Synthesis and Characterization of Citrate-Stabilized Gold-Coated Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Biomedical Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
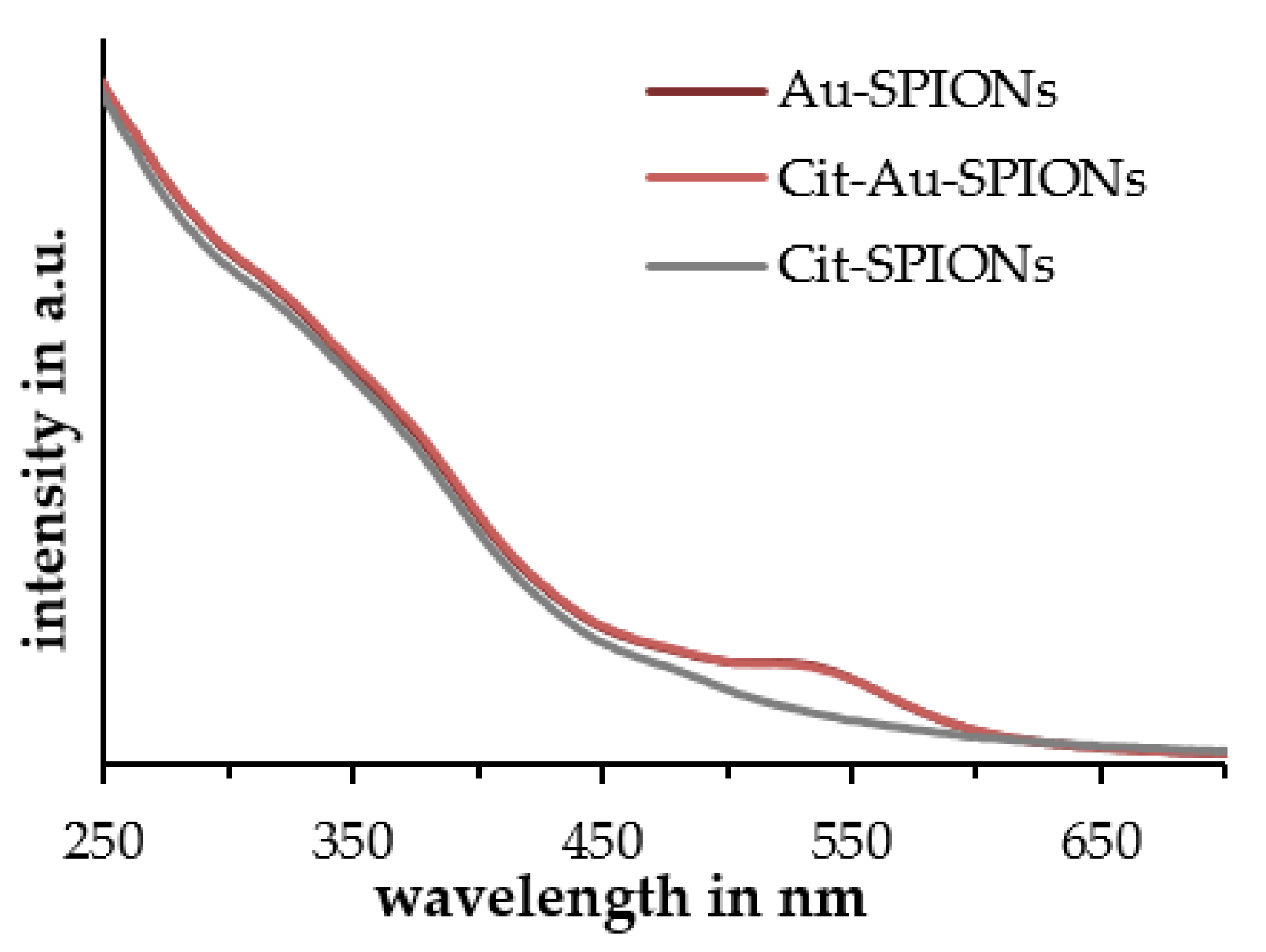
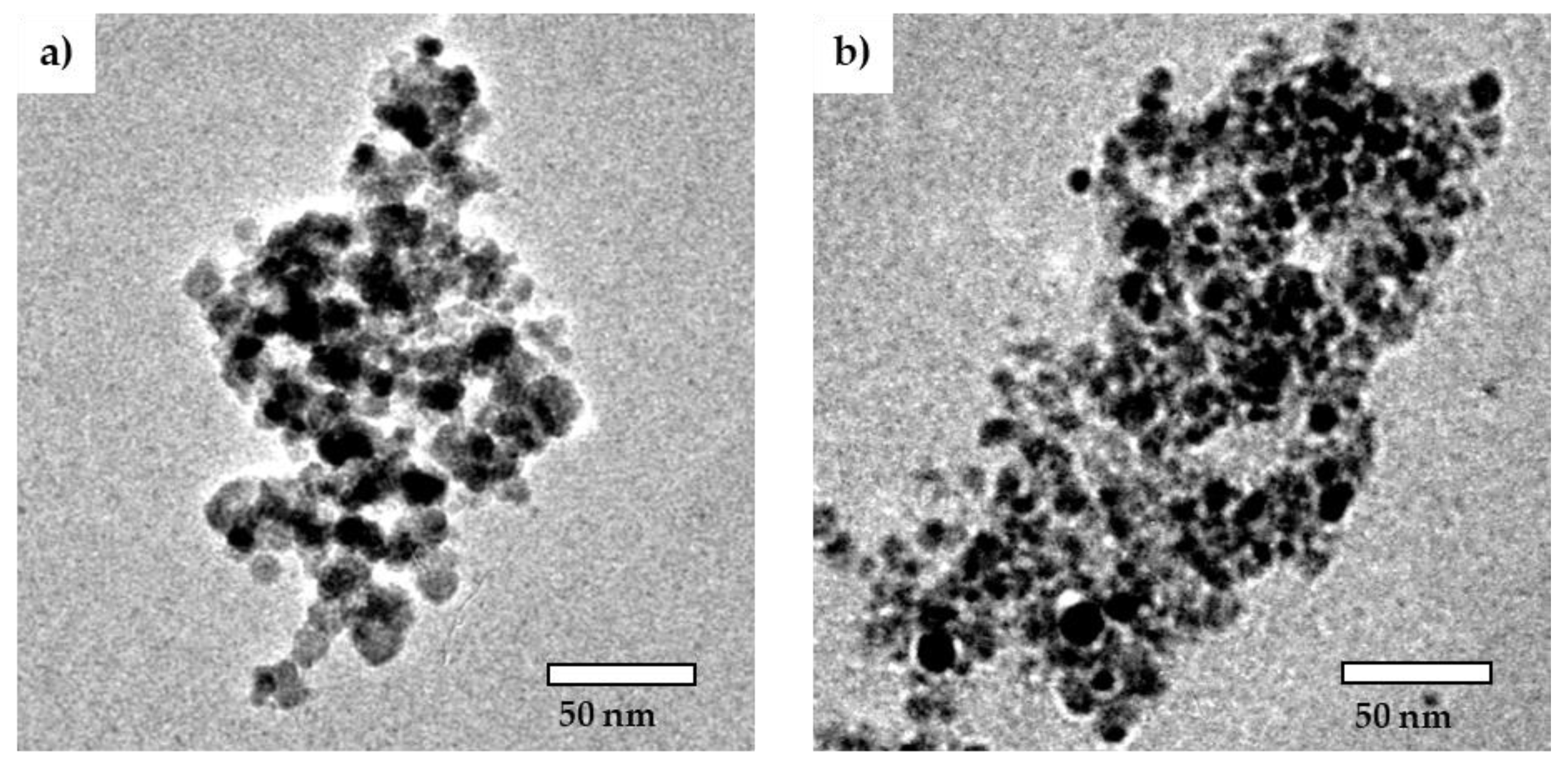
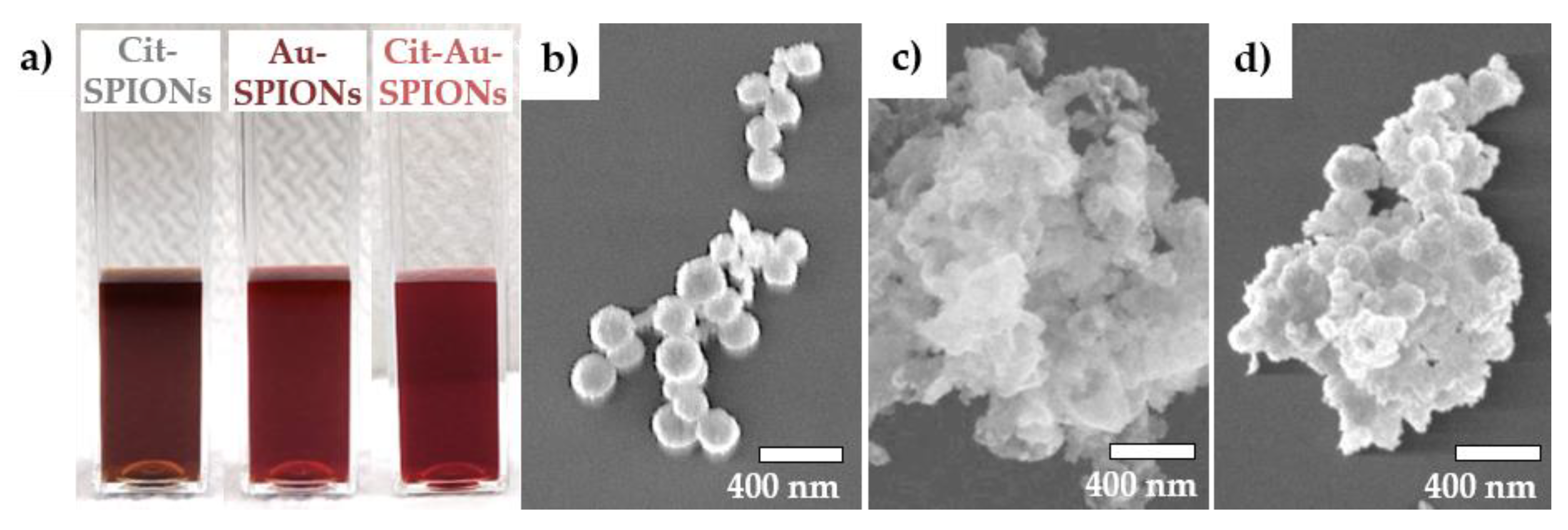
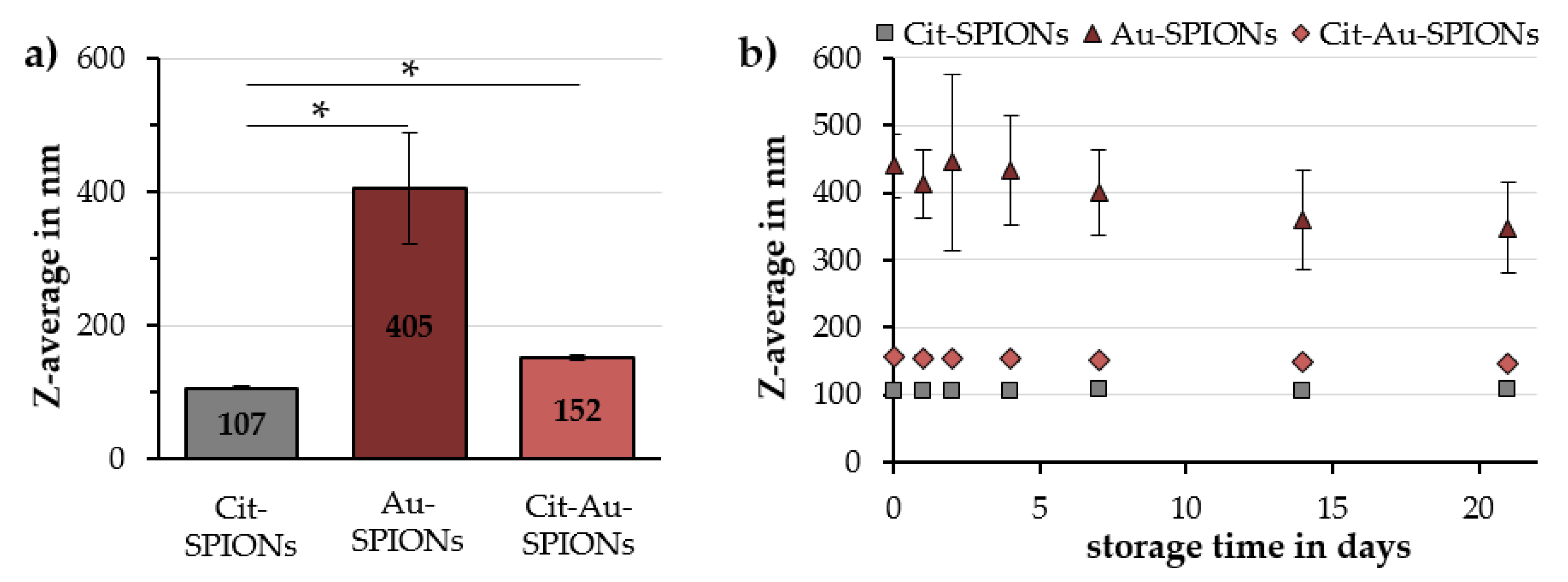
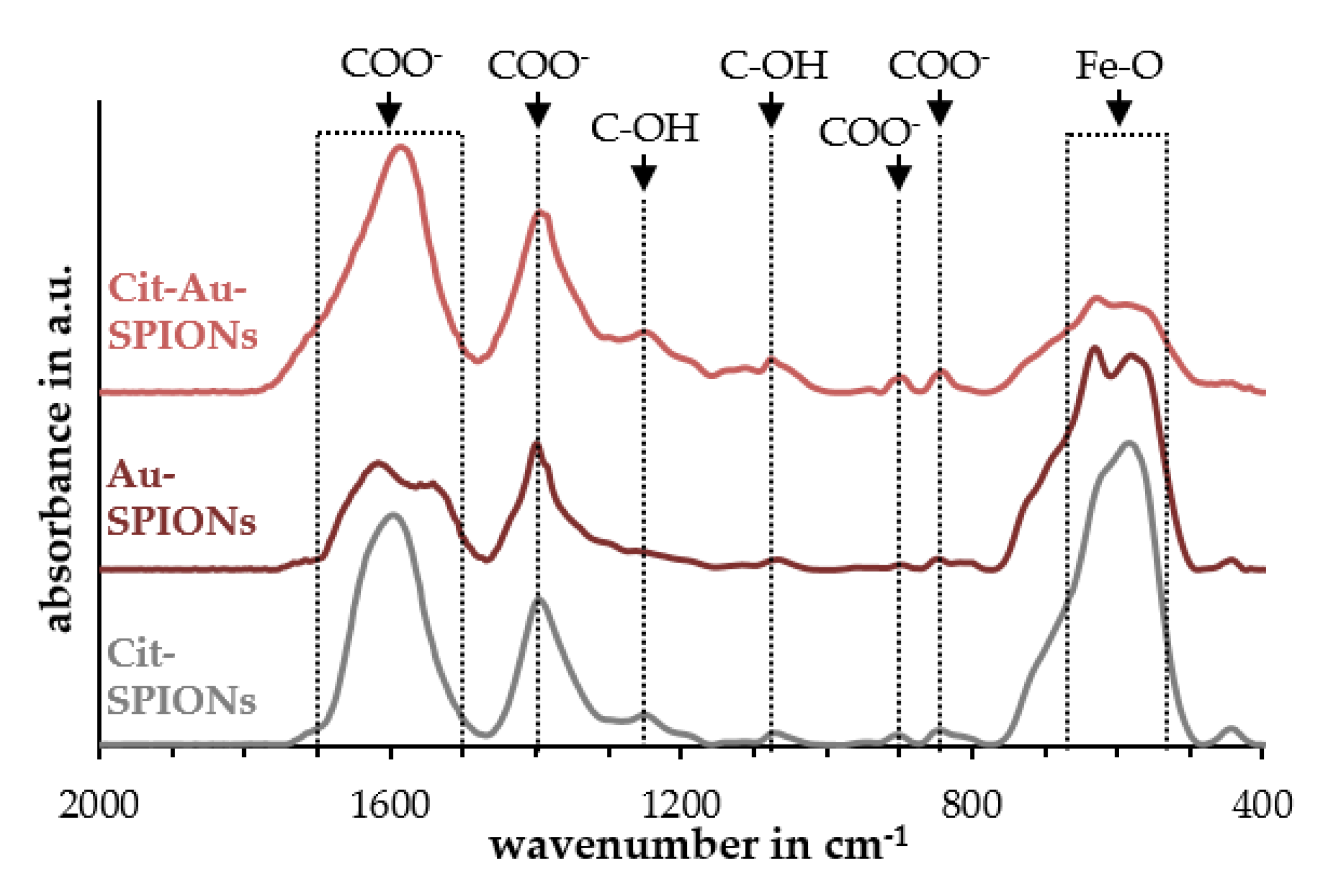
2.1. Characterization of Cit-SPIONs, Au-SPIONs and Cit-Au-SPIONs
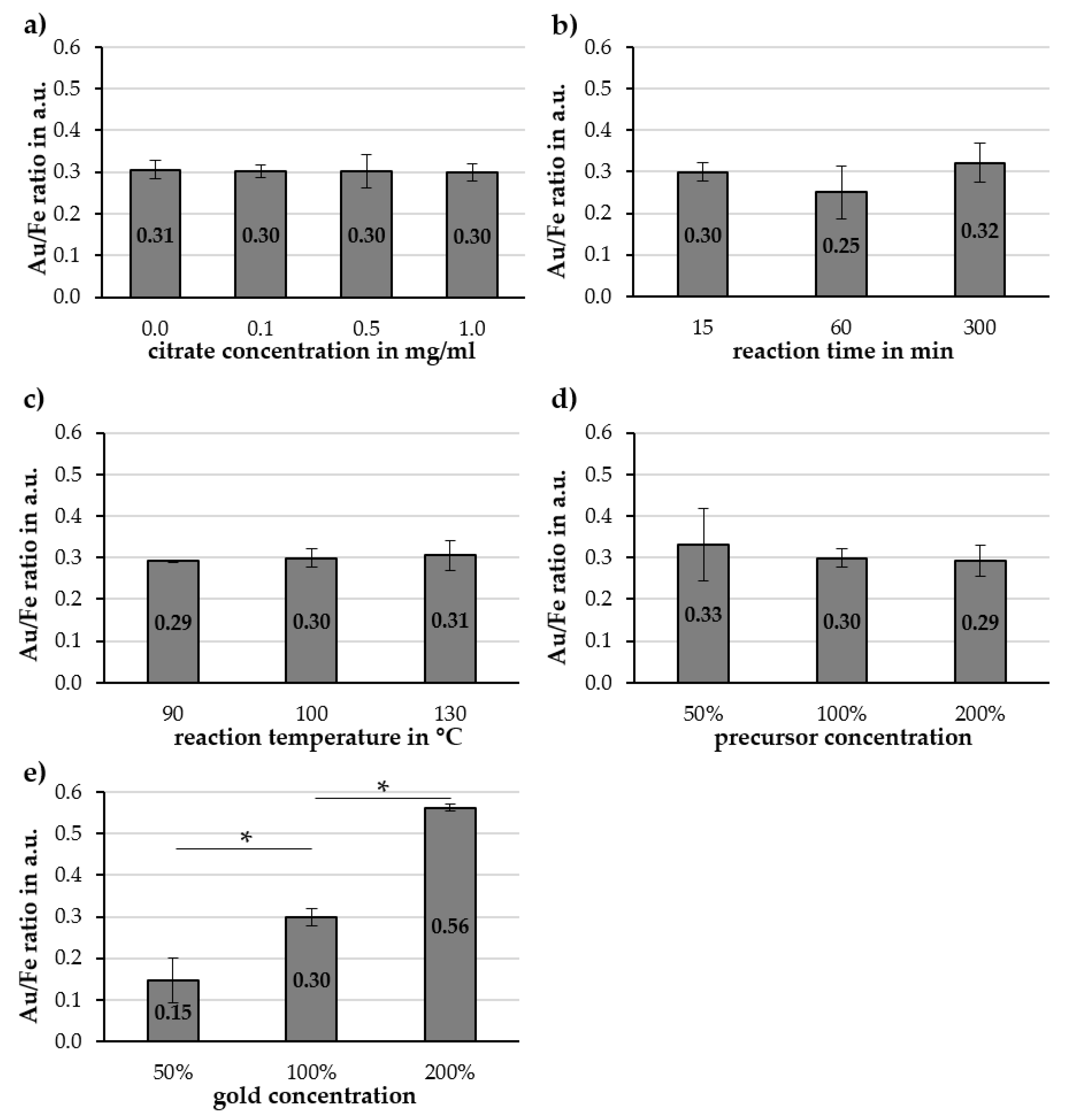
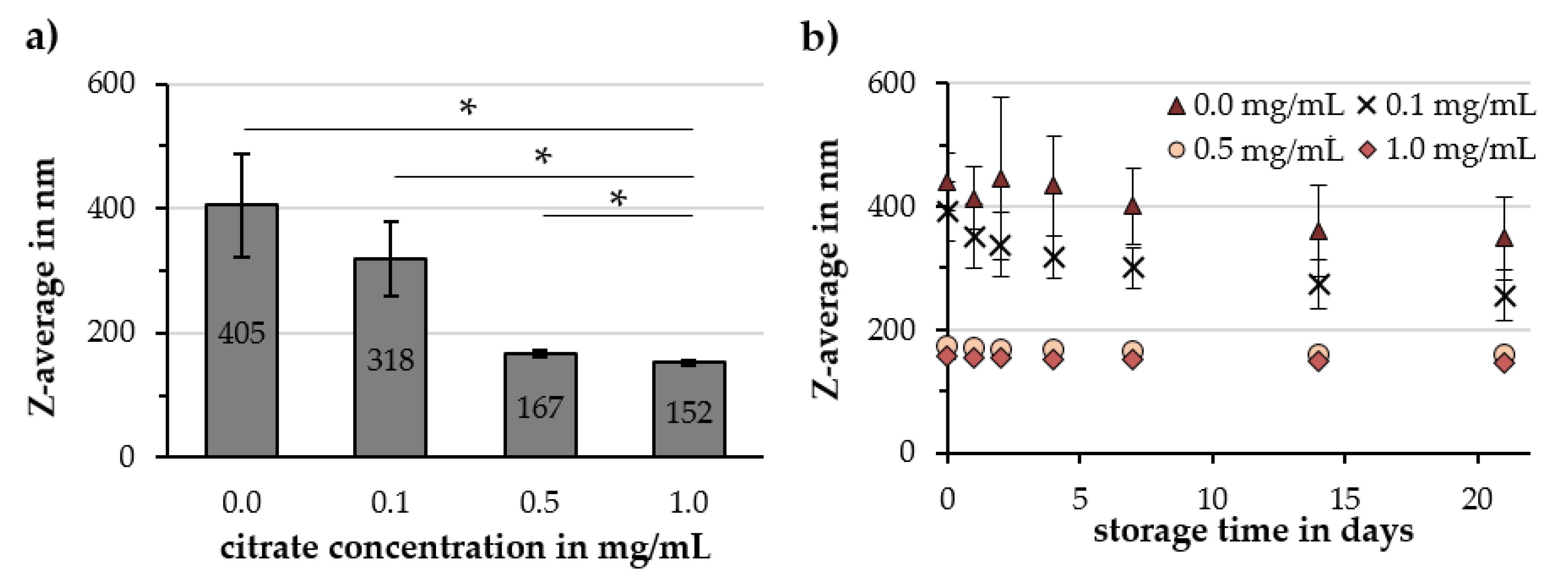
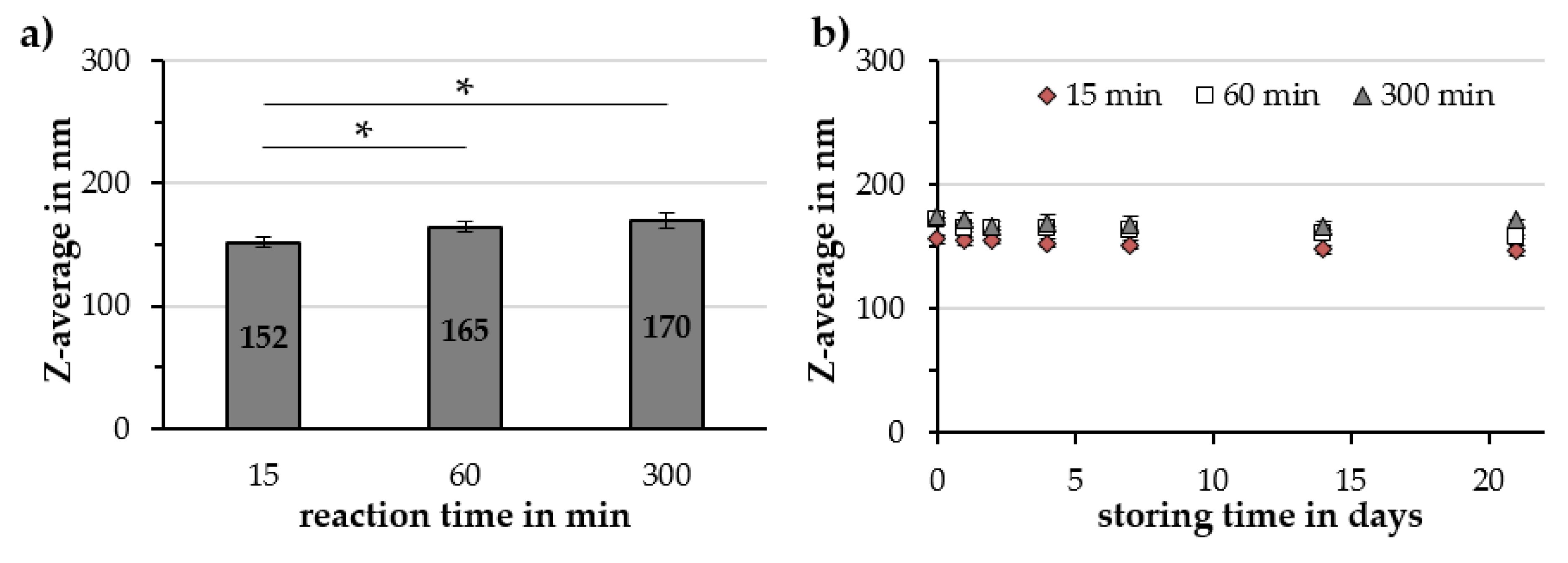
2.2. Investigation of Parameters Affecting Cit-Au-SPION Synthesis
2.2.1. Citrate Concentration
2.2.2. Reaction Time
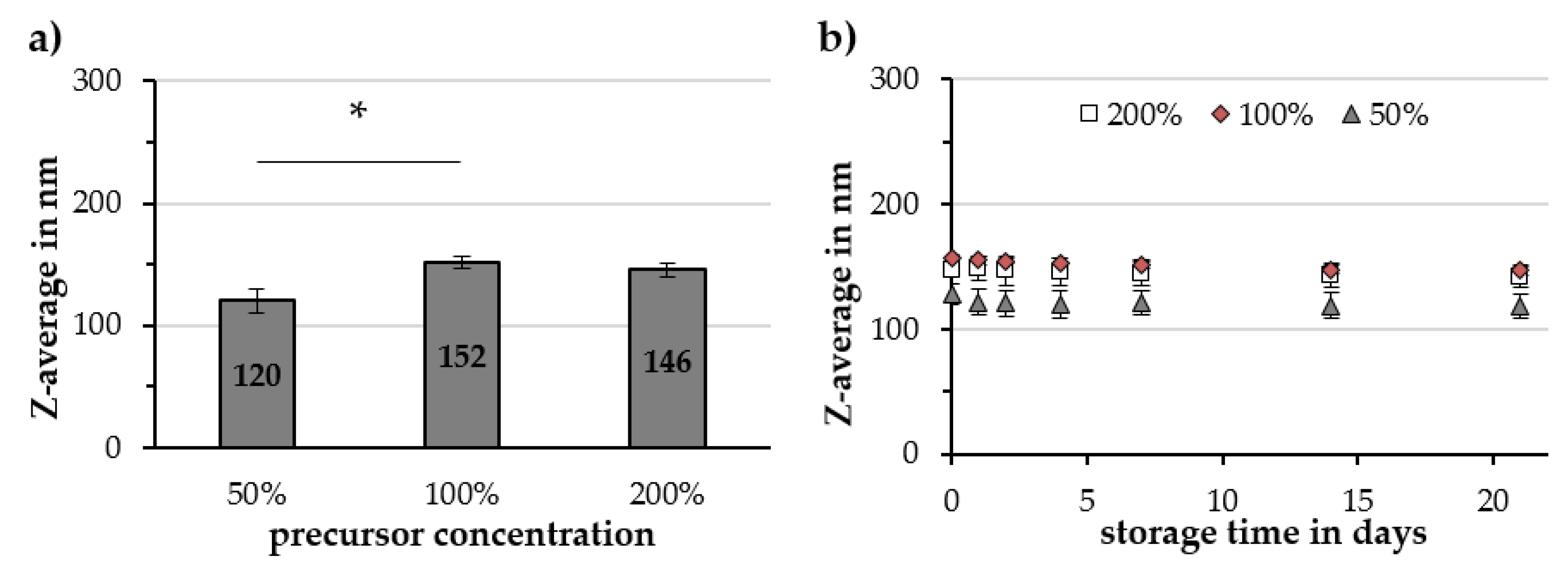
2.2.3. Reaction Temperature and Precursor Concentration
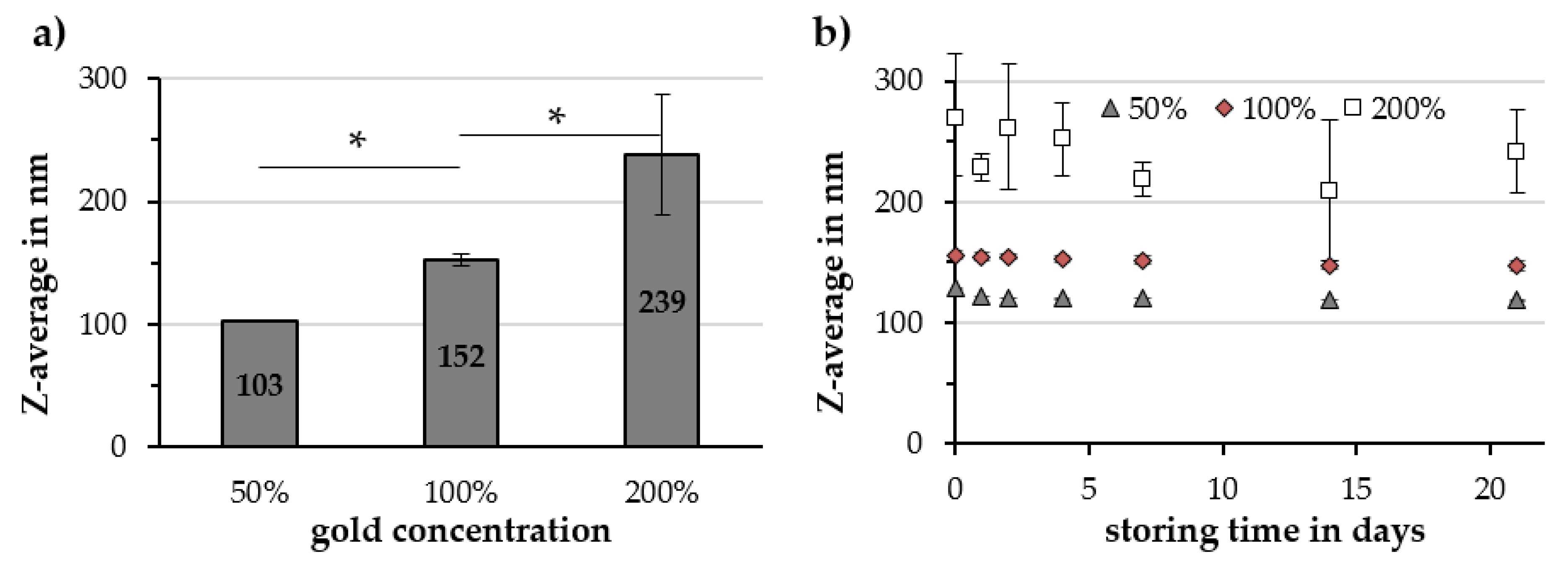
2.2.4. Gold Concentration
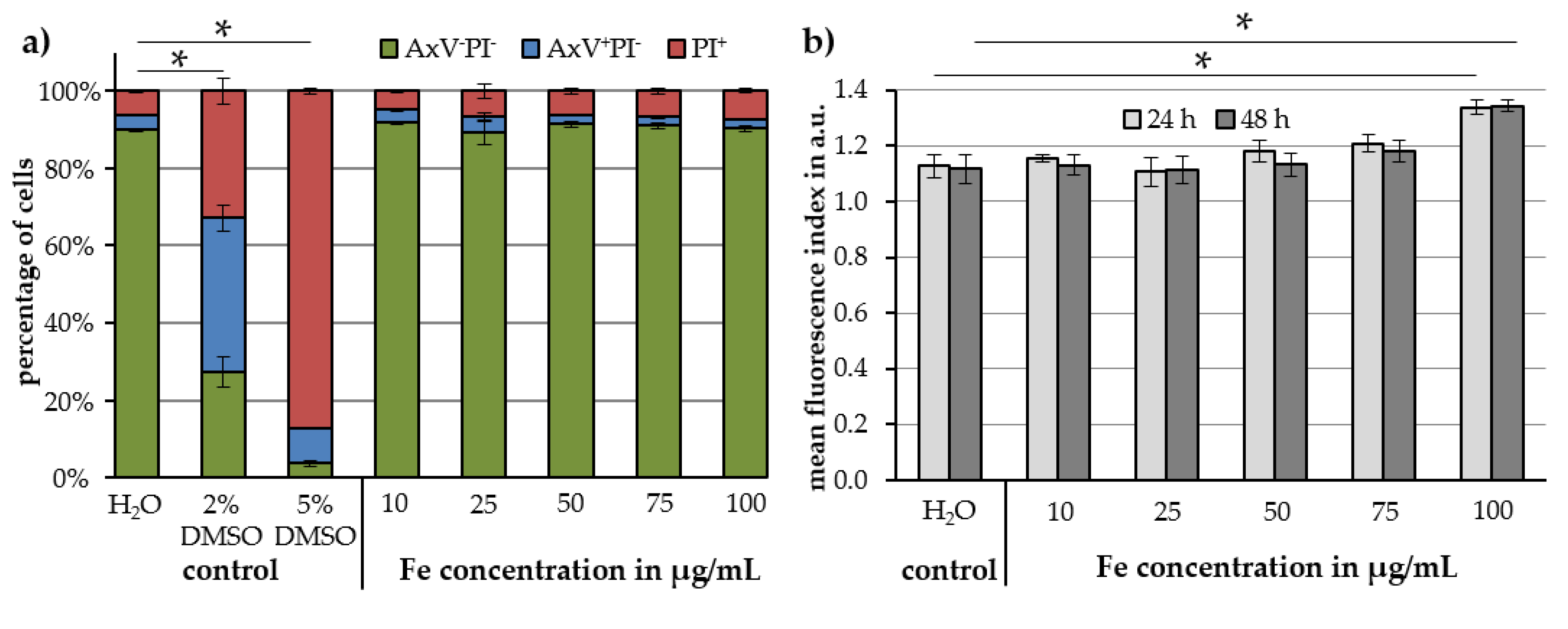
2.3. Cell Toxicity and Uptake of Cit-Au-SPIONs
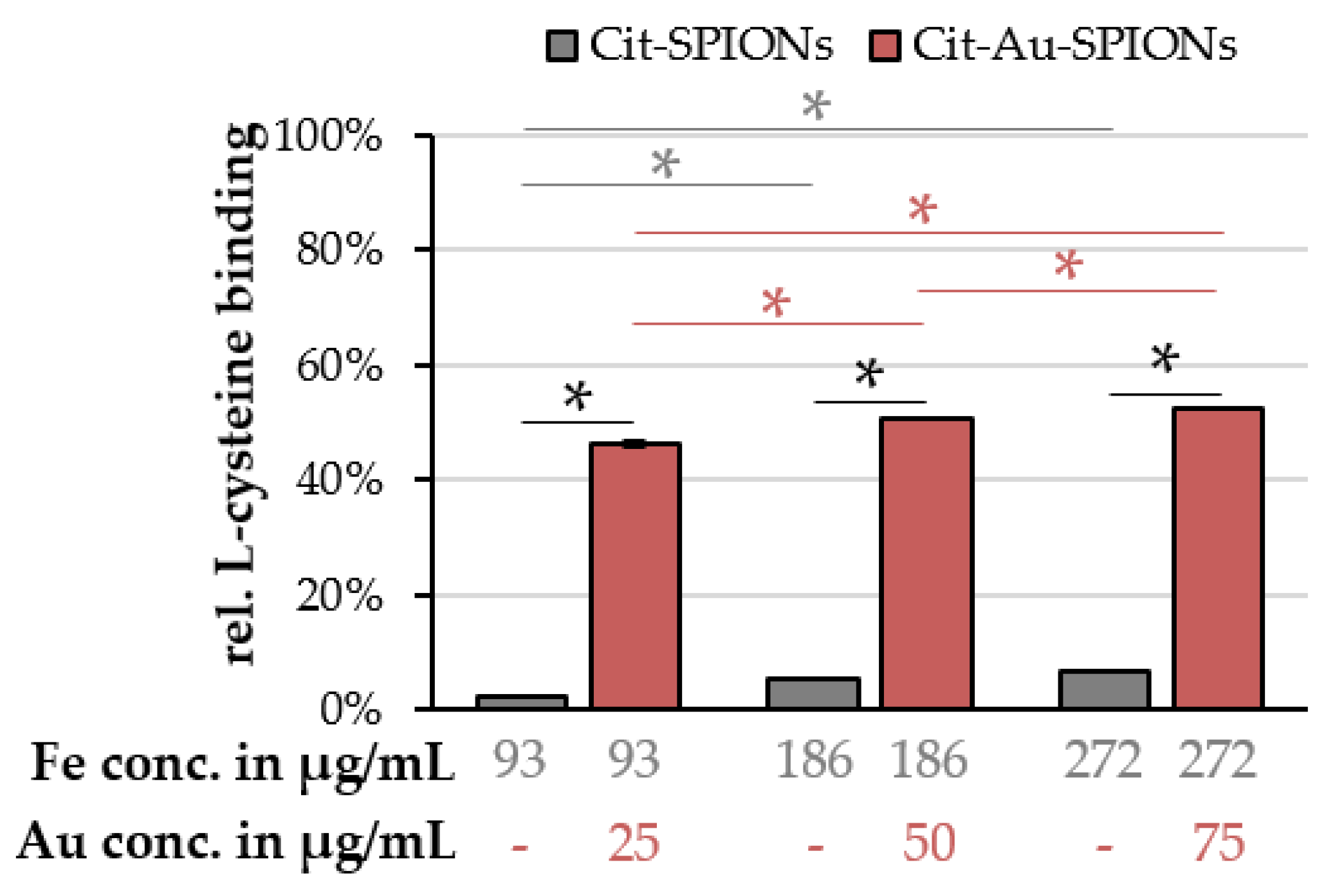
2.4. L-Cysteine Binding to Cit-Au-SPIONs
3. Discussion
3.1. Cit-SPION Characterization
3.2. Gold-Coating of Cit-SPIONs
3.3. Factors Influencing the Gold-Coating Process
3.4. Cytotoxicty and Uptake into Cells of Cit-Au-SPIONs
3.5. L-Cysteine Binding
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Synthesis of Citrate-Stabilized SPIONs (Cit-SPIONs)
4.3. Synthesis of Gold-Coated SPIONs
4.4. Synthesis of Citrate-Stabilized Gold-Coated SPIONs
4.5. Investigation of Synthesis Parameters for Cit-Au-SPIONs
4.6. Physicochemical Characterization
4.6.1. Atomic Emission Spectroscopy (AES)
4.6.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) and Energy Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy (EDX)
4.6.3. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
4.6.4. Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS)
4.6.5. ζ-Potential Measurement
4.6.6. Susceptibility Measurement
4.6.7. Vibrating Sample Magnetometry (VSM)
4.6.8. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
