Low-Level Endothelial TRAIL-Receptor Expression Obstructs the CNS-Delivery of Angiopep-2 Functionalised TRAIL-Receptor Agonists for the Treatment of Glioblastoma
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
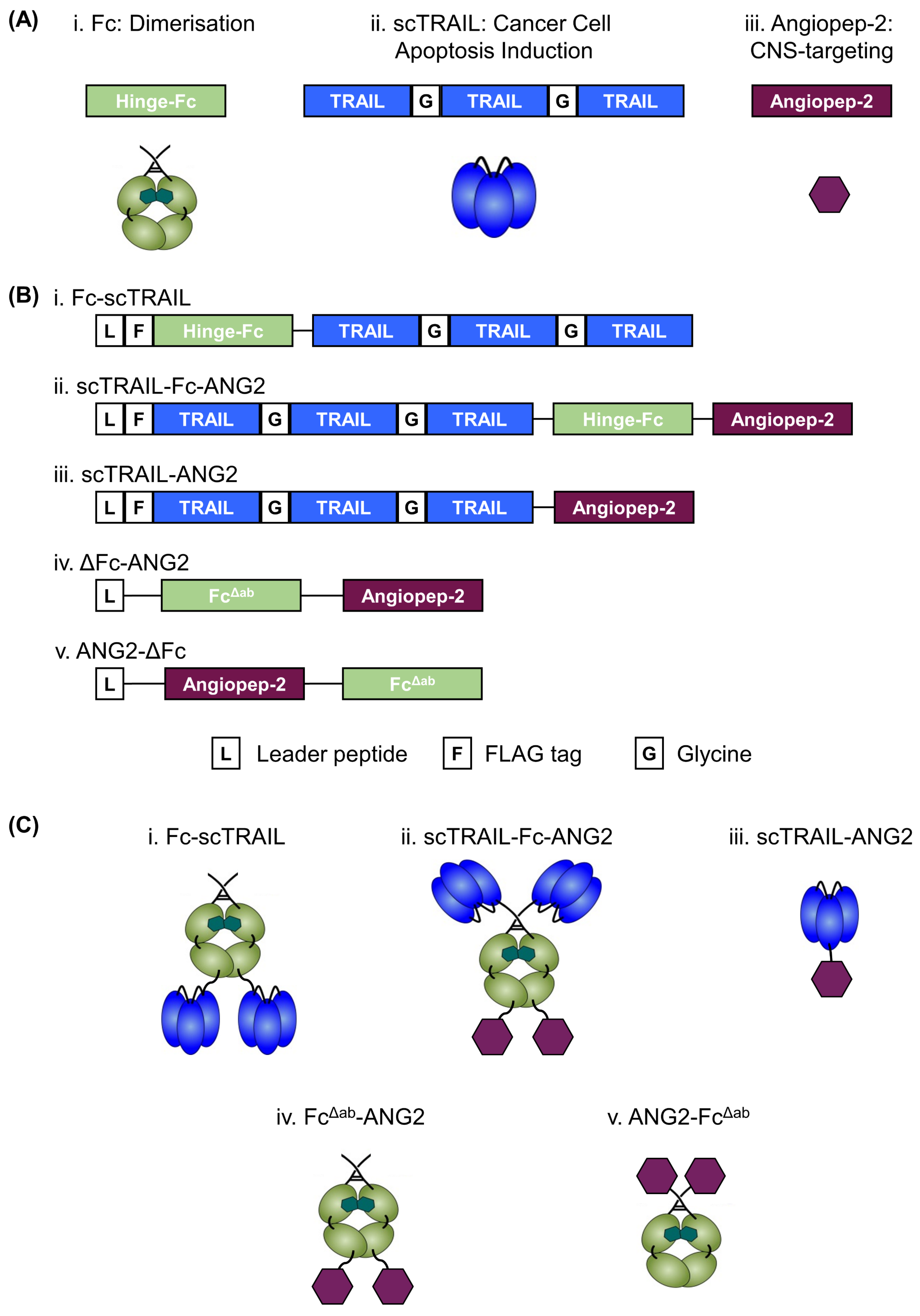
2.1. Design, Production and Purification of a CNS-Targeted Hexavalent TRAIL-Receptor Agonist
2.2. Fusion of ANG2 to Hexavalent TRAIL Maintains Its Potency in Inducing Apoptosis
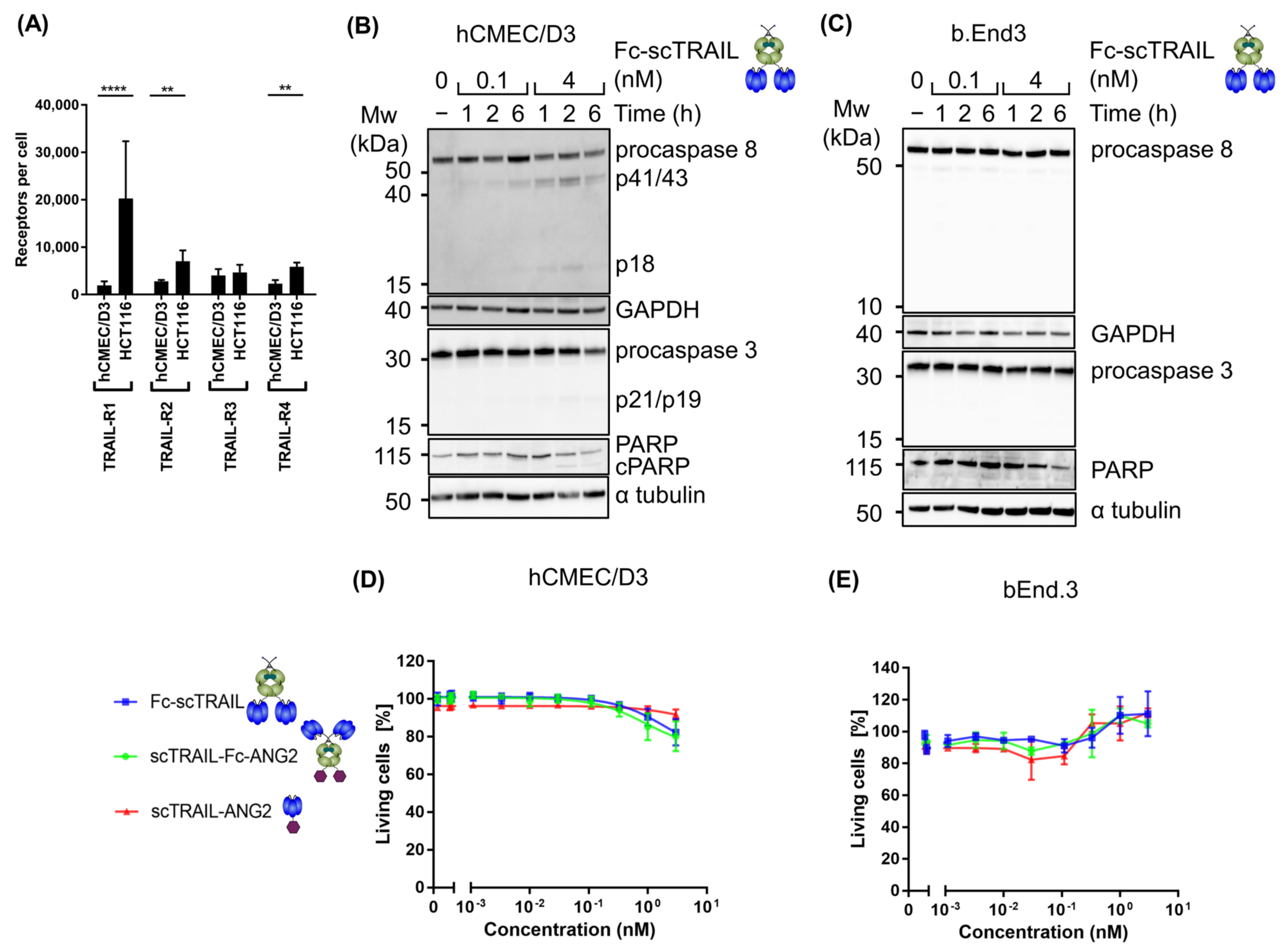
2.3. Blood–Brain Barrier Cells Are Highly Resistant to TRAIL Treatment
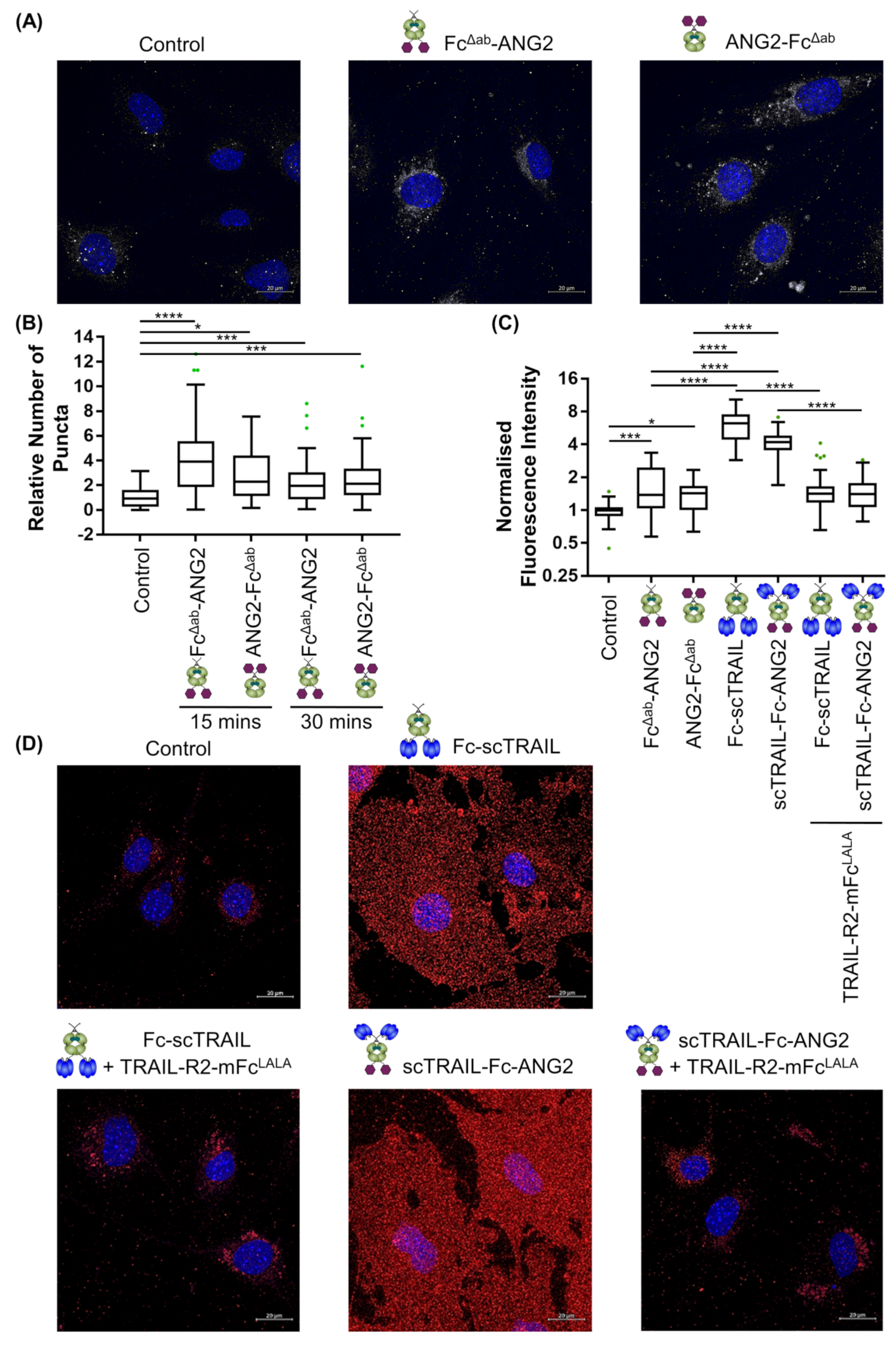
2.4. Binding of CNS-Targeted TRAIL Fusion Proteins to Blood–Brain Barrier Cells Is Predominantly TRAIL-Mediated
2.5. CNS-Transport of TRAIL-Fusion Constructs
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents and Antibodies
4.2. Generation of Constructs
4.3. Production and Purification of the Recombinant Proteins
4.4. Cell Culture
4.5. Receptor Quantification
4.6. Cell Binding Assays
4.7. Cell Death Assays
4.8. Crystal Violet Assay
4.9. Mass Spectrometry
4.10. Immunocytochemistry
4.11. Western Blotting
4.12. MTT Assay
4.13. Blood–Brain Barrier Transwell Setup and Transport Assay
4.14. ELISA for the Transport Measurement
4.15. Statistics
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Louis, D.N.; Ohgaki, H.; Wiestler, O.D.; Cavenee, W.K.; Burger, P.C.; Jouvet, A.; Scheithauer, B.W.; Kleihues, P. The 2007 WHO Classification of Tumours of the Central Nervous System. Acta Neuropathol. 2007, 114, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrom, Q.T.; Cioffi, G.; Gittleman, H.; Patil, N.; Waite, K.; Kruchko, C.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J.S. CBTRUS Statistical Report: Primary Brain and Other Central Nervous System Tumors Diagnosed in the United States in 2012–2016. Neuro-Oncology 2019, 21, v1–v100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stupp, R.; Mason, W.P.; van den Bent, M.J.; Weller, M.; Fisher, B.; Taphoorn, M.J.; Belanger, K.; Brandes, A.A.; Marosi, C.; Bogdahn, U.; et al. Radiotherapy plus Concomitant and Adjuvant Temozolomide for Glioblastoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koshy, M.; Villano, J.L.; Dolecek, T.A.; Howard, A.; Mahmood, U.; Chmura, S.J.; Weichselbaum, R.R.; McCarthy, B.J. Improved survival time trends for glioblastoma using the SEER 17 population-based registries. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2011, 107, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, B.; Rosenthal, M. Survival comparison between glioblastoma multiforme and other incurable cancers. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2010, 17, 417–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walczak, H.; Miller, R.E.; Ariail, K.; Gliniak, B.; Griffith, T.S.; Kubin, M.; Chin, W.; Jones, J.; Woodward, A.; Le, T.; et al. Tumoricidal activity of tumor necrosis factor–related apoptosis–inducing ligand in vivo. Nat. Med. 1999, 5, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; El-Deiry, W.S. TRAIL and apoptosis induction by TNF-family death receptors. Oncogene 2003, 22, 8628–8633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnstone, R.W.; Frew, A.J.; Smyth, M. The TRAIL apoptotic pathway in cancer onset, progression and therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2008, 8, 782–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gieffers, C.; Kluge, M.; Merz, C.; Sykora, J.; Thiemann, M.; Schaal, R.; Fischer, C.; Branschädel, M.; Abhari, B.A.; Hohenberger, P.; et al. APG350 Induces Superior Clustering of TRAIL Receptors and Shows Therapeutic Antitumor Efficacy Independent of Cross-Linking via Fcγ Receptors. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2013, 12, 2735–2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Miguel, D.; Lemke, J.; Anel, A.; Walczak, H.; Martinez-Lostao, L. Onto better TRAILs for cancer treatment. Cell Death Differ. 2016, 23, 733–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wajant, H. Molecular Mode of Action of TRAIL Receptor Agonists-Common Principles and Their Translational Exploitation. Cancers 2019, 11, 954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegemund, M.; Pollak, N.; Seifert, O.; Wahl, K.; Hanak, K.; Vogel, A.; Nussler, A.K.; Göttsch, D.; Münkel, S.; Bantel, H.; et al. Superior antitumoral activity of dimerized targeted single-chain TRAIL fusion proteins under retention of tumor selectivity. Cell Death Dis. 2012, 3, e295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutt, M.; Marquardt, L.; Seifert, O.; Siegemund, M.; Kulms, D.; Kontermann, R.E.; Müller, I.; Pfizenmaier, K. Superior Properties of Fc-comprising scTRAIL Fusion Proteins. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2017, 16, 2792–2802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratain, M.J.; Doi, T.; De Jonge, M.J.; Lorusso, P.; Dunbar, M.; Chiney, M.; Motwani, M.; Glasgow, J.; Petrich, A.M.; Rasco, D.W.; et al. Phase 1, first-in-human study of TRAIL receptor agonist fusion protein ABBV-621. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 3013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vetma, V.; Guttà, C.; Peters, N.; Praetorius, C.; Hutt, M.; Seifert, O.; Meier, F.; Kontermann, R.; Kulms, D.; Rehm, M. Convergence of pathway analysis and pattern recognition predicts sensitization to latest generation TRAIL therapeutics by IAP antagonism. Cell Death Differ. 2020, 27, 2417–2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, D.C.; Buchanan, F.G.; Cheng, D.; Solomon, L.R.; Xiao, Y.; Xue, J.; Tahir, S.K.; Smith, M.L.; Zhang, H.; Widomski, D.; et al. Hexavalent TRAIL Fusion Protein Eftozanermin Alfa Optimally Clusters Apoptosis-Inducing TRAIL Receptors to Induce On-Target Antitumor Activity in Solid Tumors. Cancer Res. 2021, 81, 3402–3414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardridge, W.M. The Blood-Brain Barrier: Bottleneck in Brain Drug Development. NeuroRx 2005, 2, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardridge, W.M. Blood-Brain Barrier and Delivery of Protein and Gene Therapeutics to Brain. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2020, 11, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boado, R.J.; Hui, E.K.-W.; Lu, J.Z.; Pardridge, W.M. Glycemic Control and Chronic Dosing of Rhesus Monkeys with a Fusion Protein of Iduronidase and a Monoclonal Antibody Against the Human Insulin Receptor. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2012, 40, 2021–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffy, K.R.; Pardridge, W.M.; Rosenfeld, R.G. Human blood-brain barrier insulin-like growth factor receptor. Metabolism 1988, 37, 136–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardridge, W.M.; Eisenberg, J.; Yang, J. Human blood-brain barrier transferrin receptor. Metabolism 1987, 36, 892–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuma, P.L.; Hubbard, A.L. Transcytosis: Crossing Cellular Barriers. Physiol. Rev. 2003, 83, 871–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pardridge, W. Molecular Trojan horses for blood–brain barrier drug delivery. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2006, 6, 494–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jefferies, W.A.; Brandon, M.R.; Hunt, S.V.; Williams, A.F.; Gatter, K.C.; Mason, D.Y. Transferrin receptor on endothelium of brain capillaries. Nature 1984, 312, 162–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Engelhardt, B.; Lesley, J.; Bickel, U.; Pardridge, W.M. Targeting rat anti-mouse transferrin receptor monoclonal antibodies through blood-brain barrier in mouse. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2000, 292. [Google Scholar]
- Demeule, M.; Currie, J.-C.; Bertrand, Y.; Ché, C.; Nguyen, T.; Régina, A.; Gabathuler, R.; Castaigne, J.-P.; Béliveau, R. Involvement of the low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein in the transcytosis of the brain delivery vector Angiopep-2. J. Neurochem. 2008, 106, 1534–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, F.C.; Taskar, K.; Rudraraju, V.; Goda, S.; Thorsheim, H.R.; Gaasch, J.A.; Mittapalli, R.K.; Palmieri, D.; Steeg, P.S.; Lockman, P.R.; et al. Uptake of ANG1005, A Novel Paclitaxel Derivative, Through the Blood-Brain Barrier into Brain and Experimental Brain Metastases of Breast Cancer. Pharm. Res. 2009, 26, 2486–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demeule, M.; Beaudet, N.; Régina, A.; Besserer-Offroy, E.; Murza, A.; Tétreault, P.; Belleville, K.; Ché, C.; Larocque, A.; Thiot, C.; et al. Conjugation of a brain-penetrant peptide with neurotensin provides antinociceptive properties. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 1199–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boado, R.J.; Hui, E.K.-W.; Lu, J.Z.; Pardridge, W.M. CHO cell expression, long-term stability, and primate pharmacokinetics and brain uptake of an IgG-paroxonase-1 fusion protein. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2010, 108, 186–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, A.C.; Stevens, M.Y.; Chen, M.B.; Lee, D.P.; Stähli, D.; Gate, D.; Contrepois, K.; Chen, W.; Iram, T.; Zhang, L.; et al. Physiological blood–brain transport is impaired with age by a shift in transcytosis. Nature 2020, 583, 425–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demeule, M.; Régina, A.; Ché, C.; Poirier, J.; Nguyen, T.; Gabathuler, R.; Castaigne, J.-P.; Béliveau, R. Identification and Design of Peptides as a New Drug Delivery System for the Brain. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2007, 324, 1064–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Zhan, C.; Chen, X.; Hou, J.; Xie, C.; Lu, W. Retro-Inverso Isomer of Angiopep-2: A Stable d-Peptide Ligand Inspires Brain-Targeted Drug Delivery. Mol. Pharm. 