Abstract
Today, complexes of gold(I) and gold(III) are recognized as promising drugs for the treatment of bacterial infectious diseases and oncological diseases, respectively. It is of interest to broaden the area of potential use of gold(III) compounds to the pathogenic microorganism as well. The first step towards the development of new antibacterial drugs based on Au3+ complexes is the study of their stability in an aqueous solution. The present contribution reports on the investigation of gold(III) complexation with five hydrazones derived from a well-known biologically active compound, pyridoxal 5′-phosphate (one of the aldehyde forms of the B6 vitamin). The complex formation in aqueous solutions was confirmed by mass spectrometry and fluorescent spectroscopy. The stoichiometric composition of the complexes formed and their stability constants were determined using a UV–Vis titration method. The complexes are quite stable at physiological values of pH, as the speciation diagrams show. The results of the paper are helpful for further studies of gold(III) complexes interaction with biomacromolecules.
1. Introduction
The discovery of penicillin and other antibiotics ushered in a new era that is probably now coming to an end. Antibiotic resistance among pathogenic microflora is increasing to alarmingly high levels worldwide [1]. New mechanisms of resistance are emerging and spreading all over the world, threatening the ability to treat common infectious diseases. More and more infections, such as pneumonia, tuberculosis, blood poisoning, gonorrhea, and foodborne illnesses, are becoming more difficult and sometimes impossible to treat because antibiotics are less effective. In this regard, alternative means of combating pathogens are actively sought [1]. The use of compounds of various metals, particularly gold, is among these alternatives. Gold has two main oxidation states, +1 and +3. While the Au+ complexes have been synthesized in abundance, and their antimicrobial and antifungal properties have been thoroughly studied (including well-known compounds used for other medical purposes, e.g., auranofin, an antiarthritic agent [2]), the gold(III) complexes, on the contrary, are mainly investigated as antitumor agents based on their similarity to platinum(II) preparations [3,4,5,6]. A small number of Au3+ compounds have been tested for efficacy against pathogens (see, e.g., reviews [7,8] and papers [9,10,11,12,13,14]).
In our opinion, the potential of gold(III) compounds has not been fully disclosed. From the analysis of the literature data, it can be concluded that there are two, at least, main mechanisms of the biological action of gold. First, metal has a genotoxic effect associated with the binding of coordination compounds to DNA (both intercalation [3,4,6,15,16,17,18] and covalent binding in grooves [5,19,20]) or with the cleavage of DNA caused by the formation of free cationic radicals from N-donor ligands in the presence of Au3+ ions [21] or the unwinding of the DNA double helix of DNA [15]. Second, it may cause the inhibition of thioredoxin reductase, which leads to oxidative stress and apoptosis. Although thioredoxin reductase is considered a target mainly in the treatment of oncological diseases, it can be crucial for the survival of pathogenic microorganisms [22,23].
The ligand helps the gold cation to permeate the cell membrane. Several ligands can be used in gold(III) complexes, particularly hydrazones, a versatile class of compounds that are known for their strong metal-chelating properties [24,25] and are widely applied in catalysis, the dye and pigment industry, as chemosensors and intermediates in organic synthesis [26], and in medicine [27]. Of particular note among hydrazones are the derivatives of pyridoxal or pyridoxal-5-phosphate (B6 vitamers)—biologically active compounds—in the synthesis and study of which we have accumulated some experience (see, e.g., [28,29,30,31,32]). These hydrazones are low-toxicity and membranotropic agents [33]. Having carried out a preliminary evaluation of the potential antibacterial activity using the PASS Online software [34] (the results are given in Table S1), we found that vitamin B6 hydrazones, which also contain residues of furan, thiophene, and pyridine, are likely to be active against a number of pathogenic microorganisms, such as Enterococcus faecalis, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Mycobacterium BCG, Dialister invisus, etc., including resistant strains. Furthermore, calculations show that complexation with Au3+ ions increases the probability of being active for all ligands. Despite the limitations inherent in the method [34], the results of preliminary screening can serve as a basis for the choice of ligands for research.
The study of binding between Au3+ complexes and proteins and DNA is often conducted [3,4,5,6,9,15,16,17,18,19,20,35,36]. However, in the referenced papers [3,4,5,6,9,15,16,17,18,19,20,35,36], the possible dissociation of the metal complex and separate binding of the ligand and cation to the biomolecule are not taken into account (despite the process of dissociation of metal complexes in the presence of DNA or protein being possible and abundant [30,37,38]). Furthermore, if enzymes such as thioredoxin reductase are considered biological targets, the dissociation of the Au3+ complex is necessary for inhibition, because the gold(III) ion binds to the residues of (seleno)cysteine with the formation of Au-S (Se) bonds. Therefore, the assessment of complex stability in the aqueous solution is a necessary step on the path towards the development of potential antibacterial drugs.
Due to the reasons above, the present contribution aims to study the stability of gold(III) complexes with five hydrazones derived from pyridoxal 5′-phosphate (PLP) in aqueous solution. The structures of the proposed ligands are given in Figure 1.
