Novel Novolac Phenolic Polymeric Network of Chalcones: Synthesis, Characterization, and Thermal–Electrical Conductivity Investigation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Methodology
2.1. Materials
2.2. Measurements
2.3. General Procedure for Preparation of 1-(4-Substituted Phenyl)-3-(4-Hydroxy Phenyl) Prop-2-en-1-one (3a–d)
2.4. General Procedure for Chalcone-Based Phenolic Networks Preparation (4a–d)
2.5. General Procedure for p-Hydroxybenzaldehyde Polymer (5)
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Spectral Analysis
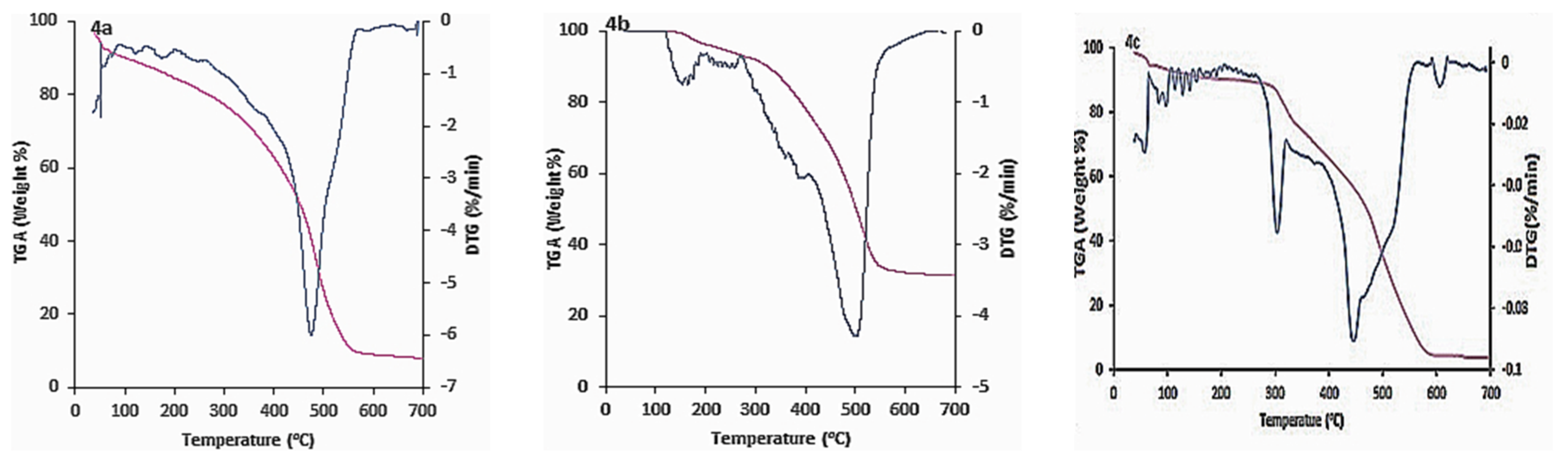
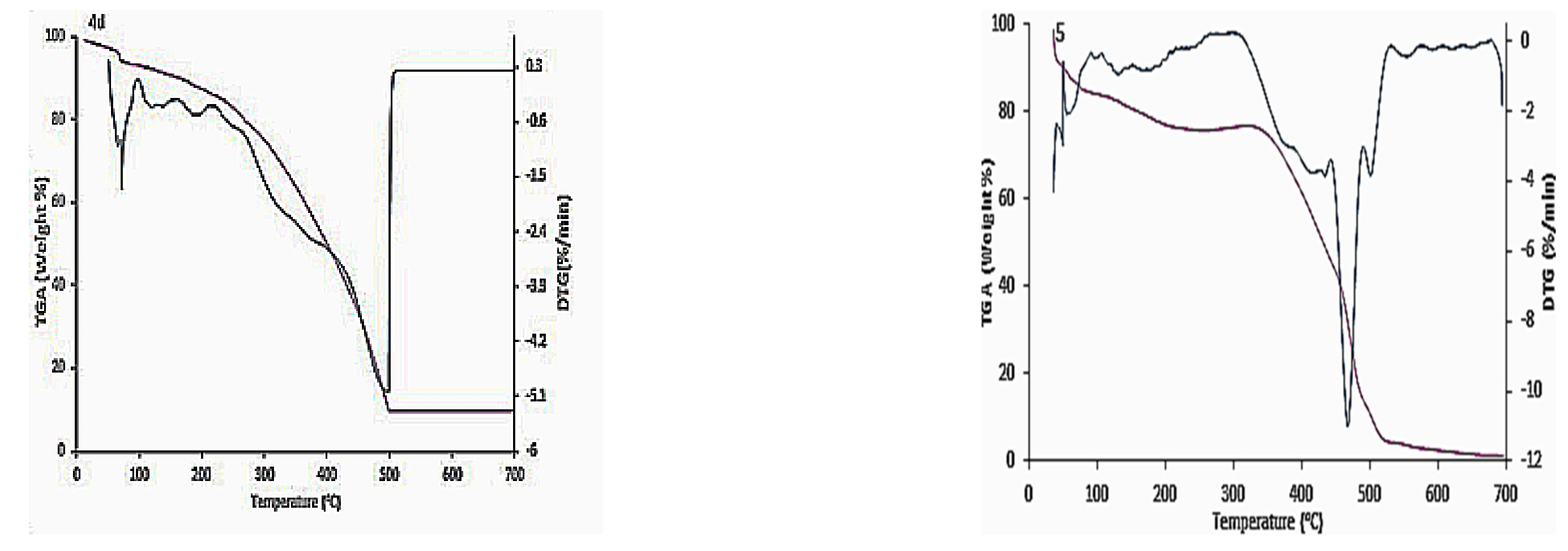
3.2. Thermal Gravimetric Analysis (TGA)
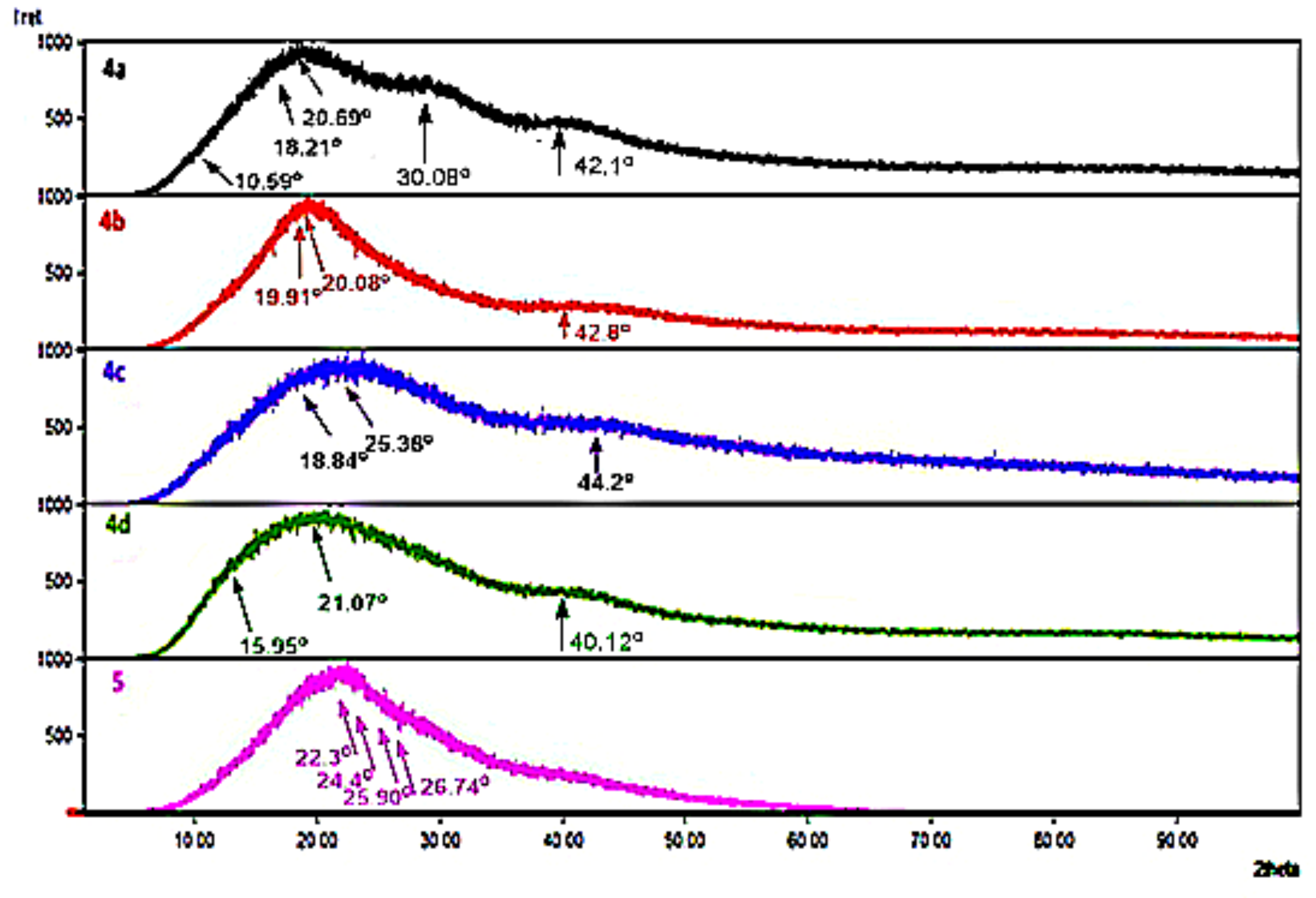
3.3. The Powder X-ray Diffraction (XRD)
3.4. Conductivity and Resistivity Measurements
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability Statement
References
- Jawad, S.F.; Bahjat, S.A.; AL-Baiati, M.N. Synthesis a novel Schiff base and Chalcone derivatives compounds and using as flame retardant for unsaturated polyester and epoxy resins. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 571, 12090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.; Gunjal, R. Review of MSP Antenna Design for Various Substrates. Available online: https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=3230632 (accessed on 13 July 2022).
- Baekeland, L.H. The synthesis, constitution, and uses of Bakelite. