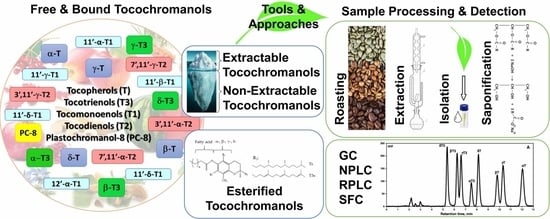
Free and Esterified Tocopherols, Tocotrienols and Other Extractable and Non-Extractable Tocochromanol-Related Molecules: Compendium of Knowledge, Future Perspectives and Recommendations for Chromatographic Techniques, Tools, and Approaches Used for Tocochromanol Determination
Abstract
:1. Introduction
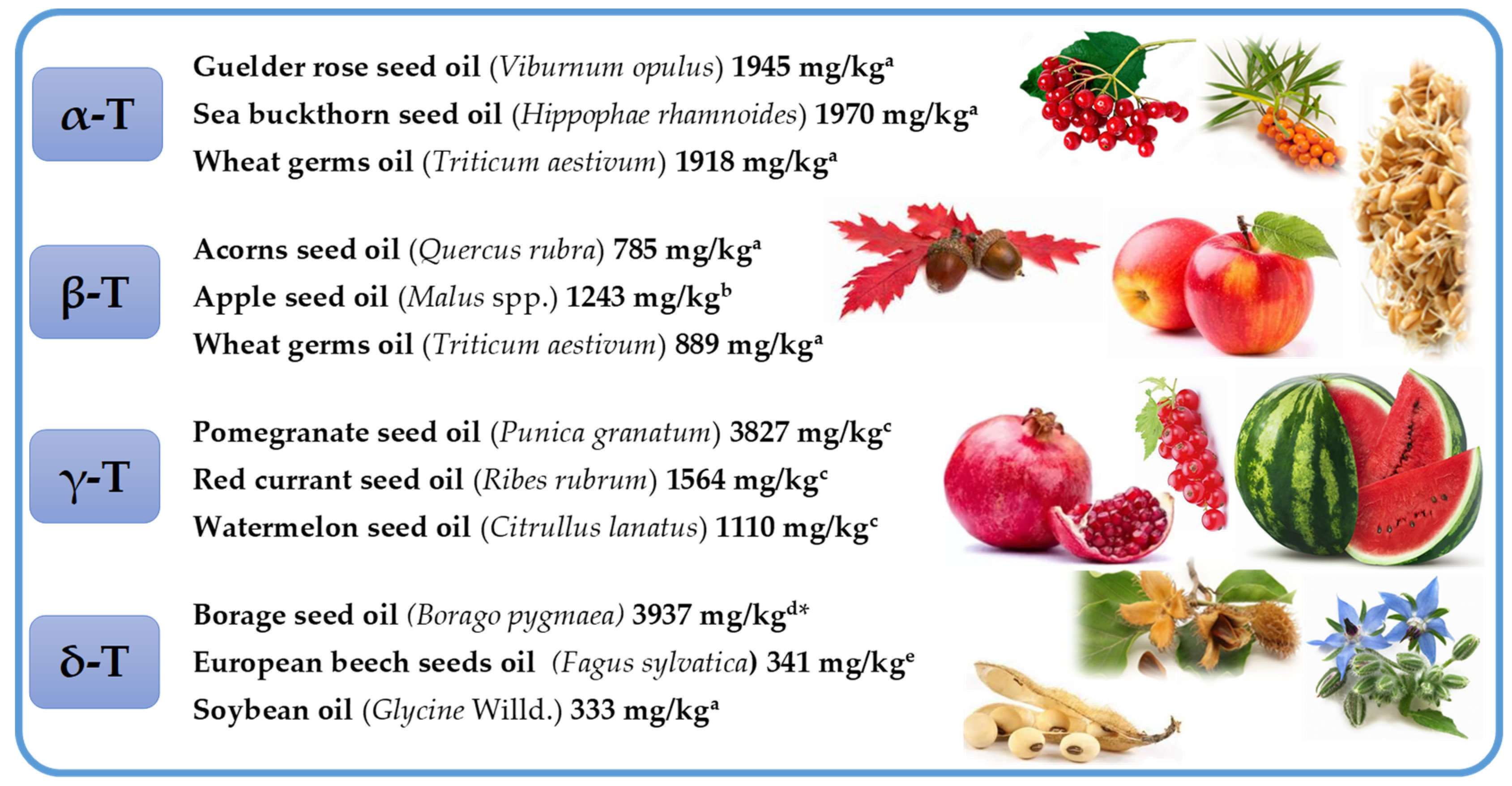
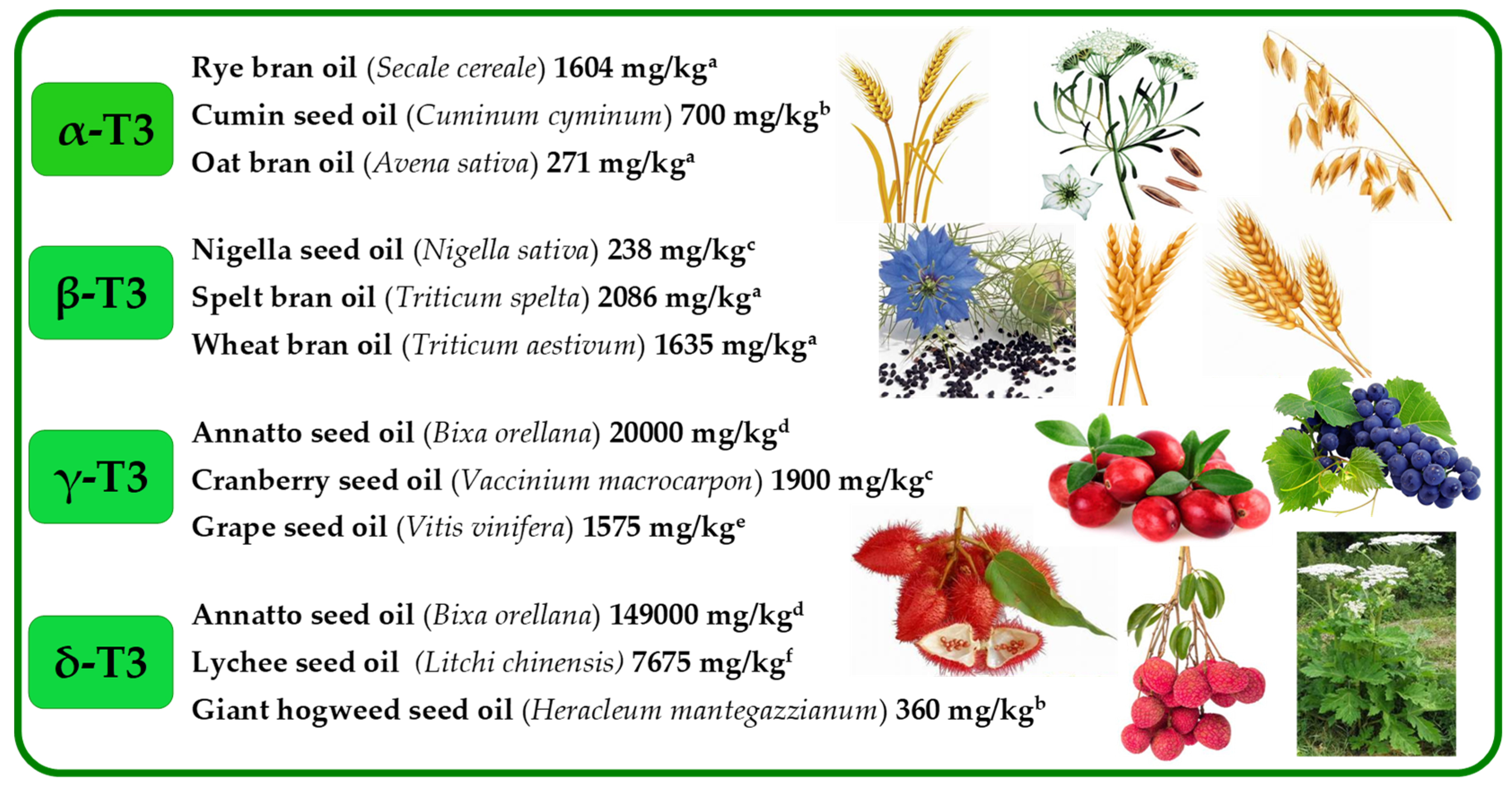
2. Tocochomanols—History, Terminology, Structure, and the Main Known Sources
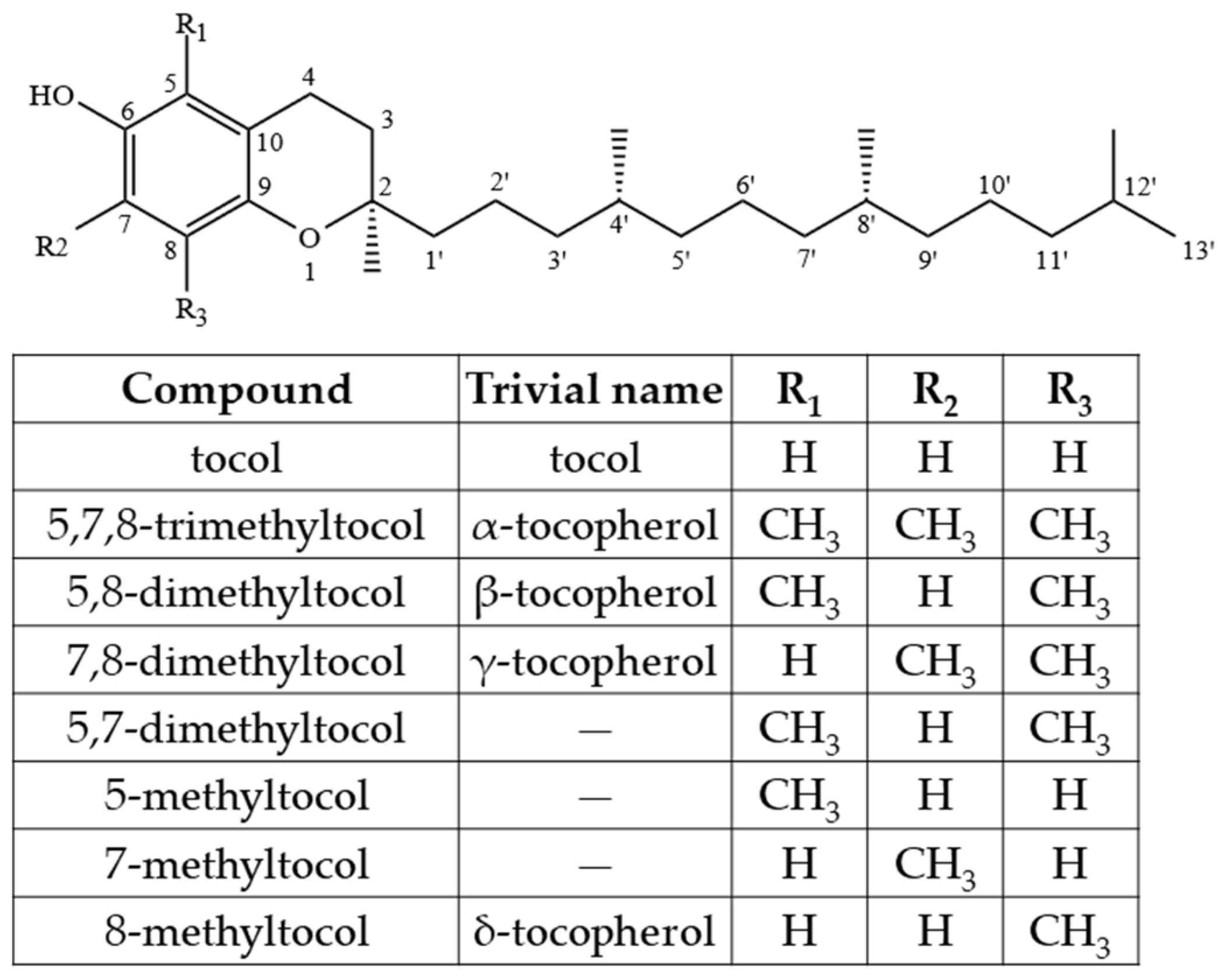
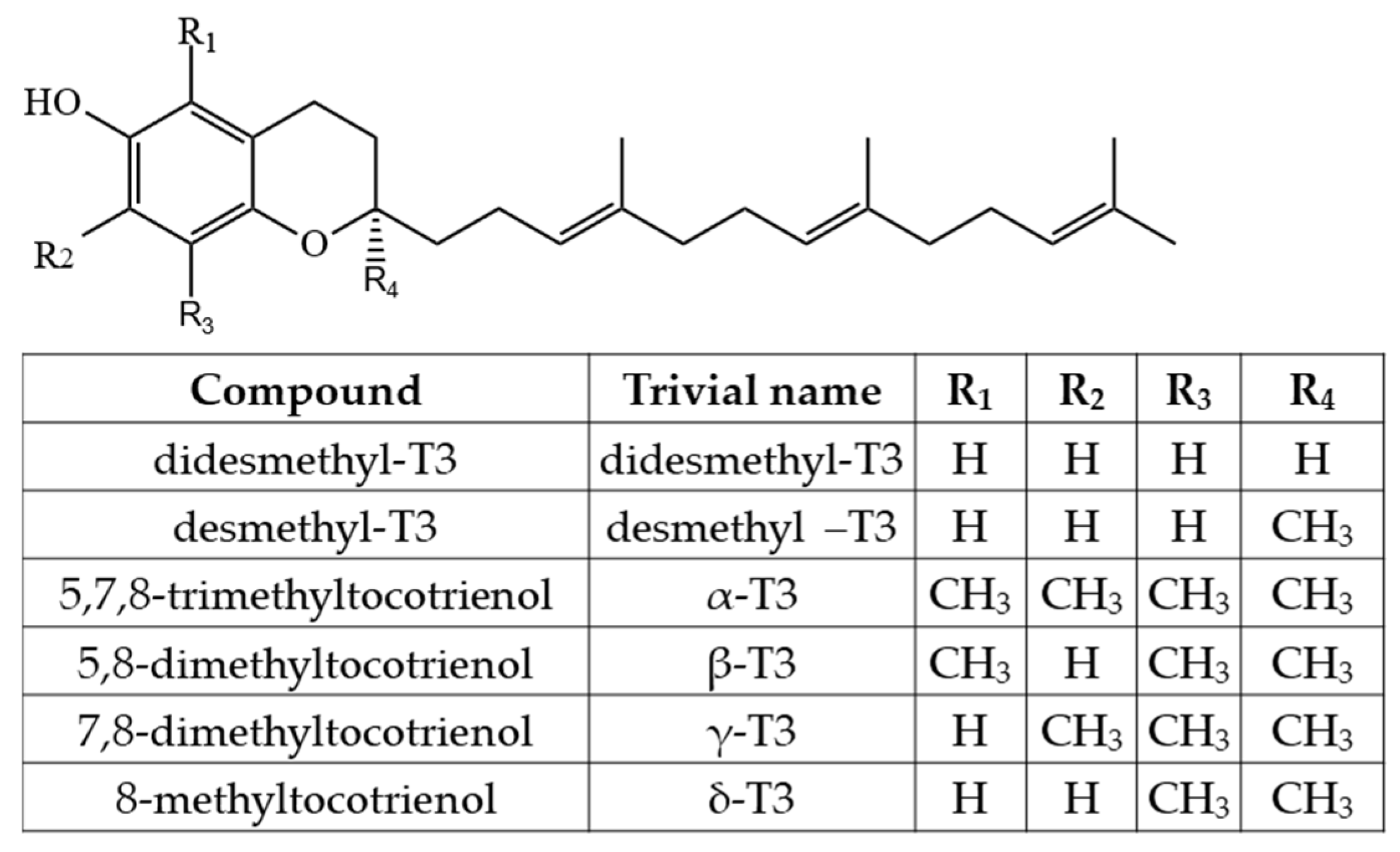
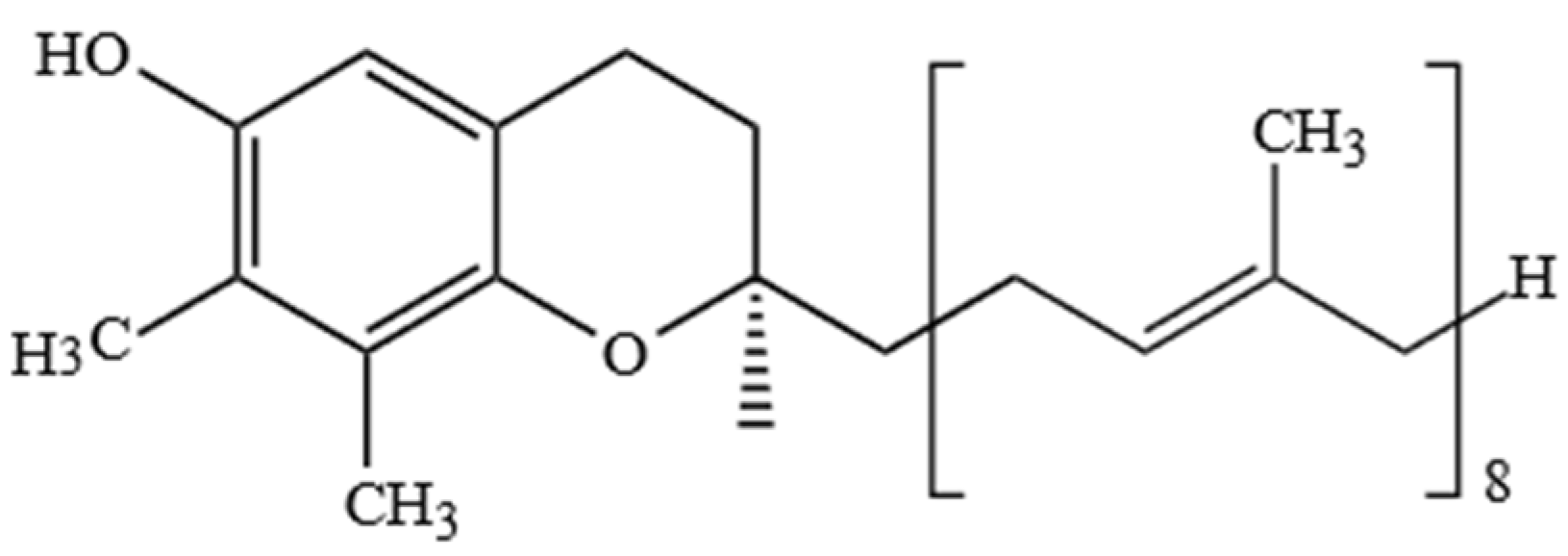
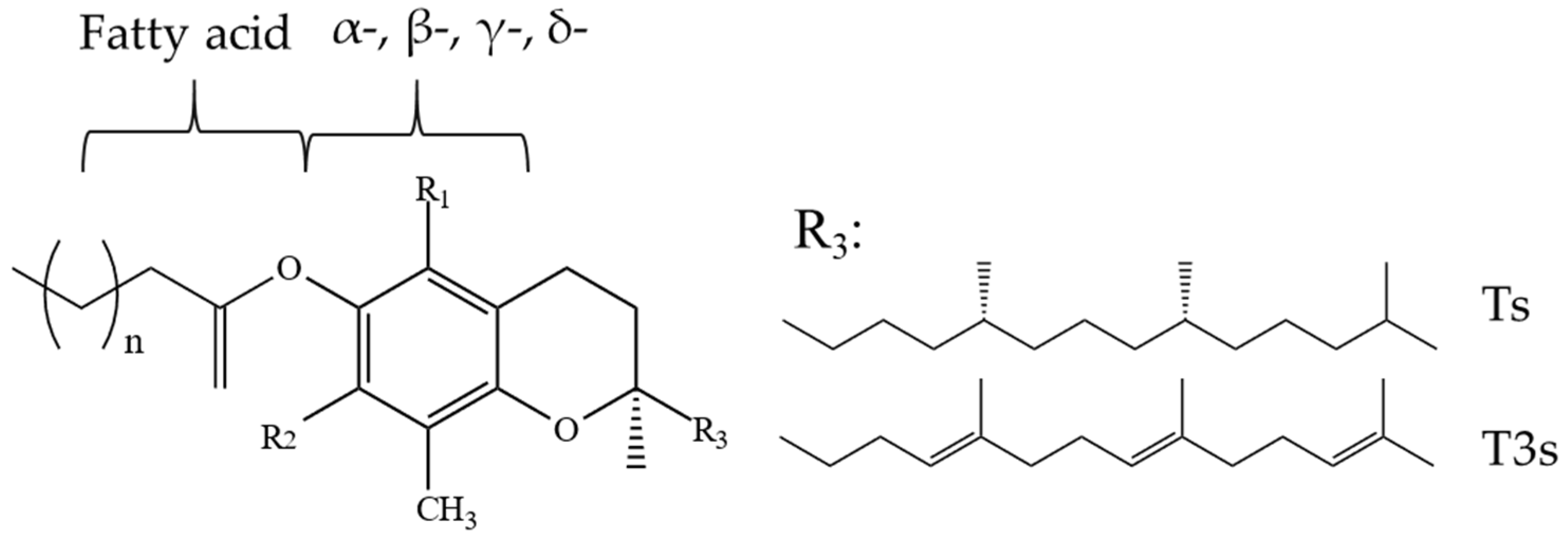
2.1. Tocopherols (Ts), Tocotrienols (T3s), and Plastochromanol-8 (PC-8)
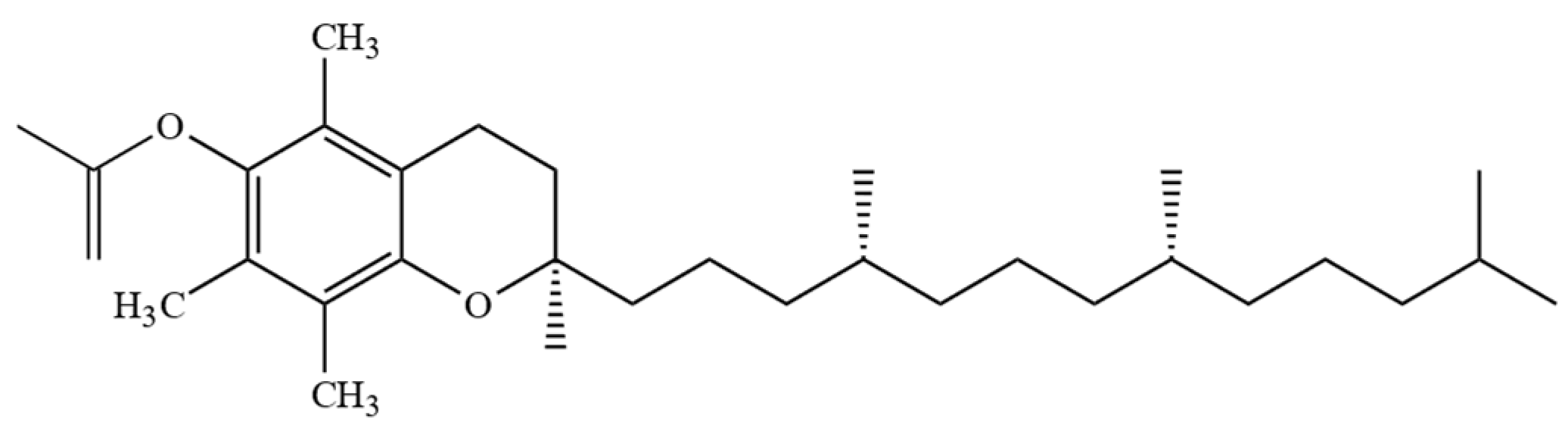
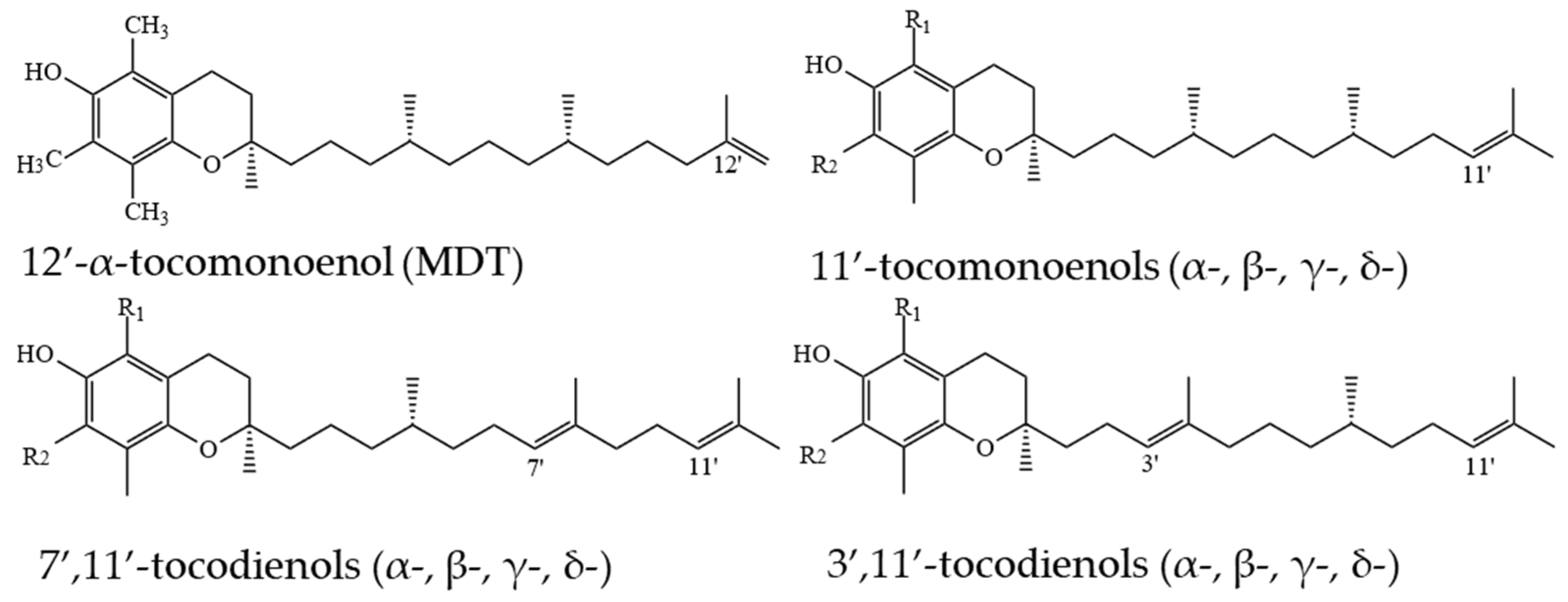
2.2. Tocomonoenols (T1s) and Tocodienols (T2s)
2.3. Bound Tocochromanols
3. Extraction of Tocochromanols
3.1. Sample Preparation and Extraction Techniques
- Sample Dilution
- Direct Solvent Extraction
- Saponification
- Alternative Techniques
3.2. Important Aspects in Extraction of Tocochromanols
- Bound and Free Tocochromanols
- Non-Extractable Tocochromanols
- Roasting—Challenges after Sample Treatment for Tocochromanol Determination
3.3. Lab-Scale Isolation, Synthesis, and Purification of Tocochromanols
4. Chromatographic Techniques Used for Tocochromanol Determination
4.1. Liquid Chromatography (LC)
- Normal-Phase (NP)
- Reverse-Phase (RP)
- PC-8 Issue
- C18 Column Issue
- Detectors Used in LC
4.2. Gas Chromatography (GC)
4.3. Supercritical Fluid Chromatography (SFC)
- Detectors Used in SFC
4.4. Mass Spectrometry Techniques
4.5. Chromatographical Determination of Tocomonoenols (T1s), Tocodienols (T2s) and Esterified Tocochromanols (ETs)
5. Summary, Future Perspectives and Recommendations
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Evans, H.M.; Bishop, K.S. On the existence of a hitherto unrecognized dietary factor essential for reproduction. Science 1922, 56, 650–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Emerson, O.H.; Emerson, G.A.; Mohammad, A.; Evans, H.M. The chemistry of vitamin E. Tocopherols from various sources. J. Biol. Chem. 1937, 122, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzi, A. Tocopherols, tocotrienols and tocomonoenols: Many similar molecules but only one vitamin E. Redox Biol. 2019, 26, 101259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shintani, D.; DellaPenna, D. Elevating the vitamin E content of plants through metabolic engineering. Science 1998, 282, 2098–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szymańska, R.; Kruk, J. Novel and rare prenyllipids—Occurrence and biological activity. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 122, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peh, H.Y.; Tan, W.S.D.; Liao, W.; Wong, W.S.F. Vitamin E therapy beyond cancer: Tocopherol versus tocotrienol. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 162, 152–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, B.B.; Sundaram, C.; Prasad, S.; Kannappan, R. Tocotrienols, the vitamin E of the 21st century: Its potential against cancer and other chronic diseases. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2010, 80, 1613–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahsan, H.; Ahad, A.; Iqbal, J.; Siddiqui, W.A. Pharmacological potential of tocotrienols: A review. Nutr. Metab. 