Beneficial Effects of Cyclic Ether 2-Butoxytetrahydrofuran from Sea Cucumber Holothuria scabra against Aβ Aggregate Toxicity in Transgenic Caenorhabditis elegans and Potential Chemical Interaction
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
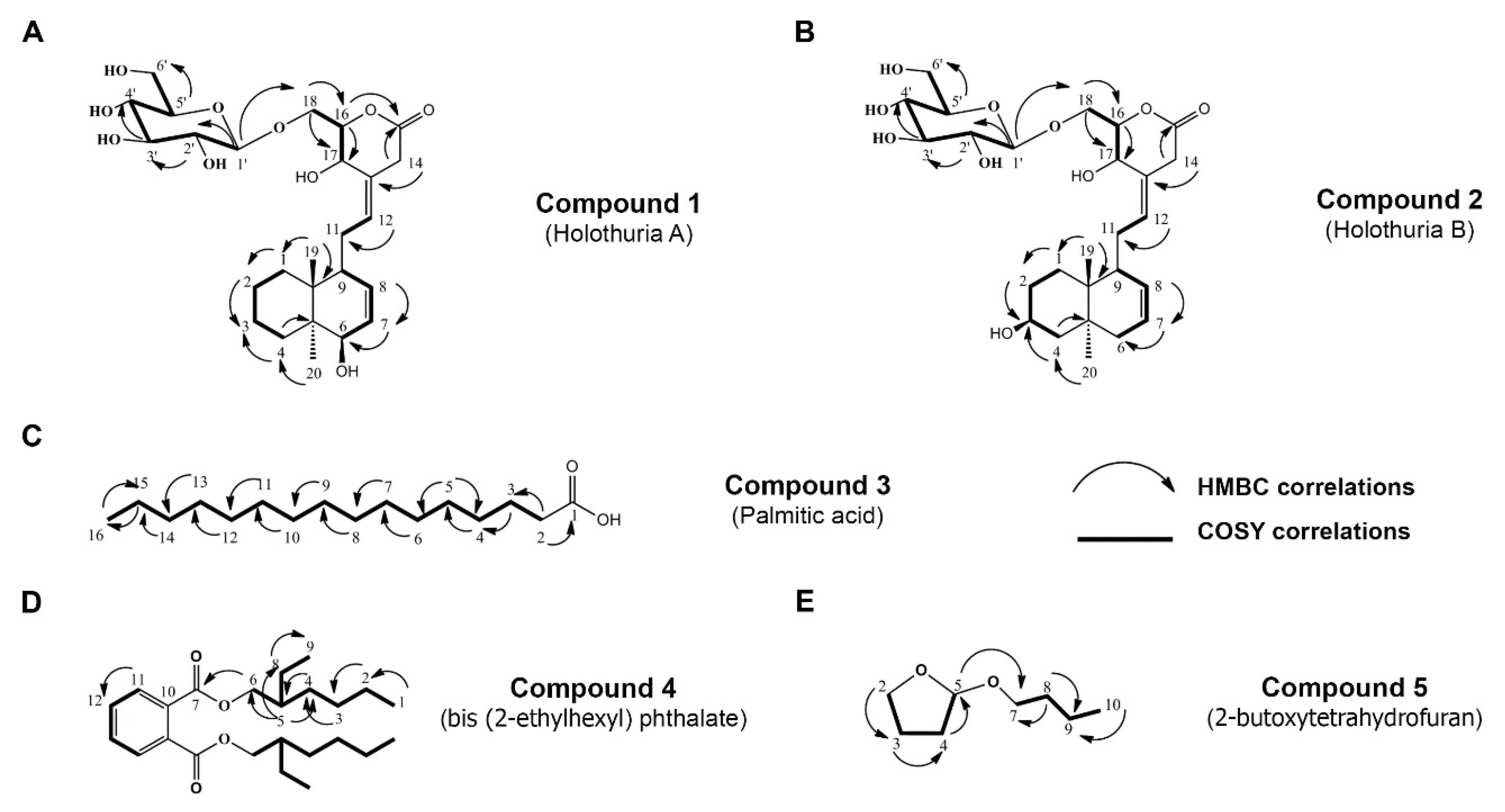
2.1. Isolation and Chemical Characterization of H. scabra Compounds
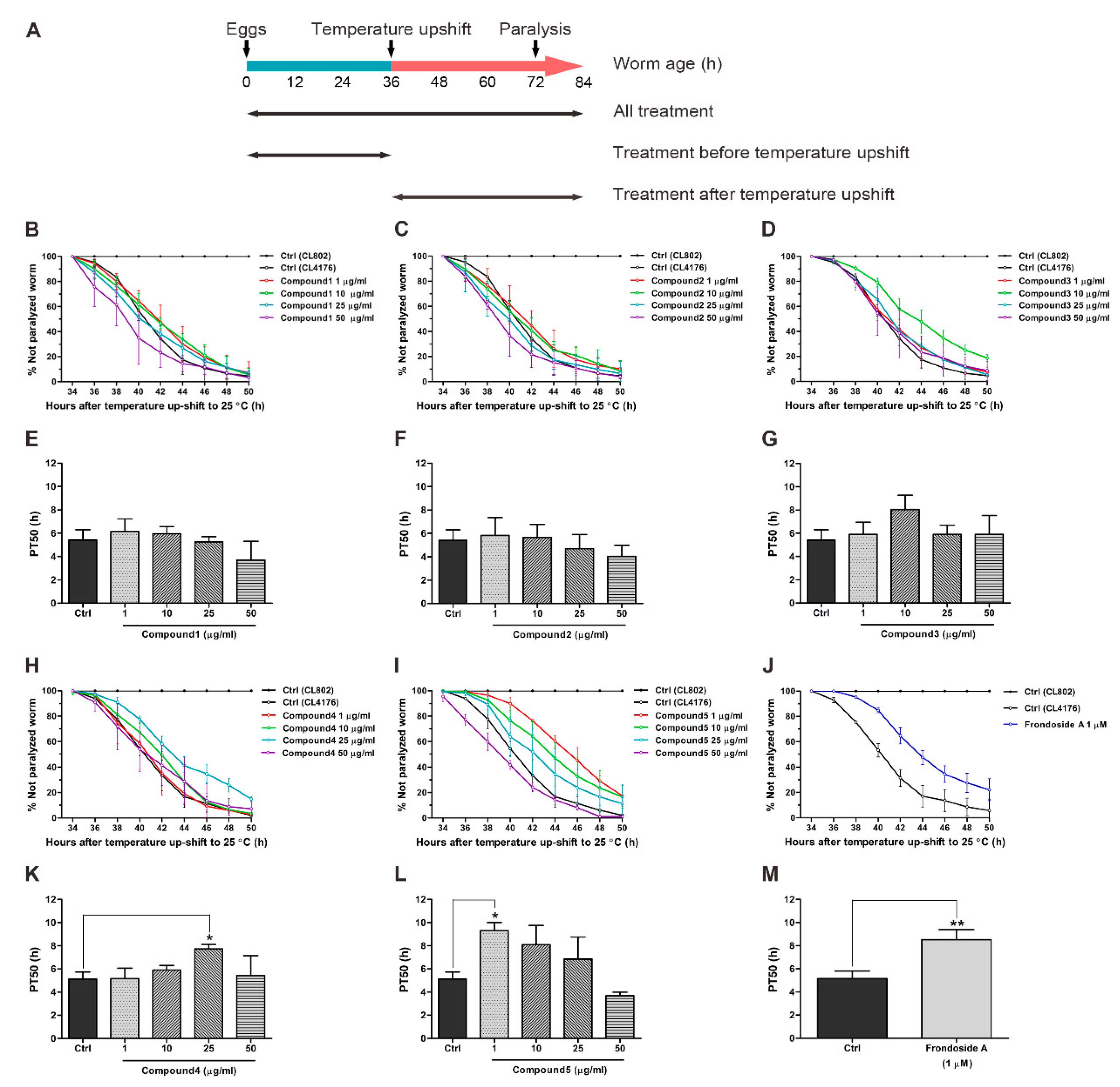
2.2. Effects of Compounds Isolated from H. scabra on Aβ-Induced Paralysis in Transgenic C. elegans
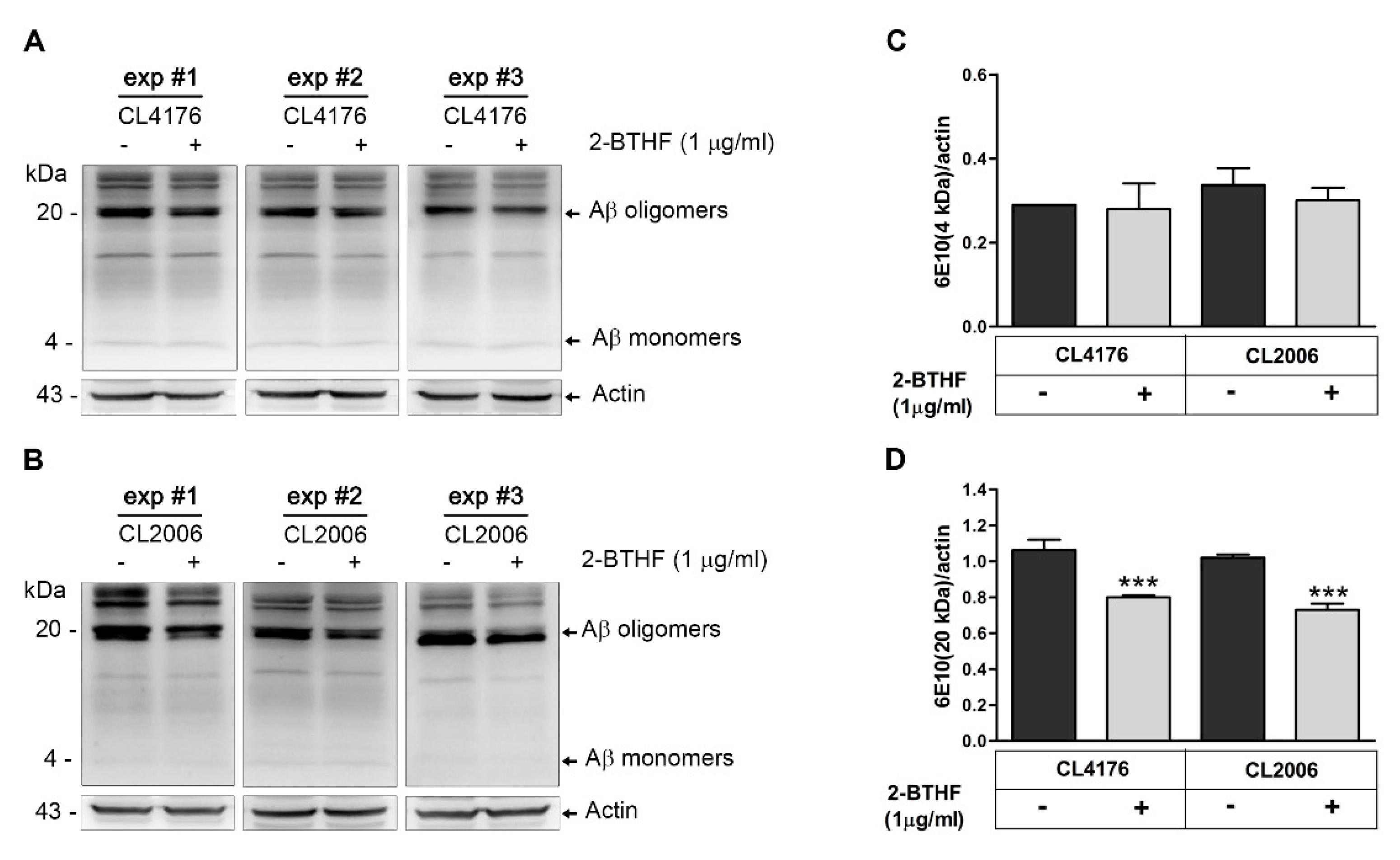
2.3. 2-BTHF (5) Alters Expression Level of Aβ Species in Transgenic C. elegans
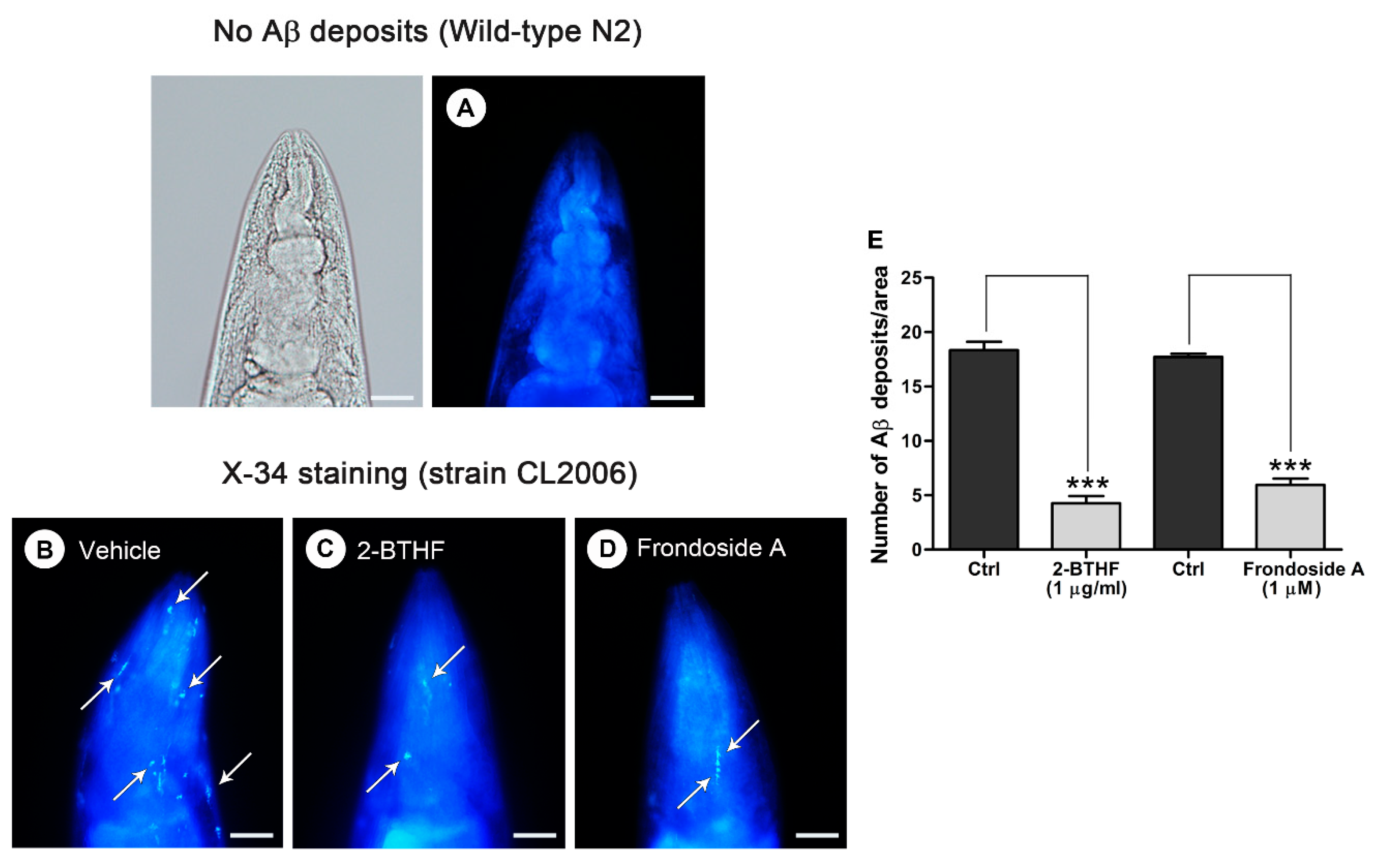
2.4. Aβ Deposit Is Inhibited by 2-BTHF (5) in Transgenic C. elegans
2.5. Effects of 2-BTHF (5) on Autophagy-Regulated Genes and Transcriptional Activities in Insulin-Like Growth Factor Signaling (IIS) Pathway in Transgenic C. elegans
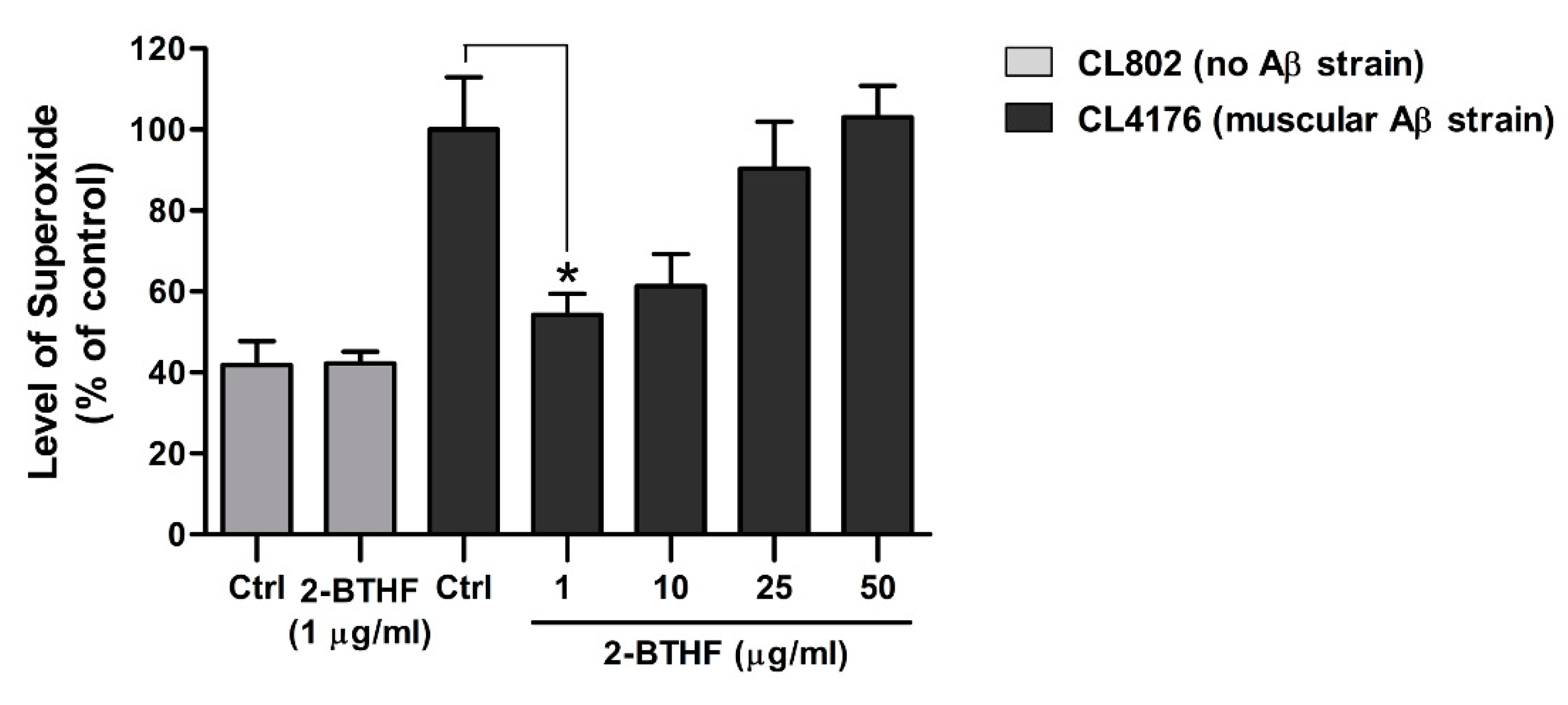
2.6. 2-BTHF (5) Suppresses ROS Production in Transgenic C. elegans
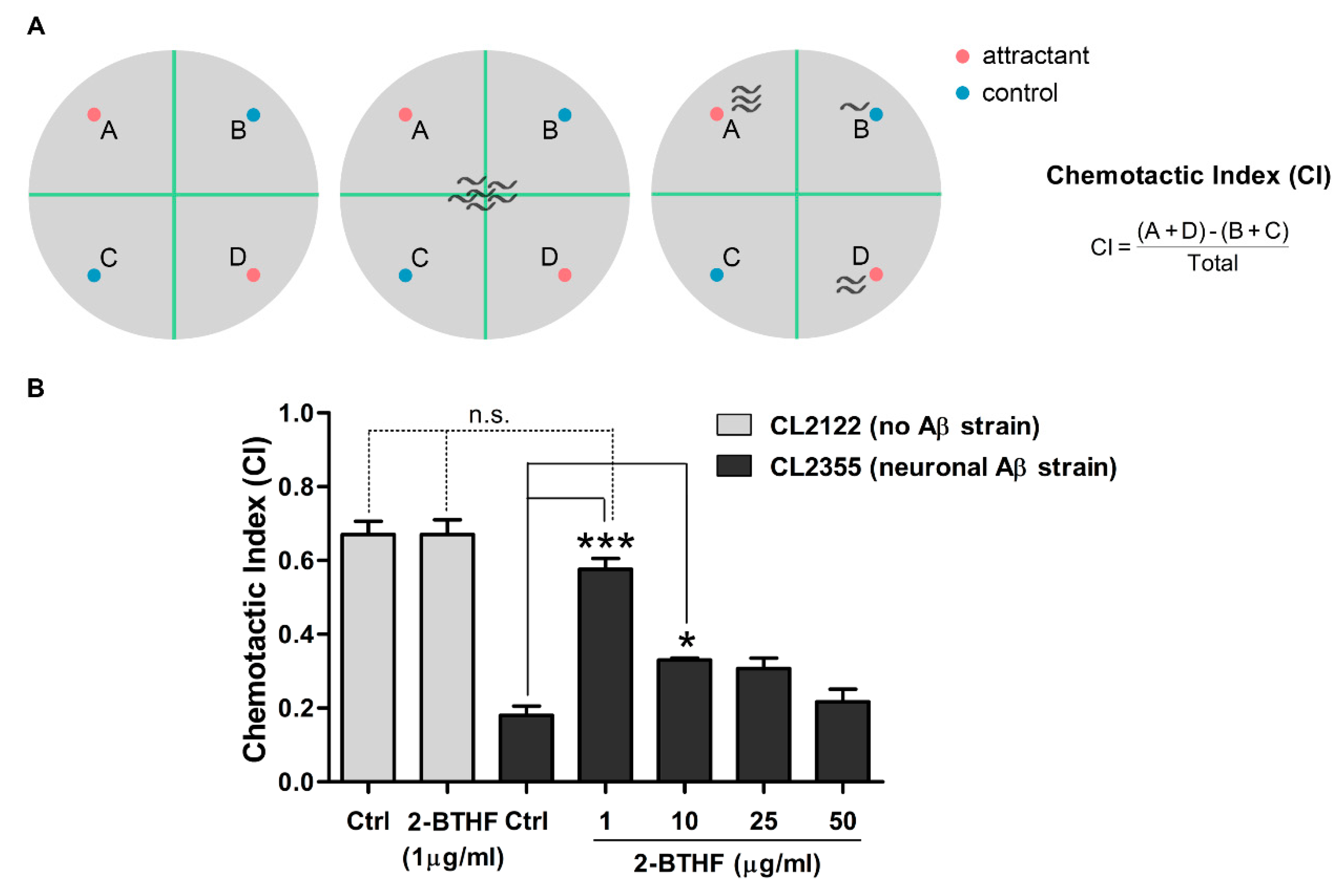
2.7. 2-BTHF (5) Suppresses Aβ Expression in Neurons and Prevents Defect in Chemotaxis Behavior
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals and Reagents
4.2. General Procedures for Extraction, Isolation, and Purification
4.3. H. scabra Preparation for Extraction
4.4. H. scabra Extraction and Isolation of Compounds
4.5. C. elegans Strains, Maintenance, and Synchronization
4.6. Dosage Information to C. elegans
4.7. Paralysis Assay
4.8. Western Blot of Aβ Species
4.9. Fluorescence Staining of Aβ Deposits
4.10. Gene Expression Analysis by Quantitative RT-PCR
4.11. Molecular Docking
4.12. Measurement of Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS)
4.13. Chemotaxis Assay
4.14. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- GBD 2016 Neurology Collaborators. Global, regional, and national burden of neurological disorders, 1990–2016: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet Neurol. 2019, 18, 459–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyner, P.M.; Cichewicz, R.H. Bringing natural products into the fold—Exploring the therapeutic lead potential of secondary metabolites for the treatment of protein-misfolding-related neurodegenerative diseases. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2011, 28, 26–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caulier, G.; Flammang, P.; Rakotoarisoa, P.; Gerbaux, P.; Demeyer, M.; Eeckhaut, I. Preservation of the bioactive saponins of Holothuria scabra through the processing of trepang. Cah. Biol. Mar. 2013, 54, 685–690. [Google Scholar]
