Biological Insights of Fluoroaryl-2,2′-Bichalcophene Compounds on Multi-Drug Resistant Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Antimicrobial Activity of the Tested Aryl-2,2′-Bichalcophene Derivatives
2.2. Minimum Inhibitory Concentrations (MIC) of the Tested Fluoroaryl-2,2′-Bichalcophene Derivatives
2.3. Structure-Activity Relationship (SAR)
2.4. Detection of the Tested Fluoroaryl-2,2′-Bichalcophenes-Resistant Variants
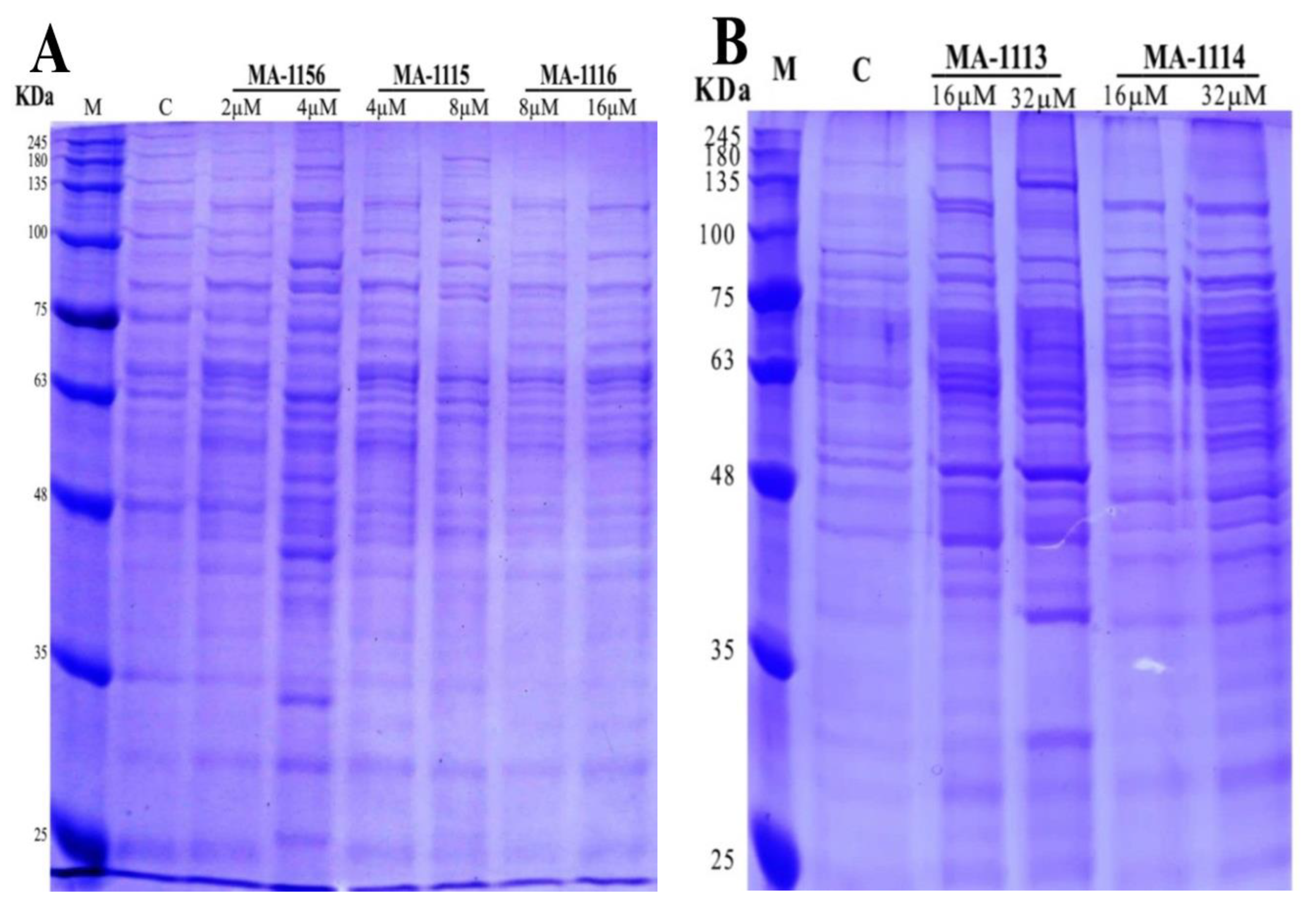
2.5. Effect of Fluoroarylbichalcophenes on S. aureus Protein Pattern
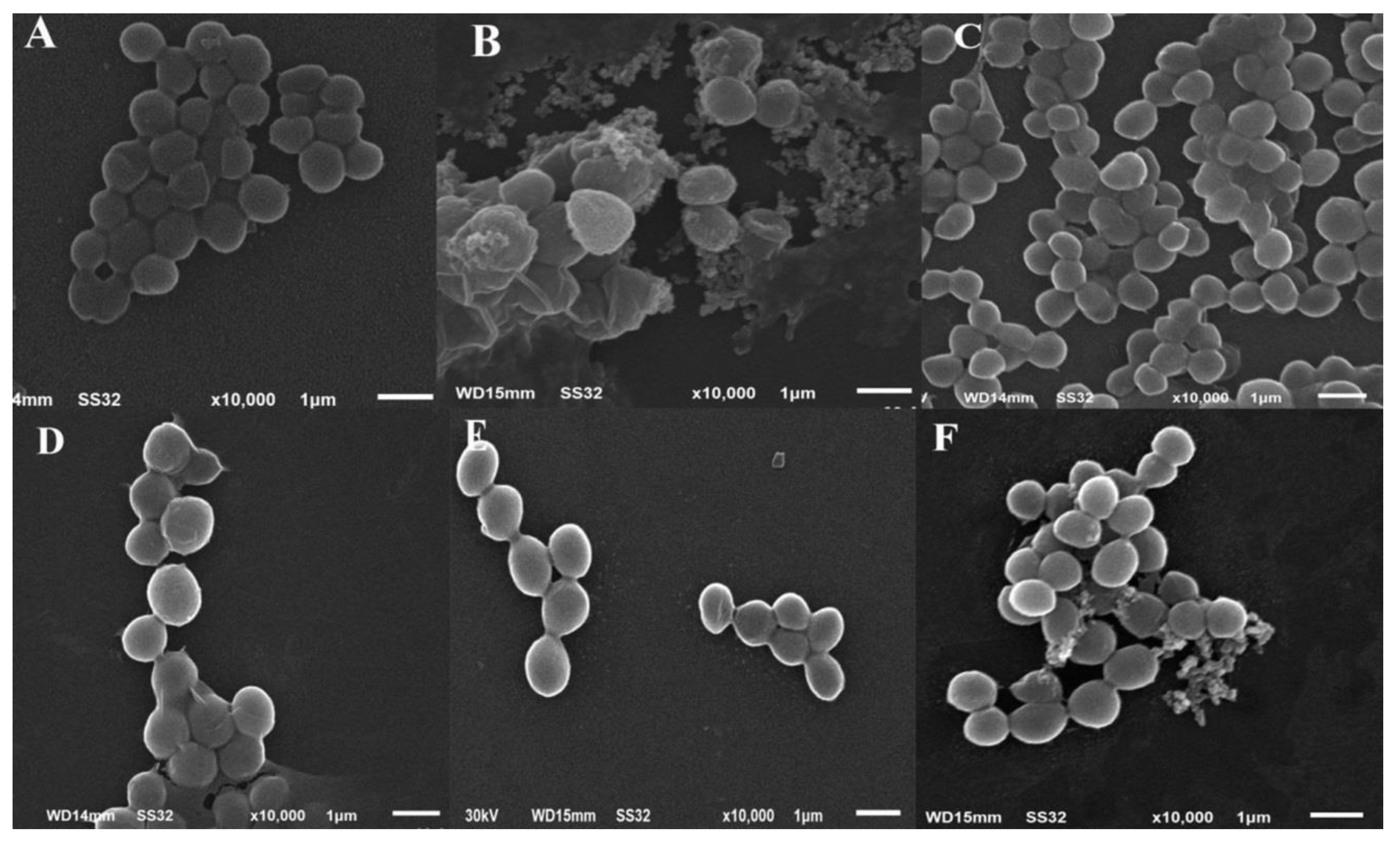
2.6. Changes in Cellular Ultrastructure of S. aureus Treated with One Sub-MIC of Fluoroarylbichalcophenes
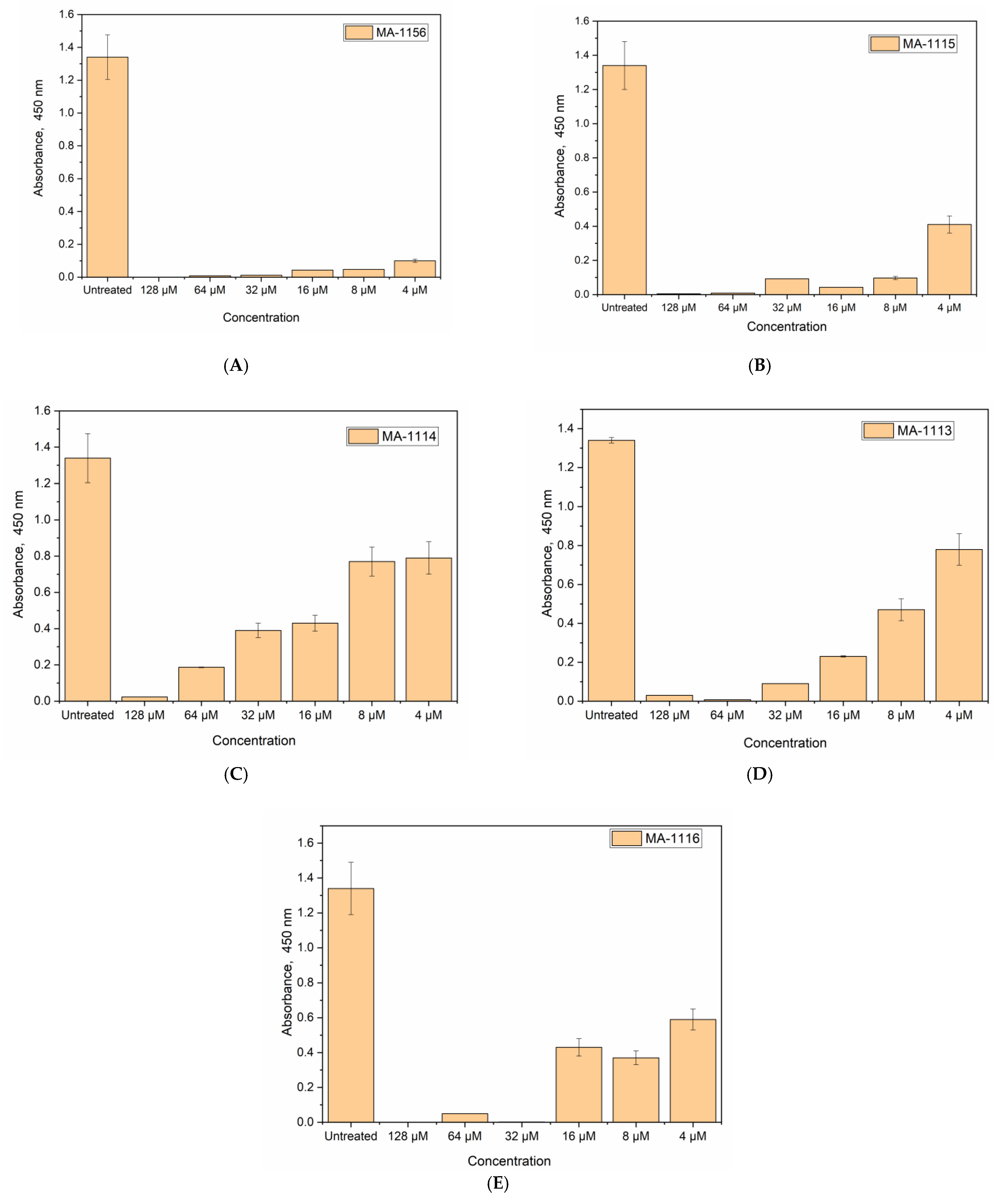
2.7. Cell Viability Determination Using WST-1 Reagent
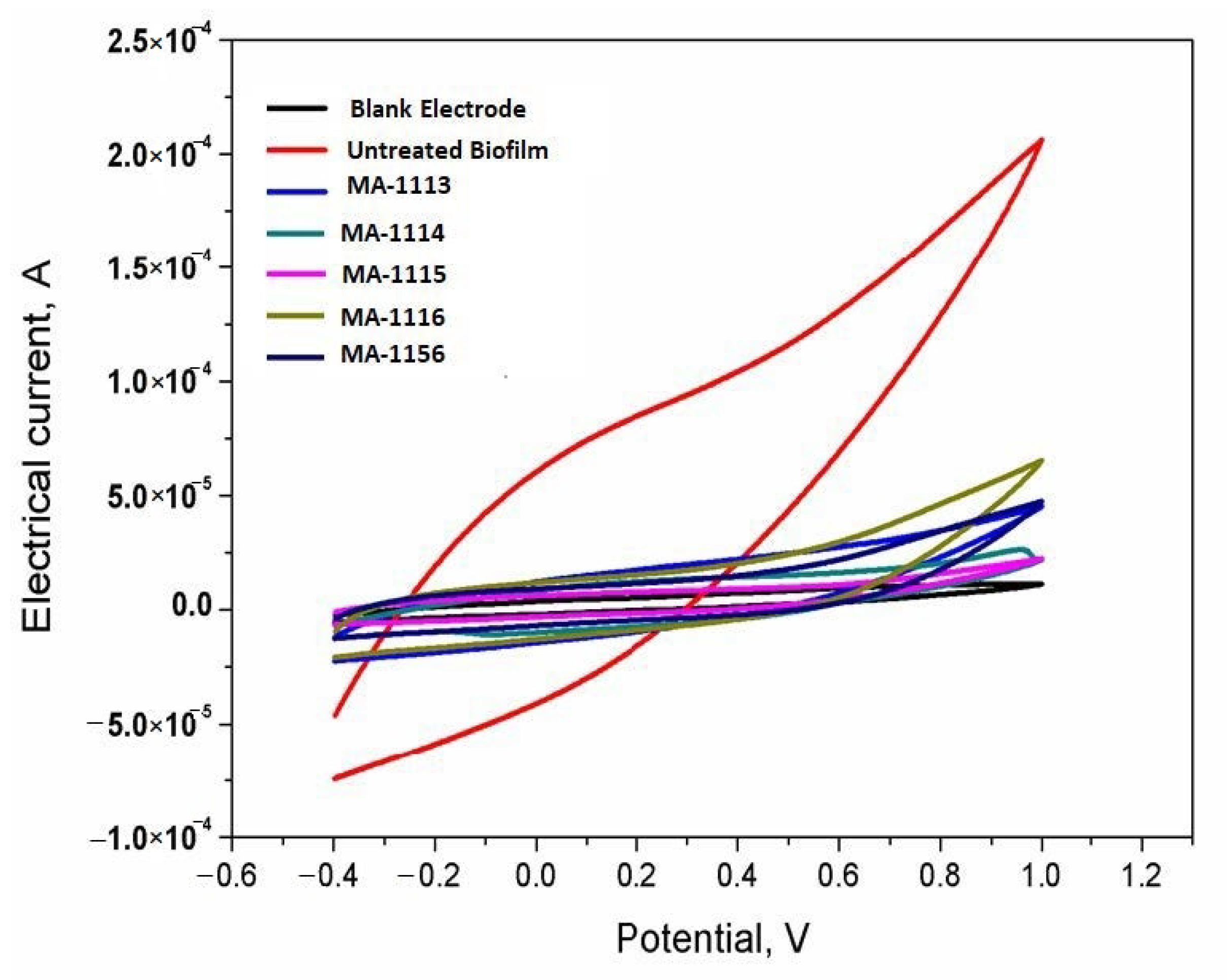
2.8. Sensing the Response of S. aureus Biofilms
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Tested Bichalcophene Derivatives and Bacteria
4.2. Detecting the Antimicrobial Activity of the Tested 2,2′-Bichalcophene Derivatives
4.3. Determination of MIC of the Tested 2,2′-Bichalcophene Derivatives
4.4. Detection of Fluoroaryl-2,2′-Bichalcophenes-Resistant Variants
4.5. SDS-PAGE of S. aureus
4.6. SEM
4.7. Cell Viability Determination Using WST-1 Reagent
4.8. Bioelectrochemical Measurements
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Trémolières, F.J.M. When the antibiotic miracle turns into a nightmare. Med. Sci. 2010, 26, 925–929. [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy, B.; O’Connor, B.; Korn, B.; Lyons, O.; Gargoum, F.; Gibbons, N.; O’Connor, T.; Keane, J. Multi-drug Resistant Tuberculosis; Early Experiences of Two Irish Tertiary Referral Centres. Ir. Med. J. 2011, 26, 925–929. [Google Scholar]
