Abstract
Unique tunable aryl imidazolium ionic liquids successfully catalyzed Friedel–Crafts acylation and thioesterification in sealed tubes. These reactions can form a C−C bond and a C−S bond with high atom economy. Ionic liquids exhibited high activity and catalyzed essential reactions with good to excellent yields while retaining their catalytic activities for recycling.
1. Introduction
Ionic liquids outperform organic solvents in industrial processes and are considered as an eco-friendly choice to the broad scope of the organic reactions [1,2,3,4,5,6]. They are important green solvents that exhibit high thermal stability, recovery, and recycling. They are also a new class of solvents that are expected to be increasingly used by the chemical industry in the next few years, replacing volatile organic solvents. Owing to their low volatility, non-flammability, and thermal stability, ionic liquids can be applied in many operations. Most ionic liquids, such as imidazolium, comprise an organic or inorganic anion and a quaternary ammonium cation [7,8,9,10]. Because they are hugely tunable and have remarkable properties, they have become a crucial part in synthesis and catalysis. Most of the interest in ionic liquids concentrates on their ability to change considerably the reactivity of dissolved solutes. The properties of ionic liquids have caused them to be identified as designer solvents, including task specific ionic liquids [11,12]. A comprehensive understanding of the physical characteristics of ionic liquids can increase their industrial use [13]. Ionic liquids have been analyzed owing to their many applications in organic synthesis, analytical chemistry, electrochemistry, separation chemistry, separation technology, polymers, fiber optics, pH sensors, and others [14,15].
In general, electronic effects and polarity of solvents play important roles in the outcomes of the product for Friedel–Crafts reaction. The changing the connected carbon and oxygen atoms were accomplished through para selective functionalization of benzoic acid in the presence of palladium catalyst [16,17,18,19]. The aromatic ketones of Friedel–Crafts acylation are a fundamental mediator in a broad range, such as pharmaceutical dyes, fragrances, and agrochemicals [20], and are convenient for use in the synthesis of poly (4-vinyl pyridine)-triflic acid, indium triflate [21,22], perfluoroalkane sulfonic acidic resin is an acid catalyst with catalytic activity for many reactions giving high selectivity. One major drawback of this catalyst is its inefficient swelling by aprotic organic solvents, which generally leads to low reaction rates and others [23]. Iron (III) chloride earns wider acceptance as a useful Lewis acid in Friedel–Crafts acylation [24]. The most exciting feature of our synthesized ionic liquids have an important role in Friedel–Crafts acylation. Previous investigations have reported that ionic liquids exhibit the dual Brønsted and Lewis acidic property, the halogen-free Brønsted–Lewis acidic ionic liquids were synthesized and exploited to catalyze the esterification of caprylic acid with methanol. The novel multifunctional MCM-41 as Brønsted–Lewis acidic ionic liquids were prepared and tested for their catalytic activities in one-pot three-component Mannich reactions [25,26,27]. Benzoylation of anisole catalyzed by metal triflate and chloroindate (III) by Lewis—acid ionic liquid were used in Friedel–Crafts reaction [28,29]. The consolidation of sp3 alkyl and sp2 aryl substituents at the nitrogen atoms of the imidazolium origin allowed a far greater variety of ionic liquids [30]. These ionic liquids have an sp2 hybridized carbon atoms as an N-substituted heterocycle are synthesized as a novel type of ionic liquids is a renowned catalyst which is moisture insensitive and stable at room temperature, use for a variety of organic transformations, including Friedel–Crafts acylation reactions. The electron-withdrawing group of the aryl ring allows easier deprotonation of imidazolium for forming a stronger Brønsted acid.
Thioesters are important molecules for organic synthesis and are obtained by coupling aldehydes and sulfur surrogates recently [31]. Kita and co-workers described the formation of thioesters from aldehydes [32] and specific pentafluorophenyl disulfide [33]. Takemoto and co-workers reported the expensive carbene-promoted coupling reaction of thiols and aldehydes [34]. Bandgar and co-workers developed that Dess–Martin periodinane and NaN3 promoted to synthesize thio-esters with aldehydes and aryl thiols [35]. Lee and co-workers demonstrated that FeBr2 is able to catalyze synthesis of thioesters from thiols, aldehydes and tert-butyl hydro peroxide (TBHP) in water [36].
2. Results and Discussion
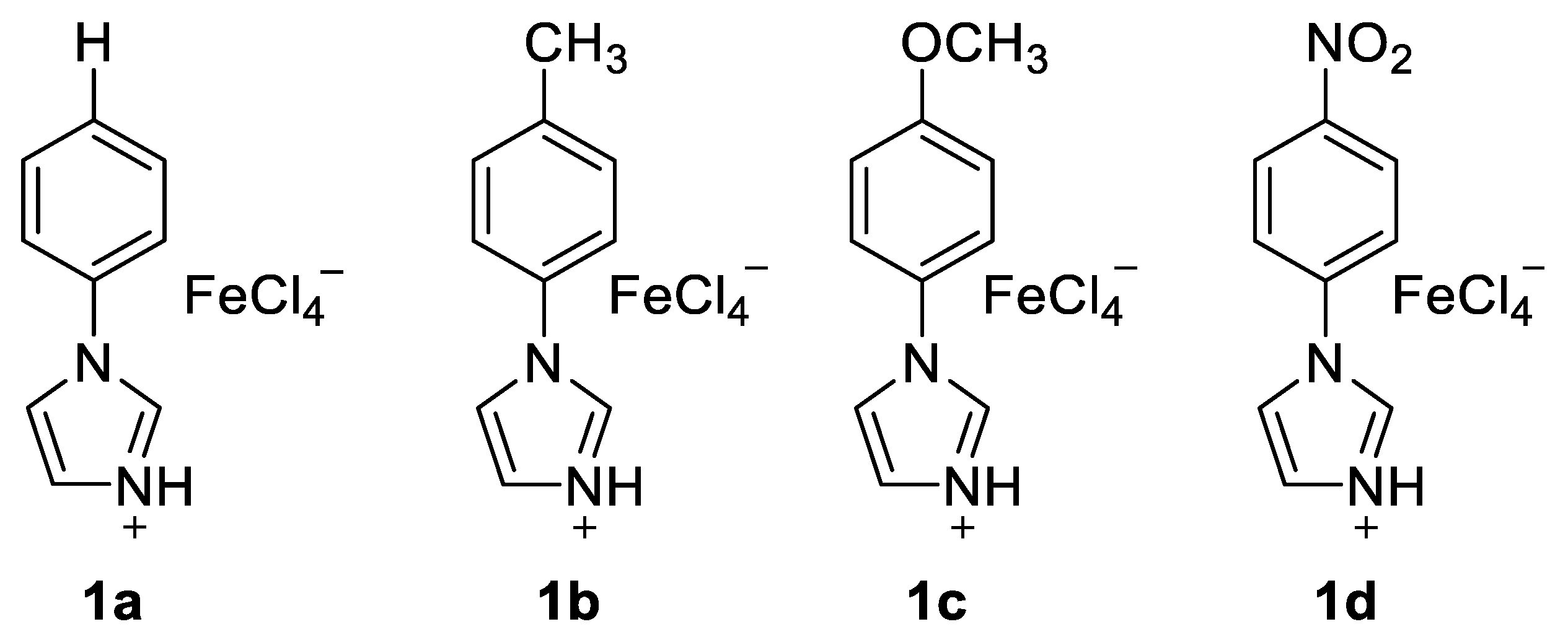
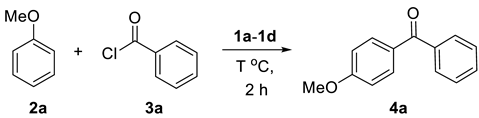
Initial studies of 2a and 3a determined the optimal reaction conditions (Table 1). The study of dual Brønsted–Lewis acidic ionic liquids 1a, 1b, 1c, and 1d of Figure 1 suggested that 1d was the best catalyst of Friedel–Crafts acylation, providing the product 4a in 74% yield (Table 1, entries 1–4) [37,38]. Increasing the temperature to 100 °C and 120 °C with 1d afforded 4a in 74% and 71% yields, respectively (Table 1, entries 5–6). Lowering the concentration of 1d to 0.9 equivalent led to higher yield (78%, Table 1, entry 7), while decreasing it to 0.8 equivalent reduced the reaction yield (73%, Table 1, entry 8).

Table 1.
Optimized condition of Friedel–Crafts acylation.
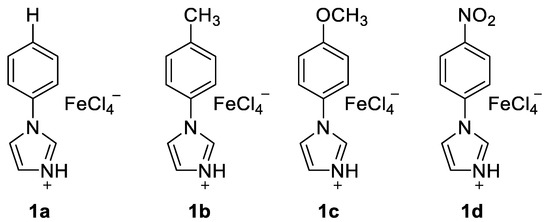
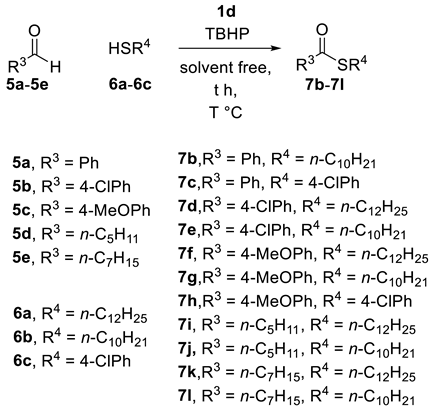
Figure 1.
