Dabrafenib Promotes Schwann Cell Differentiation by Inhibition of the MEK-ERK Pathway
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
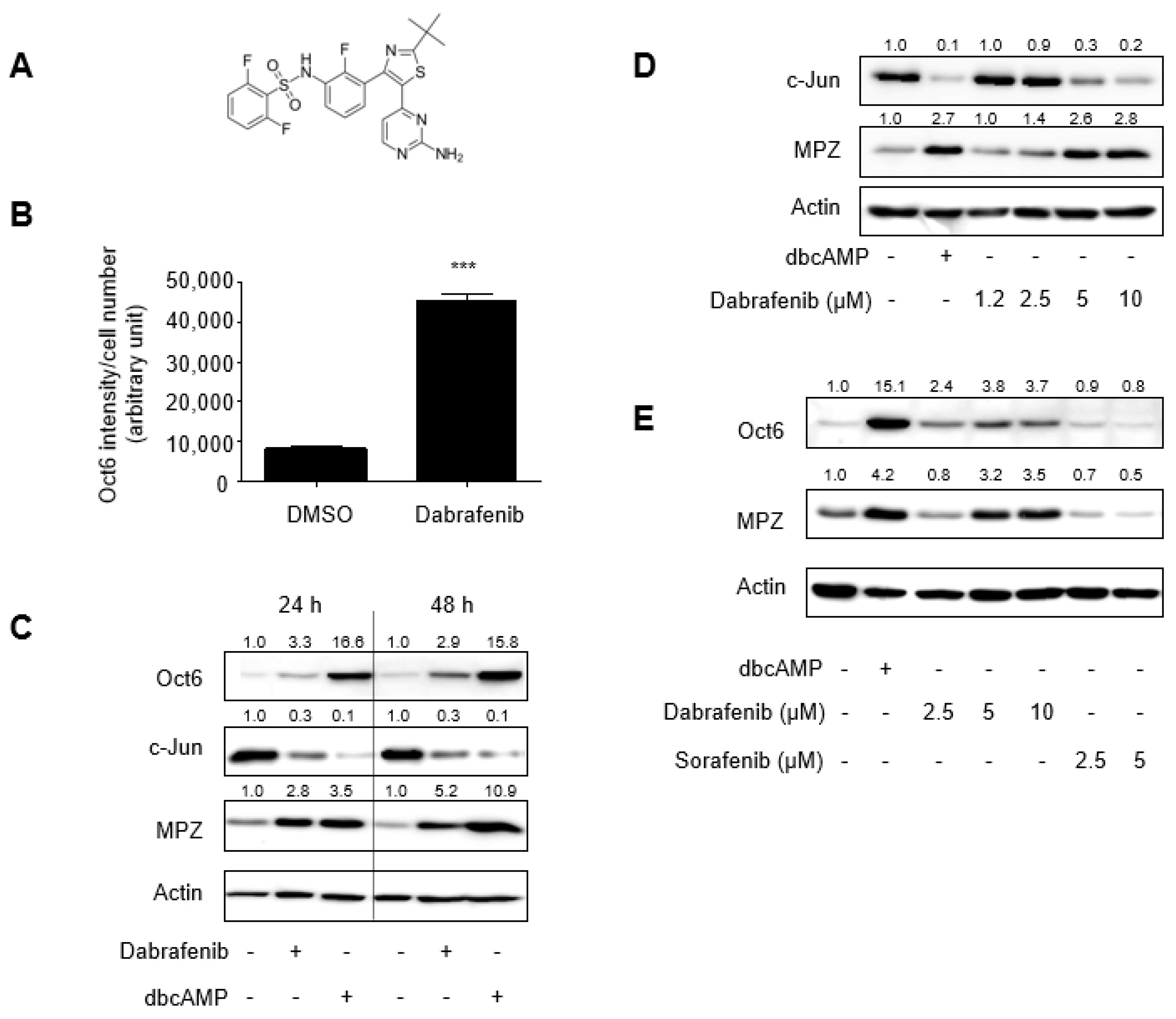
2.1. Identification of Dabrafenib That Promotes Schwann Cell Differentiation In Vitro
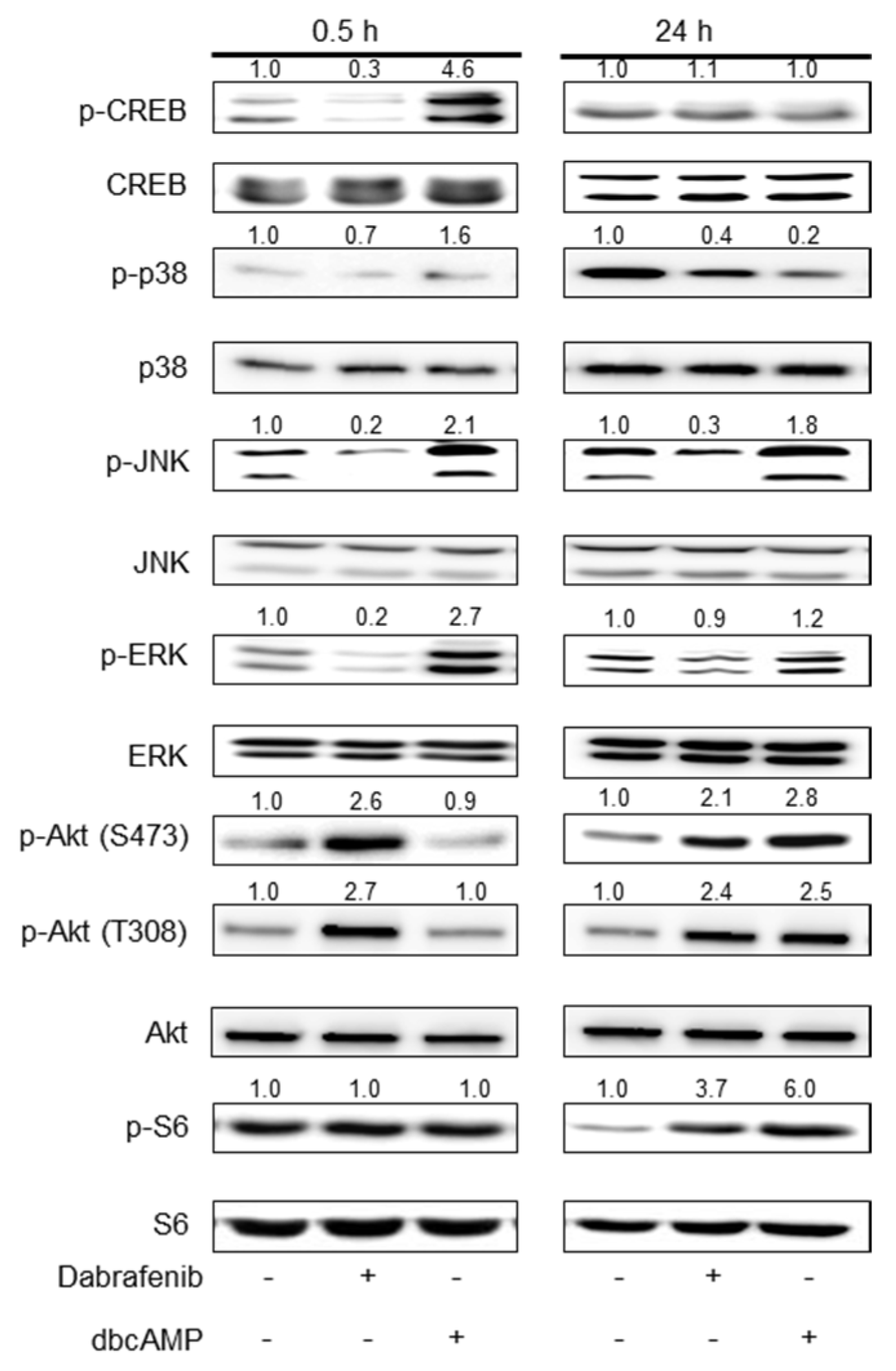
2.2. Mechanistic Insights into Dabrafenib-Induced Schwann Cell Differentiation
2.3. Inhibition of JNK Activity Exhibits No Effect on Schwann Cell Differentiation
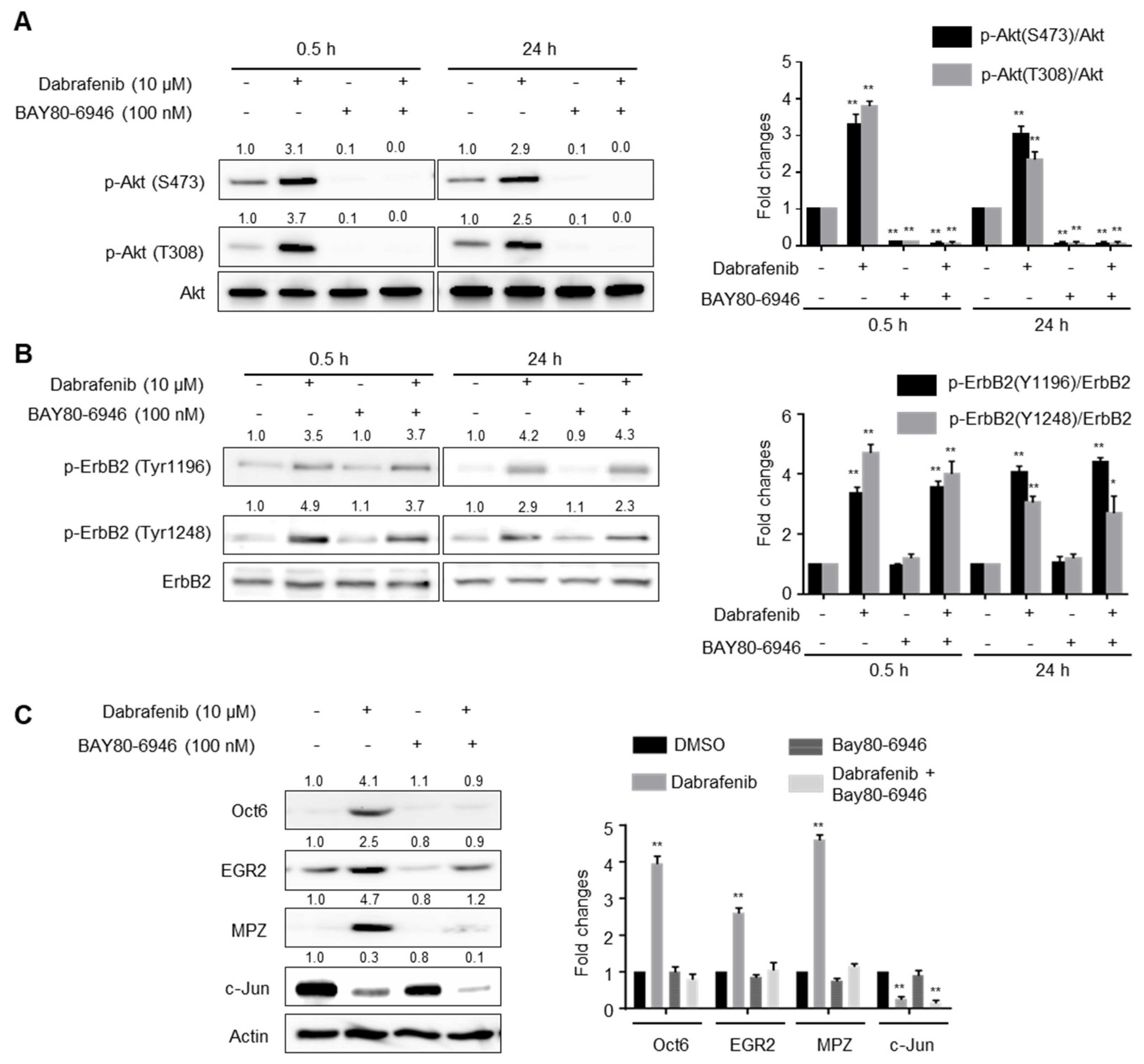
2.4. PI3K Activity Is Required for Dabrafenib-Induced Schwann Cell Differentiation
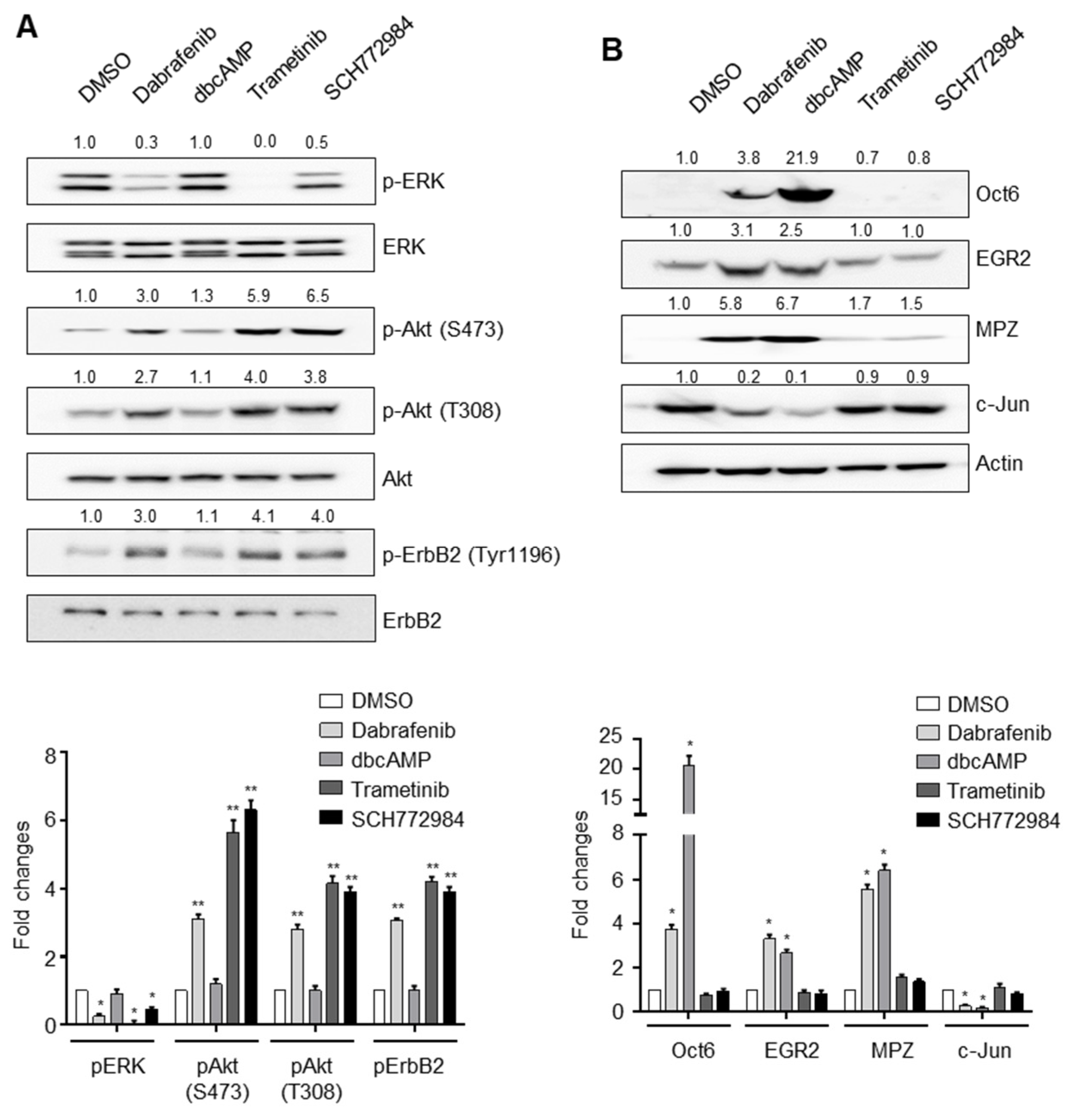
2.5. Dabrafenib Induces Autophosphorylation of ErbB2 by Inhibiting the MEK-ERK Pathway
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals
4.2. Antibodies
4.3. Primary Rat Schwann Cell Culture and Chemical Treatment
4.4. Indirect Immunofluorescence and Oct6 Quantitation
4.5. Western Blot Analysis
4.6. Statistical Analysis
4.7. Microarray Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Yeung, M.S.Y.; Djelloul, M.; Steiner, E.; Bernard, S.; Salehpour, M.; Possnert, G.; Brundin, L.; Frisen, J. Dynamics of oligodendrocyte generation in multiple sclerosis. Nature 2019, 566, 538–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stierli, S.; Imperatore, V.; Lloyd, A.C. Schwann cell plasticity-roles in tissue homeostasis, regeneration, and disease. Glia 2019, 67, 2203–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boerboom, A.; Dion, V.; Chariot, A.; Franzen, R. Molecular Mechanisms Involved in Schwann Cell Plasticity. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2017, 10, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nocera, G.; Jacob, C. Mechanisms of Schwann cell plasticity involved in peripheral nerve repair after injury. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2020, 77, 3977–3989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glenn, T.D.; Talbot, W.S. Signals regulating myelination in peripheral nerves and the Schwann cell response to injury. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2013, 23, 1041–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newbern, J.; Birchmeier, C. Nrg1/ErbB signaling networks in Schwann cell development and myelination. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2010, 21, 922–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taveggia, C.; Feltri, M.L.; Wrabetz, L. Signals to promote myelin formation and repair. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2010, 6, 276–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jessen, K.R.; Mirsky, R. The repair Schwann cell and its function in regenerating nerves. J. Physiol. 2016, 594, 3521–3531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Seeliger, M.A.; Panjarian, S.B.; Kim, H.; Deng, X.; Sim, T.; Couch, B.; Koleske, A.J.; Smithgall, T.E.; Gray, N.S. N-myristoylated c-Abl tyrosine kinase localizes to the endoplasmic reticulum upon binding to an allosteric inhibitor. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 29005–29014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Jung, J.; Koo, J.; Cho, W.; Lee, W.S.; Kim, C.; Park, W.; Park, S.B. Diversity-oriented synthetic strategy for developing a chemical modulator of protein-protein interaction. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rheault, T.R.; Stellwagen, J.C.; Adjabeng, G.M.; Hornberger, K.R.; Petrov, K.G.; Waterson, A.G.; Dickerson, S.H.; Mook, R.A., Jr.; Laquerre, S.G.; King, A.J.; et al. Discovery of Dabrafenib: A Selective Inhibitor of Raf Kinases with Antitumor Activity against B-Raf-Driven Tumors. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 4, 358–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilhelm, S.M.; Carter, C.; Tang, L.; Wilkie, D.; McNabola, A.; Rong, H.; Chen, C.; Zhang, X.; Vincent, P.; McHugh, M.; et al. BAY 43-9006 exhibits broad spectrum oral antitumor activity and targets the RAF/MEK/ERK pathway and receptor tyrosine kinases involved in tumor progression and angiogenesis. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 7099–7109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghidinelli, M.; Poitelon, Y.; Shin, Y.K.; Ameroso, D.; Williamson, C.; Ferri, C.; Pellegatta, M.; Espino, K.; Mogha, A.; Monk, K.; et al. Laminin 211 inhibits protein kinase