- Kutty, N. Treating Children without Antibiotics in Primary Healthcare. Oman Med. J. 2011, 26, 303–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsayed, A.; Mohamedin, A.; Ata, T.; Ghazala, N. Molecular characterization of multidrug resistant clinical Escherichia coli isolates. Am. J. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2016, 6, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitaku, E.; Smith, D.T.; Njardarson, J.T. Analysis of the structural diversity, substitution patterns, and frequency of nitrogen heterocycles among us FDA approved pharmaceuticals: Miniperspective. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 10257–10274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, M.; El-Sayed, W.; Shaaban, S.; Abdelwahab, G.; Hamama, W. A Review of Cationic Arylfurans and Their Isosteres: Synthesis and Biological Importance. Curr. Org. Chem. 2019, 23, 2751–2782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, M.A.; Negm, A.; Arafa, R.K.; Abdel-Latif, E.; El-Sayed, W.M. Anticancer activity, dual prooxidant/antioxidant effect and apoptosis induction profile of new bichalcophene-5-carboxamidines. Eur. J. Med.Chem. 2019, 169, 76–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boschi, D.; Guglielmo, S.; Aiello, S.; Morace, G.; Borghi, E.; Fruttero, R.J. Synthesis and in vitro antimicrobial activities of new (cyano-NNO-azoxy) pyrazole derivatives. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2011, 21, 3431–3434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- El-Sayed, W.M.; Hussin, W.A.; Ismail, M.A. Efficacy of two novel 2,2′-bifurans to inhibit methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infection in male mice in comparison to vancomycin. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2012, 6, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Youssef, M.M.; Al-Omair, M.A.; Ismail, M.A. Synthesis, DNA affinity, and antimicrobial activity of 4-substituted phenyl-2,2′-bichalcophenes and aza-analogues. Med. Chem. Res. 2012, 21, 4074–4082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussin, W.A.; Ismail, M.A.; El-Sayed, W.M. Novel 4-substituted phenyl-2,2′-bichalcophenes and aza-analogs as antibacterial agents: A structural activity relationship. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2013, 7, 185–193. [Google Scholar]
