Proteomic Analysis of Proteins Responsive to Drought and Low Temperature Stress in a Hard Red Spring Wheat Cultivar
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Glutenin Subunits Extraction and 2D Electrophoretic Analysis
4.2. Protein Staining, Image Acquisition and Gel Spots Excision
4.3. In-gel Digestion and Mass Spectrometric Analysis
4.4. Database Search and Protein Identification
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Buts, K.; Michielssens, S.; Hertog, M.L.A.T.M.; Hayakawa, E.; Cordewener, J.; America, A.H.P.; Nicolai, B.M.; Carpentier, S.C. Improving the identification rate of data independent label-free quantitative proteomics experiments on non-model crops: A case study on apple fruit. J. Proteomics 2014, 105, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chevalier, F.; Martin, O.; Rofidal, V.; Devauchelle, A.D.; Barteau, S.; Sommerer, N.; Rossignol, M. Proteomic investigation of natural variation between Arabidopsis ecotypes. Proteomics 2004, 4, 1372–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beyene, B.; Haile, G.; Matiwos, T.; Deribe, H. Review on proteomics technologies and its application for crop improvement. Innov. Sys. Design Eng. 2016, 7, 7–15. [Google Scholar]
- León, E.; Marín, S.; Giménez, M.J.; Piston, F.; Rodríguez-Quijano, M.; Shewry, P.R.; Barro, F. Mixing properties and dough functionality of transgenic lines of a commercial wheat cultivar expressing the 1Ax1, 1Dx5 and 1Dy10 HMW glutenin subunit genes. J. Cer. Sci. 2009, 49, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- León, E.; Piston, F.; Rodríguez-Quijano, M.; Shewry, P.R.; Barro, F. Stacking HMW-GS transgenes in bread wheat: Combining subunit 1Dy10 gives improved mixing properties and dough functionality. J. Cer. Sci. 2010, 51, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Altenbach, S.B.; Tanaka, C.K.; Whitehand, L.C.; Vensel, W.H. Effects of post-anthesis fertilizer on the protein composition of the gluten polymer in a US bread wheat. J. Cer. Sci. 2016, 68, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieser, H. Chemistry of gluten proteins. Food Microbiol. 2007, 24, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altenbach, S.B. New insights into the effects of high temperature, drought and post-anthesis fertilizer on wheat grain development. J. Cer. Sci. 2012, 56, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zhang, Y.X.; Guan, Z.Q.; Wei, W.; Han, L.; Chai, T.Y. Expression and function of two dehydrins under environmental stresses in I Brassica juncea L. Molecular Breeding 2008, 21, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Li, Y.; Sun, J.; Du, L.