Abstract
Ethnopharmacological relevance: The genus Polygonatum Tourn, ex Mill. contains numerous chemical components, such as steroidal saponins, polysaccharides, flavonoids, alkaloids, and others, it possesses diverse pharmacological activities, such as anti-aging, anti-tumor, immunological regulation, as well as blood glucose management and fat reducing properties. Aim of the review: This study reviews the current state of research on the systematic categorization, chemical composition, pharmacological effects, and processing changes of the plants belonging to the genus Polygonatum, to provide a theoretical foundation for their scientific development and rational application. Materials and methods: The information was obtained by searching the scientific literature published between 1977 and 2022 on online databases (including PubMed, CNKI, SciFinder, and Web of Science) and other sources (such as the Chinese Pharmacopoeia 2020 edition, and Chinese herbal books). Results: The genus Polygonatum contains 79 species, and 233 bioactive chemical compounds were identified in them. The abundance of pharmacological activities, such as antioxidant activities, anti-fatigue activities, anti-inflammatory activities, etc., were revealed for the representatives of this genus. In addition, there are numerous processing methods, and many chemical constituents and pharmacological activities change after the unappropriated processing. Conclusions: This review summarizes the taxonomy classification, chemical composition, pharmacological effects, and processing of the plants belonging to the genus Polygonatum, providing references and research tendencies for plant-based drug development and further clinical applications.
1. Introduction
The genus Polygonatum belongs to a perennial herbaceous plant whose English name is King Solomon’s seal, and it belongs to the Asparagaceae family. There are about 79 species of Polygonatum in the globe, which are extensively distributed in the northern hemisphere. About 39 species are recorded growing in China [1]. The genus Polygonatum has long been valued for its medicinal, diet, and healthcare