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1909, 1, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanley, T.L.; Burford, R.P.; Fleming, R.J.; Barber, K.W. A general review of polymeric insulation for use in HVDC cables. IEEE Electr. Insul. Mag. 2003, 19, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solyman, W.S.; Nagiub, H.M.; Alian, N.A.; Shaker, N.O.; Kandil, U.F. Synthesis and characterization of phenol/formaldehyde nanocomposites: Studying the effect of incorporating reactive rubber nanoparticles or Cloisite-30B nanoclay on the mechanical properties, morphology and thermal stability. J. Radiat. Res. Appl. Sci. 2017, 10, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watkins, P.K.; Walker, A.B.; Verschoor, G.L. Dynamical Monte Carlo modelling of organic solar cells: The dependence of internal quantum efficiency on morphology. Nano Lett. 2005, 5, 1814–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuenchum, P.; Suttinon, P.; Ruangrassamee, P. Assessment of cross-sectoral damage from water deficits under changing climate and regional development in nan River basin, Thailand. In Proceedings of the World Environmental and Water Resources Congress, Sacramento, CA, USA, 21–25 May 2017; pp. 694–709. [Google Scholar]
- Sasmitha, S.S.; Uma, R. A Critical Review on the Application of Bakelite as a Partial Replacement of Fine and Coarse Aggregate. Int. J. Sci. Res. Dev. 2018, 4, 174–178. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, D.; Li, X.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, H.-B.; Jia, B.-B.; Ma, H.-L.; Yu, Z.-Z. Thermally conductive phenol formaldehyde composites filled with carbon fillers. Mater. Lett. 2014, 118, 212–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahle, F.J.; Saller, C.; Köhler, A.; Strohriegl, P. Crosslinked semiconductor polymers for photovoltaic applications. Adv. Energy Mater. 