- Hussin, W.A.; Ismail, M.A.; Alzahrani, A.M.; El-Sayed, W.M. Evaluation of the biological activity of novel monocationic fluoroaryl-2,2′-bichalcophenes and their analogues. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2014, 8, 963–972. [Google Scholar]
- Ismail, M.A.; Arafa, R.K.; Youssef, M.M.; El-Sayed, W.M. Anticancer, antioxidant activities, and DNA affinity of novel monocationic bithiophenes and analogues. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2014, 8, 1659–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, B.K.; Kitteringham, N.R.; O’Neill, P.M. Metabolism of fluorine-containing drugs. Ann. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2001, 41, 443–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, T.-A.; Hakura, A.; Mizutani, T.; Saeki, K.-I. Anti-mutagenic structural modification by fluorine-substitution in highly mutagenic 4-methylquinoline derivatives. Mutat. Res. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 2000, 465, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamond, L.; Cherian, K.; Harvey, R.G.; DiGiovanni, J. Mutagenic activity of methyl-and fluoro-substituted derivatives of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in a human hepatoma (HepG2) cell-mediated assay. Mutat. Res. Genet. Toxicol. 1984, 136, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirao, K.; Shinohara, Y.; Tsuda, H.; Fukushima, S.; Takahashi, M. Carcinogenic activity of quinoline on rat liver. Cancer Res. 1976, 36, 329–335. [Google Scholar]
- Shinohara, Y.; Ogiso, T.; Hananouchi, M.; Nakanishi, K.; Yoshimura, T.; Ito, N. Effect of various factors on the induction of liver tumors in animals by quinoline. GANN Jpn. J. Cancer Res. 1977, 68, 785–796. [Google Scholar]