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, Q.; Liu, X. Comparative physiological and proteomic response to abrupt low temperature stress between two winter wheat cultivars differing in low temperature tolerance. Plant. Biology 2013, 15, 292–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Pan, J.; Huang, X.; Guo, D.; Lou, H.; Hou, Z.; Su, M.; Liang, R.; Xie, C.; You, M.; et al. Differential effects of a post-anthesis heat stress on wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) grain proteome determined by iTRAQ. Scient. Rep. 2017, 7, 3468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padula, M.P.; Berry, I.J.; O’Rourke, M.; Raymon, B.B.A.; Santos, J.; Djordjevic, P. A comprehensive guide for performing sample preparation and top-down protein analysis. Proteomes 2017, 5, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finnie, C.; Sultan, A.; Grasser, K.D. From protein catalogues towards targeted proteomics approaches in cereal grains. Phytochem. 2011, 72, 1145–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasheed, A.; Xia, X.; Yan, Y.; Appels, R.; Mahmood, T.; He, Z. Wheat seed storage proteins: Advances in molecular genetics, diversity and breeding applications. J. Cer. Sci. 2014, 60, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, M.; Nunes-Miranda, J.D.; Branlard, G.; Carillo, J.M.; Rodriguez-Quijano, M.; Igrejas, G. One hundred years of grain omics: identifying the glutens that feed the world. J. Proteome Res. 2013, 12, 4702–4716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vensel, W.H.; Tanaka, C.K.; Altenbach, S.B. Protein composition of wheat gluten polymer fractions determined by quantitative two-dimensional gel electrophoresis and tandem mass spectrometry. Proteome Sci. 2014, 12, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muccilli, V.; Cunsolo, V.; Saletti, R.; Foti, S.; Margiotta, B.; Scossa, F.; Masci, S.; Lafiandra, D. Characterisation of a specific class of typical low molecular weight glutenin subunits of durum wheat by a proteomic approach. J. Cer. Sci. 2010, 51, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- D’Ovidio, R.; Simeone, M.; Masci, S.; Porceddu, E.; Kasarda, D.D. Nucleotide sequence of a γ-gliadin type gene from a durum wheat: Correlation with a γ-type glutenin subunit from the same biotype. Cereal Chem. 1995, 72, 443–449. [Google Scholar]
- Masci, S.; Egorov, T.A.; Ronchi, C.; Kuzmicky, D.D.; Kasarda, D.D.; Lafiandra, D. Evidence for the presence of only one cysteine residue in the D-type Low-Molecular-Weight subunits of wheat glutenin. J. Cer. Sci. 1999, 29, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masci, S.; Rovelli, L.; Kasarda, D.D.; Vensel, W.H.; Lafiandra, D. Characterisation and chromosomal localisation of C-type low molecular weight glutenin subunits in the bread wheat cultivar Chinese Spring. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2002, 104, 422–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Ovidio, R.; Masci, S. The low-molecular-weight glutenin subunits of wheat gluten. J. Cer. Sci. 2004, 39, 321–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacRtichie, F. Theories of glutenin/dough systems. J. Cer. Sci. 2014, 60, 4–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Jørgensen, A.D.; Li, H.; Søndergard, I.; Finnie, C.; Svensson, B.; Jiang, D.; Wollenweber, B.; Jacobsen, S. Implications of high-temperature events and water deficits on protein profiles in wheat (Triticum aestivum L. cv. Vinjett) grain. Proteomics 2011, 11, 1684–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Huang, X.; Wang, L.; Wei, L.; Wu, Z.; You, M.; Li, B. Proteomics analysis of wheat seed in response to drought stress. J. Integr. Agric. 2014, 13, 919–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salekdeh, G.H.; Komatsu, S. Crop proteomics. Aim at sustainable agriculture for tomorrow. Proteomics 2007, 7, 2976–2996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holman, J.D.; Dasari, S.; Tabb, D.L. Informatics of protein and posttranslational modification detection via shotgun proteomics. Meth. Mol. Biol. 2013, 1002, 167–179. [Google Scholar]
- Cunsolo, V.; Muccilli, V.; Saletti, R.; Foti, S. Mass spectrometry in the proteome analysis of mature cereal grains. Mass. Spec. Rev. 2012, 31, 448–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, W.; Garlinge, J. The Wheat Book: Principle and Practices; Department of Agriculture, Western Australia: Perth, WA, Australia, 2000.
- Singh, N.K.; Shepherd, K.W.; Cornish, G.B. Rapid communication. A simplified SDS-PAGE procedure for separating LMW subunits of glutenin. J. Cer. Sci. 1991, 14, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuhoff, V.; Arold, N.; Taube, D.; Ehrhardt, W. Improved staining of proteins in polyacrylamide gels including isoelectric focusing gels with clear background at nanogram sensitivity using Coomassie Brilliant Blue G-250 and R-250. Electroph. 1988, 9, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Gorman, M.; Beauvallet, C.; Lepercq, P.; David, O.; Seksik, P.; Beaugerie, L.; Doré, J.; Martin, P.; Bogard, P.; Juste, C. An investigation into Crohn’s disease using the progenesis SameSpots analysis platform. In Proceedings of the 24th Journée Françaises de Spectrométrie de Masse, Pau, France, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Sestili, F.; Paoletti, F.; Botticella, E.; Masci, S.; Saletti, R.; Muccilli, V.; Lafiandra, D. Comparative proteomic analysis of kernel proteins of two high amylose transgenic durum wheat lines obtained by biolistic and