Protein-Stabilized Palm-Oil-in-Water Emulsification Using Microchannel Array Devices under Controlled Temperature
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Preparation of Palm-Oil-in-Water Emulsions by MC Emulsification
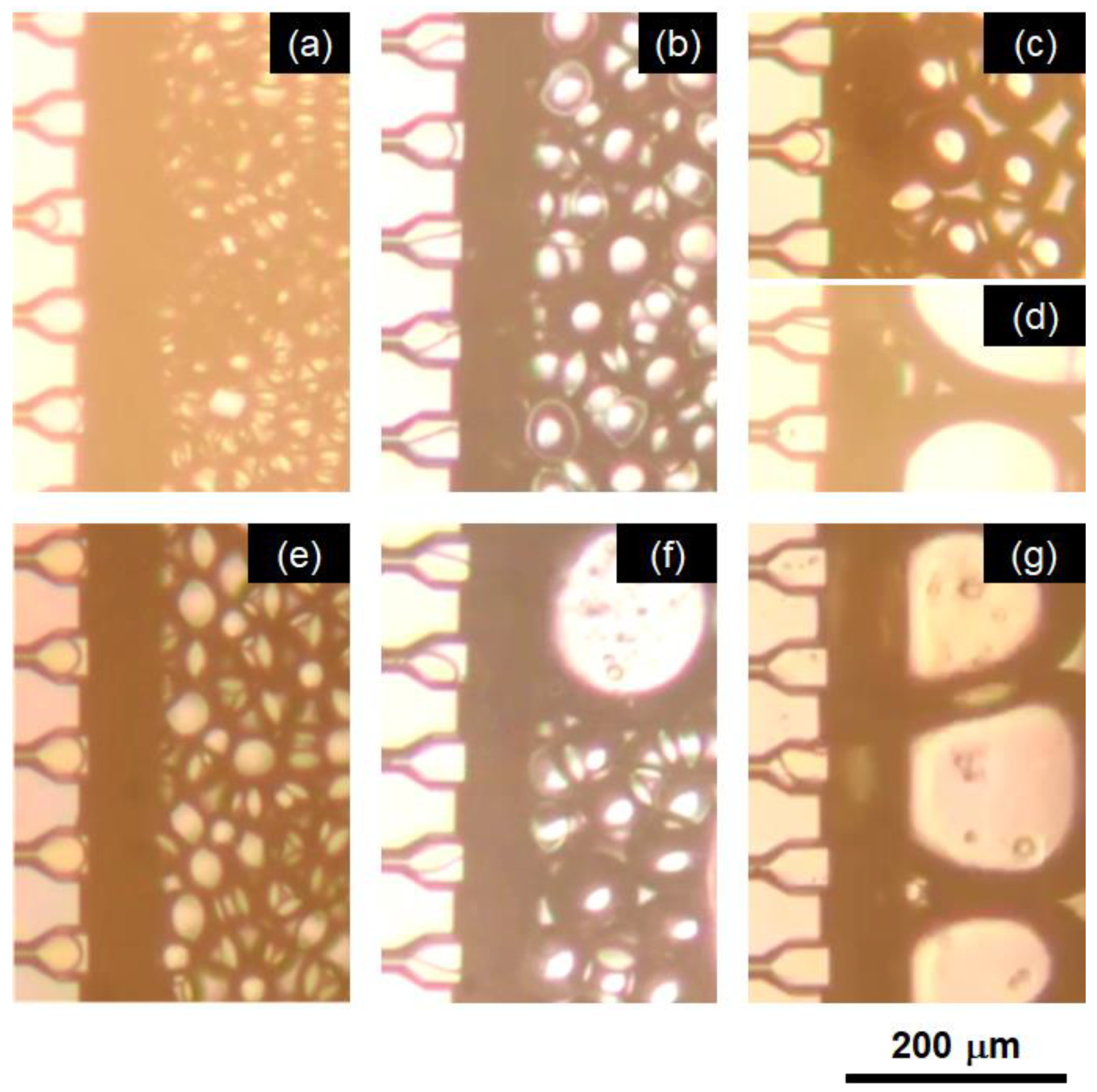
2.1.1. Effect of Emulsifier Type
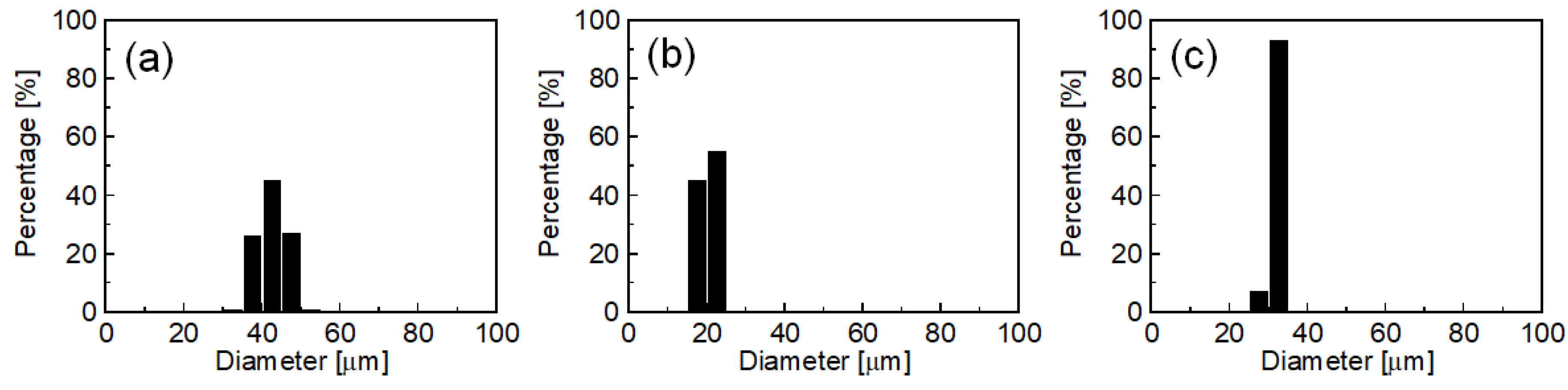
2.1.2. Effect of SC Concentration
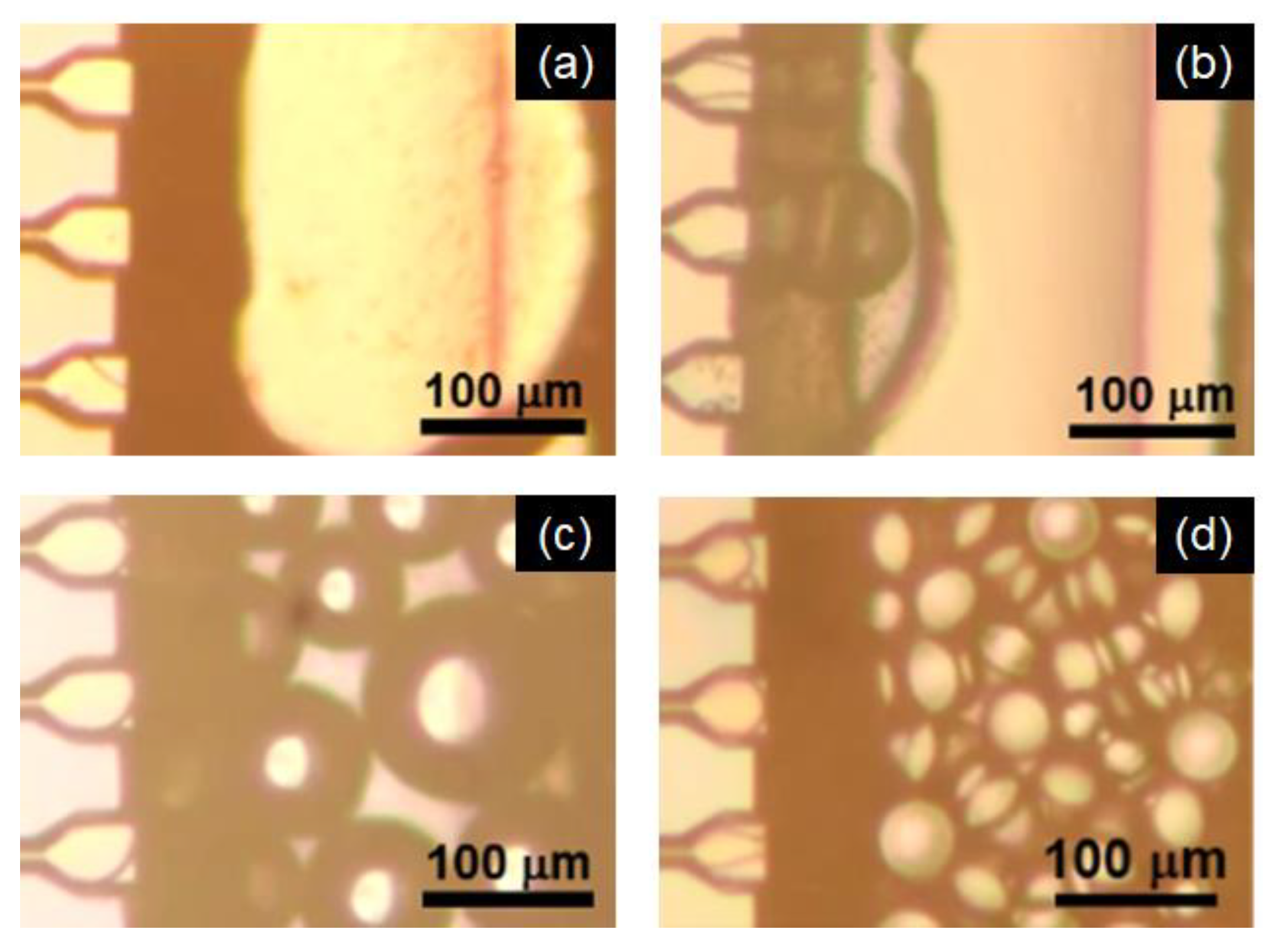
2.1.3. Effect of Emulsification Temperature
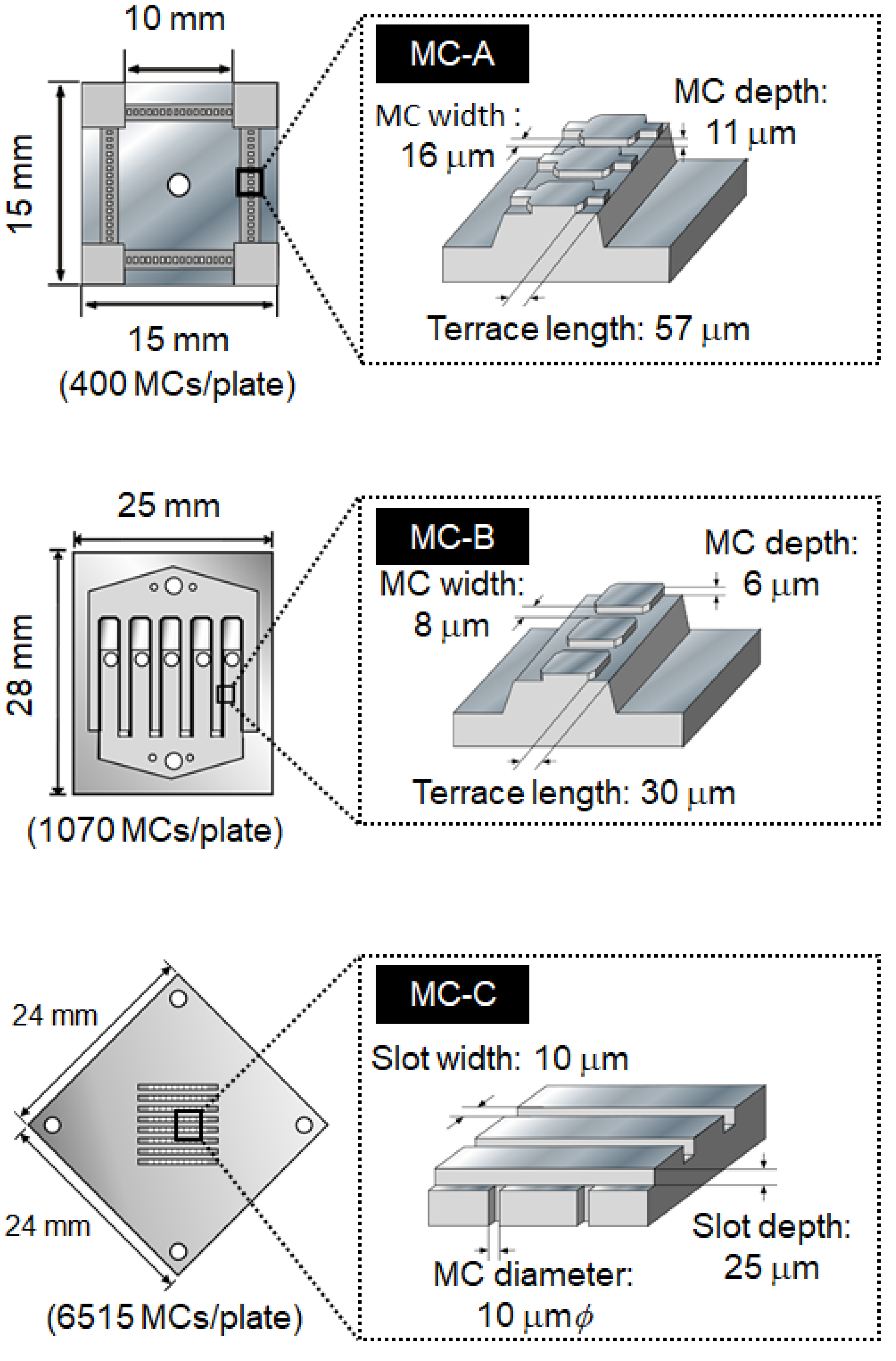
2.1.4. Effect of MC Structure
2.1.5. Effect of Flow Rate of To-Be-Dispersed Phase
2.2. Preparation of W/O/W Emulsions Containing Palm Oil
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals
3.2. Preparation of O/W Emulsions
3.3. Preparation of W/O/W Emulsions
3.4. Viscosity Measurement
3.5. Interfacial Tension Measurement
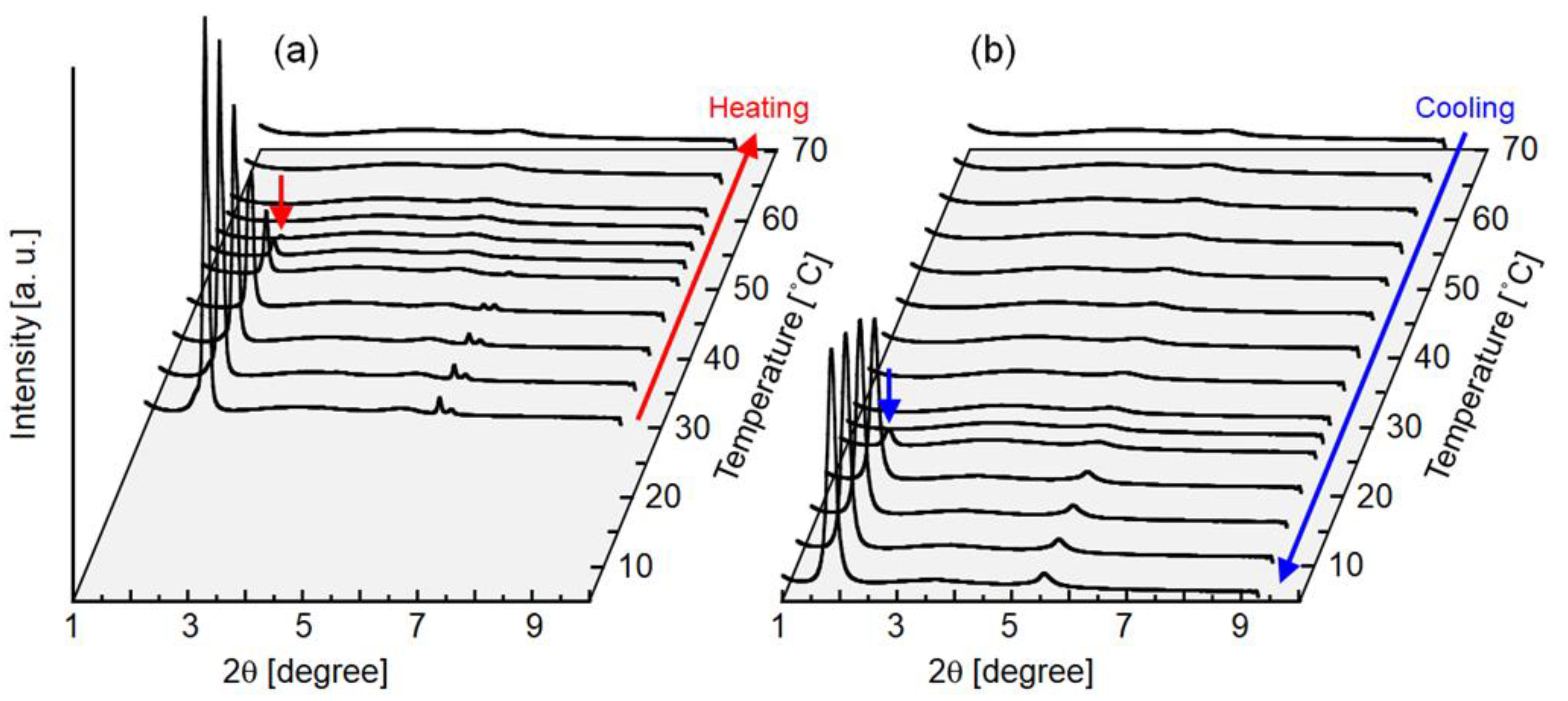
3.6. SAXD Measurement
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Attama, A.A.; Igbonekwu, C.N. In vitro properties of surface-modified solid lipid microspheres containing an antimalarial drug: Halofantrine. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2011, 4, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClements, D.J. Crystals and crystallization in oil-in-water emulsions: Implications for emulsion-based delivery systems. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 174, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McClements, D.J. Nanoparticle- and Microparticle-Based Delivery Systems: Encapsulation, Protection and Release of Active Compounds; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Battaglia, L.; Ugazio, E. Lipid nano-and microparticles: An overview of patent-related research. J. Nanomater. 2019, 2019, 2834941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Shen, L.; Wang, T.; Li, H.; Huang, R.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Quan, D. Taste masking of water-soluble drug by solid lipid microspheres: A child-friendly system established by reversed lipid-based nanoparticle technique. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2020, 72, 776–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, R.H.; Mä der, K.; Gohla, S. Solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN) for controlled drug delivery—A review of the state of the art. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2000, 50, 161–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wissing, S.A.; Müller, R.H. The influence of the crystallinity of lipid nanoparticles on their occlusive properties. Int. J. Pharm. 2002, 242, 377–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehnert, M.; Mäder, K. Solid lipid nanoparticles Production, characterization, applications. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2001, 47, 165–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornacchia, L.; Roos, Y. State of dispersed lipid carrier and interface composition as determinations of beta-carotene stability in oil-in-water emulsions. J. Food Sci. 2011, 76, C1211–C1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guery, J.; Baudry, J.; Weitz, D.A.; Chaikin, P.M.; Bibette, J. Diffusion through colloidal shells under stress. Phys. Rev. E 2009, 79, 060402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frasch-Melnik, S.; Spyropoulos, F.; Norton, I.T. W1/O/W2 double emulsions stabilised by fat crystals—Formulation, stability and salt release. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 350, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herzi, S.; Essafi, W. Different magnesium release profiles from W/O/W emulsions based on crystallized oils. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 509, 178–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coupland, J.N. Crystallization in emulsions. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2002, 7, 445–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalnin, D.; Schafer, O.; Amenitsch, H.; Ollivon, M. Fat crystallization in emulsion: Influence of emulsifier concentration on triacylglycerol crystal growth and polymorphism. Cryst. Growth Des. 2004, 4, 1283–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arima, S.; Ueno, S.; Ogawa, A.; Sato, K. Scanning microbeam small-sngle X-ray diffraction study of interfacial heterogeneous crystallization of fat crystals in oil-in-water emulsion droplets. Langmuir 2009, 25, 9777–9784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, K.; Ueno, S. Crystallization, transformation and microstructures of polymorphic fats in colloidal dispersion states. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 16, 384–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douaire, M.; di Bari, V.; Norton, J.E.; Sullo, A.; Lillford, P.; Norton, I.T. Fat crystallisation at oil-water interfaces. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 203, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sambanthamurthi, R.; Sundram, K.; Tan, Y.A. Chemistry and biochemistry of palm oil. Prog. Lipid Res. 2000, 39, 507–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edem, D.O. Palm oil: Biochemical, physiological, nutritional, hematological, and toxicological aspects: A review. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2002, 57, 319–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancini, A.; Imperlini, E.; Nigro, E.; Montagnese, C.; Daniele, A.; Orru, S.; Buono, P. Biological and nutritional properties of palm oil and palmitic acid: Effects on health. Molecules 2015, 20, 17339–17361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mba, O.I.; Dumont, M.J.; Ngadi, M. Palm oil: Processing, characterization and utilization in the food industry—A review. Food Biosci. 2015, 10, 2–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, C.L.; Kamarudin, Z.; Lesieur, P.; Marangoni, A.; Bourgaux, C.; Ollivon, M. Thermal and structural behaviour of crude palm oil: Crystallization at very slow cooling rate. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2007, 109, 410–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goon, D.E.; Kadir, S.H.S.A.; Latip, N.A.; Rahim, S.A.; Mazlan, M. Palm oil in lipid-based formulations and drug delivery systems. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawakatsu, T.; Kikuchi, Y.; Nakajima, M. Regular-sized cell creation in microchannel emulsification by visual microprocessing method. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1997, 74, 317–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiura, S.; Nakajima, M.; Iwamoto, S.; Seki, M. Interfacial tension driven monodispersed droplet formation from microfabricated channel array. Langmuir 2001, 17, 5562–5566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayasi, I.; Vladisavljevic, G.T.; Uemura, K.; Nakajima, M. CFD analysis of microchannel emulsification: Droplet generation process and size effect of asymmetric straight flow-through microchannels. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2011, 66, 5556–5565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiura, S.; Nakajima, M.; Itou, H.; Seki, M. Synthesis of polymeric microspheres with narrow size distributions employing microchannel emulsification. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2001, 22, 773–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiura, S.; Nakajima, M.; Seki, M. Preparation of monodispersed polymeric microspheres over 50 μm employing microchannel emulsification. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2002, 41, 4043–4047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikkai, F.; Iwamoto, S.; Adachi, E.; Nakajima, M. New method of producing mono-sized polymer gel particles using microchannel emulsification and UV irradiation. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2005, 283, 1149–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuah, A.M.; Kuroiwa, T.; Kobayasi, I.; Zhang, X.; Nakajima, M. Preparation of uniformly sized alginate microspheres using the novel combined methods of microchannel emulsification and external gelation. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2009, 351, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuroiwa, T.; Katsumata, T.; Sukeda, Y.; Warashina, S.; Kobayashi, I.; Uemura, K.; Kanazawa, A. Formulation of uniform-sized agar gel microbeads from water-in-oil emulsion prepared using microchannel emulsification under controlled temperature. Jpn. J. Food Eng. 2016, 17, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuroiwa, T.; Takada, H.; Shogen, A.; Saito, K.; Kobayashi, I.; Uemura, K.; Kanazawa, A. Cross-linkable chitosan-based hydrogel microbeads with pH-responsive adsorption properties for organic dyes prepared using size-tunable microchannel emulsification technique. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2017, 514, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiura, S.; Nakajima, M.; Tong, J.; Nabetani, H.; Seki, M. Preparation of monodispersed solid lipid microspheres using a microchannel emulsification technique. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2000, 227, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, I.; IItaka, Y.; Iwamoto, S.; Kimura, S.; Nakajima, M. Preparation characteristics of lipid microspheres using microchannel emulsification and solvent evaporation methods. J. Chem. Eng. Jpn. 2003, 36, 996–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujiu, K.B.; Kobayashi, I.; Uemura, K.; Nakajima, M. Temperature effect on microchannel oil-in-water emulsification. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2011, 10, 773–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujiu, K.B.; Kobayashi, I.; Neves, M.A.; Uemura, K.; Nakajima, M. Effect of temperature on production of soybean oil-in-water emulsions by microchannel emulsification using different emulsifiers. Food Sci. Technol. Res. 2011, 17, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Fujiu, K.B.; Kobayashi, I.; Neves, M.A.; Uemura, K.; Nakajima, M. Influence of temperature on production of water-in-oil emulsions by microchannel emulsification. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2012, 411, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sugiura, S.; Nakajima, M.; Oda, T.; Satake, M.; Seki, M. Effect of interfacial tension on the dynamic behavior of droplet formation during microchannel emulsification. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 269, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, M.; Uehara, M.; Wakui, R.; Shiota, M.; Kuroiwa, T. Preparation characteristics of water-in-oil emulsion using olive oil as a continuous phase in microchannel emulsification. Jpn. J. Food Eng. 2017, 18, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, R.; Marangoni, A.G. Crystallization dynamics of shear worked cocoa butter. Cryst. Growth Des. 2014, 14, 1199–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.R.; Dewettinck, K. Current update on the influence of minor lipid components, shear and presence of interfaces on fat crystallization. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2015, 3, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuller, G.T.; Gonsidine, T.; Golding, M.; Matia-Merino, L.; McGibbon, A. Aggregation behavior of partially crystalline oil-in-water emulsions: Part II—Effect of solid fat content and interfacial film composition on quiescent and shear stability. Food Hydrocoll. 2011, 51, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiura, S.; Nakajima, M.; Seki, M. Effect of channel structure on microchannel emulsification. Langmuir 2002, 18, 5708–5712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, I.; Hori, Y.; Uemura, K.; Nakajima, M. Production characteristics of large soybean oil droplets by microchannel emulsification using asymmetric through holes. Jpn. J. Food Eng. 2010, 11, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiura, S.; Nakajima, M.; Kumazawa, N.; Iwamoto, S.; Seki, M. Characterization of spontaneous transformation-based droplet formation during microchannel emulsification. J. Phys. Chem. B 2002, 106, 9405–9409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, I.; Mukataka, S.; Nakajima, M. Novel asymmetric through-hole array microfabricated on a silicon plate for formulating monodisperse emulsions. Langmuir 2005, 21, 7629–7632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiura, S.; Nakajima, M.; Yamamoto, K.; Iwamoto, S.; Oda, T.; Satake, M.; Seki, M. Preparation characteristics of water-in-oil-in-water multiple emulsions using microchannel emulsification. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 270, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuroiwa, T.; Horikoshi, K.; Suzuki, A.; Neves, M.A.; Kobayashi, I.; Uemura, K.; Nakajima, M.; Kanazawa, A.; Ichikawa, S. Efficient encapsulation of a water-soluble molecule into lipid vesicles using W/O/W multiple emulsions via solvent evaporation. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2016, 93, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, N.; Mori, T.; Igarashi, N.; Ohta, H.; Nagatani, Y.; Kosuge, T.; Ito, K. Refurbishing of small angle X-ray scattering beamline, BL-6A at the photon factory. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2013, 425, 202008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takagi, H.; Igarashi, N.; Mori, T.; Saijo, S.; Ohta, H.; Nagatani, Y.; Kosuge, T.; Shimizu, N. Upgrade of small angle X-ray scattering beamline BL-6A at the photon factory. AIP Conf. Proc. 2016, 1741, 030018. [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu, N.; Yatabe, K.; Nagatani, Y.; Saijyo, S.; Kosuge, T.; Igarashi, N. Software development for analysis of small angle X-ray scattering data. AIP Conf. Proc. 2016, 1741, 050017. [Google Scholar]
- PF Small-Angle X-ray Scattering Beamline Home Page. Available online: http://pfwww.kek.jp/saxs/SAngler.html (accessed on 28 July 2020).




Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kuroiwa, T.; Ito, M.; Okuyama, Y.; Yamashita, K.; Kanazawa, A. Protein-Stabilized Palm-Oil-in-Water Emulsification Using Microchannel Array Devices under Controlled Temperature. Molecules 2020, 25, 4805. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25204805
Kuroiwa T, Ito M, Okuyama Y, Yamashita K, Kanazawa A. Protein-Stabilized Palm-Oil-in-Water Emulsification Using Microchannel Array Devices under Controlled Temperature. Molecules. 2020; 25(20):4805. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25204805
Chicago/Turabian StyleKuroiwa, Takashi, Miki Ito, Yaeko Okuyama, Kanna Yamashita, and Akihiko Kanazawa. 2020. "Protein-Stabilized Palm-Oil-in-Water Emulsification Using Microchannel Array Devices under Controlled Temperature" Molecules 25, no. 20: 4805. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25204805
APA StyleKuroiwa, T., Ito, M., Okuyama, Y., Yamashita, K., & Kanazawa, A. (2020). Protein-Stabilized Palm-Oil-in-Water Emulsification Using Microchannel Array Devices under Controlled Temperature. Molecules, 25(20), 4805. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25204805






