Involvement of Neuropeptide Galanin Receptors 2 and 3 in Learning, Memory and Anxiety in Aging Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
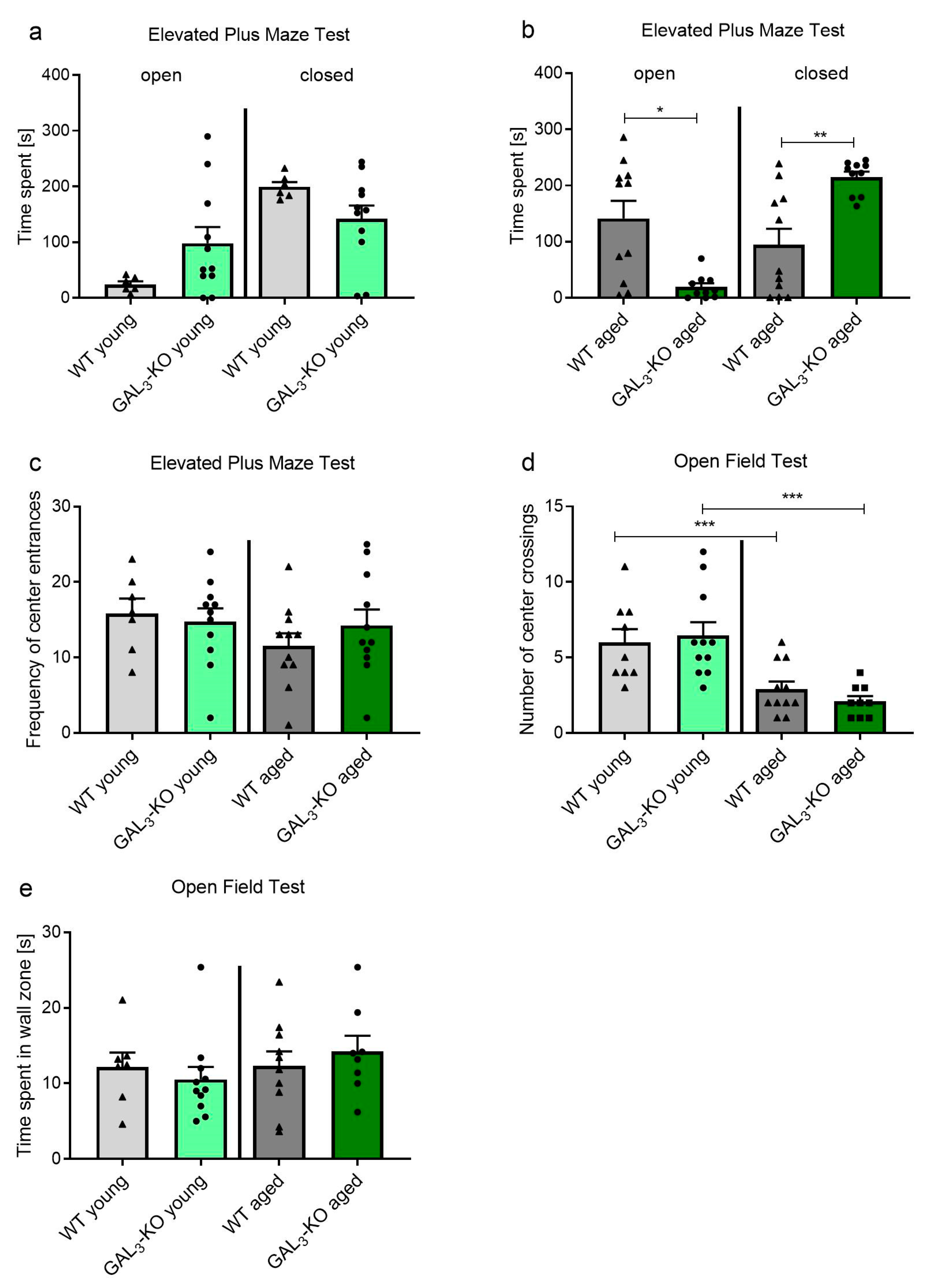
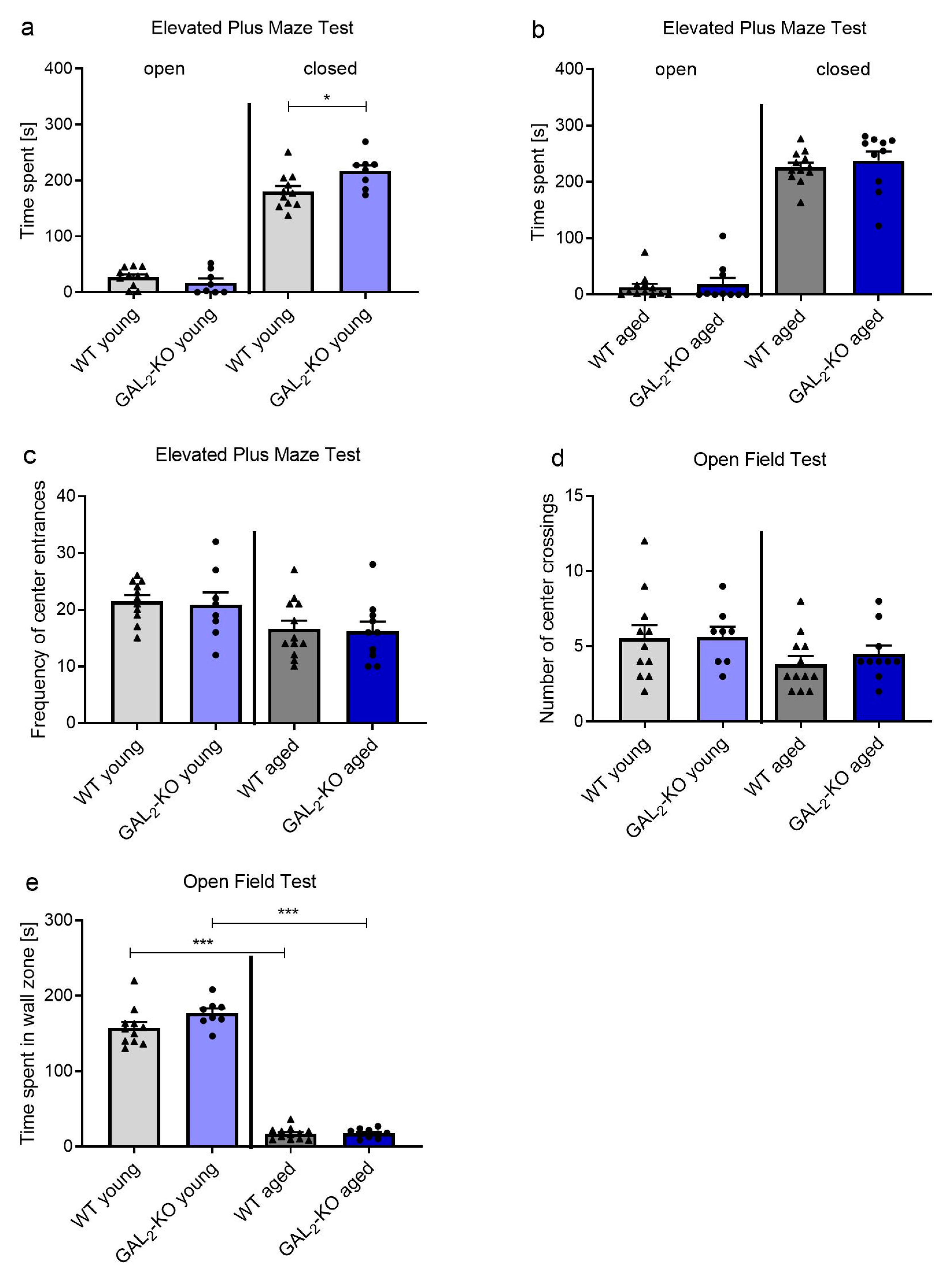
2.1. Loss of GAL3-R Induces Anxiety in Middle-Aged Mice
2.2. Age-Dependent Deficit in Spatial Learning in Mice Lacking GAL3-R
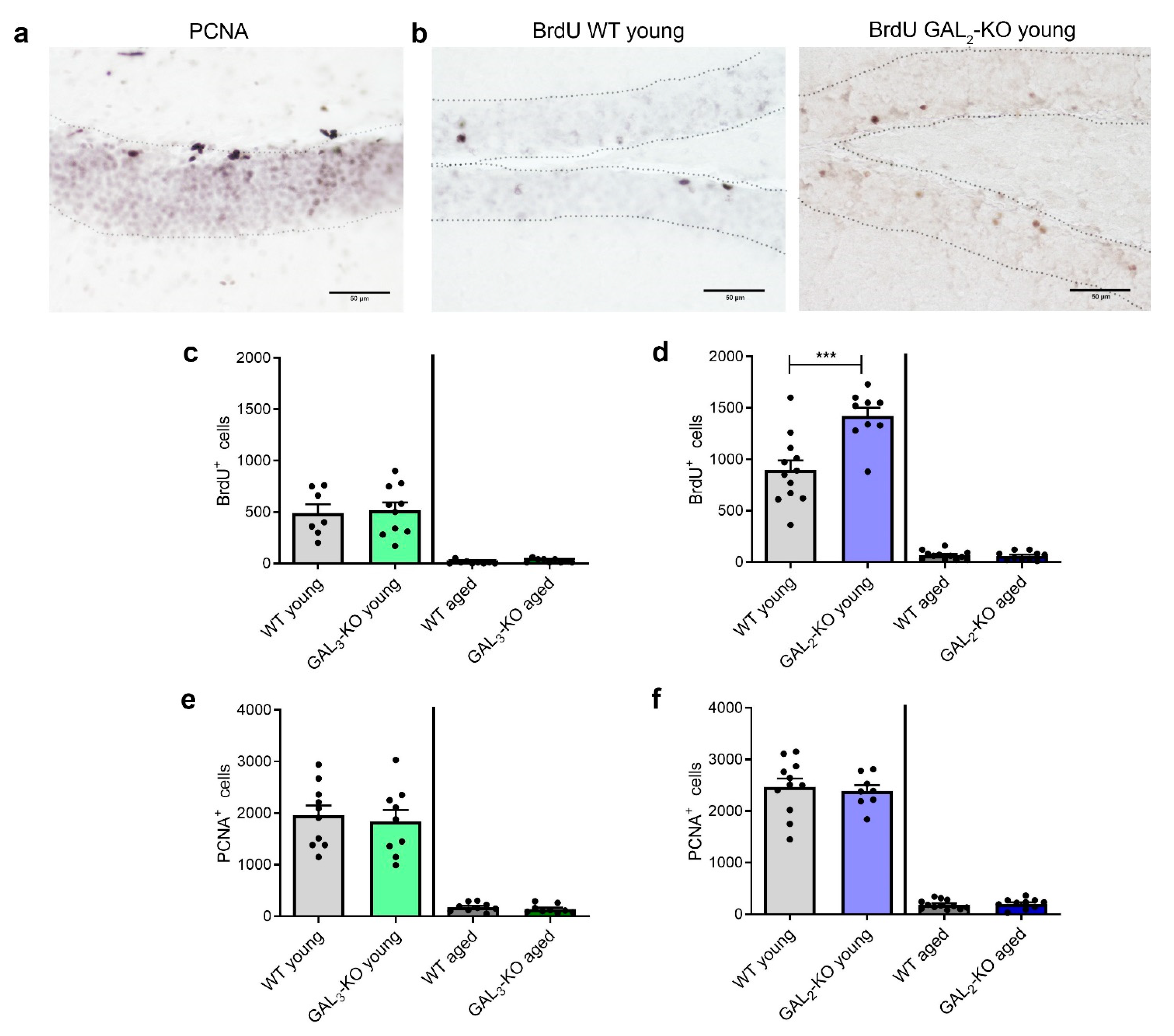
2.3. Deletion of GAL2-R Increases Survival of Newly Generated Cells in the dDG
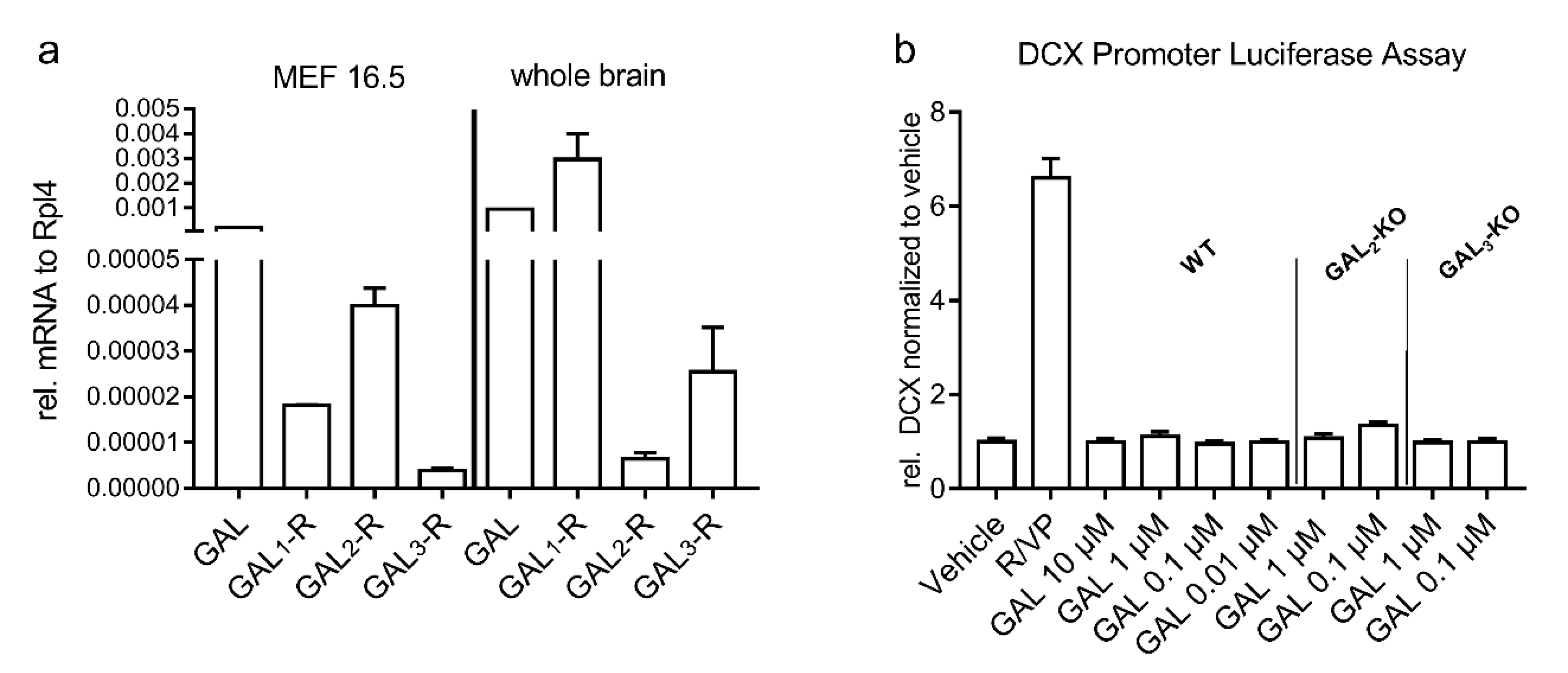
2.4. Mouse Embryonic Forebrain Cells Express GAL System mRNA but Do Not Respond to GAL Treatment In Vitro
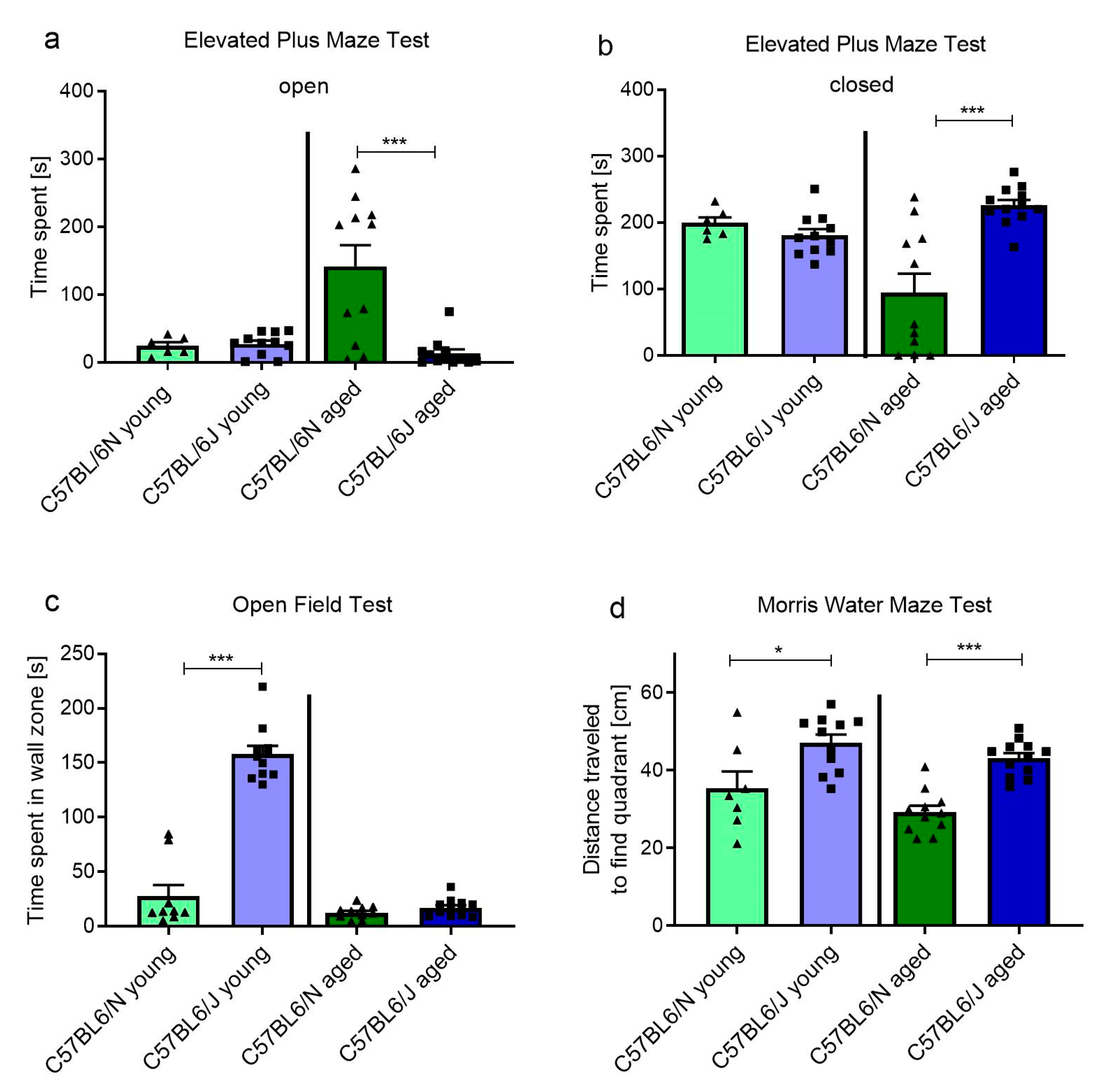
2.5. C57BL/6N and C57BL/6J Sub-Strains Differ in Behavioral and Cognitive Tasks
3. Discussion
4. Material and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. BrdU Injection
4.3. Elevated Plus Maze
4.4. Open Field
4.5. Morris Water Maze
4.6. Immunohistochemistry
4.7. Mouse Embryonic (E16.5) Forebrain Cell Culture
4.8. RNA Analysis
4.9. Peptide
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Kuhn, H.G.; Dickinson-Anson, H.; Gage, F.H. Neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus of the adult rat: Age-related decrease of neuronal progenitor proliferation. J. Neurosci. 1996, 16, 2027–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luskin, M.B. Restricted proliferation and migration of postnatally generated neurons derived from the forebrain subventricular zone. Neuron 1993, 11, 173–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kempermann, G.; Gage, F.H.; Aigner, L.; Song, H.; Curtis, M.A.; Thuret, S.; Kuhn, H.G.; Jessberger, S.; Frankland, P.W.; Cameron, H.A.; et al. Human adult neurogenesis: Evidence and remaining questions. Cell Stem Cell 2018, 23, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gould, E.; Tanapat, P.; Hastings, N.B.; Shors, T.J. Neurogenesis in adulthood: A possible role in learning. Trends Cogn. Sci. 1999, 3, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toda, T.; Parylak, S.L.; Linker, S.B.; Gage, F.H. The role of adult hippocampal neurogenesis in brain health and