Tunable aryl imidazolium recyclable ionic liquid 1a–1d with dual activity.
2.1. Friedel–Crafts Acylation
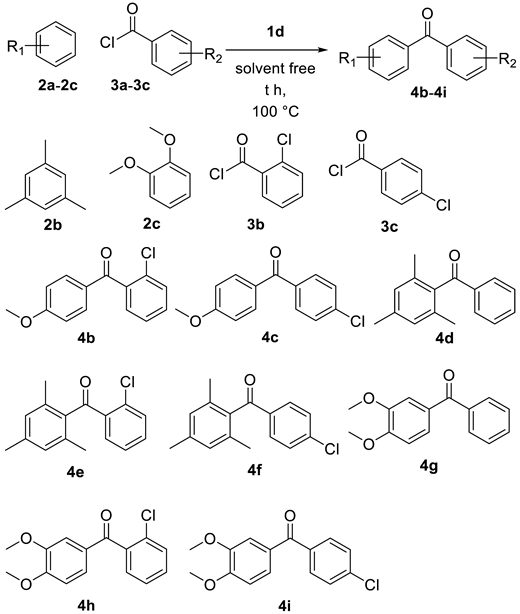
The scope of Friedel–Crafts reaction with various aryl alkanes and acyl chlorides under optimized reaction conditions was investigated (Table 2, entries 1–8). The Friedel–Crafts reactions with aryl alkanes 2a and different acyl chloride (3b–3c) under standard conditions were carried out, and the desired products 4b and 4c were isolated in 73% and 68% yields (Table 2, entries 1,2). Under the same reaction conditions, the Friedel–Crafts reaction in the presence of 2b and 3a produced 4d in 83% yield (Table 1, entry 3). The reaction proceeded very smoothly with 2b and 3b under the above conditions to yield the compound 4e with a 79% yield (Table 2, entry 4). Acyl chloride 3c reacted with 2b to afford the corresponding product 4f in 89% yield (Table 2, entry 5). Aryl alkane 2c and acyl chloride 3a were coupled under similar reaction conditions to obtain the product 4g in 81% yield (Table 2, entry 6). When the reaction was performed using 2c and 3b, the product 4h was afforded in 71% yield (Table 2, entry 7). Product 4i was furnished in 70% yield using 2c and 3c (Table 2, entry 8). While doing Friedel–Crafts acylation, HCl did not affect the reaction, so could not consider to remove HCl from ionic liquid. It is possible to remove HCl from an ionic liquid by using a high vacuum or suction pump.

Table 2.
Ionic liquids 1d catalyzed Friedel—Crafts acylation with aryl alkanes 2a–2c and acid chlorides 3a–3c without solvent.
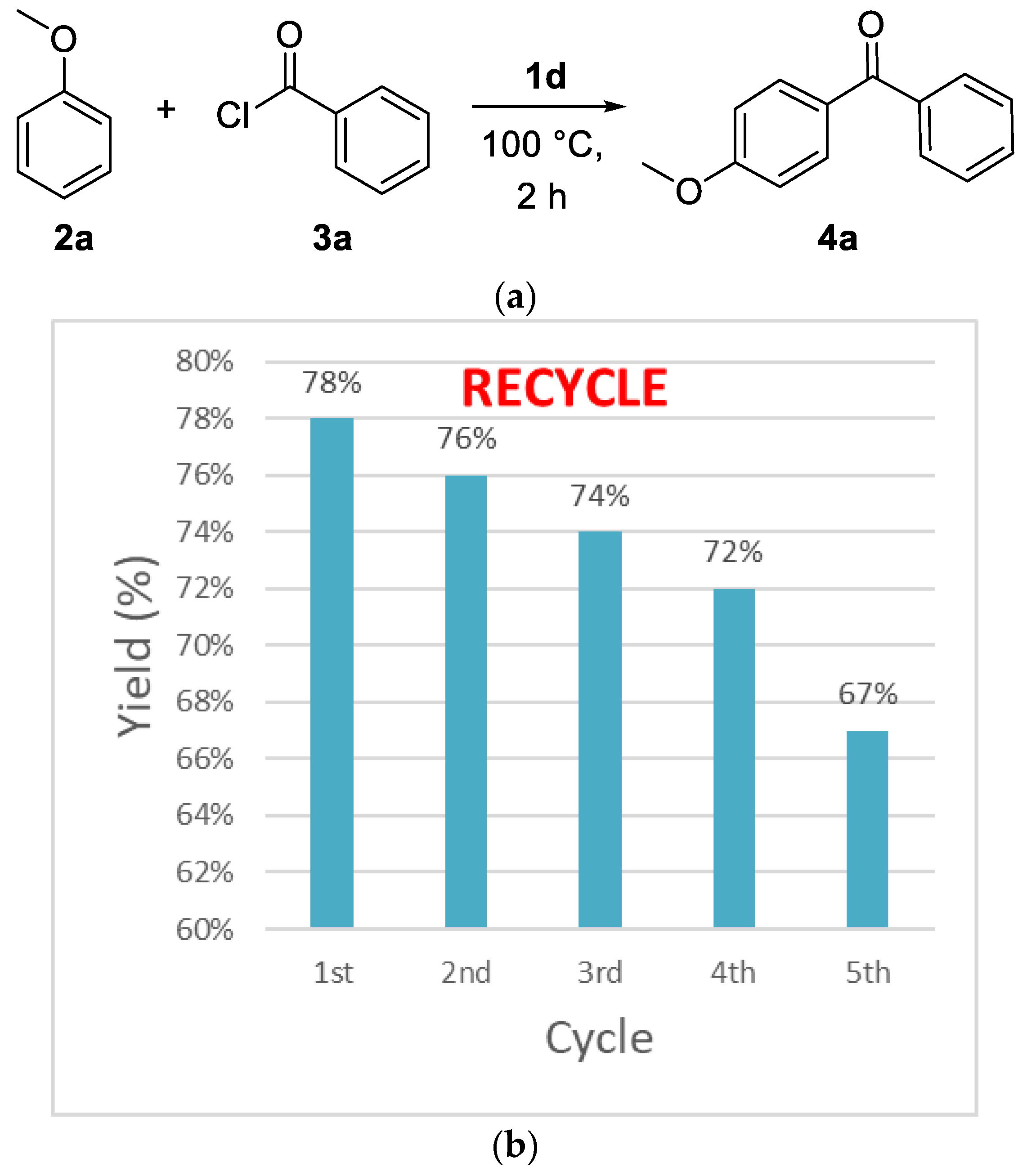
To further develop a recyclable catalytic system, the recycling of the 1d was inspected under the optimized conditions (Figure 2a). After reaction finished, diethyl ether was added. The ionic liquid 1d was recovered from water layer and dried for the next reaction under vacuum. For the first run, the activity of ionic liquid 1d remained same yield (78%). In the subsequent second (76%), third (66%), fourth (69%), and fifth (67%) cycles, the desired product was still reached with 100% conversion, when reaction was monitored on TLC plate, the desired product saw without any side product (Figure 2b).
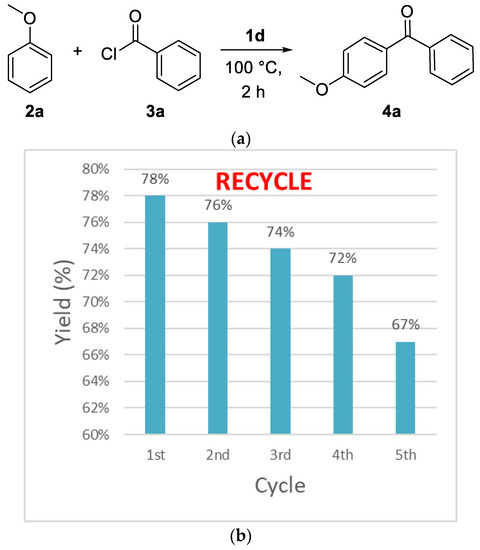
Figure 2.
(a) Friedel-Crafts acylation reaction (b) Recycling of 1d in the synthesis of (4-methoxyphenyl) phenyl-methanone 4a.
