Cobalt Catalyzed C-P Bond Formation by Cross-Coupling of Boronic Acids with P(O)H Compounds in Presence of Zinc
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Result and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Information
3.2. General Procedure for the Synthesis of Aryl Phosphonates
3.2.1. Compound 8a: Diethyl Phenylphosphonate
3.2.2. Compound 8b: Diethyl 2-Methylphenylphosphonate
3.2.3. Compound 8c: Diethyl 4-Methoxyphenylphosphonate
3.2.4. Compound 8d: Diethyl 4-Ethylphenylphosphonate
3.2.5. Compound 8e: Diethyl 3-Nitrophenylphosphonate
3.2.6. Compound 8f: Diethyl 4-Fluorophenylphosphonate
3.2.7. Compound 8h: Diethyl 2,6-Difluorophenylphosphonate
3.2.8. Compound 9a: Dimethyl Phenylphosphonate
3.2.9. Compound 9b: Dimethyl 4-Methoxyphosphonate
3.2.10. Compound 9c: Dimethyl 3-Nitrophenylphosphonate
3.2.11. Compound 10a: Diisopropyl Phenylphosphonate
3.2.12. Compound 10b: Diisopropyl 4-Methoxyphosphonate
3.2.13. Compound 10c: Diisopropyl 3-Nitrophenylphosphonate
3.2.14. Compound 11a: Diphenyl Phenylphosphonate
3.2.15. Compound 11b: Diphenyl 4-Methoxyphosphonate
3.2.16. Compound 11c: Diphenyl 3-Nitrophenylphosphonate
3.2.17. Compound 12a: Dibenzyl Phenylphosphonate
3.2.18. Compound 12b: Dibenzyl 4-Methoxyphosphonate
3.2.19. Compound 12c: Dibenzyl 3-Nitrophenylphosphonate
3.2.20. Compound 12d: Dibenzyl 4-(Trifluoromethyl)phenylphosphonate
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Giannousis, P.P.; Bartlett, P.A. Phosphorus amino acid analogs as inhibitors of leucine aminopeptidase. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1987, 30, 1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maier, L.; Spörri, H. Organic Phosphorous Compounds 96. Resolution of 1-amino-2-(4-fluorophenyl) ethylphosphonic acid as well as some di- and tri-peptides. Phosphorus Sulfur Silicon Relat. Elem. Tetrahedron Lett. 1991, 61, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikorski, J.A.; Miller, M.J.; Braccolino, D.S.; Cleary, D.G.; Corey, S.; Font, J.L.; Gruys, K.J.; Han, C.Y.; Lin, K.; Pansegrau, P.D.; et al. EPSP Synthase: The Design and Synthesis of Bisubstrate Inhibitors Incorporating Novel 3-Phosphate Mimics. Phosphorus Sulfur Silicon Relat. Elem. 1993, 76, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, J.H.; Bartlett, P.A. Macrocyclic Inhibitors of Penicillopepsin. 1. Design, Synthesis, and Evaluation of an Inhibitor Bridged between P1 and P3. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998, 120, 4600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stowasser, B.; Budt, K.; Jian-Qi, L.; Peyman, A.; Ruppert, D. New hybrid transition state analog inhibitors of HIV protease with peripheric C2-symmetry. Tetrahedron Lett. 1992, 33, 6625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratt, R. Inhibition of a class C beta-lactamase by a specific phosphonate monoester. Science 1989, 246, 917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhawan, B.; Redmor, D. Optically active 1-aminoalkylphosphonic acids. Phosphorous Sulfur Relat. Elem. 1987, 32, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, K.; Walsh, C.T. ATP-dependent inactivation and slow binding inhibition of Salmonella typhimurium D-alanine:D-alanine ligase (ADP) by (aminoalkyl)phosphinate and aminophosphonate analogues of D-alanine. Biochemistry 1988, 27, 3709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, E.; Alonso, E.; Solis, A.; del Pozo, C. Synthesis of N-Alkyl-(α-Aminoalkyl)Phosphine Oxides and Phosphonic Esters as Potential HIV-Protease Inhibitors, Starting from α-Aminoacids. Synlett 2000, 5, 698. [Google Scholar]