disease. Mol. Psychiatry 2019, 24, 67–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, R.; Gundlach, A.L.; Kofler, B. The galanin peptide family: Receptor pharmacology, pleiotropic biological actions, and implications in health and disease. Pharmacol. Ther. 2007, 115, 177–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, R.; Gundlach, A.L.; Holmes, F.E.; Hobson, S.A.; Wynick, D.; Hokfelt, T.; Kofler, B. Physiology, signaling, and pharmacology of galanin peptides and receptors: Three decades of emerging diversity. Pharmacol. Rev. 2015, 67, 118–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holets, V.R.; Hokfelt, T.; Rokaeus, A.; Terenius, L.; Goldstein, M. Locus coeruleus neurons in the rat containing neuropeptide y, tyrosine hydroxylase or galanin and their efferent projections to the spinal cord, cerebral cortex and hypothalamus. Neuroscience 1988, 24, 893–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melander, T.; Hokfelt, T.; Rokaeus, A.; Cuello, A.C.; Oertel, W.H.; Verhofstad, A.; Goldstein, M. Coexistence of galanin-like immunoreactivity with catecholamines, 5-hydroxytryptamine, gaba and neuropeptides in the rat cns. J. Neurosci. 1986, 6, 3640–3654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hokfelt, T.; Xu, Z.Q.; Shi, T.J.; Holmberg, K.; Zhang, X. Galanin in ascending systems. Focus on coexistence with 5-hydroxytryptamine and noradrenaline. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1998, 863, 252–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kordower, J.H.; Le, H.K.; Mufson, E.J. Galanin immunoreactivity in the primate central nervous system. J. Comp. Neurol. 1992, 319, 479–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.A.; Kolb, P.E.; Leverenz, J.B.; Peskind, E.R.; Raskind, M.A. Preservation of noradrenergic neurons in the locus ceruleus that coexpress galanin mrna in alzheimer’s disease. J. Neurochem. 1999, 73, 2028–2036. [Google Scholar]
