Synthesis, Biological Evaluation and Docking Studies of Ring-Opened Analogues of Ipomoeassin F
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
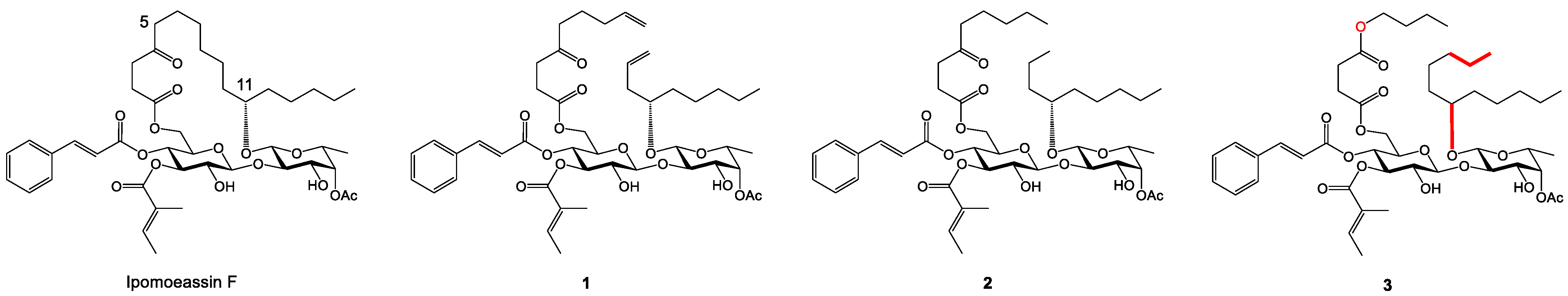
2.1. Synthesis and Cytotoxicity of Nine New Open Chain-Analogues
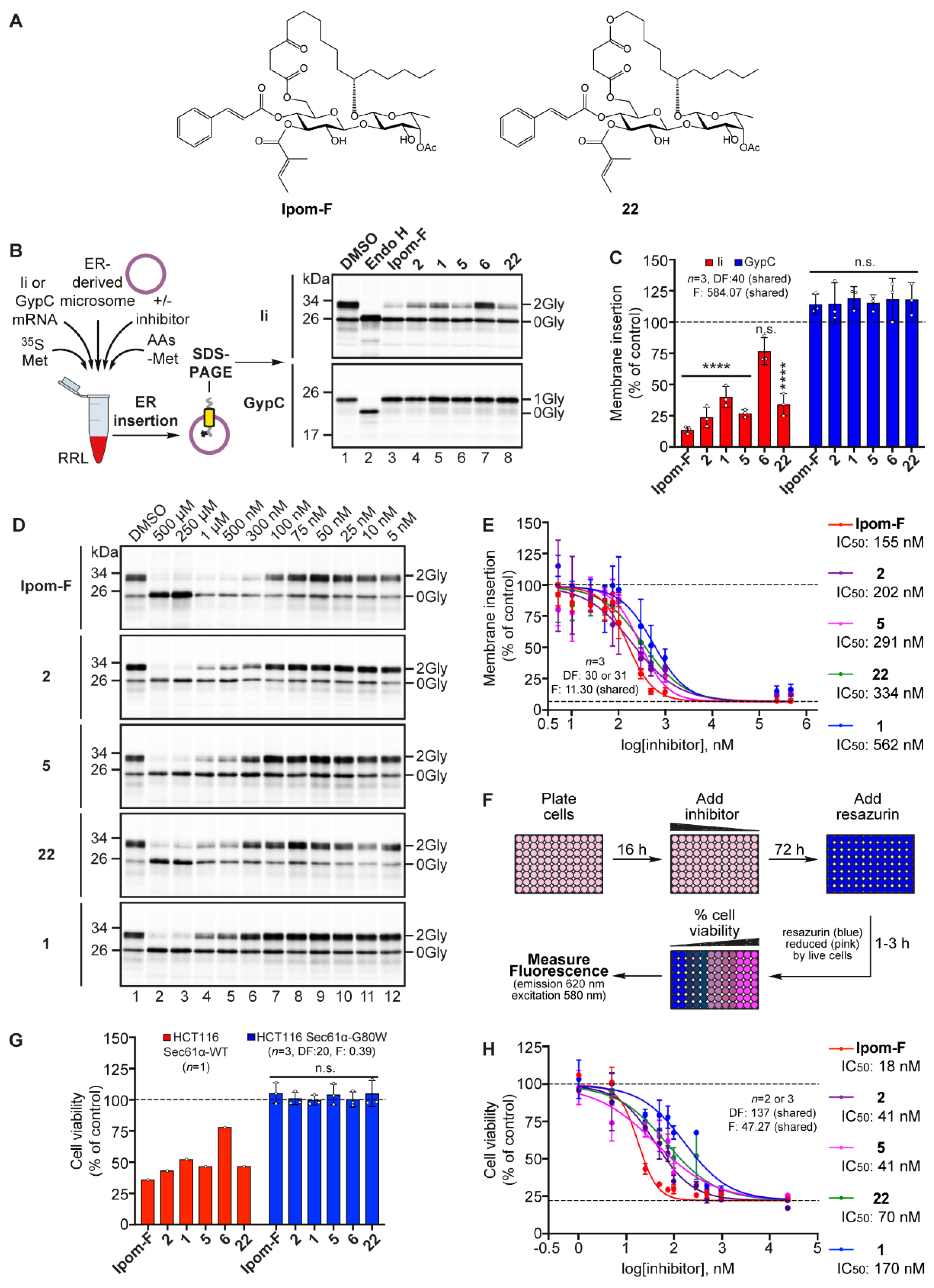
2.2. Open-Chain Analogues Selectively Inhibit Sec61-Mediated Protein Translocation In Vitro
2.3. Open-Chain Analogues Induce Cytotoxicity Via the Selective Inhibition of Sec61-Mediated Protein Translocation
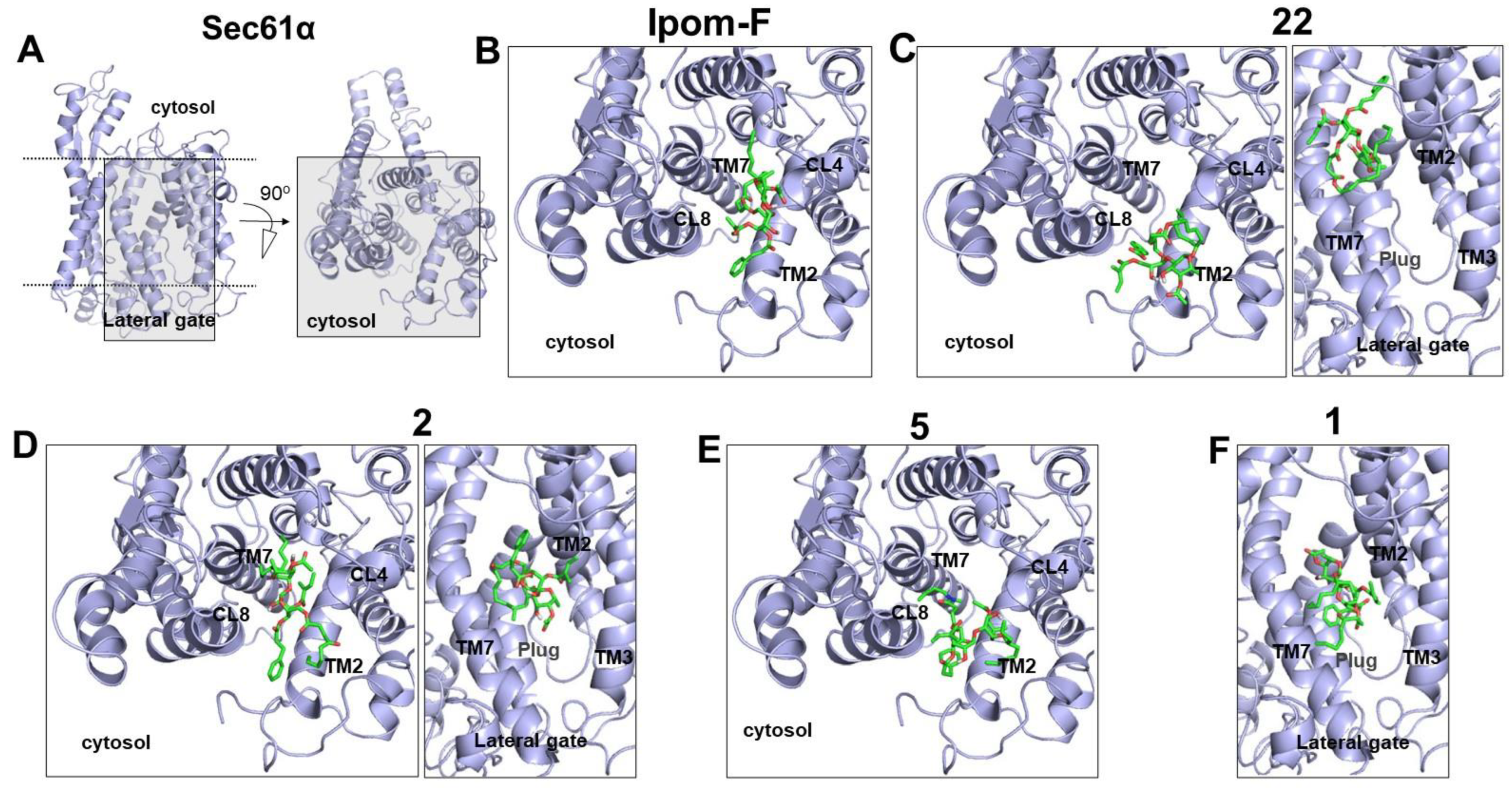
2.4. Molecular Docking of Open-Chain Analogues within the Channel Pore of Sec61α Reveals Multiple Binding Sites
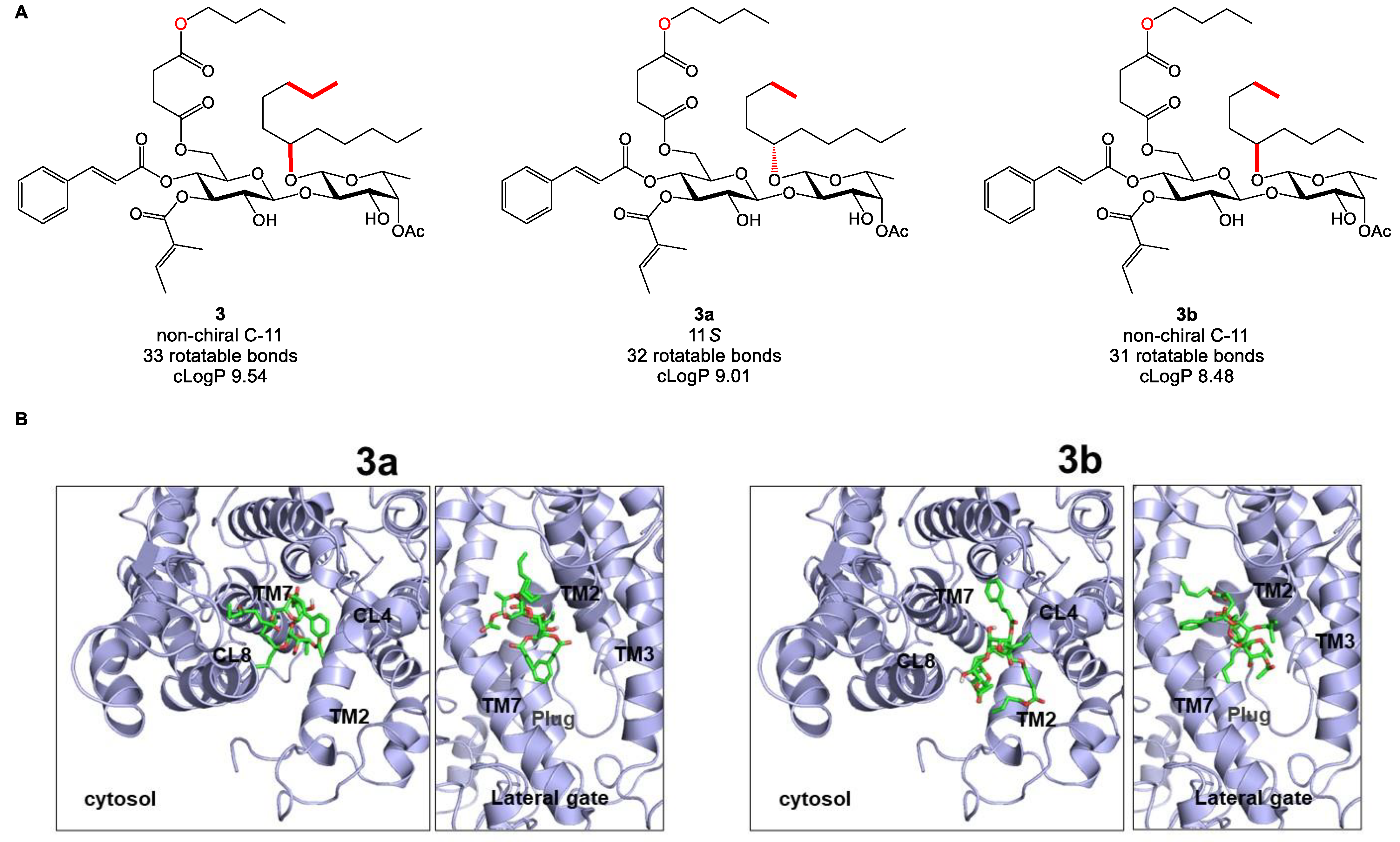
2.5. Biology-Directed and In Silico-Aided Design of Analogue 3
2.6. Synthesis of Analogue 3
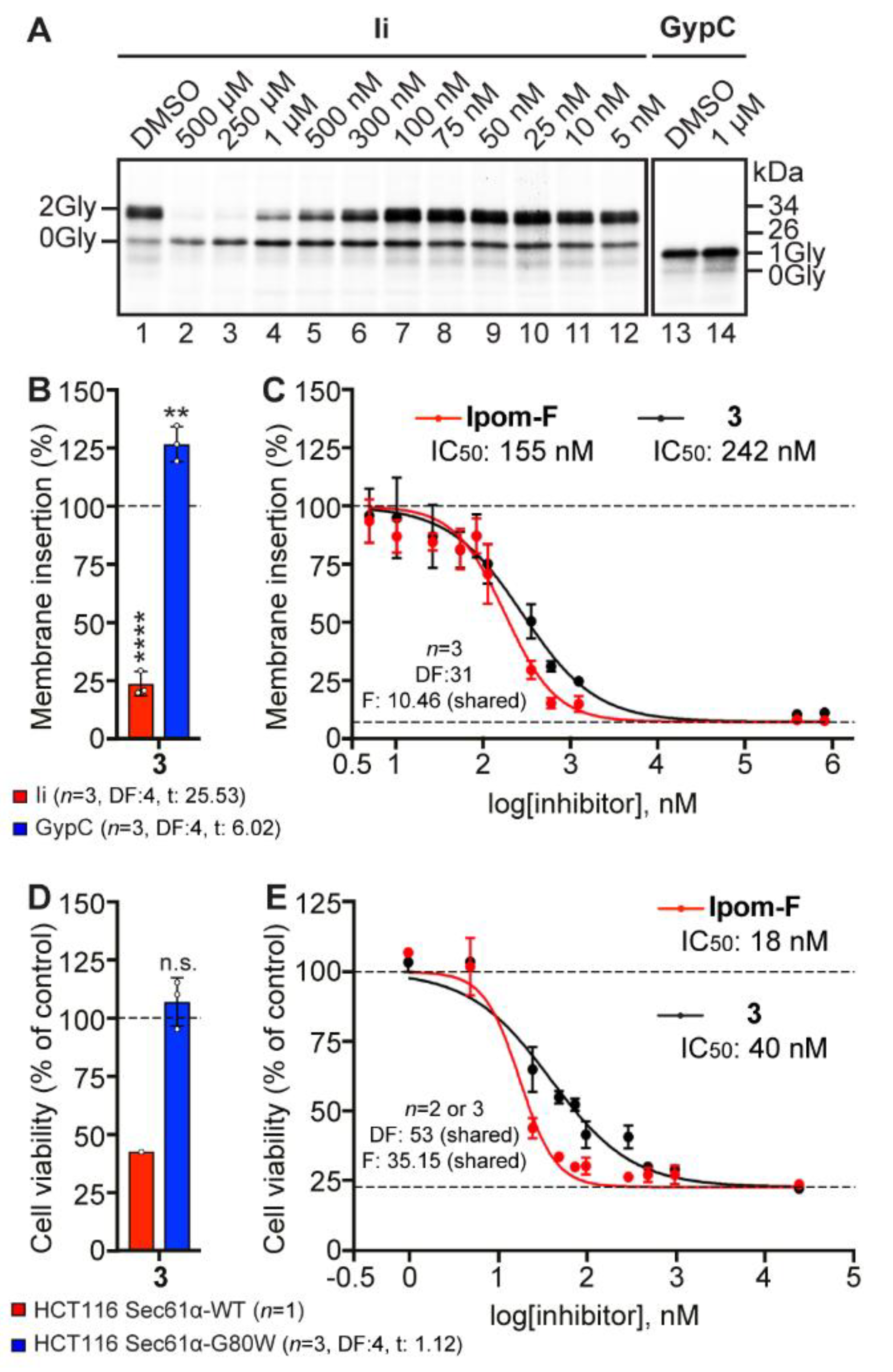
2.7. Analogue 3 Inhibits Sec61-Mediated Protein Translocation with Potency and Selectivity Comparable to Ipom-F and 2
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemical Synthesis General Methods
3.1.1. Synthesis of Compound 25
3.1.2. Synthesis of Compound 26
3.1.3. Synthesis of Compound 27
3.1.4. Synthesis of Compound 29
3.1.5. Synthesis of Compound 30
3.1.6. Synthesis of Compound 31
3.1.7. Synthesis of Compound 32
3.1.8. Synthesis of Analogue 3
3.2. Biological Analysis
3.2.1. In Vitro Membrane Insertion Assay
3.2.2. Cell Culture and Resazurin-Based Viability Assays
3.2.3. Quantification and Statistical Analysis
3.3. Homology Modeling and Docking Protocols
3.4. Data and Software
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
Abbreviations
References
- Ono, M. Resin glycosides from Convolvulaceae plants. J. Nat. Med. 2017, 71, 591–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereda-Miranda, R.; Rosas-Ramirez, D.; Castaneda-Gomez, J. Resin glycosides from the morning glory family. Prog. Chem. Org. Nat. Prod. 2010, 92, 