Soy Isoflavones Inhibit Both GPIb-IX Signaling and αIIbβ3 Outside-In Signaling via 14-3-3ζ in Platelet
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
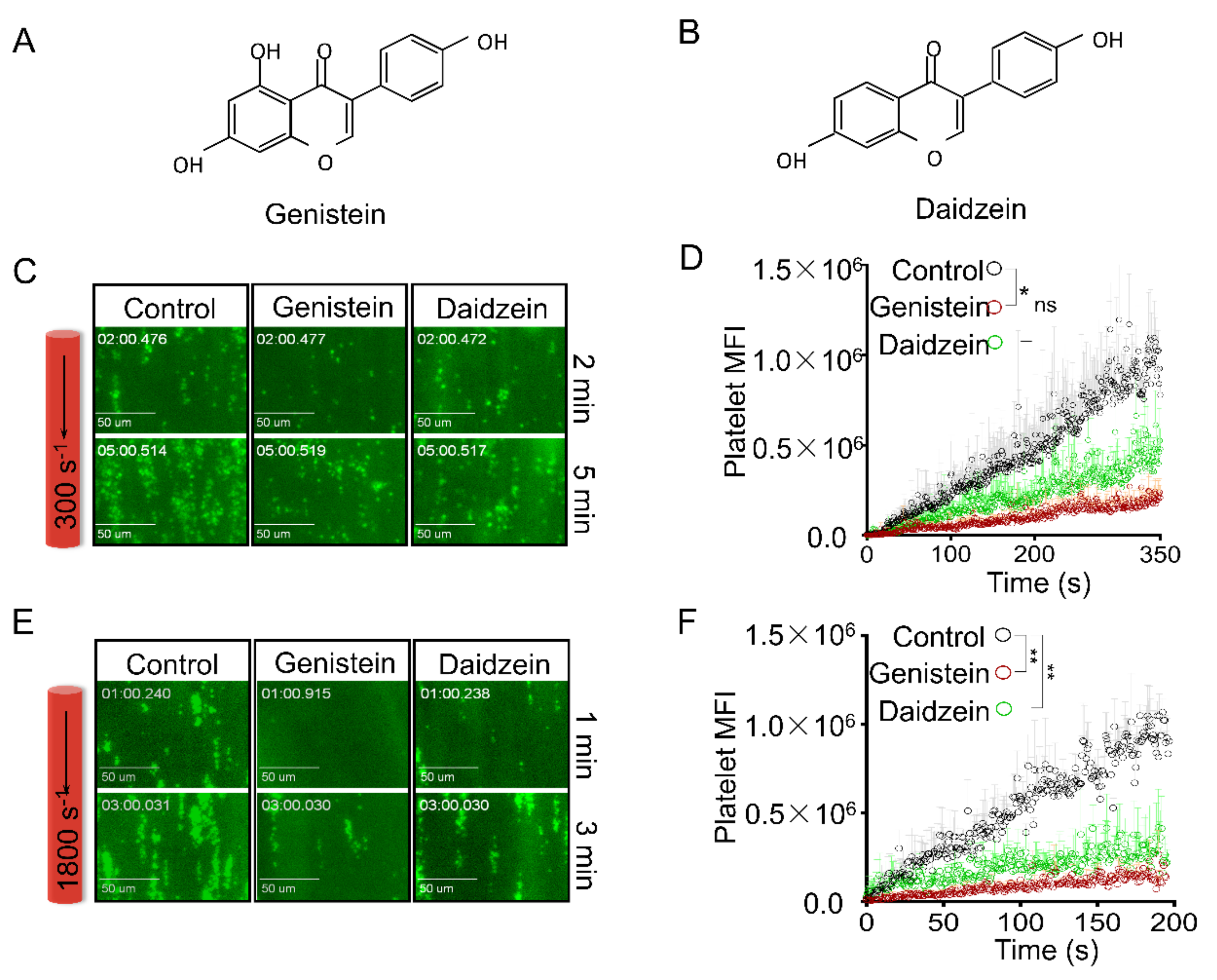
2.1. Genistein and Daidzein Inhibit Platelet Aggregation and Thrombi Formation in an Ex Vivo Thrombosis Model
2.2. Genistein and Daidzein Inhibit GPIb-IX-Mediated Platelet Aggregation
2.3. Genistein and Daidzein Inhibit αIIbβ3-Mediated Platelet Aggregation
2.4. Genistein and Daidzein Inhibit Platelet Spreading on Immobilized Fibrinogen
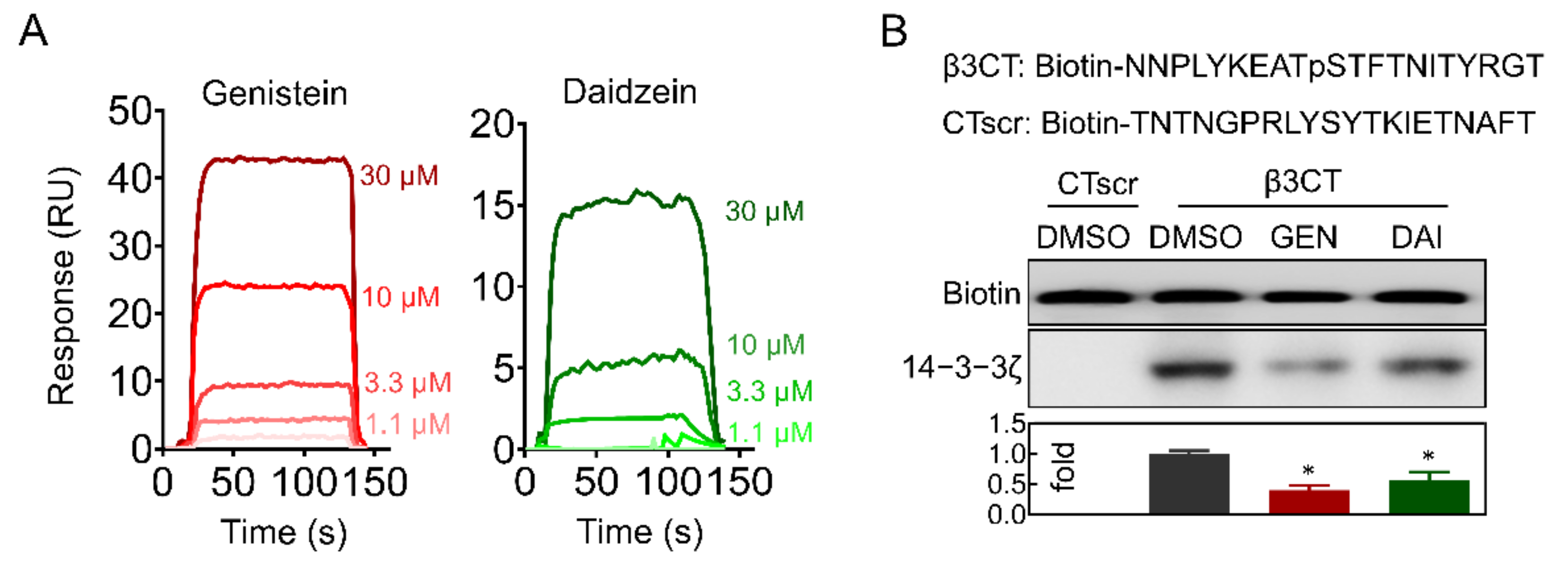
2.5. Genistein and Daidzein Bind to 14-3-3ζ
2.6. Genistein and Daidzein Inhibit 14-3-3ζ-Integrin β3 Complex Formation and Outside-In Signaling Transduction in Platelet
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. GPIbα Deficient (GPIbα-/-) Mice
3.2. Ex Vivo Perfusion Chamber
3.3. Platelet Preparation and Aggregation
3.4. Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR) Analysis
3.5. Streptavidin–Magnetic Beads Pulldown Assay
3.6. Immunoprecipitation and Western Blot
3.7. Platelet Spreading and Confocal Microscopy
3.8. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Wang, H.D.N.M.; Naghavi, M.; Allen, C.; Barber, R.M.; Bhutta, Z.A.; Carter, A.; Casey, D.C.; Charlson, F.J.; Chen, A.Z.; Coates, M.M.; et al. Global, regional, and national life expectancy, all-cause mortality, and cause-specific mortality for 249 causes of death, 1980-2015: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet 2016, 388, 1459–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McManus, D.D.; Freedman, J.E. MicroRNAs in platelet function and cardiovascular disease. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2015, 12, 711–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Shi, Z.; Reheman, A.; Jin, J.W.; Li, C.; Wang, Y.; Andrews, M.C.; Chen, P.; Zhu, G.; Ling, W. Plant food delphinidin-3-glucoside significantly inhibits platelet activation and thrombosis: Novel protective roles against cardiovascular diseases. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e37323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Andrews, M.; Yang, Y.; Lang, S.; Jin, J.W.; Cameron-Vendrig, A.; Zhu, G.; Reheman, A.; Ni, H. Platelets in thrombosis and hemostasis: Old topic with new mechanisms. Cardiovasc. Haematol. Disord. Drug Targets (Former. Curr. Drug Targets-Cardiovasc. Hematol. Disord.) 2012, 12, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michelson, A.D. Antiplatelet therapies for the treatment of cardiovascular disease. Nat. Reviews. Drug Discov. 2010, 9, 154–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuentes, E.; Palomo, I. Antiplatelet effects of natural bioactive compounds by multiple targets: Food and drug interactions. J. Funct. Foods 2014, 6, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaheer, K.; Akhtar, M.H. An updated review of dietary isoflavones: Nutrition, processing, bioavailability and impacts on human health. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. 2017, 57, 1280–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habauzit, V.; Morand, C. Evidence for a protective effect of polyphenols-containing foods on cardiovascular health: An update for clinicians. Adv. Chronic Dis. 2012, 3, 87–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, R.J.; Fei, S.H.; Chen, L.Y.; Wang, G.; Liu, M.; Zhang, W.S.; Yan, X.W.; Lai, R.; Shen, C.B. 3′-Methoxydaidzein exerts analgesic activity by inhibiting voltage-gated sodium channels. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2019, 17, 413–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagara, M.; Kanda, T.; NJelekera, M.; Teramoto, T.; Armitage, L.; Birt, N.; Birt, C.; Yamori, Y. Effects of dietary intake of soy protein and isoflavones on cardiovascular disease risk factors in high risk, middle-aged men in Scotland. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2004, 23, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokubo, Y.; Iso, H.; Ishihara, J.; Okada, K.; Inoue, M.; Tsugane, S.; Group, J.S. Association of dietary intake of soy, beans, and isoflavones with risk of cerebral and myocardial infarctions in Japanese populations: The Japan Public Health Center-based (JPHC) study cohort I. Circulation 2007, 116, 2553–2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gil-Izquierdo, A.; Penalvo, J.L.; Gil, J.I.; Medina, S.; Horcajada, M.N.; Lafay, S.; Silberberg, M.; Llorach, R.; Zafrilla, P.; Garcia-Mora, P.; et al. Soy isoflavones and cardiovascular disease epidemiological, clinical and -omics perspectives. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2012, 13, 624–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rimbach, G.; Boesch-Saadatmandi, C.; Frank, J.; Fuchs, D.; Wenzel, U.; Daniel, H.; Hall, W.L.; Weinberg, P.D. Dietary isoflavones in the prevention of cardiovascular disease—A molecular perspective. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2008, 46, 1308–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.K.; Clarkson, T.B. Dietary soy isoflavones inhibit in-vivo constrictor responses of coronary arteries to collagen-induced platelet activation. Coron. Artery Dis. 1998, 9, 759–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoene, N.W.; Guidry, C.A. Dietary soy isoflavones inhibit activation of rat platelets. J. Nutr. Biochem. 1999, 10, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beretz, A.; Cazenave, J.P.; Anton, R. Inhibition of aggregation and secretion of human platelets by quercetin and other flavonoids: Structure-activity relationships. Agents Actions 1982, 12, 382–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakashima, S.; Koike, T.; Nozawa, Y. Genistein, a protein tyrosine kinase inhibitor, inhibits thromboxane A2-mediated human platelet responses. Mol. Pharm. 1991, 39, 475–480. [Google Scholar]