2014, 11, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, C.S.; Luo, P.; Zeng, Z.; Wang, H.; Malafa, M.; Suh, N. Vitamin E and cancer prevention: Studies with different forms of tocopherols and tocotrienols. Mol. Carcinog. 2020, 59, 365–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krauß, S.; Darwisch, V.; Vetter, W. Occurrence of tocopheryl fatty acid esters in vegetables and their non-digestibility by artificial digestion juices. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 7657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panfili, G.; Fratianni, A.; Irano, M. Normal phase high-performance liquid chromatography method for the determination of tocopherols and tocotrienols in cereals. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 3940–3944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baškirovs, G.; Soliven, A.; Górnaś, P. Analytical scale supercritical fluid chromatography for the analysis of nine tocochromanols in 24 different cold-pressed plant oils: Method development, validation, and isolation of tocotrienols and plastochromanol-8. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2022, 110, 104586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siger, A.; Kachlicki, P.; Czubiński, J.; Polcyn, D.; Dwiecki, K.; Nogala-Kalucka, M. Isolation and purification of plastochromanol-8 for HPLC quantitative determinations. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2014, 116, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beppu, F.; Gotoh, N. Analysis of minor vitamin E homologues in natural products. J. Berry Res. 2021, 11, 555–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montoya-Arroyo, A.; Lehnert, K.; Lux, P.E.; Jiménez, V.M.; Esquivel, P.; Silva-Benavides, A.M.; Vetter, W.; Frank, J. 11′-α-Tocomonoenol is the major α-tocomonoenol isomer in cyanobacteria and microalgae from Costa Rica. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2022, 107, 104325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kröpfl, A.; Nemetz, N.J.; Goncalves Peca, A.; Vetter, W. Countercurrent chromatography isolation of 11′-γ-tocomonoenol from pumpkin seed oil with detection of novel minor tocochromanols. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2022, 99, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammann, S.; Kröpfl, A.; Vetter, W. More than 170 polyunsaturated tocopherol-related compounds in a vitamin E capsule: Countercurrent chromatographic enrichment, gas chromatography/mass spectrometry analysis and preliminary identification of the potential artefacts. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1476, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González, A.; Pablos, F.; Martın, M.; León-Camacho, M.; Valdenebro, M. HPLC analysis of tocopherols and triglycerides in coffee and their use as authentication parameters. Food Chem. 2001, 73, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Górnaś, P.; Siger, A.; Pugajeva, I.; Czubinski, J.; Waśkiewicz, A.; Polewski, K. New insights regarding tocopherols in Arabica and Robusta species coffee beans: RP-UPLC-ESI/MSn and NP-HPLC/FLD study. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2014, 36, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kröpfl, A.; Schweizer, S.; Vetter, W. Quantification of tocochromanols in vitamin E dietary supplements by instrumental thin-layer chromatography. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2022, 248, 1653–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandolini, A.; Glorio-Paulet, P.; Estivi, L.; Locatelli, N.; Cordova-Ramos, J.S.; Hidalgo, A. Tocopherols, carotenoids and phenolics changes during Andean lupin (Lupinus mutabilis Sweet) seeds processing. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2022, 106, 104335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buddrick, O.; Jones, O.A.; Morrison, P.D.; Small, D.M. Heptane as a less toxic option than hexane for the separation of vitamin E from food products using normal phase HPLC. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 24063–24068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birringer, M.; Siems, K.; Maxones, A.; Frank, J.; Lorkowski, S. Natural 6-hydroxy-chromanols and-chromenols: Structural diversity, biosynthetic pathways and health implications. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 4803–4841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abidi, S.L. Chromatographic analysis of tocol-derived lipid antioxidants. J. Chromatogr. A 2000, 881, 197–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, R.S.; Mah, E. Vitamin E. In Reference Module in Biomedical Sciences, 3rd ed.; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Qureshi, A.A.; Mo, H.; Packer, L.; Peterson, D.M. Isolation and identification of novel tocotrienols from rice bran with hypocholesterolemic, antioxidant, and antitumor properties. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 3130–3140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sontag, T.J.; Parker, R.S. Influence of major structural features of tocopherols and tocotrienols on their ω-oxidation by tocopherol-ω-hydroxylase. J. Lipid Res. 2007, 48, 1090–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cervinkova, B.; Krcmova, L.K.; Klabackova, S.; Solichova, D.; Solich, P. Rapid determination of lipophilic vitamins in human serum by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography using a fluorinated column and high-throughput miniaturized liquid–liquid extraction. J. Sep. Sci. 2017, 40, 3375–3382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanagi, M.M.; See, H.H.; Ibrahim, W.A.W.; Naim, A.A. Separation of tocol–derivatives by elevated temperature normal–phase liquid chromatography. J. Teknol. 2006, 45, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Górnaś, P.; Šnē, E.; Siger, A.; Segliņa, D. Sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.) leaves as valuable source of lipophilic antioxidants: The effect of harvest time, sex, drying and extraction methods. Ind. Crops Prod. 2014, 60, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymańska, R.; Kruk, J. γ-Tocopherol dominates in young leaves of runner bean (Phaseolus coccineus) under a variety of growing conditions: The possible functions of γ-tocopherol. Phytochemistry 2008, 69, 2142–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojdyło, A.; Turkiewicz, I.P.; Tkacz, K.; Hernandez, F. Fruit tree leaves as valuable new source of tocopherol and tocotrienol compounds. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2022, 102, 1466–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DellaPenna, D. A decade of progress in understanding vitamin E synthesis in plants. J. Plant Physiol. 2005, 162, 729–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakradhari, S.; Perkons, I.; Mišina, I.; Sipeniece, E.; Radziejewska-Kubzdela, E.; Grygier, A.; Rudzińska, M.; Patel, K.S.; Radzimirska-Graczyk, M.; Górnaś, P. Profiling of the bioactive components of safflower seeds and seed oil: Cultivated (Carthamus tinctorius L.) vs. wild (Carthamus oxyacantha M. Bieb.). Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2020, 246, 449–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Górnaś, P.; Soliven, A.; Segliņa, D. Seed oils recovered from industrial fruit by-products are a rich source of tocopherols and tocotrienols: Rapid separation of α/β/γ/δ homologues by RP-HPLC/FLD. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2015, 117, 773–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruszka, J.; Kruk, J. RP-LC for determination of plastochromanol, tocotrienols and tocopherols in plant oils. Chromatographia 2007, 66, 909–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trela, A.; Szymańska, R. Less widespread plant oils as a good source of vitamin E. Food Chem. 2019, 296, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Górnaś, P.; Rudzińska, M.; Raczyk, M.; Soliven, A. Lipophilic bioactive compounds in the oils recovered from cereal by-products. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2016, 96, 3256–3265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, R.C.; Casal, S.; Alves, M.R.; Oliveira, M.B. Discrimination between arabica and robusta coffee species on the basis of their tocopherol profiles. Food Chem. 2009, 114, 295–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Górnaś, P. Oak Quercus rubra L. and Quercus robur L. acorns as an unconventional source of gamma-and beta-tocopherol. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2019, 245, 257–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fromm, M.; Bayha, S.; Kammerer, D.R.; Carle, R. Identification and quantitation of carotenoids and tocopherols in seed oils recovered from different rosaceae species. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 10733–10742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Górnaś, P. Unique variability of tocopherol composition in various seed oils recovered from by-products of apple industry: Rapid and simple determination of all four homologues (α, β, γ and δ) by RP-HPLC/FLD. Food Chem. 2015, 172, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraujalis, P.; Kraujalienė, V.; Kazernavičiūtė, R.; Venskutonis, P.R. Supercritical carbon dioxide and pressurized liquid extraction of valuable ingredients from Viburnum opulus pomace and berries and evaluation of product characteristics. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2017, 122, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariod, A.A.; Elkheir, S.; Ahmed, Y.M.; Matthäus, B. Annona squamosa and Catunaregam nilotica seeds, the effect of the extraction method on the oil composition. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2010, 87, 763–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.food.actapol.net/pub/4_3_2012_err.pdf (accessed on 25 July 2022).