77–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Guza, R.C.; Wisse, J.H.; Miller, J.S.; Evans, R.; Kingston, D.G.I. Ipomoeassins A−E, Cytotoxic Macrocyclic Glycoresins from the Leaves of Ipomoea squamosa from the Suriname Rainforest1. J. Nat. Prod. 2005, 68, 487–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Norris, A.; Wisse, J.H.; Miller, J.S.; Evans, R.; Kingston, D.G.I. Ipomoeassin F, a new cytotoxic macrocyclic glycoresin from the leaves of Ipomoea squamosa from the Suriname rainforest. Nat. Prod. Res. 2007, 21, 872–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fürstner, A.; Nagano, T. Total Syntheses of Ipomoeassin B and E. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 1906–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nagano, T.; Pospíšil, J.; Chollet, G.; Schulthoff, S.; Hickmann, V.; Moulin, E.; Herrmann, J.; Müller, R.; Fürstner, A. Total Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of the Cytotoxic Resin Glycosides Ipomoeassin A–F and Analogues. Chem. A Eur. J. 2009, 15, 9697–9706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Postema, M.H.D.; TenDyke, K.; Cutter, J.; Kuznetsov, G.; Xu, Q. Total Synthesis of Ipomoeassin F. Org. Lett. 2009, 11, 1417–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, G.; Barber, E.; Aljewari, H.; Zhou, J.; Hu, Z.; Du, Y.; Shi, W.Q. Total Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Ipomoeassin F and Its Unnatural 11R-Epimer. J. Org. Chem. 2015, 80, 9279–9291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zong, G.; Aljewari, H.; Hu, Z.; Shi, W.Q. Revealing the Pharmacophore of Ipomoeassin F through Molecular Editing. Org. Lett. 2016, 18, 1674–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zong, G.; Hirsch, M.; Mondrik, C.; Hu, Z.; Shi, W.Q. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of fucose-truncated monosaccharide analogues of ipomoeassin F. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 27, 2752–2756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, G.; Sun, X.; Bhakta, R.; Whisenhunt, L.; Hu, Z.; Wang, F.; Shi, W.Q. New insights into structure–activity relationship of ipomoeassin F from its bioisosteric 5-oxa/aza analogues. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 144, 751–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zong, G.; Whisenhunt, L.; Hu, Z.; Shi, W.Q. Synergistic Contribution of Tiglate and Cinnamate to Cytotoxicity of Ipomoeassin F. J. Org. Chem. 2017, 82, 4977–4985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zong, G.; Hu, Z.; O’Keefe, S.; Tranter, D.; Iannotti, M.J.; Baron, L.; Hall, B.; Corfield, K.; Paatero, A.O.; Henderson, M.J.; et al. Ipomoeassin F Binds Sec61α to Inhibit Protein Translocation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 8450–8461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zong, G.; Hu, Z.; Duah, K.B.; Andrews, L.E.; Zhou, J.; O’Keefe, S.; Whisenhunt, L.; Shim, J.S.; Du, Y.; High, S.; et al. Ring Expansion Leads to a More Potent Analogue of Ipomoeassin F. J. Org. Chem. 2020, 85, 16226–16235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aviram, N.; Schuldiner, M. Targeting and translocation of proteins to the endoplasmic reticulum at a glance. J. Cell Sci. 2017, 130, 4079–4085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hegde, R.S.; Keenan, R.J. The mechanisms of integral membrane protein biogenesis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2022, 23, 107–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Keefe, S.; Pool, M.R.; High, S. Membrane protein biogenesis at the ER: The highways and byways. FEBS J. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gemmer, M.; Förster, F. A clearer picture of the ER translocon complex. J. Cell Sci. 2020, 133, jcs231340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voorhees, R.M.; Fernández, I.S.; Scheres, S.H.; Hegde, R.S. Structure of the Mammalian Ribosome-Sec61 Complex to 3.4 Å Resolution. Cell 2014, 157, 1632–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lang, S.; Pfeffer, S.; Lee, P.