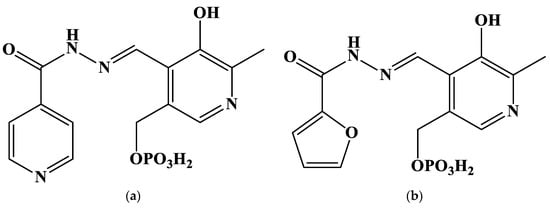
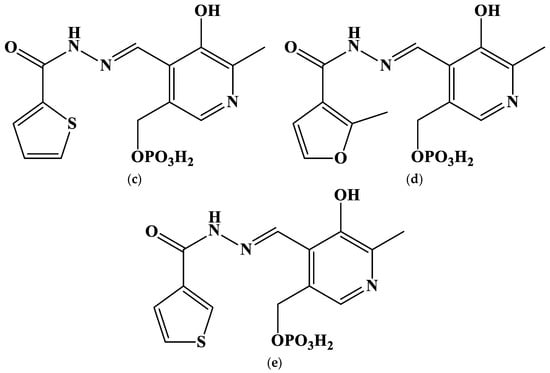
Figure 1.
Structures of the studied hydrazones derived from pyridoxal 5′-phosphate and (a) isoniazid (PLP-INH); (b) furoyl-2-hydrazide (PLP-F2H); (c) thiophene-2-carbohydrazide (PLP-T2H); (d) 2-methylfuroyl-3-hydrazide (PLP-F3H); (e) thiophene-3-carbohydrazide (PLP-T3H).
2. Results and Discussion
Gold(III) has complex chemistry in aqueous solution. The free cation readily undergoes hydrolysis, and exists as Au(OH)2+ even in 1 to 8 M strong acids [39]. Due to this, gold complexation is more convenient to study using its tetrachloride complex as a source of Au3+ ions (see, e.g., [40]). Therefore, the complexation of tetrachloroaurate(III) is a reaction of the ligand substitution. It should also be noted that chlorides can be substituted with OH− ions, when the reaction transfers from an acidic medium to an alkali solution [41]. I. V. Mironov and L. D. Tsvelodub had shown that gold(III) tends to form very stable complexes with the chelating compounds, such as ethylenediamine and diethylenetriamine [40]; however, it was unknown whether hydrazones derived from pyridoxal 5′-phosphate could chelate Au3+. The study of any metal’s complexation with hydrazones is additionally complicated by the multiple protolytic equilibria of ligands, the poor solubility of free hydrazones and their complexes in the neutral or acidic media, and the large number of possible coordination compounds that can be formed under certain experimental conditions [42].
In the mass spectrum of the complex [Au(OH)(PLP-INH)] precipitated from an aqueous solution (Figure S1), one can find peaks with m/z = 581.7 and 604.1, corresponding to the complexes [Au + OH + L + H] (calcd. M = 581.05) and [Au + OH + L + H + Na] (calcd. M = 604.0).
Furthermore, the fluorescent emission spectra of free ligands differ from those of the mixture of Au3+ and ligands (Figure 2 and Figure S2), which is also indicative of the reaction that occurs between metals and hydrazones. The Stokes shift for all the studied hydrazones decreases by 25–45 nm, when cations are added. An interesting exception is the PLP-F2H hydrazone, whose luminescence intensity decreases greatly upon addition to the gold(III) solution (Figure 2b). The bimodal emission spectrum of PLP-INH hydrazone added to the gold(III) solution is also noteworthy (Figure S2a). The decrease in the Stokes shift might be indicative of the Excited State Intramolecular Proton Transfer-off (ESIPT-off) mechanism caused by the complexation [43]. In other words, the free labile ligand capable of keto-enol tautomerism (as in most o-hydroxyl hydrazones and Schiff bases [44]) rigidifies upon complexation; the rotational freedom is limited, and the hydrazone molecule takes a less fluorescent configuration.
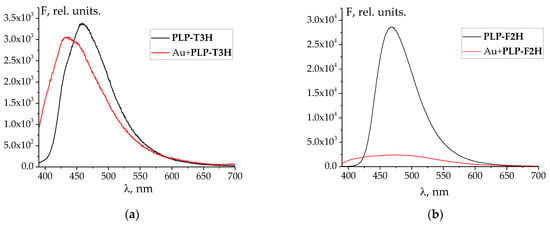
Figure 2.
Emission spectra of free hydrazones and their mixtures with Au3+: (a) PLP-T3H; (b) PLP-F2H. λex = 365 nm. Concentrations of ligands, metals, and H+ are equal to those at the end of UV–Vis titration (see below).
The UV–Vis spectra of free ligands are typical for hydrazones, showing intense absorbance at 295–315 nm. This peak refers to the electron transfer of the π-π-p-π conjugated system uniting the hydrazone molecules [29,32]. A long-wave shoulder peak at 340 nm should be presumably assigned to n-π* transfer.
