Protective Effects of Gintonin on Reactive Oxygen Species-Induced HT22 Cell Damages: Involvement of LPA1 Receptor-BDNF-AKT Signaling Pathway
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
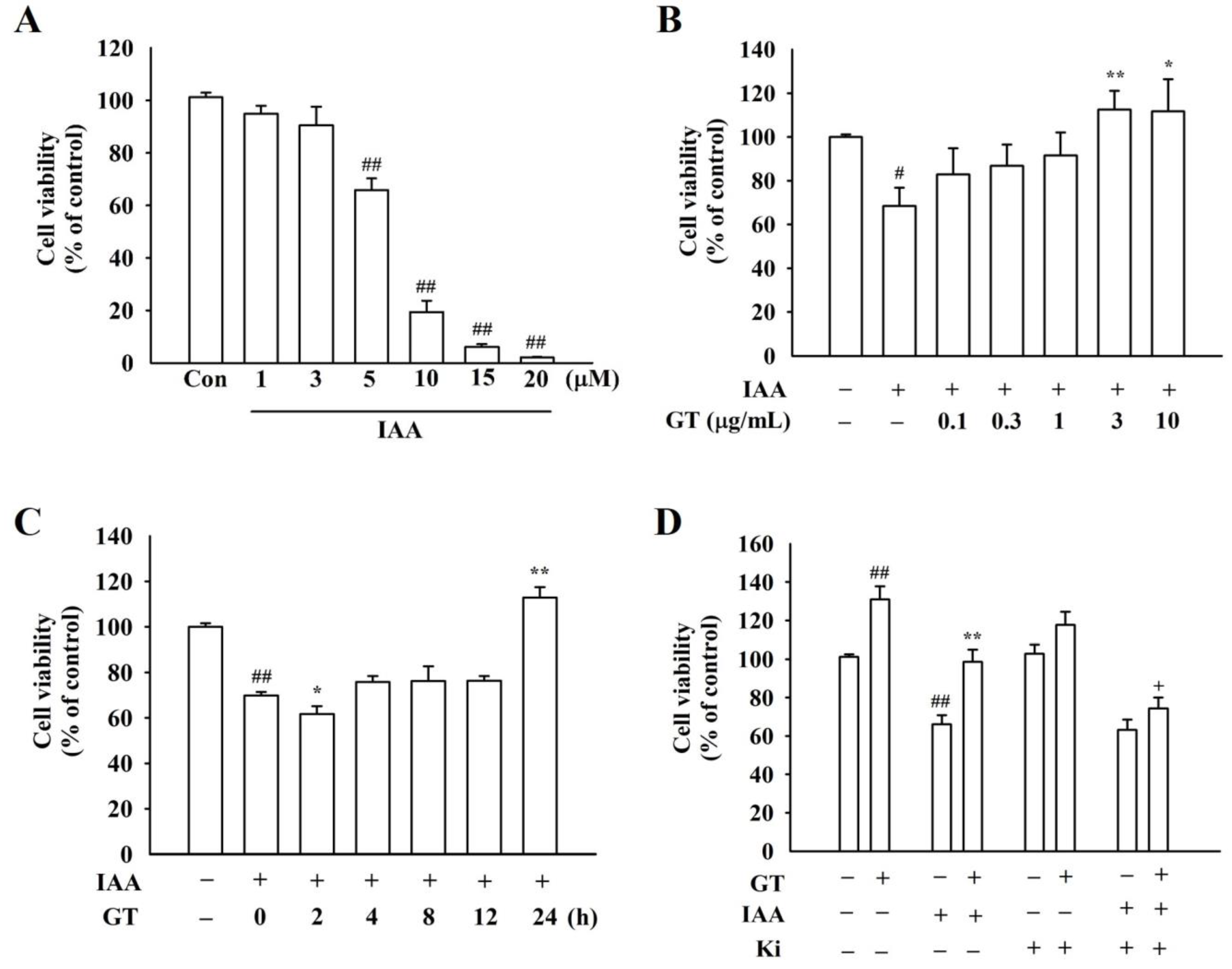
2.1. Gintonin Attenuates IAA-Induced Cell Damages in HT22 Cells
2.2. Gintonin Suppresses IAA-Induced ROS Production
2.3. Gintonin Prevents against IAA-Induced ATP Depletion
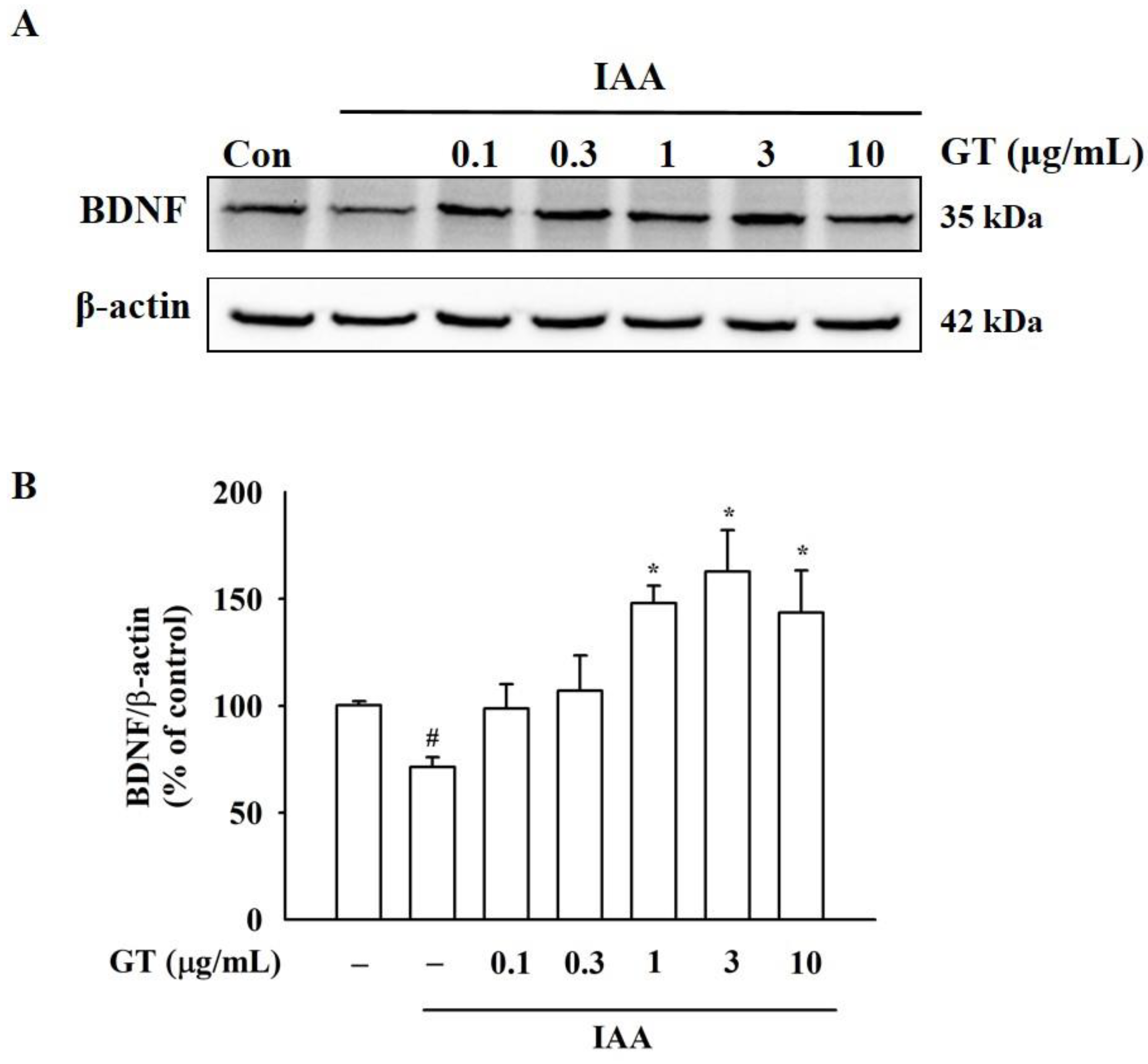
2.4. Gintonin Increases BDNF Expression under IAA Insult
2.5. Gintonin Induces [Ca2+]i Transients and Its Signal Transduction Pathway
2.6. Gintonin Ameliorates IAA-Induced Inhibition of BDNF Release
2.7. Gintonin Stimulates the TrkB/Akt Signaling Pathway through BDNF Release
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Gintonin Preparation from Ginseng
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. Measurement of Cell Viability
4.4. Measurement of Intracellular ROS Levels
4.5. Measurement of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) Release Concentration from HT22 Cells
4.6. Measurement of Phosphorylation of TrkB Receptors in HT22 Cells
4.7. Western Blot Analysis
4.8. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Choi, K.T. Botanical characteristics, pharmacological effects and medicinal components of Korean Panax ginseng C A Meyer. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2008, 29, 1109–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Choi, S.H.; Jung, S.W.; Lee, B.H.; Kim, H.J.; Hwang, S.H.; Kim, H.K.; Nah, S.Y. Ginseng pharmacology: A new paradigm based on gintonin-lysophosphatidic acid receptor interactions. Front. Pharmacol. 2015, 6, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Im, D.S. Pro-resolving effect of ginsenosides as an anti-Inflammatory mechanism of Panax ginseng. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, S.J.; In, G.; Han, S.T.; Lee, M.H.; Lee, J.W.; Shin, K.S. Structural characteristics of a red ginseng acidic polysaccharide rhamnogalacturonan I with immunostimulating activity from red ginseng. J. Ginseng Res. 2020, 44, 570–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pyo, M.K.; Choi, S.H.; Shin, T.J.; Hwang, S.H.; Lee, B.H.; Kang, J.Y.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, S.H.; Nah, S.Y. A simple method for the preparation of crude gintonin from ginseng root, stem, and leaf. J. Ginseng Res. 2011, 35, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cho, H.-J.; Choi, S.-H.; Kim, H.-J.; Lee, B.-H.; Rhim, H.; Kim, H.-C.; Hwang, S.-H.; Nah, S.