values, the rhizomes are medicinal portions [2]. Polygonatumi rhizoma and Polygonatumi odorati rhizoma belong to the genus Polygonatum and have been added to the “Chinese Pharmacopeia” (2020 edition) [3]. The genus Polygonatum contains polysaccharides, flavonoids, steroids, coumarins, and other chemical components [4]. As a medicinal plant, its dried rhizome has anti-aging, anti-oxidation, immune regulation, anti-inflammatory, and anti-cancer effects, and is clinically used to treat fatigue, weakness, diabetes, cough, and loss of appetite [5]. However, the unprocessed herbs in genus Polygonatum can irritate the throat, the raw rhizomes of Polygonatum Mill. are processed by repeated steaming and drying (nine times each) in order to reduce toxic components, and improve their primary functioning, taste, and pharmaceutical effects [6].
Previously, reviews that focused on some species, P. odoratum, P. cyrtonema, P. kingianum, and P. sibiricum have been conducted. To the authors’ knowledge, no study has reviewed the taxonomy classification, chemical composition, pharmacological effect, and processing of the whole genus. This review is aimed to critically evaluate available research reports on the genus, and systematically organize and present the findings.
2. Classification of Polygonatum Mill.
The genus Polygonatum comprises 79 species. Among them, 39 species distributed in China were recorded in the Chinese monograph “Flora of China” [1], and the other 40 species were included in the World Checklist of Selected Plant Families (WCSPF, World Checklist of Selected Plant Families: Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew). The contributions and the first recorded time of the species are summarized (Table 1).

Table 1.
Species of the genus Polygonatum.
3. Chemical Constituents of Polygonatum
As mentioned in the introduction, the herbs in the genus Polygonatum contain many chemical components, such as steroidal saponins, polysaccharides, flavonoids, and alkaloids. The author summarized 233 compounds isolated from this genus from 1977 to 2022, which contained 124 steroidal saponins, 68 flavonoids, triterpenoid saponins, 16 alkaloids, 3 quinones, and 6 lignans.
