Chemical Degradation of Androgen Receptor (AR) Using Bicalutamide Analog–Thalidomide PROTACs
Abstract
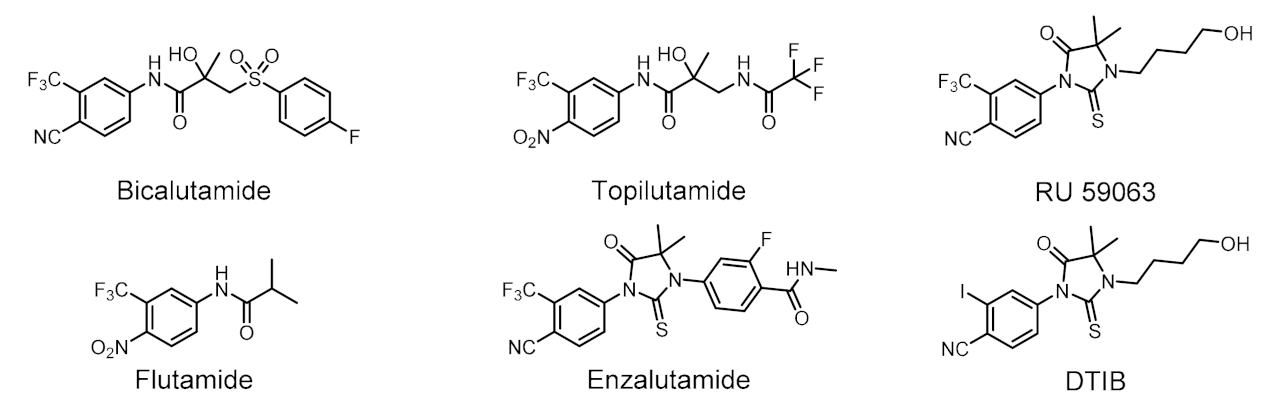
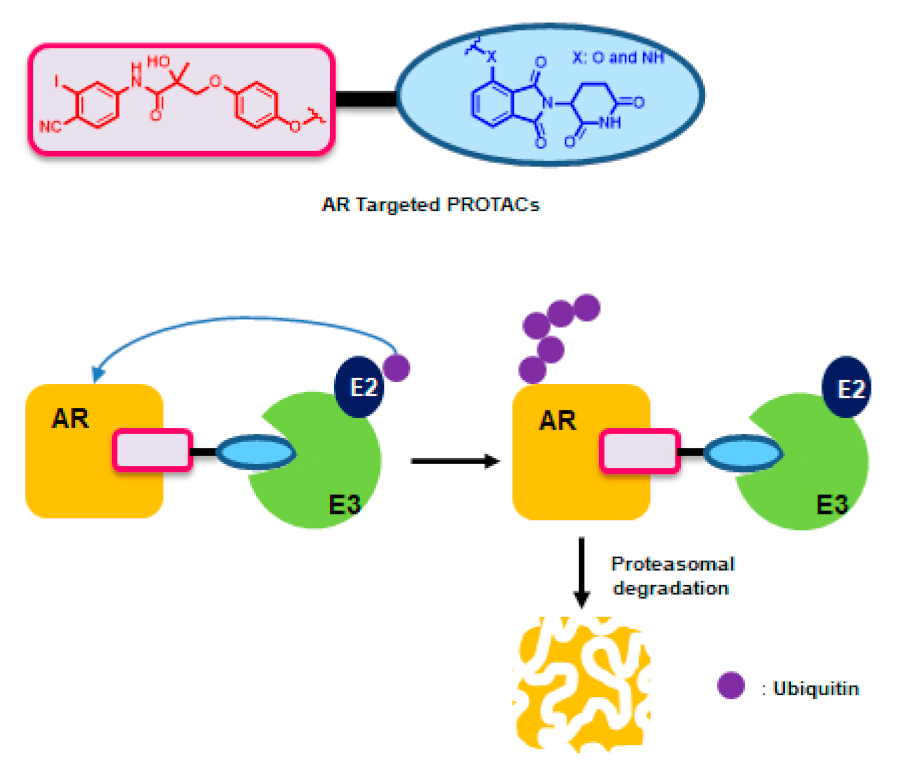
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
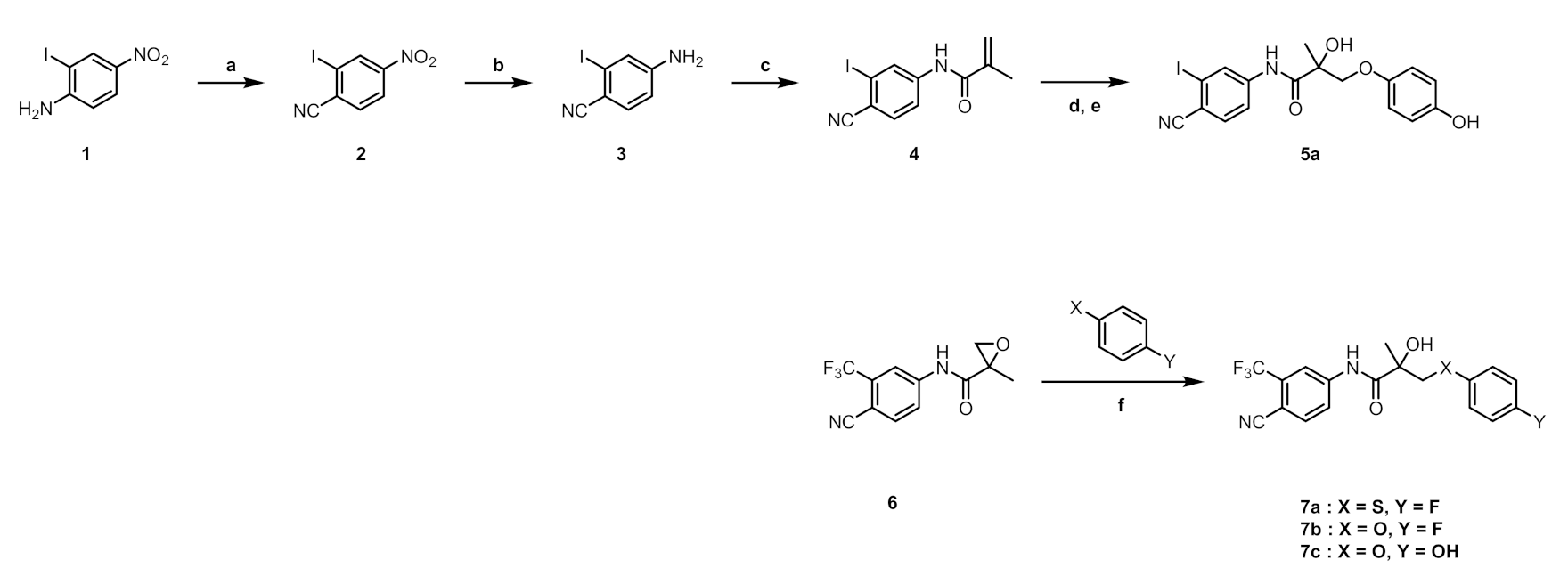
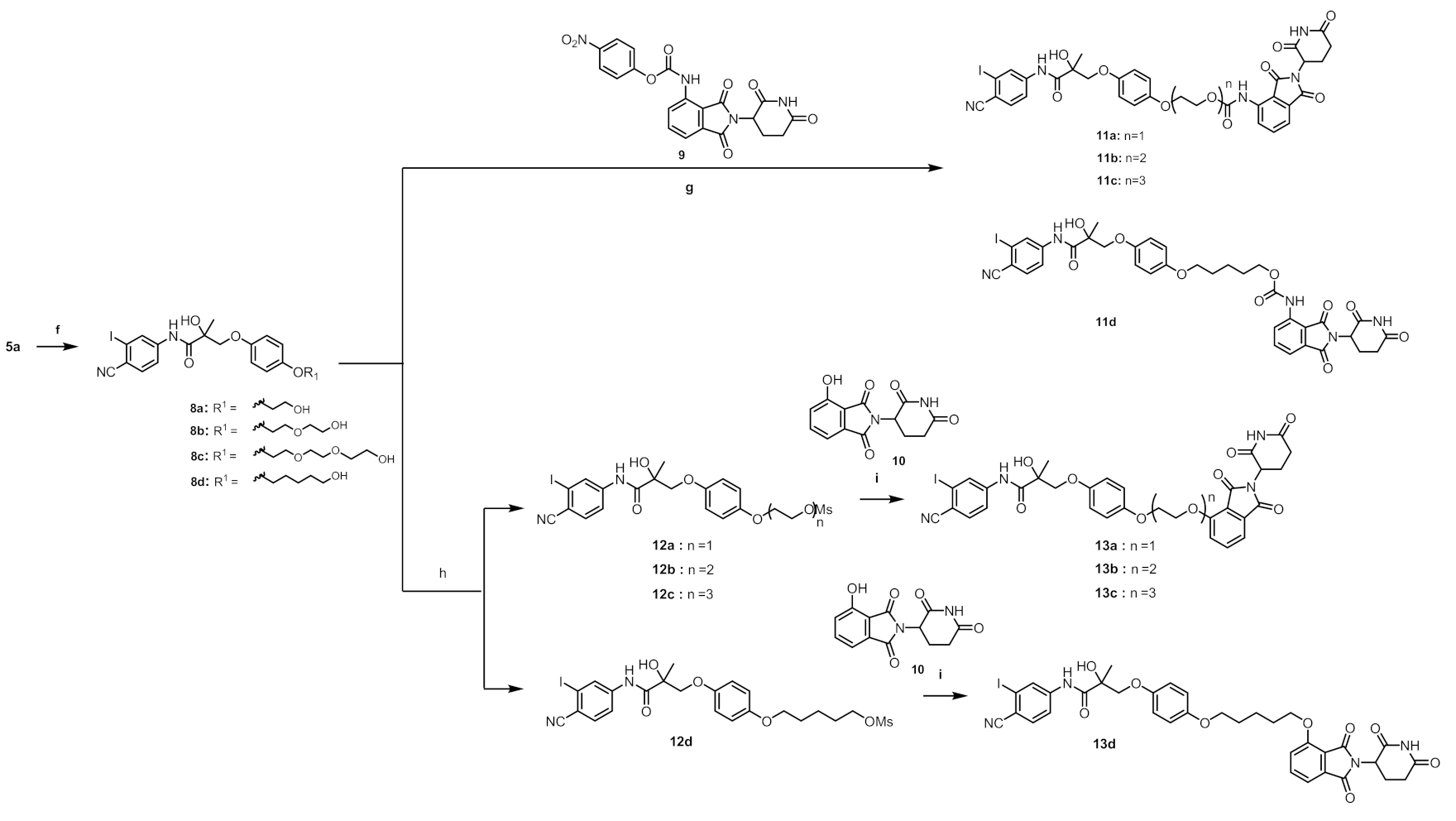
2.1. Synthesis
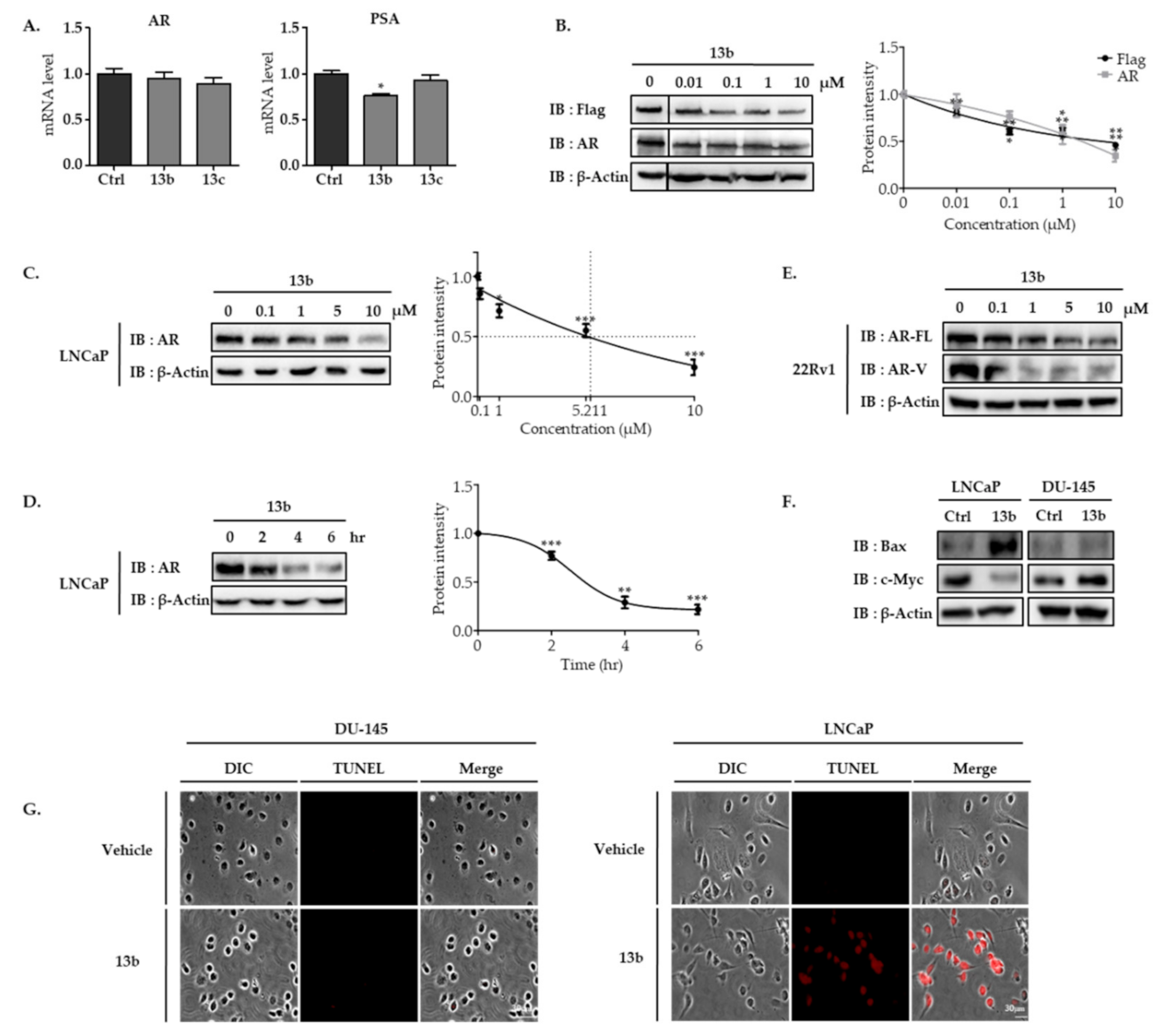
2.2. Biology
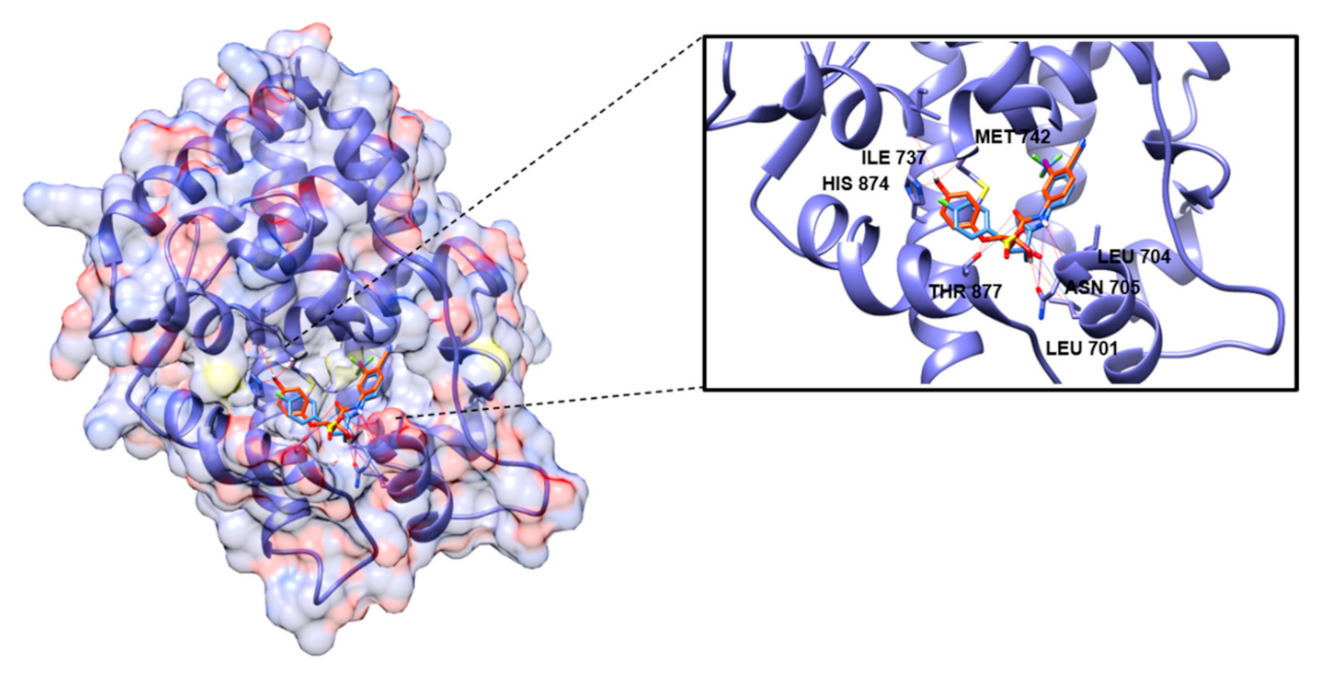
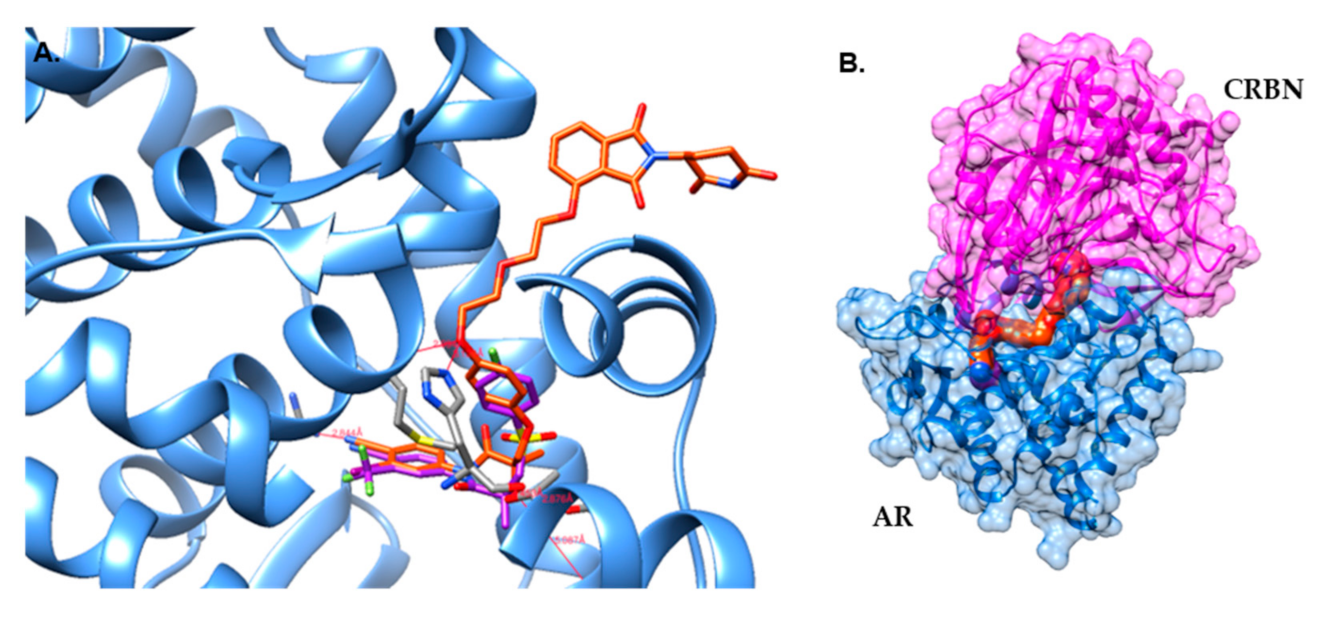
2.3. Molecular Modeling
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemistry
3.1.1. General Experimental Methods
3.1.2. Synthesis
2-Iodo-4-nitrobenzonitrile (2)
4-Amino-2-iodobenzonitrile (3)
N-(4-Cyano-3-iodophenyl)methacrylamide (4)
N-(4-Cyano-3-iodophenyl)-2-hydroxy-3-(4-hydroxyphenoxy)-2-methylpropanamide (5a)
N-(4-Cyano-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-2-hydroxy-3-((4-hydroxyphenyl)thio)-2-methylpropanamide (7a)
N-(4-Cyano-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-3-(4-fluorophenoxy)-2-hydroxy-2-methylpropanamide (7b)
N-(4-Cyano-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-2-hydroxy-3-(4-hydroxyphenoxy)-2-methylpropanamide (7c)
N-(4-Cyano-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-3-((4-fluorophenyl)thio)-2-hydroxy-2-methylpropanamide (8a)
N-(4-Cyano-3-iodophenyl)-2-hydroxy-3-(4-(2-(2-hydroxyethoxy)ethoxy)phenoxy)-2-methylpropanamide (8b)
N-(4-Cyano-3-iodophenyl)-2-hydroxy-3-(4-(2-(2-(2-hydroxyethoxy)ethoxy)ethoxy)phenoxy)-2-methylpropanamide (8c)
N-(4-Cyano-3-iodophenyl)-2-hydroxy-3-(4-((5-hydroxypentyl)oxy)phenoxy)-2-methylpropanamide (8d)
