Isotopic Characterization of 100% Agave Tequila (Silver, Aged and Extra-Aged Class) for Its Use as an Additional Parameter in the Determination of the Authenticity of the Beverage Maturation Time
Abstract
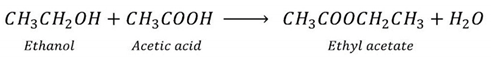
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
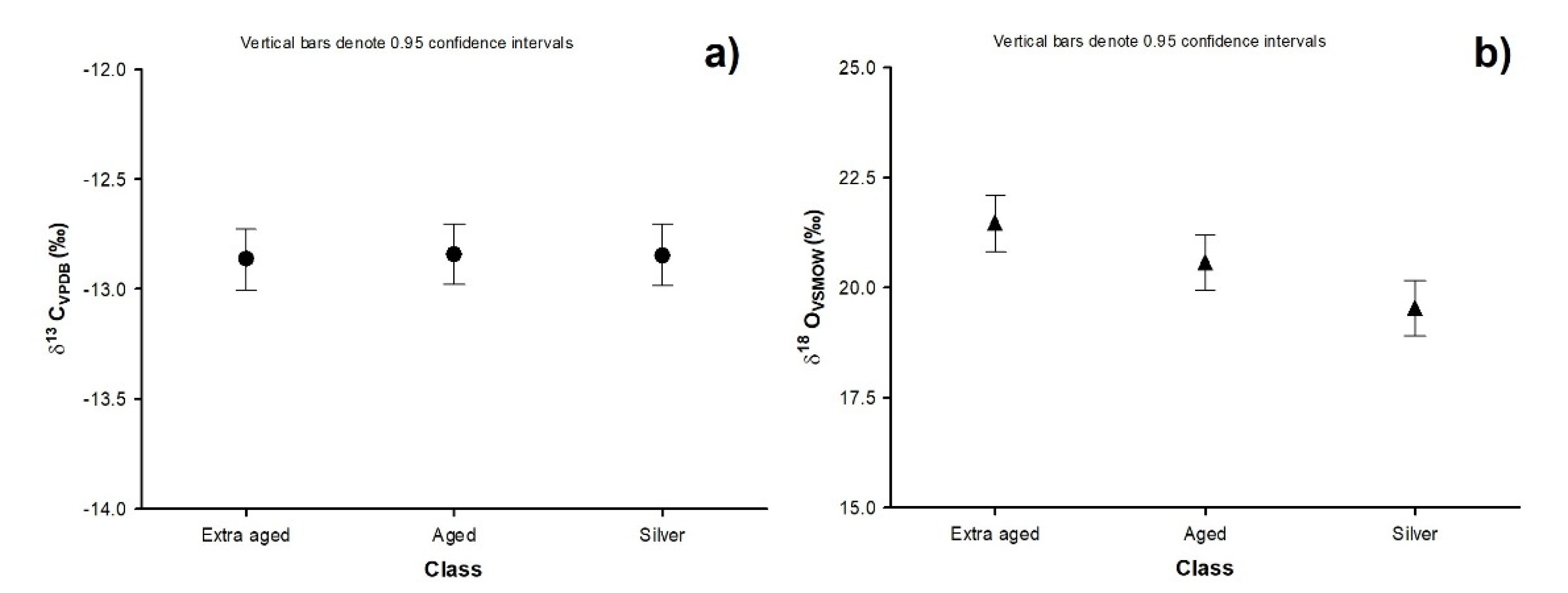
2.1. Study of Different Classes of Tequila (Silver, Aged, and Extra-Aged)
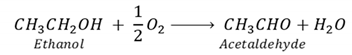

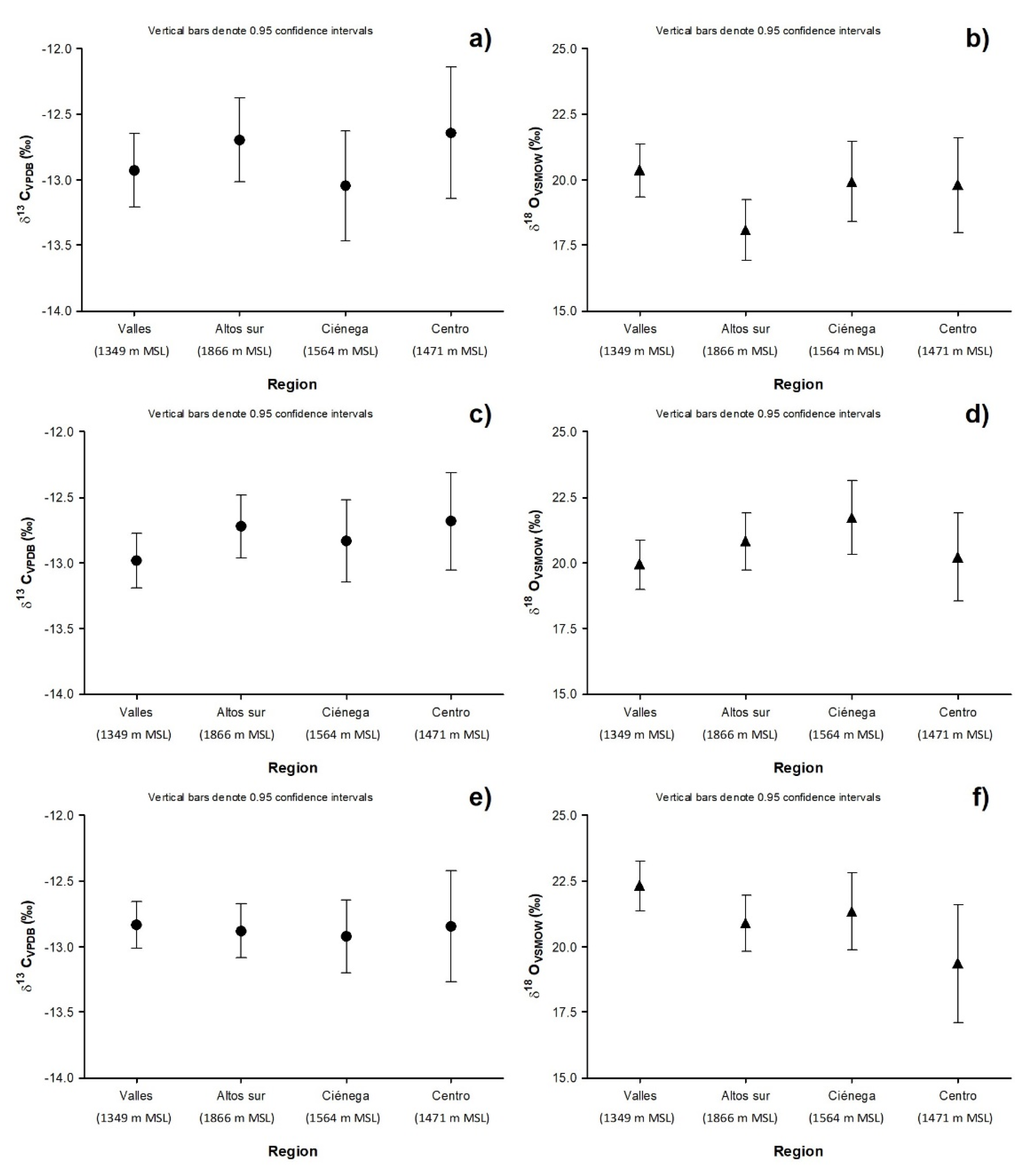
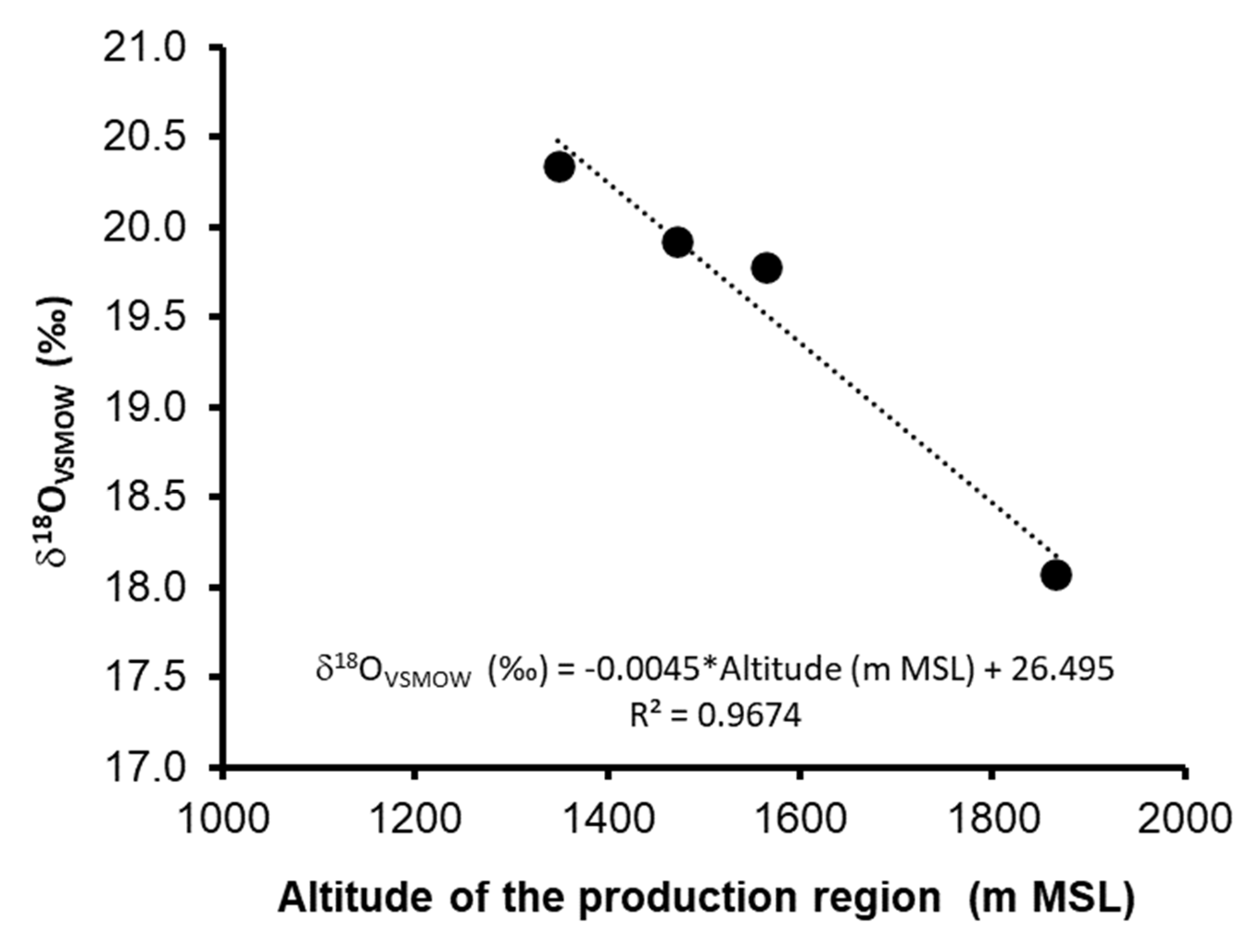
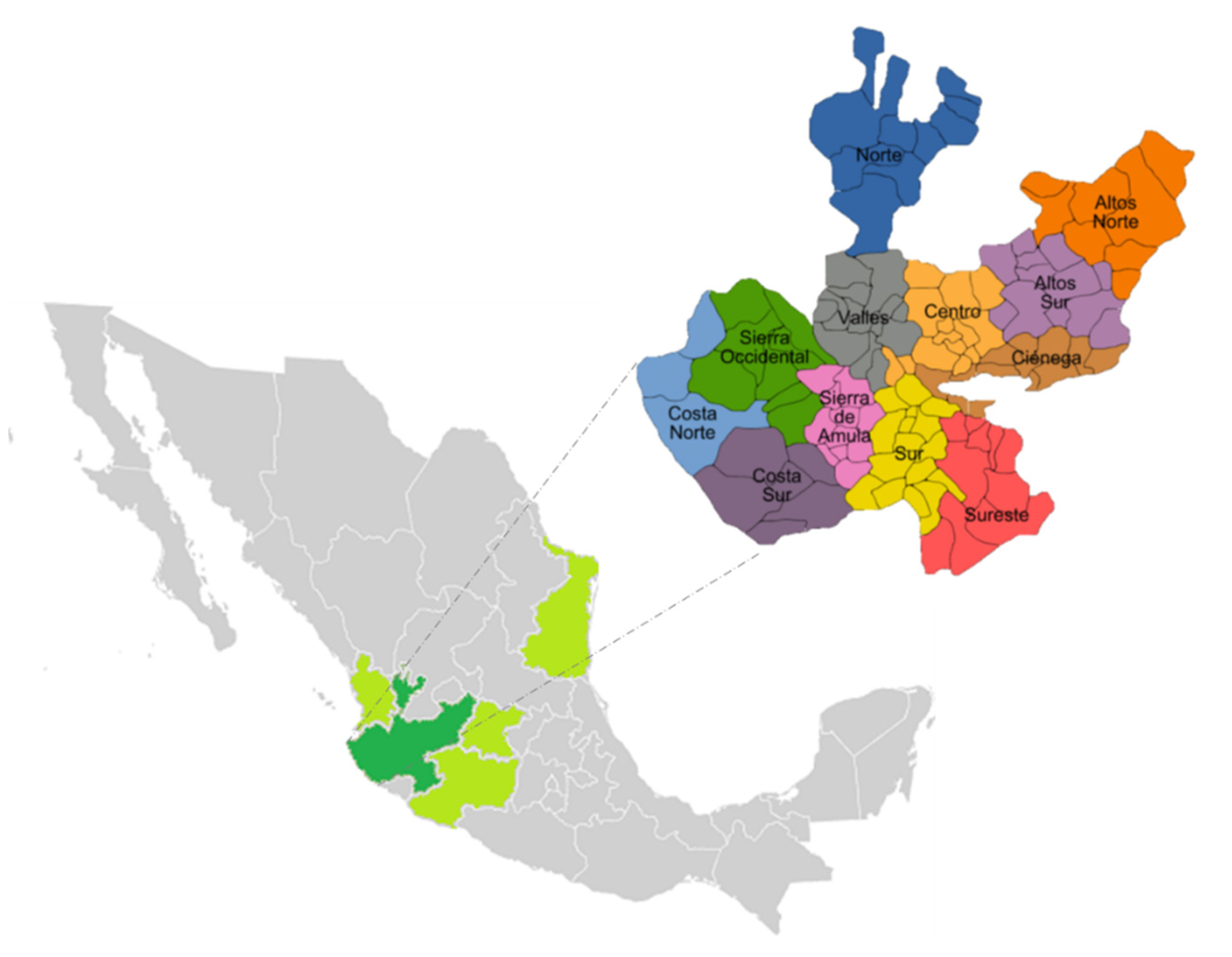
2.2. Study of the Different Regions of Tequila Production
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Samples
3.1.1. Sample Preparation
3.1.2. Determination of the Isotopic Ratio by GC/IRMS
3.2. Chromatographic Analysis
3.3. Statistic Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- NOM-006-SCFI-2012. Norma Oficial Mexicana: Bebidas Alcohólicas Tequila Especificaciones; Diario Oficial de la Federación: Ciudad de México, Mexico, 2012; pp. 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Fonseca-Aguiñaga, R.; Gómez-Ruiz, H.; Miguel-Cruz, F.; Romero-Cano, L.A. Analytical characterization of tequila (silver class) using stable isotope analyses of C, O and atomic absorption as additional criteria to determine authenticity of beverage. Food Control. 2020, 112, 107161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceballos-Magaña, S.G.; De Pablos, F.; Jurado, J.M.; Martín, M.J.; Alcázar, Á.; Muñiz-Valencia, R.; Gonzalo-Lumbreras, R.; Izquierdo-Hornillos, R. Characterisation of tequila according to their major volatile composition using multilayer perceptron neural networks. Food Chem. 2013, 136, 1309–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plutowska, B.; Wardencki, W. Application of gas chromatography-olfactometry (GC-O) in analysis and quality assessment of alcoholic beverages–A review. Food Chem. 2008, 107, 