- Pangestuti, R.; Arifin, Z. Medicinal and health benefit effects of functional sea cucumbers. J. Tradit. Complement. Med. 2018, 8, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jattujan, P.; Chalorak, P.; Siangcham, T.; Sangpairoj, K.; Nobsathian, S.; Poomtong, T.; Sobhon, P.; Meemon, K. Holothuria scabra extracts possess anti-oxidant activity and promote stress resistance and lifespan extension in Caenorhabditis elegans. Exp. Gerontol. 2018, 110, 158–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, E.; Bieschke, J.; Perciavalle, R.M.; Kelly, J.W.; Dillin, A. Opposing activities protect against age-onset proteotoxicity. Science 2006, 313, 1604–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, E.; Dillin, A. The insulin paradox: Aging, proteotoxicity and neurodegeneration. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2008, 9, 759–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chalorak, P.; Jattujan, P.; Nobsathian, S.; Poomtong, T.; Sobhon, P.; Meemon, K. Holothuria scabra extracts exhibit anti-Parkinson potential in C. elegans: A model for anti-Parkinson testing. Nutr. Neurosci. 2018, 21, 427–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LaFerla, F.M.; Green, K.N.; Oddo, S. Intracellular amyloid-beta in Alzheimer’s disease. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2007, 8, 499–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irwin, D.J.; Lee, V.M.; Trojanowski, J.Q. Parkinson’s disease dementia: Convergence of α-synuclein, tau and amyloid-β pathologies. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2013, 14, 626–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haass, C.; Selkoe, D.J. Soluble protein oligomers in neurodegeneration: Lessons from the Alzheimer’s amyloid β-peptide. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007, 8, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benilova, I.; Karran, E.; De Strooper, B. The toxic Aβ oligomer and Alzheimer’s disease: An emperor in need of clothes. Nat. Neurosci. 2012, 15, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kayed, R.; Head, E.; Thompson, J.L.; McIntire, T.M.; Milton, S.C.; Cotman, C.W.; Glabe, C.G. Common structure of soluble amyloid oligomers implies common mechanism of pathogenesis. Science 2003, 300, 486–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimmrich, V.; Ebert, U. Is Alzheimer’s disease a result of presynaptic failure? Synaptic dysfunctions induced by oligomeric beta-amyloid. Rev. Neurosci. 