- Le Maitre, E.; Barde, S.S.; Palkovits, M.; Diaz-Heijtz, R.; Hokfelt, T.G. Distinct features of neurotransmitter systems in the human brain with focus on the galanin system in locus coeruleus and dorsal raphe. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, E536–E545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Barr, A.M.; Kinney, J.W.; Sanna, P.; Conti, B.; Behrens, M.M.; Bartfai, T. A role for galanin in antidepressant actions with a focus on the dorsal raphe nucleus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 874–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, C.C.; Hohmann, J.G.; Clifton, D.K.; Steiner, R.A. Distribution of galanin messenger rna-expressing cells in murine brain and their regulation by leptin in regions of the hypothalamus. Neuroscience 2001, 103, 423–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCall, J.G.; Al-Hasani, R.; Siuda, E.R.; Hong, D.Y.; Norris, A.J.; Ford, C.P.; Bruchas, M.R. Crh engagement of the locus coeruleus noradrenergic system mediates stress-induced anxiety. Neuron 2015, 87, 605–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, M. The role of the amygdala in fear and anxiety. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 1992, 15, 353–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karlsson, R.M.; Holmes, A. Galanin as a modulator of anxiety and depression and a therapeutic target for affective disease. Amino Acids 2006, 31, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blier, P.; El Mansari, M. The importance of serotonin and noradrenaline in anxiety. Int. J. Psychiatry Clin. Pract. 2007, 11, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donnell, D.; Ahmad, S.; Wahlestedt, C.; Walker, P. Expression of the novel galanin receptor subtype galr2 in the adult rat cns: Distinct distribution from galr1. J. Comp. Neurol. 1999, 409, 469–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burazin, T.C.; Larm, J.A.; Ryan, M.C.; Gundlach, A.L. Galanin-r1 and -r2 receptor mrna expression during the development of rat brain suggests differential subtype involvement in synaptic transmission and plasticity. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2000, 12, 2901–2917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohmann, J.G.; Jureus, A.; Teklemichael, D.N.; Matsumoto, A.M.; Clifton, D.K.; Steiner, R.A. Distribution and regulation of galanin receptor 1 messenger rna in the forebrain of wild type and galanin-transgenic mice. Neuroscience 2003, 117, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Shen, P.J.; Larm, J.A.; Gundlach, A.L. Expression and plasticity of galanin systems in cortical neurons, oligodendrocyte progenitors and proliferative zones in normal brain and after spreading depression. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2003, 18, 1362–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazarati, A.M. Galanin and galanin receptors in epilepsy. Neuropeptides 2004, 38, 331–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gundlach, A.L.; Burazin, T.C. Galanin-galanin receptor systems in the hypothalamic paraventricular and supraoptic nuclei. Some recent findings and future challenges. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1998, 863, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brumovsky, P.; Mennicken, F.; O’Donnell, D.; Hokfelt, T. Differential distribution and regulation of galanin receptors-1 and -2 in the rat lumbar spinal cord. Brain Res. 2006, 1085, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawes, J.J.; Picciotto, M.R. Characterization of galr1, galr2, and galr3 immunoreactivity in catecholaminergic nuclei of the mouse brain. J. Comp. Neurol. 2004, 479, 410–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, B.; Counts, S.E.; Perez, S.E.; Hohmann, J.G.; Koprich, J.B.; Lipton, J.W.; Steiner, R.A.; Crawley, J.N.; Mufson, E.J. Ectopic galanin expression and normal galanin receptor 2 and galanin receptor 3 mrna levels in the forebrain of galanin transgenic mice. Neuroscience 2005, 133, 371–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Mennicken, F.; Hoffert, C.; Pelletier, M.; Ahmad, S.; O’Donnell, D. Restricted distribution of galanin receptor 3 (galr3) mrna in the adult rat central nervous system. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2002, 24, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheller, K.J.; Williams, S.J.; Lawrence, A.J.; Djouma, E. The galanin-3 receptor antagonist, snap 37889, suppresses alcohol drinking and morphine self-administration in mice. Neuropharmacology 2017, 118, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swanson, C.J.; Blackburn, T.P.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, K.; Xu, Z.Q.; Hokfelt, T.; Wolinsky, T.D.; Konkel, M.J.; Chen, H.; Zhong, H.; et al. Anxiolytic- and antidepressant-like profiles of the galanin-3 receptor (gal3) antagonists snap 37889 and snap 398299. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 17489–17494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunner, S.M.; Farzi, A.; Locker, F.; Holub, B.S.; Drexel, M.; Reichmann, F.; Lang, A.A.; Mayr, J.A.; Vilches, J.J.; Navarro, X.; et al. Gal3 receptor ko mice exhibit an anxiety-like phenotype. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 7138–7143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, K.R.; Pavlova, M.N.; Rohde, A.D.; Hohmann, J.G.; Crawley, J.N. Galanin receptor subtype 2 (galr2) null mutant mice display an anxiogenic-like phenotype specific to the elevated plus-maze. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2007, 86, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mahoney, S.A.; Hosking, R.; Wynick, D. The galanin antagonist m35 has intrinsic agonistic activity in the dorsal root ganglion. Neuroreport 2003, 14, 1649–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, F.E.; Mahoney, S.; King, V.R.; Bacon, A.; Kerr, N.C.; Pachnis, V.; Curtis, R.; Priestley, J.V.; Wynick, D. Targeted disruption of the galanin gene reduces the number of sensory neurons and their regenerative capacity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 11563–11568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahoney, S.A.; Hosking, R.; Farrant, S.; Holmes, F.E.; Jacoby, A.S.; Shine, J.; Iismaa, T.P.; Scott, M.K.; Schmidt, R.; Wynick, D. The second galanin receptor galr2 plays a key role in neurite outgrowth from adult sensory neurons. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 416–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott-Hunt, C.R.; Pope, R.J.; Vanderplank, P.; Wynick, D. Activation of the galanin receptor 2 (galr2) protects the hippocampus from neuronal damage. J. Neurochem. 2007, 100, 780–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elliott-Hunt, C.R.; Marsh, B.; Bacon, A.; Pope, R.; Vanderplank, P.; Wynick, D. Galanin acts as a neuroprotective factor to the hippocampus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 5105–5110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, A.S.; Sahay, A.; Hen, R. Increasing adult hippocampal neurogenesis is sufficient to reduce anxiety and depression-like behaviors. Neuropsychopharmacology 2015, 40, 2368–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, A.; Kinney, J.W.; Wrenn, C.C.; Li, Q.; Yang, R.J.; Ma, L.; Vishwanath, J.; Saavedra, M.C.; Innerfield, C.E.; Jacoby, A.S.; et al. Galanin gal-r1 receptor null mutant mice display increased anxiety-like behavior specific to the elevated plus-maze. Neuropsychopharmacology 2003, 28, 1031–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karl, C.; Couillard-Despres, S.; Prang, P.; Munding, M.; Kilb, W.; Brigadski, T.; Plotz, S.; Mages, W.; Luhmann, H.; Winkler, J.; et al. Neuronal precursor-specific activity of a human doublecortin regulatory sequence. J. Neurochem. 2005, 92, 264–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Couillard-Despres, S.; Quehl, E.; Altendorfer, K.; Karl, C.; Ploetz, S.; Bogdahn, U.; Winkler, J.; Aigner, L. Human in vitro reporter model of neuronal development and early differentiation processes. BMC Neurosci. 2008, 9, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denver, R.J. Structural and functional evolution of vertebrate neuroendocrine stress systems. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2009, 1163, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Brolosy, M.A.; Stainier, D.Y.R. Genetic compensation: A phenomenon in search of mechanisms. PLoS Genet. 2017, 13, e1006780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burdakov, D.; Peleg-Raibstein, D. The hypothalamus as a primary coordinator of memory updating. Physiol. Behav. 