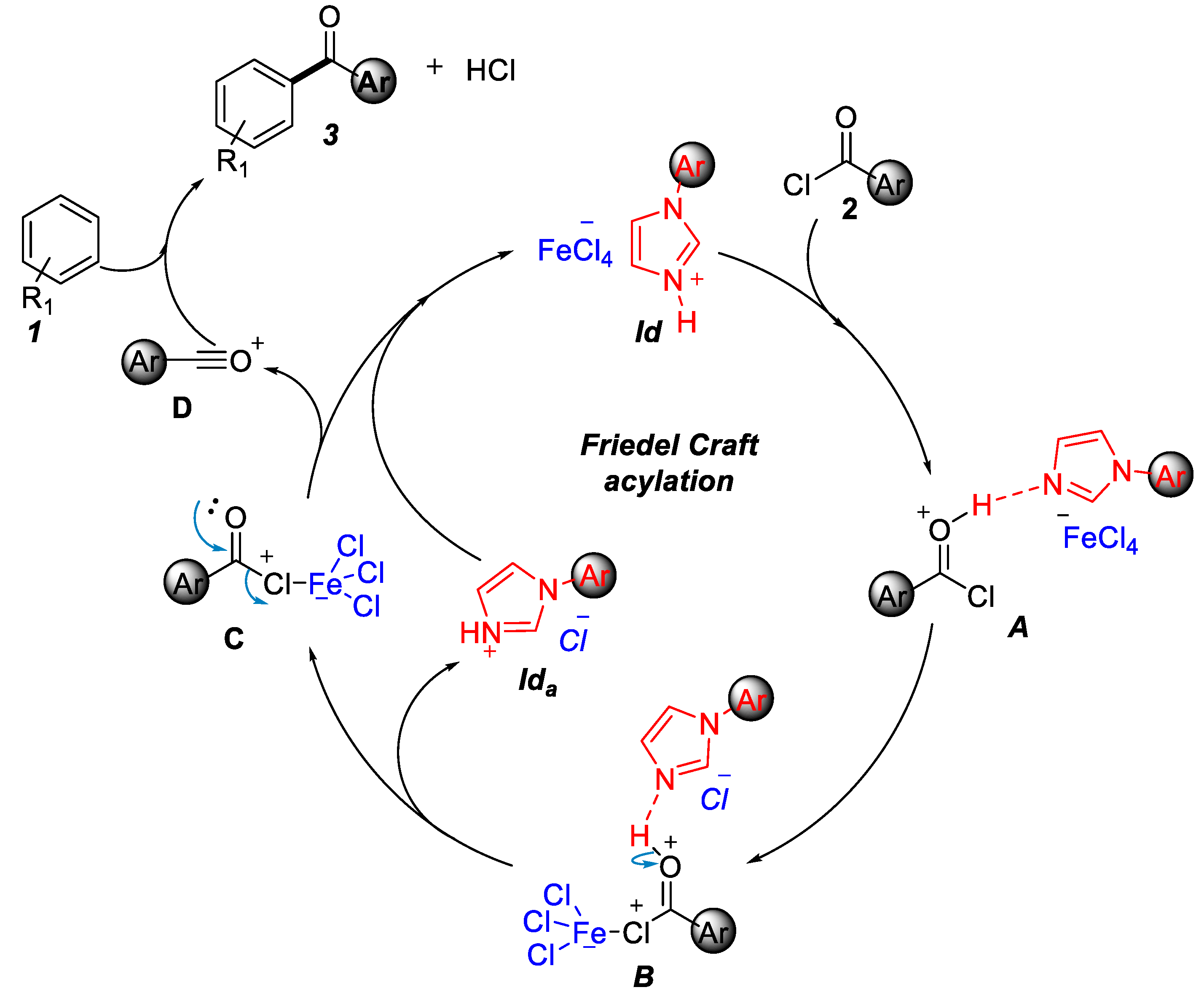
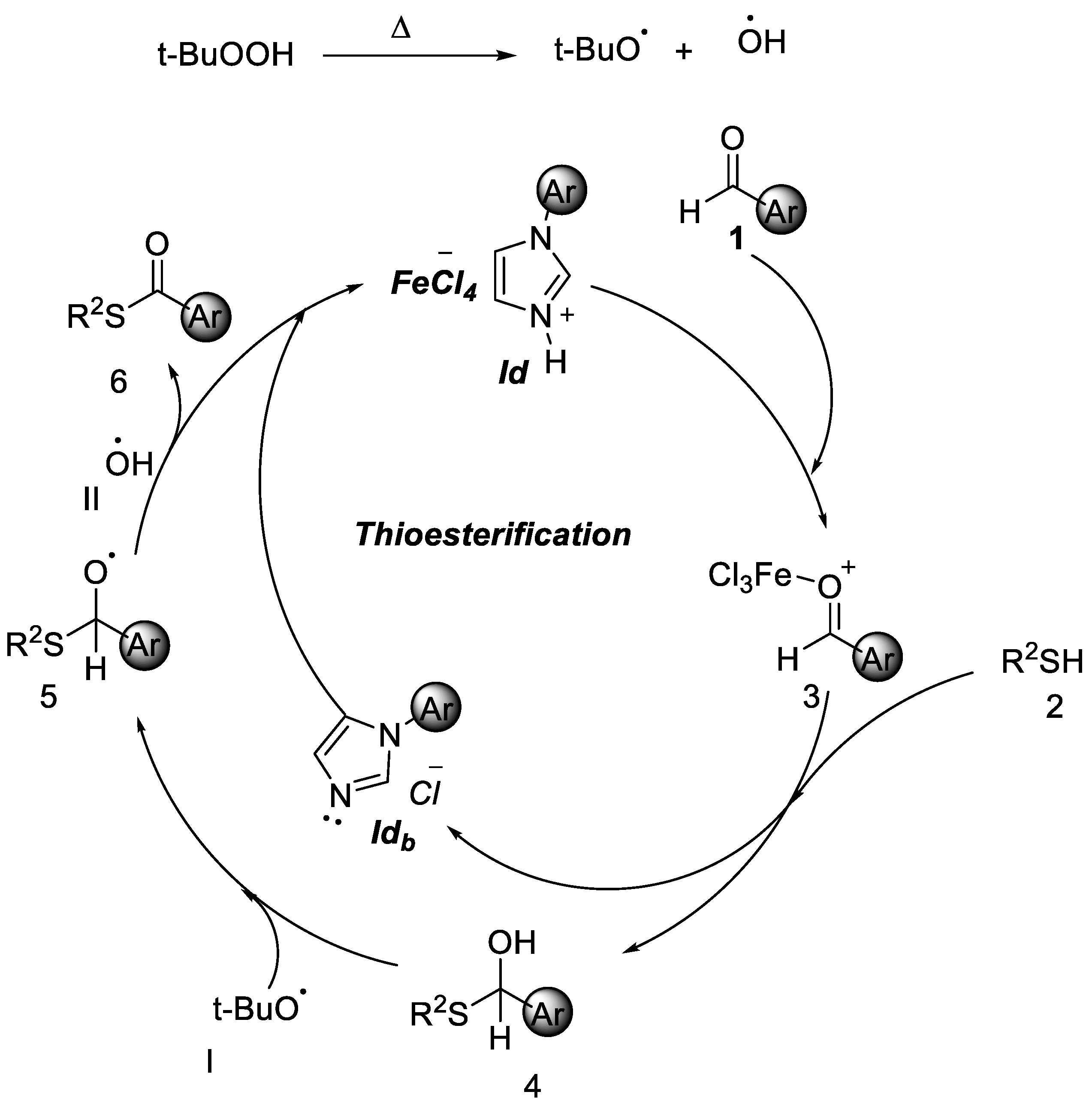
Initially, acyl chloride 2 was abstracted the proton of 1d. The acyl chloride cation A and 1da transformed to intermediate B by the release of 1db. Then, 1db captured the proton of intermediate B to give intermediate C. Subsequently, C was transformed into acyl cation D by the release of FeCl4 anion. Ultimately, the acyl cation D reacted with aryl alkane 1 to form the desired product 3 (Figure 3).
Figure 3.
Proposed mechanism of Friedel–Crafts acylation.
2.2. Thioesterification
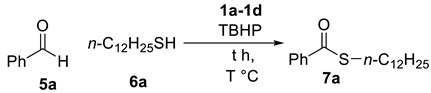
Initially, benzaldehyde 5a and 1-dodecanethiol 6a were selected as the model substrates to determine the optimized reaction conditions and the results are summarized in Table 3. We first examined the source of the ionic liquids 1a–1d (0.025 equivalent) in presence of TBHP as a oxidant at 120 °C (Table 3, entries 1–4), and 1d was the best catalyst of thioesterification providing the product 7a in 70% yield (Table 3, entries 1–4). Decreasing the temperature to 100 °C and increasing the temperature to 140 °C with 1d afforded 7a in similar yields (Table 3, entries 5–6). Decreasing the concentration of 1d to 0.010 equivalent led to lower yield (68%, Table 1, entry 7), while increasing it to 0.030 equivalent reduced the reaction yield (61%, Table 1, entry 8).

Table 3.
Optimized condition of thioesterification.