The changes in UV–Vis spectra observed during the titration of Au3+ solution against hydrazones are less indicative of complex formation (Figure 3a,b and Figure S3) than the emission spectra. However, it should also be noted that the titration of gold(III) against hydrazone is different from that of only acid with the same C(H+) as the HAuCl4 solution (Figure 3). Namely, the changes associated with the formation of deprotonated species of hydrazones begin later, when the mixture of Au + H is titrated, than in the case of merely acid titration. This shows that the gold cation competes with the proton for the ligand molecule.
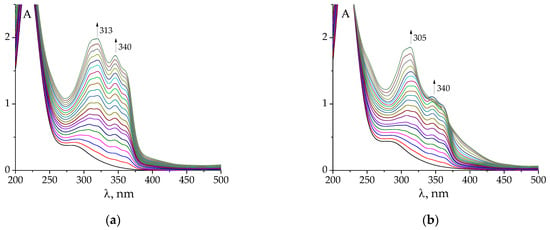
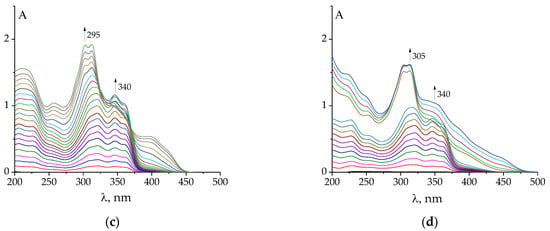
Figure 3.
Examples of changes in UV–Vis spectra of HAuCl4 (a,c) and HClO4 (b,d) after the addition of PLP-F2H (a,c), PLP-T2H (b,d). Titrant: C(AuCl4−) = 2·10−4 mol L−1; C(H+) = 5·10−4 mol L−1 (a,c); C(H+) = 5·10−4 mol L−1 (b,d). Titrant: C(PLP-F2H) = 1.5·10−3 mol L−1; C(OH−) = 0.01074 mol L−1 (a,c); Titrant: C(PLP-T2H) = 1.5·10−3 mol L−1; C(OH−) = 0.01074 mol L−1 (b,d). Twenty additions of 10 μL volume.
The pH value varied from 3.3 to 8.5 during the titration. It should be noted that in some cases (e.g., upon titration with PLP-F2H or PLP-T3H), at the end of the experiment, the appearance of a precipitated product in the solution was detected. It prevented us from further exploring the alkali region.
The results of spectrophotometric titration (Figure 3a,b and Figure S3) can be used to calculate the stability constants of the gold(III) complexes formed. The following processes of the general formula mH + nL + pAu + qOH = Aup(OH)qLnHm should be set in the stoichiometric scheme for calculations of stability constants using KEV software [45] ([AuCl4]− is denoted Au for convenience; the charges of other components are also omitted; note that all reactions involving ‘Au’ listed below are reactions of chloride substitution):
H + L = HL
2H + L = H2L
3H + L = H3L
Au + OH = AuOH
Au + 2OH = Au(OH)2
Au + 3OH = Au(OH)3
Au + 4OH = Au(OH)4
H + OH = HOH
Au + L = AuL
Au + H + L = AuHL
Au + 2H + L = AuH2L
The constants of the processes (1)–(3) are adopted from [46] for PLP-INH (log β1 = 11.37; log β2 = 19.60; log β3 = 23.81), PLP-F2H (log β1 = 11.43; log β2 = 19.72; log β3 = 23.79), PLP-T2H (log β1 = 11.47; log β2 = 19.75; log β3 = 24.24), PLP-T3H (log β1 = 11.48; log β2 = 19.31; log β3 = 24.15). The protonation constants of the PLP-F3H hydrazone are unknown; however, we took them to be equal to those of PLP-F2H, taking into account the closeness of the log βi values determined for different hydrazones to each other. The constants of the processes (4)–(7) are taken from paper [41] (log β(4) = 7.87; log β(5) = 14.79; log β(6) = 20.92; log β(7) = 25.98). The value of log β(8) = 13.91 was taken from the report [47]. The values of log β (Equations (9)–(11)) are to be determined.
We tested different stoichiometric models to find the most suitable one. They included the formation of a single complex AuHmL (m = 0–2), two complexes AuHmL and AuHm−1L (m = 0–2), and three complexes (Equations (9)–(11)). The latter gives the best fit of the calculated absorbance values to the experimental ones. It should be noted that a hydrazone substitutes three of four chloride anions in the coordination sphere; the last chloride likely remains or is substituted by the hydroxyl anion at high pH values (this possibility is taken into account in the model Equations (4)–(7)). The calculated stability constants, as well as the stepwise protonation constants log Kb1 and log Kb2 of the complexes (AuL + H = AuHL; AuHL + H = AuH2L, respectively) and the constants of gold(III) binding by the protonated ligands log Kf1 and log Kf2 (Au + HL = AuHL; Au + H2L = AuH2L, respectively), are given in Table 1.
log Kb1 = log β(AuHL) − log β(AuL)
log Kb2 = log β(AuH2L) − log β(AuHL)
log Kf1 = log β(AuHL) − log β(HL)
log Kf1 = log β(AuH2L) − log β(H2L)

Table 1.
Stability constants of gold(III) complexes with hydrazones derived from pyridoxal 5′-phosphate in aqueous solution at T = 298.2 K, I ~ 0.