Agrobacterium-mediated transformations. J. Cer. Sci. 2013, 58, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Molina, M.D.; Muccilli, V.; Saletti, R.; Foti, S.; Masci, S.; Barro, F. Comparative proteomic analysis of two transgenic low-gliadin wheat lines and non-transgenic wheat control. J. Proteomics 2017, 165, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Riverol, Y.; Csordas, A.; Bai, J.; Bernal-Llinares, M.; Hewapathirana, S.; Kundu, D.J.; Inuganti, A.; Griss, J.; Mayer, G.; Eisenacher, M.; et al. The PRIDE database and related tools and resources in 2019: improving support for quantification data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D442–D450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the flour are available from the corresponding author. |
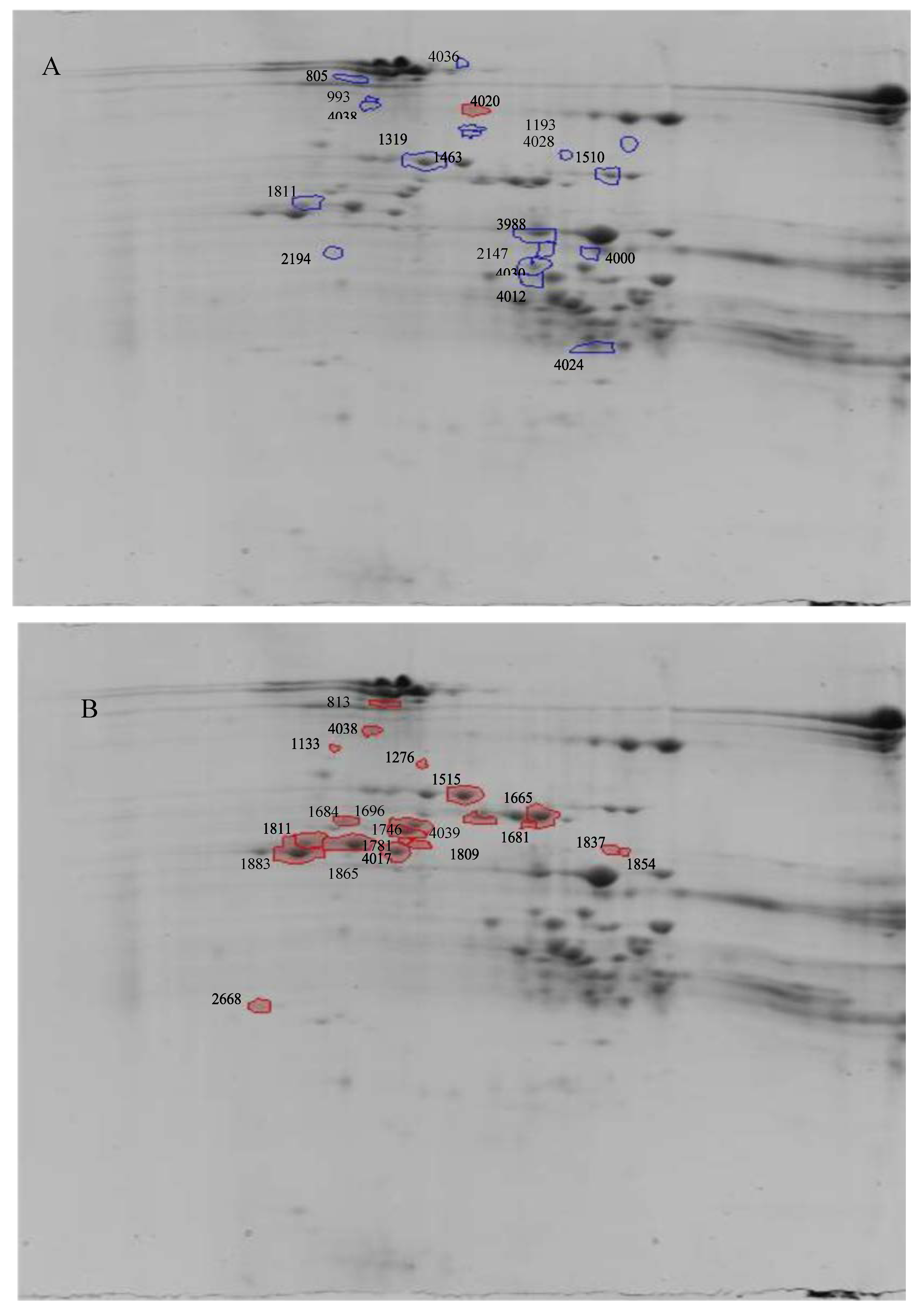
| Treatment | Spot number | P value | Q Value | Power | Fold Change | Protein Identification | Acc.No | Score; Coverage (%) | Identified Peptides | M + H*; z |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cold stress | 4020 | 0.008 | 0.82 | 0.811 | 1.7 | HMW PW212 | P08489 | 209.1; 7 | GGSFYPGETTPPQQLQQR IFWGIPALLK QpyroSGQGQQGYYSSYHVSVEHQAASLK SLQQTGQGQQSGQGQQGYYSSYHVSVEHQAASLK | 1989.9; 2 1156.7; 2 2721.2; 2 3665.7; 2 |
| 4020 | HMW 12 | P08488 | 173.9; 6 | LPWSTGLQMR LPWSTGLQMoxR QVVDQQLAGR QGYDSPYHVSAEQQAASPMoxVAK QpyroVVDQQLAGR | 1187.6; 2 1203.6; 2 1112.6; 2 2379.1; 2 1095.6; 2 | |||||
| 4000 | 0.017 | 0.82 | 0.703 | 1.3 | γ-gliadin | P08453 | 81.15; 4 | APFASIVAGIGGQ | 1186.6; 2 | |
| 3988 | 0.018 | 0.82 | 0.698 | 1.3 | LMW | P10385 | 87.7; 3 | QpyroIPEQSRHESIR QpyroIPEQSR PEQSRHESIR | 1461.7; 2 839.4; 2 1237.6; 2 | |
| 4038 | HMW 12 | P08488 | 147.5; 3 | LPWSTGLQMR LPWSTGLQMoxR QVVDQQLAGR | 1187.6; 2 1203.6; 2 1112.6; 2 | |||||
| 4038 | Fragment HMW PC256 | P02861 | 107.5; 30 | LEGGDALLASQ QWLQPR AQQLAAQLPAMoxCR | 1072.5; 2 826.4; 2 1472.7; 2 | |||||
| 1463 | 0.022 | 0.82 | 0.666 | 1.8 | HMW 12 | P08488 | 203.1; 12 | QpyroGYDSPYHVSAEQQAASPMoxVAK SLQQPGQGQQIGK LPWSTGLQMR QGYDSPYHVSAEQQAASPMoxVAK QGYYPTSLQQPGQGQQIGQGQQGYYPTSPQHTGQR LPWSTGLQMoxR | 2362.0; 2 1367.7; 2 1187.6; 2 2379.1; 2 3862.8; 3 1203.6; 2 | |
| 1193 | 0.029 | 0.82 | 0.614 | 1.6 | HMW 12 | P08488 | 217.6; 14 | LPWSTGLQMR SVAVSQVAR LPWSTGLQMoxR QVVDQQLAGR QpyroVVDQQLAGR QYEQTVVPPK QGYDSPYHVSAEQQAASPMoxVAK LVLFAAVVIALVALTTAEGEASR EpyroLQESSLE | 1187.6; 2 915.5; 2 1203.6; 2 1112.6; 2 1095.6; 2 1187.6; 2 2379.0; 3 2313.3; 3 915.4 ;2 | |
| 1193 | HMW PW212 | P08849 | 94.3; 2 | GGSFYPGETTPPQQLQQR | 1989.9; 2 | |||||
| 4028 | 0.031 | 0.82 | 0.606 | 1.6 | HMW PW212 | P08849 | 71.8; 2 | GGSFYPGETTPPQQLQQR | 1989.9; 2 | |
| 1811 | 0.032 | 0.82 | 0.595 | 1.4 | HMW PW212 | P08849 | 187.8; 2 | GGSFYPGETTPPQQLQQR ELQELQER | 1989.9; 2 1043.5; 2 | |