4.6.9. Ultraviolet–Visible Spectroscopy (UV–Vis)
4.6.10. X-ray Diffraction (XRD)
4.7. In Vitro Toxicity
4.7.1. Cell Viability
4.7.2. Particle Uptake into Cells
4.8. L-Cysteine Binding on Cit-Au-SPIONs
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A




| Reaction Temp. in °C | Z-Avg. in nm | PDI in a.u. | ζ-Potential @ pH 7 in mV | pH Value in a.u. | Relative Susceptibility in a.u. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 90 | 145 ± 4 | 0.18 ± 0.01 | −50.8 ± 1.3 | 6.14 ± 0.16 | 87% ± 4% |
| 110 | 152 ± 5 | 0.19 ± 0.01 | −48.6 ± 0.3 | 6.21 ± 0.14 | 89% ± 2% |
| 130 | 146 ± 11 | 0.19 ± 0.01 | −46.9 ± 2.6 | 6.09 ± 0.20 | 96% ± 3% |
| Precursor Concentration | Z-Avg. in nm | PDI in a.u. | ζ-Potential @ pH 7 in mV | pH Value in a.u. | Relative Susceptibility in a.u. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50% | 120 ± 10 | 0.16 ± 0.01 | −45.9 ± 2.6 | 6.59 ± 0.13 | 93% ± 0% |
| 100% | 152 ± 5 | 0.19 ± 0.01 | −48.6 ± 0.3 | 6.21 ± 0.14 | 89% ± 2% |
| 200% | 146 ± 6 | 0.17 ± 0.01 | −47.8 ± 1.3 | 5.50 ± 0.17 | 93% ± 15% |
References
- Martin, B.R.; Dermody, D.J.; Reiss, B.D.; Fang, M.; Lyon, L.A.; Natan, M.J.; Mallouk, T.E. Orthogonal self-assembly on colloidal gold-platinum nanorods. Adv. Mater. 1999, 11, 1021–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, M.; Akola, J.; Lopez-Acevedo, O.; Jadzinsky, P.D.; Calero, G.; Ackerson, C.J.; Whetten, R.L.; Grönbeck, H.; Häkkinen, H. A unified view of ligand-protected gold clusters as superatom complexes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 9157–9162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, W.; Dasog, M.; Scott, R.W.J. Probing the relative stability of thiolate-and dithiolate-protected Au monolayer-protected clusters. Langmuir 2009, 25, 12954–12961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Pérez-Segarra, W.; Shi, Q.; Wei, A. Dithiocarbamate assembly on gold. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 7328–7329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeJesus, J.F.; Sherman, L.M.; Yohannan, D.J.; Becca, J.C.; Strausser, S.L.; Karger, L.F.P.; Jensen, L.; Jenkins, D.M.; Camden, J.P. A Benchtop Method for Appending Protic Functional Groups to N-Heterocyclic Carbene Protected Gold Nanoparticles. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 7585–7590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Mou, L.; Jiang, X. Surface chemistry of gold nanoparticles for health-related applications. Chem. Sci. 2020, 11, 923–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dykman, L.A. Gold nanoparticles for preparation of antibodies and vaccines against infectious diseases. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2020, 19, 465–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.-H.; Sun, X.; Chiu, J.-F.; Sun, H.; He, Q.-Y. Transferrin-mediated gold nanoparticle cellular uptake. Bioconjug. Chem. 2005, 16, 494–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, S.D.; Nativo, P.; Smith, J.-A.; Stirling, D.; Edwards, P.R.; Venugopal, B.; Flint, D.J.; Plumb, J.A.; Graham, D.; Wheate, N.J. Gold nanoparticles for the improved anticancer drug delivery of the active component of oxaliplatin. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 4678–4684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyriazi, M.-E.; Giust, D.; El-Sagheer, A.-H.; Lackie, P.M.; Muskens, O.L.; Brown, T.; Kanaras, A.G. Multiplexed mRNA sensing and combinatorial-targeted drug delivery using DNA-gold nanoparticle dimers. Acs Nano 2018, 12, 3333–3340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Meyers, J.D.; Broome, A.-M.; Kenney, M.E.; Basilion, J.P.; Burda, C. Deep penetration of a PDT drug into tumors by noncovalent drug-gold nanoparticle conjugates. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 2583–2591. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; El-Sayed, I.H.; Qian, W.; El-Sayed, M.A. Cancer cell imaging and photothermal therapy in the near-infrared region by using gold nanorods. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 2115–2120. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Van de Broek, B.; Devoogdt, N.; D’Hollander, A.; Gijs, H.-L.; Jans, K.; Lagae, L.; Muyldermans, S.; Maes, S.; Borghs, G. Specific cell targeting with nanobody conjugated branched gold nanoparticles for photothermal therapy. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 4319–4328. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cheng, X.; Sun, R.; Yin, L.; Chai, Z.; Shi, H.; Gao, M. Light-triggered assembly of gold nanoparticles for photothermal therapy and photoacoustic imaging of tumors in vivo. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1604894. [Google Scholar]
- Dickerson, E.B.; Dreaden, E.C.; Dreaden, X.; El-Sayed, I.H.; Chu, H.; Pushpanketh, S.; McDonald, J.F.; El-Sayed, M.A. Gold nanorod assisted near-infrared plasmonic photothermal therapy (PPTT) of squamous cell carcinoma in mice. Cancer Lett. 2008, 269, 57–66. [Google Scholar]
- Khlebtsov, N.; Dykman, L. Biodistribution and toxicity of engineered gold nanoparticles: A review of in vitro and in vivo studies. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 1647–1671. [Google Scholar]
- Sonavane, G.; Tomoda, K.; Makino, K. Biodistribution of colloidal gold nanoparticles after intravenous administration: Effect of particle size. Colloids Surf. B 2008, 66, 274–280. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Kuang, H.; Zhang, W.; Aguilar, Z.P.; Wei, H.; Xu, H. Comparisons of the biodistribution and toxicological examinations after repeated intravenous administration of silver and gold nanoparticles in mice. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Unterweger, H.; Dézsi, L.; Matuszak, J.; Janko, C.; Poettler, M.; Jordan, J.; Bäuerle, T.; Szebeni, J.; Fey, T.; Boccaccini, A.R. Dextran-coated superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for magnetic resonance imaging: Evaluation of size-dependent imaging properties, storage stability and safety. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 1899. [Google Scholar]
