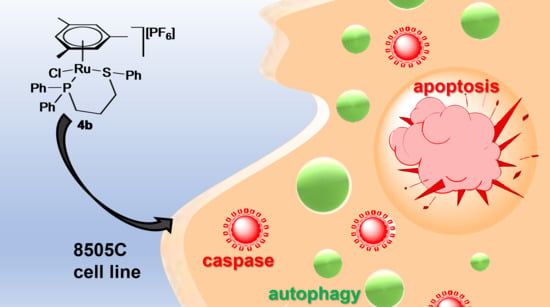
Arene Ruthenium(II) Complexes Bearing the κ-P or κ-P,κ-S Ph2P(CH2)3SPh Ligand
Abstract
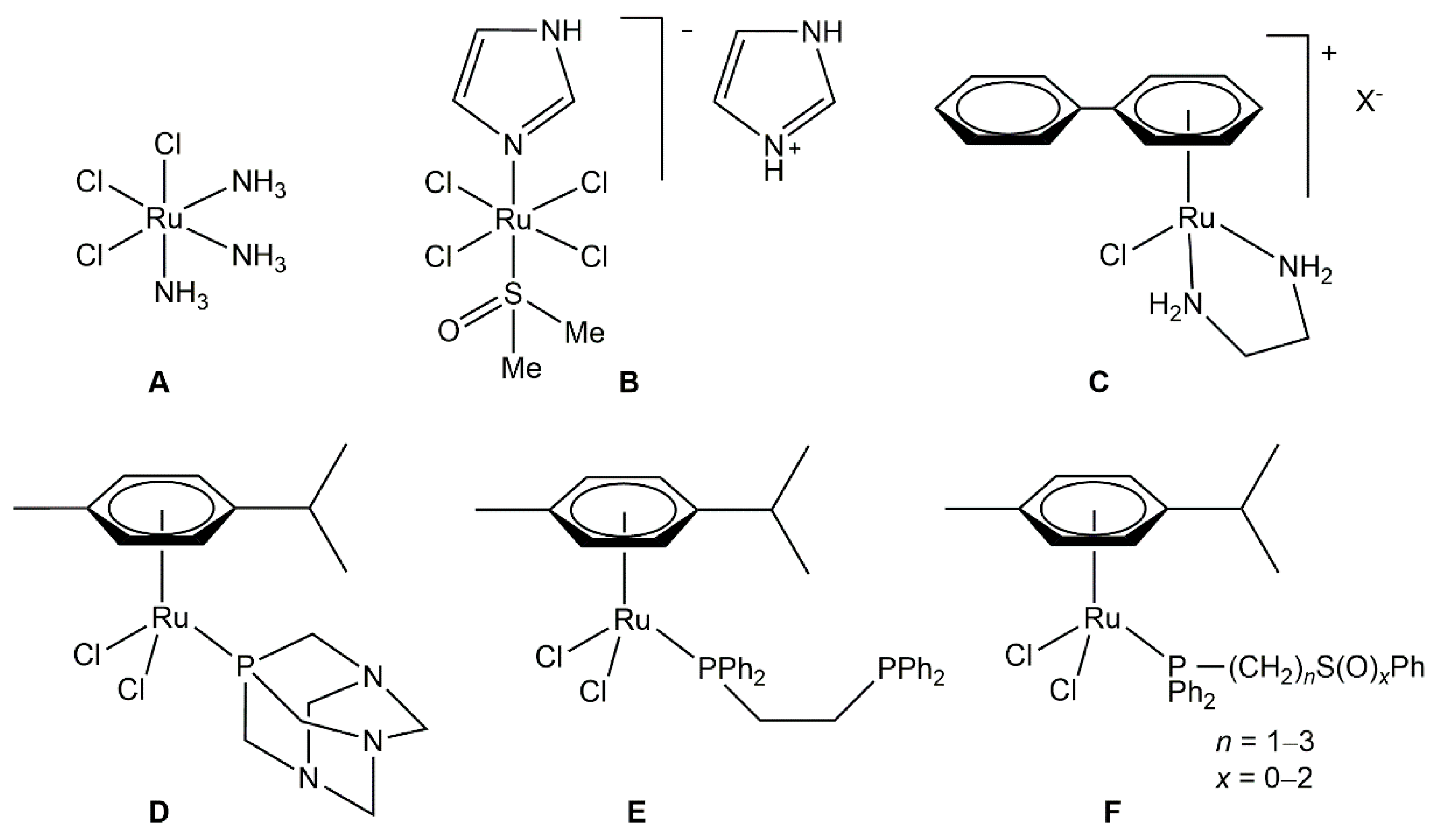
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Synthesis
2.2. Molecular Structure and Chemical Properties of the Arene Ruthenium(II) Complexes
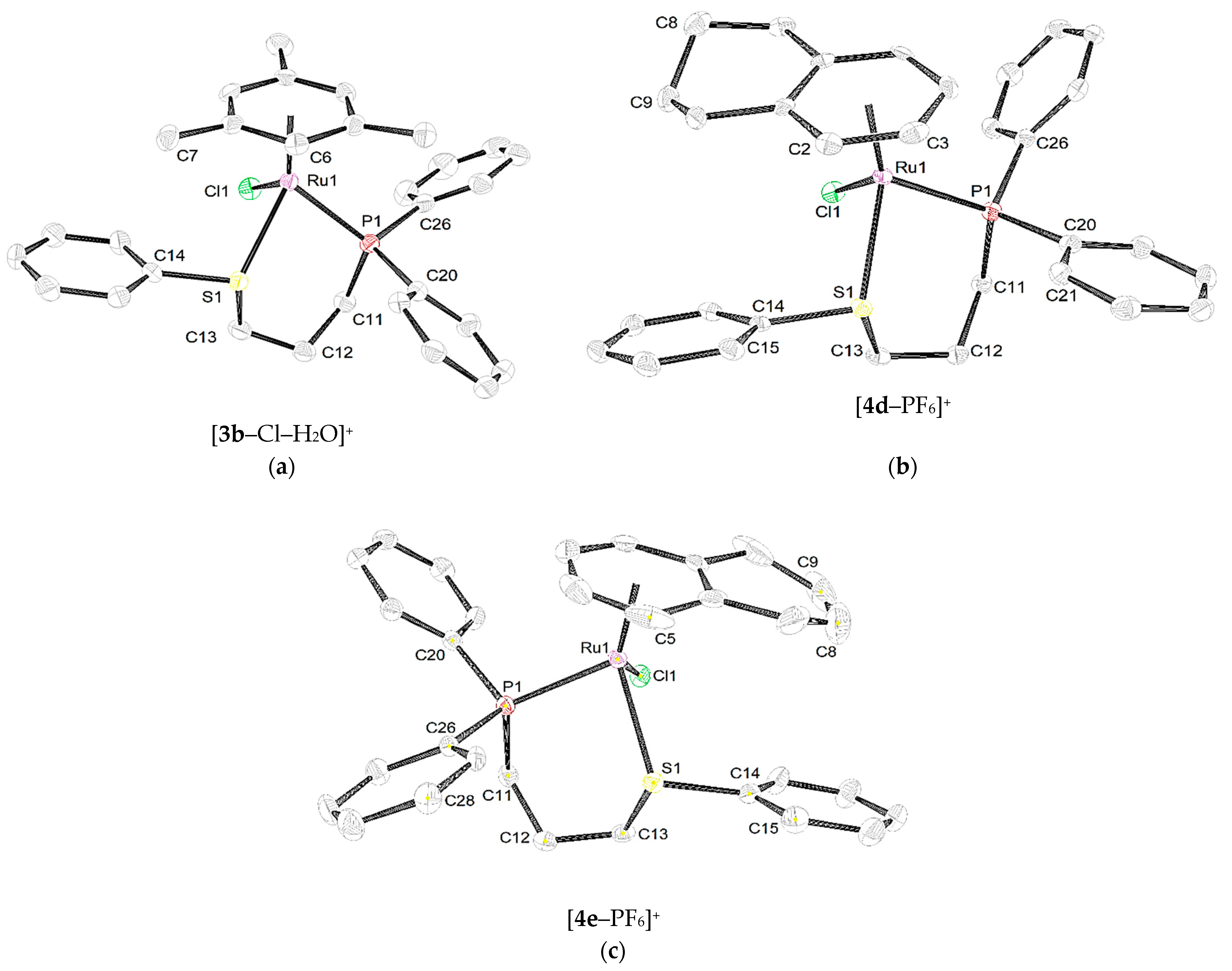
2.2.1. Crystallographic Data
2.2.2. Infrared Spectroscopic Data
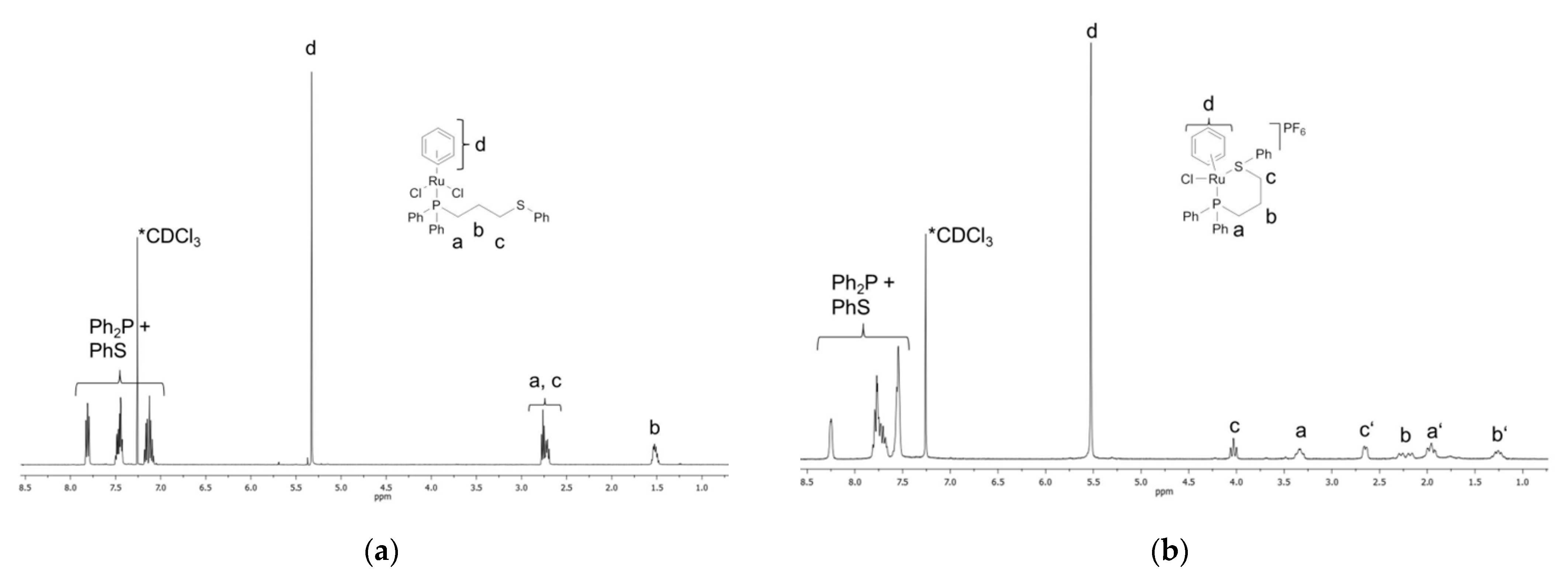
2.2.3. NMR Data
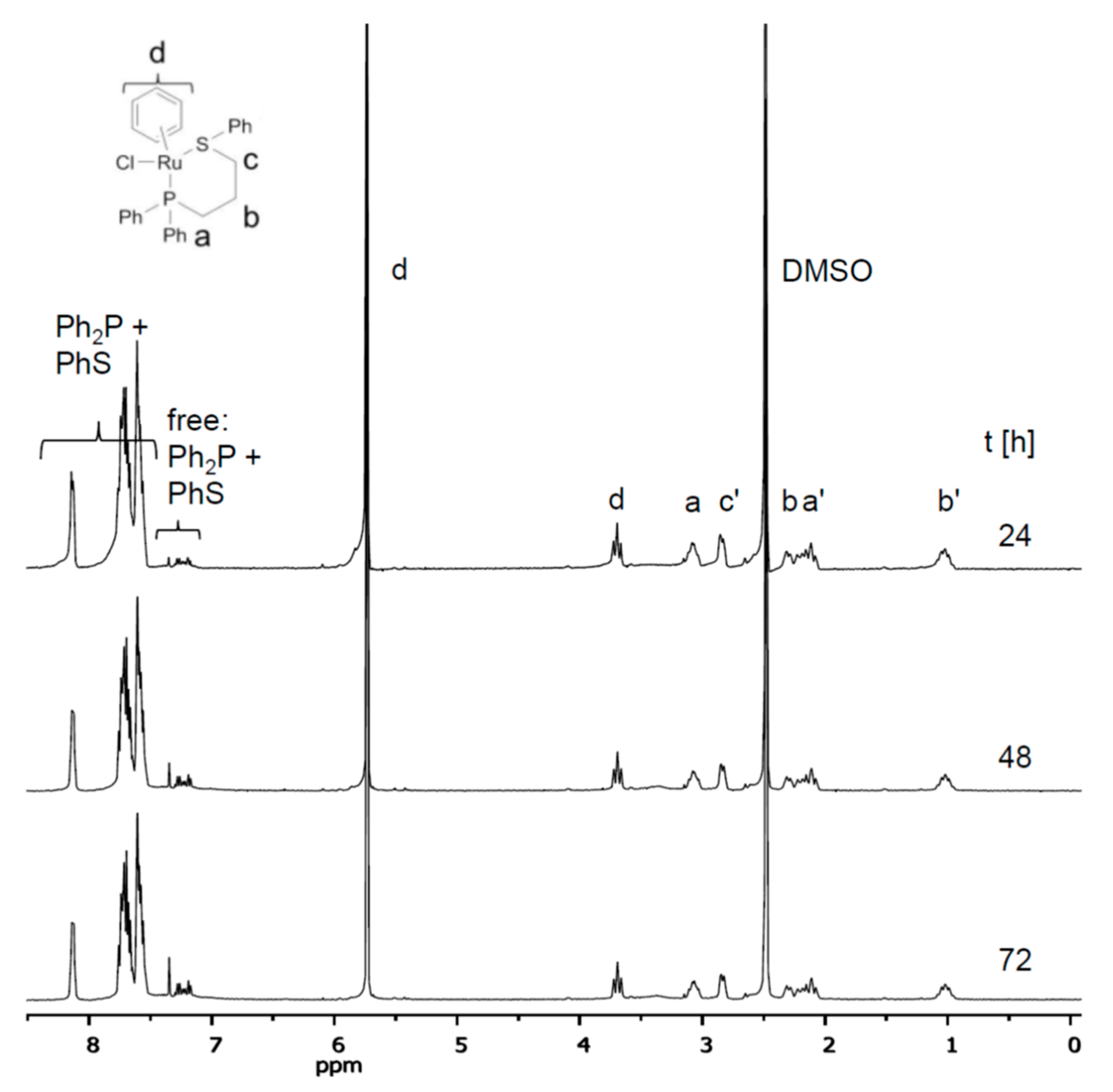
2.3. Stability of Complexes in DMSO
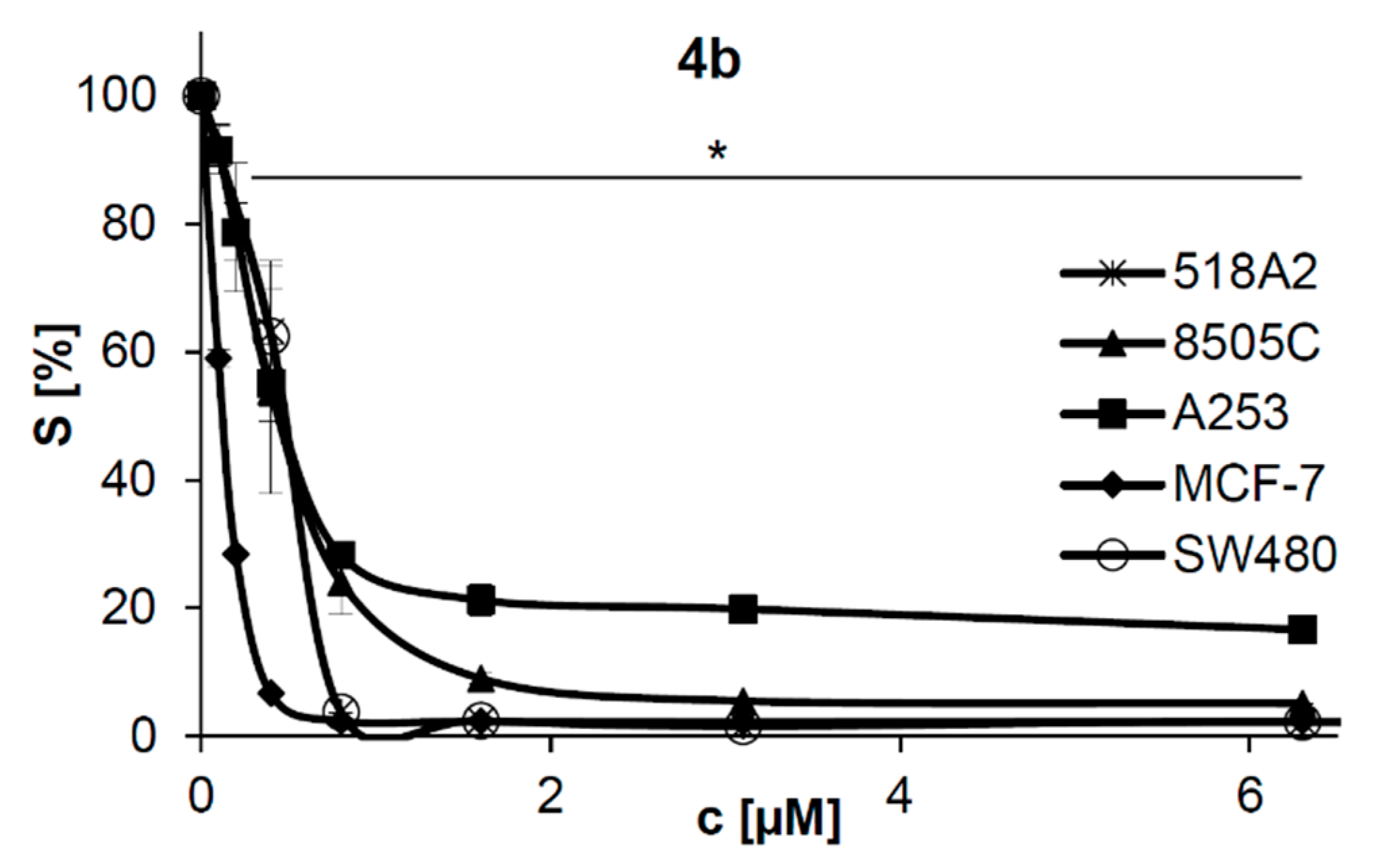
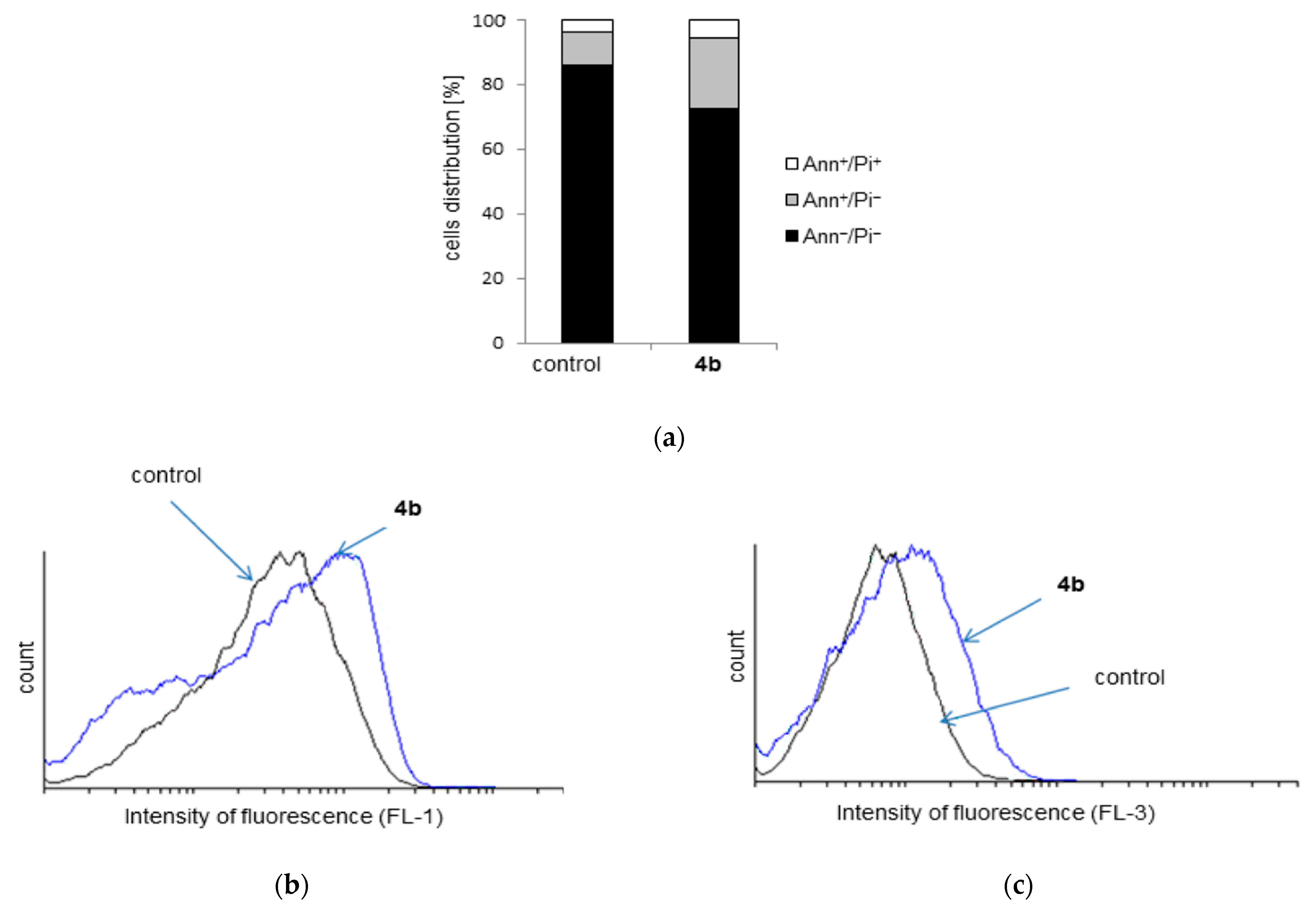
2.4. Cytotoxicity Study
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Manipulations
3.2. Synthetic Procedures
3.2.1. Preparation of [Ru(η6-arene)Cl2{Ph2P(CH2)3SPh-κP}] (2a, 2c, 2d) and [Ru(η6-arene)Cl{Ph2P(CH2)3SPh-κP,κS}]Cl (3b, 3e)
3.2.2. Preparation of [Ru(η6-arene)Cl{Ph2P(CH2)3SPh-κP,κS}][PF6] (4a–4e)
3.3. Crystallography
3.4. In Vitro Studies
3.4.1. Reagents and Cells
3.4.2. Determination of Cell Viability by Sulphorhodamine Assay (SRB)
3.4.3. AnnexinV-FITC/PI, AO Staining and Caspase Detection
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Arnesano, F.; Natile, G. Mechanistic Insight into the Cellular Uptake and Processing of Cisplatin 30 Years after Its Approval by FDA. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2009, 253, 2070–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Ruiz, S.; Maksimović-Ivanić, D.; Mijatović, S.; Kaluđerović, G.N. On the Discovery, Biological Effects, and Use of Cisplatin and Metallocenes in Anticancer Chemotherapy. Bioinorg. Chem. Appl. 2012, 2012, 140284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaluđerović, G.N.; Paschke, R. Anticancer Metallotherapeutics in Preclinical Development. Curr. Med. Chem. 2011, 18, 4738–4752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelland, L. The Resurgence of Platinum-Based Cancer Chemotherapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2007, 7, 573–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rancoule, C.; Guy, J.