2017, 7, 1700306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, A.; Liang, G.; Lan, L. Modification of polyaralkyl–phenolic resin and its copolymer with bismaleimide. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1996, 59, 975–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.S.; Nakamura, G.I.; Inoue, T. Structure development in the phenolic resin–poly (styrene-ran-acrylonitrile) copolymer blends. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1998, 70, 757–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, A.; Hasegawa, K.; Fukuda, A.; Otsuki, K. Study on modified phenolic resin. 2 modification with para-hydroxyphenylmaleimide styrene copolymer. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1992, 44, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knop, A.; Pilato, A.L. Resins: Chemistry, Application and Performance—Future Directions; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Adnan, D.; Singh, B.; Mehta, S.K.; Kumar, V.; Kataria, R. Simple and solvent free practical procedure for chalcones: An expeditious, mild and greener approach. Curr. Res. Green Sustain. Chem. 2020, 3, 100041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharshira, E.M.; Hamada, N.M.M. Synthesis and antimicrobial evaluation of some pyrazole derivatives. Molecules 2012, 17, 4962–4971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharshira, E.M.; Hamada, N.M.M. Synthesis and in vitro antimicrobial activity of some pyrazolyl-1-carboxamide derivatives. Molecules 2011, 16, 7736–7745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.; Kumar, S.; Lamba, B.Y.; Patra, J.; Mahindroo, N. Nanocatalysts: Applications in synthesis of chalcones—A review. Synth. Commun. 