449–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellado-Mojica, E.; López, M.G. Identification, classification, and discrimination of agave syrups from natural sweeteners by infrared spectroscopy and HPAEC-PAD. Food Chem. 2015, 167, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peña-Alvarez, A.; Capella, S.; Juárez, R.; Labastida, C. Determination of terpenes in tequila by solid phase microextraction-gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2006, 1134, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer-Christoph, C.; Christoph, N.; Aguilar-Cisneros, B.O.; López, M.G.; Richling, E.; Rossmann, A.; Schreier, P. Authentication of tequila by gas chromatography and stable isotope ratio analyses. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2003, 217, 438–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cross, J.L.; Gallaher, T.N.; Leary, J.J.; Schreiner, S. The Application of Site-Specific Natural Isotope Fractionation-Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (SNIF-NMR) to the Analysis of Alcoholic Beverages. Chem. Educ. 2005, 3, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De León-Rodríguez, A.; Escalante-Minakata, P.; Jiménez-García, M.I.; Ordoñez-Acevedo1, L.G.; Flores, J.L.F.; de la Rosa1, A.P.B. Characterization of Volatile Compounds from Ethnic Agave alcoholic Beverages by GCMS. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2008, 46, 448–455. [Google Scholar]
- Lachenmeier, D.W.; Sohnius, E.M.; Attig, R.; López, M.G. Quantification of selected volatile constituents and anions in Mexican Agave spirits (Tequila, Mezcal, Sotol, Bacanora). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 3911–3915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallejo-Cordoba, B.; González-Córdova, A.F.; del Carmen Estrada-Montoya, M. Tequila Volatile Characterization and Ethyl Ester Determination by Solid Phase Microextraction Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry Analysis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 