3.1. Steroidal Saponins
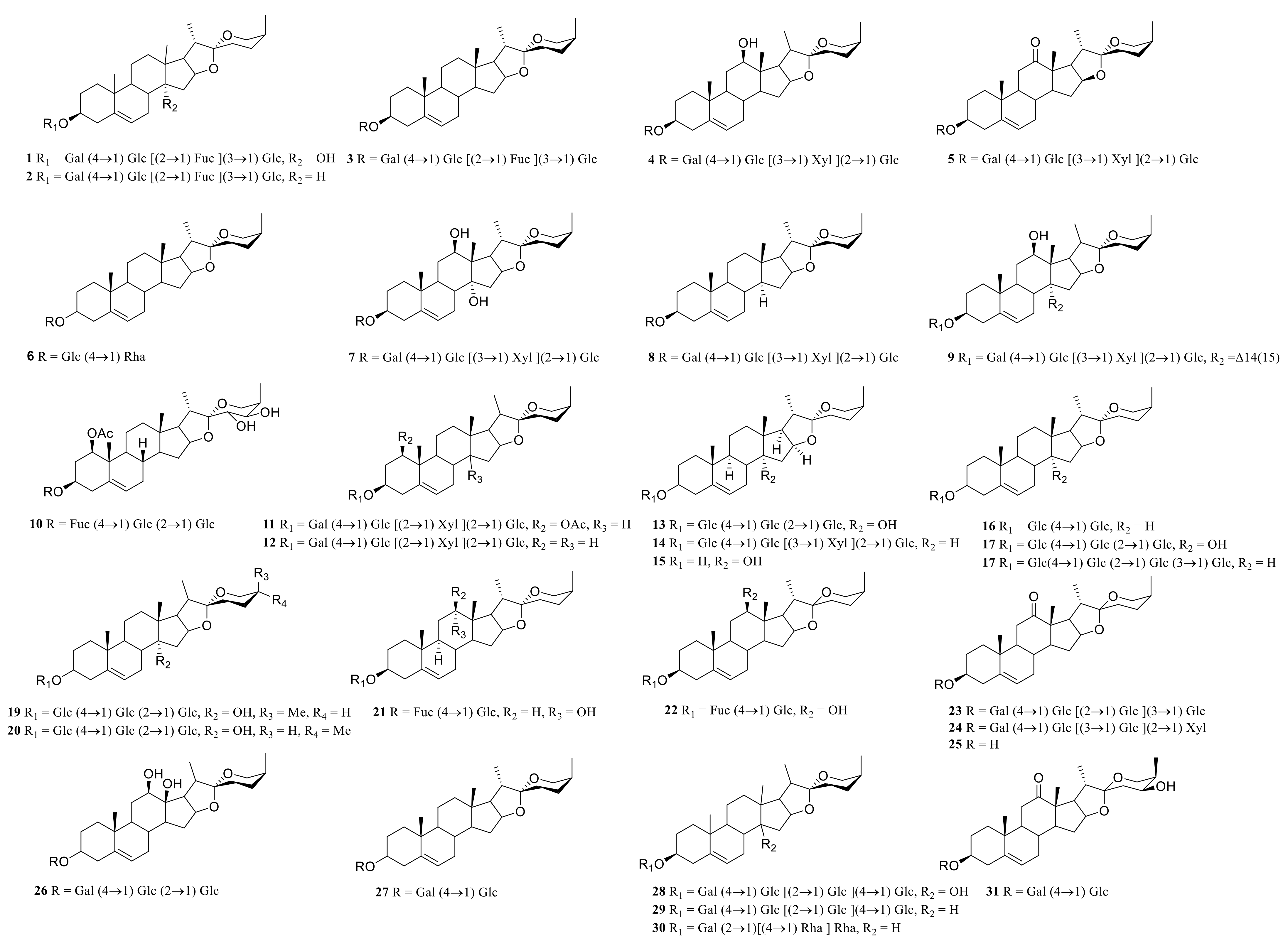
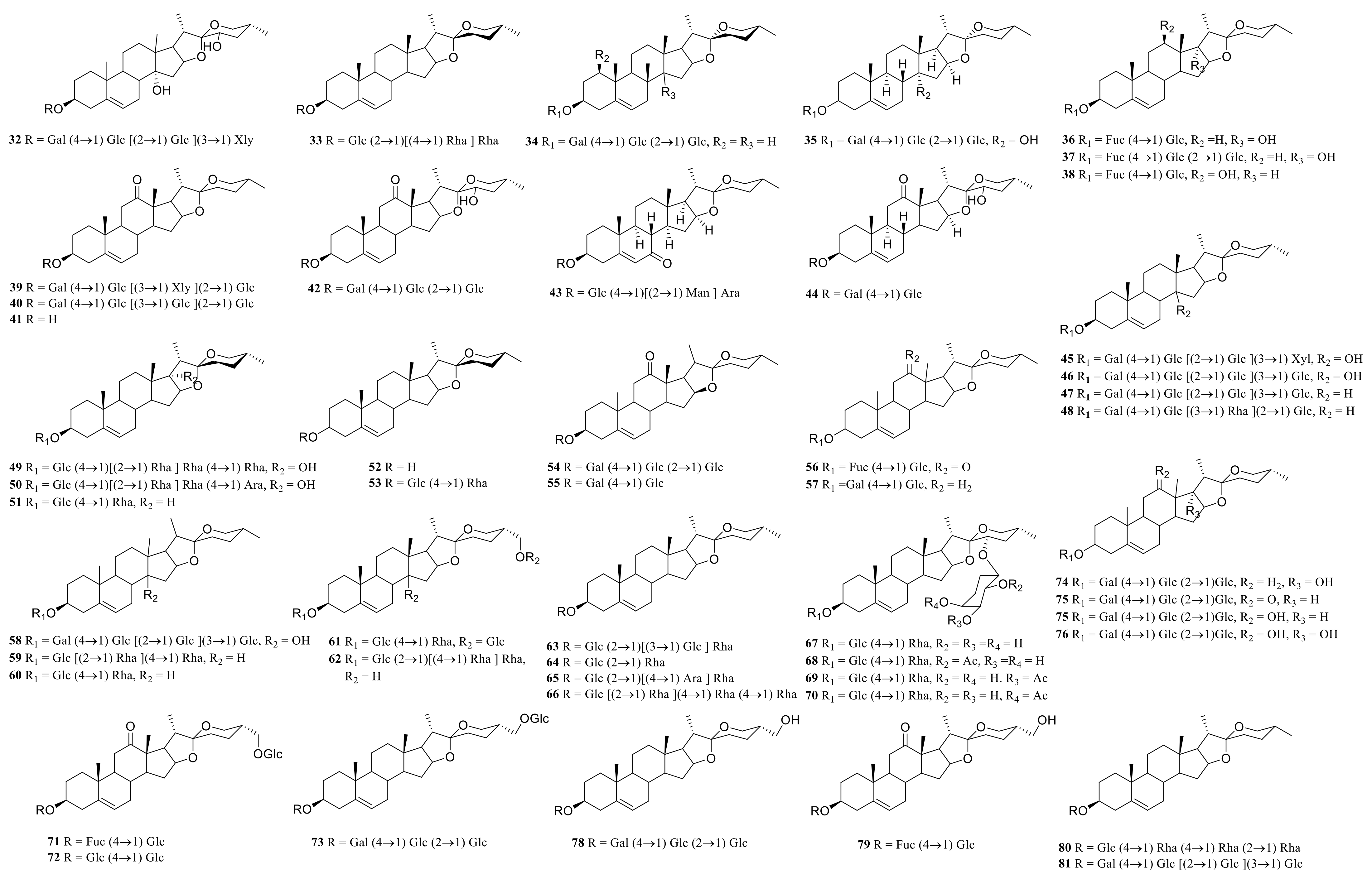
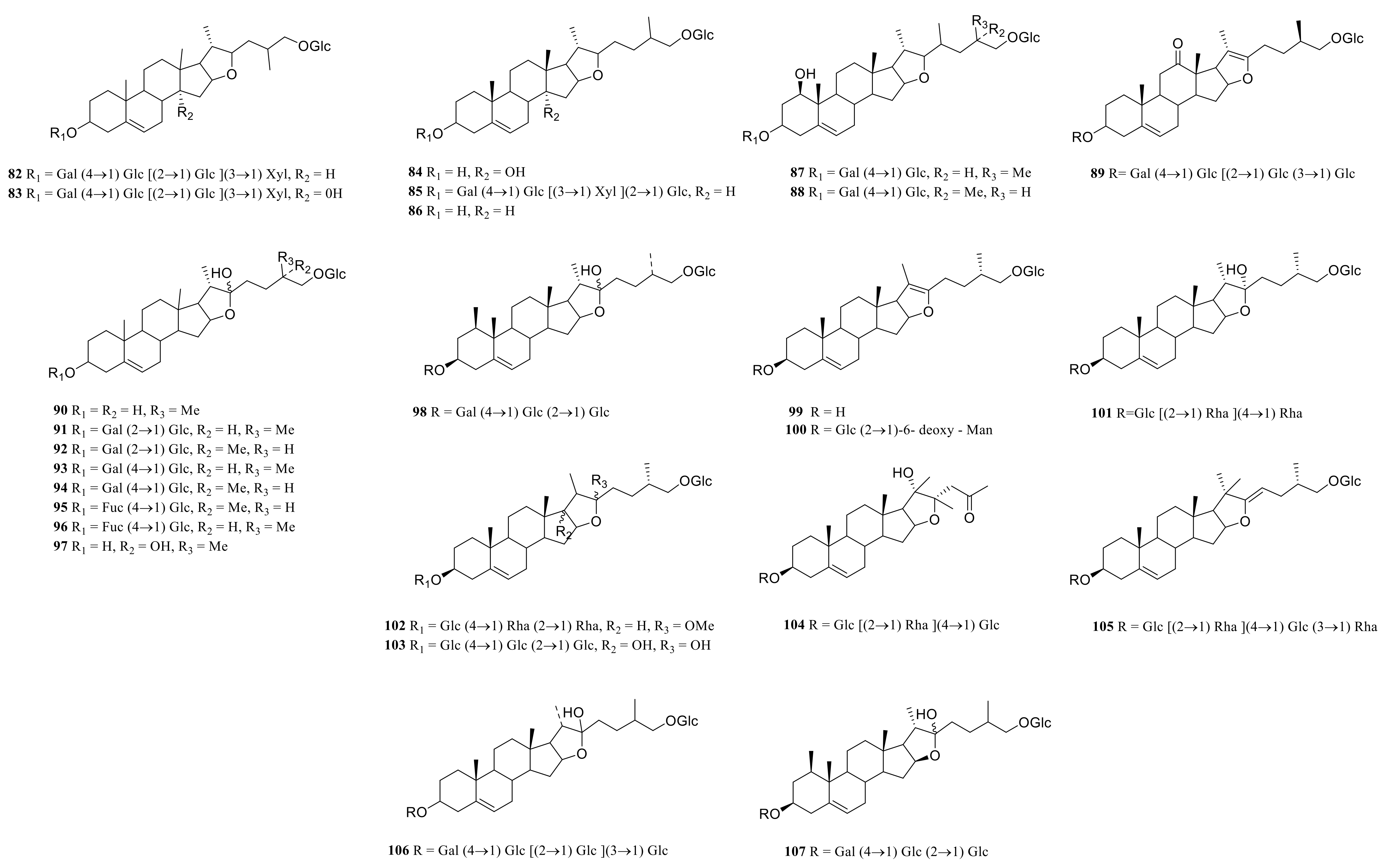
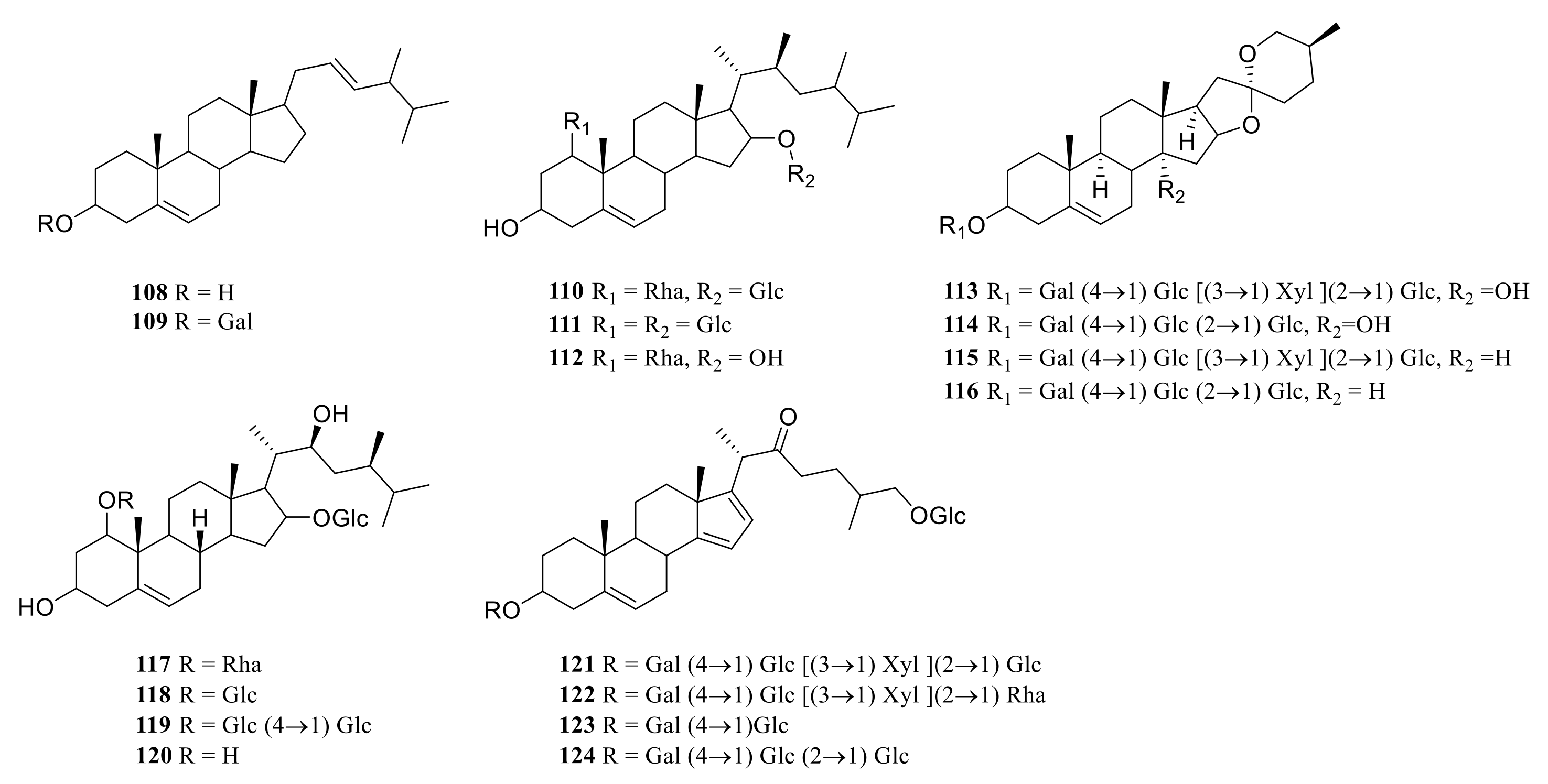
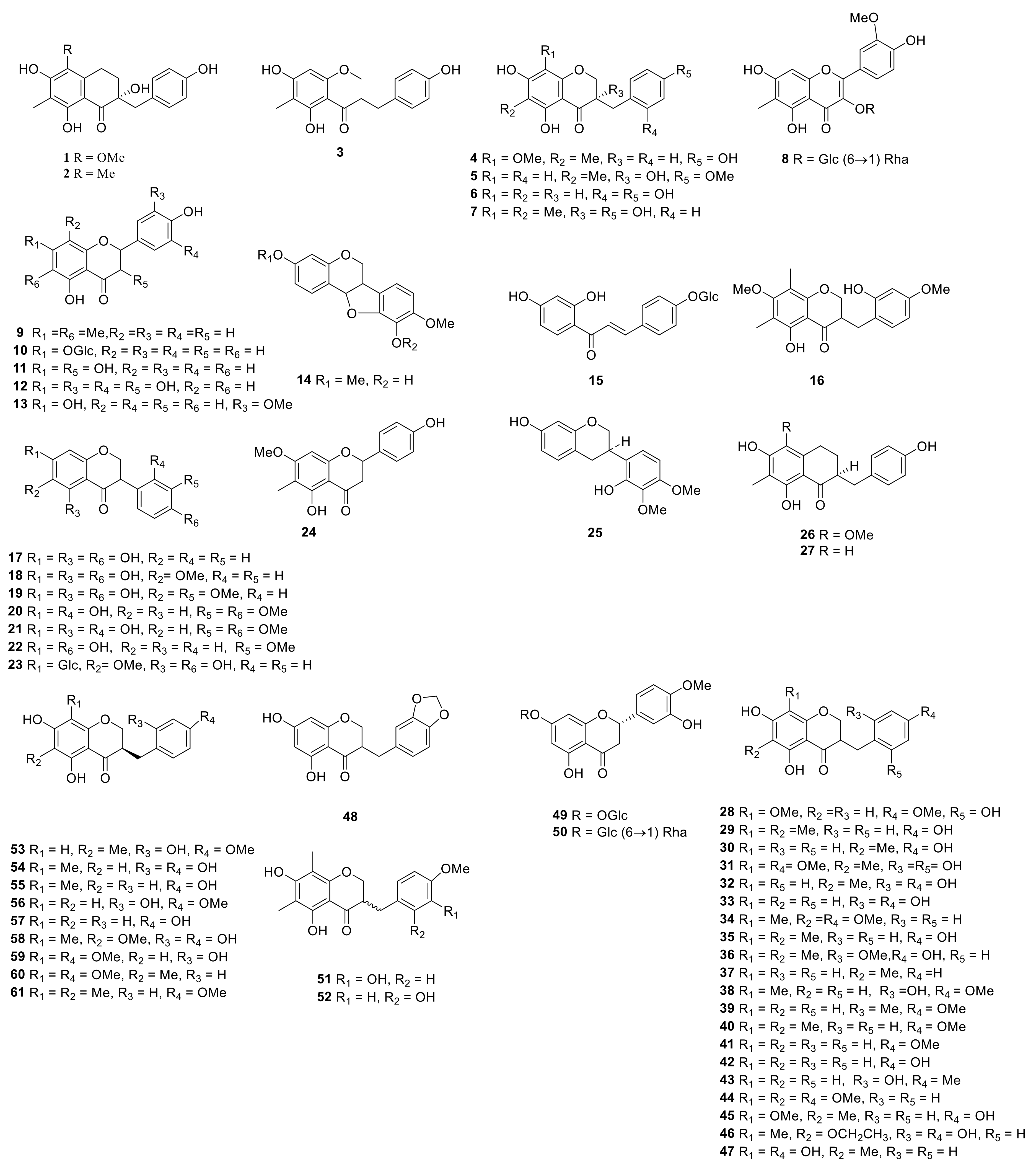
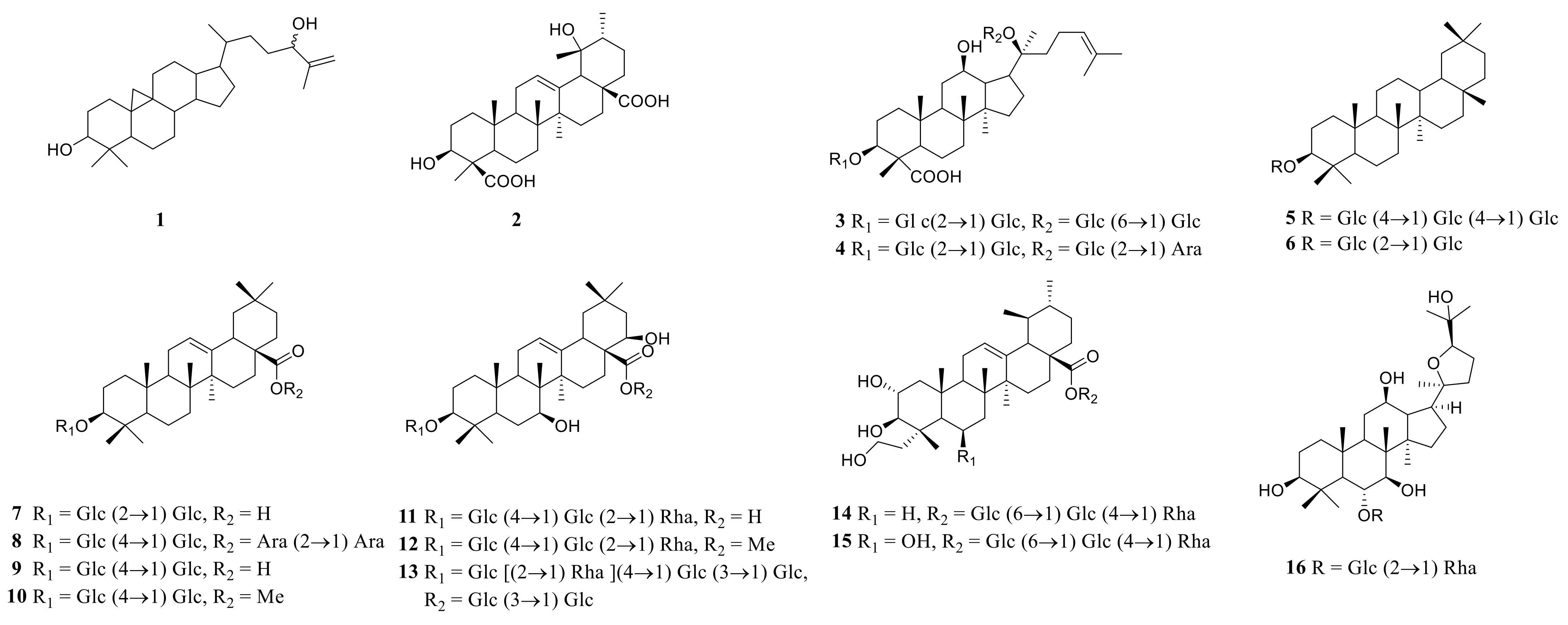
Steroid saponins are formed by the condensation of steroid sapogenins and sugar. The carbon frame of steroid sapogenins is made up of 27 carbon atoms and is based on spirostane. According to the configuration of C25 in the spirostane structure and the cyclization state of the F ring, it is divided into spirostanol, isospirostanol, furostanol, and pseudo spirostanol types. The main pharmacological active substances are the first three types of steroidal saponins in the genus Polygonatum. The glycosyl moiety (mainly glucose, galactose, xylose, rhamnose, and fucose) is an important factor in the formation of the molecular diversity of the genus Polygonatum saponins. The details of the compounds are shown in Table 2, and the structural formulas are shown in Figure 1, Figure 2, Figure 3 and Figure 4.

Table 2.
Chemical constituents of the genus Polygonatum.
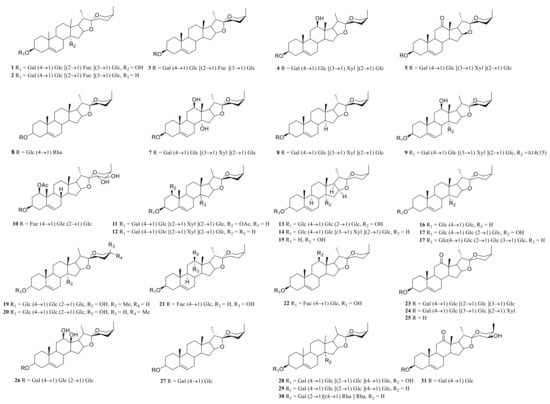
Figure 1.
Structures of spirostanol from Polygonatum Mill.
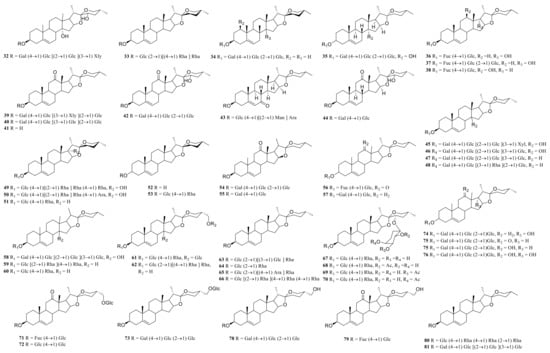
Figure 2.
Structures of isosprirostanol from Polygonatum Mill.
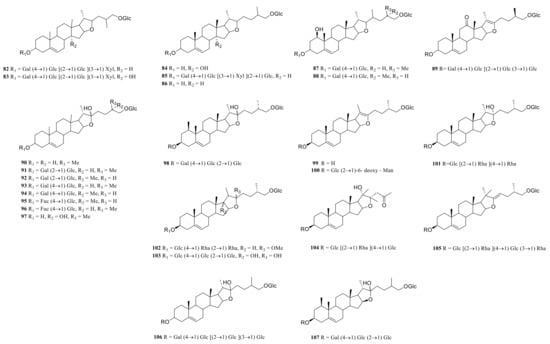
Figure 3.
Structures of furostanol from Polygonatum.
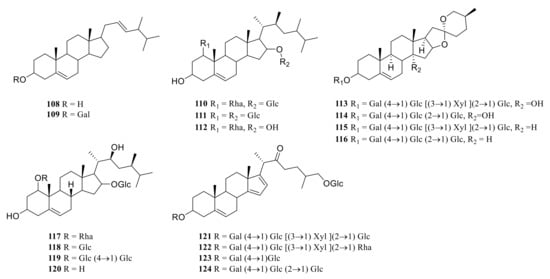
Figure 4.
Structures of other steroidal saponin from Polygonatum.
3.2. Flavonoids
Flavonoids originally refer to the general term for compounds derived from 2-phenylchromone. It generally refers to a set of compounds formed by two benzene rings connected through three carbon atoms, a general term for a series of compounds with a C6-C3-C6 structure. Flavonoids mostly include flavones, flavonols, dihydroflavonoids, isoflavones, and homoisoflavonoids in Polygonatum Mill. (Table 3, Figure 5).

Table 3.
Flavonoids of Polygonatuml.
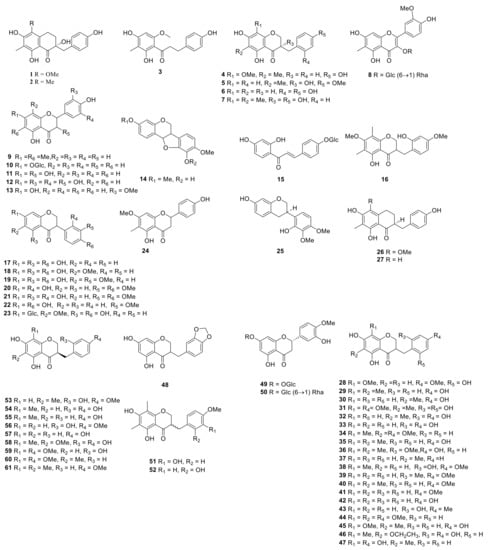
Figure 5.
Structures of flavonoid from Polygonatum.