2-(4-(3-((4-Cyano-3-iodophenyl)amino)-2-hydroxy-2-methyl-3-oxopropoxy)phenoxy)ethyl (2-(2,6-dioxopiperidin-3-yl)-1,3-dioxoisoindolin-4-yl)carbamate (11a)
2-(2-(4-(3-((4-Cyano-3-iodophenyl)amino)-2-hydroxy-2-methyl-3-oxopropoxy)phenoxy)ethoxy)ethyl (2-(2,6-dioxopiperidin-3-yl)-1,3-dioxoisoindolin-4-yl)carbamate (11b)
2-(2-(2-(4-(3-((4-Cyano-3-iodophenyl)amino)-2-hydroxy-2-methyl-3-oxopropoxy)phenoxy)ethoxy)ethoxy)ethyl (2-(2,6-dioxopiperidin-3-yl)-1,3-dioxoisoindolin-4-yl)carbamate (11c)
5-(4-(3-((4-Cyano-3-iodophenyl)amino)-2-hydroxy-2-methyl-3-oxopropoxy)phenoxy)pentyl (2-(2,6-dioxopiperidin-3-yl)-1,3-dioxoisoindolin-4-yl)carbamate (11d)
2-(4-(3-((4-Cyano-3-iodophenyl)amino)-2-hydroxy-2-methyl-3-oxopropoxy)phenoxy)ethyl methanesulfonate (12a)
2-(2-(4-(3-((4-Cyano-3-iodophenyl)amino)-2-hydroxy-2-methyl-3-oxopropoxy)phenoxy)ethoxy)ethyl methanesulfonate (12b)
2-(2-(2-(4-(3-((4-Cyano-3-iodophenyl)amino)-2-hydroxy-2-methyl-3-oxopropoxy)phenoxy)ethoxy)ethoxy)ethyl methanesulfonate (12c)
5-(4-(3-((4-Cyano-3-iodophenyl)amino)-2-hydroxy-2-methyl-3-oxopropoxy)phenoxy)pentyl methanesulfonate (12d)
N-(4-Cyano-3-iodophenyl)-3-(4-(2-((2-(2,6-dioxopiperidin-3-yl)-1,3-dioxoisoindolin-4-yl)oxy)ethoxy)phenoxy)-2-hydroxy-2-methylpropanamide (13a)
N-(4-Cyano-3-iodophenyl)-3-(4-(2-(2-((2-(2,6-dioxopiperidin-3-yl)-1,3-dioxoisoindolin-4-yl)oxy)ethoxy)ethoxy)phenoxy)-2-hydroxy-2-methylpropanamide (13b)
N-(4-Cyano-3-iodophenyl)-3-(4-(2-(2-(2-((2-(2,6-dioxopiperidin-3-yl)-1,3-dioxoisoindolin-4-yl)oxy)ethoxy)ethoxy)ethoxy)phenoxy)-2-hydroxy-2-methylpropanamide (13c)