2021, 51, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tandel, R.; Jayvirsinh, G.; Patel Nilesh, K. Synthesis and study of main chain chalcone polymers exhibiting nematic phases. Res. J. Recent Sci. 2012, 2277, 2502. [Google Scholar]
- Nechifor, M. Novel chalcone-based aromatic polyamides: Synthesis, characterization, and properties. Des. Monomers Polym. 2016, 19, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Li, X.; Sun, L.; Li, D. A low-power column-parallel gain-adaptive single-slope ADC for CMOS image sensors. Int. J. Electron. 2020, 9, 757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matter, U.E.; Pascual, C.; Pretsch, E.; Pross, A.; Simon, W.; Sternhell, S. Estimation of the chemical shifts of ole-finic protons using additive increments—II: The compilation of additive increments for 43 functional groups. Tetrahedron 1969, 25, 691–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, Y.R.; Rao, A.L.; Rambabu, R. Synthesis and antimicrobial activity of some chalcone derivatives. New J. Chem. 2008, 5, 461–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarag, K.; Pinjari, D.; Pandit, A.; Shankarling, G. Synthesis of chalcone (3-(4-fluorophenyl)-1-(4-methoxyphenyl) prop-2-en-1-one): Advantage of sonochemical method over conventional method. Ultrason Sonochem. 