With these optimized reaction conditions in hand, the scope of the substrates was then studied. The results are summarized in Table 4. A variety of alkyl thiols and aromatic thiols were conducted with aromatic and alkyl aldehydes to afford the corresponding thioesters in good to excellent yields. Aromatic aldehydes bearing electron-donating and electron-withdrawing substituents are all suitable for catalysis. Aldehyde reacted with thiol 6b and 6c to give corresponding product 7b in 88% and 7c in 55% respectively. It is important to note that this system shows good functional group tolerance; chloro (Table 4, products 7d, 7e and 7f) are tolerated by reaction condition employed. Aldehydes bearing electron donating substituents underwent thioesterification with alkyl and aryl thiols to give desired product (Table 4, products 7g and 7h). Alkyl thiols were also reacted with alkyl aldehydes to give the corresponding thioesters (Table 4, products 7i, 7j, 7k, and 7l).

Table 4.
Ionic liquids 1d catalyzed coupling reaction with aldehydes 5a–5e and thiols 6a–6c without solvent.
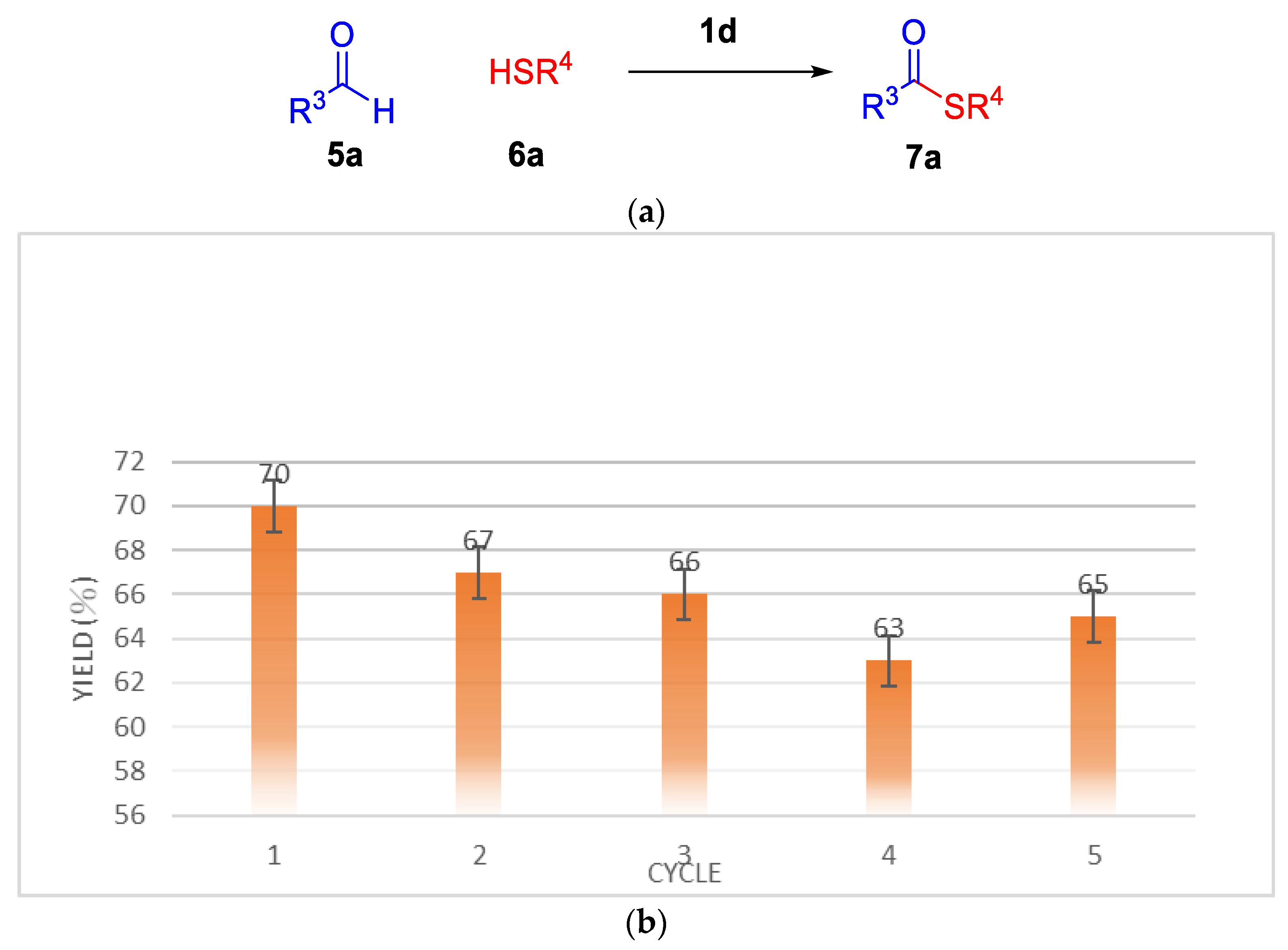
In this method, the recovery of ionic liquid 1d ranges from 63–70% yields. The catalytic activity was examined by thioesterification of thiols at 120 °C for 1 h (Figure 4a). The results are presented in (Figure 4b). Ionic liquid was recovered and reused up to five times with only slightly decreased catalytic activity.
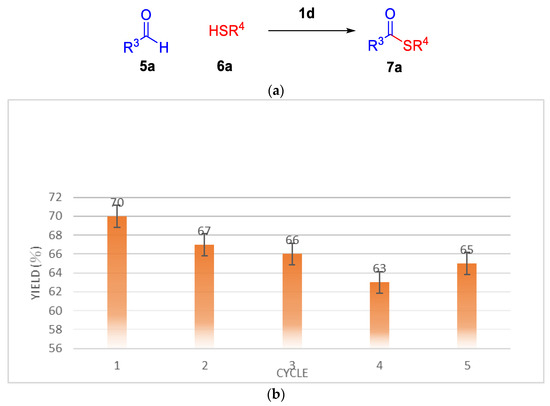
Figure 4.
(a) Thioesterification reaction of thiols (b) Recycling of ld in the synthesis of S-Dodecyl benzothioate.
Based on the above experimental results, a plausible mechanism is proposed in Figure 5. When 1d is reacted with TBHP, and t-BuOO· radical is generated at the time. Initially benzaldehyde reacted with ionic liquid 1d, which would lead to intermediate 3. Then thiols react with intermediate 3 to give 4. A hydrogen atom is then abstracted from aldehyde to give an acyl radical. Further t-BuOO· radical reacted with 4 to give complex 5 and then hydroxyl radicle II Reacts with 5 to give the final product 6.
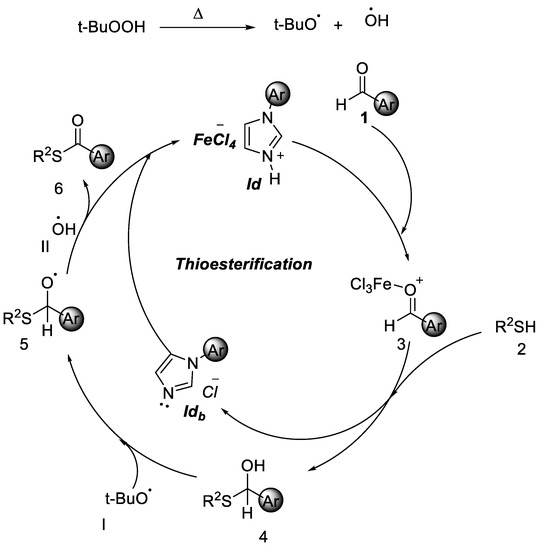
Figure 5.
Proposed mechanism of thioesterification.
3. Materials and Methods
The reactions were conducted in flame-dried glassware, under the nitrogen atmosphere. Acetonitrile and dichloromethane were purified and dried from a safe purification system containing activated Al2O3. All reagents obtained from commercial sources were used without purification unless otherwise mentioned. Flash column chromatography was carried out on Silica Gel 60. TLC was performed on pre-coated glass plates of Silica Gel 60 F254 detection was executed by spraying with a solution of Ce(NH4)2(NO3)6 (0.5 g), (NH4)6Mo7O24 (24.0 g), and H2SO4 (28.0 mL) in water (500.0 mL) and subsequent heating on a hot plate. Optical rotations were measured at 589 nm (Na), 1H, 13C NMR, DEPT, 1H-1H COSY, 1H-13C COSY, and NOESY spectra were recorded with 400 MHz instruments. Chemical shifts are in ppm from Me4Si generated from the CDCl3 lock signal at δ 7.26. IR spectra were taken with a FT-IR spectrometer using NaCl plates. Mass spectra were analyzed on instrument with an EI, ESI, APCI, and FAB source.
(4-Methoxyphenyl)-phenylmethanone (4a). To a solution of aryl alkane 2a (217 μL, 2 mmol), acyl chloride 3a (116 μL, 1 mmol), and ionic liquid 1d (349 mg, 0.9 mmol) were stirred at 100 °C for two hours. After cooling, the reaction mixture was washed by diethyl ether (2 × 40 mL). The diethyl ether layer was decanted, extracted with water, aqueous NaHCO3, and brine, and dried over MgSO4. After filtration, the organic solvent was then removed on a rotary evaporator. The residue was purified by flash chromatography to give the desired product 4a (165 mg, 78%) as a light yellow oil. Rf 0.37 (EtOAc/Hex = 1/6). IR (NaCl) v 3060, 3006, 2840, 1651, 1597, 1508, 1171 cm−1; 1H NMR (Supplementary Materials) (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.82 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 7.74 (d, J = 6.8 Hz, 2H), 7.55 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 1H), 7.45 (t, J = 7.6 Hz, 2H), 6.95 (d, J = 9.2 Hz, 2H), 3.86 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ 195.4, 163.1, 138.2, 132.4, 131.8, 130.0, 129.6, 128.1, 113.4, 55.4; HRMS (EI, M+) calculated for C14H12O2 212.0837, found 212.0834.
