Tomatidine Represses Invasion and Migration of Human Osteosarcoma U2OS and HOS Cells by Suppression of Presenilin 1 and c-Raf–MEK–ERK Pathway
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
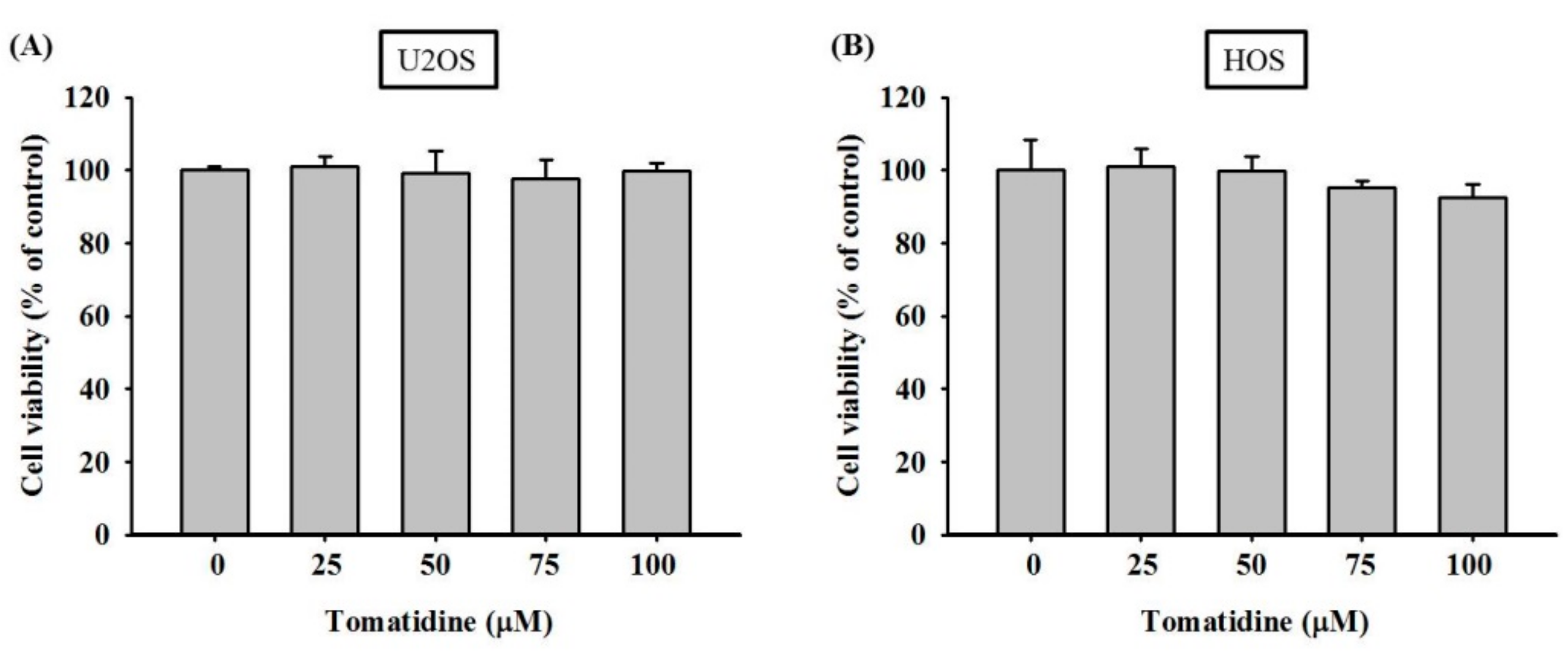
2.1. Cytotoxicity of Tomatidine in Osteosarcoma U2OS and HOS Cells
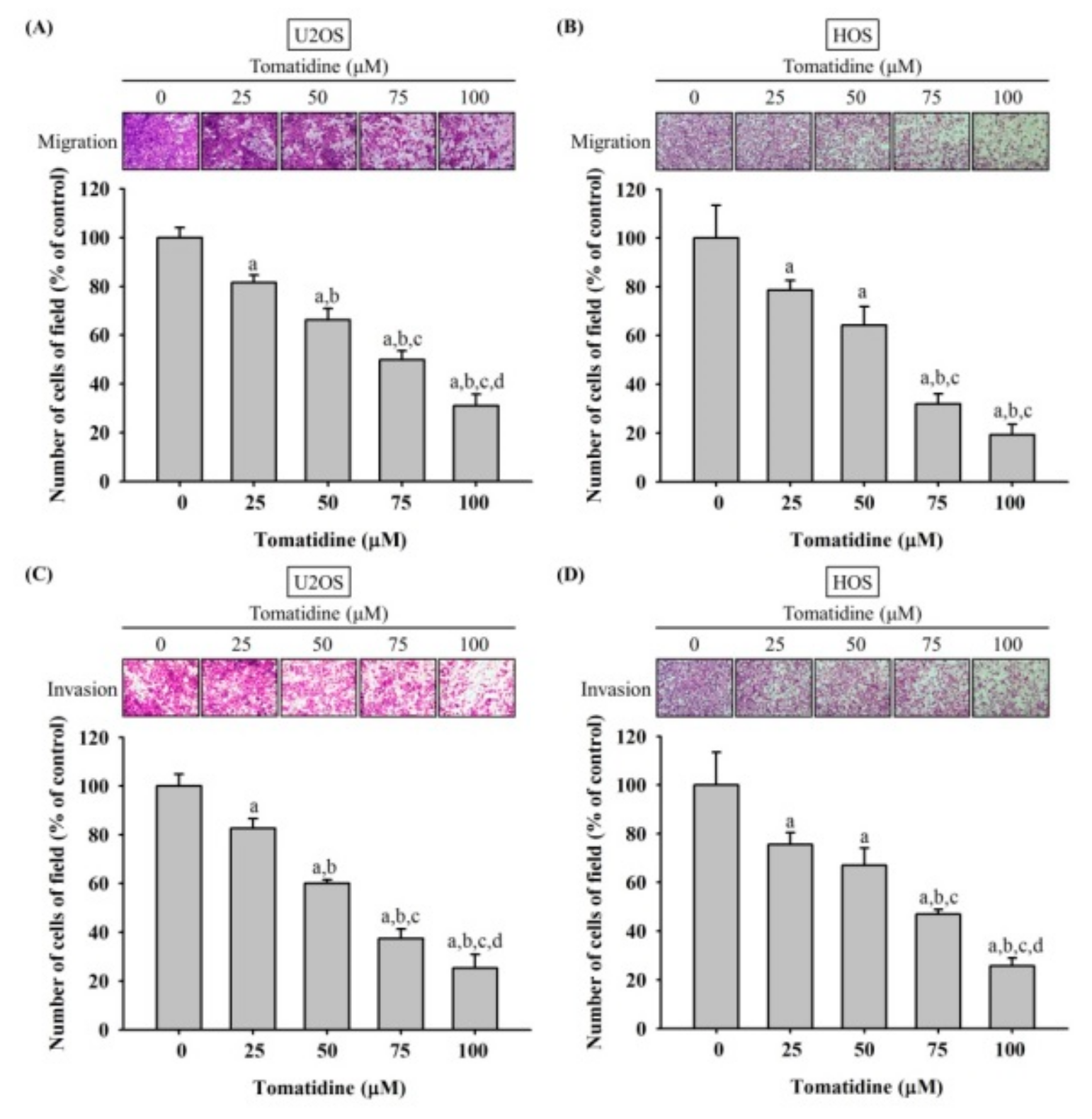
2.2. Tomatidine Represses U2OS and HOS Cells Migration and Invasiveness
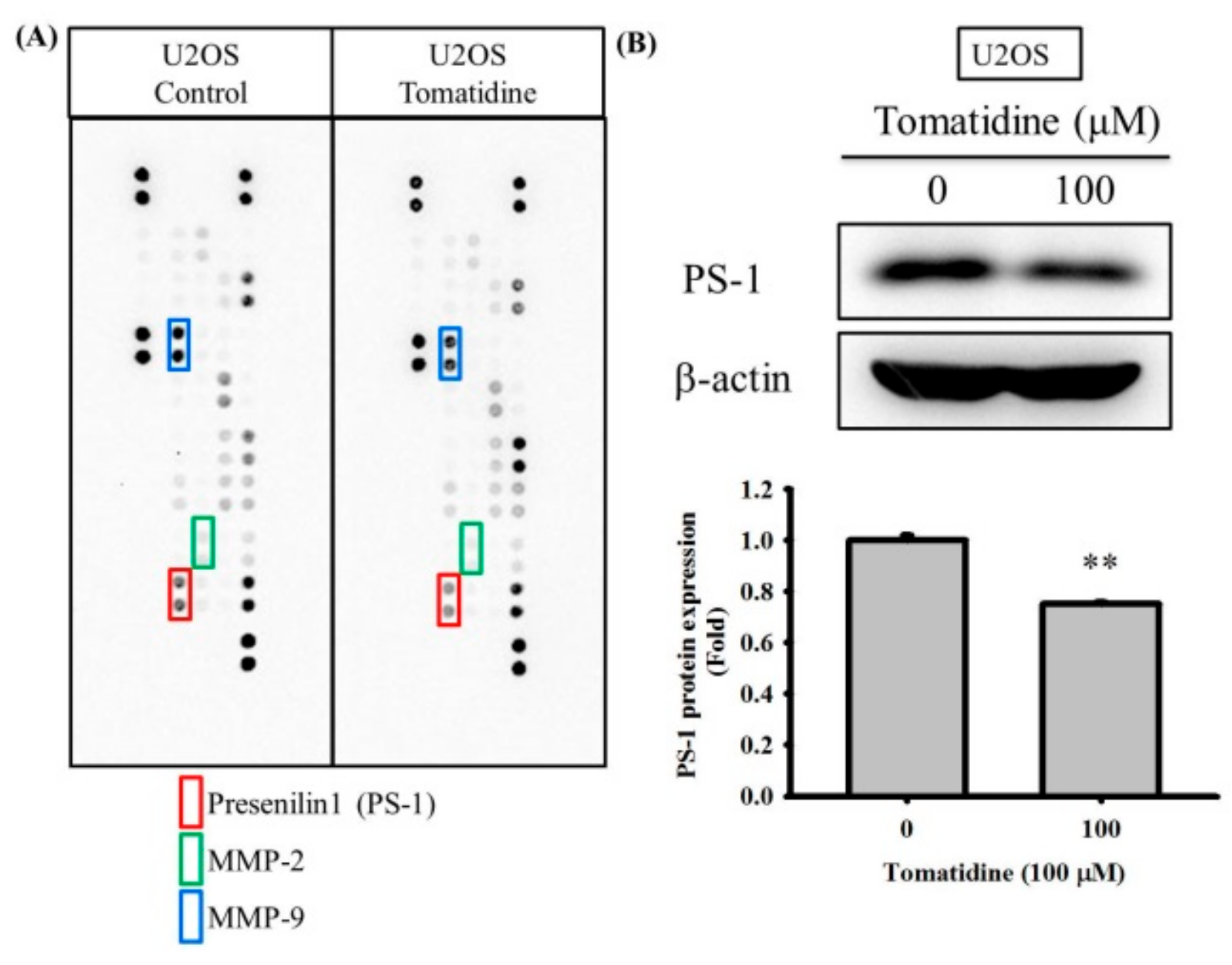
2.3. Tomatidine Reduces PS-1 Expression of U2OS Cells
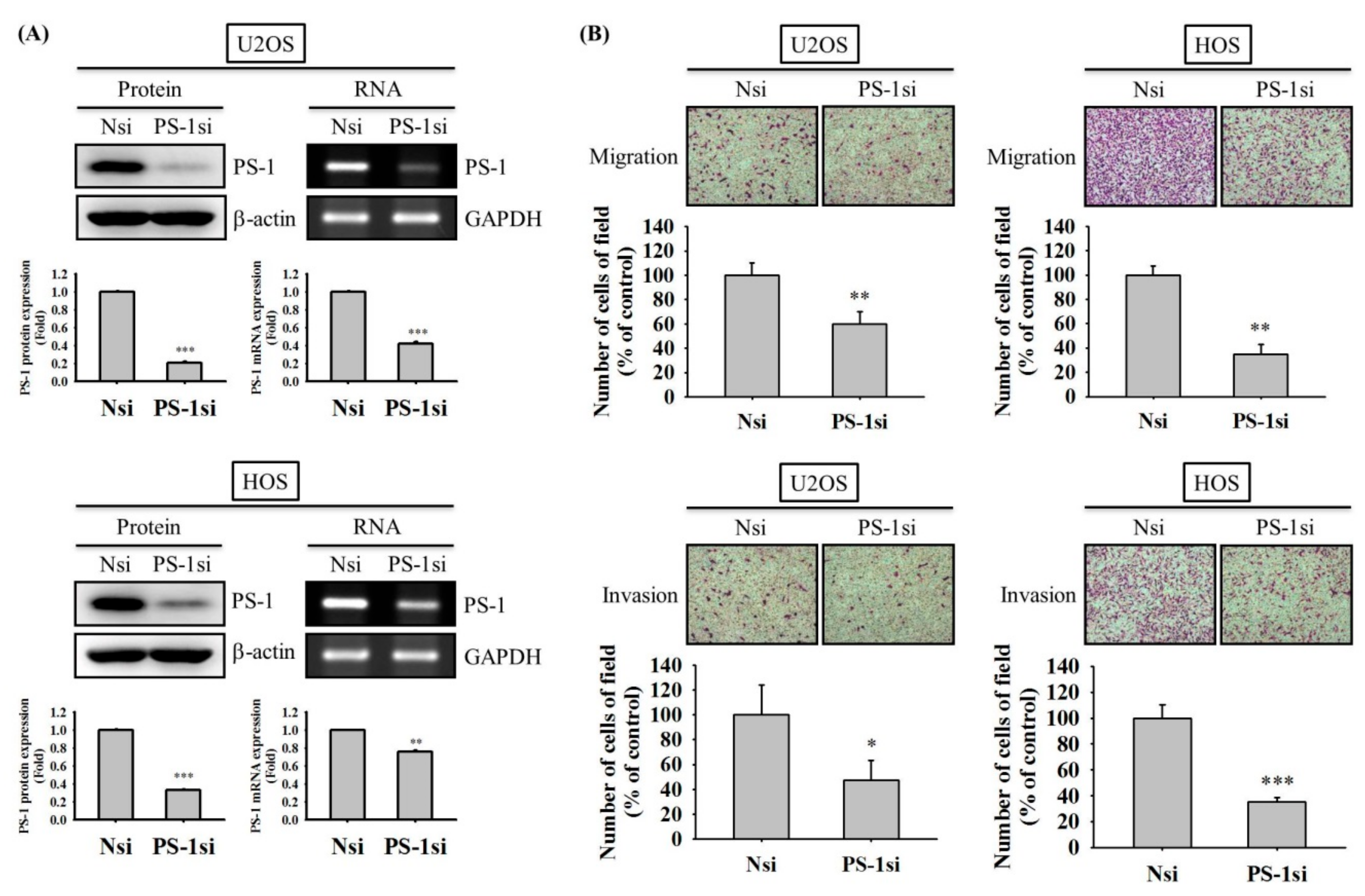
2.4. PS-1 Knockdown Reduces Migration and Invasion of U2OS and HOS Cells
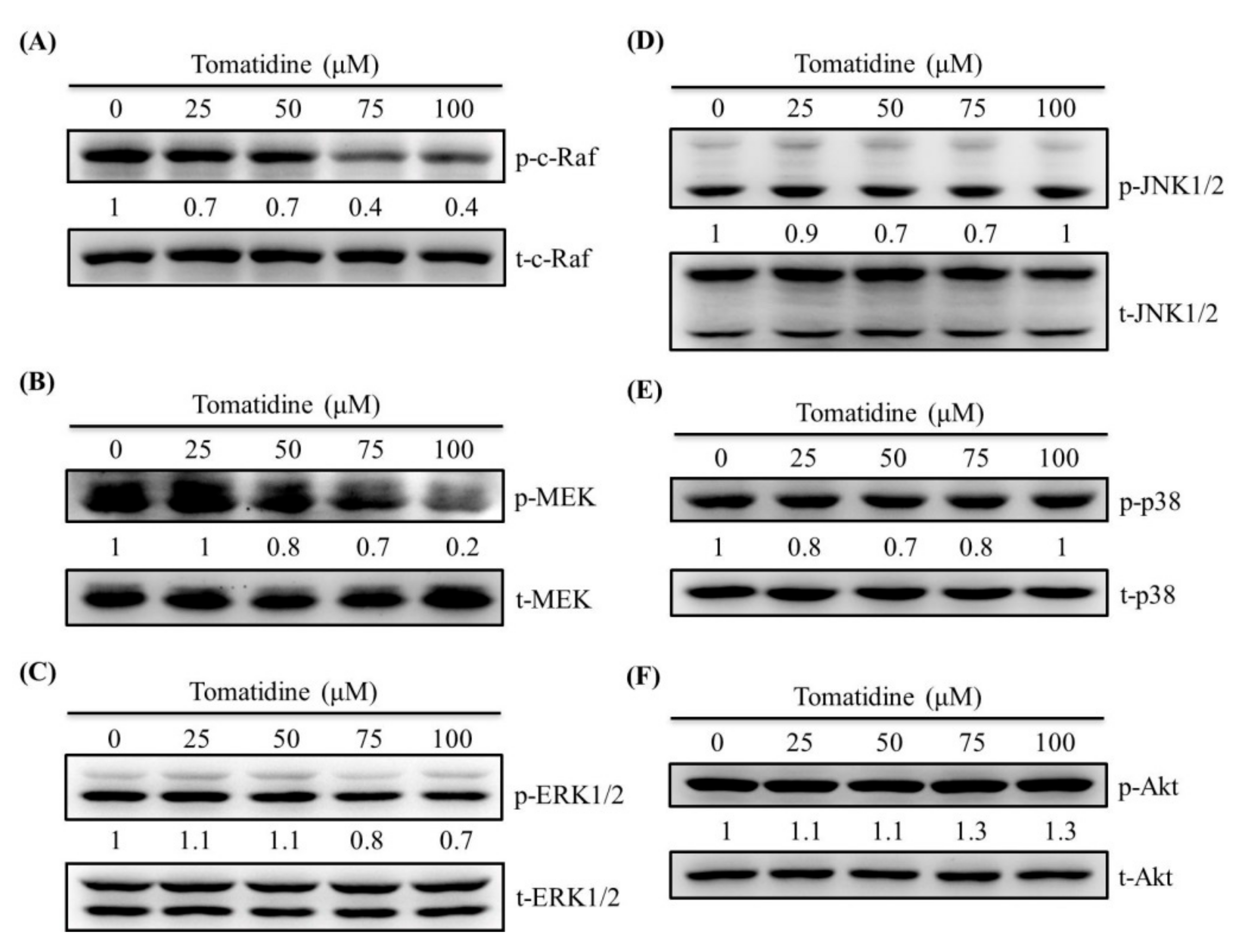
2.5. Tomatidine Reduces the c-Raf–MEK–ERK Pathway in U2OS Cells
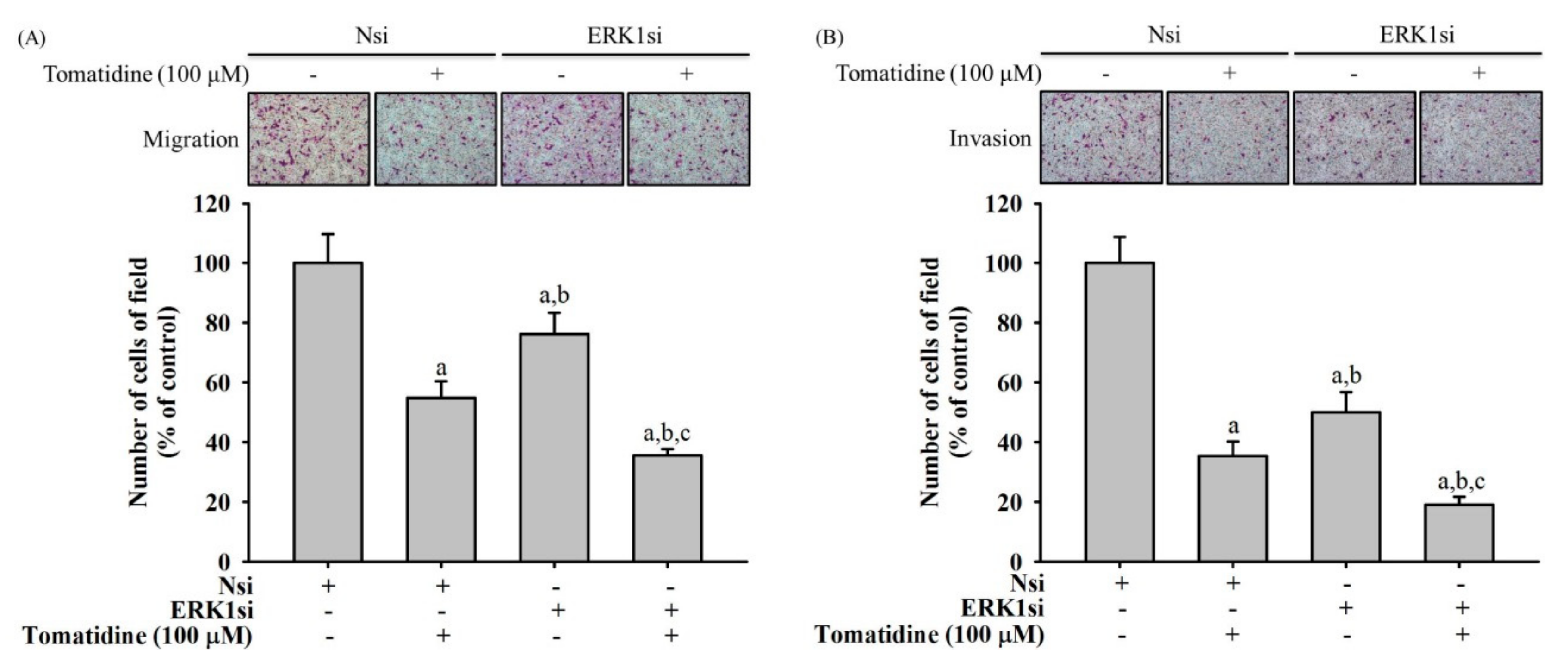
2.6. Tomatidine Inhibits Cellular Migration and Invasion in ERK 1 Knockdown U2OS Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Cell culture and Tomatidine Treatment
4.3. Microculture Tetrazolium (MTT) Assay
4.4. Cell Migration and Invasion Assays
4.5. Protease Array Analysis
4.6. Protein Extraction and Western Blot Analysis
4.7. Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR)
4.8. Small Interfering RNA
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mirabello, L.; Troisi, R.J.; Savage, S.A. Osteosarcoma incidence and survival rates from 1973 to 2004: Data from the surveillance, epidemiology, and end results program. Cancer 2009, 115, 1531–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picci, P.; Mercuri, M.; Ferrari, S.; Alberghini, M.; Briccoli, A.; Ferrari, C.; Pignotti, E.; Bacci, G. Survival in high-grade osteosarcoma: Improvement over 21 years at a single institution. Ann. Oncol. 2010, 21, 1366–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oertel, S.; Blattmann, C.; Rieken, S.; Jensen, A.; Combs, S.E.; Huber, P.E.; Bischof, M.; Kulozik, A.; Debus, J.; Schulz-Ertner, D. Radiotherapy in the treatment of primary osteosarcoma—A single center experience. Tumori 2010, 96, 582–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ottaviani, G.; Jaffe, N. The epidemiology of osteosarcoma. Cancer Treat. Res. 2009, 152, 3–13. [Google Scholar]