-H.; Cavalié, A.; Helms, V.; Förster, F.; Zimmermann, R. An Update on Sec61 Channel Functions, Mechanisms, and Related Diseases. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sicking, M.; Lang, S.; Bochen, F.; Roos, A.; Drenth, J.P.H.; Zakaria, M.; Zimmermann, R.; Linxweiler, M. Complexity and Specificity of Sec61-Channelopathies: Human Diseases Affecting Gating of the Sec61 Complex. Cells 2021, 10, 1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gérard, S.F.; Hall, B.S.; Zaki, A.M.; Corfield, K.A.; Mayerhofer, P.U.; Costa, C.; Whelligan, D.K.; Biggin, P.C.; Simmonds, R.E.; Higgins, M.K. Structure of the Inhibited State of the Sec Translocon. Mol. Cell 2020, 79, 406–415.e407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Keefe, S.; Zong, G.; Duah, K.B.; Andrews, L.E.; Shi, W.Q.; High, S. An alternative pathway for membrane protein biogenesis at the endoplasmic reticulum. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luesch, H.; Paavilainen, V.O. Natural products as modulators of eukaryotic protein secretion. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2020, 37, 717–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pauwels, E.; Schülein, R.; Vermeire, K. Inhibitors of the Sec61 Complex and Novel High Throughput Screening Strategies to Target the Protein Translocation Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linxweiler, M.; Schick, B.; Zimmermann, R. Let’s talk about Secs: Sec61, Sec62 and Sec63 in signal transduction, oncology and personalized medicine. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 2017, 2, 17002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paatero, A.O.; Kellosalo, J.; Dunyak, B.M.; Almaliti, J.; Gestwicki, J.E.; Gerwick, W.H.; Taunton, J.; Paavilainen, V.O. Apratoxin Kills Cells by Direct Blockade of the Sec61 Protein Translocation Channel. Cell Chem. Biol. 2016, 23, 561–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tranter, D.; Paatero, A.O.; Kawaguchi, S.; Kazemi, S.; Serrill, J.D.; Kellosalo, J.; Vogel, W.K.; Richter, U.; Mattos, D.R.; Wan, X.; et al. Coibamide A Targets Sec61 to Prevent Biogenesis of Secretory and Membrane Proteins. ACS Chem. Biol. 2020, 15, 2125–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrison, J.L.; Kunkel, E.J.; Hegde, R.S.; Taunton, J. A substrate-specific inhibitor of protein translocation into the endoplasmic reticulum. Nature 2005, 436, 285–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junne, T.; Wong, J.; Studer, C.; Aust, T.; Bauer, B.W.; Beibel, M.; Bhullar, B.; Bruccoleri, R.; Eichenberger, J.; Estoppey, D.; et al. Decatransin, a new natural product inhibiting protein translocation at the Sec61/SecYEG translocon. J. Cell Sci. 2015, 128, 1217–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hall, B.S.; Hill, K.; McKenna, M.; Ogbechi, J.; High, S.; Willis, A.E.; Simmonds, R.E. The Pathogenic Mechanism of the Mycobacterium ulcerans Virulence Factor, Mycolactone, Depends on Blockade of Protein Translocation into the ER. PLoS Path. 2014, 10, e1004061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKenna, M.; Simmonds, R.E.; High, S. Mechanistic insights into the inhibition of Sec61-dependent co- and post-translational translocation by mycolactone. J. Cell Sci. 2016, 129, 1404–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gamayun, I.; O’Keefe, S.; Pick, T.; Klein, M.-C.; Nguyen, D.; McKibbin, C.; Piacenti, M.; Williams, H.M.; Flitsch, S.L.; Whitehead, R.C.; et al. Eeyarestatin Compounds Selectively Enhance Sec61-Mediated Ca2+ Leakage from the Endoplasmic Reticulum. Cell Chem. Biol. 2019, 26, 571–583.e576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klein, W.; Rutz, C.; Eckhard, J.; Provinciael, B.; Specker, E.; Neuenschwander, M.; Kleinau, G.; Scheerer, P.; von Kries, J.