52, 5567–5571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa-García, O.; Ornelas-Soto, N.; Meneses-Nava, M.; Ramos-Ortíz, G.; Maldonado, J.; Pichardo-Molina, J. Analysis of tequila extracts by solid phase extraction combined with ATR-FTIR spectroscopy. Imaging Appl. Opt. Congr. 2013, ATuC5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachenmeier, D.W.; Richling, E.; López, M.G.; Frank, W.; Schreier, P. Multivariate analysis of FTIR and ion chromatographic data for the quality control of tequila. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 2151–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contreras, U.; Barbosa-garcía, O.; Pichardo-molina, J.L.; Ramos-ortíz, G.; Maldonado, J.L. Screening method for identi fi cation of adulterate and fake tequilas by using UV–VIS spectroscopy and chemometrics. FRIN 2010, 43, 2356–2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Pérez, A.; Pérez-Castañeda, J.I.; Castañeda-Guzmán, R.; Pérez-Ruiz, S.J. Determination of Tequila Quality by Photoacoustic Analysis. Int. J. 2013, 34, 1695–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luna-Moreno, D.; Monzón-Hernández, D.; Noé-Arias, E.; Regalado, E. Determination of quality and adulteration of tequila through the use of surface plasmon resonance. Appl. Opt. 2012, 51, 5161–5167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Rosa-Vázquez, J.M.; Fabila-Bustos, D.A.; Quintanar-Hernández, L.F.d.J.; Valor, A.; Stolik, S. Detection of Counterfeit Tequila by Fluorescence Spectroscopy. J. Spectrosc. 2015, 2015, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Caballero, G.; Andrade, J.M.; Olmos, P.; Molina, Y.; Jiménez, I.; Durán, J.J.; Fernandez-Lozano, C.; Miguel-Cruz, F. Authentication of tequilas using pattern recognition and supervised classification. Trac. Trends Anal. Chem. 2017, 94, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Méndez, O.; López-Álvarez, J.A.; Díaz-Pérez, A.L.; Altamirano, J.; Reyes De la Cruz, H.; Rutiaga-Quiñones, J.G.; Campos-García, J. Volatile compound profile conferred to tequila beverage by maturation in recycled and regenerated white oak barrels from Quercus alba. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2017, 243, 2073–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinosa-Vega, L.I.; Belio-Manzano, A.; Mercado-Ornelas, C.A.; Cortes-Mestizo, I.E.; Mendez-Garcia, V.H. Aging spectral markers of tequila observed by Raman spectroscopy. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2019, 245, 1031–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magana, A.A.; Wrobel, K.; Elguera, J.C.T.; Escobosa, A.R.C.; Wrobel, K. Determination of Small Phenolic Compounds in Tequila by Liquid Chromatography with Ion Trap Mass Spectrometry Detection. Food Anal. Methods 2015, 8, 864–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa-García, O.; Ramos-Ortíz, G.; Maldonado, J.L.; Pichardo-Molina, J.L.; Meneses-Nava, M.A.; Landgrave, J.E.A.; Cervantes-Martínez, J. UV-vis absorption spectroscopy and multivariate analysis as a method to discriminate tequila. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2007, 66, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mejia Diaz, L.F.; Wrobel, K.; Corrales Escobosa, A.R.; Aguilera Ojeda, D.A.; Wrobel, K. Identification of potential indicators of time-dependent tequila maturation and their determination by selected ion monitoring gas chromatography–mass spectrometry, using salting-out liquid–liquid extraction. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2019, 245, 1421–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bréas, O.; Reniero, F.; Serrini, G. Isotope Ratio Mass Spectrometry: Analysis of Wines from Different European Countriest. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 1994, 8, 967–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Cisneros, B.O.; López, M.; Richling, E.; Heckel, F.; Schreier, P. Tequila Authenticity Assessment by Headspace SPME-HRGC-IRMS Analysis of 13 C/12 C and 18 O/16 O Ratios of Ethanol. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 7520–7523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren-Vega, W.M.; Fonseca-Aguiñaga, R.; González-Gutiérrez, L.V.; Carrasco-Marín, F.; Zárate-Guzmán, A.I.; Romero-Cano, L.A. Chemical characterization of tequila maturation process and their connection with the physicochemical properties of the cask. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2021, 103804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, C.M.; Ferreira, A.C.S.; De Freitas, V.; Silva, A.M.S. Oxidation mechanisms occurring in wines. Food Res. Int. 2011, 44, 1115–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, G.H. Maturation. In Whisky Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 259–322. [Google Scholar]
- del Cea, C.E.A.J. Caracterización de las distintas regiones de Jalisco, México. Available online: https://www.ceajalisco.gob.mx/contenido/municipios/regiones/reg03.php (accessed on 20 December 2020).
- Dansgaard, W. Stable isotopes in precipitation. Tellus 1964, 16, 436–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brand, W.A.; Coplen, T.B.; Vogl, J.; Rosner, M.; Prohaska, T. Assessment of international reference materials for isotope-ratio analysis (IUPAC technical report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2014, 86, 425–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morillas, P.P.; Terra, A.I.; Uribe, C.; Mastromonaco, G.; Prieto, J.L.; Torres, M. Guía Eurachem: La Adecuación al Uso de los Métodos Analíticos-Una Guía de Laboratorio Para la Validación de Métodos y Temas Relacionados, 1st ed.; Eurachem: Teddington, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- NMX-V-005-NORMEX-2018. Bebidas Alcohólicas-Determinación de Aldehídos, Ésteres, Metanol, y Alcoholes Superiores-Métodos de Ensayo; Diario Oficial de la Federación: Ciudad de México, Mexico, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, F.; Jamin, E.; Hammond, D. 18O internal referencing method to detect water addition in wines and fruit juices: Interlaboratory study. J. Aoac Int. 2013, 96, 615–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| δ13CVPDB | |||||