- Reiter, R.J.; Rosales-Corral, S.A.; Tan, D.X.; Acuna-Castroviejo, D.; Qin, L.; Yang, S.F.; Xu, K. Melatonin, a full service anti-cancer agent: Inhibition of initiation, progression and metastasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, S.C.; Hsieh, M.J.; Yang, W.E.; Chung, W.H.; Reiter, R.J.; Yang, S.F. Cancer metastasis: Mechanisms of inhibition by melatonin. J. Pineal Res. 2017, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, T.; Hart, I.R. Mechanisms of tumour metastasis. Eur. J. Cancer 1998, 34, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, G.P.; Massague, J. Cancer metastasis: Building a framework. Cell 2006, 127, 679–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.O.; Park, S.J.; Yun, C.H.; Chung, A.S. Roles of matrix metalloproteinases in tumor metastasis and angiogenesis. J. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2003, 36, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackay, A.R.; Corbitt, R.H.; Hartzler, J.L.; Thorgeirsson, U.P. Basement membrane type iv collagen degradation: Evidence for the involvement of a proteolytic cascade independent of metalloproteinases. Cancer Res. 1990, 50, 5997–6001. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, A.R.; Fingleton, B.; Rothenberg, M.L.; Matrisian, L.M. Matrix metalloproteinases: Biologic activity and clinical implications. J. Clin. Oncol. 2000, 18, 1135–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan-Hui, P.Y.; Weaver, R. Human mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase mediates the stress-induced activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase cascades. Biochem. J. 1998, 336, 599–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Kim, S.; Koh, H.; Yoon, S.O.; Chung, A.S.; Cho, K.S.; Chung, J. Akt/pkb promotes cancer cell invasion via increased motility and metalloproteinase production. FASEB