- Hirschmann, R.; Smith, A.; Taylor, C.; Benkovic, P.; Taylor, S.; Yager, K.; Sprengler, P.; Benkovic, S. Peptide synthesis catalyzed by an antibody containing a binding site for variable amino acids. Science 1994, 265, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, J.; Atherton, F.; Hall, M.; Hassall, C.; Holmes, S.; Lambert, R.; Nisbet, L.; Ringrose, P. Phosphonopeptides, a new class of synthetic antibacterial agents. Nature 1978, 272, 56–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atherton, F.R.; Hassall, C.H.; Lambert, R.W. Synthesis and structure-activity relationships of antibacterial phosphonopeptides incorporating (1-aminoethyl)phosphonic acid and (aminomethyl)phosphonic acid. J. Med. Chem. 1986, 29, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sienczyc, M.; Oleksyszyn, J. Irreversible inhibition of serine proteases - design and in vivo activity of diaryl alpha-aminophosphonate derivatives. Curr. Med. Chem. 2009, 16, 1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Wan, Q.; Yang, S.; Song, B.; Bhadury, P.; Jin, L.; Yan, K.; Liu, F.; Chen, Z.; Xue, W. Synthesis and Antiviral Activities of Amide Derivatives Containing the α-Aminophosphonate Moiety. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Szostak, M. Decarbonylative Phosphorylation of Amides by Palladium and Nickel Catalysis: The Hirao Cross-Coupling of Amide Derivatives. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2017, 56, 12718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, M.V.N.; Annar, S.; Krishna, A.B.; Reddy, G.C.S.; Reddy, C.S. Tetramethyl guanidine (TMG) catalyzed synthesis of novel α-amino phosphonates by one-pot reaction. Org. Commun. 2010, 3, 39. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, A.J.; Rao, P.V.; Rao, V.K.; Mohan, C.; Raju, C.N.; Reddy, C.S. Microwave Assisted One-pot Synthesis of Novel α-Aminophosphonates and Their Biological Activity. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2010, 31, 1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, Z.; Firouzabadi, H.; Iranpoor, N.; Ghaderi, A.; Jafari, M.; Jafari, A.; Zare, H. Design and one-pot synthesis of α -aminophosphonates and bis(alpha-aminophosphonates) by iron(III) chloride and cytotoxic activity. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 44, 4266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, X.; Song, Z.; He, L. Synthesis and antitumor activity of novel α-aminophosphonates from diterpenic dehydroabietylamine. Heteroatom Chem. 2008, 19, 512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraicheva, I.; Bogomilova, A.; Tsacheva, I.; Momekov, G.; Troev, K. Synthesis, NMR characterization and in vitro antitumor evaluation of new aminophosphonic acid diesters. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 44, 3363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Yan, K.; Song, B.; Xu, G.; Yang, S.; Xue, W.; Hu, D.; Lu, P.; Ouyang, G.; Jin, L.; et al. Synthesis and antiviral bioactivities of α -aminophosphonates containing alkoxyethyl moieties. Molecules 2006, 11, 666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, S.; Faiger, H.; Belakhov, V.; Baasov, T. Towards the development of novel antibiotics: Synthesis and evaluation of a mechanism-based inhibitor of Kdo8P synthase. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 1999, 7, 2671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.C.; Yu, J.Q.; Spencer, J.B. Stereospecific Deoxygenation of Phosphine Oxides with Retention of Configuration Using Triphenylphosphine or Triethyl Phosphite as an Oxygen Acceptor. Org. Lett. 2004, 25, 4675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Masum, M.; Livinghouse, T. Pd(0) Cu(I) cocatalyzed coupling of methylphenylphosphine-borane with aryl halides and aryl nonaflates. Tetrahedron Lett. 1999, 40, 7731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshiki, T.; Imamoto, T. Unprecedented stereochemistry of the electrophilic arylation at chiral phosphorus. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1992, 114, 3975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ley, S.; Thomas, A. Modern synthetic methods for copper-mediated C(aryl)[bond]O, C(aryl)[bond]N, and C(aryl)[bond]S bond formation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2003, 42, 5400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andaloussi, M.; Lindh, J.; Savmarker, J.; Sjoberg, P.; Larhed, M. Microwave-Promoted Palladium(II)-Catalyzed C-P Bond Formation by Using Arylboronic Acids or Aryltrifluoroborates. Chem. Eur. J. 2009, 15, 13069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piontek, A.; Bisz, E.; Szostak, M. Iron-Catalyzed Cross-Couplings in the Synthesis of Pharmaceuticals: In Pursuit of Sustainability. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 11116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalek, M.; Ziadi, A.; Stawinski, J. Microwave-Assisted Palladium-Catalyzed Cross-Coupling of Aryl and Vinyl Halides with H-Phosphonate Diesters. Org. Lett. 2008, 10, 4637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, R.; Xu, J.; Cai, Z.; Tang, G.; Fang, M.; Zhao, Y. Copper-Catalyzed C-P Bond Construction via Direct Coupling of Phenylboronic Acids with H-Phosphonate Diesters. Org. Lett. 2011, 13, 2110–2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.; Chen, W.; Fu, T.; Peng, Z.; Qiao, H.; Gao, Y.; Zhao, Y. Nickel-Catalyzed C-P Cross-Coupling of Arylboronic Acids with P(O)H Compounds. Org. Lett. 2013, 15, 5362–5365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohmiya, H.; Wakabayashi, K.; Yorimitsu, H.; Oshima, K. Cobalt-catalyzed cross-coupling reactions of alkyl halides with aryl Grignard reagents and their application to sequential radical cyclization/cross-coupling reactions. Tetrahedron 2006, 62, 2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinokubo, H.; Oshima, K. Transition Metal-Catalyzed Carbon−Carbon Bond Formation with Grignard Reagents—Novel Reactions with a Classic Reagent. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2004, 10, 2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korn, T.J.; Schade, M.A.; Wirth, S.; Knochel, P. Cobalt(II)-Catalyzed Cross-Coupling between Polyfunctional Arylcopper Reagents and Aryl Fluorides or Tosylates. Org. Lett. 2006, 8, 725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amatore, M.; Gosmini, C.; Perichon, J. CoBr2(Bpy): An Efficient Catalyst for the Direct Conjugate Addition of Aryl Halides or Triflates onto Activated Olefins. J. Org. Chem. 2006, 71, 6130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yorimitsu, H.; Oshima, K. New synthetic reactions catalyzed by cobalt complexes. Pure Appl. Chem. 2006, 78, 441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzer, B.; Hoffman, R. Kumada–Corriu coupling of Grignard reagents, probed with a chiral Grignard reagent. Chem. Commun. 2003, 6, 732–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datilus, V.; Abdulkarim, M.; Patrizio, A.; Kaur, P. Ter-pyridine catalyzed allylation of aldehydes and ketones under metal-free condition. Tetrahedron Lett. 2016, 57, 2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahiez, G.; Moyexic, A. Cobalt catalyzed cross-coupling reactions. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Hu, H.; Yang, F.; Wu, Y. Synthesis of Aryl and Arylmethyl Phosphonates by Cross-Coupling of Aryl or Arylmethyl Halides (X = I, Br and Cl) with Diisopropyl H-Phosphonate. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2013, 2, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Qiu, D.; Mo, F.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J. Metal-Free Aromatic Carbon–Phosphorus Bond Formation via a Sandmeyer-Type Reaction. J. Org. Chem. 2016, 81, 11603–11611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds 8a–8m, 9a–9c, 10a–10c, 11a–11c and 12a–12d are available from the authors. |