2014, 11, 3261–3268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Li, J.; Han, L.; Liu, S.; Ma, H.; Huang, R.; Jiang, C. Dual targeting effect of Angiopep-2-modified, DNA-loaded nanoparticles for glioma. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 6832–6838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, K.; Huang, R.; Li, J.; Han, L.; Ye, L.; Lou, J.; Jiang, C. Angiopep-2 modified PE-PEG based polymeric micelles for amphotericin B delivery targeted to the brain. J. Control. Release 2010, 147, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boccellato, C.; Kolbe, E.; Peters, N.; Juric, V.; Fullstone, G.; Verreault, M.; Idbaih, A.; Lamfers, M.L.M.; Murphy, B.M.; Rehm, M. Marizomib sensitizes primary glioma cells to apoptosis induced by a latest-generation TRAIL receptor agonist. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böckenhoff, A.; Cramer, S.; Wölte, P.; Knieling, S.; Wohlenberg, C.; Gieselmann, V.; Galla, H.-J.; Matzner, U. Comparison of Five Peptide Vectors for Improved Brain Delivery of the Lysosomal Enzyme Arylsulfatase A. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 3122–3129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, X.; Wang, H.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, J.; Liu, Y. Recombinant expressing angiopep-2 fused anti-VEGF single chain Fab (scFab) could cross blood–brain barrier and target glioma. AMB Express 2019, 9, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armour, K.L.; Clark, M.R.; Hadley, A.G.; Williamson, L.M. Recombinant Human IgG Molecules Lacking Fcgamma Receptor I Binding and Monocyte Triggering Activities. Eur. J. Immunol. 1999, 29, 2613–2624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, G.; Ni, J.; Wei, Y.-F.; Yu, G.-L.; Gentz, R.; Dixit, V.M. An Antagonist Decoy Receptor and a Death Domain-Containing Receptor for TRAIL. Science 1997, 277, 815–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, G.; O’Rourke, K.; Chinnaiyan, A.M.; Gentz, R.; Ebner, R.; Ni, J.; Dixit, V.M. The Receptor for the Cytotoxic Ligand TRAIL. Science 1997, 276, 111–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walczak, H.; Degli-Esposti, M.A.; Johnson, R.S.; Smolak, P.J.; Waugh, J.Y.; Boiani, N.; Timour, M.S.; Gerhart, M.J.; Schooley, K.A.; Smith, C.A.; et al. TRAIL-R2: A novel apoptosis-mediating receptor for TRAIL. EMBO J. 1997, 16, 5386–5397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storck, S.; Meister, S.; Nahrath, J.; Meißner, J.N.; Schubert, N.; Di Spiezio, A.; Baches, S.; Vandenbroucke, R.; Bouter, Y.; Prikulis, I.; et al. Endothelial LRP1 transports amyloid-β1–42 across the blood-brain barrier. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 126, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertrand, Y.; Currie, J.-C.; Demeule, M.; Régina, A.; Ché, C.; Abulrob, A.; Fatehi, D.; Sartelet, H.; Gabathuler, R.; Castaigne, J.-P.; et al. Transport characteristics of a novel peptide platform for CNS therapeutics. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2010, 14, 2827–2839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Leite, D.M.; Scarpa, E.; Nyberg, S.; Fullstone, G.; Forth, J.; Matias, D.; Apriceno, A.; Poma, A.; Duro-Castano, A.; et al. On the shuttling across the blood-brain barrier via tubule formation: Mechanism and cargo avidity bias. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eabc4397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulda, S.; Wick, W.; Weller, M.; Debatin, K.-M. Smac agonists sensitize for Apo2L/TRAIL- or anticancer drug-induced apoptosis and induce regression of malignant glioma in vivo. Nat. Med. 2002, 8, 808–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Opel, D.; Westhoff, M.-A.; Bender, A.; Braun, V.; Debatin, K.-M.; Fulda, S. Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase Inhibition Broadly Sensitizes Glioblastoma Cells to Death Receptor– and Drug-Induced Apoptosis. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 6271–6280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hetschko, H.; Voss, V.; Seifert, V.; Prehn, J.H.M.; Kögel, D. Upregulation of DR5 by proteasome inhibitors potently sensitizes glioma cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis. FEBS J. 2008, 275, 1925–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lincoln, F.A.; Imig, D.; Boccellato, C.; Juric, V.; Noonan, J.; Kontermann, R.E.; Allgöwer, F.; Murphy, B.; Rehm, M. Sensitization of glioblastoma cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis by IAP- and Bcl-2 antagonism. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koessinger, A.L.; Koessinger, D.; Kinch, K.; Martínez-Escardó, L.; Paul, N.R.; Elmasry, Y.; Malviya, G.; Cloix, C.; Campbell, K.J.; Bock, F.J.; et al. Increased Apoptotic Priming of Glioblastoma Enables Therapeutic Targeting by BH3-Mimetics. bioRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagci-Onder, T.; Du, W.; Figueiredo, J.-L.; Martinez-Quintanilla, J.; Shah, K. Targeting breast to brain metastatic tumours with death receptor ligand expressing therapeutic stem cells. Brain 2015, 138, 1710–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Wagner, J.; Kline, C.L.; Zhou, L.; Campbell, K.S.; Macfarlane, A.W.; Olszanski, A.J.; Cai, K.Q.; Hensley, H.H.; Ross, E.A.; Ralff, M.D.; et al. Dose intensification of TRAIL-inducing ONC201 inhibits metastasis and promotes intratumoral NK cell recruitment. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 2325–2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khawaja, H.; Campbell, A.; Roberts, J.Z.; Javadi, A.; O’Reilly, P.; McArt, D.; Allen, W.L.; Majkut, J.; Rehm, M.; Bardelli, A.; et al. RALB GTPase: A critical regulator of DR5 expression and TRAIL sensitivity in KRAS mutant colorectal cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polanski, R.; Vincent, J.; Polanska, U.M.; Petreus, T.; Tang, E.K.Y. Caspase-8 activation by TRAIL monotherapy predicts responses to IAPi and TRAIL combination treatment in breast cancer cell lines. Cell Death Dis. 2015, 6, e1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sanmarco, L.M.; Wheeler, M.A.; Gutiérrez-Vázquez, C.; Polonio, C.M.; Linnerbauer, M.; Pinho-Ribeiro, F.A.; Li, Z.; Giovannoni, F.; Batterman, K.V.; Scalisi, G.; et al. Gut-licensed IFNγ+ NK cells drive LAMP1+TRAIL+ anti-inflammatory astrocytes. Nature 2021, 590, 473–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, C.A.; McCombe, P.A.; Pender, M.P. The roles of Fas, Fas ligand and Bcl-2 in T cell apoptosis in the central nervous system in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J. Neuroimmunol. 