3.3. Triterpenoid Saponins
Triterpene saponin is a class of glycosides in which aglycones are triterpenoid compounds, mainly distributed in terrestrial higher plants. Triterpenoids are a type of terpenoids. Their basic core skeleton is made up of 30 carbon atoms. They exist in plants in three forms; free, in the form of glycosides, or esters combined with sugars. The main active ingredients of many well-known Chinese herbal medicines, such as Ginseng, Glycyrrhiza uralensis, and Anemarrhena asphodeloides, have triterpene saponins. Some saponins also have valuable biological activities, such as antibacterial activity, sedation, and anticancer. The triterpenoid saponins isolated and identified from the plants of the genus Polygonatum are shown in Table 4, and structures are shown in Figure 6.

Table 4.
Triterpenoid saponins of Polygonatum.
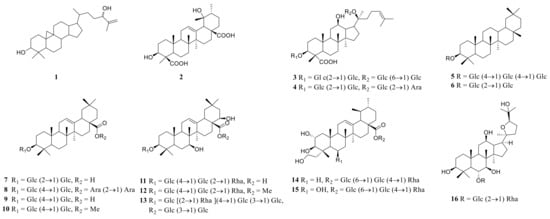
Figure 6.
Structures of triterpenoid saponin from Polygonatum.
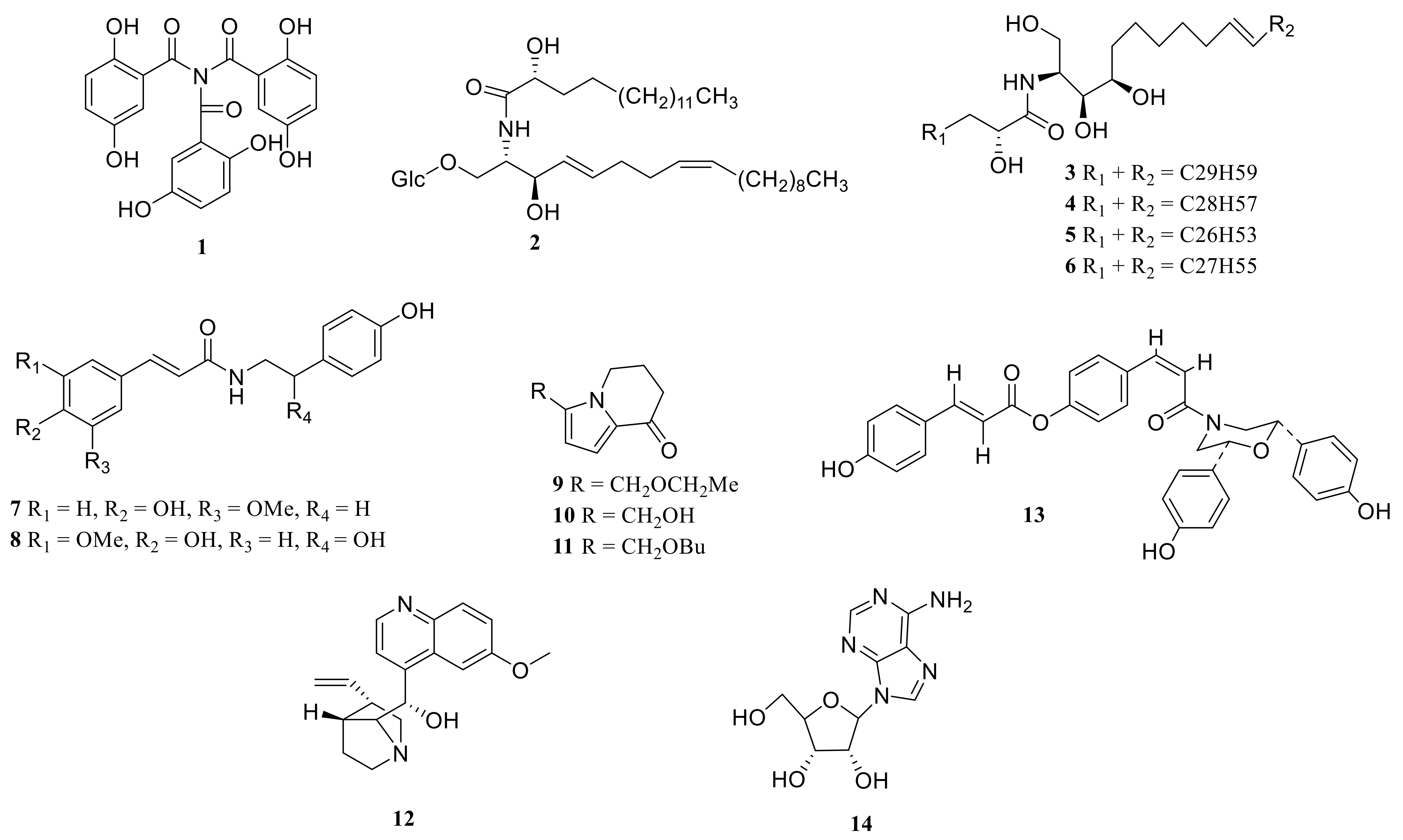
3.4. Alkaloids
Alkaloids are nitrogen-containing alkaline organic compounds in nature (mainly in plants, but some also exist in animals). They have a complex ring structure, and nitrogen is usually contained in the ring. It has significant biological activity and is one of the most effective ingredients in Chinese herbal medicine. Polygonatum has a low content of alkaloids and a changeable structure. Alkaloids have been found in P. odoratum, P. kingianum, P. cirrhifolium, P. verticillatum, and P. alte-lobatum (Table 5, Figure 7).

Table 5.
Alkaloids of Polygonatum.
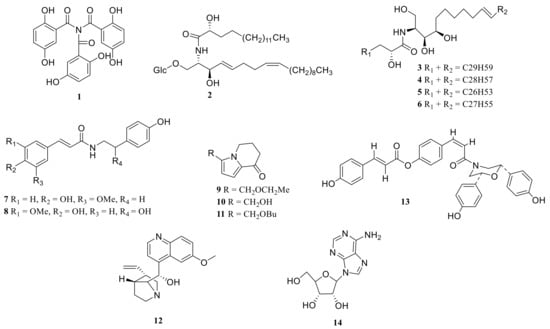
Figure 7.
Structures of alkaloid from Polygonatum.
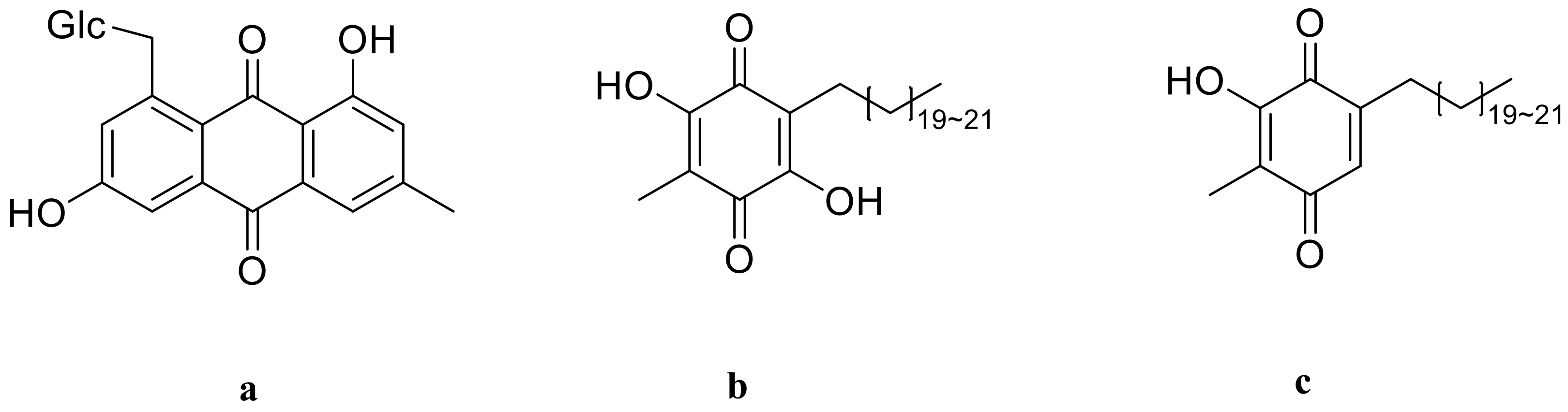
3.5. Quinones
There are now three quinones isolated from P. odoratum and P. alteolobatum [13,47]. Ubiquinones with a benzoquinone structure can engage in the redox process in vivo and are a family of coenzymes considered to coenzyme Q in biological oxidation reactions. It has significant therapeutic medical value and can be used to treat cardiovascular disease, hypertension, and cancer. The tree quinones are emodin-8-O-β-D-glucopyranoside (a), polygonaquinone A (b), and polygonaquinone B (c), and their structures are in Figure 8.
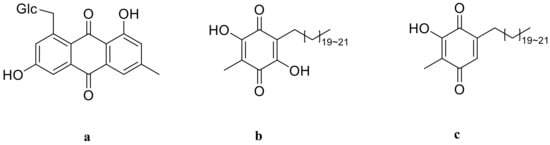
Figure 8.
Structures of quinone from Polygonatum, (a) emodin-8-O-β-D-glucopyranoside; (b) polygonaquinone A; (c) polygonaquinone B.
3.6. Lignans
Lignans exist in plants and belong to a kind of phytoestrogen that has antioxidation functions. Ru [56] isolated four lignans from P. sibiricum for the first time, which were (+)-syringaresinol, (+)-syringaresinol-O-β-D-glucopyranoside, liriodendrin, (+)-pinoresinol-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl-(6→1)-β-D-glucopyranoside. Gao [39] also found liriodendrin from the fresh P. sibiricum rhizome. Chen Hui et al. [60] published three lignans from the ethyl acetate layer of P. sibiricum rhizomes, namely (+)-syringaresinol, 5-hydroxy-7-methoxy-4,6-dimethyl- 2-benzofuranone, terpineol.
