesquiterpene (76) from marine-sponge-derived fungus Aspergillus ustus, which exhibited selective inhibition on lymphoma cell line L5178Y cells (median effective dose (ED50), 1.9 μM) [42]. Wang et al. found a β-bergamotane sesquiterpenoids (77) from marine-sediment-derived fungus Aspergillus fumigatus YK-7, which exhibited weak inhibitory activities against U937 cells, with an IC50 value of 84.9 µM [43]. Asperflavinoid A (78), a drimane-type sesquiterpenoids, was isolated from Aspergillus flavipes 297 and exerted toxic effect on HepG2 and MKN-45 cells, with the IC50 values of 38.5 and 26.8 µM, respectively [44].
3.3. Anti-Inflammatory Activity
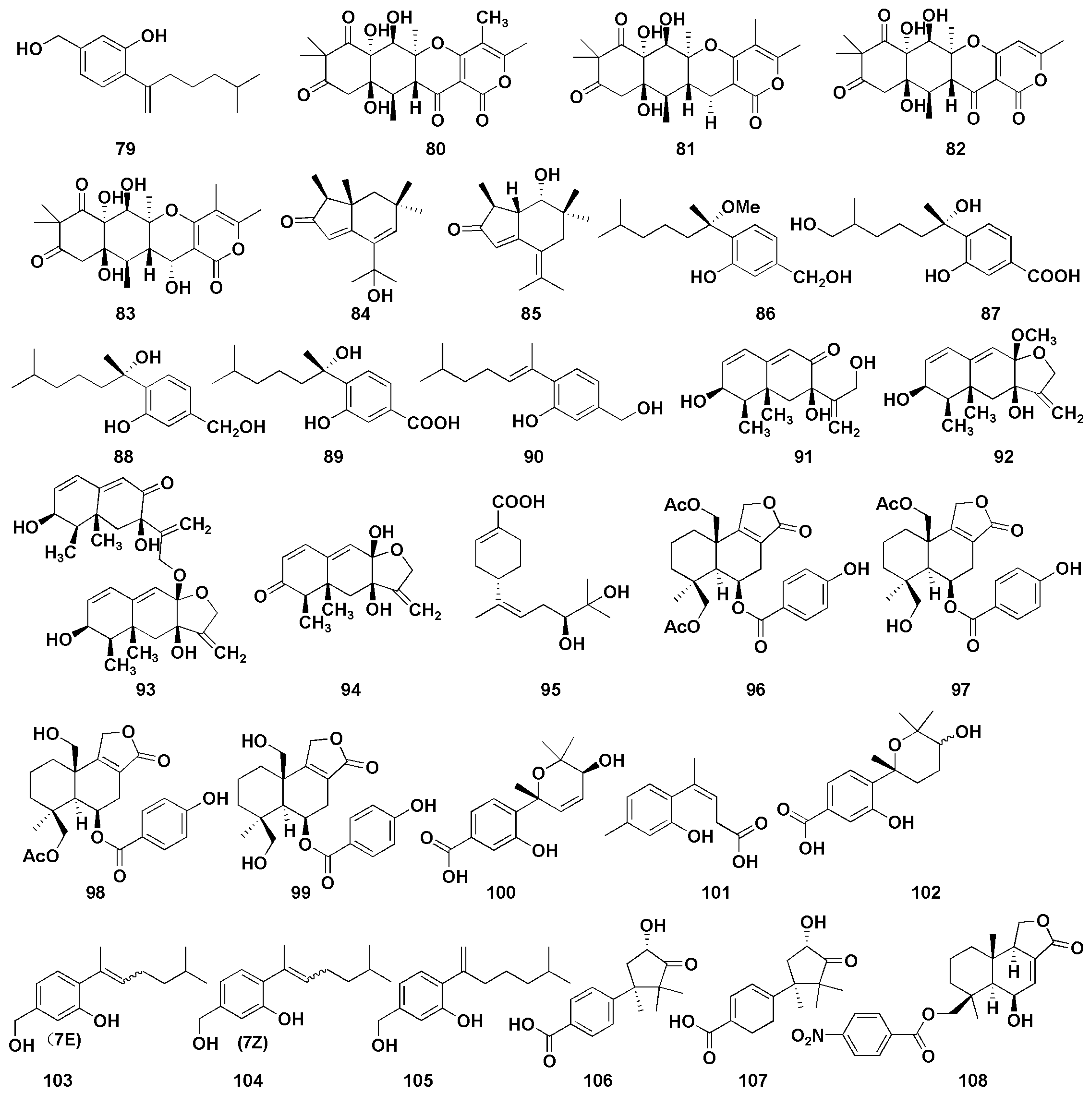
Inflammation is a comprehensive array of physiological response to a foreign organism, which has been considered as a major factor for the progression of various chronic diseases/disorders [71]. Therefore, development of effective and economical anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) is an area of importance in drug discovery while natural anti-inflammatory supplements are becoming more popular and have been the focus of many scientific investigations. This section covers 30 sesquiterpenoids (Figure 7) with anti-inflammatory activity which isolated from marine-derived Aspergillus sp.
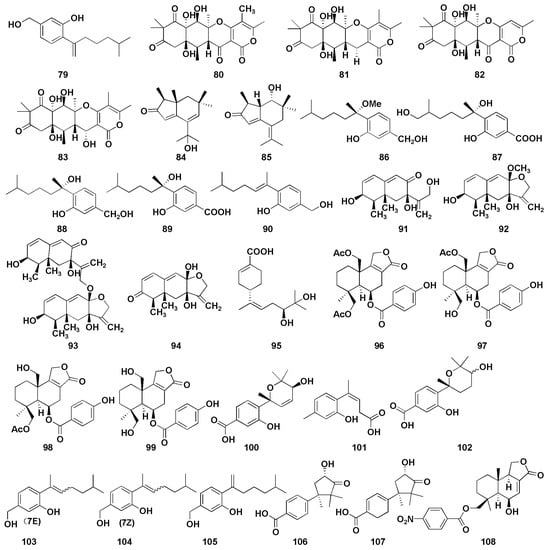
Figure 7.
Chemical structures of anti-inflammatory compounds (79–108).