-B.; Vallard, A.; Ben Mrad, M.; Rehailia, A.; Magné, N. 50th anniversary of cisplatin. Bull. Cancer 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, E.; Giandomenico, C.M. Current Status of Platinum-Based Antitumor Drugs. Chem. Rev. 1999, 99, 2451–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dugbartey, G.J.; Peppone, L.J.; de Graaf, I.A.M. An Integrative View of Cisplatin-Induced Renal and Cardiac Toxicities: Molecular Mechanisms, Current Treatment Challenges and Potential Protective Measures. Toxicology 2016, 371, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deo, K.M.; Pages, B.J.; Ang, D.L.; Gordon, C.P.; Aldrich-Wright, J.R. Transition Metal Intercalators as Anticancer Agents-Recent Advances. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Sadler, P.J. Metals in Medicine. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1999, 38, 1512–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markowska, A.; Kasprzak, B.; Jaszczyńska-Nowinka, K.; Lubin, J.; Markowska, J. Noble Metals in Oncology. Contemp. Oncol. 2015, 19, 271–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnstone, T.C.; Suntharalingam, K.; Lippard, S.J. Third Row Transition Metals for the Treatment of Cancer. Philos. Trans. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2015, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allardyce, C.S.; Dyson, P.J. Metal-Based Drugs That Break the Rules. Dalton Trans. 2016, 45, 3201–3209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palermo, G.; Magistrato, A.; Riedel, T.; von Erlach, T.; Davey, C.A.; Dyson, P.J.; Rothlisberger, U. Fighting Cancer with Transition Metal Complexes: From Naked DNA to Protein and Chromatin Targeting Strategies. ChemMedChem 2016, 11, 1199–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pantelić, N.; Stanojković, T.P.; Zmejkovski, B.B.; Sabo, T.J.; Kaluđerović, G.N. In Vitro Anticancer Activity of Gold(III) Complexes with Some Esters of (S,S)-Ethylenediamine-N,N’-Di-2-Propanoic Acid. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 90, 766–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nardon, C.; Fregona, D. Gold(III) Complexes in the Oncological Preclinical Arena: From Aminoderivatives to Peptidomimetics. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2016, 16, 360–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ott, I.; Gust, R. Non Platinum Metal Complexes as Anti-Cancer Drugs. Arch. Pharm. 2007, 340, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, N.; Guo, Z. Metal-Based Anticancer Chemotherapeutic Agents. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2014, 19, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abeysinghe, P.M.; Harding, M.M. Antitumour Bis(Cyclopentadienyl)Metal Complexes: Titanocene and Molybdocene Dichloride and Derivatives. Dalton Trans. 2007, 3474–3482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaluđerović, M.R.; Mojić, M.; Gómez-Ruiz, S.; Mijatović, S.; Maksimović-Ivanić, D. Anticancer Activity of Organogallium(III) Complexes in Colon Cancer Cells. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2016, 16, 359–364. [Google Scholar]
- Sirajuddin, M.; Ali, S. Organotin(IV) Carboxylates as a Promising Potential Drug Candidates in the Field of Cancer Chemotherapy. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2016, 22, 6665–6681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renfrew, A.K.; Phillips, A.D.; Egger, A.E.; Hartinger, C.G.; Bosquain, S.S.; Nazarov, A.A.; Keppler, B.K.; Gonsalvi, L.; Peruzzini, M.; Dyson, P.J. Influence of Structural Variation on the Anticancer Activity of RAPTA-Type Complexes: Ptn versus Pta. Organometallics 2009, 28, 1165–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scolaro, C.; Bergamo, A.; Brescacin, L.; Delfino, R.; Cocchietto, M.; Laurenczy, G.; Geldbach, T.J.; Sava, G.; Dyson, P.J. In Vitro and in Vivo Evaluation of Ruthenium(II)−Arene PTA Complexes. J. Med. Chem. 2005, 48, 