(2-Chlorophenyl)-(4-methoxyphenyl) methanone (4b). To a solution of aryl alkane 2a (217 μL, 2 mmol), acyl chloride 3b (126 μL, 1 mmol), and ionic liquid 1d (349 mg, 0.9 mmol) were stirred at 100 °C for four hours. After cooling, the reaction mixture was washed by diethyl ether (2 × 40 mL). The diethyl ether layer was decanted, extracted with water, aqueous NaHCO3, and brine, and dried over MgSO4. After filtration, the organic solvent was removed on a rotary evaporator. The residue was purified by flash chromatography to give the desired product 4b (180 mg, 73%) as a light yellow solid. Rf 0.40 (EtOAc/Hex = 1/4); mp 71–74 °C; IR (NaCl) v 3068, 3009, 2964, 2840, 1659, 1595, 1508, 1464, 1149, 843 cm−1; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.79 (d, J = 9.2 Hz, 2H), 7.47–7.38 (m, 2H), 7.37–7.36 (m, 1H), 7.35 (d, J = 1.2 Hz, 1H), 6.94 (d, J = 9.2 Hz, 2H), 3.88 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ 193.8, 164.1, 139.0, 132.5, 131.0, 130.8, 129.9, 129.4, 128.8, 126.6, 113.8, 55.5; HRMS (ESI, M + H+) calculated for C14H12ClO2 247.0526, found 247.0525
(4-Chlorophenyl)-(4-methoxyphenyl)methanone (4c). To a solution of aryl alkane 2a (217 μL, 2 mmol), acyl chloride 3c (127 μL, 1 mmol), and ionic liquid 1d (349 mg, 0.9 mmol) were stirred at 100 °C for four hours. After cooling, the reaction mixture was washed by diethyl ether (2 × 40 mL). The diethyl ether layer was decanted, extracted with water, aqueous NaHCO3, and brine, and dried over MgSO4. After filtration, the organic solvent was removed on a rotary evaporator. The residue was purified by flash chromatography to give the desired product 4c (168 mg, 68%) as a light yellow solid. Rf 0.37 (EtOAc/Hex = 1/4); mp 119–122 °C; IR (NaCl) v 2962, 2934, 2841, 1641, 1604, 1509, 1461, 1148, 760 cm−1; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.80 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H), 7.71 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H), 7.45 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H), 6.97 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 3.89 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ 194.2, 163.3, 138.2, 136.5, 132.4, 131.1, 129.7, 128.5, 113.6, 55.5; HRMS (ESI, M + H+) calculated for C14H12ClO2 247.0526, found 247.0523.
(2,4,6-Trimethylphenyl)-phenylmethanone (4d). To a solution of aryl alkane 2b (278 µL, 2 mmol), acyl chloride 3a (116 µL, 1 mmol) and ionic liquid 5 (349 mg, 0.9 mmol) were stirred at 100 °C for 2 hours. After cooling, the reaction mixture was washed by diethyl ether (2 × 40 mL). The diethyl ether layer was decanted, extracted with water, aqueous NaHCO3, and brine, and dried over MgSO4. After filtration, the organic solvent was then removed on a rotary evaporator. The residue was purified by flash chromatography to give the desired product 4d (186 mg, 83%) as a light yellow oil. Rf 0.40 (EtOAc/Hex = 1/12); IR (NaCl) v 3061, 2951, 2921, 2860, 1671, 1449, 1380 cm−1; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.81 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, 2H), 7.57 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 1H), 7.44 (t, J = 7.8 Hz, 2H), 6.90 (s, 2H), 2.34 (s, 3H), 2.09 (s, 6H); 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ 200.8, 138.5, 137.3, 136.8, 134.1, 133.5, 129.4, 128.7, 128.3, 21.1, 19.3; HRMS (ESI, M + H+) calculated for C16H17O 225.1279, found 225.1281.
(2-Chlorophenyl)-(2,4,6-trimethylphenyl) methanone (4e). To a solution of aryl alkane 2b (278 μL, 2 mmol), acyl chloride 3b (126 μL, 1 mmol), and ionic liquid 1d (349 mg, 0.9 mmol) were stirred at 100 °C for 3.5 hours. After cooling, the reaction mixture was washed by diethyl ether (2 × 40 mL). The diethyl ether layer was decanted, extracted with water, aqueous NaHCO3, and brine, and dried over MgSO4. After filtration, the organic solvent was then removed on a rotary evaporator. The residue was purified by flash chromatography to give the desired product 4e (204 mg, 79%) as a light orange solid. Rf 0.53 (EtOAc/Hex = 1/10). mp 101–102 °C; IR (NaCl) v 2917, 1671, 1610, 1584, 1436 cm−1; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.47 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 2H), 7.41 (t, J = 7.7 Hz, 1H), 7.26 (t, J = 7.5 Hz, 1H), 6.87 (s, 2H), 2.31 (s, 3H), 2.12 (s, 6H); 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ 198.9, 139.3, 137.6, 137.3, 135.0, 133.2, 132.7, 131.7, 131.4, 128.8, 126.8, 21.1, 19.7; HRMS (ESI, M + Na+) calculated for C16H15ClONa 281.0709, found 281.0710.
(4-Chlorophenyl)-(2,4,6-trimethylphenyl)methanone (4f). To a solution of aryl alkane 2b (278 μL, 2 mmol), acyl chloride 3c (127 μL, 1 mmol), and ionic liquid 1d (349 mg, 0.9 mmol) were stirred at 100 °C for two hours. After cooling, the reaction mixture was washed by diethyl ether (2 × 40 mL). The diethyl ether layer was decanted, extracted with water, aqueous NaHCO3, and brine, and dried over MgSO4. After filtration, the organic solvent was then removed on a rotary evaporator. The residue was purified by flash chromatography to give the desired product 4f (230 mg, 89%) as a white solid. Rf 0.61 (EtOAc/Hex = 1/10). mp 64–65 °C; IR (NaCl) v 2921, 1673, 1586 cm−1; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.74 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H), 7.41 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 2H), 6.90 (s, 2H), 2.33 (s, 3H), 2.07 (s, 6H); 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ 199.5, 140.1, 138.7, 136.3, 135.6, 134.1, 130.7, 129.1, 128.4, 21.1, 19.3; HRMS (APCI, M + H+) calculated for C16H16ClO 259.0890, found 259.0888.
(3,4-Dimethoxyphenyl)-phenylmethanone (4g). To a solution of aryl alkane 2c (256 µL, 2 mmol), acyl chloride 3a (116 µL, 1 mmol) and ionic liquid 1d (349 mg, 0.9 mmol) were stirred at 100 °C for three hours. After cooling, the reaction mixture was washed by diethyl ether (2 × 40 mL). The diethyl ether layer was decanted, extracted with water, aqueous NaHCO3, and brine, and dried over MgSO4. After filtration, the organic solvent was then removed on a rotary evaporator. The residue was purified by flash chromatography to give the desired product 4g (196 mg, 81%) as a white solid. Rf 0.45 (EtOAc/Hex = 1/4); mp 100–101 °C; IR (NaCl) v 3079, 3003, 2960, 2839, 1649, 1594, 1272, 1130 cm−1; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.75 (d, J = 8.2 Hz, 2H), 7.55 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 1H), 7.48 (d, J = 2.0 Hz, 1H), 7.46 (t, J = 7.5 Hz, 2H), 7.36 (dd, J = 8.3, 2.0 Hz, 1H), 6.88 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H), 3.94 (s, 3H), 3.92 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ 195.4, 152.9, 148.9, 138.1, 131.7, 130.0, 129.6, 128.0, 125.4, 111.9, 109.6, 55.9; HRMS (ESI, M + Na+) calculated for C15H14O3Na 265.0841, found 265.0844.
(2-Chlorophenyl)-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl) methanone (4h). To a solution of aryl alkane 2c (256 μL, 2 mmol), acyl chloride 3b (126 μL, 1 mmol), and ionic liquid 1d (349 mg, 0.9 mmol) were stirred at 100 °C for 3.5 hours. After cooling, the reaction mixture was washed by diethyl ether (2 × 40 mL). The diethyl ether layer was decanted, extracted with water, aqueous NaHCO3, and brine, and dried over MgSO4. After filtration, the organic solvent was then removed on a rotary evaporator. The residue was purified by flash chromatography to give the desired product 4h (196 mg, 71%) as a light yellow solid. Rf 0.34 (EtOAc/Hex = 1/2). mp 142–143 °C; IR (NaCl) v 3079, 2936, 2840, 1659, 1592, 1513, 1464, 1418, 1133 cm−1; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.56 (d, J = 2.0 Hz, 1H), 7.45–7.37 (m, 2H), 7.34 (t, J = 1.0 Hz, 1H), 7.33 (d, J = 1.1 Hz, 1H), 7.19 (dd, J = 8.4, 2.0 Hz, 1H), 6.82 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H), 3.92 (d, J = 1.8 Hz, 6H); 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ 193.8, 153.9, 149.2, 138.8, 131.0, 130.7, 129.9, 129.4, 128.8, 126.5, 126.3, 110.7, 109.9, 56.1, 55.9; HRMS (ESI, M + H+) calculated for C15H14ClO3 277.0631, found 277.0632.