-P.; Nazaré, M.; et al. Use of a sequential high throughput screening assay to identify novel inhibitors of the eukaryotic SRP-Sec61 targeting/translocation pathway. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0208641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hau, A.M.; Greenwood, J.A.; Löhr, C.V.; Serrill, J.D.; Proteau, P.J.; Ganley, I.G.; McPhail, K.L.; Ishmael, J.E. Coibamide A Induces mTOR-Independent Autophagy and Cell Death in Human Glioblastoma Cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e65250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tirincsi, A.; Sicking, M.; Hadzibeganovic, D.; Haßdenteufel, S.; Lang, S. The Molecular Biodiversity of Protein Targeting and Protein Transport Related to the Endoplasmic Reticulum. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Keefe, S.; High, S.; Demangel, C. Biochemical and Biological Assays of Mycolactone-Mediated Inhibition of Sec61. In Mycobacterium Ulcerans: Methods and Protocols; Pluschke, G., Röltgen, K., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2022; pp. 163–181. [Google Scholar]
- O’Keefe, S.; Roboti, P.; Duah, K.B.; Zong, G.; Schneider, H.; Shi, W.Q.; High, S. Ipomoeassin-F inhibits the in vitro biogenesis of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein and its host cell membrane receptor. J. Cell Sci. 2021, 134, jcs.257758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhadra, P.; Dos Santos, S.; Gamayun, I.; Pick, T.; Neumann, C.; Ogbechi, J.; Hall, B.S.; Zimmermann, R.; Helms, V.; Simmonds, R.E.; et al. Mycolactone enhances the Ca2+ leak from endoplasmic reticulum by trapping Sec61 translocons in a Ca2+ permeable state. Biochem. J. 2021, 478, 4005–4024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhadra, P.; Yadhanapudi, L.; Römisch, K.; Helms, V. How does Sec63 affect the conformation of Sec61 in yeast? PLoS Comp. Biol. 2021, 17, e1008855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Oishi, S.; Martin, C.E.; Seeberger, P.H. Diversity-oriented Synthesis of Inner Core Oligosaccharides of the Lipopolysaccharide of Pathogenic Gram-negative Bacteria. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 6262–6271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roboti, P.; O’Keefe, S.; Duah, K.B.; Shi, W.Q.; High, S. Ipomoeassin-F disrupts multiple aspects of secretory protein biogenesis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 11562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, T.; Bhushan, S.; Jarasch, A.; Armache, J.-P.; Funes, S.; Jossinet, F.; Gumbart, J.; Mielke, T.; Berninghausen, O.; Schulten, K.; et al. Structure of Monomeric Yeast and Mammalian Sec61 Complexes Interacting with the Translating Ribosome. Science 2009, 326, 1369–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fiser, A.; Šali, A. Modeller: Generation and Refinement of Homology-Based Protein Structure Models. In Methods in Enzymology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2003; Volume 374, pp. 461–491. [Google Scholar]
- Van Der Spoel, D.; Lindahl, E.; Hess, B.; Groenhof, G.; Mark, A.E.; Berendsen, H.J.C. GROMACS: Fast, flexible, and free. J. Comput. Chem. 2005, 26, 1701–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, G.M.; Huey, R.; Lindstrom, W.; Sanner, M.F.; Belew, R.K.; Goodsell, D.S.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock4 and AutoDockTools4: Automated docking with selective receptor flexibility. J. Comput. Chem. 2009, 30, 2785–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laskowski, R.A.; Swindells, M.B. LigPlot+: Multiple Ligand–Protein Interaction Diagrams for Drug Discovery. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2011, 51, 2778–2786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Compound | Ring Integrity | Other Ring Modifications | C-11 Chirality | cLogP * | In Vitro Translocation Inhibition | Cytotoxicity HCT-116 Cells |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ipom-F | Closed | None | 11S | 5.97 | 155 | 18 |