N-(4-Cyano-3-iodophenyl)-3-(4-((5-((2-(2,6-dioxopiperidin-3-yl)-1,3-dioxoisoindolin-4-yl)oxy)pentyl)oxy)phenoxy)-2-hydroxy-2-methylpropanamide (13d)
3.2. Biology
3.2.1. Cell Culture and Treatment
3.2.2. Transfection
3.2.3. Immunoblotting
3.2.4. RT-PCR
3.2.5. Transferase-Mediated Deoxyuridine Triphosphate (dUTP)-Digoxigenin Nick End Labeling (TUNEL) Assay
3.3. Molecular Modeling
Docking Studies
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Winter, G.E.; Buckley, D.L.; Paulk, J.; Roberts, J.M.; Souza, A.; Dhe-Paganon, S.; Bradner, J.E. DRUG DEVELOPMENT. Phthalimide conjugation as a strategy for in vivo target protein degradation. Science 2015, 348, 1376–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakamoto, K.M.; Kim, K.B.; Kumagai, A.; Mercurio, F.; Crews, C.M.; Deshaies, R.J. Protacs: Chimeric molecules that target proteins to the Skp1-Cullin-F box complex for ubiquitination and degradation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 8554–8559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burslem, G.M.; Crews, C.M. Small-Molecule Modulation of Protein Homeostasis. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 11269–11301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salami, J.; Alabi, S.; Willard, R.R.; Vitale, N.J.; Wang, J.; Dong, H.; Jin, M.; McDonnell, D.P.; Crew, A.P.; Neklesa, T.K.; et al. Androgen receptor degradation by the proteolysis-targeting chimera ARCC-4 outperforms enzalutamide in cellular models of prostate cancer drug resistance. Commun. Biol. 2018, 1, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Wang, C.; Qin, C.; Xiang, W.; Fernandez-Salas, E.; Yang, C.Y.; Wang, M.; Zhao, L.; Xu, T.; Chinnaswamy, K.; et al. Discovery of ARD-69 as a Highly Potent Proteolysis Targeting Chimera (PROTAC) Degrader of Androgen Receptor (AR) for the Treatment of Prostate Cancer. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 941–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Gonzalez, A.; Cyrus, K.; Salcius, M.; Kim, K.; Crews, C.M.; Deshaies, R.J.; Sakamoto, K.M. Targeting steroid hormone receptors for ubiquitination and degradation in breast and prostate cancer. Oncogene 2008, 27, 7201–7211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helsen, C.; van den Broeck, T.; Voet, A.; Prekovic, S.; van Poppel, H.; Joniau, S.; Claessens, F. Androgen receptor antagonists for prostate cancer therapy. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2014, 21, T105–T118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinlein, C.A.; Chang, C. Androgen receptor in prostate cancer. Endocr. Rev. 2004, 25, 276–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taplin, M.E.; Bubley, G.J.; Shuster, T.D.; Frantz, M.E.; Spooner, A.E.; Ogata, G.K.; Keer, H.N.; Balk, S.P. Mutation of the androgen-receptor gene in metastatic androgen-independent prostate cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 1995, 332, 1393–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masiello, D.; Cheng, S.; Bubley, G.J.; Lu, M.L.; Balk, S.P. Bicalutamide functions as an androgen receptor antagonist by assembly of a transcriptionally inactive receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 26321–26326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekar, T.; Yang, J.C.; Gao, A.C.; Evans, C.P. Mechanisms of resistance in castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC). Transl. Androl. Urol. 2015, 4, 365–380. [Google Scholar]