4161–4171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riedl, C.A.; Flocke, L.S.; Hejl, M.; Roller, A.; Klose, M.H.M.; Jakupec, M.A.; Kandioller, W.; Keppler, B.K. Introducing the 4-Phenyl-1,2,3-Triazole Moiety as a Versatile Scaffold for the Development of Cytotoxic Ruthenium(II) and Osmium(II) Arene Cyclometalates. Inorg. Chem. 2017, 56, 528–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brabec, V.; Pracharova, J.; Stepankova, J.; Sadler, P.J.; Kasparkova, J. Photo-Induced DNA Cleavage and Cytotoxicity of a Ruthenium(II) Arene Anticancer Complex. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2016, 160, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmucci, J.; Marchetti, F.; Pettinari, R.; Pettinari, C.; Scopelliti, R.; Riedel, T.; Therrien, B.; Galindo, A.; Dyson, P.J. Synthesis, Structure, and Anticancer Activity of Arene-Ruthenium(II) Complexes with Acylpyrazolones Bearing Aliphatic Groups in the Acyl Moiety. Inorg. Chem. 2016, 55, 11770–11781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alessio, E.; Mestroni, G.; Bergamo, A.; Sava, G. Ruthenium Antimetastatic Agents. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2004, 4, 1525–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonarakis, E.S.; Emadi, A. Ruthenium-Based Chemotherapeutics: Are They Ready for Prime Time? Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2010, 66, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peacock, A.F.A.; Sadler, P.J. Medicinal Organometallic Chemistry: Designing Metal Arene Complexes as Anticancer Agents. Chem. Asian J. 2008, 3, 1890–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, I.; Hanif, M.; Nazarov, A.A.; Hartinger, C.G.; John, R.O.; Kuznetsov, M.L.; Groessl, M.; Schmitt, F.; Zava, O.; Biba, F.; et al. In Vitro Anticancer Activity and Biologically Relevant Metabolization of Organometallic Ruthenium Complexes with Carbohydrate-Based Ligands. Chem. Eur. J. 2008, 14, 9046–9057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergamo, A.; Masi, A.; Dyson, P.J.; Sava, G. Modulation of the Metastatic Progression of Breast Cancer with an Organometallic Ruthenium Compound. Int. J. Oncol. 