Gintonin-Enriched Fraction Suppresses Heat Stress-Induced Inflammation through LPA Receptor
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
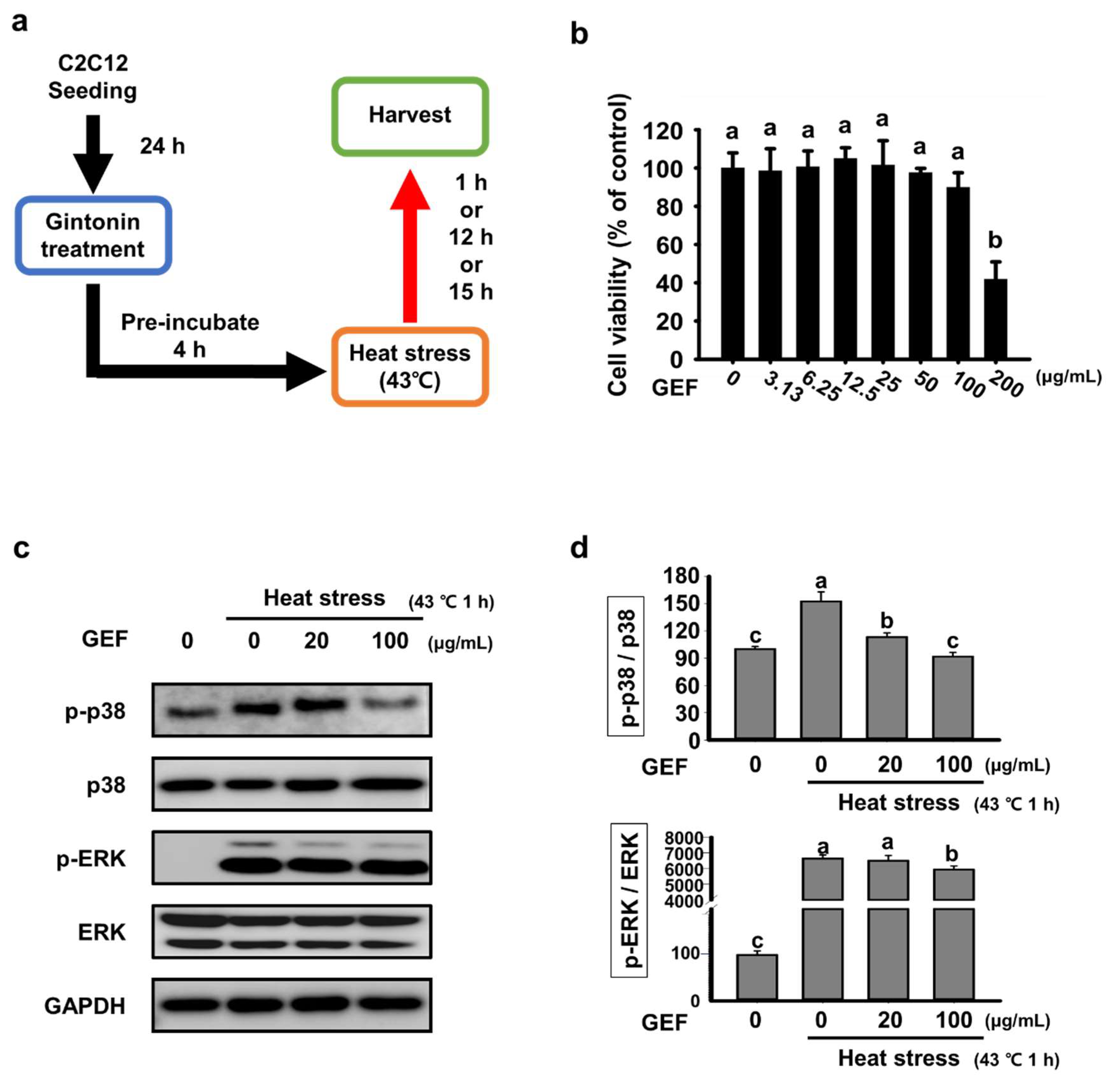
2.1. Effect of GEF on Cell Viability and Expression of MAPK Signaling Factors Induce by Heat Stress
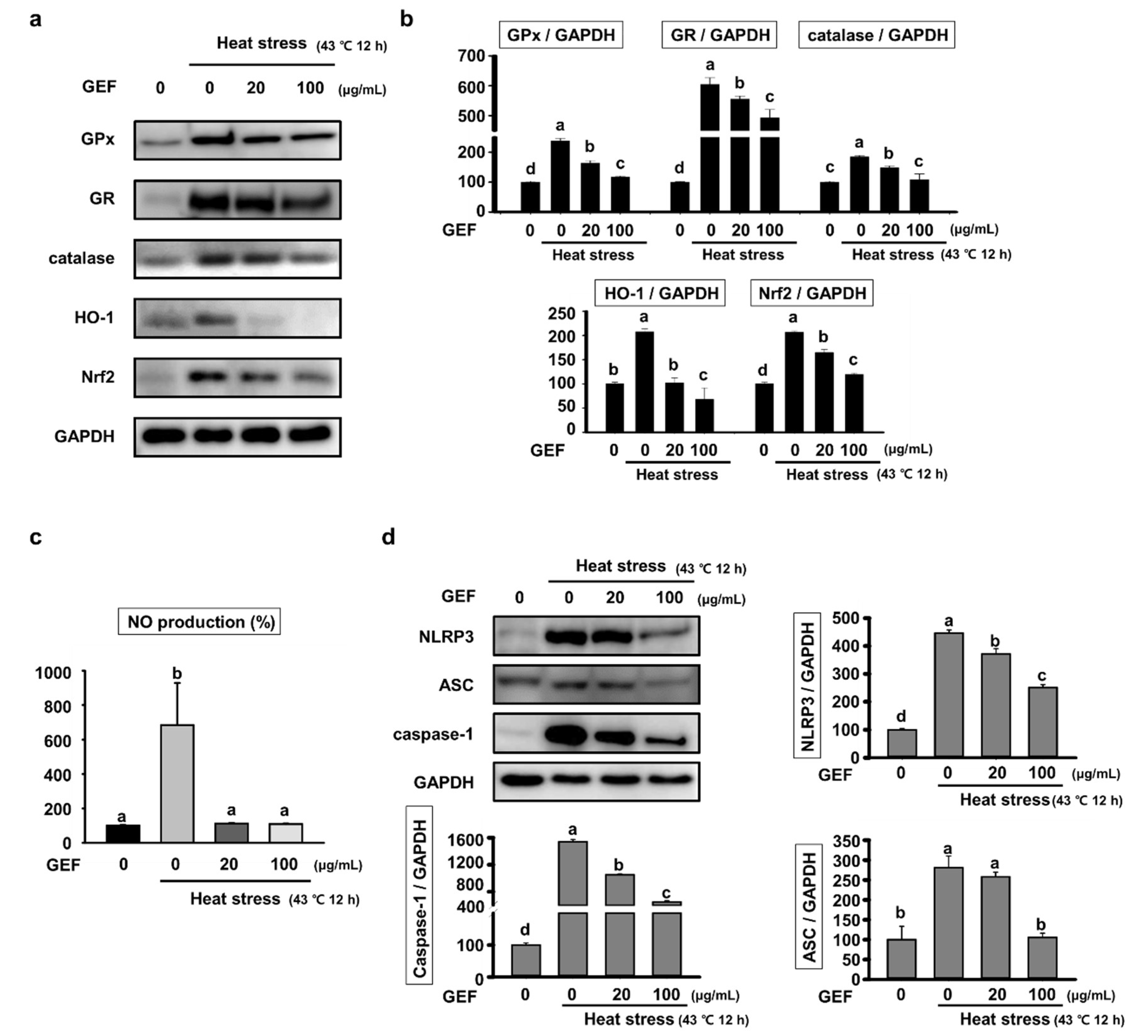
2.2. Effect of GEF on Oxidative Stress and Inflammatory Response by Heat Stress
2.3. Effect of GEF on Expression of Inflammatory Cytokines by Heat Stress
2.4. GEF Affects MAPK Signaling Pathway and Inflammatory Cytokines Through LPA Receptor
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Preparation of Gintonin-Enriched Fraction (GEF)
4.2. Chemical and Reagent
4.3. Cell Study Design
4.4. Western Blotting
4.5. Nitric Oxidative (NO) Assay
4.6. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fedyaeva, A.; Stepanov, A.; Lyubushkina, I.; Pobezhimova, T.; Rikhvanov, E. Heat shock induces production of reactive oxygen species and increases inner mitochondrial membrane potential in winter wheat cells. Biochemistry (Mosc.) 2014, 79, 1202–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson, K.E. Oxidative stress and its possible relation to lower urinary tract functional pathology. BJU Int. 2018, 121, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lobo, V.; Patil, A.; Phatak, A.; Chandra, N. Free radicals, antioxidants and functional foods: Impact on human health. Pharmacogn. Rev. 2010, 4, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, P.; Jha, A.B.; Dubey, R.S.; Pessarakli, M. Reactive oxygen species, oxidative damage, and antioxidative defense mechanism in plants under stressful conditions. J. Bot. 2012, 2012, 217037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.Y.; Nuñez, G. Sterile inflammation: sensing and reacting to damage. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 10, 826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Zhang, L.; Joo, D.; Sun, S.-C. NF-κB signaling in inflammation. Transduct. Target. Ther. 2017, 2, 17023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thalhamer, T.; McGrath, M.; Harnett, M. MAPKs and their relevance to arthritis and inflammation. Rheumatology 2008, 47, 409–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-J.; Jeon, J.-N.; Jang, M.-G.; Oh, J.Y.; Kwon, W.-S.; Jung, S.-K.; Yang, D.-C. Ginsenoside profiles and related gene expression during foliation in Panax ginseng Meyer. J. Ginseng Res. 2014, 38, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.-H.; Kim, K.-J.; Choi, S.