(4-Chlorophenyl)-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)methanone (4i). To a solution of aryl alkane 2c (256 µL, 2 mmol), acyl chloride 3c (127 µL, 1 mmol), and ionic liquid 1d (349 mg, 0.9 mmol) were stirred at 100 °C for three hours. After cooling, the reaction mixture was extracted by ethyl acetate (2 × 40 mL). The ethyl acetate layer was decanted, washed with water, aqueous NaHCO3, and brine, and dried over MgSO4. The residue was purified by flash chromatography to give the desired product 4i (193 mg, 70%) as a white solid. Rf 0.28 (EtOAc/Hex = 1/4). mp 113–114 °C; IR (NaCl) v 2935, 2839, 1649, 1594, 1514, 1272 cm−1; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.72 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H), 7.48–7.46 (m, 2H), 7.45–7.44 (m, 1H), 7.34 (dd, J = 8.0, 2.0 Hz, 1H), 6.90 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H), 3.97 (s, 3H), 3.95 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ 193.8, 152.9, 148.8, 137.9, 136.2, 130.9, 129.5, 128.2, 125.1, 111.6, 109.5, 55.8, 55.7; HRMS (ESI, M + H+) calculated for C15H14ClO3 277.0632, found 277.0656.
S-Dodecyl benzothioate (7a). To a solution of thiol 6a (240 µL, 1 mmol), aldehyde 5a (510 µL, 5 mmol), tert-butyl hydroperoxide (277 µL, 2 mmol), and ionic liquid 1d (9.7 mg, 0.025 mmol) were stirred at 120 °C for one hour in a sealed tube. After cooling, the reaction mixture was extracted with ethyl acetate (3 × 20 mL). The combined organic layers were dried over anhydrous MgSO4, filtered and concentrated. The residue was purified by flash chromatography to give the desire product 7a (214 mg, 70% yield) as a colorless liquid. Rf 0.36 (Hexane). IR (NaCl) v 3063, 3030, 2925, 2854, 1666, 1597, 1449, 1377, 1027, 1001 cm−1; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.97 (dd, J = 8.4, 1.2 Hz, 2H), 7.52 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 1H), 7.41 (t, J = 7.6 Hz, 2H), 3.06 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 2H), 1.72–1.62 (m, 2H), 1.46–1.38 (m, 2H), 1.27 (s, 16H), 0.89 (t, J = 7.0 Hz, 3H); 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ 191.7, 137.1, 133.0, 128.4, 127.0, 31.9, 29.6, 29.5, 29.4, 29.3, 29.1, 28.9, 28.88, 22.6, 14.0; HRMS (FAB, M + H+) calculated for C19H31OS 307.2096, found 307.2087.
S-Decyl benzothioate (7b). To a solution of thiol 6b (212 µL, 1 mmol), aldehyde 5a (510 µL, 5 mmol), tert-butyl hydroperoxide (277 µL, 2 mmol), and ionic liquid 1d (9.7 mg, 0.025 mmol) were stirred at 120 °C for 1 hour in a sealed tube. After cooling, the reaction mixture was extracted with ethyl acetate (3 × 20 mL). The combined organic layers were dried over anhydrous MgSO4, filtered and concentrated. The residue was purified by flash chromatography to give the desire product 7b (245 mg, 88% yield) as a colorless liquid. Rf 0.30 (Hexane). IR (NaCl) v 3063, 3031, 2926, 2854, 1666, 1597, 1449, 1377, 1027, 1001 cm−1; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.97 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, 2H), 7.53 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 1H), 7.42 (t, J = 7.8 Hz, 2H), 3.06 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 2H), 1.63–1.71 (m, 2H), 1.46–1.38 (m, 2H), 1.27 (s, 12H), 0.89 (t, J = 6.8 Hz, 3H); 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ 191.9, 137.2, 133.0, 128.4, 127.1, 31.8, 29.5, 29.49, 29.45, 29.2, 29.1, 29.0, 28.9, 22.6, 14.0; HRMS (ESI, M + Na+) calculated for C17H26NaOS 301.1602, found 301.1606.
S-(4-Chlorophenyl) benzothioate (7c). To a solution of thiol 6c (145 mg, 1 mmol), aldehyde 5a (510 µL, 5 mmol), tert-butyl hydroperoxide (277 µL, 2 mmol), and ionic liquid 1d (9.7 mg, 0.025 mmol) were stirred at 120 °C for one hour in a sealed tube. After cooling, the reaction mixture was extracted with ethyl acetate (3 × 20 mL). The combined organic layers were dried over anhydrous MgSO4, filtered and concentrated. The residue was purified by flash chromatography to give the desire product 7c (137 mg, 55% yield) as a white solid. Rf 0.25 (Hexane). mp 75–76 °C; IR (NaCl) v 3082, 3055, 1674, 1574, 1474, 1446, 1389, 1203, 1012 cm−1; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 8.03 (dd, J = 8.4, 1.2 Hz, 2H), 7.62 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 1H), 7.50 (t, J = 7.8 Hz, 2H), 7.47–7.41 (m, 4H); 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ 189.5, 136.2, 135.9, 133.8, 129.4, 128.7, 127.4, 125.7; HRMS (ESI, M + Na+) calculated for C13H9ClNaOS 270.9960, found 270.9965.
S-Dodecyl 4-chlorobenzothioate (7d). To a solution of thiol 6a (240 µL, 1 mmol), aldehyde 5b (703 µL, 5 mmol), tert-butyl hydroperoxide (277 µL, 2 mmol), and ionic liquid 1d (9.7 mg, 0.025 mmol) were stirred at 120 °C for one hour in a sealed tube. After cooling, the reaction mixture was extracted with ethyl acetate (3 × 20 mL). The combined organic layers were dried over anhydrous MgSO4, filtered, and concentrated. The residue was purified by flash chromatography to give the desire product 7d (248 mg, 73%) as a colorless liquid. Rf 0.28 (Hexane). IR (NaCl) v 2925, 2854, 1913, 1825, 1785, 1668, 1589, 1464, 1092 cm1; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.90 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 7.41 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 3.07 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 2H), 1.67 (quint, J = 7.4 Hz, 2H), 1.42 (quint, J = 7.2 Hz, 2H), 1.26 (s, 16H), 0.88 (t, J = 7.0 Hz, 3H); 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ 190.9, 139.5, 135.5, 128.8, 128.5, 31.9, 29.6, 29.56, 29.5, 29.3, 29.2, 29.1, 28.9, 22.7, 14.1; HRMS (ESI, M + H+) calculated for C19H30ClOS 341.1706, found 341.1705.
S-Decyl 4-chlorobenzothioate (7e). To a solution of thiol 6b (221 µL, 1 mmol), aldehyde 5b (703 mg, 5 mmol), tert-butyl hydroperoxide (277 µL, 2 mmol), and ionic liquid 1d (9.7 mg, 0.025 mmol) were stirred at 120 °C for one hour in a sealed tube. After cooling, the reaction mixture was extracted with ethyl acetate (3 × 20 mL). The combined organic layers were dried over anhydrous MgSO4, filtered, and concentrated. The residue was purified by flash chromatography to give the desire product 7e (228 mg, 73%) as a colorless liquid. Rf 0.31 (Hexane). IR (NaCl) v 2955, 2926, 2854, 1668, 1589, 1464, 1092 cm−1; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.90 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H), 7.41 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H), 3.06 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 2H), 1.66 (quint, J = 7.4 Hz, 2H), 1.41 (quint, J = 7.2 Hz, 2H), 1.26 (s, 12H), 0.88 (t, J = 6.8 Hz, 3H); 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ 191.0, 139.5, 135.6, 128.8, 128.5, 31.9, 29.5, 29.47, 29.3, 29.2, 29.1, 28.9, 22.7, 14.1; HRMS (ESI, M + H+) calculated for C17H26ClOS 313.1393, found 313.1355.