3.7. Polysaccharides
Polysaccharide is one of the main active ingredients of the genus Polygonatum. Due to the complexity of the structure and the relatively large molecular weight of Polygonatum Polysaccharide, there are relatively few studies on the chemical structure. At present, galactomannan galactose has two types of neutral polysaccharides (PSB-2A, PSB-1B), two types of acid polysaccharides (PSW-2A-1, PSW-3A-1), two glycoproteins (PSW-4A, PSW-5B), and neutral galactose (PSW-1B-b), separated and purified from the rhizome extract of P. sibiricum [61]. Different extraction methods result in different monosaccharide compositions. The structure of the original P. cyrtonema polysaccharide was composed of arabinose, galactose, glucose, and xylose with a molecular ratio of 1.34:7.42:54.47: 36.95 by Wu [62], and other groups also proved that cellulase-assisted extraction and hot water extracted polysaccharide of polysaccharides from P. odoratum consisted of mannose, glucosamine, rhamnose, glucose, galactose, and arabinose, with a molecular ratio of 7.80:1.08:1.63:65.93:3.58:1.00 and 11.22:0.23:0.23:17.59:2.73:9.10, respectively [63]. Interestingly, this article did not explain the specific temperature of hot water. Both 50 °C and 90 °C were hot water. Different species have different monosaccharide compositions. Zhao [64] proved that polysaccharides from P. sibiricum, P. cyrtonema, and P. kingianum were mainly composed of fructose, galacturonic acid, and galactose, with small amounts of rhamnose, arabinose, xylose, and glucose; while polysaccharides from P. odoratum mainly consisted of fructose with trace amounts of galacturonic acid, galactose, rhamnose, arabinose, xylose, and glucose.
4. Pharmacological Activities
4.1. Antioxidant Activities
The P. sibiricum (PSP) may modulate the Klotho-FGF23 endocrine axis, reduce oxidative stress, and maintain calcium and phosphorus metabolism balance [65]. Polygonatum cyrtonema polysaccharide (PCP) significantly increased superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px) activities and decreased malondialdehyde (MDA), indicating PCP could increase antioxidant enzyme activity to protect against lipid peroxidation and oxidative stress induced by exhaustive exercise. Additionally, PCP dramatically increased the protein levels of bone morphogenetic protein-2 (BMP-2), phosphor-Smad1, Runt-related transcription factor 2 (Runx2), and osteocalcin (OC). These findings revealed a link between PCP’s antioxidant property and its anti-fatigue function [66]. By decreasing oxidative stress, oral treatment of PSP may mitigate the aging and damage generated by D-galactose in the heart. D-gal treatment decreased reactive oxygen species (ROS) and MDA and enhanced SOD levels in the hearts of mice. By reducing the levels of 8-hydroxydeoxyguanosine (8-OHdG) and 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal, PSP also prevented oxidative stress-induced DNA damage and lipid peroxidation (4-HNE) [67]. Regarding other species, extracts of P. alte-lobatum (EPA) dose-dependently reduced exercise-induced urea nitrogen and malondialdehyde and enhanced hepatic glycogen, an essential workout fuel [68]. In addition, the surface structure of PSP was smooth and irregular, and bead-like structures were identified, suggesting that PSP could be employed for encapsulating purposes in the design of drug delivery systems [69]. In other research, PSP was used as a stabilizer to fabricate SeNPs (selenium nanoparticles) under a simple redox system. The ability of SeNPs to get rid of free radicals was greatly improved by adding PSP to the surface of the nanoparticles [70].
4.2. Anti-Fatigue Activities
The trend analysis showed that EPA supplementation improved endurance running time 1.62-fold. EPA boosted rats’ endurance time to exhaustion, showing it may increase exercise tolerance [71]. Swimming time was used to test the anti-fatigue activity of PCP. Dose- and age-dependent increases in fatigue time were seen after PCP treatment, indicating that PCP may enhance the endurance of mice during exercise. A significant correlation was found between exhaustive swimming duration and osteocalcin levels in mouse muscle fibers treated with PCP, showing that PCP’s anti-fatigue effect is linked to energy metabolism and osteocalcin signaling [72].
4.3. Anti-Inflammatory Activities
The anti-inflammatory mechanism of P. sibiricum that suppressed the production of pro-inflammatory mediators and was linked to the downregulation of the NF-B pathway was discovered [73]. In vitro anti-inflammatory effects of P. verticillatum were positively correlated with the total phenolic content, flavonoid content, and condensed tannin content. It showed that P. verticillatum had powerful antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and cancer-preventing properties caused by the plant’s secondary metabolites [74]. Using reverse transcription-quantitative PCR and western blotting, PSP decreased body weight, blood lipids, blood glucose, insulin, resistin, adiponectin, and abdominal fat pad weight. It also reversed abnormal expression levels of inflammatory factors and lipid metabolism genes [75].
4.4. Antihypoglycemic Activities
Polygonatum Mill. has been used as herbal medicine to treat type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). The polysaccharides of Polygonatum rhizoma were analyzed for their structure and bioactivity. At concentrations between 1.0 and 10.0 mg/mL, polysaccharides from Polygonatum rhizoma showed varied levels of hypoglycemic action in a dose-dependent manner [76]. The active ingredients are not just polysaccharides but also saponins. The total saponins extract from P. sibiricum could inhibit α-amylase and α-glucosidase, a in insulin resistant (IR) -HepG2 cells model [77]. In the same activity as other species, polysaccharides of P. kingianum increased the expression of insulin receptor substrate-1 (IRS-1), phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K), and protein kinase B (AKT), showing that polysaccharides of P. kingianum adjust glucose metabolism by activating the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway.
4.5. Immunological Activities
The vitality of macrophages is a measure of immune activation and activator cytotoxicity [78]. In a dose-dependent way, PSP caused dendritic-like morphological alterations in RAW 264.7 cells and enhanced the production of nitric oxide, TNF-α, and IL-6. The expression of iNOS, COX-2, NF-kB, and phosphorylated p38 MAPK was increased in RAW 264.7 cells treated with PSP [79]. Different concentrations of extractants have different effects. The P. sibiricum ethanol 75 (PSE75) increased the mRNA expression of Th1 and Th2 molecular markers compared to P. sibiricum ethanol 30 (PSE30). Immunoglobulins G and M were substantially higher in PSE75 than in PSE30. The immunological regulatory action of PSE75 may be mediated by a change in the makeup of gut microbes [80]. In another study, PSP increased the expression of IL-2 and TNF-α in lymphocytes of the spleen. In addition, PSP therapy increased the dose-dependent recovery of natural killer cell activity [81]. The same as other species, P. odoratum polysaccharides (POP) also exhibit immunomodulatory activity [82]. Immunomodulation, infection prevention, gut environment enhancement, and cancer suppression of the Polygonatum genus have been studied extensively.
4.6. Other Activities of Polygonatum Mill.
P. kingianum polysaccharides (PKP) and P. kingianum aqueous extract (PKAE) alleviated uranium-induced cytotoxicity by regulating mitochondria-mediated apoptosis and the GSK-3β/Fyn/Nrf2 pathway [83]. PCP exerted antidepressant effects by regulating the oxidative stress-calpain-1- NOD-like receptor protein 3 (NLRP3) signaling axis. PCP prevented chronic unpredictable mild stress-induced changes in the calpain system and reduced depression-like behavior [84]. Moreover, methanol extract from P. odoratum administration reversed intestinal microbiota compositions, inhibiting H2S-related bacteria, a lower level of H2S, and higher content of short-chain fatty acid-related bacteria [85]. PSP also can act as a prebiotic, regulating the intestinal tract probiotics. At the phylum level, PSP treatment raised the number of Lactobacillus and decreased the abundance of Lachnospiraceae and Bacteroides (at the genus level). The make-up of microbes shifted. The PSP group increased SCFAs, such as acetic acid, propionic acid, and butyric acid than the control mice [86].
5. Processing of Polygonatum Mill.
5.1. Processing Methods of Polygonatum Mill.
There were many methods of processing the genus Polygonatum in the past to increase the curative effect and reduce toxicity. Calcium oxalate monohydrate (COM) raphides may be some of the irritating components of the genus Polygonatum. After processing, there were far fewer COM raphides. The raphide bundles that remained adhered together and were difficult to separate and most single raphides were disintegrated, particularly at their tips [87]. Some scholars believe that volatile components, such as n-hexanal and camphene, are also irritating components of the genus Polygonatum [88]. There are big differences in the processing and use of traditional Chinese medicine. According to the records of relevant documents in various regions, the processing methods of Polygonatum plants include steaming, wine steaming, and wine stewing. There are big differences in the auxiliary materials [89]. The most commonly used methods are steaming, wine steaming, and wine stewing. The “Chinese Pharmacopeia” includes wine steaming and stewing [3]. Whether steaming or stewing can achieve the purpose, using wine as an auxiliary material can increase the dissolution of certain compounds [90]. The author summarizes all methods of processing the genus Polygonatum. (Table 6).

Table 6.
Processing of Polygonatum.
5.2. Effect of Processing on the Chemical Composition
Polysaccharides are one of the main components of the medicinal Polygonatum Mill., which changes after processing. During the nine steaming and nine drying processes of the genus Polygonatum, with the increase in steaming times, the polysaccharide content first decreases and then stabilizes. Baolai Fan [96] analyzed polysaccharide component changes in distilled and processed P. cyrtonema by PMP(1-phenyl-3-methyl-5-pyrazolone) pre-column derivatization, and high-performance liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry/mass spectrometry (HPLC–MS/MS) technology; the processed Polygonatum polysaccharide is mainly composed of galactose and mannose, followed by glucose. Moreover, other groups [97] showed that as the number of repetitions of steaming increases, polysaccharides gradually decompose into small monosaccharides. For these monosaccharides, the content after four steaming seems relatively stable [98]. All these dynamic changes in polysaccharides and monosaccharides result from the decomposition of glycosidic bonds that steaming can destroy. Others [99] revealed that the content of 5-hydroxymethyl furfural, galactose, and glucose increased after the fourth steaming and tended to be stable. Moreover, the raw rhizome’s strong numb tongue taste decreased progressively until disappearance after the fourth steaming, and the sweet taste gradually turned from slight to strong at the fourth steaming, which indicated that the toxic components were greatly reduced and the flavor was greatly developed at the fourth steaming.
During the nine steaming and nine drying processes of P. cyrtonema, the content of saponins increased first and then stabilized with the increase of steaming and drying. Since diosgenin is a prerequisite for many other saponins, some researchers have found that the content of diosgenin in P. cyrtonema after the wine is lower than that of raw products [100].
5.3. Influence of Processing on Pharmacological Effects
5.3.1. Antioxidant Activities after Processing
There are various processing methods for evaluating the antioxidant activity of P. odoratum flavones and determining which procedure could preserve such activity. The yeast fermentation had the least effect on the antioxidant activity of P. odoratum flavones, making it the optimal way of food processing for P. odoratum. In contrast, extrusion and high-pressure treatment marginally diminished the flavones’ antioxidant activity [101]. The same is true for P. odoratum flavones, and the fermentation method evaluated the antioxidant properties of flavones extracted from fermented P. odoratum samples. Lactobacillus, yeast, and Aspergillus fermentation were examined. By fermenting with Lactobacillus and yeast, the antioxidant capacity of P. odoratum flavones was found to be diminished. Fermentation with Aspergillus niger enhanced the antioxidant capacity of P. odoratum flavones [102]. The flavones are not the only compounds that have antioxidant activity. Using radical scavenging experiments, the antioxidant activity of PSP was evaluated. It was discovered that the radical scavenging activity of PSP was significantly enhanced after steaming and increased steadily with increasing numbers of steaming processes [99]. Although the polysaccharides content was decreased after steam-processing, antioxidant and hypoglycemic activities of P. cyrtonema were enhanced [103].