2020, 223, 112988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maroni, M.J.; Capri, K.M.; Arruda, N.L.; Gelineau, R.R.; Deane, H.V.; Concepcion, H.A.; DeCourcey, H.; Monteiro De Pina, I.K.; Cushman, A.V.; Chasse, M.H.; et al. Substrain specific behavioral responses in male c57bl/6n and c57bl/6j mice to a shortened 21-h day and high-fat diet. Chronobiol. Int. 2020, 37, 809–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuo, N.; Takao, K.; Nakanishi, K.; Yamasaki, N.; Tanda, K.; Miyakawa, T. Behavioral profiles of three c57bl/6 substrains. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2010, 4, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryant, C.D.; Zhang, N.N.; Sokoloff, G.; Fanselow, M.S.; Ennes, H.S.; Palmer, A.A.; McRoberts, J.A. Behavioral differences among c57bl/6 substrains: Implications for transgenic and knockout studies. J. Neurogenet. 2008, 22, 315–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, A.; Xia, F.; Guskjolen, A.J.; Ramsaran, A.I.; Santoro, A.; Josselyn, S.A.; Frankland, P.W. Elevation of hippocampal neurogenesis induces a temporally graded pattern of forgetting of contextual fear memories. J. Neurosci. 2018, 38, 3190–3198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobson, S.A.; Holmes, F.E.; Kerr, N.C.; Pope, R.J.; Wynick, D. Mice deficient for galanin receptor 2 have decreased neurite outgrowth from adult sensory neurons and impaired pain-like behaviour. J. Neurochem. 2006, 99, 1000–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotheneichner, P.; Romanelli, P.; Bieler, L.; Pagitsch, S.; Zaunmair, P.; Kreutzer, C.; Konig, R.; Marschallinger, J.; Aigner, L.; Couillard-Despres, S. Tamoxifen activation of cre-recombinase has no persisting effects on adult neurogenesis or learning and anxiety. Front. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Couillard-Despres, S.; Winner, B.; Schaubeck, S.; Aigner, R.; Vroemen, M.; Weidner, N.; Bogdahn, U.; Winkler, J.; Kuhn, H.G.; Aigner, L. Doublecortin expression levels in adult brain reflect neurogenesis. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2005, 21, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oberbauer, E.; Urmann, C.; Steffenhagen, C.; Bieler, L.; Brunner, D.; Furtner, T.; Humpel, C.; Baumer, B.; Bandtlow, C.; Couillard-Despres, S.; et al. Chroman-like cyclic prenylflavonoids promote neuronal differentiation and neurite outgrowth and are neuroprotective. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2013, 24, 1953–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Locker, F.; Vidali, S.; Holub, B.S.; Stockinger, J.; Brunner, S.M.; Ebner, S.; Koller, A.; Trost, A.; Reitsamer, H.A.; Schwarzenbacher, D.; et al. Lack of galanin receptor 3 alleviates psoriasis by altering vascularization, immune cell infiltration, and cytokine expression. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2018, 138, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Locker, F.; Bieler, L.; Nowack, L.M.F.; Leitner, J.; Brunner, S.M.; Zaunmair, P.; Kofler, B.; Couillard-Despres, S. Involvement of Neuropeptide Galanin Receptors 2 and 3 in Learning, Memory and Anxiety in Aging Mice. Molecules 2021, 26, 1978. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26071978
Locker F, Bieler L, Nowack LMF, Leitner J, Brunner SM, Zaunmair P, Kofler B, Couillard-Despres S. Involvement of Neuropeptide Galanin Receptors 2 and 3 in Learning, Memory and Anxiety in Aging Mice. Molecules. 2021; 26(7):1978. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26071978
Chicago/Turabian StyleLocker, Felix, Lara Bieler, Lioba M. F. Nowack, Julia Leitner, Susanne Maria Brunner, Pia Zaunmair, Barbara Kofler, and Sebastien Couillard-Despres. 2021. "Involvement of Neuropeptide Galanin Receptors 2 and 3 in Learning, Memory and Anxiety in Aging Mice" Molecules 26, no. 7: 1978. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26071978
APA StyleLocker, F., Bieler, L., Nowack, L. M. F., Leitner, J., Brunner, S. M., Zaunmair, P., Kofler, B., & Couillard-Despres, S. (2021). Involvement of Neuropeptide Galanin Receptors 2 and 3 in Learning, Memory and Anxiety in Aging Mice. Molecules, 26(7), 1978. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26071978