J. 2001, 15, 1953–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukla, S.; Maclennan, G.T.; Hartman, D.J.; Fu, P.; Resnick, M.I.; Gupta, S. Activation of pi3k-akt signaling pathway promotes prostate cancer cell invasion. Int. J. Cancer 2007, 121, 1424–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Liu, W.Z.; Liu, T.; Feng, X.; Yang, N.; Zhou, H.F. Signaling pathway of mapk/erk in cell proliferation, differentiation, migration, senescence and apoptosis. J. Recept Signal. Transduct. Res. 2015, 35, 600–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.S.; Shih, Y.W.; Huang, H.C.; Cheng, H.W. Diosgenin, a steroidal saponin, inhibits migration and invasion of human prostate cancer pc-3 cells by reducing matrix metalloproteinases expression. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e20164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, Y.S.; Chu, S.C.; Yang, S.F.; Chen, P.N.; Liu, Y.C.; Lu, K.H. Silibinin suppresses human osteosarcoma mg-63 cell invasion by inhibiting the erk-dependent c-jun/ap-1 induction of mmp-2. Carcinogenesis 2007, 28, 977–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, Y.W.; Shieh, J.M.; Wu, P.F.; Lee, Y.C.; Chen, Y.Z.; Chiang, T.A. Alpha-tomatine inactivates pi3k/akt and erk signaling pathways in human lung adenocarcinoma a549 cells: Effect on metastasis. Food Chem. Toxicol 2009, 47, 1985–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marambaud, P.; Shioi, J.; Serban, G.; Georgakopoulos, A.; Sarner, S.; Nagy, V.; Baki, L.; Wen, P.; Efthimiopoulos, S.; Shao, Z.; et al. A presenilin-1/gamma-secretase cleavage releases the e-cadherin intracellular domain and regulates disassembly of adherens junctions. EMBO J. 2002, 21, 1948–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, D.; Okamoto, I.; Nagano, O.; Kawano, Y.; Tomita, T.; Iwatsubo, T.; De Strooper, B.; Yumoto, E.; Saya, H. Presenilin-dependent gamma-secretase activity mediates the intramembranous cleavage of cd44. Oncogene 2003, 22, 