2008, 33, 1281–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schluga, P.; Hartinger, C.G.; Egger, A.; Reisner, E.; Galanski, M.; Jakupec, M.A.; Keppler, B.K. Redox Behavior of Tumor-Inhibiting Ruthenium(III) Complexes and Effects of Physiological Reductants on Their Binding to GMP. Dalton Trans. 2006, 1796–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, R.E.; Aird, R.E.; del Socorro Murdoch, P.; Chen, H.; Cummings, J.; Hughes, N.D.; Parsons, S.; Parkin, A.; Boyd, G.; Jodrell, D.I.; et al. Inhibition of Cancer Cell Growth by Ruthenium(II) Arene Complexes. J. Med. Chem. 2001, 44, 3616–3621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aird, R.E.; Cummings, J.; Ritchie, A.A.; Muir, M.; Morris, R.E.; Chen, H.; Sadler, P.J.; Jodrell, D.I. In Vitro and in Vivo Activity and Cross Resistance Profiles of Novel Ruthenium (II) Organometallic Arene Complexes in Human Ovarian Cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2002, 86, 1652–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, G.; Kaluđerović, G.N.; Bette, M.; Block, M.; Paschke, R.; Steinborn, D. Highly Active Neutral Ruthenium(II) Arene Complexes: Synthesis, Characterization, and Investigation of Their Anticancer Properties. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2012, 113, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, G.; Kaluđerović, G.N.; Rueffer, T.; Bette, M.; Korb, M.; Block, M.; Paschke, R.; Lang, H.; Steinborn, D. Cationic Arene Ruthenium(II) Complexes with Chelating P-Functionalized Alkyl Phenyl Sulfide and Sulfoxide Ligands as Potent Anticancer Agents. Dalton Trans. 2013, 42, 3771–3774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allardyce, C.S.; Dyson, P.J.; Ellis, D.J.; Heath, S.L. [Ru(η6-p-Cymene)Cl2(Pta)] (Pta = 1,3,5-Triaza-7-Phosphatricyclo- [3.3.1.1]Decane): A Water Soluble Compound That Exhibits PH Dependent DNA Binding Providing Selectivity for Diseased Cells. Chem. Commun. 