Cui et al. [45] isolated a sesquiterpene derivative (79) from the mangrove endophytic fungus Aspergillus versicolor SYSU-SKS025, which was found to inhibit nitric oxide (NO) production RAW 264.7 macrophages, with an IC50 value of 12.5 µM (positive control, indomethacin, IC50 = 37.5 µM). Wang et al. [46] found four triketide-sesquiterpenoids A−D (80–83) from the marine-algal-associated fungus Aspergillus sp. ZL0-1B14, which exhibited anti-inflammatory activity in LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 macrophages. In addition, compound 83 inhibited the production of IL-6 with an inhibition rate of 69% at 40 μM. Wu et al. [47] firstly discovered two brasilane sesquiterpenoids (84–85) with α and β unsaturated ketones from marine-derived fungus Aspergillus terreus, both of which showed moderate inhibitory effects; the inhibitory rates of nitric oxide were 47.7% and 37.3%, respectively, at 40 μM. Chung et al. [48] isolated five sesquiterpenoids (86–90) with anti-inflammatory activity from Aspergillus sydowii in marine sediments. Among them, compounds 88 and 90 displayed selective inhibition against fMLP/CB-induced superoxide anion generation by human neutrophils, with IC50 values of 5.23 and 6.11 µM, respectively. At the same time, they also exhibited the most potent inhibitory activity against the release of elastase induced by fMLP/CB, with the IC50 values of 16.39 and 8.80 µM, respectively. Interestingly, the anti-inflammatory activity of compound 88 was better than that of compound 86 indicating the important role of hydroxy group on C-7. Moreover, compounds containing methylene alcohol on C-3 (86, 88, and 90) showed more potent anti-inflammatory activity compared with the derivatives with carboxylic acid functional groups (87 and 89). Four Eremophilane sesquiterpenoids (91–94) were isolated from deep-marine-sediment-derived fungus Aspergillus sp. SCSIOW2, and all showed inhibitory activity of NO production in a dose-dependent manner [49]. Additionally, five sesquiterpenoids (95–99) were isolated from the mangrove endophytic fungus Aspergillus sp. GXNU-MA1 by Zhou et al., which exhibited moderate inhibitory activities against NO production, with IC50 values ranging from 16.15 to 27.08 µM [50]. Niu et al. isolated six phenolic bisabolane (100–105) and two cuparene sesquiterpenoids (106–107) from Aspergillus sydowii MCCC3A00324 derived from deep sea sediments [51]. Compounds 100, 101, and 103–105 showed anti-inflammatory activity against NO secretion in LPS-activated BV-2 microglia cells, with the inhibition rates of more than 45% at 10 µM, while those of compounds 102, 106, and 107 were 32.8%, 32.6% and 45.4%, respectively. Furthermore, compound 101 exerted an anti-inflammatory effect by inhibiting NF-κB activation pathway in a dose-dependent manner. Tan et al. isolated a new nitrobenzoyl sesquiterpenoid (108) from Aspergillus ochraceus, which could suppress the RANKL-induced osteoclats formation and bone resorption by targeting NF-κB [52]. Additionally, compound 108 attenuated inflammatory bone loss in vivo.
3.4. Enzymatic Inhibitory Activity
Enzyme inhibitors are of value in treating many diseases in clinical use, and have become a very attractive target for drug development and discovery. In recent years, the prominence of various enzyme inhibitors has been discussed extensively by many researchers in comprehensive systematic reviews [72]. In this section, the inhibitory activities of sesquiterpenoids (Figure 8) from marine Aspergillus sp. against three enzymes (α-glucosidase, cholinesterase, and neuraminidase) are briefly reviewed.
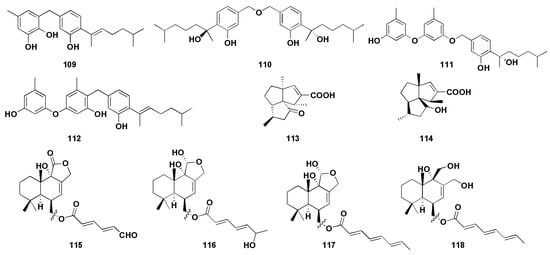
Figure 8.
Chemical structures of enzymatic inhibitory compounds (109–118).
α-Glucosidase is a membrane-bound enzyme present in the small intestinal epithelium [73], whose role is to promote the absorption of glucose in the small intestine by catalyzing the hydrolysis of oligosaccharides into absorbable glucose. α-Glucosidase inhibitors are the most widely used drugs in the clinical treatment of diabetes in China. By inhibiting the activity of α-glucosidase, the formation and absorption of glucose can be reduced to achieve the goal of lowering blood glucose. At the same time, it can also reduce the stimulation of blood glucose on the pancreas, effectively preventing and relieving diabetic complications [74]. 7-Deoxy-7,14-didehydrosydonol (79) was found from the mangrove endophytic fungus Aspergillus versicolor and possessed a significant inhibitory effect on α-glucosidase, with an IC50 value of 7.5 μM (acarbose as 350 μM), and the terminal ethylene group at C-7 may play a key role in α-glucosidase inhibition activity [45]. Wu et al. [53] isolated four phenolic bisabolane sesquiterpenoids (109–112) from the mangrove endophytic fungus Aspergillus flavus QQSG-3. The inhibitory activity studies of α-glucosidase showed that the compounds (109–112) had strong inhibitory effects, with IC50 values of 4.5, 3.1, 1.5, and 2.3 µM, respectively (all lower than the positive control drug acarbose).
Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) is a degenerative disease with unknown causes, mainly involving cerebral cortical neurons, which is the major cause of dementia [75]. The currently accepted pathogenesis is the cholinergic deficiency hypothesis [76]. Cholinesterase inhibitors (ChEI) are a class of drugs that can bind to cholinesterase (ChE) and inhibit ChE activity; they are also approved as first-line drugs for the treatment of mild-to-moderate AD [77]. Feng et al. firstly isolated the potential reversible cholinesterase inhibitor cyclopentapentalane sesquiterpenoid subergorgic (113) and its analogues 2-deoxy-2β-hydroxysubergorgic (114) from the soft-coral-derived fungus Aspergillus sp. EGF15-0-3 [54].
Neuraminidase (NA) is the most critical enzyme for influenza virus replication and diffusion in host cells and has become an important target for anti-influenza virus drug design [78]. Li et al. [55] isolated four drimane sesquiterpenoids (115–118) from the ascidian endophytic fungus Aspergillus ustus TK-5, which showed significant inhibitory activity against neuraminidase, with IC50 values of 31.8, 37.3, 28.4, and 36.8 µM, respectively. Further results showed that the degree of unsaturation of 11-OH and C-6 linked side chains, which can improve their neuraminidase inhibitory activity.