- Nagao, M.; Yahagi, T.; Seino, Y.; Sugimura, T.; Ito, N. Mutagenicities of quinoline and its derivatives. Mutat. Res. Mol. Mech. Mutagen. 1977, 42, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamiya, M.; Sengoku, Y.; Takahashi, K.; Kohda, K.; Kawazoe, Y. Antimutagenic structure modification of quinoline: Fluorine-substitution at position-3. In Antimutagenesis and Anticarcinogenesis Mechanisms II; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1990; pp. 441–446. [Google Scholar]
- Miyata, Y.; Saeki, K.-i.; Kawazoe, Y.; Hayashi, M.; Sofuni, T.; Suzuki, T. Antimutagenic structural modification of quinoline assessed by an in vivo mutagenesis assay using lacZ-transgenic mice. Mutat. Res. Genet. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 1998, 414, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.-P.; He, X.-B.; Peng, Z.-Y.; Xiong, T.-J.; Peng, J.; Chen, L.-H.; Zhu, H. Synthesis, structure, molecular docking, and structure–activity relationship analysis of enamines: 3-Aryl-4-alkylaminofuran-2(5H)-ones as potential antibacterials. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2011, 19, 1571–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thebault, P.; De Givenchy, E.T.; Levy, R.; Vandenberghe, Y.; Guittard, F.; Géribaldi, S. Preparation and antimicrobial behaviour of quaternary ammonium thiol derivatives able to be grafted on metal surfaces. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 44, 717–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, K.; Nishida, S.; Sontag, E.D.; Cluzel, P. Mechanism-independent method for predicting response to multidrug combinations in bacteria. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 12254–12259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DiMagno, S.G.; Sun, H. The strength of weak interactions: Aromatic fluorine in drug design. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2006, 6, 1473–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abousalem, A.S.; Ismail, M.A.; Fouda, A.S. A complementary experimental and in silico studies on the action of fluorophenyl-2, 2′-bichalcophenes as ecofriendly corrosion inhibitors and biocide agents. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 276, 255–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biffinger, J.C.; Kim, H.W.; DiMagno, S.G. The polar hydrophobicity of fluorinated compounds. ChemBioChem 2004, 5, 622–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paulsen, I.T.; Brown, M.H.; Skurray, R.A. Proton-dependent multidrug efflux systems. Microbiol. Rev. 1996, 60, 575–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lolkema, J.S.; Poolman, B.; Konings, W.N. Bacterial solute uptake and efflux systems. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 1998, 1, 248–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikaido, H. Multiple antibiotic resistance and efflux. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 1998, 1, 516–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, P.-C.; Siegel, S.A.; Rogers, B.; Davis, D.; Lewis, K. Bacteria lacking a multidrug pump: A sensitive tool for drug discovery. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 6602–6606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, K. Multidrug resistance: Versatile drug sensors of bacterial cells. Curr. Biol. 1999, 9, R403–R407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillai, S.P.; Pillai, C.A.; Shankel, D.M.; Mitscher, L.A.J.M.R.G.T.; Mutagenesis, E. The ability of certain antimutagenic agents to prevent development of antibiotic resistance. Mutat. Res. Genet. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 2001, 496, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenwood, D.; O’Grady, F. Scanning Electron Microscopy of Staphylococcus aureus Exposed to Some Common Anti-staphylococcal Agents. J. Gen. Microbiol. 1972, 70, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Booyens, J.; Labuschagne, M.C.; Thantsha, M.S. In Vitro Antibacterial Mechanism of Action of Crude Garlic (Allium sativum) Clove Extract on Selected Probiotic Bifidobacterium Species as Revealed by SEM, TEM, and SDS-PAGE Analysis. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2014, 6, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, I.P.; Chopra, K.; Saini, A. Probiotics: Potential pharmaceutical applications. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2002, 15, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Depauw, S.; Lambert, M.; Jambon, S.; Paul, A.; Peixoto, P.; Nhili, R.; Marongiu, L.; Figeac, M.; Dassi, C.; Paul-Constant, C.; et al. Heterocyclic Diamidine DNA Ligands as HOXA9 Transcription Factor Inhibitors: Design, Molecular Evaluation, and Cellular Consequences in a HOXA9-Dependant Leukemia Cell Model. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 1306–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nhili, R.; Peixoto, P.; Depauw, S.; Flajollet, S.; Dezitter, X.; Munde, M.M.; Ismail, M.A.; Kumar, A.; Farahat, A.A.; Stephens, C.E.; et al. Targeting the DNA-binding activity of the human ERG transcription factor using new heterocyclic dithiophene diamidines. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, R.Y.A.; Bilitewski, U. Direct electrochemical determination of Candida albicans activity. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 49, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khater, D.Z.; El-Khatib, K.M.; Hazaa, M.M.; Hassan, R.Y.A. Development of Bioelectrochemical System for Monitoring the Biodegradation Performance of Activated Sludge. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2015, 175, 3519–3530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, R.Y.A.; Bilitewski, U. A viability assay for Candida albicans based on the electron transfer mediator 2,6-dichlorophenolindophenol. Anal. Biochem. 2011, 419, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedki, M.; Hassan, R.Y.A.; Andreescu, S.; El-Sherbiny, I.M. Online-monitoring of biofilm formation using nanostructured electrode surfaces. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 100, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, D.F.; Mahmood, M.B. Biosynthesis of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Using Escherichia coli. Iraqi J. Sci. 2019, 453–459. [Google Scholar]