-Y.; Koh, E.-J.; Park, J.; Lee, B.-Y. Korean ginseng extract ameliorates abnormal immune response through the regulation of inflammatory constituents in Sprague Dawley rat subjected to environmental heat stress. J. Ginseng Res. 2019, 43, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Min, H. Ginseng, the’immunity boost’: the effects of Panax ginseng on immune system. J. Ginseng Res. 2012, 36, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-D.; Kim, Y.-J.; Huh, J.-S.; Kim, S.-W.; Sohn, D.-W. Improvement of erectile function by Korean red ginseng (Panax ginseng) in a male rat model of metabolic syndrome. Asian J. Androl. 2013, 15, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.-H.; Kim, K.-J.; Chei, S.; Seo, Y.-J.; Lee, K.; Lee, B.-Y. Korean red ginseng and Korean black ginseng extracts, JP5 and BG1, prevent hepatic oxidative stress and inflammation induced by environmental heat stress. J. Ginseng Res. 2020, 44, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attele, A.S.; Wu, J.A.; Yuan, C.-S. Ginseng pharmacology: multiple constituents and multiple actions. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1999, 58, 1685–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, E.J.; Kim, K.J.; Choi, J.; Jeon, H.J.; Seo, M.J.; Lee, B.Y. Ginsenoside Rg1 suppresses early stage of adipocyte development via activation of C/EBP homologous protein-10 in 3T3-L1 and attenuates fat accumulation in high fat diet-induced obese zebrafish. J. Ginseng Res. 2017, 41, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, K.S.; Yi, Y.S.; Son, Y.J.; Yoo, S.; Sung, N.Y.; Kim, Y.; Hong, S.; Aravinthan, A.; Kim, J.H.; Cho, J.Y. In vitro and in vivo anti-inflammatory activities of Korean Red Ginseng-derived components. J. Ginseng Res. 2016, 40, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Kim, P.; Shin, C.Y. A comprehensive review of the therapeutic and pharmacological effects of ginseng and ginsenosides in central nervous system. J. Ginseng Res. 2013, 37, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.J.; Choi, S.H.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, B.H.; Rhim, H.; Kim, H.C.; Hwang, S.H.; Nah, S.Y. Bioactive lipids in gintonin-enriched fraction from ginseng. J. Ginseng Res. 2019, 43, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, K.; Haslbeck, M.; Buchner, J. The heat shock response: Life on the verge of death. Mol. Cell 2010, 40, 253–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, B.-Z.; Xu, Z.-Q.; Han, B.-Z.; Su, D.