- Neklesa, T.; Snyder, L.B.; Willard, R.R.; Vitale, N.; Raina, K.; Pizzano, J.; Gordon, D.; Bookbinder, M.; Macaluso, J.; Dong, H.; et al. Abstract 5236: ARV-110: An androgen receptor PROTAC degrader for prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2018, 78 (Suppl. 13), 5236. [Google Scholar]
- Haven, N. Meeting. A Proof-of-Concept with PROTACs in Prostate Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2020, 10, 1084. [Google Scholar]
- Gooren, L.J.G.; Bunck, M.C.M. Androgen Replacement Therapy. Drugs 2004, 64, 1861–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furr, B.J.A.; Tucker, H. The preclinical development of bicalutamide: Pharmacodynamics and mechanism of action. Urology 1996, 47 (Suppl. 1), 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohl, C.E.; Gao, W.; Miller, D.D.; Bell, C.E.; Dalton, J.T. Structural basis for antagonism and resistance of bicalutamide in prostate cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 6201–6206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Dort, M.E.; Robins, D.M.; Wayburn, B. Design, Synthesis, and Pharmacological Characterization of 4-[4,4-Dimethyl-3-(4-hydroxybutyl)-5-oxo-2-thioxo-1-imidazolidinyl]- 2-iodobenzonitrile as a High-Affinity Nonsteroidal Androgen Receptor Ligand. J. Med. Chem. 2000, 43, 3344–3347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bassetto, M.; Ferla, S.; Pertusati, F.; Kandil, S.; Westwell, A.D.; Brancale, A.; McGuigan, C. Design and synthesis of novel bicalutamide and enzalutamide derivatives as antiproliferative agents for the treatment of prostate cancer. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 118, 230–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habibi, D.; Heydari, S.; Nasrollahzadeh, M. Synthesis of Aryl Nitriles using the Stable Aryl Diazonium Silica Sulfates. J. Chem. Res. 2012, 36, 573–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parent, E.E.; Dence, C.S.; Jenks, C.; Sharp, T.L.; Welch, M.J.; Katzenellenbogen, J.A. Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of [18F]Bicalutamide, 4-[76Br]Bromobicalutamide, and 4-[76Br]Bromo-thiobicalutamide as Non-Steroidal Androgens for Prostate Cancer Imaging. J. Med. Chem. 2007, 50, 1028–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, P.M.; Woo, L.W.L.; Labrosse, J.-R.; Trusselle, M.N.; Abbate, S.; Longhi, G.; Castiglioni, E.; Lebon, F.; Purohit, A.; Reed, M.J.; et al. Chiral Aromatase and Dual Aromatase−Steroid Sulfatase Inhibitors from the Letrozole Template: Synthesis, Absolute Configuration, and In Vitro Activity. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 4226–4238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romeiro, L.A.S.; Ferreira, M.d.; da Silva, L.L.; Castro, H.C.; Miranda, A.L.P.; Silva, C.L.M.; Noël, F.; Nascimento, J.B.; Araújo, C.V.; Tibiriçá, E.; et al. Discovery of LASSBio-772, a 1,3-benzodioxole N-phenylpiperazine derivative with potent alpha 1A/D-Adrenergic receptor blocking properties. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 46, 3000–3012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sramkoski, R.M.; Pretlow, T.G.; Giaconia, J.M.; Pretlow, T.P.; Schwartz, S.; Sy, M.; Marengo, S.R.; Rhim, J.S.; Zhang, D.; Jacobberger, J.W. A new human prostate carcinoma cell line, 22R v1. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. Anim. 1999, 35, 403–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharp, A.; Coleman, I.; Yuan, W.; Sprenger, C.; Dolling, D.; Rodrigues, D.N.; Russo, J.W.; Figueiredo, I.; Bertan, C.; Seed, G. Androgen receptor splice variant-7 expression emerges with castration resistance in prostate cancer. J. Clin. Invest. 2019, 129, 192–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orrego, F.; Villanueva, S. The chemical nature of the main central excitatory transmitter: a critical appraisal based upon release studies and synaptic vesicle localization. Neuroscience 1993, 56, 539–555. [Google Scholar]
- Capitosti, S.M.; Hansen, T.P.; Brown, M.L. Facile synthesis of an azido-labeled thalidomide analogue. Org. Lett. 2003, 5, 2865–2867. [Google Scholar]
- Ruchelman, A.L.; Man, H.; Zhang, W.; Chen, R.; Capone, L.; Kang, J.; Parton, A.; Corral, L.; Schafer, P.H.; Babusis, D. Isosteric analogs of lenalidomide and pomalidomide: Synthesis and biological activity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 360–365. [Google Scholar]
- Phillips, A.J.; Nasveschuk, C.G.; Henderson, J.A.; Liang, Y.; Fitzgerald, M.E.; He, M.; Michael, R.E. Heterocyclic degronimers for target protein degradation. U.S. Patent No 10,646,575, 12 May 2020. [Google Scholar]


| Gene | Forward Primer Sequence | Reverse Primer Sequence |
|---|---|---|