- Fabrikov, D.; Guil-Guerrero, J.L.; González-Fernández, M.J.; Rodríguez-García, I.; Gómez-Mercado, F.; Urrestarazu, M.; Lao, M.T.; Rincón-Cervera, M.Á.; Alvaro, J.E.; Lyashenko, S. Borage oil: Tocopherols, sterols and squalene in farmed and endemic-wild Borago species. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2019, 83, 103299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siger, A.; Dwiecki, K.; Borzyszkowski, W.; Turski, M.; Rudzińska, M.; Nogala-Kałucka, M. Physicochemical characteristics of the cold-pressed oil obtained from seeds of Fagus sylvatica L. Food Chem. 2017, 225, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horvath, G.; Wessjohann, L.; Bigirimana, J.; Jansen, M.; Guisez, Y.; Caubergs, R.; Horemans, N. Differential distribution of tocopherols and tocotrienols in photosynthetic and non-photosynthetic tissues. Phytochemistry 2006, 67, 1185–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagci, E. Fatty acids and tocochromanol patterns of some Turkish Apiaceae (Umbelliferae) plants; a chemotaxonomic approach. Acta Bot. Gall. 2007, 154, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, S.A.; Aitzetmüller, K. Untersuchungen über die Tocopherol-und Tocotrienolzusammensetzung der Samenöle einiger Vertreter der Familie Apiaceae. Lipid/Fett 1995, 97, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramadan, M.F. Healthy blends of high linoleic sunflower oil with selected cold pressed oils: Functionality, stability and antioxidative characteristics. Ind. Crops Prod. 2013, 43, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gee, P.T.; Liew, C.Y.; Thong, M.C.; Gay, M.C.L. Vitamin E analysis by ultra-performance convergence chromatography and structural elucidation of novel α-tocodienol by high-resolution mass spectrometry. Food Chem. 2016, 196, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunphy, P.J.; Whittle, K.J.; Pennock, J.F.; Morton, R.A. Identification and estimation of tocotrienols in Hevea latex. Nature 1965, 207, 521–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabot, G.L.; Moraes, M.N.; Meireles, M. Process integration for producing tocotrienols-rich oil and bixin-rich extract from annatto seeds: A techno-economic approach. Food Bioprod. Process. 2018, 109, 122–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nehdi, I.A. Characteristics and composition of Washingtonia filifera (Linden ex André) H. Wendl. seed and seed oil. Food Chem. 2011, 126, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Ahotupa, M.; Määttä, P.; Kallio, H. Composition and antioxidative activities of supercritical CO2-extracted oils from seeds and soft parts of northern berries. Food Res. Int. 2011, 44, 2009–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, L.; Casal, S.; Cruz, R.; Pereira, J.A.; Ramalhosa, E. Seed oils of ten traditional Portuguese grape varieties with interesting chemical and antioxidant properties. Food Res. Int. 2013, 50, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiozaki, S.; Murakami, K. Lipids in the seeds of wild grapes native to Japan: Vitis coignetiae and Vitis ficifolia var. ganebu. Sci. Hortic. 2016, 201, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Górnaś, P.; Rudzińska, M.; Grygier, A.; Lācis, G. Diversity of oil yield, fatty acids, tocopherols, tocotrienols, and sterols in the seeds of 19 interspecific grapes crosses. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2019, 99, 2078–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horvath, G.; Wessjohann, L.; Bigirimana, J.; Monica, H.; Jansen, M.; Guisez, Y.; Caubergs, R.; Horemans, N. Accumulation of tocopherols and tocotrienols during seed development of grape (Vitis vinifera L. cv. Albert Lavallée). Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2006, 44, 724–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Górnaś, P.; Šnē, E.; Siger, A.; Segliņa, D. Sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.) vegetative parts as an unconventional source of lipophilic antioxidants. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2016, 23, 512–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sipeniece, E.; Mišina, I.; Grygier, A.; Qian, Y.; Rudzińska, M.; Kaufmane, E.; Segliņa, D.; Siger, A.; Górnaś, P. Impact of the harvest year of three cultivars of Japanese quince (Chaenomeles japonica) on the oil content and its composition. Sci. Hortic. 2021, 275, 109683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthäus, B.; Vosmann, K.; Pham, L.Q.; Aitzetmüller, K. FA and tocopherol composition of Vietnamese oilseeds. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2003, 80, 1013–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whittle, K.J.; Dunphy, P.J.; Pennock, J.F. Plastochromanol in the leaves of Hevea brasiliensis. Biochem. J. 1965, 96, 17C–19C. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kruk, J.; Szymańska, R.; Cela, J.; Munne-Bosch, S. Plastochromanol-8: Fifty years of research. Phytochemistry 2014, 108, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nogala-Kalucka, M.; Gogolewski, M.; Musnicki, C. Changes of tocopherol and plastochromanol-8 contents during growth of the spring oilseed rape plant [Brassica napus L.]. Oilseed Crops 2002, 23, 157–164. [Google Scholar]
- Fleta-Soriano, E.; Munné-Bosch, S. Enhanced plastochromanol-8 accumulation during reiterated drought in maize (Zea mays L.). Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 112, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymańska, R.; Kruk, J. Identification of hydroxy-plastochromanol in Arabidopsis leaves. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2010, 57, 105–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matsumoto, A.; Takahashi, S.; Nakano, K.; Kijima, S. Identification of new vitamin E in plant oil. J. Jpn. Oil Chem. Soc. 1995, 44, 593–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamamoto, Y.; Maita, N.; Fujisawa, A.; Takashima, J.; Ishii, Y.; Dunlap, W.C. A new vitamin E (α-tocomonoenol) from eggs of the pacific salmon Oncorhynchus keta. J. Nat. Prod. 1999, 62, 1685–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunlap, W.C.; Fujisawa, A.; Yamamoto, Y.; Moylan, T.J.; Sidell, B.D. Notothenioid fish, krill and phytoplankton from Antarctica contain a vitamin E constituent (α-tocomonoenol) functionally associated with cold-water adaptation. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B: Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2002, 133, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, M.H.; Choo, Y.M.; Ma, A.N.; Chuah, C.H.; Hashim, M.A. Separation of vitamin E (tocopherol, tocotrienol, and tocomonoenol) in palm oil. Lipids 2004, 39, 1031–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, M.; Kröpfl, A.; Vetter, W. Identification of two α-tocodienol isomers in palm oil after countercurrent chromatographic enrichment. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2020, 412, 795–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruk, J.; Pisarski, A.; Szymańska, R. Novel vitamin E forms in leaves of Kalanchoe daigremontiana and Phaseolus coccineus. J. Plant Physiol. 2011, 168, 2021–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiorentino, A.; Mastellone, C.; D’Abrosca, B.; Pacifico, S.; Scognamiglio, M.; Cefarelli, G.; Caputo, R.; Monaco, P. δ-Tocomonoenol: A new vitamin E from kiwi (Actinidia chinensis) fruits. Food Chem. 2009, 115, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariani, C.; Bellan, G. Content of tocopherols, deidrotocopherols, tocodienols, tocotrienols in vegetable oils. Riv. Ital. Sostanze Grasse 1996, 73, 533–543. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Gujarathi, S.; Zhang, X.; Shao, L.; Boerma, M.; Compadre, C.M.; Crooks, P.A.; Hauer-Jensen, M.; Zhou, D.; Zheng, G. Synthesis of (2R, 8′ S, 3′ E)-δ-tocodienol, a tocoflexol family member designed to have a superior pharmacokinetic profile compared to δ-tocotrienol. Tetrahedron 2016, 72, 4001–4006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Compadre, C.M.; Singh, A.; Thakkar, S.; Zheng, G.; Breen, P.J.; Ghosh, S.; Kiaei, M.; Boerma, M.; Varughese, K.I.; Hauer-Jensen, M. Molecular dynamics guided design of tocoflexol: A new radioprotectant tocotrienol with enhanced bioavailability. Drug Dev. Res. 2014, 75, 10–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baxter, J.G.; Robeson, C.D.; Taylor, J.D.; Lehman, R.W. Natural α-, β-and γ-tocopherols and certain esters of physiological interest. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1943, 65, 918–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zingg, J.-M. Water-Soluble Vitamin E—Tocopheryl Phosphate. Adv. Food Nutr. Res. 2018, 83, 311–363. [Google Scholar]
- Kato, A.; Tanabe, K.; Yamaoka, M. Esterified tocopherols and tocotrienols in rice bran oil, soybean oil, and sesame oil. J. Jpn. Oil Chem. Soc. 1981, 30, 515–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kato, A.; Gapor, A.; Tanabe, K.; Yamaoka, M.; Mamuro, H. Esterified a-tocopherol and tocotrienols in palm oils. J. Jpn. Oil Chem. Soc. 1981, 30, 590–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olejnik, D. The occurrence of free and bounded forms of tocopherols in certain oil seeds. Rocz. Technol. Chem. Żywn. 1972, 22, 15–23. [Google Scholar]