- Usman, A.; Patterson, A.J.; Yuan, J.; Cluroe, A.; Patterson, I.; Graves, M.J.; Gillard, J.H.; Sadat, U. Ferumoxytol-enhanced three-dimensional magnetic resonance imaging of carotid atheroma-a feasibility and temporal dependence study. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Tietze, R.; Lyer, S.; Dürr, S.; Struffert, T.; Engelhorn, T.; Schwarz, M.; Eckert, E.; Göen, T.; Vasylyev, S.; Peukert, W.; et al. Efficient drug-delivery using magnetic nanoparticles—biodistribution and therapeutic effects in tumour bearing rabbits. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2013, 9, 961–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaloga, J.; Pöttler, M.; Leitinger, G.; Friedrich, R.P.; Almer, G.; Lyer, S.; Baum, E.; Tietze, R.; Heimke-Brinck, R.; Mangge, H.; et al. Pharmaceutical formulation of HSA hybrid coated iron oxide nanoparticles for magnetic drug targeting. Eur. J. Pharmaceutics Biopharm. 2016, 101, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matuszak, J.; Lutz, B.; Sekita, A.; Zaloga, J.; Alexiou, C.; Lyer, S.; Cicha, I. Drug delivery to atherosclerotic plaques using superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 8443–8460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maleki, H.; Simchi, A.; Imani, M.; Costa, B.F.O. Size-controlled synthesis of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles and their surface coating by gold for biomedical applications. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2012, 324, 3997–4005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baniukevic, J.; Boyaci, I.H.; Bozkurt, A.G.; Tamer, U.; Ramanavicius, A.; Ramanaviciene, A. Magnetic gold nanoparticles in SERS-based sandwich immunoassay for antigen detection by well oriented antibodies. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 43, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montazerabadi, A.R.; Oghabian, M.A.; Irajirad, R.; Muhammadnejad, S.; Ahmadvand, D.; Hamid Delavari H, H.D.; Mahdavi, S.R. Development of gold-coated magnetic nanoparticles as a potential MRI contrast agent. Nano 2015, 10, 1550048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Félix, L.L.; Sanz, B.; Sebastián, V.; Torres, T.E.; Sousa, M.H.; Coaquira, J.A.H.; Ibarra, M.R.; Goya, G.F. Gold-decorated magnetic nanoparticles design for hyperthermia applications and as a potential platform for their surface-functionalization. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammad, F.; Balaji, G.; Weber, A.; Uppu, R.M.; Kumar, C.S.S.R. Influence of gold nanoshell on hyperthermia of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 19194–19201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias-Silva, E.; Vilas, J.L.; López-Quintela, M.A.; Rivas, J. Synthesis of gold-coated iron oxide nanoparticles. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2010, 356, 1233–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-K.; Jin-Woong, K.; Yong-Yeon, J.; Sang-Yong, J. Antibiofouling polymer coated gold@ iron oxide nanoparticle (GION) as a dual contrast agent for CT and MRI. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2009, 30, 1855–1857. [Google Scholar]
- Tintoré, M.; Mazzini, S.; Polito, L.; Marelli, M.; Latorre, A.; Somoza, Á.; Aviñó, A.; Fàbrega, C.; Eritja, R. Gold-coated superparamagnetic nanoparticles for single methyl discrimination in DNA aptamers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 27625–27639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nassireslami, E.; Ajdarzade, M. Gold coated superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles as effective nanoparticles to eradicate breast cancer cells via photothermal therapy. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2018, 8, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carneiro, M.F.H.; Machado, A.R.T.; Antunes, L.M.G.; Souza, T.E.; Freitas, V.A.; Oliveira, L.C.A.; Rodrigues, J.L.; Pereira, M.C.; Barbosa, F., Jr. Gold-Coated Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Attenuate Collagen-Induced Arthritis after Magnetic Targeting. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2020, 194, 502–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elbialy, N.S.; Fathy, M.M.; Khalil, W.M. Preparation and characterization of magnetic gold nanoparticles to be used as doxorubicin nanocarriers. Physica Med. 2014, 30, 843–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neshastehriz, A.; Khosravi, Z.; Ghaznavi, H.; Shakeri-Zadeh, A. Gold-coated iron oxide nanoparticles trigger apoptosis in the process of thermo-radiotherapy of U87-MG human glioma cells. Radiat. Environ. Biophys. 2018, 57, 405–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Namduri, H.; Nasrazadani, S. Quantitative analysis of iron oxides using Fourier transform infrared spectrophotometry. Corros. Sci. 2008, 50, 2493–2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-S.; Church, J.S.; Woodhead, A.L. Infrared and Raman spectroscopic studies on iron oxide magnetic nano-particles and their surface modifications. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2012, 324, 1543–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, K.M.; Swamy, C. Infrared Spectra of Potassium Citrate Monohydrate Single Crystals. Indian J. Phys. 1974, 48, 225–235. [Google Scholar]
- Badertscher, M.; Bühlmann, P.; Pretsch, E. Structure Determination of Organic Compounds, 4th ed.; Springer: Berlin Heidelberg, Germany, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Wulandari, P.; Nagahiro, T.; Fukada, N.; Kimura, Y.; Niwano, M.; Tamada, K. Characterization of citrates on gold and silver nanoparticles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 438, 244–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swanson, H.E.; McMurdie, H.F.; Morris, M.C.; Evans, E.H. Standard X-ray Diffraction Powder Patterns, 5th ed.; US Department of Commerce, National Bureau of Standards: Washington, DC, USA, 1967; Volume 25.