2001, 1396–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, A.; Berndsen, R.H.; Dubois, M.; Müller, C.; Schibli, R.; Griffioen, A.W.; Dyson, P.J.; Nowak-Sliwinska, P. In Vivo Anti-Tumor Activity of the Organometallic Ruthenium(II)-Arene Complex [Ru(η6-p-Cymene)Cl2(Pta)] (RAPTA-C) in Human Ovarian and Colorectal Carcinomas. Chem. Sci. 2014, 5, 4742–4748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, G.; Ranđelović, I.; Maksimović-Ivanić, D.; Mijatović, S.; Bulatović, M.Z.; Miljković, D.; Korb, M.; Lang, H.; Steinborn, D.; Kaluđerović, G.N. Anticancer Potential of (Pentamethylcyclopentadienyl)Chloridoiridium(III) Complexes Bearing κP and κP,κS-Coordinated Ph2PCH2CH2CH2S(O)xPh (x=0–2) Ligands. ChemMedChem 2014, 9, 1586–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, G.; Mijatovic, S.; Randelovic, I.; Bulatovic, M.; Miljkovic, D.; Maksimovic-Ivanic, D.; Korb, M.; Lang, H.; Steinborn, D.; Kaluđerović, G.N. Biological Activity of Neutral and Cationic Iridium(III) Complexes with κP and κP,κS Coordinated Ph2PCH2S(O)xPh (x=0–2) Ligands. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 69, 216–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, G.; Mojić, M.; Bulatović, M.Z.; Mijatović, S.; Maksimović-Ivanić, D.; Steinborn, D.; Kaluđerović, G.N. Biological Potential of Halfsandwich Ruthenium(II) and Iridium(III) Complexes. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2015, 16, 1455–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalrempuia, R.; Rao Kollipara, M. Reactivity Studies of η6-Arene Ruthenium(II) Dimers with Polypyridyl Ligands: Isolation of Mono, Binuclear p-Cymene Ruthenium(II) Complexes and Bisterpyridine Ruthenium(II) Complexes. Polyhedron 2003, 22, 3155–3160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.N.; Venkatachalam, G.; Ramesh, R.; Liu, Y. Half-Sandwich Para-Cymene Ruthenium(II) Naphthylazophenolato Complexes: Synthesis, Molecular Structure, Light Emission, Redox Behavior and Catalytic Oxidation Properties. Polyhedron 2008, 27, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, M.A.; Smith, A.K. Arene Ruthenium(II) Complexes Formed by Dehydrogenation of Cyclohexadienes with Ruthenium(III) Trichloride. J. Chem. Soc. Dalton Trans. 