3.5. Other Activities
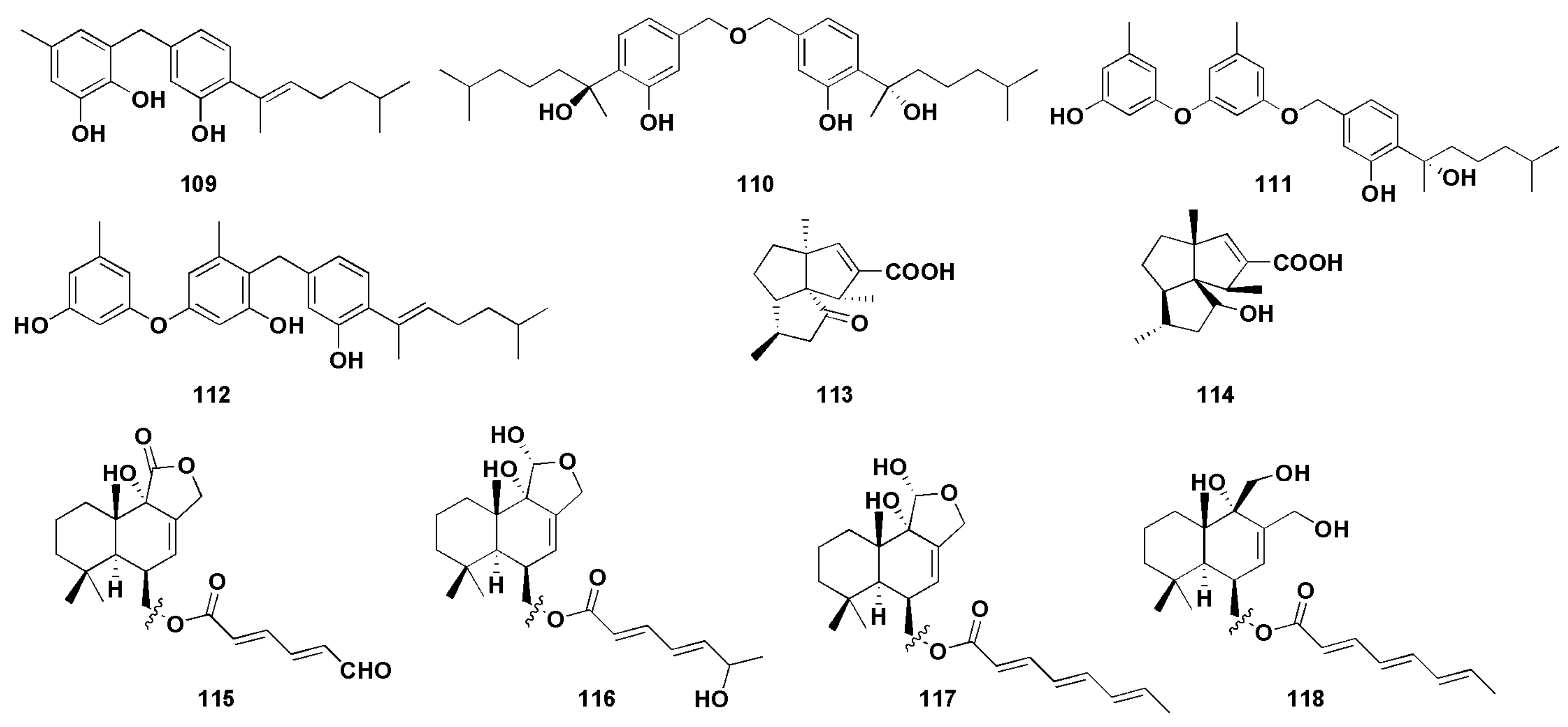
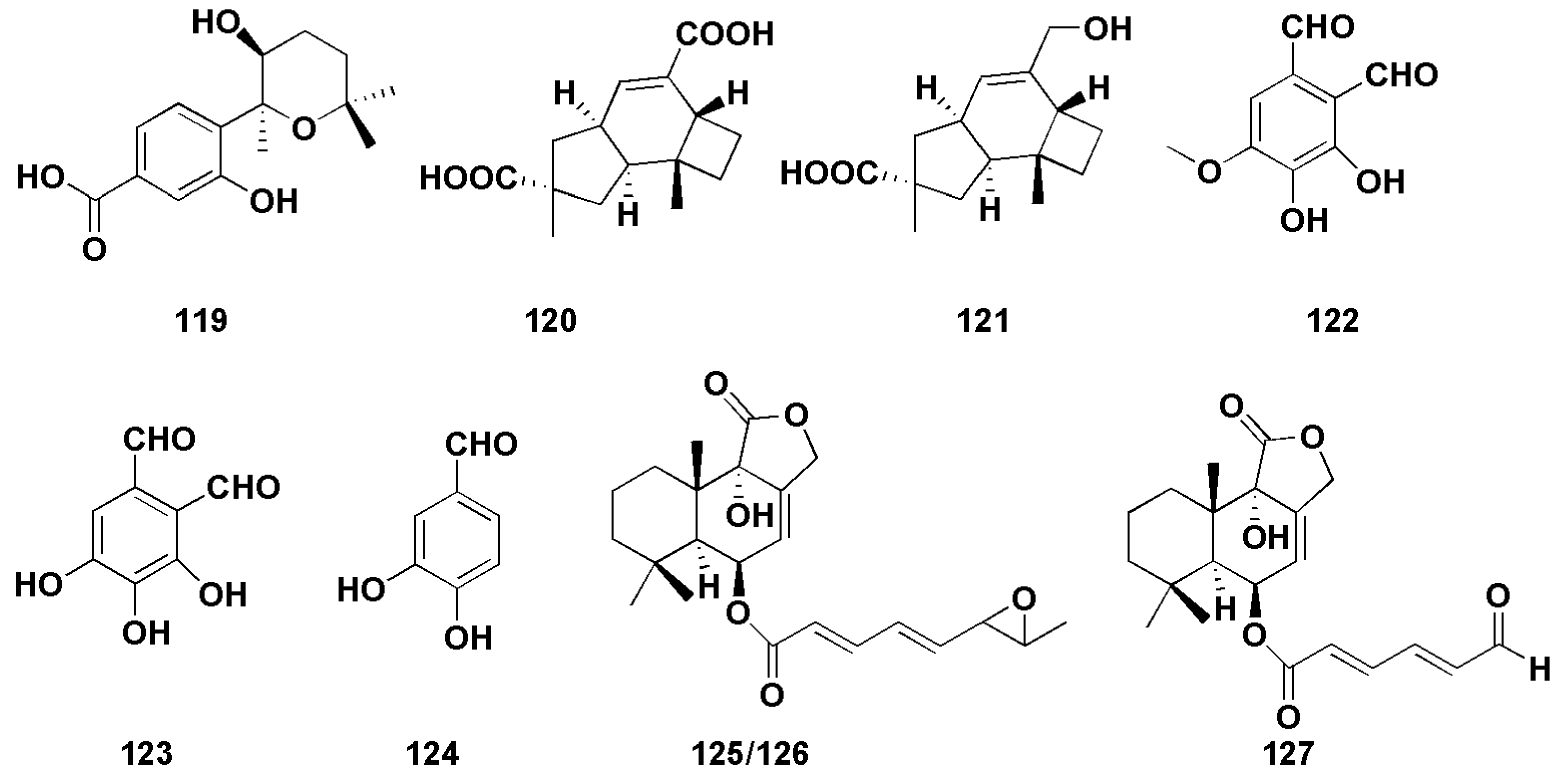
Hu et al. isolated an aromatic bisabolane sesquiterpenoid (7S,8S)-8-hydroxysydowic acid (119, Figure 9)) from the marine red algae endophytic fungus Aspergillus sydowii EN-434, which exhibited DPPH free radical scavenging activity, with an IC50 value of 113.5 µM [79]. An et al. found two sesquiterpenoids (120–121, Figure 9) with weak DPPH radical scavenging activity, with IC50 values of 1.8 mM and 0.6 mM, respectively (VC as 0.04 mM) [80]. Zhong et al. isolated three sesquiterpenoids (122–124, Figure 9) from the marine-offshore-mud-derived fungus Aspergillus pseudoglaucus [81]. Among them, compounds 122 and 123 showed strong DPPH radical scavenging activity, with IC50 values of 2.42 and 1.86 μg/mL (VC was 3.25 μg/mL), respectively, while compound 124 exhibited moderate antioxidant activity (IC50 was 10.89 μg/mL).