- Sneha, K.; Sathishkumar, M.; Kim, S.; Yun, Y.-S. Counter ions and temperature incorporated tailoring of biogenic gold nanoparticles. Process Biochem. 2010, 45, 1450–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mühlberger, M.; Janko, C.; Unterweger, H.; Friedrich, R.P.; Friedrich, B.; Band, J.; Cebulla, N.; Alexiou, C.; Dudziak, D.; Lee, G.; et al. Functionalization Of T Lymphocytes With Citrate-Coated Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles For Magnetically Controlled Immune Therapy. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 8421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turkevich, J.; Stevenson, P.C.; Hillier, J. A study of the nucleation and growth processes in the synthesis of colloidal gold. Discuss. Faraday Soc. 1951, 11, 55–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amendola, V.; Pilot, R.; Frasconi, M.; Maragò, O.M.; Iatì, M.A. Surface plasmon resonance in gold nanoparticles: A review. J. Physics. Condens. Matter 2017, 29, 203002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Gandhi, K.S.; Kumar, R. Modeling of formation of gold nanoparticles by citrate method. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2007, 46, 3128–3136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swanson, H.E.; McMurdie, H.F.; Morris, M.C.; Evans, E.H. Standard X-ray Diffraction Powder Patterns; US Department of Commerce, National Bureau of Standards: Washington, DC, USA, 1953; Volume 1.
- Schwertmann, U.; Taylor, R.M. Iron oxides. Miner. Soil Environ. 1989, 1, 379–438. [Google Scholar]
- Cruz, M.M.; Ferreira, L.P.; Alves, A.F.; Mendo, S.G.; Ferreira, P.; Godinho, M.; Carvalho, M.D. Nanoparticles for magnetic hyperthermia. In Nanostructures for Cancer Therapy; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 485–511. [Google Scholar]
- Kolhatkar, A.G.; Jamison, A.C.; Litvinov, D.; Willson, R.C.; Lee, T.R. Tuning the magnetic properties of nanoparticles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 15977–16009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Li, N.; Astruc, D. State of the art in gold nanoparticle synthesis. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2013, 257, 638–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, Y.-C.; Creran, B.; Rotello, V.M. Gold nanoparticles: Preparation, properties, and applications in bionanotechnology. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 1871–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, R.; Bansal, V.; Chaudhary, M.; Basu, A.; Bhonde, R.R.; Sastry, M. Biocompatibility of gold nanoparticles and their endocytotic fate inside the cellular compartment: A microscopic overview. Langmuir 2005, 21, 10644–10654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Wang, Q.; Chen, W.; Pang, Y. One-step synthesis of water-dispersible cysteine functionalized magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles for mercury (II) removal from aqueous solutions. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 317, 1028–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasprzyk, W.; Bednarz, S.; Bogdał, D. Luminescence phenomena of biodegradable photoluminescent poly (diol citrates). Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 6445–6447. [Google Scholar]
- Cullity, B.D. Elements of X-ray Diffraction; Addison-Wesley Publishing: Middlesex, MA, USA, 1956. [Google Scholar]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |


| Z-Avg. in nm | PDI in a.u. | ζ-Potential @ pH 7 in mV | pH Value in a.u. | Relative Susceptibility in a.u. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cit-SPIONs | 107 ± 3 | 0.15 ± 0.03 | –48.0 ± 6.3 | 8.27 ± 0.07 | 100% |
| Au-SPIONs | 405 ± 83 | 0.25 ± 0.06 | −43.5 ± 0.6 | 2.89 ± 0.14 | 94% ± 2% |
| Cit-Au-SPIONs | 152 ± 5 | 0.19 ± 0.01 | −48.6 ± 0.3 | 6.21 ± 0.14 | 89% ± 2% |
| Citrate Conc. in mg/mL | Z-Avg. in nm | PDI in a.u. | ζ-Potential @ pH 7 in mV | pH Value in a.u. | Relative Susceptibility in a.u. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.0 | 405 ± 83 | 0.25 ± 0.06 | −43.5 ± 0.6 | 2.89 ± 0.14 | 94% ± 2% |
| 0.1 | 318 ± 60 | 0.25 ± 0.03 | −44.9 ± 2.5 | 3.19 ± 0.25 | 89% ± 4% |
| 0.5 | 167 ± 5 | 0.21 ± 0.01 | −47.6 ± 2.0 | 5.52 ± 0.17 | 90% ± 2% |
| 1.0 | 152 ± 5 | 0.19 ± 0.01 | −48.6 ± 0.3 | 6.21 ± 0.14 | 89% ± 2% |
| Reaction Time in min | Z-Avg. in nm | PDI in a.u. | ζ-Potential @ pH 7 in mV | pH Value in a.u. | Relative Susceptibility in a.u. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15 | 152 ± 5 | 0.19 ± 0.01 | −48.6 ± 0.3 | 6.21 ± 0.14 | 89% ± 2% |
| 60 | 165 ± 6 | 0.18 ± 0.01 | −50.0 ± 0.9 | 6.25 ± 0.13 | 84% ± 3% |
| 300 | 170 ± 6 | 0.19 ± 0.01 | −48.2 ± 1.8 | 6.34 ± 0.19 | 85% ± 2% |
| Gold Concentration | Z-Avg. in nm | PDI in a.u. | ζ-Potential @ pH 7 in mV | pH Value in a.u. | Relative Susceptibility in a.u. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50% | 103 ± 1 | 0.15 ± 0.01 | −50.3 ± 0.9 | 6.66 ± 0.06 | 87% ± 9% |
| 100% | 152 ± 5 | 0.19 ± 0.01 | −48.6 ± 0.3 | 6.21 ± 0.14 | 89% ± 2% |
| 200% | 239 ± 49 | 0.14 ± 0.06 | −46.7 ± 1.5 | 5.05 ± 0.10 | 86% ± 3% |
| Z-avg. in nm | PDI in a.u. | Volumetric Susceptibility ×10−3 in a.u. | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cit-Au-SPIONs | 145 ± 2 | 0.17 ± 0.01 | 5.0 ± 0.3 |
| Sterile Cit-Au-SPIONs | 141 ± 1 | 0.17 ± 0.01 | 5.1 ± 0.1 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stein, R.; Friedrich, B.; Mühlberger, M.; Cebulla, N.; Schreiber, E.; Tietze, R.; Cicha, I.; Alexiou, C.; Dutz, S.; Boccaccini, A.R.; et al. Synthesis and Characterization of Citrate-Stabilized Gold-Coated Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Biomedical Applications. Molecules 2020, 25, 4425. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25194425
Stein R, Friedrich B, Mühlberger M, Cebulla N, Schreiber E, Tietze R, Cicha I, Alexiou C, Dutz S, Boccaccini AR, et al. Synthesis and Characterization of Citrate-Stabilized Gold-Coated Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Biomedical Applications. Molecules. 2020; 25(19):4425. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25194425
Chicago/Turabian StyleStein, René, Bernhard Friedrich, Marina Mühlberger, Nadine Cebulla, Eveline Schreiber, Rainer Tietze, Iwona Cicha, Christoph Alexiou, Silvio Dutz, Aldo R. Boccaccini, and et al. 2020. "Synthesis and Characterization of Citrate-Stabilized Gold-Coated Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Biomedical Applications" Molecules 25, no. 19: 4425. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25194425
APA StyleStein, R., Friedrich, B., Mühlberger, M., Cebulla, N., Schreiber, E., Tietze, R., Cicha, I., Alexiou, C., Dutz, S., Boccaccini, A. R., & Unterweger, H. (2020). Synthesis and Characterization of Citrate-Stabilized Gold-Coated Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Biomedical Applications. Molecules, 25(19), 4425. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25194425