It is interesting that hydrazones, despite being tridentate ligands, form less stable complexes than bidentate ethylenediamine [40]. This can be explained by the steric hindrance caused by the necessity of hydrazone molecule arrangement around the large Au(III) cation.
UV–Vis spectra of individual complex species (AuL, AuHL, AuH2L) were also calculated (Figure 4 and Figure S4). They explain why the changes in the UV–Vis spectra during spectrophotometric titration were not significant: the spectra of the complexes are similar to those of the protonated species. The similarity of the spectra, in turn, can be explained by the weak interaction of Au atomic orbitals (possessing high energy) with the low-energy molecular orbitals of ligands. For this reason, there is no band of charge transfer (ligand to metal or metal to ligand) in the UV–Vis spectra, which is typical for d-metal complexes with hydrazones, as studied previously [28,30]. Further quantum chemical calculations are required to confirm this assumption.
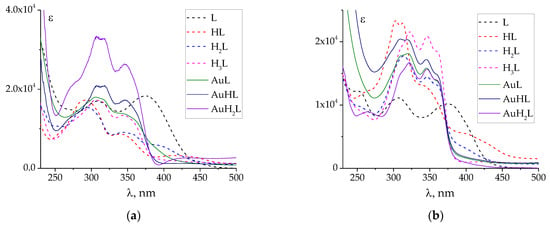
Figure 4.
Calculated UV–Vis spectra of individual protonated and complex species of PLP-INH (a) and PLP-F2H (b). The spectra of protonated species are adopted from [44]. ‘Au’ denotes tetrachloroaurate(III).
The relatively high values of the stability constant errors (Table 1) are the consequence of the difficulties experienced while studying the complexation of hydrazones, as well as the similarity of the spectra of protonated and complex species. They are characteristic for such systems, as was noted by the authors [42].
Finally, let us plot the speciation diagrams for all the studied complexes for the case C(HAuCl4) = C(L) = 0.0001 mol L−1 (Figure 5).
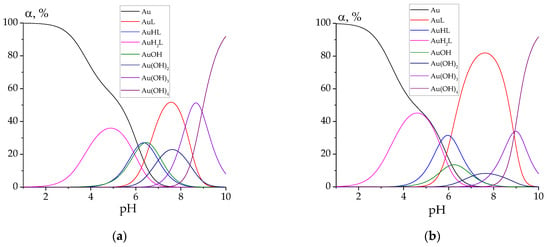
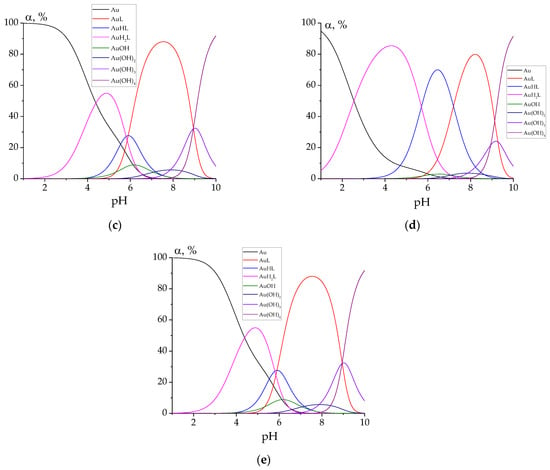
Figure 5.
Speciation diagrams for the solutions containing 0.0001 mol L−1 of HAuCl4 and 0.0001 mol L−1 of hydrazones: PLP-INH (a); PLP-F2H (b); PLP-F3H (c); PLP-T2H (d); PLP-T3H (e). ‘Au’ denotes tetrachloroaurate.
For every studied hydrazone, the following complex species of gold(III) are predominant at biologically relevant pH values (7.0–7.4): AuL, AuHL, AuOH, Au(OH)2. Hydrazone PLP-T2H shows the best binding chelating ability toward Au3+ ions. This can be explained by the possible additional stabilization of the complex due to the bond between the heterocyclic S atom and Au cation.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals
HAuCl4 (Aurat, Moscow, Russia) with purity of 99.9%, as claimed by the manufacturer, was used without additional purification. The synthesis of PLP-INH, PLP-F2H, PLP-T2H, PLP-F3H, PLP-T3H was performed as described in previous papers [29,32,48] from PLP and the corresponding hydrazones. HClO4 and NaOH (Reakhim, Russia) were standardized titrimetrically prior to use. In particular, perchloric acid was titrated against twice-recrystallized Na2B4O7·10H2O in the presence of methyl orange (indicator). This acid was further used for the titration of NaOH with two indicators (phenolphthalein and methyl orange) to control the traces of Na2CO3. The sodium carbonate did not exceed 2% compared to the NaOH concentration.
3.2. Methods
Spectrophotometric titrations were carried out using a double-beamed spectrophotometer, UV1800 (Shimadzu, Columbia, MD, USA), equipped with an external thermostat maintaining the temperature with an error of ±0.1 K. UV–Vis spectra were registered in the wavelength interval of 200–500 nm (error of wavelength determination was ±0.5 nm) and in the absorbance range of 0–2.5 units (the error of absorbance measurement ±0.004 units). Water was used as a blank solution. Standard quartz cells with an optical path length of 1 cm were used.