A in Schwann cells to modulate neuregulin 1 type III-driven myelination. Plos Biol. 2017, 15, e2001408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, H.S.; Johnson, T.V.; Joe, M.K.; Abu-Asab, M.; Zhang, J.; Chan, C.C.; Tomarev, S.I. Myocilin mediates myelination in the peripheral nervous system through ErbB2/3 signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 26357–26371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Rowley, B.R.; Bull, C.O.; Schneider, C.; Haegebarth, A.; Schatz, C.A.; Fracasso, P.R.; Wilkie, D.P.; Hentemann, M.; Wilhelm, S.M.; et al. BAY 80-6946 is a highly selective intravenous PI3K inhibitor with potent p110alpha and p110delta activities in tumor cell lines and xenograft models. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2013, 12, 2319–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawasaki, Y.; Sakimura, A.; Park, C.M.; Tomaru, R.; Tanaka, T.; Ozawa, T.; Zhou, Y.; Narita, K.; Kishi, H.; Muraguchi, A.; et al. Feedback control of ErbB2 via ERK-mediated phosphorylation of a conserved threonine in the juxtamembrane domain. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 31502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, R.J. Signal transduction by the JNK group of MAP kinases. Cell 2000, 103, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrisingh, M.C.; Perez-Nadales, E.; Parkinson, D.B.; Malcolm, D.S.; Mudge, A.W.; Lloyd, A.C. The Ras/Raf/ERK signalling