- Bauer, A.; Kirby, W.; Sherris, J.; Tursk, M. Antibiotic susceptibility testing by a standardized single disc method. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 1966, 45, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Methods for Dilution Antimicrobial Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria that Grow Aerobically: Approved Standard; M7–A7; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Soliman, H.; Elsayed, A.; Dyaa, A. Antimicrobial activity of silver nanoparticles biosynthesised by Rhodotorula sp. strain ATL72. Egypt. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2018, 5, 228–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, M.; Berditsch, M.; Hawecker, J.; Ardakani, M.F.; Gerthsen, D.; Ulrich, A.S. Damage of the Bacterial Cell Envelope by Antimicrobial Peptides Gramicidin S and PGLa as Revealed by Transmission and Scanning Electron Microscopy. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 3132–3142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosmann, T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: Application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J. Immunol. Methods 1983, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, D.M.; Balkis, M.; Chandra, J.; Mukherjee, P.K.; Ghannoum, M.A. Uses and Limitations of the XTT Assay in Studies of Candida Growth and Metabolism. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2003, 41, 506–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedki, M.; Hefnawy, A.; Hassan, R.Y.A.; El-Sherbiny, I.M. Core-shell hyperbranched chitosan nanostructure as a novel electrode modifier. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 93, 543–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

