Discovery of New Apoptosis-Inducing Agents for Breast Cancer Based on Ethyl 2-Amino-4,5,6,7-Tetra Hydrobenzo[b]Thiophene-3-Carboxylate: Synthesis, In Vitro, and In Vivo Activity Evaluation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Chemistry
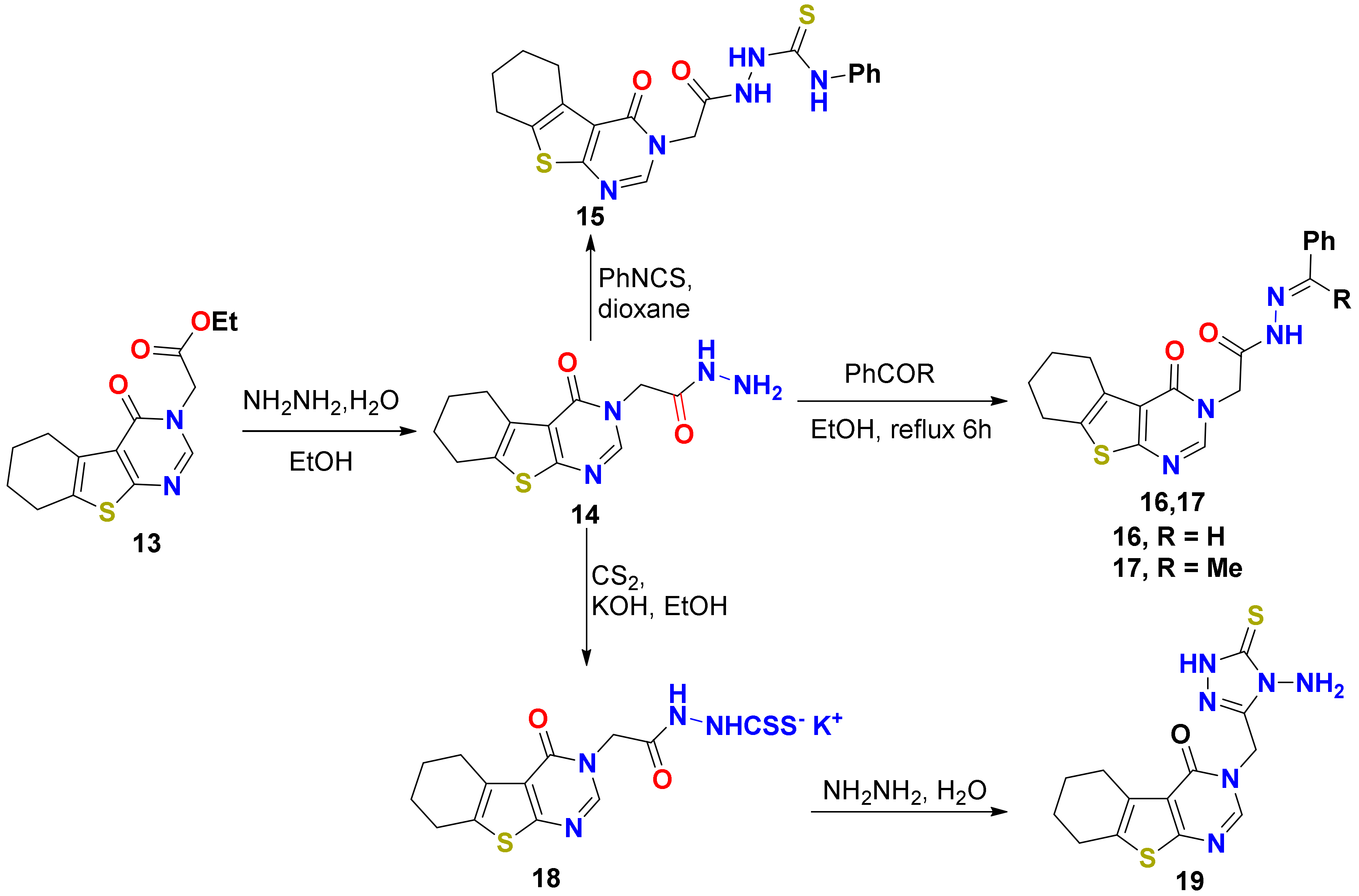