5.3.2. Anti-Fatigue Activities after Processing
Polysaccharides in the processed products of P. cyrtonema were the active compounds against exercise tiredness, which were more active in the plant’s processed products than in its raw materials. It offers anti-fatigue benefits for swimming exhausted mice, liver glycogen content rose, and the impact of the processed product was superior to that of the raw materials [104,105].
5.3.3. Anti-Inflammatory Activities after Processing
Lung damage caused by LPS may be treated with PSP polysaccharides and its honey-processed polysaccharides, both of which include anti-inflammatory properties. The honey-processed polysaccharides had a greater anti-inflammatory impact than raw materials polysaccharides, which inhibited the synthesis and release of IL-1, IL-6, and TNF-α [106]. In another study, raw polysaccharides and nine-steam-nine-bask processing P. cyrtonema demonstrated no toxicity and side effects on lipopolysaccharide-induced RAW264.7 cells and showed obvious inhibitory effects on the inflammatory cytokines NO, TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, and MCP1 in a dose-dependent manner. Thus, it is assumable that polysaccharides from raw materials and nine-steam-nine-bask processing P. cyrtonema play an anti-inflammatory role by inhibiting the expression of related inflammatory factors [107].
5.3.4. Anti-Hypoglycemic Activities after Processing
The different extractions parts from the crude and steam-processed P. cyrtonema were tested for inhibiting α-glucosidase activities from exploring potential active sites [108]. The result shows that the inhibition rate of the ethyl acetate phase of the steamed product reached 87.21%, IC50 = 1.369 mg/mL, and the inhibition rate of the ethyl acetate phase of the raw product reached 59.38%, indicating that the active ingredient in the ethyl acetate phase of the steamed product has a strong effect on α-glucose. Li [109] found that fermented P. sibiricum ameliorated the lipid accumulation in liver and white adipose tissue by inhibiting lipogenesis, enhancing lipolysis, and fatty acid oxidation. Therefore, it lowered the fasting blood glucose, insulin, total cholesterol, and triglyceride. In addition, it could reduce glycated hemoglobin in the homeostasis model after P. sibiricum was fermented. When P. sibiricum was processed using the traditional technology of “Nine-Steam-Nine-Bask”, its 70% ethanol extracts exhibited the relief of glycolipid metabolism abnormalities in type 2 diabetic mice [110].
5.3.5. Immunological Activities after Processing
As mentioned above, PCP content was considerably reduced by steaming. Compared to PCP from the raw rhizome, the immunological activities of PCP after 2 and 4 h were greater on PCP. The longer the steaming duration (6–12 h), the more PCP was destroyed, which had a detrimental effect on the immune system [111]. In another study [112], IL-2, IL-6, TNF-α, and IFN-α secretions reversed to normal levels after treatment with the water-soluble PSP extracted from crude and wine-processed PSP in the immunosuppressive model for spleen-deficient mice. PSP that had been wine-processed had more immunological effects than PSP from crude. The steam-processed PSP might be linked to the regulation of the JAK1-STAT1 pathway and the elevation of hematopoietic cytokines (erythropoietin, granulocyte colony-stimulating factor, TNF-a, and IL-6). It could also significantly increase peripheral blood cells, restore the splenic trabecular structure, and bring immune cytokines back to normal levels [113].
6. Conclusions
In conclusion, based on the current state of research, Polygonatum Mill. belongs to a renewable resource herb with many species. It has numerous chemical components and pharmacological activities. Various research studies have been conducted to evaluate the traditional uses of the genus Polygonatum, and all of the research supports the traditional claims. The authors believe that corresponding standards of Polygonatum Mill. should be established according to their various clinical applications first [6]. Secondly, an abundance of traditional uses has not been evaluated, especially in species other than P. sibiricum, P. cyrtonema, P. kingianum, and P. odoratum. Hence, further research is needed to exploit the many uses of the Polygonatum species. The final objective should be to research the usefulness of parts on the ground and fibrous roots to ensure effective protection and the sustainable development of resource applications.
Author Contributions
L.L.: developed the study; Y.Q.: executed the analyses and manuscript writing; L.G., R.W. and W.W.: provided valuable assistance in revising the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the General Projects of Changsha Science and Technology Bureau (kq200405), Hunan Provincial Department of Education Youth Program (20B446), 2018 Pharmacy First-Class Open Fund (2018YX08), and 2021 Pharmacy First-Class Open Fund (2021YX13).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not Applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not Applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The information that supports the findings of this study is available in this article.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to acknowledge Xudong Zhou for her help and valuable suggestions.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Institutional Repository of the Chinese Academy of Sciences. Flora of China; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1978; Volume 15, p. 52. [Google Scholar]
- Chinese Materia Medica Editorial Committee of the State Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine. Chinese Materia Medica; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1999; Volume 5, pp. 134–151. [Google Scholar]
- National Pharmacopoeia Commission. Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China. One; China Medical Science and Technology Press: Beijing, China, 2020; Volume 4, pp. 387–388. [Google Scholar]
- Qiang, L.; Wei, L.; Nagata, K.; Hongwei, F.; Kazuo, K. Separation from Polygonatum odoratum, structure Elucidation and analysis of steroidal glycosides by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Acta Agri-Food Chem. 2018, 66, 521–531. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, J.B.; Ge, J.C.; Zhang, W.J.; Liu, W.; Luo, J.P.; Xu, F.Q.; Wu, D.L.; Xie, S.Z. Physicochemical, morpho-structural, and biological characterization of polysaccharides from three Polygonatum spp. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 37952–37965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.; Liu, P.; Wu, W.; Li, D.; Shang, E.-X.; Guo, S.; Qian, D.; Yan, H.; Wang, W.; Duan, J.-A. Multi-constituents variation in medicinal crops processing: Investigation of nine cycles of steam-sun drying as the processing method for the rhizome of Polygonatum cyrtonema. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2022, 209, 114497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, K.H.; Do, J.C.; Kang, S.S. Steroidal Saponins from the Rhizomes of Polygonatum sibiricum. J. Nat. Prod. 1990, 53, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Han, G.; Liao, S. Study on the effective ingredients of Chinese medicine Polygonatum odoratum. Acta Pharm. Sci. 1994, 29, 215. [Google Scholar]
- Gvazava, L.N.; Skhirtladze, A.V. Steroidal saponin from Polygonatum verticillatum. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2016, 52, 1052–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dongmei, W.; Jingfang, Z.; Xiaoming, L.; Chen, G.X.; Zhao, T.Z. The chemical constituents of steroidal saponins and their antibacterial activities in the root of Polygonatum cirrhifolium. For. Sci. 2007, 8, 91–95. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Li, D.; Zhu, W.; Zhang, J.; Peng, P. Steroidal saponins from the rhizomes of Polygonatum odoratum. Nat. Prod. Res. 2009, 23, 940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, M.; Kim, C.Y.; Yoon, K.; Ryu, M.Y.; Cheong, J.H.; Chin, Y.W.; Kim, J. Steroidal saponins from the rhizomes of Polygonatum sibiricum. Nat. Prod. 2006, 69, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, X.; Zhao, J.-Y.; Wang, Y.-J.J.; Zheng, W.; Zhang, J.; Chen, X.-J.; Chen, S.; Yu, L.-Y.; Ma, B.-P. Steroidal glycosides, homoisoflavanones and cinnamic acid derivatives from Polygonatum odoratum and their inhibitory effects against influenza A virus. Fitoterapia 2020, 146, 104689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Li, W.; Nagata, K.; Zheng, W.; Ma, B.P. Isolation, structural elucidation, and liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry analysis of steroidal glycosides from Polygonatum odoratum. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, H.; Li, W.; Zhao, H.; Anzai, Y.; Li, H.; Guo, H.; Kato, F.; Koike, K. Isolation and structural elucidation of novel cholestane glycosides and spirostane saponins from Polygonatum odoratum. Steroids 2014, 80, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Yu, Y.; Qi, Q.; Wu, X.-D.; Wang, J.; Tang, S.-A. Steroidal saponins from the rhizome of Polygonatum sibiricum. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2018, 21, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, H.; Wu, Q.; Ping, Y.; Yuan, M.; Zhou, Z.; Qian, Y.; Xu, Y.; Ning, H. Simultaneous determination of 5-Hydroxy Maltol, 5-Hydroxymethyl Furfural and Polygonatine A in Polygonatum Cyrtonema by HPLC. Chin. J. Exp. Formulas 2018, 21, 1683–1686. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, K.; Huang, X.; Kong, L. Steroidal saponins from Polygonatum cyrtonema. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2013, 49, 888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, H.H.; Yuan, M.; Wu, Q.-P.; Ping, Y.-H.; Zhou, Z.-Q.; Xu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Yin, H.-X. Identification of Chemical Constituents from Polygonatum cyrtonema. Chin. J. Exp. Tradit. Med. Formulae 2018, 24, 77–82. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, S.; Yuan, M.; Ning, H.; Kan, R.; Huang, L.; Fu, X.; Wu, Y. Chemical Consitiuetns of Ethly Acetate Extract from Stewed Polygonatum Ehizoma. J. Chin. Med. Mater. 2021, 44, 2332–2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhou, J.; Ju, Y.; Zhang, H.; Liu, M.; Li, X. Effects of two saponins extracted from the Polygonatum zanlanscianense pamp on the human leukemia (HL-60) cells. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2001, 24, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, H.S.; Ma, B.P.; Kang, L.P.; Zhang, T.; Jiang, F.J.; Zhang, J.; Zou, P.; Zhao, Y.; Xiong, C.Q.; Tan, D.W.; et al. Saponins from the processed rhizomes of Polygonatum kingianum. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2009, 57, 1011–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, H.; Zhang, J.; Kang, L.; Han, L.F.; Zou, P.; Zhao, Y.; Xiong, C.Q.; Tan, D.W.; Song, X.B.; Yu, K.; et al. Three new saponins from the fresh rhizomes of Polygonatum kingianum. Pharm. Soc. Jpn. 2009, 57, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, H.S.; Ma, B.P.; Song, X.B.; Kang, L.P.; Zhang, T.; Fu, J.; Zhou, Y.; Xiong, C.Q.; Tan, D.W.; Zhang, L.J.; et al. Two new steroidal saponins from the processed Polygonatum kingianum. Helv. Chim. Acta 2010, 93, 1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dongmei, W.; Wei, Z.; Juanli, L. Chemical constituents and antibacterial activity of Polygonatum cirrhifolium rhizome research. J. Sichuan Univ. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2007, 44, 918. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.C.; Yang, C.R.; Ichikawa, M.; Matsuura, H.; Kasai, R.; Yamasaki, K. Steroid saponins from Polygonatum kingianum. Phytochemistry 1992, 31, 3559. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Q.X.; Yang, C.R. Cytotoxic steroidal saponins from Polygonatum punctatum. Chem. Biodivers. 2006, 3, 1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Lin, W.; Ye, S.; Wang, H.; Wang, T.; Su, Y.; Wu, L.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Q.; Xu, C.; et al. Protective Effects of an Ancient Chinese Kidney-Tonifying Formula against H2O2-Induced Oxidative Damage to MES23.5 Cells. Parkinsons Dis. 2017, 2017, 2879495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jin, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H.; Yang, C.R. Cytotoxic steroidal saponins from Polygonatum zanlanscianense. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhang, J.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Zhu, W. The chemical formation of steroidal saponins in the root of Polygonatum cirrhifolium and its antibacterial activity. For. Sci. 2007, 8, 91. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.C.; Yang, C.R.; Matsuura, H.; Kasai, R.; Yamasaki, K. Steroid glycosides from Polygonatum prattii. Phytochemistry 1993, 33, 465. [Google Scholar]