2011, 18, 617–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, L.; Fang, L.; Dai, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J.; Xu, P. Antibacterial and anti-inflammatory activity of valproic acid-pyrazole conjugates as a potential agent against periodontitis. Drug Dev. Res. 2022, 83, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narwal, S.; Kumar, S.; Verma, P.K. Synthesis and biological activity of new chalcone scaffolds as prospective antimicrobial agents. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2021, 47, 1625–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.Y.; Kao, C.L.; Huang, S.T.; Kuo, C.E.; Song, P.L.; Li, W.J.; Li, H.T. Secondary Metabolites of Litchi chinensis. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2022, 58, 107–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.S.; Huang, J.M. A mild and highly efficient conversion of arylboronic acids into phenols by oxidation with MCPBA. Synlett 2013, 24, 499–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunnarshaug, A.; Metallinou, M.M.; Log, T. Study of industrial grade thermal insulation at elevated temperatures. Materials 2020, 13, 4613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smorygo, O.; Marukovich, A.; Mikutski, V.; Stathopoulos, V.; Hryhoryeu, S.; Sadykov, V. Tailoring properties of reticulated vitreous carbon foams with tunable density. Front. Mater. Sci. 2016, 10, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomaa, M.M.; Hugenschmidt, C.; Dickmann, M.; Abdel-Hady, E.E.; Mohamed, H.F.; Abdel-Hamed, M.O. Crosslinked PVA/SSA proton exchange membranes: Correlation between physiochemical properties and free volume determined by positron annihilation spectroscopy. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2018, 20, 28287–28299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prime, R. Cure behavior of an epoxy-phenolic magnetic recording ink. J. Therm. Anal. 1986, 31, 1091–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toxqui-Terán, A.; Leyva-Porras, C.; Ruíz-Cabrera, M.Á.; Cruz-Alcantar, P.; Saavedra-Leos, M.Z. Thermal study of polyols for the technological application as plasticizers in food industry. Polymers 2018, 10, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, T.; Li, J.; Feng, W.; Nian, H.e. Enhanced thermal conductivity of form-stable phase change composite with single-walled carbon nanotubes for thermal energy storage. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 44710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, S.B.; Rasheed, M.A.; Ahmed, H.M. Synthesis of Polymer Nanocomposites Based on [Methyl Cellulose] (1−x):(CuS) × (0.02 M ≤ × ≤ 0.08 M) With Desired Optical Band Gaps. Polymers 2017, 9, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brza, M.A.; Aziz, S.B.; Anuar, H.; Al Hazza, M.H.F. From Green Remediation to Polymer Hybrid Fabrication with Improved Optical Band Gaps. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, R.M.; Aziz, S.B.; Mamand, S.M.; Hassan, A.; Hussen, S.A.; Kadir, M.F.Z. Reducing the Crystallite Size of Spherulites in PEO-Based Polymer Nanocomposites Mediated by Carbon Nanodots and Ag Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, S.B.; Abdulwahid, R.T.; Rsaul, H.A.; Ahmed, H.M. In situ synthesis of CuS nanoparticle with a distinguishable SPR peak in NIR region. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2016, 27, 4163–4171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumara, L.S.R.; Sakata, O.; Kobayashi, H.; Song, C.; Kohara, S.; Ina, T.; Yoshimoto, T.; Yoshioka, S.; Matsumura, S.; Kitagawa, H. Hydrogen storage and stability properties of Pd–Pt solid-solution nanoparticles revealed via atomic and electronic structure. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 14606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burroughes, J.H.; Bradley, D.D.C.; Brown, A.R.; Marks, R.N.; MacKay, K.; Friend, R.H.; Burns, P.L.; Holmes, A.B. Light-emitting diodes based on conjugated polymers. Nature 1990, 6293, 539–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

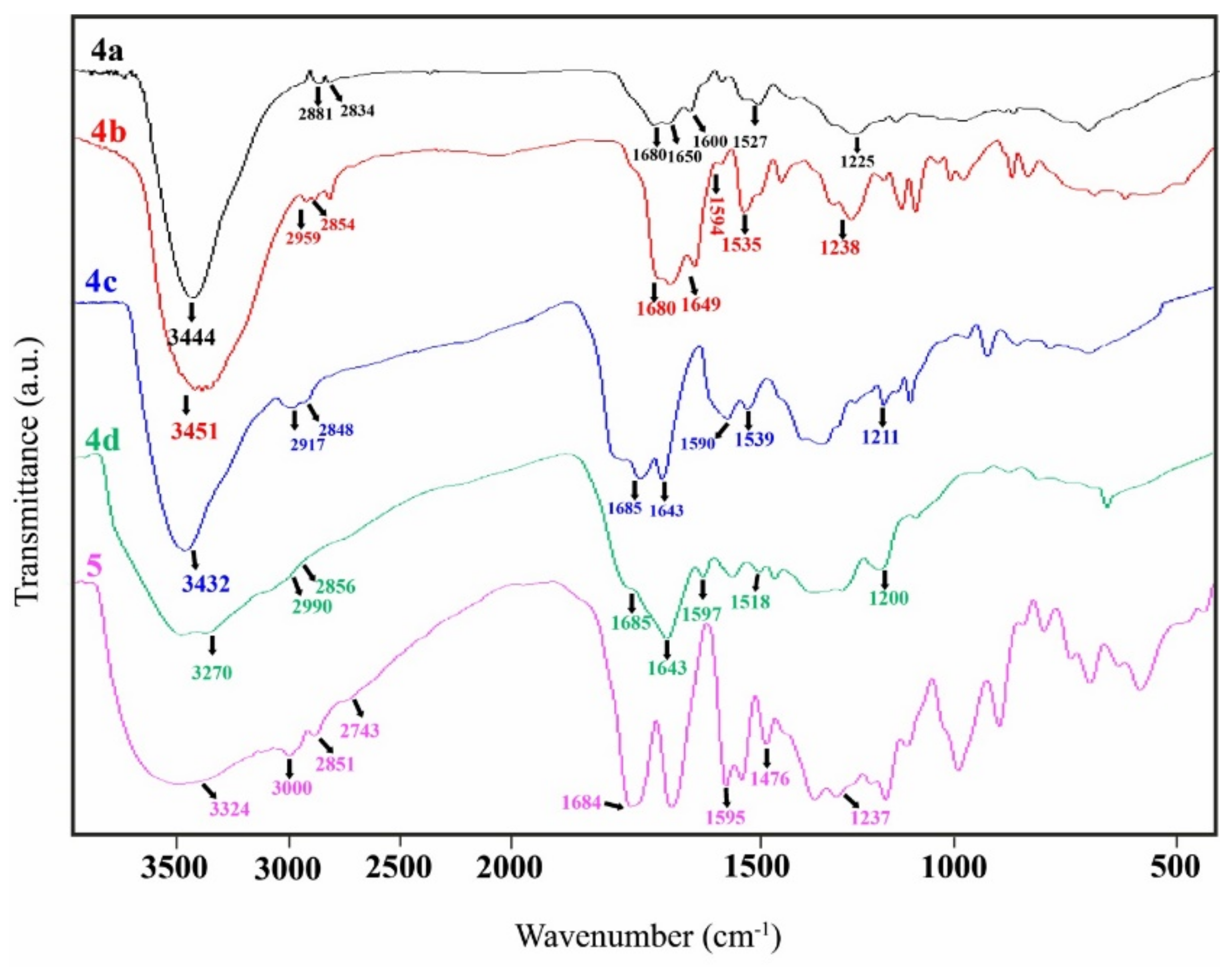
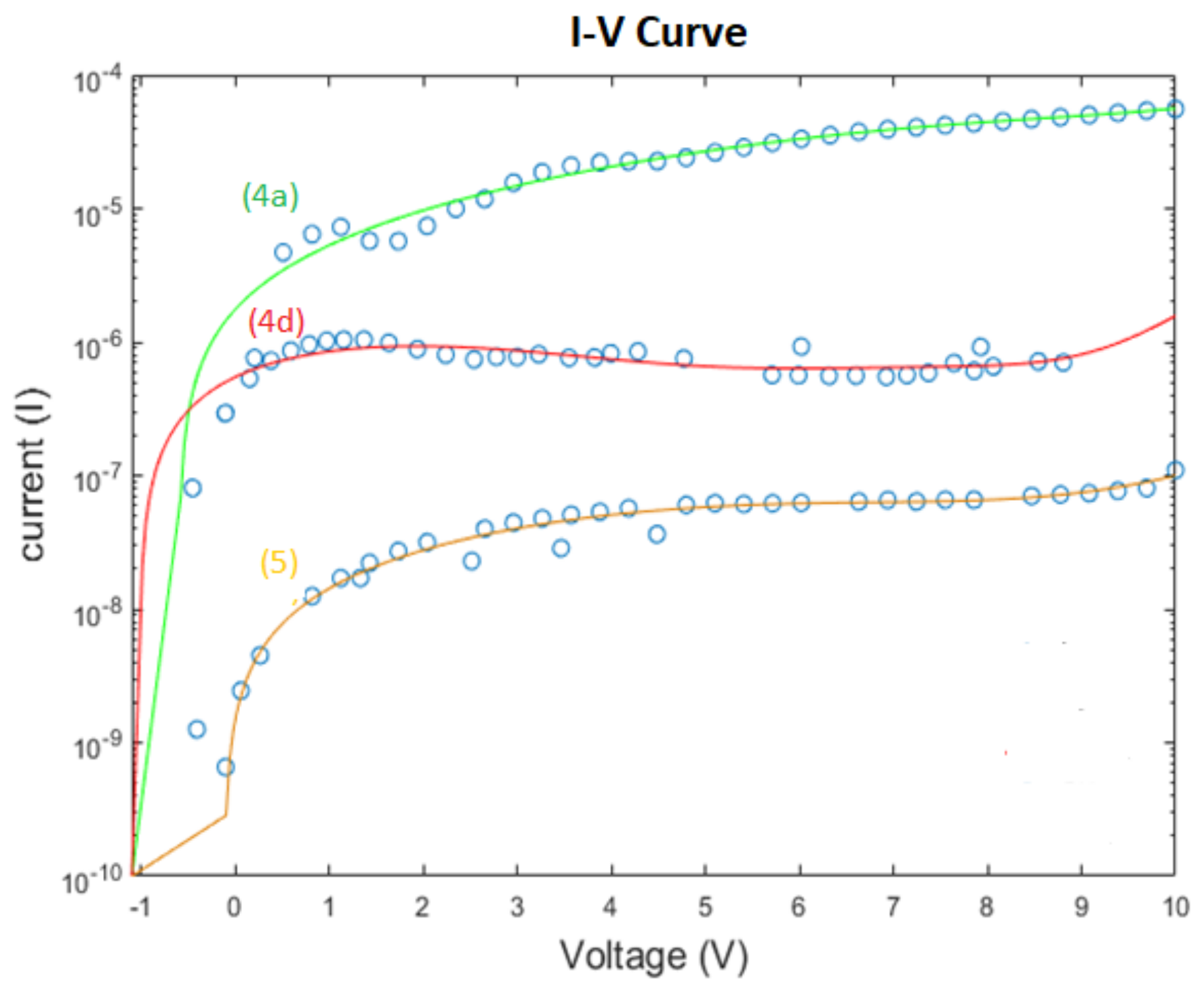
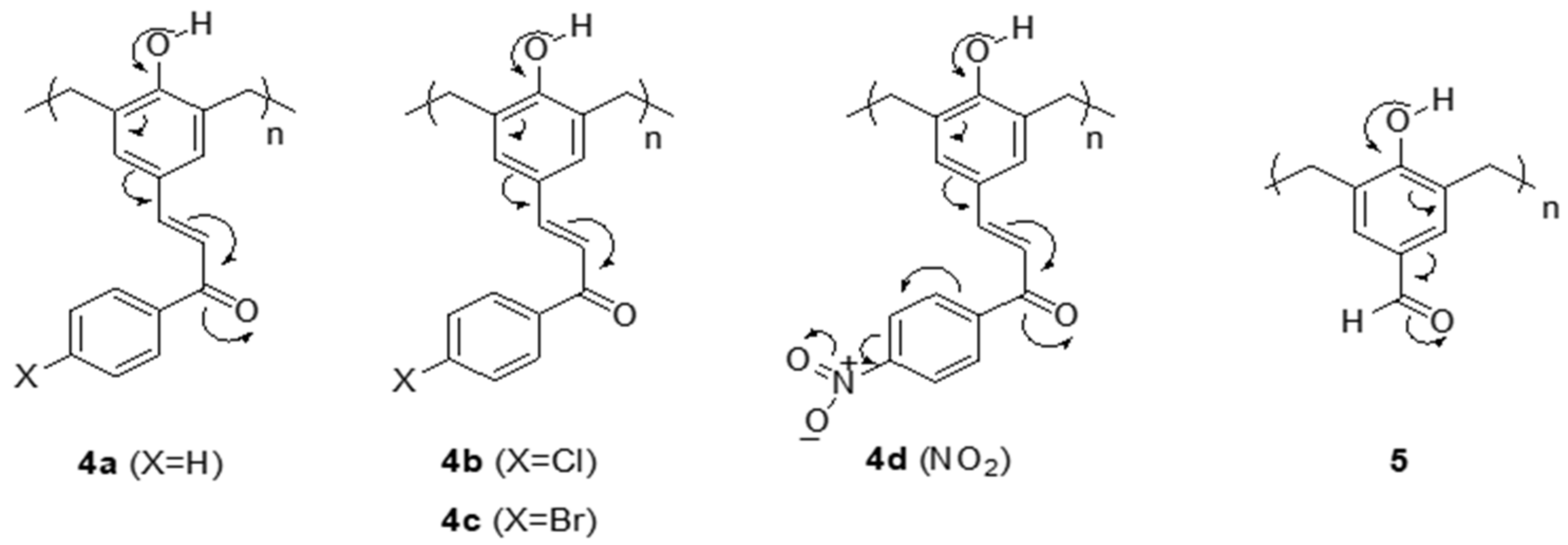
| Compound Number | Yield (%) | Reaction Time (min) | Color/Morphology |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3a | 88 | 10 | Yellow/needles |
| 3b | 82 | 15 | Yellow/needles |
| 3c | 76 | 30 | Yellow/crystals |
| 3d | 84 | 25 | Yellow/crystals |
| Compound Number | Yield (%) | Heating Time (min) | Color |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4a | 98 | 240 | Brown |
| 4b | 83 | 240 | Black |
| 4c | 95 | 240 | Black |
| 4d | 97 | 240 | Brown |
| 5 | 98 | 30 | Pale green |
| Compounds | Acidic Medium (This Study) | Alkaline Medium [Literature] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yield% | Reaction Time (min) | Yield% | Reaction Time (h) | Ref. | |
| 3a | 88 | 10 | 69 | 24 | [25] |
| 3b | 82 | 15 | 84 | 24 | [25] |
| 3c | 76 | 30 | 84 | 24 | [25] |
| 3d | 84 | 25 | 70.97 | 24 | [26] |