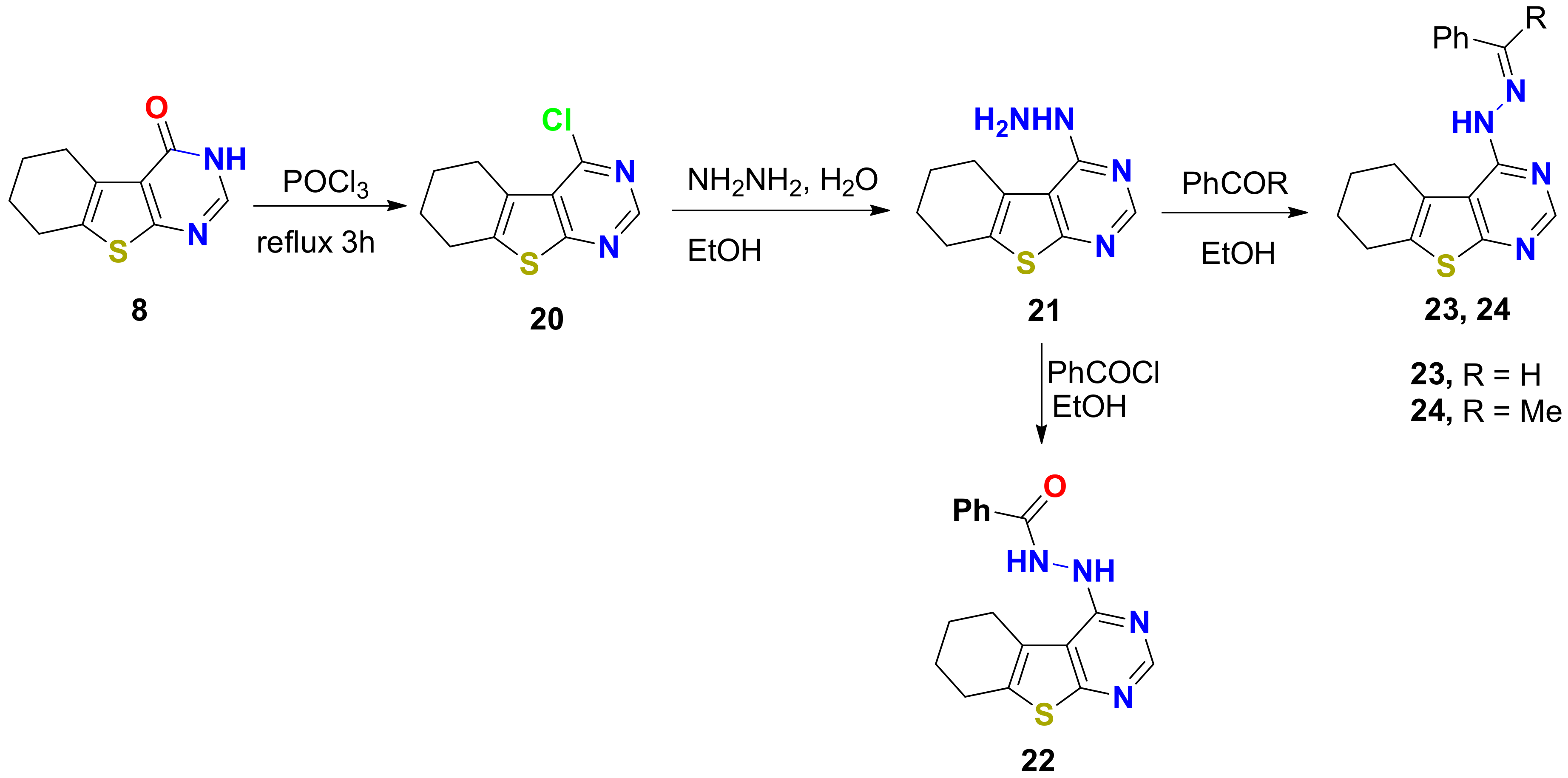
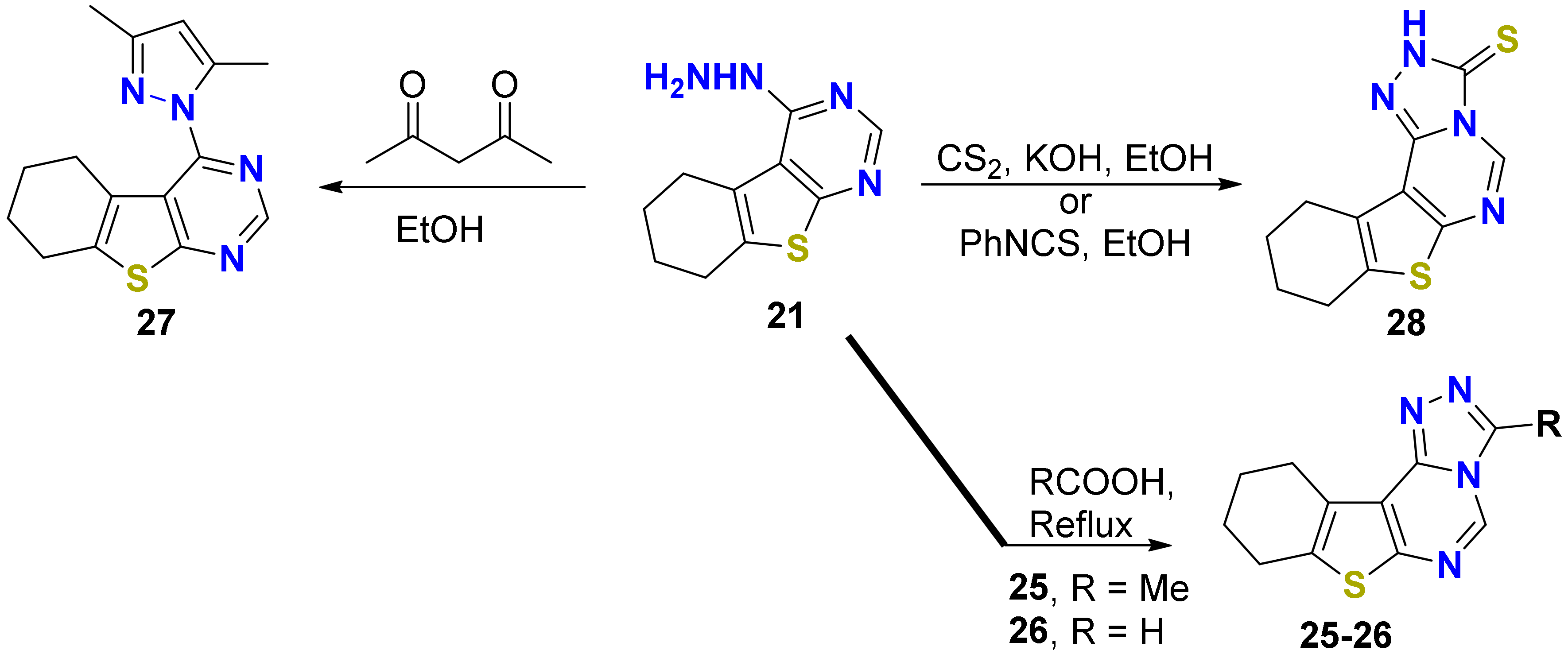
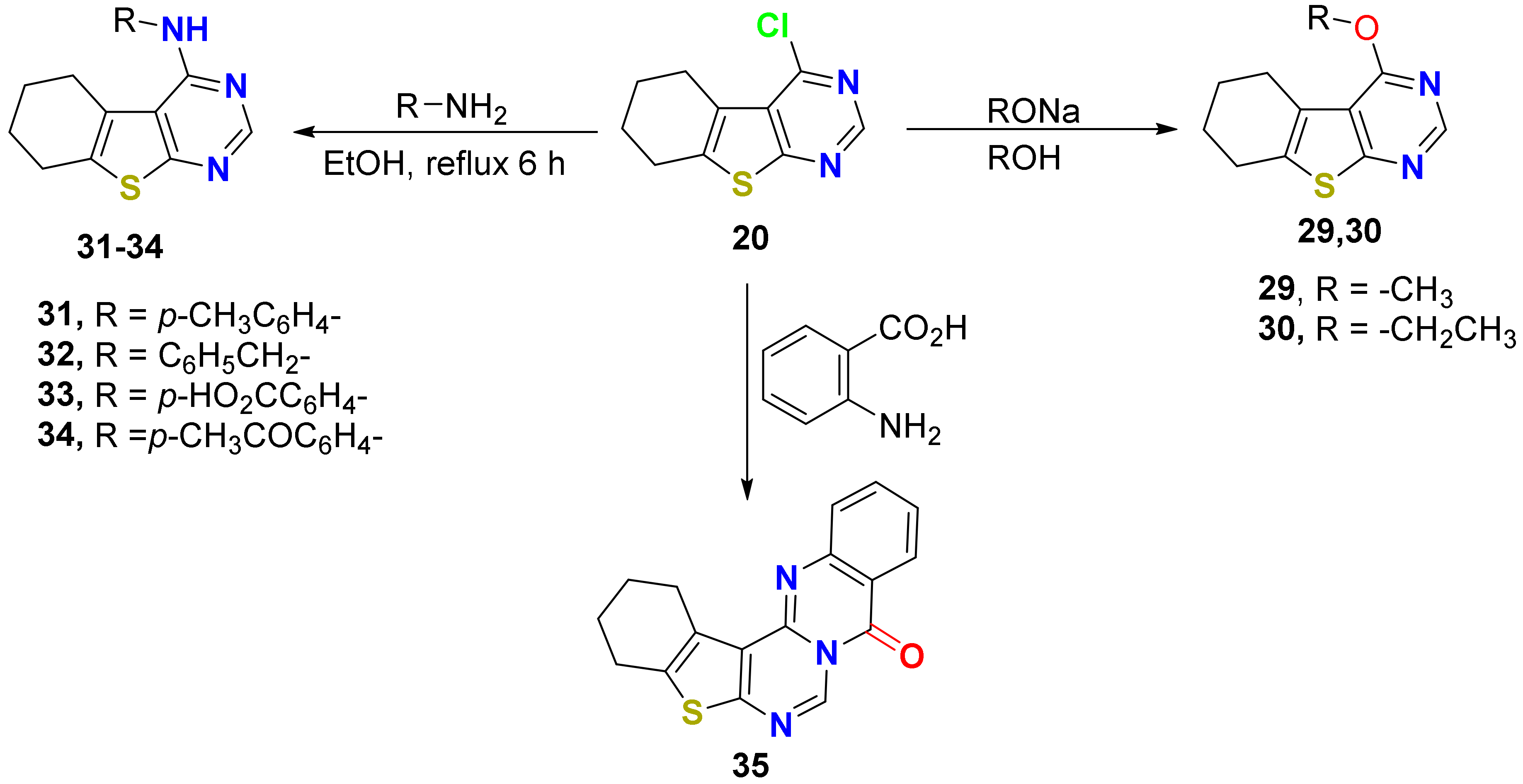
2.1.1. Synthesis