| 2147 | 0.033 | 0.82 | 0.590 | 1.3 | γ-gliadin | P8453 | 97.14; 4 | APFASIVAGIGGQ | 1186.6; 2 | |
| 2147 | HMW PW212 | P08849 | 187.8; 3 | GGSFYPGETTPPQQLQQR | 1989.9; 2 | |||||
| 2194 | 0.034 | 0.82 | 0.587 | 1.5 | HMW PW212 | P08849 | 1164.1; 3 | GGSFYPGETTPPQQLQQR IFWGIPALLK | 1989.9; 2 1156.7; 2 | |
| 2194 | LMW PTDUCD1 | P16315 | 48.3; 3 | QLPQIPEQSR | 1194.6 | |||||
| 1319 | 0.034 | 0.82 | 0.584 | 1.5 | HMW 12 | P08488 | 204.4; 15 | QpyroGYYPTSLQQPGQGQQIGQGQQGYYPTSPQHTGQR QGYDSPYHVSAEQQAASPMoxVAK QpyroVVDQQLAGR LPWSTGLQMR EpyroQQAASPMVAKAQQPATQLPTVCRMEGGDALSASQ QpyroGYDSPYHVSAEQQAASPMoxVAK LPWSTGLQMoxR | 3845.7; 3 2379.1; 3 1095.6; 3 1187.6; 2 3637.7; 3 2362.1; 2 1203.6; 2 | |
| 4012 | 0.044 | 0.82 | 0.537 | 1.4 | α/β-gliadin A-IV | P04724 | 101.1; 12 | GSVQPQQLPQFEEIR QpyroLPQFEEIR DVVLQQHSIAHGSSQVLQQSTY SVQPQQLPQFEEIR | 1754.8; 2 1141.6; 2 2424.2; 3 1697.8; 2 | |
| 4024 | 0.046 | 0.82 | 0.531 | 1.3 | α/β-gliadin | P02863 | 232.4; 21 | PSQQNPQAQGSVQPQQLPQFEEIR SVQPQQLPQFEEIR GSVQPQQLPQFEEIR PQQLPQFEEIR QQQQPSSQVSFQQPLQQYPLGQGSFR PQFEEIR AIILHQQQK | 2733.3; 3 1697.8; 2 1754.8; 2 1383.7; 3 2990.5; 3 917.4; 1 1077.6; 2 | |
| 4024 | α/β-gliadin clone PTO-A10 | P04728 | 63.1; 14 | QQQQPSSQFSFQQPLQQYPLGQGSFR | 3038.5; 3 | |||||
| 4024 | γ-gliadin | P08453 | 92.9; 5 | GIIQPQQPAQLEAIR | 1660.9; 2 | |||||
| 1510 | 0.047 | 0.82 | 0.526 | 1.3 | HMW PW212 | P08849 | 100.6; 3 | GGSFYPGETTPPQQLQQR ELQELQER | 1989.9; 2 1043.5; 2 | |
| Drought stress | 1883 | 0.003 | 0.74 | 0.907 | 1.6 | HMW PW212 | P08849 | 110.4; 2 | GGSFYPGETTPPQQLQQR | 1989.9; 2 |
| 1811 | 0.003 | 0.74 | 0.902 | 1.7 | HMW PW212 | P08849 | 187.3; 2 | GGSFYPGETTPPQQLQQR ELQELQER | 1989.9; 2 1043.5; 2 | |
| 1865 | 0.006 | 0.74 | 0.850 | 1.6 | HMW PW212 | P08849 | 98.3; 2 | GGSFYPGETTPPQQLQQR | 1989.9; 2 | |
| 4017 | 0.006 | 0.74 | 0.843 | 1.4 | HMW PW212 | P08849 | 120.2; 3 | GGSFYPGETTPPQQLQQR | 1989.9; 2 | |
| 4039 | 0.016 | 0.74 | 0.718 | 1.5 | Eukaryotic translation initiation factor isoform 4G-2 | Q41583 | 37.7; 5 | NGRNAPGGPLSPGGFS FDLLKGELLDSGITTADILKDVISLIF | 1483.7; 2 2948.6; 3 | |
| 1854 | 0.025 | 0.74 | 0.641 | 1.5 | HMW 12 | P08488 | 134.3; 3 | LPWSTGLQMoxR LPWSTGLQMR QYEQTVVPPK | 1203.6; 2 1187.6; 2 1187.6; 2 | |
| 1854 | α/β-gliadin A-II | P04722 | 70.8; 3 | LWQIPEQSR | 1155.6; 2 | |||||
| 1133 | 0.027 | 0.74 | 0.630 | 1.4 | HMW PW212 | P08489 | 79.7; 2 | GGSFYPGETTPPQQLQQR | 1989.9; 2 | |
| 1781 | 0.027 | 0.74 | 0.628 | 1.6 | HMW PW212 | P08489 | 100.7; 2 | GGSFYPGETTPPQQLQQR | 1989.9; 2 | |
| 4038 | HMW 12 | P08488 | 147.5; 3 | LPWSTGLQMR LPWSTGLQMoxR QVVDQQLAGR | 1187.6; 2 1203.6; 2 1112.6; 2 | |||||
| 4038 | Fragment HMW PC256 | P02861 | 107.5; 30 | LEGGDALLASQ QWLQPR AQQLAAQLPAMoxCR | 1072.5; 2 826.4; 2 1472.7; 2 | |||||