| Effect | SS | DF | MS | F | P |
| Intercept | 19,816.36 | 1 | 19,816.36 | 100,418.7 | 0.0000 |
| Class | 0.01 | 2 | 0.01 | 0.0 | 0.9674 |
| Error | 23.09 | 117 | 0.20 | ||
| δ18OVSMOW | |||||
| Effect | SS | DF | MS | F | P |
| Intercept | 50,468.73 | 1 | 50,468.73 | 12,281.15 | 0.0000 |
| Class | 74.79 | 2 | 37.39 | 9.10 | 0.0002 |
| Error | 480.81 | 117 | 4.11 | ||
| Silver Class (δ13CVPDB) | |||||
| Effect | SS | DF | MS | F | P |
| Intercept | 5388.58 | 1 | 5388.58 | 17,852.46 | 0.0000 |
| Region | 0.863 | 3 | 0.288 | 0.95 | 0.4252 |
| Error | 10.866 | 36 | 0.302 | ||
| Silver Class (δ18OVSMOW) | |||||
| Effect | SS | DF | MS | F | P |
| Intercept | 12,492.77 | 1 | 12,492.77 | 3166.75 | 0.0000 |
| Region | 37.60 | 3 | 12.53 | 3.177 | 0.0356 |
| Error | 142.02 | 36 | 3.94 | ||
| Aged Class (δ13CVPDB) | |||||
| Effect | SS | DF | MS | F | P |
| Intercept | 5368.92 | 1 | 5368.92 | 32,296.68 | 0.0000 |
| Region | 0.616 | 3 | 0.205 | 1.23 | 0.3114 |
| Error | 5.985 | 36 | 0.166 | ||
| Aged Class (δ18OVSMOW) | |||||
| Effect | SS | DF | MS | F | P |
| Intercept | 13,995.19 | 1 | 13,995.19 | 4102.25 | 0.0000 |
| Region | 17.33 | 3 | 5.78 | 1.693 | 0.1857 |
| Error | 122.82 | 36 | 3.41 | ||
| Extra-Aged (δ13CVPDB) | |||||
| Effect | SS | DF | MS | F | P |
| Intercept | 4331.06 | 1 | 4331.065 | 33,066.47 | 0.0000 |
| Region | 0.0444 | 3 | 0.015 | 0.11 | 0.9532 |
| Error | 4.715 | 36 | 0.131 | ||
| Extra-Aged (δ18OVSMOW) | |||||
| Effect | SS | DF | MS | F | P |
| Intercept | 11,498.78 | 1 | 11,498.78 | 3154.77 | 0.0000 |
| Region | 29.82 | 3 | 9.94 | 2.727 | 0.0582 |
| Error | 131.22 | 36 | 3.64 | ||