pathway drives Schwann cell dedifferentiation. EMBO J. 2004, 23, 3061–3071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, A.; Furusho, M.; Bansal, R. Sustained activation of ERK1/2 MAPK in oligodendrocytes and schwann cells enhances myelin growth and stimulates oligodendrocyte progenitor expansion. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newbern, J.M.; Li, X.; Shoemaker, S.E.; Zhou, J.; Zhong, J.; Wu, Y.; Bonder, D.; Hollenback, S.; Coppola, G.; Geschwind, D.H.; et al. Specific functions for ERK/MAPK signaling during PNS development. Neuron 2011, 69, 91–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogata, T.; Iijima, S.; Hoshikawa, S.; Miura, T.; Yamamoto, S.; Oda, H.; Nakamura, K.; Tanaka, S. Opposing extracellular signal-regulated kinase and Akt pathways control Schwann cell myelination. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 6724–6732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, N.; Reddy, K.; Yang, D.P.; Taveggia, C.; Salzer, J.L.; Maurel, P.; Kim, H.A. Soluble neuregulin-1 has bifunctional, concentration-dependent effects on Schwann cell myelination. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 6122–6131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brockes, J.P.; Fields, K.L.; Raff, M.C. Studies on cultured rat Schwann cells. I. Establishment of purified populations from cultures of peripheral nerve. Brain Res. 1979, 165, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Gene | Fold Changes (Mean ± SD, n = 2) |