2009, 20, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, M.; Moore, S.; Mayes, J.; Parkin, E.; Beeg, M.; Canovi, M.; Gobbi, M.; Mann, D.M.; Allsop, D. Development of a proteolytically stable retro-inverso peptide inhibitor of beta-amyloid oligomerization as a potential novel treatment for Alzheimer’s disease. Biochemistry 2010, 49, 3261–3272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlstrom, S.; Soderman, P.; Swahn, B.M.; Rakos, L.; Ohberg, L. Cycloalkyl Ether Compounds and Their Use as Bace Inhibitors. U.S. Patent 9,000,185 B2, 7 April 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Milton, N.G. Anandamide and noladin ether prevent neurotoxicity of the human amyloid-beta peptide. Neurosci. Lett. 2002, 332, 127–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Shoup, T.M.; Teng, X.; Elmaleh, D.R.; Moore, A.; Ran, C. Crown ethers attenuate aggregation of amyloid beta of Alzheimer’s disease. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 15792–15795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, N.; Skelton, A. 12-crown-4 ether disrupts the Patient Brain-derived Amyloid-βeta Fibril Trimer: Insight from All-atom Molecular Dynamics Simulations. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2016, 7, 1433–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lublin, A.L.; Link, C.D. Alzheimer’s disease drug discovery: In vivo screening using Caenorhabditis elegans as a model for beta-amyloid peptide-induced toxicity. Drug Discov. Today Technol. 2013, 10, e115–e119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sangha, J.S.; Sun, X.; Wally, O.S.D.; Zhang, K.; Ji, X.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zidichouski, J.; Prithiviraj, B.; Zhang, J. Liuwei Dihuang (LWDH), a traditional Chinese medicinal formula, protects against β-amyloid toxicity in transgenic Caenorhabditis elegans. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e43990. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.-G.; Wang, X.; Zhou, T.-T.; Wu, X.-F.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, W.-Q.; Li, S.; Zhao, J. Scorpion Venom Heat-Resistant Peptide Protects Transgenic Caenorhabditis elegans from β-Amyloid Toxicity. Front. Pharmacol. 2016, 7, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tangrodchanapong, T.; Sobhon, P.; Meemon, K. Frondoside A Attenuates Amyloid-β Proteotoxicity in Transgenic Caenorhabditis elegans by Suppressing Its Formation. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 553579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Wu, Z.; Butko, P.; Christen, Y.; Lambert, M.P.; Klein, W.L.; Link, C.D.; Luo, Y. Amyloid-β-induced pathological behaviors are suppressed by Ginkgo biloba extract EGb 761 and ginkgolides in transgenic Caenorhabditis elegans. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 13102–13113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diomede, L.; Cassata, G.; Fiordaliso, F.; Salio, M.; Ami, D.; Natalello, A.; Doglia, S.M.; De Luigi, A.; Salmona, M. Tetracycline and its analogues protect Caenorhabditis elegans from β amyloid-induced toxicity by targeting oligomers. Neurobiol. Dis. 2010, 40, 424–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Cao, Z.; Klein, W.L.; Luo, Y. Heat shock treatment reduces beta amyloid toxicity in vivo by diminishing oligomers. Neurobiol. Aging 2010, 31, 1055–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McColl, G.; Roberts, B.R.; Gunn, A.P.; Perez, K.A.; Tew, D.J.; Masters, C.L.; Barnham, K.J.; Cherny, R.A.; Bush, A.I. The Caenorhabditis elegans Aβ1–42 model of Alzheimer disease predominantly expresses Aβ3–42. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 22697–22702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Scarcelli, V.; Legouis, R. Approaches for Studying Autophagy in Caenorhabditis elegans. Cells 2017, 6, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarasoff-Conway, J.M.; Carare, R.O.; Osorio, R.S.; Glodzik, L.; Butler, T.; Fieremans, E.; Axel, L.; Rusinek, H.; Nicholson, C.; Zlokovic, B.V.; et al. Clearance systems in the brain—implications for Alzheimer disease. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2015, 11, 457–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, C.A.; Curran, S.P. Gene-diet interactions and aging in C. elegans. Exp. Gerontol. 2016, 86, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Link, C.D.; Taft, A.; Kapulkin, V.; Duke, K.; Kim, S.; Fei, Q.; Wood, D.E.; Sahagan, B.G. Gene expression analysis in a transgenic Caenorhabditis elegans Alzheimer’s disease model. Neurobiol. Aging 2003, 24, 397–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Link, C.D.; Johnson, C.J.; Fonte, V.; Paupard, M.; Hall, D.H.; Styren, S.; Mathis, C.A.; Klunk, W.E. Visualization of fibrillar amyloid deposits in living, transgenic Caenorhabditis elegans animals using the sensitive amyloid dye, X-34. Neurobiol. Aging 2001, 22, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regitz, C.; Dußling, L.M.; Wenzel, U. Amyloid-beta (Aβ₁₋₄₂)-induced paralysis in Caenorhabditis elegans is inhibited by the polyphenol quercetin through activation of protein degradation pathways. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2014, 58, 1931–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regitz, C.; Fitzenberger, E.; Mahn, F.; Dußling, L.; Wenzel, U. Resveratrol reduces amyloid-beta (Aβ1–42)-induced paralysis through targeting proteostasis in an Alzheimer model of Caenorhabditis elegans. Eur. J. Nutr. 2015, 55, 741–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Cui, X.; Ma, X.; Wang, Z. rBTI reduced β-amyloid-induced toxicity by promoting autophagy-lysosomal degradation via DAF-16 in Caenorhabditis elegans. Exp. Gerontol. 2017, 89, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neudegger, T.; Verghese, J.; Hayer-Hartl, M.; Hartl, F.U.; Bracher, A. Structure of human heat-shock transcription factor 1 in complex with DNA. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2016, 23, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drake, J.; Link, C.D.; Butterfield, D.A. Oxidative stress precedes fibrillar deposition of Alzheimer’s disease amyloid beta-peptide (1–42) in a transgenic Caenorhabditis elegans model. Neurobiol. Aging 2003, 24, 415–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobert, O. Behavioral plasticity in C. elegans: Paradigms, circuits, genes. J. Neurobiol. 2003, 54, 203–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiew, P.L.; Don, M.M. Jewel of the seabed: Sea cucumbers as nutritional and drug candidates. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2012, 63, 616–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawson, A.P.; Klang, J.A. Synthesis of 2-Tetrahydrofuranyl Ethers from Aqueous 4-Hydroxybutanal. Synth. Commun. 1993, 23, 3205–3210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahmen, M.; Marquardt, W. Model-Based Design of Tailor-Made Biofuels. Energy Fuels 2016, 30, 1109–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, L.-S.; Wullenkord, J.; Li, Y.; Herbinet, O.; Zeng, M.; Qi, F.; Kohse-Höinghaus, K.; Battin-Leclerc, F. Probing the low-temperature chemistry of di-n-butyl ether: Detection of previously unobserved intermediates. Combust. Flame 2019, 210, 9–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diomede, L.; Rigacci, S.; Romeo, M.; Stefani, M.; Salmona, M. Oleuropein aglycone protects transgenic C. elegans strains expressing Aβ42 by reducing plaque load and motor deficit. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e58893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolff, M.; Zhang-Haagen, B.; Decker, C.; Barz, B.; Schneider, M.; Biehl, R.; Radulescu, A.; Strodel, B.; Willbold, D.; Nagel-Steger, L. Aβ42 pentamers/hexamers are the smallest detectable oligomers in solution. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pryor, N.E.; Moss, M.A.; Hestekin, C.N. Unraveling the early events of amyloid-β protein (Aβ) aggregation: Techniques for the determination of Aβ aggregate size. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 3038–3072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karamanos, T.K.; Kalverda, A.P.; Thompson, G.S.; Radford, S.E. Mechanisms of amyloid formation revealed by solution NMR. Prog. Nucl. Magn. Reson. Spectrosc. 2015, 88–89, 86–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Osta, A.; Alberini, C.M. Amyloid beta mediates memory formation. Learn Mem. 2009, 16, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puzzo, D.; Arancio, O. Amyloid-β peptide: Dr. Jekyll or Mr. Hyde? J. Alzheimers Dis. 2013, 33 (Suppl. 1), S111–S120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brothers, H.M.; Gosztyla, M.L.; Robinson, S.R. The Physiological Roles of Amyloid-β Peptide Hint at New Ways to Treat Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2018, 10, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbanc, B.; Cruz, L.; Yun, S.; Buldyrev, S.V.; Bitan, G.; Teplow, D.B.; Stanley, H.E. In silico study of amyloid beta-protein folding and oligomerization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 17345–17350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salminen, A.; Ojala, J.; Suuronen, T.; Kaarniranta, K.; Kauppinen, A. Amyloid-beta oligomers set fire to inflammasomes and induce Alzheimer’s pathology. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2008, 12, 2255–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, M.E.; Lesné, S.E. Soluble Aβ oligomer production and toxicity. J. Neurochem. 2012, 120 (Suppl. 1), 125–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, X.; Jiang, S.; Qin, M.; Liu, K.; Cao, P.; Chen, S.; Deng, J.; Gao, C. Compounds from the fruits of mangrove Sonneratia apetala: Isolation, molecular docking and antiaging effects using a Caenorhabditis elegans model. Bioorg. Chem. 2020, 99, 103813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumsta, C.; Chang, J.T.; Schmalz, J.; Hansen, M. Hormetic heat stress and HSF-1 induce autophagy to improve survival and proteostasis in C. elegans. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultana, R.; Perluigi, M.; Butterfield, D.A. Oxidatively modified proteins in Alzheimer’s disease (AD), mild cognitive impairment and animal models of AD: Role of Abeta in pathogenesis. Acta Neuropathol. 