| Jalisco Region | Total Number of Tequila Producers Active in the Region | % | Samples (Silver Class) | % | Samples (Aged Class) | % | Samples (Extra Aged Class) | % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Valles | 55 | 41 | 16 | 40 | 16 | 40 | 17 | 42 |
| Altos sur | 41 | 31 | 12 | 31 | 12 | 31 | 13 | 32 |
| Ciénega | 21 | 16 | 7 | 17 | 7 | 17 | 7 | 17 |
| Centro | 16 | 12 | 5 | 12 | 5 | 12 | 3 | 9 |
| Total | 133 | 100 | 40 | 100 | 40 | 100 | 40 | 100 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fonseca-Aguiñaga, R.; Warren-Vega, W.M.; Miguel-Cruz, F.; Romero-Cano, L.A. Isotopic Characterization of 100% Agave Tequila (Silver, Aged and Extra-Aged Class) for Its Use as an Additional Parameter in the Determination of the Authenticity of the Beverage Maturation Time. Molecules 2021, 26, 1719. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26061719
Fonseca-Aguiñaga R, Warren-Vega WM, Miguel-Cruz F, Romero-Cano LA. Isotopic Characterization of 100% Agave Tequila (Silver, Aged and Extra-Aged Class) for Its Use as an Additional Parameter in the Determination of the Authenticity of the Beverage Maturation Time. Molecules. 2021; 26(6):1719. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26061719
Chicago/Turabian StyleFonseca-Aguiñaga, Rocío, Walter M. Warren-Vega, Floriberto Miguel-Cruz, and Luis A. Romero-Cano. 2021. "Isotopic Characterization of 100% Agave Tequila (Silver, Aged and Extra-Aged Class) for Its Use as an Additional Parameter in the Determination of the Authenticity of the Beverage Maturation Time" Molecules 26, no. 6: 1719. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26061719
APA StyleFonseca-Aguiñaga, R., Warren-Vega, W. M., Miguel-Cruz, F., & Romero-Cano, L. A. (2021). Isotopic Characterization of 100% Agave Tequila (Silver, Aged and Extra-Aged Class) for Its Use as an Additional Parameter in the Determination of the Authenticity of the Beverage Maturation Time. Molecules, 26(6), 1719. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26061719