| Compound Number | The Maximum Peak Temperature, Tmax (°C) | Residual Weight, % |
|---|---|---|
| 4a | 120 | 89.18 |
| 476 | 39.94 | |
| 4b | 154 | 99.11 |
| 503 | 49.50 | |
| 4c | 305 | 83.07 |
| 448 | 42.11 | |
| 4d | 72 | 88.53 |
| 493 | 9.32 | |
| 5 | 62 | 87.72 |
| 467 | 31.44 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sharshira, E.M.; Ataalla, A.A.; Hagar, M.; Salah, M.; Jaremko, M.; Shehata, N. Novel Novolac Phenolic Polymeric Network of Chalcones: Synthesis, Characterization, and Thermal–Electrical Conductivity Investigation. Molecules 2022, 27, 5409. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27175409
Sharshira EM, Ataalla AA, Hagar M, Salah M, Jaremko M, Shehata N. Novel Novolac Phenolic Polymeric Network of Chalcones: Synthesis, Characterization, and Thermal–Electrical Conductivity Investigation. Molecules. 2022; 27(17):5409. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27175409
Chicago/Turabian StyleSharshira, Essam Mohamed, Ahmed A. Ataalla, Mohamed Hagar, Mohammed Salah, Mariusz Jaremko, and Nader Shehata. 2022. "Novel Novolac Phenolic Polymeric Network of Chalcones: Synthesis, Characterization, and Thermal–Electrical Conductivity Investigation" Molecules 27, no. 17: 5409. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27175409
APA StyleSharshira, E. M., Ataalla, A. A., Hagar, M., Salah, M., Jaremko, M., & Shehata, N. (2022). Novel Novolac Phenolic Polymeric Network of Chalcones: Synthesis, Characterization, and Thermal–Electrical Conductivity Investigation. Molecules, 27(17), 5409. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27175409