- Ciemniewska-Żytkiewicz, H.; Verardo, V.; Pasini, F.; Bryś, J.; Koczoń, P.; Caboni, M.F. Determination of lipid and phenolic fraction in two hazelnut (Corylus avellana L.) cultivars grown in Poland. Food Chem. 2015, 168, 615–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klink, G.; Buchs, A.; Gülacar, F.O. Tocopheryl esters from Nymphea alba and Nuphar luteum. Phytochemistry 1994, 36, 813–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krauß, S.; Hermann-Ene, V.; Vetter, W. Fate of free and bound phytol and tocopherols during fruit ripening of two Capsicum cultivars. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreps, F.; Kyselka, J.; Burčová, Z.; Schmidt, Š.; Filip, V.; Dubaj, T.; Gajdoš, P.; Čertík, M. Synthesis and analysis of tocopheryl quinone and tocopherol esters with fatty acids in heated sunflower oil. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2016, 118, 788–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreps, F.; Kyselka, J.; Burčová, Z.; Schmidt, Š.; Rajchl, A.; Filip, V.; Ház, A.; Jablonský, M.; Sládková, A.; Šurina, I. Influence of deodorization temperature on formation of tocopherol esters and fatty acids polymers in vegetable oil. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2017, 119, 1600027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, L.; Akoh, C.C. Identification of tocopherols, tocotrienols, and their fatty acid esters in residues and distillates of structured lipids purified by short-path distillation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimoda, K.; Kondo, Y.; Akagi, M.; Abe, K.; Hamada, H.; Hamada, H. Glycosylation of tocopherols by cultured cells of Eucalyptus perriniana. Phytochemistry 2007, 68, 2678–2683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Górnaś, P.; Siger, A.; Czubinski, J.; Dwiecki, K.; Segliņa, D.; Nogala-Kalucka, M. An alternative RP-HPLC method for the separation and determination of tocopherol and tocotrienol homologues as butter authenticity markers: A comparative study between two European countries. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2014, 116, 895–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Górnaś, P.; Siger, A. Simplified sample preparation and rapid detection by RP-HPLC/FLD of tocopherols and tocotrienols in margarines: Preliminary screening of plant fats—Potential quality markers. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2015, 117, 1589–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Górnaś, P.; Siger, A.; Juhņeviča, K.; Lācis, G.; Šnē, E.; Segliņa, D. Cold-pressed Japanese quince (Chaenomeles japonica (Thunb.) Lindl. ex Spach) seed oil as a rich source of α-tocopherol, carotenoids and phenolics: A comparison of the composition and antioxidant activity with nine other plant oils. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2014, 116, 563–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Méjean, M.; Brunelle, A.; Touboul, D. Quantification of tocopherols and tocotrienols in soybean oil by supercritical-fluid chromatography coupled to high-resolution mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 5133–5142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puspitasari-Nienaber, N.L.; Ferruzzi, M.G.; Schwartz, S.J. Simultaneous detection of tocopherols, carotenoids, and chlorophylls in vegetable oils by direct injection C30 RP-HPLC with coulometric electrochemical array detection. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2002, 79, 633–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansolin, M.; de Souza, P.T.; de Almeida Meirelles, A.J.; Batista, E.A.C. Tocopherols and tocotrienols: An adapted methodology by UHPLC/MS without sample pretreatment steps. Food Anal. Methods 2017, 10, 2165–2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalogeropoulos, N.; Chiou, A.; Ioannou, M.; Karathanos, V.T.; Hassapidou, M.; Andrikopoulos, N.K. Nutritional evaluation and bioactive microconstituents (phytosterols, tocopherols, polyphenols, triterpenic acids) in cooked dry legumes usually consumed in the Mediterranean countries. Food Chem. 2010, 121, 682–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.W.; Zhang, H.; Liang, X.; Ong, C.N. Simultaneous determination of carotenoids, tocopherols and phylloquinone in 12 Brassicaceae vegetables. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 130, 109649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.W.; Bi, X.; Henry, C.J. Carotenoids, tocopherols and phylloquinone content of 26 green leafy vegetables commonly consumed in Southeast Asia. Food Chem. 2022, 385, 132729. [Google Scholar]
- Saini, R.K.; Keum, Y.-S. Tocopherols and tocotrienols in plants and their products: A review on methods of extraction, chromatographic separation, and detection. Food Res. Int. 2016, 82, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knecht, K.; Sandfuchs, K.; Kulling, S.E.; Bunzel, D. Tocopherol and tocotrienol analysis in raw and cooked vegetables: A validated method with emphasis on sample preparation. Food Chem. 2015, 169, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryynänen, M.; Lampi, A.-M.; Salo-Väänänen, P.; Ollilainen, V.; Piironen, V. A small-scale sample preparation method with HPLC analysis for determination of tocopherols and tocotrienols in cereals. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2004, 17, 749–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Górnaś, P.; Pugajeva, I.; Segliņa, D. Seeds recovered from by-products of selected fruit processing as a rich source of tocochromanols: RP-HPLC/FLD and RP-UPLC-ESI/MSn study. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2014, 239, 519–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, S.; Yang, R.; Mao, J.; Jiang, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Q.; Li, P. Simultaneous determination of tocopherols, carotenoids and phytosterols in edible vegetable oil by ultrasound-assisted saponification, LLE and LC-MS/MS. Food Chem. 2019, 289, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souza, A.H.P.; Gohara, A.K.; Rodrigues, Â.C.; Ströher, G.L.; Silva, D.C.; Visentainer, J.V.; Souza, N.E.; Matsushita, M. Optimization conditions of samples saponification for tocopherol analysis. Food Chem. 2014, 158, 315–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Piironen, V.; Syvaoja, E.L.; Varo, P.; Salminen, K.; Koivistoinen, P. Tocopherols and tocotrienols in cereal products from Finland. Cereal Chem. 1986, 63, 78–81. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, M.G.; Hamerski, F.; Andrade, E.F.; Scheer, A.d.P.; Corazza, M.L. Assessment of subcritical propane, ultrasound-assisted and Soxhlet extraction of oil from sweet passion fruit (Passiflora alata Curtis) seeds. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2017, 128, 338–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fratianni, A.; Caboni, M.; Irano, M.; Panfili, G. A critical comparison between traditional methods and supercritical carbon dioxide extraction for the determination of tocochromanols in cereals. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2002, 215, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Górnaś, P.; Siger, A.; Rudzińska, M.; Grygier, A.; Marszałkiewicz, S.; Ying, Q.; Sobieszczańska, N.; Segliņa, D. Impact of the extraction technique and genotype on the oil yield and composition of lipophilic compounds in the oil recovered from Japanese quince (Chaenomeles japonica) seeds. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2019, 121, 1800262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiao, X.-H.; Wang, J.-X.; Wang, G.; Wang, J.-Y.; Li, G.-K. Evaluation of vacuum microwave-assisted extraction technique for the extraction of antioxidants from plant samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2009, 1216, 8867–8873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vafaei, N.; Rempel, C.B.; Scanlon, M.G.; Jones, P.J.H.; Eskin, M.N.A. Application of supercritical fluid extraction (SFE) of tocopherols and carotenoids (hydrophobic antioxidants) compared to non-SFE methods. AppliedChem 2022, 2, 68–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Jiménez, J.; Saura-Calixto, F. Fruit peels as sources of non-extractable polyphenols or macromolecular antioxidants: Analysis and nutritional implications. Food Res. Int. 2018, 111, 148–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez-Rodríguez, G.; Marina, M.L.; Plaza, M. Enzyme-assisted extraction of bioactive non-extractable polyphenols from sweet cherry (Prunus avium L.) pomace. Food Chem. 2021, 339, 128086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.; Huang, S.; Shi, Y.; Shao, Y.; Qiu, J.; Sedjoah, R.-C.A.-A.; Yan, Z.; Ding, L.; Zou, D.; Xin, Z. Extraction, isolation, characterization and antimicrobial activities of non-extractable polyphenols from pomegranate peel. Food Chem. 2021, 351, 129232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynoso-Camacho, R.; Sotelo-González, A.M.; Patiño-Ortiz, P.; Rocha-Guzmán, N.E.; Pérez-Ramírez, I.F. Berry by-products obtained from a decoction process are a rich source of low-and high-molecular weight extractable and non-extractable polyphenols. Food Bioprod. Process. 2021, 127, 371–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez-Rodríguez, G.; Plaza, M.; Marina, M.L. High-performance thin-layer chromatography and direct analysis in real time-high resolution mass spectrometry of non-extractable polyphenols from tropical fruit peels. Food Res. Int. 2021, 147, 110455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domínguez-Rodríguez, G.; Marina, M.L.; Plaza, M. Rapid fingerprinting of extractable and non-extractable polyphenols from tropical fruit peels using direct analysis in real time coupled to orbitrap mass spectrometry. Food Chem. 2022, 371, 131191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez-Rodríguez, G.; Marina, M.L.; Plaza, M. Strategies for the extraction and analysis of non-extractable polyphenols from plants. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1514, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahidi, F.; De Camargo, A.C. Tocopherols and tocotrienols in common and emerging dietary sources: Occurrence, applications, and health benefits. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, K.; Gemechu, F.G.; De Meulenaer, B. A novel insight on the high oxidative stability of roasted mustard seed oil in relation to phospholipid, Maillard type reaction products, tocopherol and canolol contents. Food Res. Int. 2013, 54, 587–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murkovic, M.; Piironen, V.; Lampi, A.M.; Kraushofer, T.; Sontag, G. Changes in chemical composition of pumpkin seeds during the roasting process for production of pumpkin seed oil (Part 1: Non-volatile compounds). Food Chem. 2004, 84, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siger, A.; Kaczmarek, A.; Rudzińska, M. Antioxidant activity and phytochemical content of cold-pressed rapeseed oil obtained from roasted seeds. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2015, 117, 1225–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, R.J.; Mateo, C.M.; Fernández, M.B.; Nolasco, S.M. Bidimensional modeling applied to oil extraction kinetics of microwave-pretreated canola seeds. J. Food Eng. 2017, 192, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, K.; De Meulenaer, B. Effect of seed roasting on canolol, tocopherol, and phospholipid contents, Maillard type reactions, and oxidative stability of mustard and rapeseed oils. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 5412–5419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eitenmiller, R.; Lee, J. Vitamin E: Food Chemistry, Composition, and Analysis; Marcel Dekker Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Dawson, R.M.C.; Elliott, D.C.; Elliott, W.H.; Jones, K.M. Data for Biochemical Research; Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Saito, M.; Yamauchi, Y. Isolation of tocopherols from wheat germ oil by recycle semi-preparative supercritical fluid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 1990, 505, 257–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, J.; Zhang, W.; Jiang, B.; Guo, Y.; Hu, C. Separation of individual tocopherols from soybean distillate by low pressure column chromatography. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2008, 85, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruszka, J.; Pawlak, A.; Kruk, J. Tocochromanols, plastoquinol, and other biological prenyllipids as singlet oxygen quenchers—Determination of singlet oxygen quenching rate constants and oxidation products. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2008, 45, 920–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotoh, N.; Watanabe, H.; Oka, T.; Mashimo, D.; Noguchi, N.; Hata, K.; Wada, S. Dietary marine-derived tocopherol has a higher biological availability in mice relative to alpha-tocopherol. Lipids 2009, 44, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beppu, F.; Sakuma, A.; Kasatani, S.; Aoki, Y.; Gotoh, N. Application of partial hydrogenation for the generation of minor tocochromanol homologs and functional evaluation of hydrogenated tocotrienol-rich vitamin E oil in diabetic obese mice. J. Oleo Sci. 2021, 70, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Büsing, A.; Ternes, W. Separation of α-tocotrienol oxidation products and eight tocochromanols by HPLC with DAD and fluorescence detection and identification of unknown peaks by DAD, PBI-EIMS, FTIR, and NMR. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 401, 2843–2854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Niekerk, P.J. The direct determination of free tocopherols in plant oils by liquid-solid chromatography. Anal. Biochem. 1973, 52, 533–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamal-Eldin, A.; Görgen, S.; Pettersson, J.; Lampi, A.-M. Normal-phase high-performance liquid chromatography of tocopherols and tocotrienols: Comparison of different chromatographic columns. J. Chromatogr. A 2000, 881, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abidi, S.L.; Mounts, T.L. Normal phase high-performance liquid chromatography of tocopherols on polar phases. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 1996, 19, 509–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balz, M.K.; Schulte, E.; Thier, H.P. Simultaneous determination of α-tocopheryl acetate, tocopherols and tocotrienols by HPLC with fluorescence detection in foods. Lipid/Fett 1993, 95, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z. Analysis of tocopherols and tocotrienols. Curr. Protoc. Food Anal. Chem. 2002, 4, D1.5.1–D1.5.12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthaus, B.; Özcan, M.M. Chemical evaluation of citrus seeds, an agro-industrial waste, as a new potential source of vegetable oils. Grasas Aceites 2012, 63, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siger, A.; Michalak, M.; Cegielska-Taras, T.; Szała, L.; Lembicz, J.; Nogala-Kałucka, M. Genotype and environment effects on tocopherol and plastochromanol-8 contents of winter oilseed rape doubled haploid lines derived from F1 plants of the cross between yellow and black seeds. Ind. Crops Prod. 2015, 65, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grebenstein, N.; Frank, J. Rapid baseline-separation of all eight tocopherols and tocotrienols by reversed-phase liquid-chromatography with a solid-core pentafluorophenyl column and their sensitive quantification in plasma and liver. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1243, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimmer, C.A.; Putzbach, K.; Sharpless, K.E.; Sander, L.C.; Yen, J.H. Preparation and certification of standard reference material 3278 tocopherols in edible oils. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 6794–6798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irías-Mata, A.; Stuetz, W.; Sus, N.; Hammann, S.; Gralla, K.; Cordero-Solano, A.; Vetter, W.; Frank, J. Tocopherols, tocomonoenols, and tocotrienols in oils of costa rican palm fruits: A comparison between six varieties and chemical versus mechanical extraction. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 7476–7482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strohschein, S.; Pursch, M.; Lubda, D.; Albert, K. Shape selectivity of C30 phases for RP-HPLC separation of tocopherol isomers and correlation with MAS NMR data from suspended stationary phases. Anal. Chem. 1998, 70, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urvaka, E.; Mišina, I.; Soliven, A.; Górnaś, P. Rapid separation of all four tocopherol homologues in selected fruit seeds via supercritical fluid chromatography using a solid-core C18 column. J. Chem. 2019, 2019, 5307340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, B.; Brzuskiewicz, L. Separation of tocopherol and tocotrienol isomers using normal-and reverse-phase liquid chromatography. Anal. Biochem. 1989, 180, 368–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irakli, M.N.; Samanidou, V.F.; Papadoyannis, I.N. Development and validation of an HPLC method for the simultaneous determination of tocopherols, tocotrienols and carotenoids in cereals after solid-phase extraction. J. Sep. Sci. 2011, 34, 1375–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irakli, M.N.; Samanidou, V.F.; Papadoyannis, I.N. Optimization and validation of the reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection method for the separation of tocopherol and tocotrienol isomers in cereals, employing a novel sorbent material. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 2076–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Q.; Xia, M.; Sun, D.; Cao, J.; Xiao, Y.; Lin, M.; Hou, B.; Jia, L.; Li, D. Deep eutectic solvent-based liquid-phase microextraction coupled with reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography for determination of α-, β-, γ-, and δ-tocopherol in edible oils. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2021, 413, 577–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucchetti, S.; Ambra, R.; Pastore, G. Effects of peeling and/or toasting on the presence of tocopherols and phenolic compounds in four Italian hazelnut cultivars. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2018, 244, 1057–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Górnaś, P. Optimizing the Separation of Four Tocopherols and Four Tocotrienols via RP-HPLC by Screening Five Different SPP Phases. Available online: https://resources.perkinelmer.com/lab-solutions/resources/docs/ABR_Optimizing-the-Separation-of-FourTocopherols-and-FourTocotrienols-via-RP-HPLC.pdf (accessed on 8 May 2022).
- Richheimer, S.L.; Kent, M.C.; Bernart, M.W. Reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatographic method using a pentafluorophenyl bonded phase for analysis of tocopherols. J. Chromatogr. A 1994, 677, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashu-Arrah, B.A.; Glennon, J.D.; Albert, K. Synthesis, characterisation and chromatographic evaluation of pentafluorophenyl and phenyl bonded silica phases prepared using supercritical carbon dioxide as a reaction solvent. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1273, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinis, J.; Kessler, F.; Glauser, G. A novel method for prenylquinone profiling in plant tissues by ultra-high pressure liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Plant Methods 2011, 7, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsochatzis, E.D.; Bladenopoulos, K.; Papageorgiou, M. Determination of tocopherol and tocotrienol content of Greek barley varieties under conventional and organic cultivation techniques using validated reverse phase high-performance liquid chromatography method. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2012, 92, 1732–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Walia, S.; Sharma, K.; Banerjee, K. Suitability of stationary phase for LC analysis of biomolecules. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 2856–2873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segliņa, D.; Krasnova, I.; Grygier, A.; Radziejewska-Kubzdela, E.; Rudzińska, M.; Górnaś, P. Unique bioactive molecule composition of sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.) oils obtained from the peel, pulp, and seeds via physical “solvent-free” approaches. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2021, 98, 1009–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Yin, J.-J.; Yu, L. Phenolic acid, tocopherol and carotenoid compositions, and antioxidant functions of hard red winter wheat bran. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 3916–3922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Górnaś, P.; Radenkovs, V.; Pugajeva, I.; Soliven, A.; Needs, P.W.; Kroon, P.A. Varied composition of tocochromanols in different types of bran: Rye, wheat, oat, spelt, buckwheat, corn, and rice. Int. J. Food Prop. 2016, 19, 1757–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, H.; Angiuli, M.; Ferrari, C.; Tombari, E.; Salvetti, G.; Bramanti, E. Tocopherol speciation as first screening for the assessment of extra virgin olive oil quality by reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography/fluorescence detector. Food Chem. 2011, 125, 1423–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, M.L.; Marangon, K.; Bugatti, C. CoulArray® electrochemical evaluation of tocopherol and tocotrienol isomers in barley, oat and spelt grains. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2009, 4, 251–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sarzanini, C.; Mentasti, E.; Vincenti, M.; Nerva, M.; Gaido, F. Determination of plasma tocopherols by high-performance liquid chromatography with coulometric detection. J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Sci. Appl. 1993, 620, 268–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, S.C.; Amaral, J.S.; Fernandes, J.O.; Oliveira, M.B.P.P. Quantification of tocopherols and tocotrienols in Portuguese olive oils using HPLC with three different detection systems. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 3351–3356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruperez, F.J.; Martın, D.; Herrera, E.; Barbas, C. Chromatographic analysis of α-tocopherol and related compounds in various matrices. J. Chromatogr. A 2001, 935, 45–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leray, C.; Andriamampandry, M.; Gutbier, G.; Cavadenti, J.; Klein-Soyer, C.; Gachet, C.; Cazenave, J.-P. Quantitative analysis of vitamin E, cholesterol and phospholipid fatty acids in a single aliquot of human platelets and cultured endothelial cells. J. Chromatogr. B: Biomed. Sci. Appl. 1997, 696, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mottier, P.; Gremaud, E.; Guy, P.A.; Turesky, R.J. Comparison of gas chromatography–mass spectrometry and liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry methods to quantify α-tocopherol and α-tocopherolquinone levels in human plasma. Anal. Biochem. 