1511–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimi, N.; Golde, T.E.; Meyer, R.D. Identification of ligand-induced proteolytic cleavage and ectodomain shedding of vegfr-1/flt1 in leukemic cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 2607–2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cespedes, M.V.; Larriba, M.J.; Pavon, M.A.; Alamo, P.; Casanova, I.; Parreno, M.; Feliu, A.; Sancho, F.J.; Munoz, A.; Mangues, R. Site-dependent e-cadherin cleavage and nuclear translocation in a metastatic colorectal cancer model. Am. J. Pathol. 2010, 177, 2067–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peltonen, H.M.; Haapasalo, A.; Hiltunen, M.; Kataja, V.; Kosma, V.M.; Mannermaa, A. Gamma-secretase components as predictors of breast cancer outcome. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e79249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, X.; Qian, S.; Soriano, S.; Wu, Y.; Fletcher, A.M.; Wang, X.J.; Koo, E.H.; Wu, X.; Zheng, H. Loss of presenilin 1 is associated with enhanced beta-catenin signaling and skin tumorigenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 10863–10868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Lin, X.; Zhang, J.R.; Li, Y.; Lu, J.; Huang, F.C.; Zheng, C.H.; Xie, J.W.; Wang, J.B.; Huang, C.M. The expression of presenilin 1 enhances carcinogenesis and metastasis in gastric cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 10650–10662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.C.; Peng, Y.; Liu, Y.M.; Wang, L.L.; Wu, X.L. Gastric cancer cell growth and epithelial-mesenchymal transition are inhibited by gamma-secretase inhibitor dapt. Oncol. Lett. 2014, 7, 2160–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Maraver, A.; Fernandez-Marcos, P.J.; Herranz, D.; Munoz-Martin, M.; Gomez-Lopez, G.; Canamero, M.; Mulero, F.; Megias, D.; Sanchez-Carbayo, M.; Shen, J.; et al. Therapeutic effect of gamma-secretase inhibition in krasg12v-driven non-small cell lung carcinoma by derepression of dusp1 and inhibition of erk. Cancer Cell 2012, 22, 222–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, M. Tomato glycoalkaloids: Role in the plant and in the diet. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 5751–5780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.H.; Ahn, J.B.; Kozukue, N.; Kim, H.J.; Nishitani, Y.; Zhang, L.; Mizuno, M.; Levin, C.E.; Friedman, M. Structure-activity relationships of alpha-, beta(1)-, gamma-, and delta-tomatine and tomatidine against human breast (mda-mb-231), gastric (kato-iii), and prostate (pc3) cancer cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 3891–3899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, S.; Ihara, T.; Tamura, H.; Tanaka, S.; Ikeda, T.; Kajihara, H.; Dissanayake, C.; Abdel-Motaal, F.F.; El-Sayed, M.A. Alpha-tomatine, the major saponin in tomato, induces programmed cell death mediated by reactive oxygen species in the fungal pathogen fusarium oxysporum. FEBS Lett. 2007, 581, 3217–3222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, M.; Levin, C.E.; Lee, S.U.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, I.S.; Byun, J.O.; Kozukue, N. Tomatine-containing green tomato extracts inhibit growth of human breast, colon, liver, and stomach cancer cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 5727–5733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.T.; Wong, P.F.; Cheah, S.C.; Mustafa, M.R. Alpha-tomatine induces apoptosis and inhibits nuclear factor-kappa b activation on human prostatic adenocarcinoma pc-3 cells. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e18915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasegawa, H.; Uchiyama, M. Antimetastatic efficacy of orally administered ginsenoside rb1 in dependence on intestinal bacterial hydrolyzing potential and significance of treatment with an active bacterial metabolite. Planta Med. 1998, 64, 696–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, K.H.; Lee, L.M.; Yan, S.H.; Huang, H.C.; Li, C.C.; Lin, H.T.; Chen, P.S. Tomatidine inhibits invasion of human lung adenocarcinoma cell a549 by reducing matrix metalloproteinases expression. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2013, 203, 580–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, P.Y.; Hsieh, M.J.; Hsieh, Y.S.; Chen, P.N.; Yang, J.S.; Lo, F.C.; Yang, S.F.; Lu, K.H. Tricetin inhibits human osteosarcoma cells metastasis by transcriptionally repressing mmp-9 via p38 and akt pathways. Environ. Toxicol. 2017, 32, 2032–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.L.; Hsieh, M.J.; Yang, J.S.; Lin, C.W.; Lue, K.H.; Lu, K.H.; Yang, S.F. Nobiletin inhibits human osteosarcoma cells metastasis by blocking erk and jnk-mediated mmps expression. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 35208–35223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K.H.; Chen, P.N.; Hsieh, Y.H.; Lin, C.Y.; Cheng, F.Y.; Chiu, P.C.; Chu, S.C.; Hsieh, Y.S. 3-hydroxyflavone inhibits human osteosarcoma u2os and 143b cells metastasis by affecting emt and repressing u-pa/mmp-2 via fak-src to mek/erk and rhoa/mlc2 pathways and reduces 143b tumor growth in vivo. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2016, 97, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.S.; Lin, C.W.; Hsieh, Y.S.; Cheng, H.L.; Lue, K.H.; Yang, S.F.; Lu, K.H. Selaginella tamariscina (beauv.) possesses antimetastatic effects on human osteosarcoma cells by decreasing mmp-2 and mmp-9 secretions via p38 and akt signaling pathways. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 59, 801–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacs, D.M.; Mancini, R.; Henderson, J.; Na, S.J.; Schmidt, S.D.; Kim, T.W.; Tanzi, R.E. Staurosporine-induced activation of caspase-3 is potentiated by presenilin 1 familial alzheimer’s disease mutations in human neuroglioma cells. J. Neurochem. 