S-Dodecyl 4-methoxybenzothioate (7f). To a solution of thiol 6a (239 μL, 1 mmol), aldehyde 5c (609 μL, 5 mmol), tert-butyl hydroperoxide (276 μL, 2 mmol), and ionic liquid 1d (10 mg, 0.025 mmol) were stirred at 140 °C for one hour in a sealed tube. After cooling, the reaction mixture was extracted with ethyl acetate (3 × 20 mL). The combined organic layers were dried over anhydrous MgSO4, filtered, and concentrated. The residue was purified by flash chromatography to give the desire product 7f (255 mg, 76%) as a colorless liquid. Rf 0.20 (hexane); IR (NaCl) v 2924, 2853, 1658, 1602, 1508, 1463, 1259, 837; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.93 (d, J = 9.2 Hz, 2H), 6.89 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 3.83 (s, 3H), 3.03 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 2H), 1.68–1.60 (m, 2H), 1.44–1.36 (m, 2H), 1.24 (s, 16H), 0.86 (t, J = 6.8 Hz, 3H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 190.4, 163.5, 130.0, 129.2, 113.5, 55.3, 31.9, 29.6, 29.58, 29.54, 29.5, 29.3, 29.1, 28.9, 28.8, 22.6, 14.0; HRMS (ESI, M + Na+) calculated for C20H32NaO2S 359.2020, found 359.2032.
S-Decyl 4-methoxybenzothioate (7g). To a solution of thiol 6b (207 μL, 1 mmol), aldehyde 5c (609 μL, 5 mmol), tert-butyl hydroperoxide (276 μL, 2 mmol), and ionic liquid 1d (10 mg, 0.025 mmol) were stirred at 120 °C for one hour in a sealed tube. After cooling, the reaction mixture was extracted with ethyl acetate (3 × 20 mL). The combined organic layers were dried over anhydrous MgSO4, filtered, and concentrated. The residue was purified by flash chromatography to give the desire product 7g (226 mg, 73%) as a colorless liquid. Rf 0.25 (hexane); IR (NaCl) v 2925, 2854, 1658, 1602, 1508, 1463, 1259, 838; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.93 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 6.90 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 3.84 (s, 3H), 3.02 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 2H), 1.68–1.60 (m, 2H), 1.44–1.35 (m, 2H), 1.24 (s, 12H), 0.86 (t, J = 6.8 Hz, 3H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 190.4, 163.5, 130.0, 129.2, 113.6, 55.3, 31.8, 29.6, 29.5, 29.4, 29.2, 29.1, 28.9, 28.8, 22.6, 14.0; HRMS (ESI, M + Na+) calculated for C18H28NaO2S 331.1708, found 331.1702.
S-(4-Chlorophenyl) 4-methoxybenzothioate (7h). To a solution of thiol 6c (145 mg, 1 mmol), aldehyde 5c (609 μL, 5 mmol), tert-butyl hydroperoxide (276 μL, 2 mmol), and ionic liquid 1d (10 mg, 0.025 mmol) were stirred at 120 °C for one hour in a sealed tube. After cooling, the reaction mixture was extracted with ethyl acetate (3 × 20 mL). The combined organic layers were dried over anhydrous MgSO4, filtered and concentrated. The residue was purified by flash chromatography to give the desire product 7h (142 mg, 51%) as a white solid. Rf 0.45 (EtOAc /Hex = 1/4); mp 96–97 °C; IR (NaCl) v 1690, 1660, 1602, 1508, 1261, 833; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.98 (d, J = 9.2 Hz, 2H), 7.41 (d, J = 3.2 Hz, 4H), 6.94 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 3.84 (s, 3H).; 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 187.7, 164.0, 136.2, 135.6, 129.6, 129.2, 128.9, 126.0, 113.8, 55.4; HRMS (ESI, M + Na+) calculated for C14H11ClNaO2S 301.0066, found 301.0059.
S-Dodecyl hexanethioate (7i). To a solution of thiol 6a (239 μL, 1 mmol), aldehyde 5d (615 μL, 5 mmol), tert-butyl hydroperoxide (276 μL, 2 mmol), and ionic liquid 1d (10 mg, 0.025 mmol) were stirred at 120 °C for one hour in a sealed tube. After cooling, the reaction mixture was extracted with ethyl acetate (3 × 20 mL). The combined organic layers were dried over anhydrous MgSO4, filtered, and concentrated. The residue was purified by flash chromatography to give the desire product 7i (240 mg, 80%) as a colorless liquid. Rf 0.35 (hexane); IR (NaCl) v 2957, 2926, 2855, 1693, 1464, 1121; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 2.85 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 2H), 2.52 (t, J = 7.6 Hz, 2H), 1.69–1.61 (m, 2H), 1.59–1.51 (m, 2H), 1.37–1.27 (m, 8H), 1.25 (s, 14H), 0.90–0.85 (m, 6H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 199.5, 199.3, 44.0, 31.9, 31.0, 29.6, 29.5, 29.4, 29.3, 29.1, 28.8, 28.7, 25.3, 22.6, 22.3, 14.0, 13.8; HRMS (FAB, M + H+) calculated for C18H37OS 301.2565, found 301.2568.
S-Decyl hexanethioate (7j). To a solution of thiol 6b (221 µL, 1 mmol), aldehyde 5d (615 µL, 5 mmol), tert-butyl hydroperoxide (277 µL, 2 mmol), and ionic liquid 1d (9.7 mg, 0.025 mmol) were stirred at 120 °C for one hour in a sealed tube. After cooling, the reaction mixture was extracted with ethyl acetate (3 × 20 mL). The combined organic layers were dried over anhydrous MgSO4, filtered, and concentrated. The residue was purified by flash chromatography to give the desire product 7j (194 mg, 71%) as a colorless liquid. Rf 0.40 (Hexane). IR (NaCl) v 2927, 2855, 2731, 2671, 1693, 1463, 1030 cm−1; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 2.85 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 2H), 2.52 (t, J = 7.6 Hz, 2H), 1.65 (quint, J = 7.4 Hz, 2H), 1.55 (quint, J = 7.3 Hz, 2H), 1.30 (m, 8H), 1.25 (s, 10H), 0.88 (q, J = 6.4 Hz, 6H); 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ 199.9, 44.1, 31.9, 31.1, 29.6, 29.5, 29.48, 29.3, 29.1, 28.82, 28.8, 25.4, 22.7, 22.3, 14.1, 13.9; HRMS (ESI, M + Na+) calculated for C16H32NaOS 295.2072, found 295.2072.
S-Dodecyl octanethioate (7k). To a solution of thiol 6a (240 µL, 1 mmol), aldehyde 5e (781 µL, 5 mmol), tert-butyl hydroperoxide (277 µL, 2 mmol), and ionic liquid 1d (9.7 mg, 0.025 mmol) were stirred at 120 °C for one hour in a sealed tube. After cooling, the reaction mixture was extracted with ethyl acetate (3 × 20 mL). The combined organic layers were dried over anhydrous MgSO4, filtered, and concentrated. The residue was purified by flash chromatography to give the desire product 7k (223 mg, 68% yield) as a colorless liquid. Rf 0.48 (Hexane). IR (NaCl) v 2923, 2855, 1694, 1463, 1377, 1043 cm−1; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 2.83 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 2H), 2.50 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 2H), 1.69–1.58 (m, 2H), 1.58–1.48 (m, 2H), 1.23 (s, 26H), 0.85 (t, J = 6.6 Hz, 6H); 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ 199.6, 44.1, 31.9, 31.6, 29.6, 29.58, 29.55, 29.5, 29.3, 29.1, 28.9, 28.88, 28.8, 28.7, 25.7, 22.7, 22.6, 14.1, 14.0; HRMS (FAB, M + H+) calculated for C20H41OS 329.2878, found 329.2878.
S-Decyl octanethioate (7l). To a solution of thiol 6b (221 µL, 1 mmol), aldehyde 5e (781 µL, 5 mmol), tert-butyl hydroperoxide (277 µL, 2 mmol), and ionic liquid 1d (9.7 mg, 0.025 mmol) were stirred at 120 °C for one hour in a sealed tube. After cooling, the reaction mixture was extracted with ethyl acetate (3 × 20 mL). The combined organic layers were dried over anhydrous MgSO4, filtered, and concentrated. The residue was purified by flash chromatography to give the desire product 7l (192 mg, 64%) as a colorless liquid. Rf 0.35 (Hexane). IR (NaCl) v 2956, 2926, 2855, 2730, 2671, 1693, 1464, 1124 cm−1; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 2.85 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 2H), 2.52 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 2H), 1.64 (quint, J = 7.2 Hz, 2H), 1.55 (quint, J = 7.3 Hz, 2H), 1.36–1.26 (m, 10H), 1.25 (s, 12H), 0.87 (t, J = 7.0 Hz, 6H); 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ 199.8, 44.1, 31.9, 31.6, 29.6, 29.5, 29.48, 29.3, 29.1, 28.9, 28.8, 28.79, 25.7, 22.7, 22.6, 14.1, 14.0; HRMS (ESI, M + Na+) calculated for C18H36NaOS 323.2385, found 323.2373.
4. Conclusions
The designed ionic liquid 1d were successfully catalyze the Friedel–Crafts acylation reaction and thioesterification reaction. It provides good to excellent yield in both the reactions under optimal conditions. The ionic liquid 1d exhibits the dual Brønsted and Lewis acidic property. The catalyst showed high atom economy, high thermal stability, and could be recycled with minor loss in activity and also moisture insensitive. The catalyst shows some limitations, which exhibited good solubility in many organic solvents and deionized water, but not in hexane.