2002, 301, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmo-García, L.; Polari, J.J.; Li, X.; Bajoub, A.; Fernández-Gutiérrez, A.; Wang, S.C.; Carrasco-Pancorbo, A. Deep insight into the minor fraction of virgin olive oil by using LC-MS and GC-MS multi-class methodologies. Food Chem. 2018, 261, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadioglu, Y.; Demirkaya, F.; Kursat Demirkaya, A. Quantitative determination of underivatized α-tocopherol in cow milk, vitamin and multivitamin drugs by GC-FID. Chromatographia 2009, 70, 665–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, N.; Jabeen, Z.; Li, Y.-l.; Chen, M.-x.; Li, Z.-l.; Guo, W.-l.; Shamsi, I.H.; Chen, X.-y.; Jiang, L.-x. Detection of tocopherol in oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.) using gas chromatography with flame ionization detector. J. Integr. Agric. 2013, 12, 803–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.K.; Ha, S.-H.; Park, S.-Y.; Lee, S.M.; Kim, H.J.; Lim, S.H.; Suh, S.-C.; Kim, D.H.; Cho, H.S. Determination of lipophilic compounds in genetically modified rice using gas chromatography–time-of-flight mass spectrometry. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2012, 25, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piironen, V.I.; Liljeroos, A.I.; Koivistoinen, P.E. Transfer of alpha-tocopherol stereoisomers from feeds to eggs. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1991, 39, 99–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartosińska, E.; Buszewska-Forajta, M.; Siluk, D. GC–MS and LC–MS approaches for determination of tocopherols and tocotrienols in biological and food matrices. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2016, 127, 156–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirkaya, F.; Kadioglu, Y. Simple GC-FID method development and validation for determination of α-tocopherol (vitamin E) in human plasma. J. Biochem. Biophys. Methods 2007, 70, 363–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frega, N.; Mozzon, M.; Bocci, F. Identification and estimation of tocotrienols in the annatto lipid fraction by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1998, 75, 1723–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lytovchenko, A.; Beleggia, R.; Schauer, N.; Isaacson, T.; Leuendorf, J.E.; Hellmann, H.; Rose, J.K.C.; Fernie, A.R. Application of GC-MS for the detection of lipophilic compounds in diverse plant tissues. Plant Methods 2009, 5, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Plutowska, B.; Jeleń, H. Analiza Żywności. In Chemia Zywnosci. Biologiczne Właściwości Składników Żywności; Sikorski, Z.E., Hanna, S., Eds.; Wydawnictwo Naukowe PWN: Warsaw, Poland, 2017; pp. 269–306. [Google Scholar]
- Dispas, A.; Jambo, H.; André, S.; Tyteca, E.; Hubert, P. Supercritical fluid chromatography: A promising alternative to current bioanalytical techniques. Bioanalysis 2018, 10, 107–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vera, C.M.; Shock, D.; Dennis, G.R.; Farrell, W.; Shalliker, R.A. Comparing the selectivity and chiral separation of D-and L-fluorenylmethyloxycarbonyl chloride protected amino acids in analytical high performance liquid chromatography and supercritical fluid chromatography; evaluating throughput, economic and environmental impact. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1493, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vera, C.M.; Shock, D.; Dennis, G.R.; Samuelsson, J.; Enmark, M.; Fornstedt, T.; Shalliker, R.A. A preliminary study on the selectivity of linear polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons in SFC using phenyl-type stationary phases. Microchem. J. 2015, 121, 136–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vera, C.M.; Shock, D.; Dennis, G.R.; Samuelsson, J.; Enmark, M.; Fornstedt, T.; Shalliker, R.A. Contrasting selectivity between HPLC and SFC using phenyl-type stationary phases: A study on linear polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons. Microchem. J. 2015, 119, 40–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galea, C.M.; Mangelings, D.; Vander Heyden, Y. Investigation of the effect of mobile phase composition on selectivity using a solvent-triangle based approach in achiral SFC. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2017, 132, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyśkiewicz, K.; Gieysztor, R.; Maziarczyk, I.; Hodurek, P.; Rój, E.; Skalicka-Woźniak, K. Supercritical fluid chromatography with photodiode array detection in the determination of fat-soluble vitamins in hemp seed oil and waste fish oil. Molecules 2018, 23, 1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tomai, P.; Dal Bosco, C.; D’Orazio, G.; Scuto, F.R.; Felli, N.; Gentili, A. Supercritical fluid chromatography for vitamin and carotenoid analysis: An update covering 2011–2021. J. Chromatogr. Open 2022, 2, 100027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, N.; Gong, X.; Feng, C.; Wang, X.; Xu, Y.; Lin, L. Simultaneous analysis of eight vitamin E isomers in Moringa oleifera Lam. leaves by ultra performance convergence chromatography. Food Chem. 2016, 207, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iijima, S.; Terada, A.; Tognarelli, D.J.; Burchell, J.; Kanomata, T.; Bounoshita, M.; Sato, Y.; Kuwajima, M. High Sensitivity Fluorescence Detector for Supercritical Fluid Chromatography. Available online: https://jascoinc.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/05/SFC-FP-for-SFC-2017-.pdf (accessed on 25 July 2022).
- Yamamoto, K.; Kotani, A.; Hakamata, H. Electrochemical detection of tocopherols in vegetable oils by supercritical fluid chromatography equipped with carbon fiber electrodes. Anal. Methods 2018, 10, 4414–4418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, K.; Nishimura, T.; Machida, K.; Kotani, A.; Hakamata, H. Supercritical fluid chromatography with post-column addition of supporting electrolyte solution for electrochemical determination of tocopherol and tocotrienol isomers. J. Sep. Sci. 2022, 45, 1797–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustamante-Rangel, M.; Delgado-Zamarreño, M.M.; Sánchez-Pérez, A.; Carabias-Martínez, R. Determination of tocopherols and tocotrienols in cereals by pressurized liquid extraction–liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2007, 587, 216–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rentel, C.; Strohschein, S.; Albert, K.; Bayer, E. Silver-plated vitamins: A method of detecting tocopherols and carotenoids in LC/ESI-MS coupling. Anal. Chem. 1998, 70, 4394–4400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanina, S.A.; Toledo, P.; Sampels, S.; Kamal-Eldin, A.; Jastrebova, J.A. Comparison of reversed-phase liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry with electrospray and atmospheric pressure chemical ionization for analysis of dietary tocopherols. J. Chromatogr. A 2007, 1157, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desfontaine, V.; Veuthey, J.-L.; Guillarme, D. Hyphenated detectors: Mass spectrometry. In Supercritical Fluid Chromatography; Poole, C.F., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 213–244. [Google Scholar]
- Viñas, P.; Bravo-Bravo, M.; López-García, I.; Pastor-Belda, M.; Hernández-Córdoba, M. Pressurized liquid extraction and dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction for determination of tocopherols and tocotrienols in plant foods by liquid chromatography with fluorescence and atmospheric pressure chemical ionization-mass spectrometry detection. Talanta 2014, 119, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagy, K.; Courtet-Compondu, M.-C.; Holst, B.; Kussmann, M. Comprehensive analysis of vitamin E constituents in human plasma by liquid chromatography—Mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 7087–7096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butinar, B.; Bučar-Miklavčič, M.; Mariani, C.; Raspor, P. New vitamin E isomers (gamma-tocomonoenol and alpha-tocomonoenol) in seeds, roasted seeds and roasted seed oil from the Slovenian pumpkin variety ‘Slovenska golica’. Food Chem. 2011, 128, 505–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, O.H.; Tan, E.H.P.; Ooi, H. Fast gradient normal-phase high pressure liquid chromatography for rapid baseline separation of vitamin E forms in palm-derived tocotrienol rich fractions (TRFs). Anal. Methods 2017, 9, 5211–5218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Common Name | Latin Name | Homologue Occurrence | Phase, Column | Ref. | Homologue Occurrence and β % of Σβ + γ | Phase, Column | Ref. | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| β-T | γ-T | β-T3 | γ-T3 | β-T | γ-T | β-T % | β-T3 | γ-T3 | β-T3 % | ||||||
| Black caraway | Nigella sativa | – | yes | - | yes | RP, C18 | [37] | yes | yes | 21% | yes | – | 100% | NP, Diol | [51] |
| European cranberrybush | Viburnum opulus | – | yes | - | – | RP, C18 | [56] | yes | yes | 91–96% | – | – | – | RP, C30 | [43] |
| Sea buckthorn | Hippophaë rhamnoides | – | yes | - | – | RP, C18 | [56] | yes | yes | 15–79% | yes | yes | 9% | RP, PFP | [156] |
| Wheat | Triticum sp. | – | yes | - | – | RP, C18 | [157] | yes | yes | 92% | yes | - | 100% | RP, PFP | [158] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Górnaś, P.; Baškirovs, G.; Siger, A. Free and Esterified Tocopherols, Tocotrienols and Other Extractable and Non-Extractable Tocochromanol-Related Molecules: Compendium of Knowledge, Future Perspectives and Recommendations for Chromatographic Techniques, Tools, and Approaches Used for Tocochromanol Determination. Molecules 2022, 27, 6560. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27196560
Górnaś P, Baškirovs G, Siger A. Free and Esterified Tocopherols, Tocotrienols and Other Extractable and Non-Extractable Tocochromanol-Related Molecules: Compendium of Knowledge, Future Perspectives and Recommendations for Chromatographic Techniques, Tools, and Approaches Used for Tocochromanol Determination. Molecules. 2022; 27(19):6560. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27196560
Chicago/Turabian StyleGórnaś, Paweł, Georgijs Baškirovs, and Aleksander Siger. 2022. "Free and Esterified Tocopherols, Tocotrienols and Other Extractable and Non-Extractable Tocochromanol-Related Molecules: Compendium of Knowledge, Future Perspectives and Recommendations for Chromatographic Techniques, Tools, and Approaches Used for Tocochromanol Determination" Molecules 27, no. 19: 6560. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27196560
APA StyleGórnaś, P., Baškirovs, G., & Siger, A. (2022). Free and Esterified Tocopherols, Tocotrienols and Other Extractable and Non-Extractable Tocochromanol-Related Molecules: Compendium of Knowledge, Future Perspectives and Recommendations for Chromatographic Techniques, Tools, and Approaches Used for Tocochromanol Determination. Molecules, 27(19), 6560. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27196560