2.1.2. Structural Characterization
2.2. Biological Activity
2.2.1. Antitumor Activity Evaluation
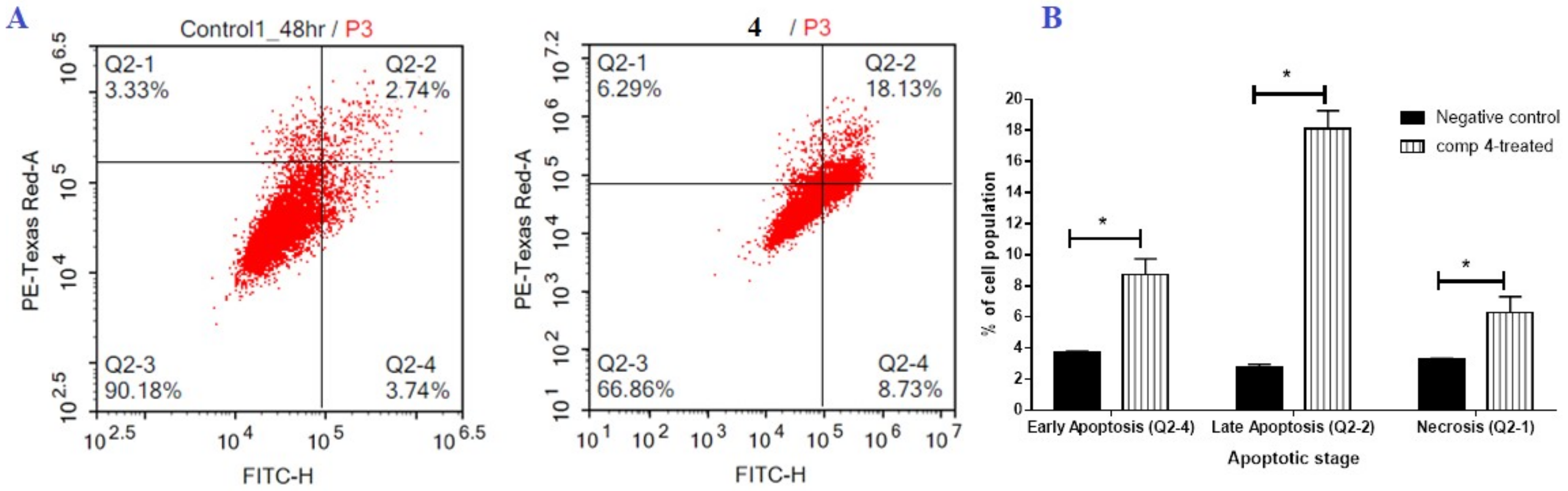