1999, 73, 2278–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, J.; Fernandez, A.P.; Martinez-Murillo, R.; Martinez, A. High sensitivity to carcinogens in the brain of a mouse model of alzheimer’s disease. Oncogene 2010, 29, 2165–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Wang, R.; Zhao, C.; Wen, J.; Dong, H.; Wang, S.; Li, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Li, J.; Yang, Y.; et al. Notch signaling regulates osteosarcoma proliferation and migration through erk phosphorylation. Tissue Cell 2019, 59, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, K.B.; Nabha, S.M.; Atanaskova, N. Role of map kinase in tumor progression and invasion. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2003, 22, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yelken, B.O.; Balci, T.; Susluer, S.Y.; Kayabasi, C.; Avci, C.B.; Kirmizibayrak, P.B.; Gunduz, C. The effect of tomatine on metastasis related matrix metalloproteinase (mmp) activities in breast cancer cell model. Gene 2017, 627, 408–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shieh, J.M.; Cheng, T.H.; Shi, M.D.; Wu, P.F.; Chen, Y.; Ko, S.C.; Shih, Y.W. Alpha-tomatine suppresses invasion and migration of human non-small cell lung cancer nci-h460 cells through inactivating fak/pi3k/akt signaling pathway and reducing binding activity of nf-kappab. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2011, 60, 297–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, F.L.; Lin, J.K. Tomatidine inhibits inos and cox-2 through suppression of nf-kappab and jnk pathways in lps-stimulated mouse macrophages. FEBS Lett. 2008, 582, 2407–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujiwara, Y.; Kiyota, N.; Tsurushima, K.; Yoshitomi, M.; Horlad, H.; Ikeda, T.; Nohara, T.; Takeya, M.; Nagai, R. Tomatidine, a tomato sapogenol, ameliorates hyperlipidemia and atherosclerosis in apoe-deficient mice by inhibiting acyl-coa:Cholesterol acyl-transferase (acat). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 2472–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavie, Y.; Harel-Orbital, T.; Gaffield, W.; Liscovitch, M. Inhibitory effect of steroidal alkaloids on drug transport and multidrug resistance in human cancer cells. Anticancer Res. 2001, 21, 1189–1194. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, K.H.; Yang, H.W.; Su, C.W.; Lue, K.H.; Yang, S.F.; Hsieh, Y.S. Phyllanthus urinaria suppresses human osteosarcoma cell invasion and migration by transcriptionally inhibiting u-pa via erk and akt signaling pathways. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 52, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, Y.S.; Yang, S.F.; Chu, S.C.; Chen, P.N.; Chou, M.C.; Hsu, M.C.; Lu, K.H. Expression changes of gelatinases in human osteoarthritic knees and arthroscopic debridement. Arthroscopy 2004, 20, 482–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hsieh, M.-H.; Yang, J.-S.; Lin, R.-C.; Hsieh, Y.-H.; Yang, S.-F.; Chang, H.-R.; Lu, K.-H. Tomatidine Represses Invasion and Migration of Human Osteosarcoma U2OS and HOS Cells by Suppression of Presenilin 1 and c-Raf–MEK–ERK Pathway. Molecules 2020, 25, 326. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25020326
Hsieh M-H, Yang J-S, Lin R-C, Hsieh Y-H, Yang S-F, Chang H-R, Lu K-H. Tomatidine Represses Invasion and Migration of Human Osteosarcoma U2OS and HOS Cells by Suppression of Presenilin 1 and c-Raf–MEK–ERK Pathway. Molecules. 2020; 25(2):326. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25020326
Chicago/Turabian StyleHsieh, Min-Hong, Jia-Sin Yang, Renn-Chia Lin, Yi-Hsien Hsieh, Shun-Fa Yang, Horng-Rong Chang, and Ko-Hsiu Lu. 2020. "Tomatidine Represses Invasion and Migration of Human Osteosarcoma U2OS and HOS Cells by Suppression of Presenilin 1 and c-Raf–MEK–ERK Pathway" Molecules 25, no. 2: 326. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25020326
APA StyleHsieh, M.-H., Yang, J.-S., Lin, R.-C., Hsieh, Y.-H., Yang, S.-F., Chang, H.-R., & Lu, K.-H. (2020). Tomatidine Represses Invasion and Migration of Human Osteosarcoma U2OS and HOS Cells by Suppression of Presenilin 1 and c-Raf–MEK–ERK Pathway. Molecules, 25(2), 326. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25020326