2009, 118, 131–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butterfield, D.A. beta-Amyloid-associated free radical oxidative stress and neurotoxicity: Implications for Alzheimer’s disease. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 1997, 10, 495–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheignon, C.; Tomas, M.; Bonnefont-Rousselot, D.; Faller, P.; Hureau, C.; Collin, F. Oxidative stress and the amyloid beta peptide in Alzheimer’s disease. Redox Biol. 2018, 14, 450–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kienlen-Campard, P.; Miolet, S.; Tasiaux, B.; Octave, J.N. Intracellular amyloid-beta 1–42, but not extracellular soluble amyloid-beta peptides, induces neuronal apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 15666–15670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umeda, T.; Ramser, E.M.; Yamashita, M.; Nakajima, K.; Mori, H.; Silverman, M.A.; Tomiyama, T. Intracellular amyloid β oligomers impair organelle transport and induce dendritic spine loss in primary neurons. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2015, 3, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chokchaisiri, R.; Chaneiam, N.; Svasti, S.; Fucharoen, S.; Vadolas, J.; Suksamrarn, A. Labdane Diterpenes from the Aerial Parts of Curcuma comosa Enhance Fetal Hemoglobin Production in an Erythroid Cell Line. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 724–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Mathúna, D.P.; Doskotch, R.W. New labdane diterpene glycosides from Amphiachyris amoena. J. Nat. Prod. 1995, 58, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Pietro, M.E.; Mannu, A.; Mele, A. NMR Determination of Free Fatty Acids in Vegetable Oils. Processes 2020, 8, 410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namikoshi, M.; Fujiwara, T.; Nishikawa, T.; Ukai, K. Natural Abundance (14)C Content of Dibutyl Phthalate (DBP) from Three Marine Algae. Mar. Drugs 2006, 4, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohn, I.; Raschke, S.; Aschner, M.; Tuck, S.; Kuehnelt, D.; Kipp, A.; Schwerdtle, T.; Bornhorst, J. Treatment of Caenorhabditis Elegans with Small Selenium Species Enhances Antioxidant Defense Systems. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2019, 63, 1801304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, J.V.; Luo, Y. Elevation of oxidative free radicals in Alzheimer’s disease models can be attenuated by Ginkgo biloba extract EGb 761. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2003, 5, 287–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Margie, O.; Palmer, C.; Chin-Sang, I. C. elegans chemotaxis assay. J. Vis. Exp. 2013, 74, e50069. [Google Scholar]