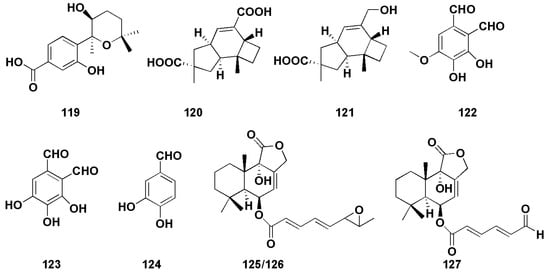
Figure 9.
Chemical structures of other biological compounds (119–127).
Two bisabolane-type sesquiterpenoids (4–5) were derived from sponge-derived fungus Aspergillus sp., among which compound 4 completely inhibited larval settlement at 25.0 μg/mL, while compound 5 displayed an obvious toxic effect on larvae at the same concentration [14]. Compound 7 also showed weak anti-H3N2 activity, with IC50 values of 57.4 μM [15]. (−)-(7S)-10-hydroxysydonic acid (28) was found to have a mild DPPH radical scavenging activity, with an IC50 value of 72.1 μM [21]. Nitrobenzoyl sesquiterpenoids (49) also showed moderate antiviral activities against H3N2 and EV71, with IC50 values of 17.0 and 9.4 μM, respectively [30]. Liu et al. [82] isolated three drimane sesquiterpenoids (125–127, Figure 9) from the marine-green-alga-derived fungus Aspergillus ustus. In the brine shrimp (Artemia salina) toxicity assay, there was more than 75% lethality at the concentration of 100 μg/mL, and the LC50 values were 41.8, 62.2 and 48.9 μg/mL, respectively.
4. Chemical Synthesis and Biosynthesis of Sesquiterpenoids from Marine Aspergillus sp.
4.1. Chemically Induced Synthesis
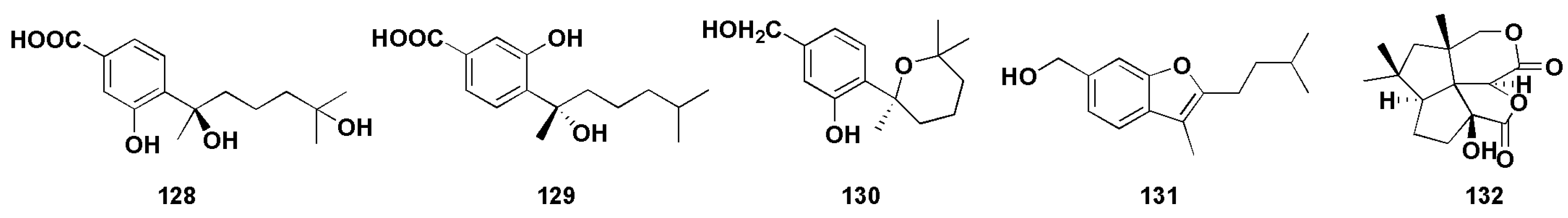
Aspergillus sp. is the important source for the discovery of natural active products with novel and diverse structures. However, in recent years, the continual study of secondary metabolites of marine fungi has led to a high frequency of repeated discovery of known compounds [83]. This encourages us to develop new strategies to obtain new natural products. Studies have found that a large number of secondary metabolite biosynthesis gene clusters exist in the genome of Aspergillus fungi. Furthermore, the genome can be segmented into active and silent clusters, while the silent clusters are inactive under normal environmental conditions [84,85,86]. In order to obtain more active metabolites, researchers have applied a variety of methods to activate silenced biological genetic gene clusters, such as transcription factor regulation, targeted genome mining, heterologous expression of gene clusters, and chemical epigenetic regulation [87,88,89]. Because of its simplicity and effectiveness, chemical epigenetic regulation has been widely used in marine fungi to activate silenced gene clusters, which could lead to the production of new secondary metabolites or known components with a higher concentration. Wang et al. [90] cultivated the gorgonian-derived fungus Aspergillus sp. SC-20090066 with a DNA methyltransferase inhibitor 5-azacytidae (5-AZA) in the culture medium and led to the isolation of six new bisabolane-type sesquiterpenoids (Figure 10). Among them, compounds (128–130) exhibited broad spectrum activities against S. aureus, Bacillus cereus, Rhizophila, Pseudomonas putida, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa, with MICs of less than 25 μM. In particular, compound 130 exhibited significant antibacterial activity against S. aureus, with MIC value of 3.13 μM, which was close to the positive control ciprofloxacin (MIC value was 2.5 μM). In order to trigger the chemical diversity of marine-derived fungus Aspergillus versicolor XS-2009006, epigenetic agents (histone deacetylase inhibitor SAHA and DNA methyltransferase inhibitor 5-AZA) were added to the culture medium by Wu et al. [91] Interestingly, the secondary metabolites was significantly increased and a new bisabolane sesquiterpene aspergillusene E (131, Figure 10) was isolated, which showed anti-larval attachment activity against bryozoan B. neritina, with the EC50 and (lethal concentration 50%) LC50 values of 6.25 μg/mL and 25 μg/mL, respectively. In addition, compound 131 showed certain antibacterial activities against Staphylococcus epidermidis and S. aureus, with MIC values ranging from 8 to 16 μM. By adding DNA methyltransferase inhibitors to the medium of Aspergillus sydowii, the composition of secondary metabolites was further changed and new bisabolane sesquiterpenoids (86–87) were isolated [48]. In addition, Wang et al. [49] applied chemical epigenetic manipulation to Aspergillus sp. SCSIOW2 and obtained four eremophilane sesquiterpenes with anti-inflammatory activity (91–94).
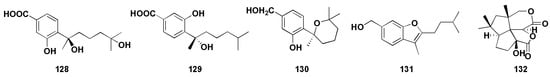
Figure 10.
Structures of sesquiterpenoids obtained from chemical synthesis and biosynthesis from the Aspergillus sp. (128–132).
4.2. Biosynthetic Pathways
The skeleton structures of sesquiterpenoids were derived from farnesyl diphosphate (FPP) and underwent a series of reaction steps, including intramolecular rearrangement, cyclysis, and other biosynthetic transformations, leading to their structural diversity [92]. Ingavat et al. [93] studied the proposed biosynthesis of sesquiterpene compound 132 in Aspergillus aculeatus, which starts from a double-bond migration (C1/C2 to C2/C3) of silphineneene intermediate 2, and then the double bond of C2/C3 undergoes oxidative cleavage to generate intermediate 3, which, in turn, undergoes a series of oxidation and lactonizations to finally give 132 (Figure 10).