| Entry | Ligand | Cobalt Source | Additive | Base | Yield% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | CoCl2 | - | Cs2CO3 | 19 |
| 2 | 1 | CoCl2 | - | K2CO3 | 32 |
| 3 | 1 | CoCl2 | Zn | DIPEA | 34 |
| 4 | 1 | CoCl2 | Zn | K2CO3 | 38 |
| 5 | 1 | CoCl2 | Zn | Et3N | 44 |
| 6 | 1 | CoCl2 | Zn | - | 42 |
| 7 | 2 | CoCl2 | Zn | - | 56 |
| 8 | 3 | CoCl2 | Zn | - | 65 |
| 9 | 4 | CoCl2 | Zn | - | 79 |
| 10 | 5 | CoCl2 | Zn | - | 60 |
| 11 | 4 | Co(NO3)2 | Zn | - | 61 |
| 12 | 4 | CoI2 | Zn | - | 84 |
| 13 | 4 | Co(OAc)2 | Zn | - | 56 |
| 14 15 | 4 4 | CoBr2 Co(acac)2 | Zn Zn | - - | 91 63 |
| Entry | Ligand | % Yield |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Pyridine (ligand 1) | 54 |
| 2 | 2-picolylamine (ligand 2) | 56 |
| 3 | di-(2-picolyl)amine (ligand 3) | 65 |
| 4 | ter-pyridine (ligand 4) | 79 |
| 5 | 2,2′-dipyridylamine (ligand 5) | 60 |
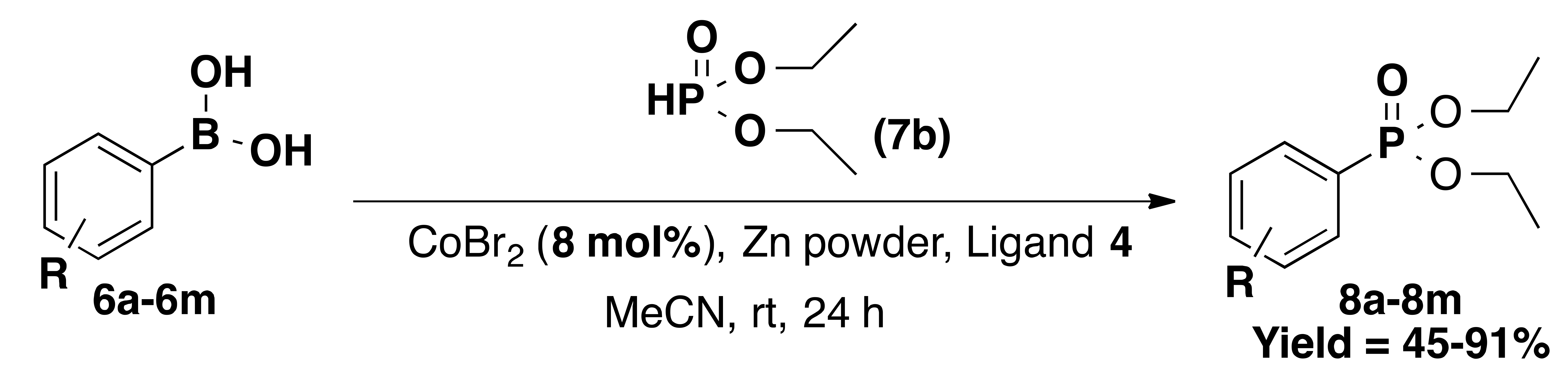
| Entry | R | Product | Yield% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | H (6a) | 8a | 91 |
| 2 | 2-methyl (6b) | 8b | 89 |
| 3 | 4-methoxy (6c) | 8c | 87 |
| 4 | 4-ethynyl (6d) | 8d | 78 |
| 5 | 3-nitro (6e) | 8e | 66 |
| 6 | 4-fluoro (6f) | 8f | 65 |
| 7 | 2-fluoro (6g) | 8g | 82 |
| 8 | 2,6-difluoro (6h) | 8h | 63 |
| 9 | 4-trifluoromethyl (6i) | 8i | 45 |
| 10 11 12 13 | 1-Naphthyl (6j) 4-nitro (6k) 4-cyano (6l) 4-pyridyl (6m) | 8j 8k 8l 8m | 76 74 68 57 |

| Entry | R | R′ | Product | Yield% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | H (6a) | Me (7a) | 9a | 79 |
| 2 | 4-methoxy (6c) | Me (7a) | 9b | 78 |
| 3 | 3-nitro (6e) | Me (7a) | 9c | 81 |
| 4 | H (6a) | iPr (7c) | 10a | 79 |
| 5 | 4-methoxy (6c) | iPr (7c) | 10b | 62 |
| 6 | 3-nitro (6e) | iPr (7c) | 10c | 71 |
| 7 | H (6a) | Ph (7d) | 11a | 84 |
| 8 | 4-methoxy (6c) | Ph (7d) | 11b | 74 |
| 9 | 3-nitro (6e) | Ph (7d) | 11c | 56 |
| 10 | H (6a) | Bn (7e) | 12a | 89 |
| 11 | 4-methoxy (6c) | Bn (7e) | 12b | 78 |
| 12 | 3-nitro (6e) | Bn (7e) | 12c | 67 |
| 13 | 4-trifluoro(methyl) (6i) | Bn (7e) | 12d | 59 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hicks, I.; McTague, J.; Hapatsha, T.; Teriak, R.; Kaur, P. Cobalt Catalyzed C-P Bond Formation by Cross-Coupling of Boronic Acids with P(O)H Compounds in Presence of Zinc. Molecules 2020, 25, 290. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25020290
Hicks I, McTague J, Hapatsha T, Teriak R, Kaur P. Cobalt Catalyzed C-P Bond Formation by Cross-Coupling of Boronic Acids with P(O)H Compounds in Presence of Zinc. Molecules. 2020; 25(2):290. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25020290
Chicago/Turabian StyleHicks, Ian, Jonathan McTague, Tatiana Hapatsha, Rania Teriak, and Parminder Kaur. 2020. "Cobalt Catalyzed C-P Bond Formation by Cross-Coupling of Boronic Acids with P(O)H Compounds in Presence of Zinc" Molecules 25, no. 2: 290. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25020290
APA StyleHicks, I., McTague, J., Hapatsha, T., Teriak, R., & Kaur, P. (2020). Cobalt Catalyzed C-P Bond Formation by Cross-Coupling of Boronic Acids with P(O)H Compounds in Presence of Zinc. Molecules, 25(2), 290. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25020290