The main experiments included twenty additions (each of 10 μL) of aqueous solution of 1.5·10−3 mol L−1 hydrazones and 0.01074 mol L−1 NaOH to 2.7 mL of 2·10−4 mol L−1 AuCl4− and 5·10−4 mol L−1 H+. The pH value during the titration varied within the range of 3.3 to 8.5. The ionic strength value set by HClO4 varied from 0.001 to 0.002 mol L−1 during titration. Stability constants and speciation diagrams were calculated using the KEV software [45]. See the Results and Discussion Section for details of equilibria in the stoichiometric model (Equations (1)–(11)).
The emission fluorescent spectra were registered using an RF6000 setup (Shimadzu, Columbia, MD, USA) at the excitation wavelength λex = 365 nm, in the emission wavelength range 390–700 nm, at a scanning rate of 6000 nm/min. Excitation and emission slit widths were set at 5 nm. Standard quartz cells with an optical path length of 1 cm were used. The concentrations of ligands, metals, and H+ were equal to those at the end of UV–Vis titration.
Mass spectra (MALDI TOF) were recorded using a Shimadzu Biotech Axima Confidence setup (Shimadzu, Columbia, MD, USA).
The following definitions were used for the equilibrium constants:
- (1)
- The symbol β refers to the total equilibrium constant of the reaction with the general formula mH + nL + pAu + qOH = Aup(OH)qLnHm;
- (2)
- The symbol Kbm refers to the stepwise protonation constant of the process with the general formula AuLHm-1 + H = AuLHm;
- (3)
- The symbol Kfm refers to the equilibrium constant of the reaction of gold(III) binding to the protonated ligands with the general formula Au + HmL = AuLHm.
4. Conclusions
The complexation of gold(III) taken as tetrachloroaurate with hydrazones derived from pyridoxal 5′-phosphate was studied in aqueous solution at T = 298.2 K. Complexes of AuL, AuHL, AuH2L stoichiometry were found to be formed under the applied experimental conditions. Complex formation slightly (except for the hydrazone derived from PLP and 2-furoylhydrazide) quenched the intrinsic fluorescence of the ligands and decreased the Stokes shift. The stability constants were determined for complexes of different stoichiometry. Analysis of the speciation diagrams has shown that the predominate complex species of gold(III) in the physiological range of pH values are AuL, AuHL, AuOH, and Au(OH)2.
The present contribution is hopefully the first step on the path to studying the coordination chemistry of gold(III) in aqueous solution regarding its further use in medicine. The following topics should be addressed and questions answered (as in our future papers):
- Why are the UV–Vis spectra of gold(III) complexes with hydrazones similar to those of free hydrazones? The high-level quantum chemical calculations might be of great use to answer this question.
- Because gold(III) is not completely bound to the complex with hydrazone, the study of the interactions between gold(III) (in the form of a tetrachloroaurate or mixed chloride and hydroxyl complex) and proteins or DNA is in order.
- Would the gold(III) complexes with hydrazones dissociate completely in the presence of proteins or nucleic acid?
- Would gold(III) complexes with hydrazones derived from pyridoxal 5′-phosphate have any effect against pathogenic microorganisms?
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/molecules27217346/s1, Table S1: Preliminary virtual screening results using PASS Online software. Figure S1: Mass spectrum of Au-PLP-INH complex precipitated from an aqueous solution. Figure S2: Emission spectra of free hydrazones and their mixtures with Au3+: (a) PLP-INH; (b) PLP-F3H; (c) PLP-T2H. λex = 365 nm. Figure S3: Examples of changes in UV–Vis spectra of HAuCl4 upon addition of PLP-INH (a), PLP-F3H (b), PLP-T3H (c). Titrant: C(AuCl4−) = 2·10−4 mol L−1; C(H+) = 5·10−4 mol L−1. Titrant: C(PLP-INH) = 1.5·10−3 mol L−1; C(OH−) = 0.01074 mol L−1 (a); Titrant: C(PLP-F3H) = 1.5·10−3 mol L−1; C(OH−) = 0.01074 mol L−1 (b); Titrant: C(PLP-T3H) = 1.5·10−3 mol L−1; C(OH−) = 0.01074 mol L−1 (b). Twenty additions of 10 μL volume. Figure S4: Calculated UV–Vis spectra of individual protonated and complex species of PLP-T2H (a), PLP-F3H (b), PLP-T3H. Spectra of protonated species are adopted from paper 10.1016/j.molliq.2020.112822. Reference [49] has been cited in the Supplementary Materials file.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, G.A.G.; methodology, G.A.G., N.N.K. and M.N.Z.; software, G.A.G.; validation, D.N.Y., N.N.K. and M.N.Z.; formal analysis, G.A.G., D.N.Y. and N.N.K.; investigation, G.A.G., N.N.K., D.N.Y. and M.N.Z.; resources, G.A.G. and M.N.Z.; data curation, G.A.G. and N.N.K.; writing—original draft preparation, G.A.G.; writing—review and editing, G.A.G.; visualization, G.A.G.; supervision, G.A.G.; project administration, G.A.G.; funding acquisition, G.A.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Russian Science Foundation, grant number 22-73-10009, https://rscf.ru/project/22-73-10009/ (accessed on 1 October 2022).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the Center of Collective Use of Ivanovo State University of Chemistry and Technology (supported by the Ministry of Science and Higher Education of Russia, project 075-15-2021-671), for allowing us the use of its equipment to perform the MS and fluorescence study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Sample Availability
Samples of the compounds are available elsewhere.