| 1809 | 0.031 | 0.74 | 0.600 | 1.7 | HMW PW212 | P08849 | 148.9; 3 | GGSFYPGETTPPQQLQQR IFWGIPALLK | 1989.9; 2 1156.7; 2 | |
| 1696 | 0.033 | 0.74 | 0.592 | 1.6 | HMW PW212 | P08489 | 98.3; 2 | GGSFYPGETTPPQQLQQR | 1989.9; 2 | |
| 1681 | 0.036 | 0.74 | 0.575 | 1.4 | HMW PW212 | P08849 | 113.4; 6 | GGSFYPGETTPPQQLQQR MoxAKRLVLFVAVVVALVALTVAEGEASEQLQCER | 1989.9; 2 3614.9; 3 | |
| 1681 | HMW 12 | P08488 | 24.9; 5 | QpyroGYYPTSLQQPGQGQQIGQGQQGYYPTSPQHTGQR | 3845.7; 3 | |||||
| 1684 | 0.043 | 0.74 | 0.544 | 1.3 | HMW PW212 | P08849 | 187.3; 3 | GGSFYPGETTPPQQLQQR IFWGIPALLK ELQELQER | 1989.9; 2 1156.7; 2 1043.5; 2 | |
| 1515 | 0.046 | 0.74 | 0.531 | 1.4 | HMW PW212 | P08489 | 174.9; 4 | GGSFYPGETTPPQQLQQR | 1989.9; 2 | |
| 1837 | 0.049 | 0.74 | 0.519 | 1.6 | Plasma membrane ATPase | P83970 | 36.9; 6 | EpyroMSALYLQVSIVSQALIFVT EpyroMoxSALYLQVSIVSQALIFVT LGMoxGTNMYPSSALLGQSK LGDIVPADARLLEGDPLK | 2193.1; 2 2209.1; 2 1869.9; 2 1891.7; 2 | |
| 1665 | 0.049 | 0.74 | 0.516 | 1.3 | HMW PW212 | P08849 | 147.9; 4 | GGSFYPGETTPPQQLQQR | 1989.9; 2 | |
| Cold and drought stress | 1811 | 0.003 | 0.61 | 0.901 | 1.7 | HMW PW212 | P08849 | 187.3; 3 | GGSFYPGETTPPQQLQQR ELQELQER | 1989.9; 2 1043.5; 2 |
| 4038 | HMW 12 | P08488 | 147.5; 3 | LPWSTGLQMR LPWSTGLQMoxR QVVDQQLAGR | 1187.6; 2 1203.6; 2 1112.6; 2 | |||||
| 4038 | Fragment HMW PC256 | P02861 | 107.5; 30 | LEGGDALLASQ QWLQPR AQQLAAQLPAMoxCR | 1072.5; 2 826.4; 2 1472.7; 2 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Labuschagne, M.; Masci, S.; Tundo, S.; Muccilli, V.; Saletti, R.; van Biljon, A. Proteomic Analysis of Proteins Responsive to Drought and Low Temperature Stress in a Hard Red Spring Wheat Cultivar. Molecules 2020, 25, 1366. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25061366
Labuschagne M, Masci S, Tundo S, Muccilli V, Saletti R, van Biljon A. Proteomic Analysis of Proteins Responsive to Drought and Low Temperature Stress in a Hard Red Spring Wheat Cultivar. Molecules. 2020; 25(6):1366. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25061366
Chicago/Turabian StyleLabuschagne, Maryke, Stefania Masci, Silvio Tundo, Vera Muccilli, Rosaria Saletti, and Angeline van Biljon. 2020. "Proteomic Analysis of Proteins Responsive to Drought and Low Temperature Stress in a Hard Red Spring Wheat Cultivar" Molecules 25, no. 6: 1366. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25061366
APA StyleLabuschagne, M., Masci, S., Tundo, S., Muccilli, V., Saletti, R., & van Biljon, A. (2020). Proteomic Analysis of Proteins Responsive to Drought and Low Temperature Stress in a Hard Red Spring Wheat Cultivar. Molecules, 25(6), 1366. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25061366