|---|---|
| Myelin Basic Protein | 5.48 ± 0.72 |
| Myelin Protein Zero | 4.30 ± 0.14 |
| Early Growth Response 2 | 5.13 ± 0.58 |
| Myelin Associated Glycoprotein | 3.47 ± 0.24 |
| Oct6 (Pou3f1) | 3.08 ± 0.84 |
| Brn2 (Pou3f2) | 2.01 ± 0.01 |
| Sox10 | 1.01 ± 0.01 |
| Zeb2 | 1.02 ± 0.03 |
| PAX3 | 1.01 ± 0.01 |
| c-Jun | −4.85 ± 0.63 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, K.; Shin, Y.; Lee, G.; Park, H.; Choi, Y. Dabrafenib Promotes Schwann Cell Differentiation by Inhibition of the MEK-ERK Pathway. Molecules 2021, 26, 2141. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26082141
Park K, Shin Y, Lee G, Park H, Choi Y. Dabrafenib Promotes Schwann Cell Differentiation by Inhibition of the MEK-ERK Pathway. Molecules. 2021; 26(8):2141. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26082141
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Kyuhee, Yoonkyoung Shin, Gyeongbeen Lee, Hwantae Park, and Yongmun Choi. 2021. "Dabrafenib Promotes Schwann Cell Differentiation by Inhibition of the MEK-ERK Pathway" Molecules 26, no. 8: 2141. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26082141
APA StylePark, K., Shin, Y., Lee, G., Park, H., & Choi, Y. (2021). Dabrafenib Promotes Schwann Cell Differentiation by Inhibition of the MEK-ERK Pathway. Molecules, 26(8), 2141. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26082141