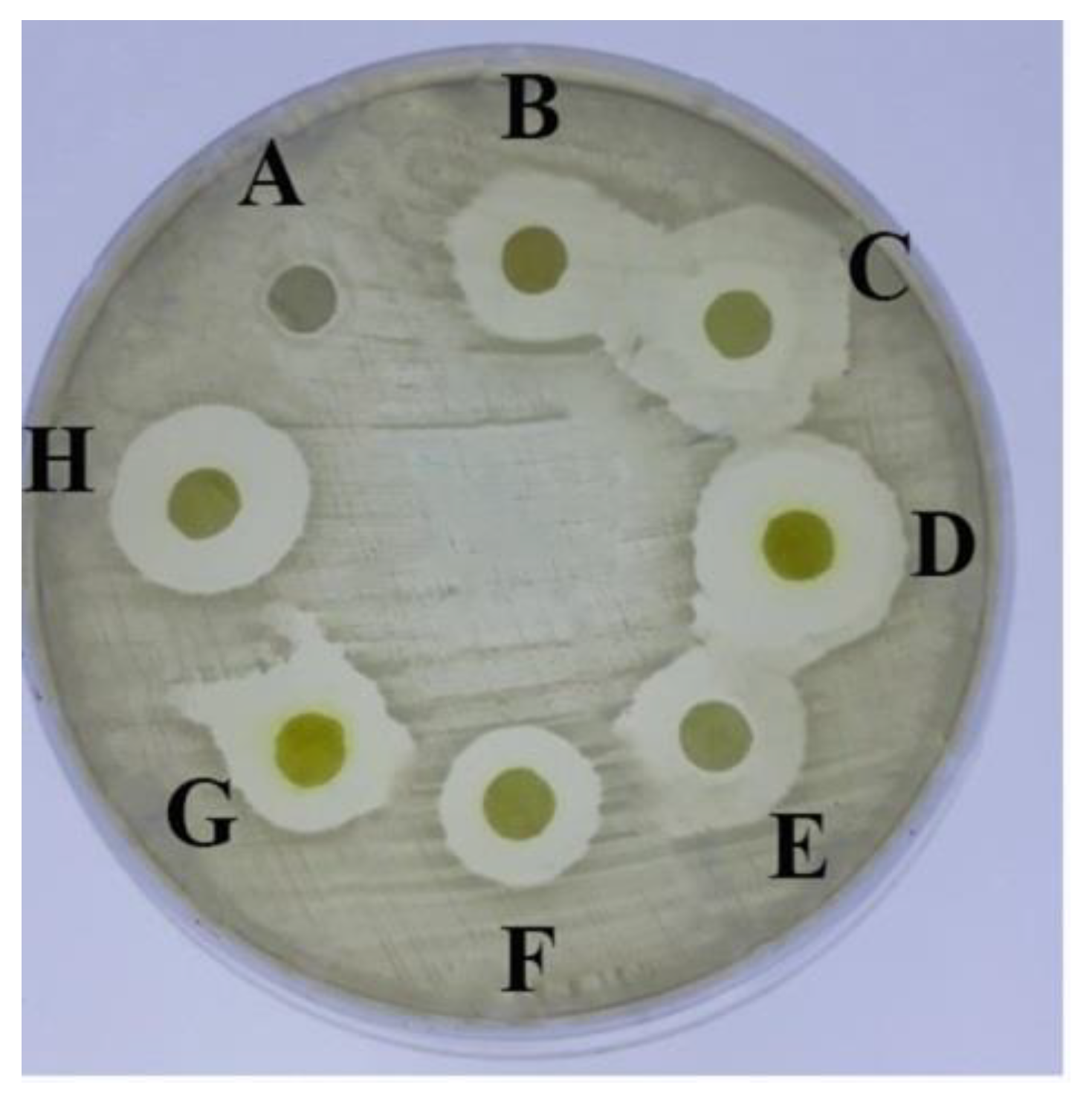

| Tested Compound (10 mM) | Inhibition Zone Diameter (mm) |
|---|---|
| MA-0944 (1a) | 14 ± 0.2 |
| MA-0947 (1b) | 15.5 ± 0.0 |
| MA-1156 (1c) | 15 ± 0.2 |
| MA-1115 (1d) | 20 ± 0.2 |
| MA-1116 (1e) | 16 ± 0.2 |
| MA-1113 (1f) | 16 ± 0.1 |
| MA-1114 (1g) | 20 ± 0.2 |
| Compound | MIC (µM) | MBC |
|---|---|---|
| MA-0944 (1a) | 128 | not detected |
| MA-0947 (1b) | 128 | not detected |
| MA-1156 (1c) | 16 | 16 |
| MA-1115 (1d) | 32 | 32 |
| MA-1116 (1e) | 64 | 128 |
| MA-1113 (1f) | 128 | 128 |
| MA-1114 (1g) | 128 | 128 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Elmogy, S.; Ismail, M.A.; Hassan, R.Y.A.; Noureldeen, A.; Darwish, H.; Fayad, E.; Elsaid, F.; Elsayed, A. Biological Insights of Fluoroaryl-2,2′-Bichalcophene Compounds on Multi-Drug Resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Molecules 2021, 26, 139. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26010139
Elmogy S, Ismail MA, Hassan RYA, Noureldeen A, Darwish H, Fayad E, Elsaid F, Elsayed A. Biological Insights of Fluoroaryl-2,2′-Bichalcophene Compounds on Multi-Drug Resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Molecules. 2021; 26(1):139. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26010139
Chicago/Turabian StyleElmogy, Sally, Mohamed A. Ismail, Rabeay Y. A. Hassan, Ahmed Noureldeen, Hadeer Darwish, Eman Fayad, Fahmy Elsaid, and Ashraf Elsayed. 2021. "Biological Insights of Fluoroaryl-2,2′-Bichalcophene Compounds on Multi-Drug Resistant Staphylococcus aureus" Molecules 26, no. 1: 139. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26010139
APA StyleElmogy, S., Ismail, M. A., Hassan, R. Y. A., Noureldeen, A., Darwish, H., Fayad, E., Elsaid, F., & Elsayed, A. (2021). Biological Insights of Fluoroaryl-2,2′-Bichalcophene Compounds on Multi-Drug Resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Molecules, 26(1), 139. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26010139