-Y. Bioactive lipids in gintonin-enriched fraction from ginseng. J. Ginseng Res. 2019, 43, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, S.H.; Shin, T.J.; Choi, S.H.; Cho, H.J.; Lee, B.H.; Pyo, M.K.; Lee, J.H.; Kang, J.; Kim, H.J.; Park, C.W.; et al. Gintonin, newly identified compounds from ginseng, is novel lysophosphatidic acids-protein complexes and activates G protein-coupled lysophosphatidic acid receptors with high affinity. Mol. Cells 2012, 33, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yung, Y.C.; Stoddard, N.C.; Chun, J. Thematic review series: Lysophospholipids and their receptor LPA receptor signaling: Pharmacology, physiology, and pathophysiology. J. Lipid Res. 2014, 55, 1192–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hwang, S.H.; Lee, B.H.; Choi, S.H.; Kim, H.J.; Jung, S.W.; Kim, H.S.; Shin, H.C.; Park, H.J.; Park, K.H.; Lee, M.K.; et al. Gintonin, a novel ginseng-derived lysophosphatidic acid receptor ligand, stimulates neurotransmitter release. Neurosci. Lett. 2015, 584, 356–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.H.; Lee, R.M.; Nam, S.M.; Kim, D.G.; Cho, I.H.; Kim, H.C.; Cho, Y.J.; Rhim, H.W.; Nah, S.Y. Ginseng gintonin, aging societies and geriatric brain diseases. Integr. Med. Res. 2021, 10, 100450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoyer, S.; Krier, C. Ischemia and aging brain—Studies on glucose and energy metabolism in rat cerebral cortex. Neurobiol. Aging 1986, 7, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maher, P.; Salgado, K.F.; Zivin, J.A.; Lapchak, P.A. A novel approach to screening for new neuroprotective compounds for the treatment of stroke. Brain Res. 2007, 1173, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lipton, P. Ischemic cell death in brain neurons. Physiol. Rev. 1999, 79, 1431–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.H.; Zhu, L.J.; Wang, L.; Guo, B.J.; Zhang, G.X.; Sun, Y.W.; Zhang, Z.J.; Lee, S.M.Y.; Yu, P.; Wang, Y.Q. Protective effect of Edaravone in primary cerebellar granule neurons against iodoacetic acid-induced cell injury. Oxidative Med. Cell Longev. 2015, 2015, 606981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, R.M.; Lee, N.E.; Choi, S.H.; Nam, S.M.; Kim, H.C.; Rhim, H.W.; Cho, I.H.; Hang, S.H.; Nah, S.Y. Effects of gintonin-enriched fraction on hippocampal gene expressions. Integr. Med. Res. 2020, 10, 100475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, M.; Zou, W.; Wang, C.Y.; Chen, X.; Tan, H.Y.; Zeng, H.Y.; Zhang, P.; Gu, H.F.; Tang, X.Q. Hydrogen sulfide protects against chronic unpredictable mild stress-induced oxidative stress in hippocampus by upregulation of BDNF-TrkB pathway. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 2153745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, J.B.; Maher, P. Protein kinase C activation inhibits glutamate-induced cytotoxicity in neuronal cell line. Brain Res. 1994, 652, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olianas, M.C.; Dedoni, S.; Onali, P. LPA 1 is a key mediator of intracellular signaling and neuroprotection triggered by tetracyclic antidepressants in hippocampal neurons. J. Neurochem. 2017, 143, 183–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sung, J.Y.; Bae, J.H.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, Y.N.; Kim, D.K. The melatonin signaling pathway in a long-term memory in vitro study. Molecules 2018, 23, 737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, S.P.; Li, W.J.; Winters, A.; Liu, R.; Yang, S.H. Artemisinin prevents glutamate-induced neuronal cell death via Akt pathway activation. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sommerburg, O.; Karius, N.; Siems, W.; Langhans, C.D.; Leichsenring, M.; Breusing, N.; Grune, T. Proteasomal degradation of beta-carotene metabolite—Modified proteins. BioFactors 2009, 35, 449–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanatos, R.; Sanz, A. The role of mitochondrial ROS in the aging brain. FEBS Lett. 2018, 592, 743–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eguchi, Y.; Shimizu, S.; Tsujimoto, Y. Intracellular ATP levels determine cell death fate by apoptosis or necrosis. Cancer Res. 1997, 57, 1835–1840. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, R.L.; Lai, U.H.; Zhu, L.L.; Singh, A.; Ahmed, M.; Forsyth, N.R. Reactive oxygen species formation in brain at different oxygen levels: The role of hypoxia inducible factors. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2018, 6, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gandhi, S.; Abramov, A.Y. Mechanism of oxidative stress in neurodegeneration. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2012, 2012, 428010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, H.J.; Kim, D.J.; Shin, E.J.; Lee, B.H.; Choi, S.H.; Hwang, S.H.; Rhim, H.; Cho, I.H.; Kim, H.C.; Nah, S.Y. Effects of gintonin-enriched fraction on hippocampal cell proliferation in wild-type mice and an APPswe/PSEN-1 double Tg mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurochem. Int. 2016, 101, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, R.; Lee, N.E.; Hwang, H.; Rhim, H.; Cho, I.H.; Nah, S.Y. Ginseng Gintonin Enhances Hyaluronic Acid and Collagen Release from Human Dermal Fibroblasts Through Lysophosphatidic Acid Receptor Interaction. Molecules 2019, 24, 4438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herr, D.R.; Chew, W.S.; Satish, R.L.; Ong, W.Y. Pleotropic Roles of Autotaxin in the Nervous System Present Opportunities for the Development of Novel Therapeutics for Neurological Diseases. Mol. Neurobiol. 