1974, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelonka, R.A.; Baird, M.C. Benzene Complexes of Ruthenium(II). Can. J. Chem. 1972, 50, 3063–3072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durig, J.R.; Gounev, T.K.; Lee, M.S.; Little, T.S. Spectra and Structure of Organophosphorus Compounds. LI. IR and Raman Spectra, Conformational Stability, Barriers to Internal Rotation, Vibrational Assignment, and Ab Initio Calculations of n-Propylphosphine. J. Mol. Struct. 1994, 327, 23–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiti, S.K.; Kalita, M.; Singh, A.; Deka, J.; Barman, P. Investigation of DNA Binding and Bioactivities of Thioether Containing Schiff Base Copper(II), Cobalt(II) and Palladium(II) Complexes: Synthesis, Characterization, Spectrochemical Study, Viscosity Measurement. Polyhedron 2020, 184, 114559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patra, M.; Joshi, T.; Pierroz, V.; Ingram, K.; Kaiser, M.; Ferrari, S.; Spingler, B.; Keiser, J.; Gasser, G. DMSO-Mediated Ligand Dissociation: Renaissance for Biological Activity of N-Heterocyclic-[Ru(η6-Arene)Cl2] Drug Candidates. Chem. Eur. J. 2013, 19, 14768–14772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vichai, V.; Kirtikara, K. Sulforhodamine B Colorimetric Assay for Cytotoxicity Screening. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 1112–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldrick, G.M. SHELXT—Integrated Space-Group and Crystal-Structure Determination. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. A 2015, 71, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Compound | 518A2 | 8505C | A253 | MCF-7 | SW480 |
| 2a | 0.77 ± 0.04 | 0.88 ± 0.05 | 0.64 ± 0.05 | 0.52 ± 0.06 | 1.23 ± 0.08 |
| 2c | 2.16 ± 0.04 | 1.03 ± 0.08 | 0.59 ± 0.06 | 0.70 ± 0.04 | 1.91 ± 0.15 |