-F.; Liu, C. NLRP3 inflammasome and its inhibitors: A review. Front. Pharmacol. 2015, 6, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.-T.; Liu, T.-T.; Lin, Y.-F.; Chen, C.-C.; Kung, W.-M.; Huang, C.-C.; Lin, T.-J.; Wang, Y.-H.; Wei, L. Heatstroke effect on brain heme oxygenase-1 in rats. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2015, 12, 737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laumonier, T.; Yang, S.; Konig, S.; Chauveau, C.; Anegon, I.; Hoffmeyer, P.; Menetrey, J. Lentivirus mediated HO-1 gene transfer enhances myogenic precursor cell survival after autologous transplantation in pig. Mol. Ther. 2008, 16, 404–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, S.H.; Shin, T.-J.; Choi, S.-H.; Cho, H.-J.; Lee, B.-H.; Pyo, M.K.; Lee, J.-H.; Kang, J.; Kim, H.-J.; Park, C.-W. Gintonin, newly identified compounds from ginseng, is novel lysophosphatidic acids-protein complexes and activates G protein-coupled lysophosphatidic acid receptors with high affinity. Mol. Cells 2012, 33, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plastira, I.; Bernhart, E.; Goeritzer, M.; Reicher, H.; Kumble, V.B.; Kogelnik, N.; Wintersperger, A.; Hammer, A.; Schlager, S.; Jandl, K. 1-Oleyl-lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) promotes polarization of BV-2 and primary murine microglia towards an M1-like phenotype. J. Neuroinflamm. 2016, 13, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Natarajan, V. Lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) and its receptors: Role in airway inflammation and remodeling. BBA-Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2013, 1831, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saba, E.; Jeon, B.R.; Jeong, D.-H.; Lee, K.; Goo, Y.-K.; Kwak, D.; Kim, S.; Roh, S.-S.; Kim, S.D.; Nah, S.-Y. A novel Korean red ginseng compound gintonin inhibited inflammation by MAPK and NF-κB pathways and recovered the levels of mir-34a and mir-93 in RAW 264.7 cells. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2015, 2015, 624132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.H.; Jang, M.; Oh, S.; Nah, S.-Y.; Cho, I.-H. Multi-target protective effects of gintonin in 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1, 2, 3, 6-tetrahydropyridine-mediated model of Parkinson’s disease via lysophosphatidic acid receptors. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.-H.; Jung, S.-W.; Lee, B.-H.; Kim, H.-J.; Hwang, S.-H.; Kim, H.-K.; Nah, S.-Y. Ginseng pharmacology: A new paradigm based on gintonin-lysophosphatidic acid receptor interactions. Front. Pharmacol. 