| AR | 5′-CAGTGGATGGGCTGAAAAAT-3′ | 5′-GGAGCTTGGTGAGCTGGTAG-3′ |
| PSA | 5′-ACGCTGGACAGGGGGCAAAAG-3′ | 5′-GGGCAGGGCACATGGTTCACT-3′ |
| TMPRSS2 | 5′-CAGGAGTGTACGGGAATGTGATGGT-3′ | 5′-GATTAGCCGTCTGCCCTCATTTGT-3′ |
| β-actin | 5′-AGTTGCGTTACACCCTTTCTTG-3′ | 5′-GCTGTCACCTTCACCGTTCC-3′ |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, G.Y.; Song, C.W.; Yang, Y.-S.; Lee, N.-R.; Yoo, H.-S.; Son, S.H.; Lee, S.J.; Park, J.S.; Lee, J.K.; Inn, K.-S.; et al. Chemical Degradation of Androgen Receptor (AR) Using Bicalutamide Analog–Thalidomide PROTACs. Molecules 2021, 26, 2525. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26092525
Kim GY, Song CW, Yang Y-S, Lee N-R, Yoo H-S, Son SH, Lee SJ, Park JS, Lee JK, Inn K-S, et al. Chemical Degradation of Androgen Receptor (AR) Using Bicalutamide Analog–Thalidomide PROTACs. Molecules. 2021; 26(9):2525. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26092525
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Ga Yeong, Chae Won Song, Yo-Sep Yang, Na-Rae Lee, Hyung-Seok Yoo, Seung Hwan Son, Soo Jin Lee, Jong Seon Park, Jong Kil Lee, Kyung-Soo Inn, and et al. 2021. "Chemical Degradation of Androgen Receptor (AR) Using Bicalutamide Analog–Thalidomide PROTACs" Molecules 26, no. 9: 2525. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26092525
APA StyleKim, G. Y., Song, C. W., Yang, Y.-S., Lee, N.-R., Yoo, H.-S., Son, S. H., Lee, S. J., Park, J. S., Lee, J. K., Inn, K.-S., & Kim, N.-J. (2021). Chemical Degradation of Androgen Receptor (AR) Using Bicalutamide Analog–Thalidomide PROTACs. Molecules, 26(9), 2525. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26092525