- Janeczko, Z.; Jansson, P.E.; Sendra, J. A new stereoidal saponin from Polygonatum Officinale. Planta Med. 1987, 53, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.-P.; Hu, C.-Y.; Zhang, Y. Two new steroidal saponins from the rhizome of Polygonatum sibiricum. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2009, 11, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.-Y.; Hu, W.-C.; Ma, G.-X.; Zhu, N.L.; Sun, X.-B.; Wu, H.F.; Xu, X.D. A new steroidal saponin from Polygonatum sibiricum. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2018, 20, 586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, H.; Li, Z.; Wang, P. New secondary metabolites in the traditional Chinese medicine Yuzhu. Chin. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2004, 29, 42. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Ma, B.P.; Kang, L.P.; Yu, H.S.; Yang, Y.; Yan, X.Z.; Dong, F.T. Furostanol saponins from the fresh rhizomes of Polygonatum kingianum. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2006, 54, 931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, X.; Patil, S.; Qian, A.; Zhao, C. Bioactive Compounds of Polygonatum sibiricum - Therapeutic Effect and Biological Activity. Endocr. Metab. Immune Disord. Drug Targets 2022, 22, 26–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Virk, J.K.; Kumar, S.; Singh, R.; Tripathi, A.C.; Saraf, S.K.; Gupta, V.; Bansal, P. Isolation and characterization of quinine from Polygonatum verticillatum: A new marker approach to identify substitution and adulteration. J. Adv. Pharm. Technol. Res. 2016, 7, 153–158. [Google Scholar]
- Ying, G.; Chulu, Q.; Lei, Z. The chemical constituents of Polygonatum fresh medicinal materials. Pharm. Clin. Res. 2015, 23, 365. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Ren, F.; Chen, S.; Zhang, Q. The new dihydro high isoflavones in Polygonatum odoratum. Med. J. Sci. 2009, 44, 764. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Lai, G.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, G.B.; Luo, S.D. Study on the chemical constituents of Polygonatum yunnanensis (II). Chin. Herb. Med. 2008, 39, 825. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Dabu, X.; He, J.; Yang, H.; Yang, S.; Chen, J.; Fan, W.; Zhang, G.; Cai, J.; Ai, H.; et al. Polygonatone H, a new homoisoflavanone with cytotoxicity from Polygonatum cyrtonema Hua. Nat. Prod. Res. 2019, 33, 1727–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Mu, T.; Chen, J. Study on the chemical constituents of Polygonatum kingianum. China Pharm. J. 2003, 28, 524. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Yang, F.; Qi, J.; Song, X.C.; Hu, Z.F.; Zhu, D.N.; Yu, B.Y. Homoisoflavonoids from the fibrous roots of Polygonatum odoratum with glucose uptake-stimulatory activity in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.-L.; Gan, K.-H.; Wu, R.-R.; Lin, C.-N. Benzoquinones, a homoisoflavanone and other constituents from Polygonatum alte-lobatum. Phytochemistry 1997, 44, 1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-F.; Lu, C.-H.; Lai, G.-F.; Cao, J.X.; Luo, S.D. A new indolizinone from Polygonatum kingianum. Planta Med. 2003, 69, 1066. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.L.; Yuping, Z.; Zhao, H.D. Antioxidant homoisoflavonoids from Polygonatum odoratum. Food Chem. 2015, 186, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshikawa, K.; Eiko, K.; Mimura, N.; Kondo, Y.; Arihara, S. Hovetrichosides C-G, five new glycosides of two auronols, two neolignans, and a phenylpropanoid from the bark of Hovenia trichocarea. J. Nat. Prod. 1998, 61, 786–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Zhang, J.; Li, D. High Isoflavanization of Polygonatum Odoratum Rhizome in Qinling Mountains. For. Sci. 2008, 44, 125. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, Y.; Liang, J.Y.; Qu, W.; Che, Y. Two new homoisoflavanones from Polygonatum odoratum (Mill.) Druce. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2010, 21, 706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Shi, H.B.; Ma, H.; Miao, Y.B.; Liu, T.J.; Wang, W. Homoisoflavanones from Polygonatum odoratum rhizomes inhibit advanced glycation end product formation. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2010, 33, 669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, Y.-Y.; Qian, Y.; Wu, Y.; Qu, W.; Liang, J.Y. Two new homoisoflavanones from the rhizome of Polygonatum odoratum. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2015, 51, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Sun, J.; Qi, B. Extraction, Separation and Structure of Triterpene Saponins from Polygonatum Identification. Chin. Herb. Med. 2006, 37, 1470. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, C.Y.; Xu, D.P.; Wu, Y.M. Triterpenoid saponins from the rhizome of Polygonatum sibiricum. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2010, 12, 801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Zhang, J.; Kang, L. Research on the NMR of a triterpene saponin in Polygonatum yunnanensis (English). Nat. Prod. Res. Dev. 2007, 19, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, L.; Wang, S.; Li, X. New alkaloids in the traditional Chinese medicine Polygonatum. Chin. Med. J. Chem. 1997, 7, 54. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, L.R.; Li, X.; Wang, S.X. Two new alkaloids from the rhizome of Polygonatum sibiricum. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2005, 7, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.N.; Huang, P.L.; Lu, C.M.; Wu, R.R.; Hu, W.P.; Wang, J.J. Polygonapholine, an alkaloid with a novel skeleton, isolated from Polygonatum alte-lobatum. Tetrahedron 1997, 53, 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kun, H.S.; Jae, C.D.; Sam, S.K. Isolation of adenosine from the rhizomes of Polygonatum sibidcum. Arch. Pharm. Res. 1991, 14, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Gu, N.; Hao, Z. Chemical Constituents of Ethyl Acetate Extract from the Rhizomes of Polygonatum sibiricum. J. Chin. Med. Mater. 2017, 40, 1345–1347. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Dong, Q.; Dong, X.T.; Fang, J.N.; Ding, K. Structural investigation of two neutral polysaccharides isolated from rhizome of Polygonatum sibiricum. Carbohydr. Polym. 2007, 70, 304–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Huang, N.; Huang, J.; Wang, L.; Wu, L.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, H. Effects of the steaming process on the structural properties and immunological activities of polysaccharides from Polygonatum cyrtonema. J. Funct. Foods 2022, 88, 104866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, M.; Guo, K.; Jia, A.; Shi, Y.; Gao, G.; Sun, Z.; Liu, C. Cellulase-assisted extraction, characterization, and bioactivity of polysaccharides from Polygonatum odoratum. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 75, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, P.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Yan, Y.; Guo, L.; Huang, L.; Gao, W. Characterization and saccharide mapping of polysaccharides from four common Polygonatum spp. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 233, 115836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, S. Protective effect of Polygonatum sibiricum Polysaccharide on D-galactose-induced aging rats model. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shen, W.-D.; Li, X.-Y.; Deng, Y.-Y.; Zha, X.-Q.; Pan, L.-H.; Li, Q.-M.; Luo, J.-P. Polygonatum cyrtonema Hua polysaccharide exhibits anti-fatigue activity via regulating osteocalcin signaling. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 175, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Wei, S.; Peng, W.; Sun, T.; Huang, J.; Yu, R.; Zhang, B.; Li, W. Antioxidant Effect of Polygonatum sibiricum Polysaccharides in D-Galactose-Induced Heart Aging Mice. BioMed Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 6688855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horng, C.-T.; Huang, J.-K.; Wang, H.Y.; Huang, C.C.; Chen, F.A. Antioxidant and antifatigue activities of Polygonatum Alte-lobatum Hayata rhizomes in rats. Nutrients 2014, 6, 5327–5337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, G.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Qiang, Y.; Wang, B.; Zou, J.; Niu, J.; Wang, Z. Structural characterization and antioxidant activity of Polygonatum sibiricum polysaccharides. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 291, 119524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Cheng, H.; Xia, W. Construction of Polygonatum sibiricum Polysaccharide Functionalized Selenium Nanoparticles for the Enhancement of Stability and Antioxidant Activity. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Joshi, R.; Kumar, D. Quantitative analysis of flavonols, flavonol glycoside and homoisoflavonoids in Polygonatum verticillatum using UHPLC-DAD-QTOF-IMS and evaluation of their antioxidant potential. Phytochem. Anal. 2020, 31, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Li, Z.P.; Zhu, T.; Fung, H.Y.; Wong, T.L.; Wen, X.; Ma, D.L.; Leung, C.H.; Han, Q.B. Anti-Fatigue Effects of the Unique Polysaccharide Marker of Dendrobium officinale on BALB/c Mice. Molecules 2017, 22, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, H.; Wang, Q.; Hou, S.; Chen, G. Chemical constituents from the rhizomes of Polygonatum sibiricum Red. and anti-inflammatory activity in RAW264.7 macrophage cells. Nat. Prod. Res. 2019, 33, 2359–2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar Singh, S.; Patra, A. Evaluation of phenolic composition, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and anticancer activities of Polygonatum verticillatum (L.). J. Integr. Med. 2018, 16, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Tang, Y.; Song, Z.; Ge, J. Polygonatum sibiricum F. Delaroche polysaccharide ameliorates HFD-induced mouse obesity via regulation of lipid metabolism and inflammatory response. Mol. Med. Rep. 2021, 24, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Jiang, Y.; Jin, S.; Wang, D.; Wu, K.; Yang, Q.; Han, R.; Chen, S.; Liang, Z.; Jia, Q. Structure characterization and bioactivity of neutral polysaccharides from different sources of Polygonatum Mill. Biopolymers 2022, 23, e23490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Chai, Y.; Zhao, M.; Guo, Q.; Bao, Y. Hypoglycemic effects and modulation of gut microbiota of diabetic mice by saponin from Polygonatum sibiricum. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 4327–4338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, N.; Sun, C.; Sun, D.; Wang, Y. Polysaccharides from Polygonatum sibiricum Delar. ex Redoute induce an immune response in the RAW264.7 cell line via an NF-κB/MAPK pathway. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 17988–17994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, M.; Zhao, S.; Zhu, P.; Nie, C.; Ma, S.; Wang, N.; Du, X.; Zhou, Y. Purification, characterization and immunomodulatory activity of water extractable polysaccharides from the swollen culms of Zizania latifolia. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 107, 882–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Huang, L.; Jiang, P.; Xu, G.; Sun, T. Immunological regulation of the active fraction from Polygonatum sibiricum F. Delaroche based on improvement of intestinal microflora and activation of RAW264.7 cells. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 293, 115240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Liu, J.; Kong, X.; Li, H. Characterization and Immunological Activities of Polysaccharides from Polygonatum sibiricum. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2020, 43, 959–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Zhou, H.; Zhao, C.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Huang, L.; Gao, W. Purification, characterization and immunomodulatory activity of fructans from Polygonatum odoratum and P. cyrtonema. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 214, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Yu, L.; Fu, B.; Chu, J.; Chen, C.; Li, X.; Ma, J.; Tang, W. Protective effects of Polygonatum kingianum polysaccharides and aqueous extract on uranium-induced toxicity in human kidney (HK-2) cells. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 202, 68–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, F.; Xie, P.; Li, C.; Bian, Z.; Wang, X.; Peng, D.; Zhu, G. Polysaccharides from Polygonatum cyrtonema Hua Reduce Depression-Like Behavior in Mice by Inhibiting Oxidative Stress-Calpain-1-NLRP3 Signaling Axis. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2022, 2022, 2566917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, X.; Pi, X.; Zheng, W.; Cen, Y.; Ni, J.; Xu, L.; Wu, K.; Liu, W.; Li, L. The Methanol Extract of Polygonatum odoratum Ameliorates Colitis by Improving Intestinal Short-Chain Fatty Acids and Gas Production to Regulate Microbiota Dysbiosis in Mice. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 899421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Fang, Q.; Lai, Y.; Lei, H.; Zhang, D.; Niu, H.; Wang, R.; Song, C. Polysaccharides from the leaves of Polygonatum sibiricum Red. regulate the gut microbiota and affect the production of short-chain fatty acids in mice. AMB Express. 2022, 12, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Fu, B.; Yan, C.; Xie, H.; Zhang, X.; Xiang, L.; Hu, J.; Ma, J.; Tan, C.; Yuan, H. Analysis on the times of Polygonati Rhizoma steamed by multiple times based on entropy weight and gray relative analysis method. China J. Tradit. Chin. Med. Pharm. 2021, 36, 6764–6769. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Yue, Y.; Tang, F.; Tao, W. Comparative analysis of volatile fractions in Polygonati Rhizoma and its processed products by GC-MS. China J. Chin. Materia Medica 2011, 36, 2187–2191. [Google Scholar]
- Li, R.; Tao, A.; Yang, R.; Fan, M.; Zhang, X.; Du, Z.; Shang, F.; Xia, C.; Duan, B. Structural characterization, hypoglycemic effects and antidiabetic mechanism of a novel polysaccharides from Polygonatum kingianum Coll. et Hemsl. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 131, 110687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Zhang, J.; Deng, Y.; Ye, X.; Xia, L.; Liu, M.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, T. Analysis of Chemical Constitutions of Polygonatum cyrtonema Dried Rhizomes Before and After Processing with Wine Based on UPLC-Q-TOF-MS. Chin. J. Exp. Tradit. Med. Formulae 2021, 4, 110–121. [Google Scholar]
- Sirong, Y.; Jian, Q.; Pinming, L. Research progress in the preparation of Polygonatum. Chin. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2017, 32, 4575–4578. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Ye, D. A Collection of Traditional Chinese Medicine Processing Methods in Past Dynasties (Ancient Part); Jiangxi Science and Technology Press: Nanchang, China, 1998; p. 136. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, L.; Li, S.; Wang, C.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, S. Brief on the Academic Thought of Zhang Shanlei’s Rectification of the Meaning of Materia Medica. World J. Integr. Tradit. West. Med. 2014, 6, 573–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Yu, B.; Qian, Z. Accelerate the compilation of the “National Standards for the Processing of Chinese Herbal Medicines” and standardize the unified national standards for the processing of Chinese herbal medicines. Chin. J. Chin. Materia Medica 2011, 36, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, C. Huizhitang Experience Prescription; Chinese Medicine Ancient Books Publishing House: Beijing, China, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, B.; Wei, G.; Gan, X.; Li, T.; Qu, Y.; Xu, S.; Liu, C.; Qian, C. Study on the varied content of Polygonatum cyrtonema polysaccharides in the processing of steaming and shining for nine times based on HPLC-MS/MS and chemometrics. Microchem. J. 2020, 159, 105352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Dai, W.; Fang, J.; Cao, C.; Die, Y.; Liu, Q.; Wang, C.; et al. Physicochemical properties and immunological activities of polysaccharides from both crude and wine-processed Polygonatum sibiricum. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 143, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, J.; Lao, J.; Zhou, R.; He, W.; Qin, Y.; Zhong, C.; Xie, J.; Liu, H.; Wan, D.; Zhang, S. Simultaneous Identification and Dynamic Analysis of Saccharides during Steam Processing of Rhizomes of Polygonatum cyrtonema by HPLC–QTOF–MS/MS. Molecules 2018, 23, 2855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, Q.; Zeng, J.; Gong, P.; Wu, Y.; Li, H. Effect of steaming process on the structural characteristics and antioxidant activities of polysaccharides from Polygonatum sibiricum rhizomes. Glycoconj. J. 2021, 38, 561–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Yang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Huang, Y.F.; He, L.H.; Zhang, Z.F. Changes in the content of polysaccharides and saponins during the processing of Huangjing “Nine Steaming and Nine Preparations”. J. Hunan Normal Univ. Med. Ed. 2015, 5, 141–144. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, G.; Li, X.; Zhang, Z.; Jiang, Y. Effect of food processing on the antioxidant activity of flavones from Polygonatum odoratum (Mill.) Druce. Open Life Sci. 2021, 16, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, G.H.; Li, X.H.; Zhang, Z.; Jiang, Y.H. Effects of fermentation treatments on Polygonatum odoratum flavones’ antioxidant activities. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 5011–5016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, H.; Wang, R.; Wu, D.; Liu, C.; Tang, X.; Huang, S.; Xu, F. Antioxidant and hypoglycemic activities of different polar extracts from crude and steam-processed Polygonatum cyrtonema Hua. Food Ferment. Ind. 2022, 48, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Liang, Z.; Xia, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, W.; Han, J.; Wu, Z. Comparative study on anti-exercise fatigue effects of different extracts from raw materials of Polygonatum cyrtonema Hua and its processed products. J. Anhui Agric. Univ. 2021, 48, 26–30. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Hu, H.; Feng, G.; Wei, T.; Li, X.; Yu, L.; He, X. Anti-Fatigue and Anti-Oxidant Effects of Crude and Processed Polygonatum Cyrtonema on Exhaustive Swimming Mice. Tradit. Chin. Med. Pharmacol. Clin. 2021, 2, 92–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, Q.; Wang, X.; Cao, M.; Zheng, S.; Ma, Y.; Huang, Q. NF-κB and AMPK-Nrf2 pathways support the protective effect of polysaccharides from Polygonatum cyrtonema Hua in lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 291, 115153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q. Study on the Anti-Inflammatory and Hypoglycemic Effects Produced by Crude Polysaccharides Between Raw Materials and Nine-Steam-Nine-Bask Processing, P. cyrtonema Hua. Master’s Thesis, Anhui University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Hefei, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Huanhuan, T.; Renzhong, W.; Deling, W. Antioxidative and hypoglycemic activity of different polar parts of Polygonatum polyflora before and after processing. Food Ferment. Ind. 2022, 48, 70–75. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Li, J.; Shang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Gao, J.; Xue, N.; Huang, C.; Li, F.; Li, J. Hypoglycemic and Hypolipidemic Activity of Polygonatum sibiricum Fermented with Lactobacillus brevis YM 1301 in Diabetic C57BL/6 Mice. J. Med. Food. 2021, 2, 720–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.X.; Zhang, X.; Dabu, X.; Juan, H.; Yang, S.C.; Chen, J.W.; Wei, F.; Zhang, G.H.; Ai, H.L.; Meirong, H. Analysis of chemical constituents from Polygonatum cyrtonema after “Nine-Steam-Nine-Bask” processing. Phytochem. Lett. 2019, 29, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yang, B.; Huang, J.; Li, W.; Yi, P.; Yi, M.; Peng, W. Identification of the protective effect of Polygonatum sibiricum polysaccharide on d-galactose-induced brain ageing in mice by the systematic characterization of a circular RNA-associated ceRNA network. Pharm. Biol. 2021, 59, 347–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yelithao, K.; Surayot, U.; Park, W.; Lee, S.; Lee, D.H.; You, S. Effect of sulfation and partial hydrolysis of polysaccharides from Polygonatum sibiricum on immune-enhancement. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 122, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, F.; Yuan, L.; Ruan, H.; Zhu, Z.; Fan, X.; Zhu, L.; Peng, X. Blood-Enriching Effects and Immune-Regulation Mechanism of Steam-Processed Polygonatum Sibiricum Polysaccharide in Blood Deficiency Syndrome Mice. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 813676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).