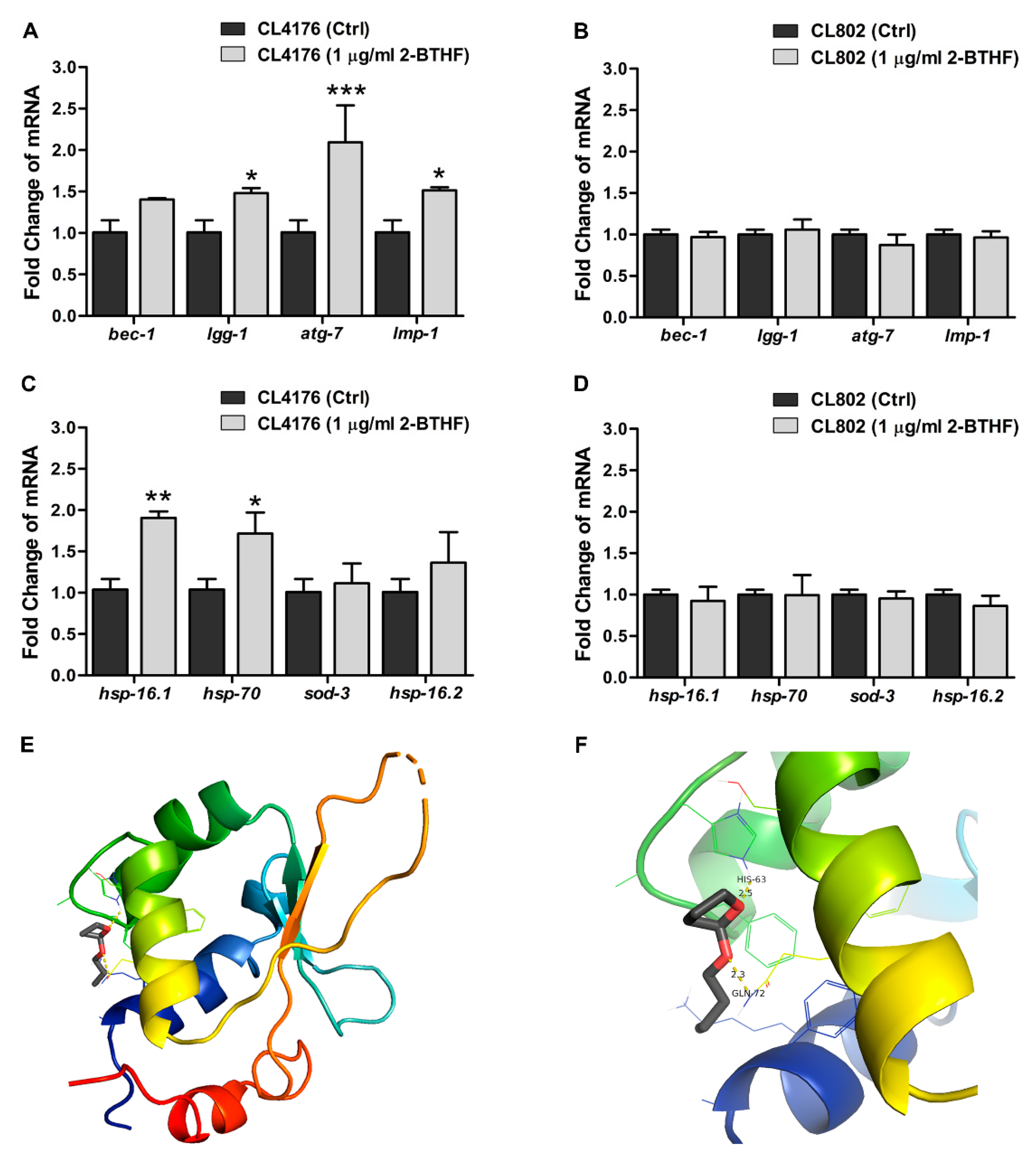
| Gene | Forward 5’→3’ | Reverse 5’→3’ |
|---|---|---|
| bec-1 | AGATCTCAAAGCTGCGTGTG | AAAAGGCAGAATTCCAGCAGA |
| lgg-1 | AATGGAAACCCAAAGCCCCT | AGGGGAGAAGAGCAACTTCG |
| atg-7 | TCTGCAGGATGGATGGTTCG | CTCGGCAAGGTCCATGTGTA |
| lmp-1 | CTCGCACCAACGAAGTTGTC | GTATCCGACGAGCACAACCA |
| hsp-16.1 | GCAGAGGCTCTCCATCTGAA | GCTTGAACTGCGAGACATTG |
| hsp-70 | GCCGGTTGAAAAGGCACTTC | CGAGTTGATCCCCCAACCAA |
| sod-3 | GCACACTCTCCCAGATCTCC | TCGAAACAGCCTCGTGAAGT |
| hsp-16.2 | GTCACTTTACCACTATTTCCGT | CAATCTCAGAAGACTCAGATGG |
| act-1 | ATCGTCACCACCAGCTTTCT | CACACCCGCAAATGAGTGAA |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tangrodchanapong, T.; Sornkaew, N.; Yurasakpong, L.; Niamnont, N.; Nantasenamat, C.; Sobhon, P.; Meemon, K. Beneficial Effects of Cyclic Ether 2-Butoxytetrahydrofuran from Sea Cucumber Holothuria scabra against Aβ Aggregate Toxicity in Transgenic Caenorhabditis elegans and Potential Chemical Interaction. Molecules 2021, 26, 2195. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26082195
Tangrodchanapong T, Sornkaew N, Yurasakpong L, Niamnont N, Nantasenamat C, Sobhon P, Meemon K. Beneficial Effects of Cyclic Ether 2-Butoxytetrahydrofuran from Sea Cucumber Holothuria scabra against Aβ Aggregate Toxicity in Transgenic Caenorhabditis elegans and Potential Chemical Interaction. Molecules. 2021; 26(8):2195. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26082195
Chicago/Turabian StyleTangrodchanapong, Taweesak, Nilubon Sornkaew, Laphatrada Yurasakpong, Nakorn Niamnont, Chanin Nantasenamat, Prasert Sobhon, and Krai Meemon. 2021. "Beneficial Effects of Cyclic Ether 2-Butoxytetrahydrofuran from Sea Cucumber Holothuria scabra against Aβ Aggregate Toxicity in Transgenic Caenorhabditis elegans and Potential Chemical Interaction" Molecules 26, no. 8: 2195. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26082195
APA StyleTangrodchanapong, T., Sornkaew, N., Yurasakpong, L., Niamnont, N., Nantasenamat, C., Sobhon, P., & Meemon, K. (2021). Beneficial Effects of Cyclic Ether 2-Butoxytetrahydrofuran from Sea Cucumber Holothuria scabra against Aβ Aggregate Toxicity in Transgenic Caenorhabditis elegans and Potential Chemical Interaction. Molecules, 26(8), 2195. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26082195