1998, 82, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hilliard, B.; Wilmen, A.; Seidel, C.; Liu, T.-S.T.; Göke, R.; Chen, Y. Roles of TNF-Related Apoptosis-Inducing Ligand in Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis. J. Immunol. 2001, 166, 1314–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardridge, W.M.; Eisenberg, J.; Yang, J. Human Blood—Brain Barrier Insulin Receptor. J. Neurochem. 1985, 44, 1771–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, M.W.; Sipols, A.; Kahn, S.E.; Lattemann, D.F.; Taborsky, G.J.; Bergman, R.N.; Woods, S.C.; Porte, D. Kinetics and specificity of insulin uptake from plasma into cerebrospinal fluid. Am. J. Physiol. Metab. 1990, 259, E378–E383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumthekar, P.; Tang, S.-C.; Brenner, A.J.; Kesari, S.; Piccioni, D.E.; Anders, C.K.; Carrillo, J.A.; Chalasani, P.; Kabos, P.; Puhalla, S.L.; et al. ANG1005, a Brain-Penetrating Peptide–Drug Conjugate, Shows Activity in Patients with Breast Cancer with Leptomeningeal Carcinomatosis and Recurrent Brain Metastases. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 2789–2799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashkenazi, A.; Pai, R.C.; Fong, S.; Leung, S.; Lawrence, D.A.; Marsters, S.A.; Blackie, C.; Chang, L.; McMurtrey, A.E.; Hebert, A.; et al. Safety and antitumor activity of recombinant soluble Apo2 ligand. J. Clin. Investig. 1999, 104, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.D.; Nguyen, T.; Thomas, W.D.; Sanders, J.E.; Hersey, P. Mechanisms of resistance of normal cells to TRAIL induced apoptosis vary between different cell types. FEBS Lett. 2000, 482, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zauli, G.; Secchiero, P. The role of the TRAIL/TRAIL receptors system in hematopoiesis and endothelial cell biology. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2006, 17, 245–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wosik, K.; Biernacki, K.; Khouzam, M.-P.; Prat, A. Death receptor expression and function at the human blood brain barrier. J. Neurol. Sci. 2007, 259, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridder, D.A.; Wenzel, J.; Müller, K.; Töllner, K.; Tong, X.-K.; Assmann, J.; Stroobants, S.; Weber, T.; Niturad, C.; Fischer, L.; et al. Brain endothelial TAK1 and NEMO safeguard the neurovascular unit. J. Exp. Med. 2015, 212, 1529–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booth, R.; Kim, H. Characterization of a microfluidic in vitro model of the blood-brain barrier (μBBB). Lab Chip 2012, 12, 1784–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Mei, S.; Jin, H.; Zhu, B.; Tian, Y.; Huo, J.; Cui, X.; Guo, A.; Zhao, Z. Identification of two immortalized cell lines, ECV304 and bEnd3, for in vitro permeability studies of blood-brain barrier. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0187017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, R.C.; Morris, A.P.; O’Neil, R.G. Tight junction protein expression and barrier properties of immortalized mouse brain microvessel endothelial cells. Brain Res. 2007, 1130, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.J.; Zhang, Y.; Kenrick, M.; Hoyte, K.; Luk, W.; Lu, Y.; Atwal, J.; Elliott, J.M.; Prabhu, S.; Watts, R.J.; et al. Boosting Brain Uptake of a Therapeutic Antibody by Reducing Its Affinity for a Transcytosis Target. Sci. Transl. Med. 2011, 3, 84ra44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haqqani, A.S.; Thom, G.; Burrell, M.; Delaney, C.E.; Brunette, E.; Baumann, E.; Sodja, C.; Jezierski, A.; Webster, C.; Stanimirovic, D.B. Intracellular sorting and transcytosis of the rat transferrin receptor antibody OX26 across the blood-brain barrierin vitrois dependent on its binding affinity. J. Neurochem. 2018, 146, 735–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niewoehner, J.; Bohrmann, B.; Collin, L.; Urich, E.; Sade, H.; Maier, P.; Rueger, P.; Stracke, J.O.; Lau, W.; Tissot, A.C.; et al. Increased Brain Penetration and Potency of a Therapeutic Antibody Using a Monovalent Molecular Shuttle. Neuron 2014, 81, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kariolis, M.S.; Wells, R.C.; Getz, J.A.; Kwan, W.; Mahon, C.S.; Tong, R.; Kim, D.J.; Srivastava, A.; Bedard, C.; Henne, K.R.; et al. Brain delivery of therapeutic proteins using an Fc fragment blood-brain barrier transport vehicle in mice and monkeys. Sci. Transl. Med. 2020, 12, eaay1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hultqvist, G.; Syvänen, S.; Fang, X.T.; Lannfelt, L.; Sehlin, D. Bivalent Brain Shuttle Increases Antibody Uptake by Monovalent Binding to the Transferrin Receptor. Theranostics 2017, 7, 308–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webster, C.I.; Hatcher, J.; Burrell, M.; Thom, G.; Thornton, P.; Gurrell, I.; Chessell, I. Enhanced delivery of IL-1 receptor antagonist to the central nervous system as a novel anti–transferrin receptor-IL-1RA fusion reverses neuropathic mechanical hypersensitivity. Pain 2016, 158, 660–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bien-Ly, N.; Yu, Y.J.; Bumbaca, D.; Elstrott, J.; Boswell, C.; Zhang, Y.; Luk, W.; Lu, Y.; Dennis, M.S.; Weimer, R.M.; et al. Transferrin receptor (TfR) trafficking determines brain uptake of TfR antibody affinity variants. J. Exp. Med. 2014, 211, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villaseñor, R.; Schilling, M.; Sundaresan, J.; Lutz, Y.; Collin, L. Sorting Tubules Regulate Blood-Brain Barrier Transcytosis. Cell Rep. 2017, 21, 3256–3270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Degli-Esposti, M.A.; Smolak, P.J.; Walczak, H.; Waugh, J.; Huang, C.-P.; DuBose, R.F.; Goodwin, R.G.; Smith, C.A. Cloning and Characterization of TRAIL-R3, a Novel Member of the Emerging TRAIL Receptor Family. J. Exp. Med. 1997, 186, 1165–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degli-Esposti, M.A.; Dougall, W.C.; Smolak, P.J.; Waugh, J.Y.; Smith, C.A.; Goodwin, R.G. The Novel Receptor TRAIL-R4 Induces NF-κB and Protects against TRAIL-Mediated Apoptosis, yet Retains an Incomplete Death Domain. Immunity 1997, 7, 813–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchida, Y.; Ohtsuki, S.; Katsukura, Y.; Ikeda, C.; Suzuki, T.; Kamiie, J.; Terasaki, T. Quantitative targeted absolute proteomics of human blood-brain barrier transporters and receptors. J. Neurochem. 2011, 117, 333–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, S.; Uchida, Y.; Mittapalli, R.K.; Sane, R.; Terasaki, T.; Elmquist, W.F. Quantitative Proteomics of Transporter Expression in Brain Capillary Endothelial Cells Isolated from P-Glycoprotein (P-gp), Breast Cancer Resistance Protein (Bcrp), and P-gp/Bcrp Knockout Mice. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2012, 40, 1164–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shawahna, R.; Uchida, Y.; Declèves, X.; Ohtsuki, S.; Yousif, S.; Dauchy, S.; Jacob, A.; Chassoux, F.; Daumas-Duport, C.; Couraud, P.-O.; et al. Transcriptomic and Quantitative Proteomic Analysis of Transporters and Drug Metabolizing Enzymes in Freshly Isolated Human Brain Microvessels. Mol. Pharm. 2011, 8, 1332–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasparian, M.E.; Chernyak, B.V.; Dolgikh, D.A.; Yagolovich, A.V.; Popova, E.N.; Sycheva, A.M.; Moshkovskii, S.A.; Kirpichnikov, M.P.; Ekaterina, P. Generation of new TRAIL mutants DR5-A and DR5-B with improved selectivity to death receptor 5. Apoptosis 2009, 14, 778–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seifert, O.; Pollak, N.; Nusser, A.; Steiniger, F.; Rüger, R.; Pfizenmaier, K.; Kontermann, R.E. Immuno-LipoTRAIL: Targeted Delivery of TRAIL-Functionalized Liposomal Nanoparticles. Bioconjugate Chem. 2014, 25, 879–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seifert, O.; Plappert, A.; Fellermeier, S.; Siegemund, M.; Pfizenmaier, K.; Kontermann, R.E. Tetravalent Antibody-scTRAIL Fusion Proteins with Improved Properties. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2013, 13, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McQuin, C.; Goodman, A.; Chernyshev, V.; Kamentsky, L.; Cimini, B.A.; Karhohs, K.W.; Doan, M.; Ding, L.; Rafelski, S.M.; Thirstrup, D.; et al. CellProfiler 3.0: Next-generation image processing for biology. PLoS Biol. 2018, 16, e2005970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Krishna Moorthy, N.; Seifert, O.; Eisler, S.; Weirich, S.; Kontermann, R.E.; Rehm, M.; Fullstone, G. Low-Level Endothelial TRAIL-Receptor Expression Obstructs the CNS-Delivery of Angiopep-2 Functionalised TRAIL-Receptor Agonists for the Treatment of Glioblastoma. Molecules 2021, 26, 7582. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26247582
Krishna Moorthy N, Seifert O, Eisler S, Weirich S, Kontermann RE, Rehm M, Fullstone G. Low-Level Endothelial TRAIL-Receptor Expression Obstructs the CNS-Delivery of Angiopep-2 Functionalised TRAIL-Receptor Agonists for the Treatment of Glioblastoma. Molecules. 2021; 26(24):7582. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26247582
Chicago/Turabian StyleKrishna Moorthy, Nivetha, Oliver Seifert, Stephan Eisler, Sara Weirich, Roland E. Kontermann, Markus Rehm, and Gavin Fullstone. 2021. "Low-Level Endothelial TRAIL-Receptor Expression Obstructs the CNS-Delivery of Angiopep-2 Functionalised TRAIL-Receptor Agonists for the Treatment of Glioblastoma" Molecules 26, no. 24: 7582. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26247582
APA StyleKrishna Moorthy, N., Seifert, O., Eisler, S., Weirich, S., Kontermann, R. E., Rehm, M., & Fullstone, G. (2021). Low-Level Endothelial TRAIL-Receptor Expression Obstructs the CNS-Delivery of Angiopep-2 Functionalised TRAIL-Receptor Agonists for the Treatment of Glioblastoma. Molecules, 26(24), 7582. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26247582