2015, 6, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-F.; Li, R.-S.; Sonia, B.; Samuel, R.C.; Li, X.-Y.; Hong, W.; Yang, X.-F. Lysophospholipids and their G protein-coupled receptors in atherosclerosis. Front. Biosci. 2016, 21, 70–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.-H.; Shin, T.-J.; Lee, B.-H.; Hwang, S.H.; Kang, J.; Kim, H.-J.; Park, C.-W.; Nah, S.-Y. An edible gintonin preparation from ginseng. J. Ginseng Res. 2011, 35, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.-H.; Jung, S.-W.; Kim, H.-S.; Lee, B.-H.; Kim, J.-Y.; Hwang, S.-H.; Rhim, H.; Kim, H.-C.; Nah, S.-Y. A brief method for preparation of gintonin-enriched fraction from ginseng. J. Ginseng Res. 2015, 39, 398–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chei, S.; Oh, H.J.; Song, J.H.; Seo, Y.J.; Lee, K.; Lee, B.Y. Magnolol Suppresses TGF-beta-Induced Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition in Human Colorectal Cancer Cells. Front. Oncol. 2020, 9, 752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chei, S.; Oh, H.J.; Song, J.H.; Seo, Y.J.; Lee, K.; Kim, K.J.; Lee, B.Y. Spirulina maxima extract prevents activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome by inhibiting ERK signaling. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |


© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chei, S.; Song, J.-H.; Oh, H.-J.; Lee, K.; Jin, H.; Choi, S.-H.; Nah, S.-Y.; Lee, B.-Y. Gintonin-Enriched Fraction Suppresses Heat Stress-Induced Inflammation through LPA Receptor. Molecules 2020, 25, 1019. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25051019
Chei S, Song J-H, Oh H-J, Lee K, Jin H, Choi S-H, Nah S-Y, Lee B-Y. Gintonin-Enriched Fraction Suppresses Heat Stress-Induced Inflammation through LPA Receptor. Molecules. 2020; 25(5):1019. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25051019
Chicago/Turabian StyleChei, Sungwoo, Ji-Hyeon Song, Hyun-Ji Oh, Kippeum Lee, Heegu Jin, Sun-Hye Choi, Seung-Yeol Nah, and Boo-Yong Lee. 2020. "Gintonin-Enriched Fraction Suppresses Heat Stress-Induced Inflammation through LPA Receptor" Molecules 25, no. 5: 1019. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25051019
APA StyleChei, S., Song, J.-H., Oh, H.-J., Lee, K., Jin, H., Choi, S.-H., Nah, S.-Y., & Lee, B.-Y. (2020). Gintonin-Enriched Fraction Suppresses Heat Stress-Induced Inflammation through LPA Receptor. Molecules, 25(5), 1019. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25051019