References
- Nwobodo, D.C.; Ugwu, M.C.; Anie, C.O.; Al-Ouqaili, M.T.S.; Ikem, J.C.; Chigozie, U.V.; Saki, M. Antibiotic resistance: The challenges and some emerging strategies for tackling a global menace. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2022, 36, e24655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzo, T.; Cirri, D.; Pollini, S.; Prato, M.; Fallani, S.; Cassetta, M.I.; Novelli, A.; Rossolini, G.M.; Messori, L. Auranofin and its Analogues Show Potent Antimicrobial Activity against Multidrug-Resistant Pathogens: Structure–Activity Relationships. ChemMedChem 2018, 13, 2448–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, G.; Chen, C.; Wang, Q.; Gao, Z.; Xu, M. Cytotoxicity and DNA Binding Ability of Two Novel Gold(III) Complexes. J. Appl. Spectrosc. 2019, 86, 618–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankarganesh, M.; Raja, J.D.; Revathi, N.; Solomon, R.V.; Kumar, R.S. Gold(III) complex from pyrimidine and morpholine analogue Schiff base ligand: Synthesis, characterization, DFT, TDDFT, catalytic, anticancer, molecular modeling with DNA and BSA and DNA binding studies. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 294, 111655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abyar, F.; Tabrizi, L. New cyclometalated gold (III) complex targeting thioredoxin reductase: Exploring as cytotoxic agents and mechanistic insights. Biometals 2020, 33, 107–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radisavljević, S.; Kesić, A.D.; Ćoćić, D.; Puchta, R.; Senft, L.; Milutinović, M.; Milivojević, N.; Petrović, B. Studies of the stability, nucleophilic substitution reactions, DNA/BSA interactions, cytotoxic activity, DFT and molecular docking of some tetra- and penta-coordinated gold(III) complexes. New J. Chem. 2020, 44, 11172–11187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glisic, B.D.; Djuran, M.I. Gold complexes as antimicrobial agents: An overview of different biological activities in relation to the oxidation state of the gold ion and the ligand structure. Dalton Trans. 2014, 43, 5950–5969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pooja, P.; Ramesh, K.; Sourabh; Amit, K.; Pratibha, C.; Rajeev, S. Reviewing Gold(III) complexes as effective biological operators. Main Group Chem. 2018, 17, 35–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanthecha, D.N.; Bhatt, B.S.; Patel, M.N.; Vaidya, F.M.; Pathak, C. DNA interaction, anticancer, cytotoxicity and genotoxicity studies with potential pyrazine-bipyrazole dinuclear µ-oxo bridged Au(III) complexes. Mol. Divers. 2022, 26, 2085–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Khodir, F.A.I.; Refat, M.S. Synthesis, spectroscopic, thermal and anticancer studies of metal-antibiotic chelations: Ca(II), Fe(III), Pd(II) and Au(III) chloramphenicol complexes. J. Mol. Struct. 2016, 1119, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radulović, N.C.; Stojanović, N.M.; Glišić, B.D.; Randjelović, P.J.; Stojanović-Radić, Z.Z.; Mitić, K.V.; Nikolić, M.G.; Djuran, M.I. Water-soluble gold(III) complexes with N-donor ligands as potential immunomodulatory and antibiofilm agents. Polyhedron 2018, 141, 164–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, I.; Ullah, A.; Khan, A.U.; Khan, W.U.; Ullah, R.; Naser, A.A.S.A.A.; Mahmood, H.M. Synthesis, Characterization and Biological Activities of Hydrazone Schiff Base and its Novel Metals Complexes. Sains Malays. 2019, 48, 1439–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melha, K.S.A.A.; Al-Hazmi, G.A.A.; Refat, M.S. Synthesis of Nano-Metric Gold Complexes with New Schiff Bases Derived from 4-Aminoantipyrene, Their Structures and Anticancer Activity. Russ. J. Gen. Chem. 2017, 87, 3043–3051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alibrahim, K.A.; Al-Saif, F.A.; Bakhsh, H.A.; Refat, M.S. Synthesis, Physicochemical, and Biological Studies of New Pyridoxine HCl Mononuclear Drug Complexes of V(III), Ru(III), Pt(II), Se(IV), and Au(III) Metal Ions. Russ. J. Gen. Chem. 2018, 88, 2400–2409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Westhuizen, D.; Slabber, C.A.; Fernandes, M.A.; Joubert, D.F.; Kleinhans, G.; van der Westhuizen, C.J.; Stander, A.; Munro, O.Q.; Bezuidenhout, D.I. A Cytotoxic Bis(1,2,3-triazol-5-ylidene)carbazolide Gold(III) Complex Targets DNA by Partial Intercalation. Chem. Eur. J. 2021, 27, 8295–8307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messori, L.; Orioli, P.; Tempi, C.; Marcon, G. Interactions of Selected Gold(III) Complexes with Calf Thymus DNA. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2001, 281, 352–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Tu, C.; Zhang, J.; Lin, L.