- Dobrydneva, Y.; Williams, R.L.; Morris, G.Z.; Blackmore, P.F. Dietary phytoestrogens and their synthetic structural analogues as calcium channel blockers in human platelets. J. Cardiovasc. Pharm. 2002, 40, 399–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerrero, J.A.; Lozano, M.L.; Castillo, J.; Benavente-Garcia, O.; Vicente, V.; Rivera, A. Flavonoids inhibit platelet function through binding to the thromboxane A(2) receptor. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2005, 3, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, K.; Suzuki, Y.; Ikeda, Y.; Umemura, K. Genistein, an isoflavone included in soy, inhibits thrombotic vessel occlusion in the mouse femoral artery and in vitro platelet aggregation. Eur. J. Pharm. 2002, 455, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choo, M.K.; Park, E.K.; Yoon, H.K.; Kim, D.H. Antithrombotic and antiallergic activities of daidzein, a metabolite of puerarin and daidzin produced by human intestinal microflora. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2002, 25, 1328–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shen, C.; Liu, M.; Xu, R.; Wang, G.; Li, J.; Chen, P.; Ma, W.; Mwangi, J.; Lu, Q.; Duan, Z.; et al. The 14-3-3ζ-c-Src-integrin-β3 complex is vital for platelet activation. Blood 2020, 136, 974–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruggeri, Z.M. Platelet GPIb: Sensing force and responding. Blood J. Am. Soc. Hematol. 2015, 125, 423–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, W.; Deng, W.; Zhou, L.; Xu, Y.; Yang, W.; Liang, X.; Wang, Y.; Kulman, J.D.; Zhang, X.F.; Li, R. Identification of a juxtamembrane mechanosensitive domain in the platelet mechanosensor glycoprotein Ib-IX complex. Blood J. Am. Soc. Hematol. 2015, 125, 562–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, D.; Vanhoorelbeke, K.; Cauwenberghs, N.; Meiring, M.; Depraetere, H.; Kotze, H.F.; Deckmyn, H. Inhibition of the von Willebrand (VWF)–collagen interaction by an antihuman VWF monoclonal antibody results in abolition of in vivo arterial platelet thrombus formation in baboons. Blood J. Am. Soc. Hematol. 2002, 99, 3623–3628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Flood, V.H.; Schlauderaff, A.C.; Haberichter, S.L.; Slobodianuk, T.L.; Jacobi, P.M.; Bellissimo, D.B.; Christopherson, P.A.; Friedman, K.D.; Gill, J.C.; Hoffmann, R.G. Crucial role for the VWF A1 domain in binding to type IV collagen. Blood 2015, 125, 2297–2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Gallant, R.C.; Ni, H. Extracellular matrix proteins in the regulation of thrombus formation. Curr. Opin. Hematol. 