| 2d | 0.81 ± 0.04 | 2.98 ± 0.15 | 0.98 ± 0.12 | 0.78 ± 0.06 | 1.56 ± 0.10 |
| 2f | 3.02 ± 0.06 | 3.64 ± 0.13 | 3.94 ± 0.11 | 1.75 ± 0.45 | 2.68 ± 0.10 |
| 4a | 1.35 ± 0.02 | 0.76 ± 0.04 | 0.30 ± 0.02 | 0.24 ± 0.04 | 0.75 ± 0.02 |
| 4b | 0.43 ± 0.01 | 0.41 ± 0.01 | 0.35 ± 0.02 | 0.12 ± 0.01 | 0.43 ± 0.01 |
| 4c | 0.84 ± 0.09 | 0.97 ± 0.07 | 0.73 ± 0.06 | 0.23 ± 0.05 | 1.52 ± 0.13 |
| 4d | 0.75 ± 0.03 | 0.90 ± 0.09 | 0.82 ± 0.09 | 0.36 ± 0.03 | 1.97 ± 0.16 |
| 4e | 0.80 ± 0.03 | 0.28 ± 0.02 | 0.40 ± 0.03 | 0.49 ± 0.03 | 0.77 ± 0.02 |
| 4f | 1.32 ± 0.10 | 1.32 ± 0.10 | 0.37 ± 0.06 | 0.17 ± 0.01 | 1.30 ± 0.05 |
| cisplatin | 1.52 ± 0.19 | 5.02 ± 0.23 | 0.81 ± 0.02 | 2.03 ± 0.11 | 3.24 ± 0.21 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arlt, S.; Petković, V.; Ludwig, G.; Eichhorn, T.; Lang, H.; Rüffer, T.; Mijatović, S.; Maksimović-Ivanić, D.; Kaluđerović, G.N. Arene Ruthenium(II) Complexes Bearing the κ-P or κ-P,κ-S Ph2P(CH2)3SPh Ligand. Molecules 2021, 26, 1860. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26071860
Arlt S, Petković V, Ludwig G, Eichhorn T, Lang H, Rüffer T, Mijatović S, Maksimović-Ivanić D, Kaluđerović GN. Arene Ruthenium(II) Complexes Bearing the κ-P or κ-P,κ-S Ph2P(CH2)3SPh Ligand. Molecules. 2021; 26(7):1860. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26071860
Chicago/Turabian StyleArlt, Sören, Vladana Petković, Gerd Ludwig, Thomas Eichhorn, Heinrich Lang, Tobias Rüffer, Sanja Mijatović, Danijela Maksimović-Ivanić, and Goran N. Kaluđerović. 2021. "Arene Ruthenium(II) Complexes Bearing the κ-P or κ-P,κ-S Ph2P(CH2)3SPh Ligand" Molecules 26, no. 7: 1860. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26071860
APA StyleArlt, S., Petković, V., Ludwig, G., Eichhorn, T., Lang, H., Rüffer, T., Mijatović, S., Maksimović-Ivanić, D., & Kaluđerović, G. N. (2021). Arene Ruthenium(II) Complexes Bearing the κ-P or κ-P,κ-S Ph2P(CH2)3SPh Ligand. Molecules, 26(7), 1860. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26071860