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Q.; Ding, J.; Xu, Q.; Guo, Z. Novel Au(III) complexes of aminoquinoline derivatives: Crystal structure, DNA binding and cytotoxicity against melanoma and lung tumour cells. Dalton Trans. 2003, 3419–3424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, M.; Bieńko, D.C.; Komarnicka, U.K.; Kyzioł, A.; Dryś, M.; Świtlicka, A.; Dyguda-Kazimierowicz, E.; Jedwabny, W. Synthesis, structural characterization, docking simulation and in vitro antiproliferative activity of the new gold(III) complex with 2-pyridineethanol. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2021, 215, 111311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Possato, B.; Dalmolin, L.F.; Pereira, L.M.; Alves, J.Q.; Silva, R.T.C.; Gelamo, R.V.; Yatsuda, A.P.; Lopez, R.F.V.; de Albuquerque, S.; Leite, N.B.; et al. Gold(III) complexes with thiosemicarbazonate ligands as potential anticancer agents: Cytotoxicity and interactions with biomolecular targets. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 162, 105834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radisavljević, S.; Scheurer, A.; Bockfeld, D.; Ćoćić, D.; Puchta, R.; Senft, L.; Pešić, M.; Damljanović, I.; Petrović, B. New mononuclear gold(III) complexes: Synthesis, characterization, kinetic, mechanistic, DNA/BSA/HSA binding, DFT and molecular docking studies. Polyhedron 2021, 209, 115446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masaaki, T.; Ahsan, H.; Keiichi, W. DNA Cleavage by Good’s Buffers in the Presence of Au(III). Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2005, 78, 1263–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, A.; Åslund, F.; Pontis, E.; Reichard, P.; Holmgren, A. Characterization of Escherichia coli NrdH: A GLUTAREDOXIN-LIKE PROTEIN WITH A THIOREDOXIN-LIKE ACTIVITY PROFILE. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 18044–18050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phulera, S.; Mande, S.C. The Crystal Structure of Mycobacterium tuberculosis NrdH at 0.87 Å Suggests a Possible Mode of Its Activity. Biochemistry 2013, 52, 4056–4065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kargar, H.; Fallah-Mehrjardi, M.; Behjatmanesh-Ardakani, R.; Munawar, K.S.; Ashfaq, M.; Tahir, M.N. Synthesis, spectral characterization, SC-XRD, HSA, DFT and catalytic activity of novel dioxovanadium(V) complex with aminobenzohydrazone Schiff base ligand: An experimental and theoretical approach. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2021, 526, 120535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kargar, H.; Fallah-Mehrjardi, M.; Behjatmanesh-Ardakani, R.; Munawar, K.S.; Ashfaq, M.; Tahir, M.N. Diverse coordination of isoniazid hydrazone Schiff base ligand towards iron(III): Synthesis, characterization, SC-XRD, HSA, QTAIM, MEP, NCI, NBO and DFT study. J. Mol. Struct. 2022, 1250, 131691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsharif, M.A.; Naeem, N.; Mughal, E.U.; Sadiq, A.; Jassas, R.S.; Kausar, S.; Altaf, A.A.; Zafar, M.N.; Mumtaz, A.; Obaid, R.J.; et al. Experimental and theoretical insights into the photophysical and electrochemical properties of flavone-based hydrazones. J. Mol. Struct. 2021, 1244, 130965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsantali, R.A.; Mughal, E.U.; Naeem, N.; Alsharif, M.A.; Sadiq, A.; Ali, A.; Jassas, R.S.; Javed, Q.; Javid, A.; Sumrra, S.H.; et al. Flavone-based hydrazones as new tyrosinase inhibitors: Synthetic imines with emerging biological potential, SAR, molecular docking and drug-likeness studies. J. Mol. Struct. 2022, 1251, 131933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamov, G.A.; Zavalishin, M.N.; Petrova, M.V.; Khokhlova, A.Y.; Gashnikova, A.V.; Kiselev, A.N.; Sharnin, V.A. Interaction of pyridoxal-derived hydrazones with anions and Co2+, Co3+, Ni2+, Zn2+ cations. Phys. Chem. Liq. 2021, 59, 666–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamov, G.A.; Khodov, I.A.; Belov, K.V.; Zavalishin, M.N.; Kiselev, A.N.; Usacheva, T.R.; Sharnin, V.A. Spatial structure, thermodynamics and kinetics of formation of hydrazones derived from pyridoxal 5′-phosphate and 2-furoic, thiophene-2-carboxylic hydrazides in solution. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 283, 825–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamov, G.A.; Zavalishin, M.N.; Aleksandriiskii, V.V.; Sharnin, V.A. Pyrazine-2-carbohydrazone of Pyridoxal 5′-Phosphate: Synthesis, Stability, Formation Kinetics, and Interaction with DNA. Russ. J. Gen. Chem. 2019, 89, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamov, G.A.; Aleksandriiskii, V.V.; Zavalishin, M.N.; Khokhlova, A.Y.; Sharnin, V.A. The Schiff bases of pyridoxal-5-phosphate and hydrazides of certain pyrazoles: Stability, kinetics of formation, and synthesis. Russ. J. Gen. Chem. 2017, 87, 1161–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamov, G.A.; Kiselev, A.N.; Aleksandriiskii, V.V.; Sharnin, V.A. Influence of regioisomerism on stability, formation kinetics and ascorbate oxidation preventive properties of Schiff bases derived from pyridinecarboxylic acids hydrazides and pyridoxal 5′-phosphate. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 242, 1148–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brittenham, G.M. Pyridoxal Isonicotinoyl Hydrazone. Effective Iron Chelation after Oral Administration. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1990, 612, 315–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filimonov, D.A.; Druzhilovskiy, D.S.; Lagunin, A.A.; Gloriozova, T.A.; Rudik, A.V.; Dmitriev, A.V.; Pogodin, P.V.; Poroikov, V.V. Computer-aided Prediction of Biological Activity Spectra for Chemical Compounds: Opportunities and Limitations. Biomed. Chem. Res. Methods 2018, 1, e00004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radisavljević, S.; Petrović, B. Gold(III) Complexes: An Overview on Their Kinetics, Interactions With DNA/BSA, Cytotoxic Activity, and Computational Calculations. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, T.S.; Privér, S.H.; Mirzadeh, N.; Luwor, R.B.; Reddy, V.G.; Ramesan, S.; Bhargava, S.K. Antitumor and Antiangiogenic Properties of Gold(III) Complexes Containing Cycloaurated Triphenylphosphine Sulfide Ligands. Inorg. Chem. 2020, 59, 5662–5673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamov, G.A.; Zavalishin, M.N.; Sharnin, V.A. Comment on the frequently used method of the metal complex-DNA binding constant determination from UV–Vis data. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spec. 2019, 206, 160–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamov, G.A. Processing of the spectrofluorimetric data using the graphical methods and the maximum likelihood approach. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spec. 2021, 249, 119334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mironov, I.V. Communication about properties of hydroxyl and aquahydroxyl complexes of gold(III) in aqueous solution. Zh. Neorg. Khim. 2005, 50, 1204–1209. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Mironov, I.V.; Tsvelodub, L.D. Equilibria of Cl− substitution by ammonia, ethylenediamine and diethylenetriamine in the AuCl4− complex in aqueous solution. Zh. Neorg. Khim. 2000, 45, 425–430. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Mironov, I.V.; Tsvelodub, L.D. Chlorohydroxyl complexes of gold(III) in aqueous alkali solutions. Zh. Neorg. Khim. 2000, 45, 706–711. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Wis Vitolo, L.M.; Hefter, G.T.; Clare, B.W.; Webb, J. Iron chelators of the pyridoxal isonicotinoyl hydrazone class Part II. Formation constants with iron(III) and iron(II). Inorg. Chim. Acta 1990, 170, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedgwick, A.C.; Wu, L.; Han, H.; Bull, S.D.; He, X.; James, T.D.; Sessler, J.L.; Tang, B.Z.; Tian, H.; Yoon, J. Excited-state intramolecular proton-transfer (ESIPT) based fluorescence sensors and imaging agents. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 8842–8880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berhanu, A.L.; Gaurav; Mohiuddin, I.; Malik, A.K.; Aulakh, J.S.; Kumar, V.; Kim, K. A review of the applications of Schiff bases as optical chemical sensors. Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 116, 74–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meshkov, A.N.; Gamov, G.A. KEV: A free software for calculating the equilibrium composition and determining the equilibrium constants using UV–Vis and potentiometric data. Talanta 2019, 198, 200–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamov, G.A.; Meshkov, A.N.; Zavalishin, M.N.; Khokhlova, A.Y.; Gashnikova, A.V.; Aleksandriiskii, V.V.; Sharnin, V.A. Protonation of hydrazones derived from pyridoxal 5′-phosphate: Thermodynamic and structural elucidation. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 305, 112822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandura, A.V.; Lvov, S.N. The Ionization Constant of Water over Wide Ranges of Temperature and Density. J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data 2006, 35, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zavalishin, M.N.; Gamov, G.A.; Pimenov, O.A.; Pogonin, A.E.; Aleksandriiskii, V.V.; Usoltsev, S.D.; Marfin, Y.S. Pyridoxal 5′-phosphate 2-methyl-3-furoylhydrazone as a selective sensor for Zn2+ ions in water and drug samples. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2022, 432, 114112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: http://www.way2drug.com/antibac/ (accessed on 11 October 2022).
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).