2020, 57, 372–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amidfar, M.; de Oliveira, J.; Kucharska, E.; Budni, J.; Kim, Y.K. The role of CREB and BDNF in neurobiology and treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Life Sci. 2020, 257, 118020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, X.; Finkbeiner, S.; Arnold, D.B.; Shaywitz, A.J.; Greenberg, M.E. Ca2+ influx regulates BDNF transcription by a CREB family transcription factor-dependent mechanism. Neuron 1998, 20, 709–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, B.D.; Yoo, J.M.; Baek, S.Y.; Li, F.Y.; Sok, D.E.; Kim, M.R. 3, 3′-diindolylmethane promotes BDNF and antioxidant enzyme formation via TrkB/Akt pathway activation for neuroprotection against oxidative stress-induced apoptosis in hippocampal neuronal cells. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoo, J.M.; Lee, B.D.; Sok, D.E.; Ma, J.Y.; Kim, M.R. Neuroprotective action of N-acetyl serotonin in oxidative stress-induced apoptosis through the activation of both TrkB/CREB/BDNF pathway and Akt/Nrf2/Antioxidant enzyme in neuronal cells. Redox Biol. 2017, 11, 592–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikram, M.; Jo, M.G.; Park, T.J.; Kim, M.W.; Khan, I.; Jo, M.H.; Kim, M.O. Oral Administration of Gintonin Protects the Brains of Mice against Aβ-Induced Alzheimer Disease Pathology: Anti-oxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Effects. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 10, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, M.G.; Ikram, M.; Jo, M.H.; Yoo, L.; Chung, K.C.; Nah, S.Y.; Hwang, S.H.; Rhim, H.; Kim, M.O. Gintonin Mitigates MPTP-Induced Loss of Nigrostriatal Dopaminergic Neurons and Accumulation of α-Synuclein via the Nrf2/HO-1 Pathway. Mol. Neurobiol. 2019, 56, 39–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, M.; Choi, J.H.; Chang, Y.; Lee, S.J.; Nah, S.Y.; Cho, I.H. Gintonin, a ginseng-derived ingredient, as a novel therapeutic strategy for Huntington’s disease: Activation of the Nrf2 pathway through lysophosphatidic acid receptors. Brain Behav. Immun. 