Wang et al. [46] proposed a biogenetic pathway for the synthesis of aspertetranones A-D (80–83). Common drimane-type merosesquiterpene were obtained by cyclization of farnesylated pyrone, followed by oxidation and retro-aldo/aldo rearrangement to produce the unique terpenoid part of aspertetranones. After nucleophilic attack and dehydration, the leaborate preaspertetranone was obtained. Illudalanes derive biosynthetically from a humulene precursor after cyclization, producing a protoilludanes, which is eventually rearranged to form the irudane derivative [94]. According to this report, Orfali et al. speculated a biosynthetic pathway of asperorlactone (41), in which illudol was a key intermediate. The iluane-type sesquiterpene asperorlactone can be synthesized by dehydration, oxidation, and four-membered ring opening [27].
5. Potency of Sesquiterpenoids from Marine Aspergillus sp.
Secondary metabolites of microorganisms in the marine environment, mainly derived from marine fungi, are a great source for new drug screening. Currently, the marine drug library includes 15 approved drugs (primarily for cancer treatment), 7 phase I compounds, 12 phase II compounds, and 5 compounds in phase III clinical trials, the latter including a recently recommended drug for symptomatic treatment of COVID-19 (Plitidepsin) [95,96]. Compound 13 displayed significant inhibitory activity against E. coli (MIC 1.0 μg/mL), and its antibacterial effect was more potent than that of the positive control chloramphenicol (MIC 2.0 μg/mL), which was expected to be a lead compound for antibiotics [17]. The sesquiterpene compound (79) isolated from Aspergillus versicolor exhibited better inhibitory effect on α-glucosidase than acarbose, while its anti-inflammatory effect was also stronger than that of indomethacin [45]. Compound 88 derived from marine sediments, showed a significant anti-inflammatory effect and hypoglycemic effect. In addition, compound 88 could also inhibit fat accumulation in adipocytes [48]. These results indicated compound 79 and 88 has the potential to be a lead compound targeting the vicious diabetes-inflammation cycle. Feng et al. found that sesquiterpene compound 113, the reversible cholinesterase inhibitor, is a promising new drug candidate for the treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease and a preclinical trial is already under way [54].
6. Conclusions and Perspective
In this paper, the biosources, bioactivities, structural types, biosynthetic, and pharmacogenic potential of sesquiterpenoids found from marine fungi Aspergillus sp. were reviewed. A total of 268 sesquiterpenes were isolated, including 131 bioactive sesquiterpenes, most of which were bisabolanes, followed by drimanes and nitrobenzoyl, etc. Most Aspergillus species derived from sponges, marine sediments, algae, mangroves, corals, etc. The main Aspergillus species involved are as follows: Aspergillus fumigatus, Aspergillus versicolor, Aspergillus flavus, Aspergillus ustus, Aspergillus sydowii, and so on. These sesquiterpenes exhibited excellent pharmacological activities such as antibacterial, antitumor, anti-inflammatory, and enzyme inhibitory activities. Additionally, the biosynthesis and total synthesis of sesquiterpenes derived from marine Aspergillus sp. have also promoted the in-depth understanding of these sesquiterpenes. Because of the chemical and biological activity of these sesquiterpenoids, it is worthwhile to find promising lead compounds for the development of marine drugs in further studies from marine fungi.
Author Contributions
Conception and design of the manuscript: Z.Z.; conducting literature search and analysis of the information: L.S.; draft and revision of the manuscript: L.S. and H.W.; editing the manuscript: M.Y. and C.S.; finalization and approval of the revised manuscript for submission: Z.Z. and H.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Projects of Medical and Health Technology Development Program in Shandong Province (grant No 2019WS358, 202013050864), Research Fund for Lin He’s Academician Workstation of New Medicine and Clinical Translation in Jining Medical University (grant No JYHL2021MS17).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no potential conflict of interest.
References
- Wang, Y.N.; Meng, L.H.; Wang, B.G. Progress in research on bioactive secondary metabolites from deep-sea derived microorganisms. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.H.; Cai, R.L.; Liu, Z.M.; Cui, H.; She, Z.G. Secondary metabolites from mangrove-associated fungi: Source, chemistry and bioactivities. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2022, 39, 560–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiteller, P. Chemical ecology of fungi. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2015, 32, 971–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rateb, M.E.; Ebel, R. Secondary metabolites of fungi from marine habitats. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2011, 28, 290–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debbab, A.; Aly, A.H.; Proksch, P. Bioactive secondary metabolites from endophytes and associated marine derived fungi. Fungal Divers. 2011, 49, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Tang, Z.J.; Chen, N.; Xu, Y.; Ji, Y.B. Research progress of butyrolactones isolated from marine-derived Aspergillus sp. Chin. J. Mar. Drugs 2021, 40, 59–70. [Google Scholar]
- Numata, A.; Takahashi, C.; Matsushita, T.; Miyamoto, T.; Kawai, K.; Usami, Y.; Matsumura, E.; Inoue, M.; Ohishi, H. Fumiquinazolines, novel metabolites of a fungus isolated from a saltfish. Tetrahedron Lett. 1992, 33, 1621–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.Y.; Liu, H.S.; Zhu, W.M. New natural products from the marine-derived Aspergillus fungi-a review. Acta Microbiol. Sin. 2016, 56, 331–362. [Google Scholar]
- Ebel, R. Terpenes from marine-derived fungi. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 2340–2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elissawy, A.M.; El-Shazly, M.; Ebada, S.S.; Singab, A.B.; Proksch, P. Bioactive terpenes from marine-derived fungi. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 1966–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.J. Natural products from marine fungi. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraga, B.M. Natural sesquiterpenoids. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2012, 29, 1334–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.Y.; Yi, J.; Chang, Y.B.; Sun, C.P.; Ma, X.C. Recent studies on terpenoids in Aspergillus fungi: Chemical diversity, biosynthesis, and bioactivity. Phytochemistry 2022, 193, 113011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Xu, Y.; Shao, C.L.; Yang, R.Y.; Zheng, C.J.; Chen, Y.Y.; Fu, X.M.; Qian, P.Y.; She, Z.G.; de Voogd, N.J.; et al. Antibacterial bisabolane-type sesquiterpenoids from the sponge-derived fungus Aspergillus sp. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.F.; Lin, X.P.; Qin, C.; Liao, S.; Wan, J.T.; Zhang, T.Y.; Liu, J.; Fredimoses, M.; Chen, H.; Yang, B.; et al. Antimicrobial and antiviral sesquiterpenoids from sponge-associated fungus, Aspergillus sydowii ZSDS1-F6. J. Antibiot. 2014, 67, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhu, H.Y.; Xu, L.C.; Wang, S.P.; Liu, S.; Liu, G.D.; Luo, W.H.; Cao, G.Y.; Zhang, Z.X. Antimicrobial and cytotoxic phenolic bisabolane sesquiterpenoids from the fungus Aspergillus flavipes 297. Fitoterapia 2021, 155, 105038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.D.; Li, X.; Li, X.M.; Yin, X.L.; Wang, B.G. Antimicrobial bisabolane-type sesquiterpenoids from the deep-sea sediment-derived fungus Aspergillus versicolor SD-330. Nat. Prod. Res. 2021, 35, 4265–4271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.J.; Zhang, J.L.; Li, C.; Mu, X.G.; Liu, X.L.; Wang, L.; Zhao, Y.C.; Zhang, P.; Li, X.D.; Zhang, X.X. Antimicrobial secondary metabolites from the seawater-derived fungus Aspergillus sydowii SW9. Molecules 2019, 24, 4596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.D.; Li, X.M.; Yin, X.L.; Li, X.; Wang, B.G. Antimicrobial sesquiterpenoid derivatives and monoterpenoids from the deep-sea sediment-derived fungus Aspergillus versicolor SD-330. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.Y.; Wang, C.Y.; Liu, Q.A.; Shao, C.L.; She, Z.G.; Lin, Y.C. Five sesquiterpenoids from a marine-derived fungus Aspergillus sp. isolated from a gorgonian Dichotella gemmacea. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 941–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Yu, J.H.; Zhu, K.K.; Wang, Y.Y.; Cheng, Z.Q.; Jiang, C.S.; Dai, J.G.; Wu, J.; Zhang, H. Phenolic bisabolane sesquiterpenoids from a Thai mangrove endophytic fungus, Aspergillus sp. xy02. Fitoterapia 2018, 27, 322–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Dai, H.; Konuklugil, B.; Orfali, R.S.; Lin, W.H.; Kalscheuer, R.; Liu, Z.; Proksch, P. Phenolic bisabolanes from the sponge-derived fungus Aspergillus sp. Phytochem Lett. 2016, 18, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.H.; Miao, F.P.; Li, X.D.; Yin, X.L.; Ji, N.Y. A new sesquiterpene from an endophytic Aspergillus versicolor strain. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2012, 7, 819–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, S.T.; Liu, X.H.; Yan, B.F.; Miao, F.P.; Yin, X.L.; Li, W.Z.; Ji, N.Y. Terpenoids from the marine-derived fungus Aspergillus sp. RR-YLW-12, associated with the Red alga Rhodomela confervoides. J. Nat. Prod. 2021, 84, 1763–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.J.; Shao, C.L.; Wang, K.L.; Zhao, D.L.; Wang, Y.N. Secondary metabolites and their bioactivities of a soft coral-derived fungus Aspergillus versicolor(ZJ-2008015). Chin. J. Mar. Drugs 2012, 31, 7–13. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, E.; Koch, L.; Thu, K.M.; Rahamim, Y.; Aluma, Y.; Ilan, M.; Yarden, O.; Carmeli, S. Novel terpenoids of the fungus Aspergillus insuetus isolated from the Mediterranean sponge Psammocinia sp. collected along the coast of Israel. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2011, 19, 6587–6593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orfali, R.; Perveen, S.; Khan, M.F.; Ahmed, A.F.; Wadaan, M.A.; Al-Taweel, A.M.; Alqahtani, A.S.; Nasr, F.A.; Tabassum, S.; Luciano, P.; et al. Antiproliferative illudalane sesquiterpenes from the marine sediment ascomycete Aspergillus oryzae. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.F.; Yue, Y.F.; Feng, L.X.; Zhu, H.J.; Cao, F. Asperienes A-D, bioactive sesquiterpenes from the marine-derived fungus Aspergillus flavus. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yurchenko, A.N.; Trinh, P.T.H.; Girich, E.V.; Smetanina, O.F.; Rasin, A.B.; Popov, R.S.; Dyshlovoy, S.A.; von Amsberg, G.; Menchinskaya, E.S.; Van, T.T.T.; et al. Biologically active metabolites from the marine sediment-derived fungus Aspergillus flocculosus. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, W.; Lin, X.P.; Zhou, X.F.; Wan, J.T.; Lu, X.; Yang, B.; Ai, W.; Lin, J.; Zhang, T.Y.; Tu, Z.C.; et al. Cytotoxic and antiviral nitrobenzoyl sesquiterpenoids from the marine-derived fungus Aspergillus ochraceus Jcma1F17. Med. Chem. Comm. 2014, 5, 701–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.Y.; Anbuchezhian, R.; Sun, W.; Shao, C.L.; Zhang, F.L.; Yin, Y.; Yu, Z.S.; Li, Z.Y.; Wang, C.Y. Cytotoxic nitrobenzoyloxy-substituted sesquiterpenes from sponge derived endozoic fungus Aspergillus insulicola MD10-2. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2016, 17, 271–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.H.; Yang, B.; Lin, X.P.; Luo, X.W.; Pang, X.Y.; Tang, L.; Liu, Y.H.; Li, X.J.; Zhou, X.F. Nitrobenzoyl sesquiterpenoids with cytotoxic activities from a marine-derived Aspergillus ochraceus fungus. J. Nat. Prod. 2018, 81, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.X.; Liu, X.Y.; Sun, N.; Zhang, X.M.; Shah, M.; Zhang, G.J.; Che, Q.; Zhu, T.J.; Li, J.; Li, D.H. Cytotoxic nitrobenzoyl sesquiterpenoids from an antarctica sponge-derived Aspergillus insulicola. J. Nat. Prod. 2022, 85, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.B.; Edrada-Ebel, R.; Ebel, R.; Wang, Y.; Schulz, B.; Draeger, S.; Muller, W.E.G.; Wray, V.; Lin, W.H.; Proksch, P. Drimane sesquiterpenoids from the fungus Aspergillus ustus isolated from the marine sponge Suberites domuncula. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 1585–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.N.; Zhu, T.J.; Cai, S.X.; Gu, Q.Q.; Li, D.H. Drimane sesquiterpenoids from the mangrove-derived fungus Aspergillus ustus. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2011, 59, 762–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.L.; Shao, C.L.; Chen, J.F.; Guo, Z.Y.; Fu, X.M.; Chen, M.; Chen, Y.Y.; Li, R.; de Voogd, N.J.; She, Z.G.; et al. New bisabolane sesquiterpenoids from a marine-derived fungus Aspergillus sp. isolated from the sponge Xestospongia testudinaria. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2012, 22, 1326–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wang, H.; Su, M.; Hwang, G.J.; Hong, J.; Jung, J.H. New metabolites from the sponge-derived fungus Aspergillus sydowii J05B-7F-4. Nat. Prod. Res. 2017, 31, 1682–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, C.M.; Huang, C.H.; Wu, Q.L.; Pang, J.Y.; Lin, Y.C. A new sesquiterpene from the mangrove endophytic fungus Aspergillus terreus (No. GX7-3B). Nat. Prod. Res. 2013, 27, 1882–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.S.; Huang, Y.L.; Li, C.M.; Ma, L.Y.; Pan, X.H.; Ferreira, D.; Liu, W.Z. A new sesquiterpenoid derivative from the coastal saline soil fungus Aspergillus fumigatus. Rec. Nat. Prod. 2016, 10, 708–713. [Google Scholar]