2016, 23, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, K.S.; Bodnar, R.; Berndt, M.C.; Du, X.P. A critical role for 14-3-3 zeta protein in regulating the VWF binding function of platelet glycoprotein Ib-IX and its therapeutic implications. Blood 2005, 106, 1975–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fong, K.P.; Zhu, H.; Span, L.M.; Moore, D.T.; Yoon, K.; Tamura, R.; Yin, H.; DeGrado, W.F.; Bennett, J.S. Directly Activating the Integrin alphaIIbbeta3 Initiates Outside-In Signaling by Causing alphaIIbbeta3 Clustering. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 11706–11716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Durrant, T.N.; van den Bosch, M.T.; Hers, I. Integrin alphaIIbbeta3 outside-in signaling. Blood 2017, 130, 1607–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shen, B.; Delaney, M.K.; Du, X. Inside-out, outside-in, and inside-outside-in: G protein signaling in integrin-mediated cell adhesion, spreading, and retraction. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2012, 24, 600–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ni, H.; Freedman, J. Platelets in hemostasis and thrombosis: Role of integrins and their ligands. Transfus. Apher. Sci. 2003, 28, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estevez, B.; Du, X.P. New Concepts and Mechanisms of Platelet Activation Signaling. Physiology 2017, 32, 162–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Su, X.; Mi, J.; Yan, J.; Flevaris, P.; Lu, Y.; Liu, H.; Ruan, Z.; Wang, X.; Kieffer, N.; Chen, S.; et al. RGT, a synthetic peptide corresponding to the integrin beta 3 cytoplasmic C-terminal sequence, selectively inhibits outside-in signaling in human platelets by disrupting the interaction of integrin alpha IIb beta 3 with Src kinase. Blood 2008, 112, 592–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Setchell, K.D.R. The history and basic science development of soy isoflavones. Menopause 2017, 24, 1338–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setchell, K.D.; Zimmer-Nechemias, L.; Cai, J.; Heubi, J.E. Exposure of infants to phyto-oestrogens from soy-based infant formula. Lancet 1997, 350, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setchell, K.D. Soy isoflavones--benefits and risks from nature’s selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs). J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2001, 20, 354S–362S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setchell, K.D.; Brown, N.M.; Zimmer-Nechemias, L.; Brashear, W.T.; Wolfe, B.E.; Kirschner, A.S.; Heubi, J.E. Evidence for lack of absorption of soy isoflavone glycosides in humans, supporting the crucial role of intestinal metabolism for bioavailability. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2002, 76, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Goodman-Gruen, D.; Kritz-Silverstein, D. Usual dietary isoflavone intake is associated with cardiovascular disease risk factors in postmenopausal women. J. Nutr. 2001, 131, 1202–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaiswal, N.; Akhtar, J.; Singh, S.P.; Ahsan, F. An Overview on Genistein and its Various Formulations. Drug Res. 2019, 69, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Axelson, M.; Sjövall, J.; Gustafsson, B.E.; Setchell, K.D. Soya—A dietary source of the non-steroidal oestrogen equol in man and animals. J. Endocrinol. 1984, 102, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiyama, T.; Ogawara, H. Use and specificity of genistein as inhibitor of protein-tyrosine kinases. Methods Enzymol. 1991, 201, 362–370. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cho, M.J.; Liu, J.L.; Pestina, T.I.; Steward, S.A.; Thomas, D.W.; Coffman, T.M.; Wang, D.M.; Jackson, C.W.; Gartner, T.K. The roles Of alpha(IIb)beta(3)-mediated outside-in signal transduction, thromboxane A2, and adenosine diphosphate in collagen-induced platelet aggregation. Blood 2003, 101, 2646–2651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Slusky, J.S.; Berger, B.W.; Walters, R.S.; Vilaire, G.; Litvinov, R.I.; Lear, J.D.; Caputo, G.A.; Bennett, J.S.; DeGrado, W.F. Computational design of peptides that target transmembrane helices. Science 2007, 315, 1817–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van Erp-Baart, M.A.; Brants, H.A.; Kiely, M.; Mulligan, A.; Turrini, A.; Sermoneta, C.; Kilkkinen, A.; Valsta, L.M. Isoflavone intake in four different European countries: The VENUS approach. Br. J. Nutr. 2003, 89, S25–S30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nagata, C.; Wada, K.; Tamura, T.; Konishi, K.; Goto, Y.; Koda, S.; Kawachi, T.; Tsuji, M.; Nakamura, K. Dietary soy and natto intake and cardiovascular disease mortality in Japanese adults: The Takayama study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 105, 426–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, M.; Li, J.; Neves, M.A.D.; Zhu, G.; Carrim, N.; Yu, R.; Gupta, S.; Marshall, J.; Rotstein, O.; Peng, J.; et al. GPIbα is required for platelet-mediated hepatic thrombopoietin generation. Blood 2018, 132, 622–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ware, J.; Russell, S.; Ruggeri, Z.M. Generation and rescue of a murine model of platelet dysfunction: The Bernard-Soulier syndrome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 2803–2808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ware, J.; Russell, S.R.; Marchese, P.; Ruggeri, Z.M. Expression of human platelet glycoprotein Ib alpha in transgenic mice. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 8376–8382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, X.; Reheman, A.; Hou, Y.; Zhou, H.; Wang, Y.M.; Marshall, A.H.; Liang, C.F.; Dai, X.R.; Li, B.X.; Vanhoorelbeke, K.; et al. Anfibatide, a novel GPIb complex antagonist, inhibits platelet adhesion and thrombus formation in vitro and in vivo in murine models of thrombosis. Thromb. Haemost. 2014, 111, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Van Der Wal, D.E.; Zhu, G.; Xu, M.; Yougbare, I.; Ma, L.; Vadasz, B.; Carrim, N.; Grozovsky, R.; Ruan, M. Desialylation is a mechanism of Fc-independent platelet clearance and a therapeutic target in immune thrombocytopenia. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Long, C.; Liu, M.; Tian, H.; Li, Y.; Wu, F.; Mwangi, J.; Lu, Q.; Mohamed Abd El-Aziz, T.; Lai, R.; Shen, C. Potential Role of Platelet-Activating C-Type Lectin-Like Proteins in Viper Envenomation Induced Thrombotic Microangiopathy Symptom. Toxins 2020, 12, 749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, L.; Guo, X.M.; Shen, C.B.; Hao, X.; Sun, P.; Li, P.P.; Xu, T.; Hu, C.M.; Rose, O.; Zhou, H.N.; et al. Salivary factor LTRIN from Aedes aegypti facilitates the transmission of Zika virus by interfering with the lymphotoxin-beta receptor. Nat. Immunol. 2018, 19, 342–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Liu, M.; Tian, H.; Li, J.; Xu, R.; Mwangi, J.; Lu, Q.; Hao, X.; Lai, R. Conformation-Specific Blockade of αIIbβ3 by a Non-RGD Peptide to Inhibit Platelet Activation without Causing Significant Bleeding and Thrombocytopenia. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 120, 1432–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, M.; Wang, G.; Xu, R.; Shen, C.; Ni, H.; Lai, R. Soy Isoflavones Inhibit Both GPIb-IX Signaling and αIIbβ3 Outside-In Signaling via 14-3-3ζ in Platelet. Molecules 2021, 26, 4911. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26164911
Liu M, Wang G, Xu R, Shen C, Ni H, Lai R. Soy Isoflavones Inhibit Both GPIb-IX Signaling and αIIbβ3 Outside-In Signaling via 14-3-3ζ in Platelet. Molecules. 2021; 26(16):4911. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26164911
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Ming, Gan Wang, Runjia Xu, Chuanbin Shen, Heyu Ni, and Ren Lai. 2021. "Soy Isoflavones Inhibit Both GPIb-IX Signaling and αIIbβ3 Outside-In Signaling via 14-3-3ζ in Platelet" Molecules 26, no. 16: 4911. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26164911
APA StyleLiu, M., Wang, G., Xu, R., Shen, C., Ni, H., & Lai, R. (2021). Soy Isoflavones Inhibit Both GPIb-IX Signaling and αIIbβ3 Outside-In Signaling via 14-3-3ζ in Platelet. Molecules, 26(16), 4911. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26164911