2019, 80, 146–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Du, J.J.; Pan, Y.; Chen, T.T.; Zhao, L.H.; Zhu, Y.M.; Chen, Y.F.; Zheng, Y.Y.; Liu, Y.; Sun, L.H.; et al. Activation of cardiac TrkB receptor by its small molecular agonist 7, 8-dihydroxyflavone inhibits doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity via enhancing mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2019, 130, 557–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hang, P.Z.; Zhao, J.; Sun, L.; Li, M.H.; Han, Y.; Du, Z.M.; Li, Y. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor attenuates doxorubicin-induced cardiac dysfunction through activating Akt signaling in rats. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2017, 21, 685–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gan, Z.R.; Wells, W.W. Preparation of homogeneous pig liver thioltransferase by a thioldisulfide mediated pI shift. Anal. Biochem. 1987, 162, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, K.; Sha, Y.; Mo, Y.; Wei, S.; Wu, H.; Lu, D.; Xia, Y.; Yang, Q.; Zheng, W.; Wei, X. Androgenic and Teratogenic Effects of Iodoacetic Acid Drinking Water Disinfection Byproduct in vitro and in vivo. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 3827–3835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cho, Y.-J.; Choi, S.-H.; Lee, R.-M.; Cho, H.-S.; Rhim, H.; Kim, H.-C.; Kim, B.-J.; Kim, J.-H.; Nah, S.-Y. Protective Effects of Gintonin on Reactive Oxygen Species-Induced HT22 Cell Damages: Involvement of LPA1 Receptor-BDNF-AKT Signaling Pathway. Molecules 2021, 26, 4138. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26144138
Cho Y-J, Choi S-H, Lee R-M, Cho H-S, Rhim H, Kim H-C, Kim B-J, Kim J-H, Nah S-Y. Protective Effects of Gintonin on Reactive Oxygen Species-Induced HT22 Cell Damages: Involvement of LPA1 Receptor-BDNF-AKT Signaling Pathway. Molecules. 2021; 26(14):4138. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26144138
Chicago/Turabian StyleCho, Yeon-Jin, Sun-Hye Choi, Ra-Mi Lee, Han-Sung Cho, Hyewhon Rhim, Hyoung-Chun Kim, Byung-Joo Kim, Jong-Hoon Kim, and Seung-Yeol Nah. 2021. "Protective Effects of Gintonin on Reactive Oxygen Species-Induced HT22 Cell Damages: Involvement of LPA1 Receptor-BDNF-AKT Signaling Pathway" Molecules 26, no. 14: 4138. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26144138
APA StyleCho, Y.-J., Choi, S.-H., Lee, R.-M., Cho, H.-S., Rhim, H., Kim, H.-C., Kim, B.-J., Kim, J.-H., & Nah, S.-Y. (2021). Protective Effects of Gintonin on Reactive Oxygen Species-Induced HT22 Cell Damages: Involvement of LPA1 Receptor-BDNF-AKT Signaling Pathway. Molecules, 26(14), 4138. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26144138