- Kitano, M.; Yamada, T.; Amagata, T.; Minoura, K.; Tanaka, R.; Numata, A. Novel pyridino-alpha-pyrone sesquiterpene type pileotin produced by a sea urchin-derived Aspergillus sp. Tetrahedron Lett. 2012, 53, 4192–4194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.Y.; Wang, Y.; Miao, C.D.; Liu, P.P.; Hong, K.; Zhu, W.M. Sesquiterpenoids and benzofuranoids from the marine-derived fungus Aspergillus ustus 094102. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 1761–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proksch, P.; Ebel, R.; Edrada, R.; Riebe, F.; Liu, H.; Diesel, A.; Bayer, M.; Li, X.; Lin, W.H.; Grebenyuk, V.; et al. Sponge-associated fungi and their bioactive compounds: The Suberites case. Bot. Mar. 2008, 51, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, D.H.; Li, Z.L.; Sun, Y.J.; Hua, H.M.; Liu, T.; Bai, J. Terpenoids from the marine-derived fungus Aspergillus fumigatus YK-7. Molecules 2015, 21, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.C.; Liu, G.D.; Chen, Y.; Liu, S.; Luo, W.H.; Hu, P.F.; Huang, C.M.; Ji, X.; Wang, S.P.; Cao, G.Y. Cytotoxic drimane-type sesquiterpenoids from the fungus Aspergillus flavipes 297. Rec. Nat. Prod. 2021, 16, 488–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Liu, Y.N.; Li, T.M.; Zhang, Z.R.; Ding, M.; Long, Y.H.; She, Z.G. 3-Arylisoindolinone and sesquiterpene derivatives from the mangrove endophytic fungi Aspergillus versicolor SYSU-SKS025. Fitoterapia 2018, 124, 177–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Z.; Qi, S.; Zhan, Y.; Zhang, N.W.; Wu, A.A.; Gui, F.; Guo, K.; Yang, Y.R.; Cao, S.G.; Hu, Z.Y.; et al. Aspertetranones A-D, putative meroterpenoids from the marine algal-associated fungus Aspergillus sp. ZL0-1b14. J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 78, 2405–2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.D.; Li, D.Y.; Zeng, F.R.; Tong, Q.Y.; Zheng, Y.Y.; Liu, J.J.; Zhou, Q.; Li, X.N.; Chen, C.M.; Lai, Y.J.; et al. Brasilane sesquiterpenoids and dihydrobenzofuran derivatives from Aspergillus terreus [CFCC 81836]. Phytochemistry 2018, 156, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, Y.M.; Wei, C.K.; Chuang, D.W.; El-Shazly, M.; Hsieh, C.T.; Asai, T.; Oshima, Y.; Hsieh, T.J.; Hwang, T.L.; Wu, Y.C.; et al. An epigenetic modifier enhances the production of anti-diabetic and anti-inflammatory sesquiterpenoids from Aspergillus sydowii. Bioorgan. Med. Chem. 2013, 21, 3866–3872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.Y.; Li, M.J.; Tang, J.Q.; Li, X.F. Eremophilane sesquiterpenes from a deep marine-derived fungus, Aspergillus sp. SCSIOW2, cultivated in the presence of epigenetic modifying agents. Molecules 2016, 21, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.X.; Zhang, W.X.; Hao, L.L.; Qin, X.Y.; Yang, R.Y.; Li, J.; Huang, X.S. A new sesquiterpene from mangrove endophytic fungus Aspergillus sp. GXNU-MA1. Nat. Prod. Res. 2022, 36, 1857–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, S.W.; Yang, L.H.; Zhang, G.Y.; Chen, T.T.; Hong, B.H.; Pei, S.X.; Shao, Z.Z. Phenolic bisabolane and cuparene sesquiterpenoids with anti-inflammatory activities from the deep-sea-derived Aspergillus sydowii MCCC 3A00324 fungus. Bioorg. Chem. 2020, 105, 104420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, Y.H.; Deng, W.D.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Ke, M.H.; Zou, B.H.; Luo, X.W.; Su, J.B.; Wang, Y.Y.; Xu, J.L.; Nandakumar, K.S.; et al. A marine fungus-derived nitrobenzoyl sesquiterpenoid suppresses receptor activator of NF-κB ligand-induced osteoclastogenesis and inflammatory bone destruction. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 177, 4242–4260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.N.; Chen, Y.; Huang, X.S.; Pan, Y.H.; Liu, Z.M.; Yan, T.; Cao, W.H.; She, Z.G. α-Glucosidase inhibitors: Diphenyl ethers and phenolic bisabolane sesquiterpenoids from the mangrove endophytic fungus Aspergillus flavus QQSG-3. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.; Wei, X.; Hu, J.S.; Wang, S.Y.; Liu, B.X.; Xie, Z.Y.; Rong, L.; Li, X.H.; Zhang, C.X. Researches on the subergane-type sesquiterpenes from the soft coral-derived fungus Aspergillus sp. EGF15-0-3. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2020, 40, 1275–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Li, X.M.; Li, H.L.; Belma, K.; Li, X.; Wang, B.G. Chemical constituents of Aspergillus ustus TK-5, an endophytic fungus derived from the ascidian Herdmania momus. Mar. Sci. 2018, 42, 130–137. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, Q.; Zhang, F.L.; Feng, T. Sesquiterpenoids specially produced by fungi: Structures, biological activities, chemical and biosynthesis (2015–2020). J. Fungi 2021, 7, 1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Li, F.H.; Li, C.K.; Li, B.M.; Chen, R.Y.; Kang, J. Reviews on natural monocyclic sesquiterpenoids and their bioactivities. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2019, 44, 3672–3683. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.H.; Xu, Y.; Wang, C.Y.; Cao, F. Alkaloids and sesquiterpenoids from the marine-derived fungus Aspergillus versicolor. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2020, 56, 971–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.Z.; Peng, S.; Yang, J.; Cong, Z.W.; Lin, X.P.; Liao, S.R.; Yang, B.; Zhou, X.F.; Zhou, X.J.; Liu, Y.H.; et al. Structurally diverse sesquiterpenoids and polyketides from a sponge-associated fungus Aspergillus sydowii SCSIO41301. Fitoterapia 2019, 135, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, X.Y.; Lin, X.P.; Zhou, X.F.; Yang, B.; Tian, X.P.; Wang, J.F.; Xu, S.H.; Liu, Y.H. New quinoline alkaloid and bisabolane-type sesquiterpenoid derivatives from the deep-sea-derived fungus Aspergillus sp. SCSIO06786. Fitoterapia 2020, 140, 104406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trisuwan, K.; Rukachaisirikul, V.; Kaewpet, M.; Phongpaichit, S.; Hutadilok-Towatana, N.; Preedanon, S.; Sakayaroj, J. Sesquiterpene and xanthone derivatives from the sea fan-derived fungus Aspergillus sydowii PSU-F154. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 1663–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuravleva, O.I.; Afiyatullov, S.S.; Denisenko, V.A.; Ermakova, S.P.; Slinkina, N.N.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Kim, N.Y. Secondary metabolites from a marine-derived fungus Aspergillus carneus Blochwitz. Phytochemistry 2012, 80, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weigel, L.M.; Donlan, R.M.; Shin, D.H.; Jensen, B.; Clark, N.C.; McDougal, L.K.; Zhu, W.M.; Musser, K.A.; Thompson, J.; Kohlerschinidt, D.; et al. High-level vancomycin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates associated with a polymicrobial biofilm. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2007, 51, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.Y.; Shen, Y.C.; Chen, Y.J.; Sheu, J.H.; Duh, C.Y. Bioactive sesquiterpenes from a Taiwanese marine sponge Parahigginsia sp. J. Nat. Prod. 1999, 62, 573–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mcenroe, F.J.; Fenical, W. Structures and synthesis of some new antibacterial sesquiterpenoids from the gorgonian coral Pseudopterogorgia rigida. Tetrahedron 1978, 34, 1661–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulhaupt, T.; Kaspar, H.; Otto, S.; Reichert, M.; Bringmann, G.; Lindel, T. Isolation, structural elucidation, and synthesis of curcutetraol. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2005, 2005, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montaser, R.; Luesch, H. Marine natural products: A new wave of drugs? Future Med. Chem. 2011, 3, 1475–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Temraz, A. Novel illudalane sesquiterpenes from Encephalartos villosus Lehm. antimicrobial activity. Nat. Prod. Res. 2016, 30, 2791–2797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, J.; Lee, H.; Seo, Y.H.; Yun, J.; Lee, J.; Kwon, H.C.; Guo, Y.Q.; Kang, J.S.; Kim, J.J.; Lee, D. Cytotoxic drimane sesquiterpenoids isolated from Perenniporia maackiae. J. Nat. Prod. 2018, 81, 1444–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Lou, W.; Zhu, Y.; Nadiminty, N.; Schwartz, C.T.; Evans, C.P. Niclosamide inhibits androgen receptor variants expression and overcomes enzalutamide resistance in castration-resistant prostate cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 3198–3210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arulselvan, P.; Fard, M.T.; Tan, W.S.; Gothai, S.; Fakurazi, S.; Norhaizan, M.E.; Kumar, S.S. Role of antioxidants and natural products in inflammation. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2016, 2016, 5276130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orhan, I.E. Enzyme inhibitors as the attractive targets for the treatment of various diseases. Curr. Med. Chem. 2019, 26, 3206–3207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amin, S.; Ullah, B.; Ali, M.; Rauf, A.; Khan, H.; Uriarte, E.; Sobarzo-Sanchez, E. Potent in vitro α-glucosidase inhibition of secondary metabolites derived from dryopteris cycadina. Molecules 2019, 24, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Ma, S. Recent advances in synthetic α-glucosidase inhibitors. Chem. Med. Chem. 2017, 12, 819–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.; Barve, K.H.; Kumar, M.S. Recent advancements in pathogenesis, diagnostics and treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2020, 18, 1106–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francis, P.T. The interplay of neurotransmitters in Alzheimer’s disease. CNS Spectr. 2005, 10, 6–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bono, G.F.; Simao-Silva, D.P.; Batistela, M.S.; Josviak, N.D.; Dias, P.F.R.; Nascimento, G.A.; Souza, R.L.R.; Piovezan, M.R.; Souza, R.K.M.; Furtado-Alle, L. Butyrylcholinesterase: K variant, plasma activity, molecular forms and rivastigmine treatment in Alzheimer’s disease in a Southern Brazilian population. Neurochem. Int. 2015, 81, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Air, G.M. Influenza neuraminidase. Influenza Other Resp. 2012, 6, 245–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.Y.; Li, X.M.; Meng, L.H.; Wang, B.G. Antioxidant bisabolane-type sesquiterpenoids from algal-derived fungus Aspergillus sydowii EN-434. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2020, 38, 1532–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, C.L.; Kong, F.D.; Ma, Q.Y.; Xie, Q.Y.; Yuan, J.Z.; Zhou, L.M.; Dai, H.F.; Yu, Z.F.; Zhao, Y.X. Chemical constituents of the marine-derived fungus Aspergillus sp. SCS-KFD66. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, M.J.; Kang, H.H.; Ma, L.Y.; Liu, D.S.; Liu, W.Z. Study on the secondary metabolites from Aspergillus pseudoglaucus derived from offshore mud in Dandong. Chin. J. Mar. Drugs 2021, 40, 16–22. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.H.; Miao, F.P.; Qiao, M.F.; Cichewicz, R.H.; Ji, N.Y. Terretonin, ophiobolin, and drimane terpenes with absolute configurations from an algicolous Aspergillus ustus. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 588–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penesyan, A.; Kjelleberg, S.; Egan, S. Development of novel drugs from marine surface associated microorganisms. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 438–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keller, N.P. Fungal secondary metabolism: Regulation, function and drug discovery. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 17, 167–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slot, J.C. Fungal gene cluster diversity and evolution. Adv. Genet. 2017, 100, 141–178. [Google Scholar]
- Lind, A.L.; Wisecaver, J.H.; Lameiras, C.; Wiemann, P.; Palmer, J.M.; Keller, N.P.; Rodrigues, F.; Goldman, G.H.; Rokas, A. Drivers of genetic diversity in secondary metabolic gene clusters within a fungal species. PLoS Biol. 2017, 15, e2003583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutledge, P.J.; Challis, G.L. Discovery of microbial natural products by activation of silent biosynthetic gene clusters. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 13, 509–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Y.; Awakawa, T.; Mori, T.; Ling, M.Q.; Hu, D.; Wu, B.; Abe, I. Heterodimeric non-heme iron enzymes in fungal meroterpenoid biosynthesis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 21425–21432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Zou, Z.M. Discovery of new secondary metabolites by epigenetic regulation and NMR comparison from the plant endophytic fungus monosporascus eutypoides. Molecules 2020, 25, 4192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.Y.; Liu, Y.F.; Cao, F.; Wang, C.Y. Bisabolane-type sesquiterpenoids from a gorgonian-derived Aspergillus sp fungus induced by DNA methyltransferase inhibitor. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2016, 52, 1129–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.S.; Yao, G.S.; Shi, X.H.; Rehman, S.U.; Xu, Y.; Fu, X.M.; Zhang, X.L.; Liu, Y.; Wang, C.Y. Epigenetic agents trigger the production of bioactive nucleoside derivatives and bisabolane sesquiterpenes from the marine-derived fungus Aspergillus versicolor. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adekenov, S.M. Sesquiterpene lactones with unusual structure. Their biogenesis and biological activity. Fitoterapia 2017, 121, 16–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ingavat, N.; Mahidol, C.; Ruchirawat, S.; Kittakoop, P. Asperaculin A, a sesquiterpenoid from a marine-derived fungus, Aspergillus aculeatus. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 1650–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morisaki, N.; Furukawa, J.; Kobayashi, H.; Iwasaki, S.; Nozoe, S. Cyclobutyl cation rearrangements of 6-protoilluden-8α-ol, 7-protoilluden-6-ol and related compounds. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1987, 35, 2678–2685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- White, K.M.; Rosales, R.; Yildiz, S.; Kehrer, T.; Miorin, L.; Moreno, E.; Jangra, S.; Uccellini, M.B.; Rathnasinghe, R.; Coughlan, L.; et al. Plitidepsin has potent preclinical efficacy against SARS-CoV-2 by targeting the host protein eEF1A. Science 2021, 371, 926–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taglialatela-Scafati, O. New hopes for drugs against COVID-19 come from the sea. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).