Supplementary Materials
1H NMR and 13C NMR are available online.
Author Contributions
S.-Y.L. and W.-Y.H. designed the research. H.-R.W. analyzed the data. Y.-J.L., M.T., Y.-P.W., M.-W.H., W.L. and M.L. were prepared the compounds. S.-H.C. and W.-T.C. prepared ionic liquid. M.T. wrote the manuscript with the help of D.M.R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by National Chung Hsing University, and Chia Nan University of Pharmacy and Science.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Ministry of Science and Technology in Taiwan (MOST 106-2113-M-005-007 and 107-2113-M-005-021 for S.-Y.L. and MOST 106-2221-E-041-004 for W.-Y.H.), National Chung Hsing University, and Chia Nan University of Pharmacy and Science for financial support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Natalia, V.P.; Kenneth, R.S. Application of ionic liquids in chemical industry. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 123–150. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, R.; Wang, Y.-T. Dual ionic and organic nature of ionic liquids. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 19644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.L.; Ding, J.; Welton, T.; Armstrong, D.W. Characterizing ionic liquids on the basis of multiple solvation interactions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 14247–14254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weyershausen, B.; Lehmann, K. Industrial application of ionic liquids as performance additives. Green. Chem. 2005, 7, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Z.; Chen, B.; Koo, Y.-M.; MacFarlane, D.R. Introduction: Ionic liquids. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 6633–6635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Creary, X.; Willis, E.D.; Gagnon, M. Carbocation-forming reactions in ionic liquids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 18114–18120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallakpour, S.; Dinari, M. Green Solvents II, Properties and Applications of Ionic Liquids; Inamuddin, A.M., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 1–32. [Google Scholar]
- Neves, C.M.S.S.; Freire, M.G.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Improved recovery of ionic liquids from contaminated aqueous streams using aluminium-based salts. RSC Adv. 2012, 2, 10882–10890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doorslaer, C.V.; Glas, D.; Peeters, A.; Odena, A.C.; Vankelecom, I.; Binnemans, K.; Mertensa, P.; Vos, D.D. Product recovery from ionic liquids by solvent-resistant nanofiltration; application to ozonation of acetals and methyl oleate. Green Chem. 2010, 12, 1726–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faßbach, T.A.; Kirchmann, R.; Behr, A.; Vorholt, A.J. Recycling of homogeneous catalysts in reactive ionic liquids-solvent-free amino functionalization of alkenes. Green Chem. 2017, 19, 5243–5249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladnak, V.; Hofmann, N.; Brausch, N.; Wasserscheida, P. Continuous, ionic liquids-catalysed propylation of toluene in a liquid-liquid biphasic reaction mode using a loop reactor concept. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2007, 349, 719–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canales, R.I.; Brennecke, J.F. Comparison of ionic liquids to conventional organic solvents for extraction of aromatics from aliphatics. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2016, 61, 1685–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyson, P.J. Transition metal chemistry in ionic liquids. Transition Met. Chem. 2002, 27, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinnappan, A.; Kim, H. Transition metal based ionic liquid (bulk and nanofiber composites) use as catalyst for reduction of aromatic nitro compounds under mild conditions. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 3399–3406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Yin, M.; Zhang, A.P.; Prescher, S.; Antonietti, M.; Yuan, J. Helically structured nanoporous poly (ionic liquids) membranes: Facile preparation and application in fiber-optic pH sensing. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 5549–5552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallett, J.P.; Pollet, P.; Liotta, C.L.; Eckert, C.A. Reversible in situ catalyst formation. Acc. Chem. Res. 2008, 41, 458–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- William, S.B.; Guillaume, P.; André, B.C. Chemoselective synthesis of ketones and ketimines by addition of organometallic reagents to secondary amides. Nat. Chem. 2012, 4, 228–234. [Google Scholar]
- Maji, A.; Dahiya, A.; Lu, G.; Bhattacharya, T.; Brochetta, M.; Zanoni, G.; Liu, P.; Maiti, D. H-bonded reusable template assisted para-selective ketonization using soft electrophilic vinyl ethers. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.-H.; Shang, M.; Xu, H.; Wang, X.; Dai, H.-X.; Yu, J.-Q. Remote Para-C–H acetoxylation of electron-deficient arenes. Org. Lett. 2019, 21, 540–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gmouh, S.; Yang, H.; Vaultier, M. Activation of bismuth(III) derivatives in ionic liquids: Novel and recyclable catalytic systems for Friedel—Crafts acylation of aromatic compounds. Org. Lett. 2003, 5, 2219–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, G.K.S.; Farzaneh, P.; Aditya, K.; Arjun, N.; Fang, W.; Golam, R.; Thomas, M.; George, A.O. Taming of superacids: PVP triflic acid as an effective solid triflic acid equivalent for Friedel—Crafts hydroxyalkylation and acylation. J. Fluor. Chem. 2014, 171, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, P.H.; Hansen, P.E.; Hoang, H.M.; Chau, D.K.N.; Le, T.N. Indium triflate in 1-isobutyl-3-methylimidazolium dihydrogenphosphate: An efficient and green catalytic system for Friedel—Crafts acylation. Tetrahedron Lett. 2015, 56, 2187–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olah, G.A.; Malhotra, R.; Narang, S.C.; Olah, J.A. Heterogeneous Catalysis by Solid Superacids. 14. Perfluorinated Resinsulfonic Acid Catalyzed Friedel—Crafts Acylation of Benzene and Substituted Benzenes. Synthesis 1978, 672–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miles, W.H.; Nutaitis, C.F.; Anderton, C.A. Iron(III) Chloride as a Lewis Acid in the Friedel—Crafts Acylation Reaction. J. Chem. Educ. 1996, 73, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, G.; Jiang, L.; Li, J.; Sun, G.; Xia, C.; Li, F.-W. Ionic liquids as precursor for efficient mesoporous iron-nitrogen doped oxygen reduction electrocatalyst. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 1494–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.-X.; Du, H.; Hung, C.-T.; Liu, L.-L.; Wu, P.-H.; Ren, D.-H.; Huang, S.-J.; Liu, S.-B. Syntheses of novel halogen-free Brønsted—Lewis acidic ionic liquid catalysts and their applications for synthesis of methyl caprylate. Green Chem. 2015, 17, 499–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.B.; Yao, N.; Wang, L.; Hu, Y.L. Brønsted—Lewis dual acidic ionic liquid immobilized on mesoporous silica materials as an efficient cooperative catalyst for Mannich reactions. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 10528–10531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, J.; Xiao, J. Friedel—Crafts acylation reactions using metal triflates in ionic liquid. Green. Chem. 2002, 4, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Earle, M.J.; Hakala, U.; Hardacre, C.; Karkkainen, J.; McAuley, B.J.; Rooney, D.W.; Seddon, K.R.; Thompson, J.M.; Wähälä, K. Chloroindate(III) ionic liquids: Recyclable media for Friedel—Crafts acylation reactions. Chem. Commun. 2005, 903–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahrens, S.; Peritz, A.; Strassner, T. Tunable aryl alkyl ionic liquids (TAAILs): The next generation of ionic liquids. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 7908–7910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.-T.; Lu, S.-Y.; Yi, C.-L.; Lee, C.-F. Iron-catalyzed synthesis of thioesters from thiols and aldehydes in water. J. Org. Chem. 2014, 79, 4561–4568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nambu, H.; Hata, K.; Matsugi, M.; Kita, Y. The direct synthesis of thioesters using an intermolecular radical reaction of aldehydes with dipentafluorophenyl disulfide in water. Chem. Commun. 2002, 1082–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nambu, H.; Hata, K.; Matsugi, M.; Kita, Y. Efficient Synthesis of thioesters and amides from aldehydes by using an intermolecular radical reaction in water. Chem. Eur. J. 2005, 11, 719–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uno, T.; Inokuma, T.; Takemoto, Y. NHC-catalyzed thioesterification of aldehydes by external redox activation. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 1901–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandgar, B.P.; Bandgar, S.B.; Korbad, B.L.; Sawant, S.S. Dess—Martin periodinane mediated synthesis of thioesters from aldehydes. Tetrahedron Lett. 2007, 48, 1287–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jhuang, H.-S.; Liu, Y.-W.; Reddy, D.M.; Tzeng, Y.-Z.; Lin, W.-Y.; Lee, C.-F. Microwave-assisted Synthesis of thioesters from aldehydes and thiols in water. Chin. Chem. Soc. 2018, 65, 24–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.C.; Yang, C.H.; Sun, I.W.; Ho, W.Y.; Wu, T.-Y. Synthesis and properties of magnetic aryl-imidazolium ionic liquids with dual Brønsted/Lewis acidity. Materials 2018, 11, 2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.H.; Chang, J.C.; Wu, T.Y.; Sun, I.W.; Wu, J.H.; Ho, W.Y. Novel aryl-imidazolium ionic liquids with dual Brønsted/Lewis acidity as both solvents and catalysts for Friedel—Crafts alkylation. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).