| 2 | Open | None | 11S | 8.72 | 202 | 41 |
| 5 | Open | Dialkene, aza | 11S | 6.98 | 291 | 41 |
| 22 | Closed | Diester | 11S | 4.94 | 334 | 70 |
| 1 | Open | Dialkene | 11S | 7.75 | 562 | 170 |
| 6 | Open | Dialkene, ketone removed | 11S | 9.39 | Not determined | Not determined |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
O’Keefe, S.; Bhadra, P.; Duah, K.B.; Zong, G.; Tenay, L.; Andrews, L.; Schneider, H.; Anderson, A.; Hu, Z.; Aljewari, H.S.; et al. Synthesis, Biological Evaluation and Docking Studies of Ring-Opened Analogues of Ipomoeassin F. Molecules 2022, 27, 4419. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27144419
O’Keefe S, Bhadra P, Duah KB, Zong G, Tenay L, Andrews L, Schneider H, Anderson A, Hu Z, Aljewari HS, et al. Synthesis, Biological Evaluation and Docking Studies of Ring-Opened Analogues of Ipomoeassin F. Molecules. 2022; 27(14):4419. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27144419
Chicago/Turabian StyleO’Keefe, Sarah, Pratiti Bhadra, Kwabena B. Duah, Guanghui Zong, Levise Tenay, Lauren Andrews, Hayden Schneider, Ashley Anderson, Zhijian Hu, Hazim S. Aljewari, and et al. 2022. "Synthesis, Biological Evaluation and Docking Studies of Ring-Opened Analogues of Ipomoeassin F" Molecules 27, no. 14: 4419. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27144419
APA StyleO’Keefe, S., Bhadra, P., Duah, K. B., Zong, G., Tenay, L., Andrews, L., Schneider, H., Anderson, A., Hu, Z., Aljewari, H. S., Hall, B. S., Simmonds, R. E., Helms, V., High, S., & Shi, W. Q. (2022). Synthesis, Biological Evaluation and Docking Studies of Ring-Opened Analogues of Ipomoeassin F. Molecules, 27(14), 4419. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27144419