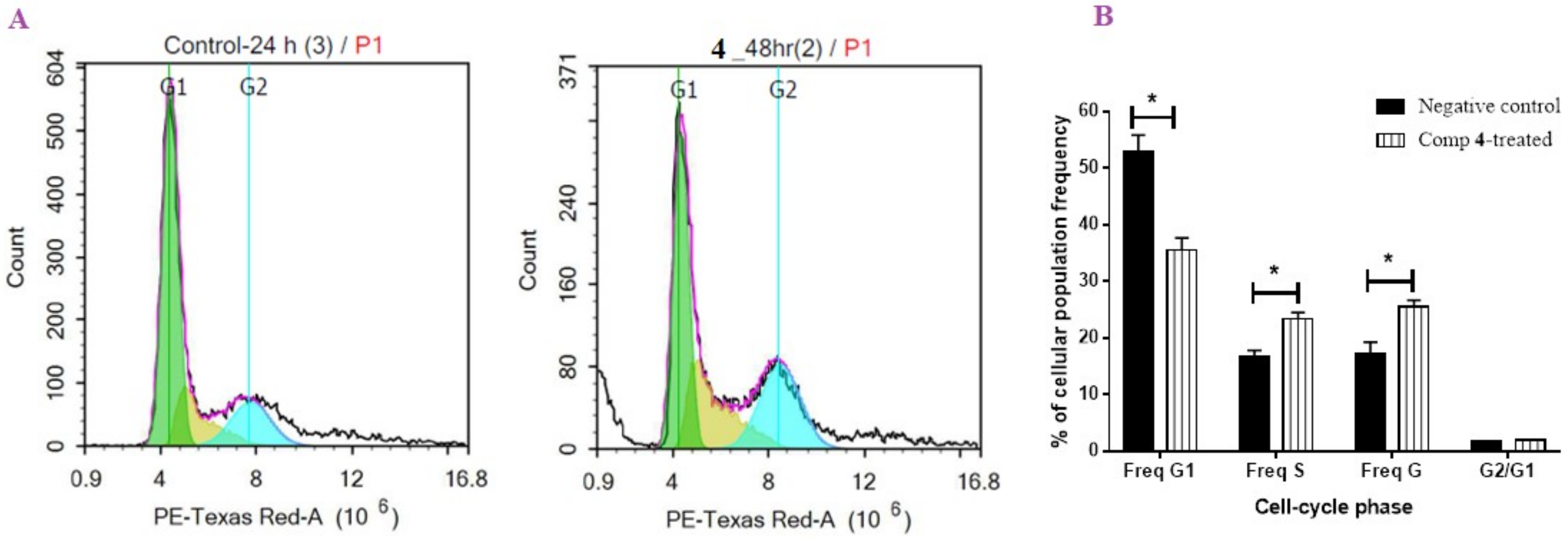
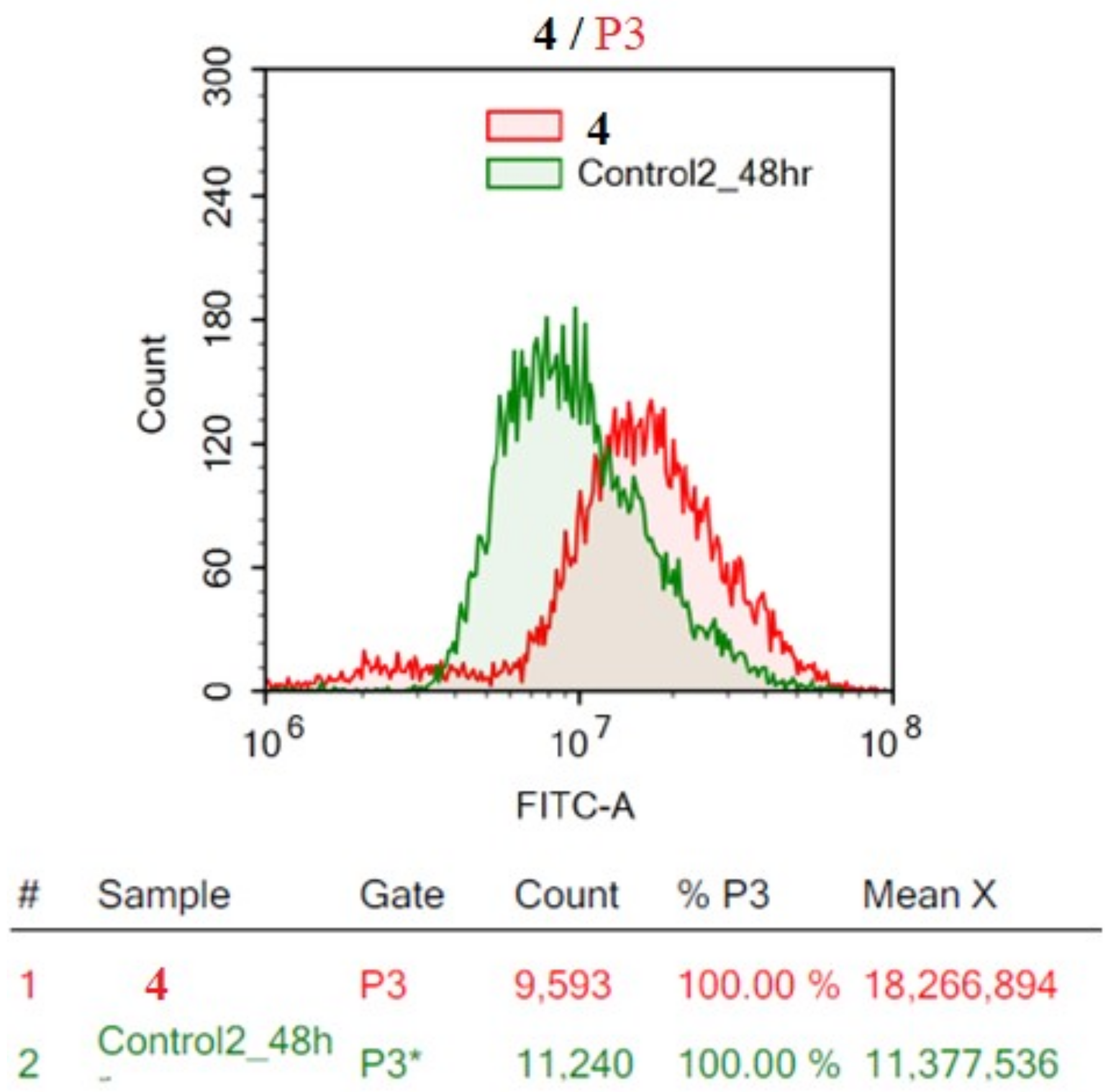
2.2.2. Flow Cytometric Analysis
FITC/Annexin-V-FITC/PI Differential Apoptosis/Necrosis Assessment
DNA Content-Flow Cytometry Aided Cell Cycle Analysis
Acridine Orange Quantitative Autophagy Assessment
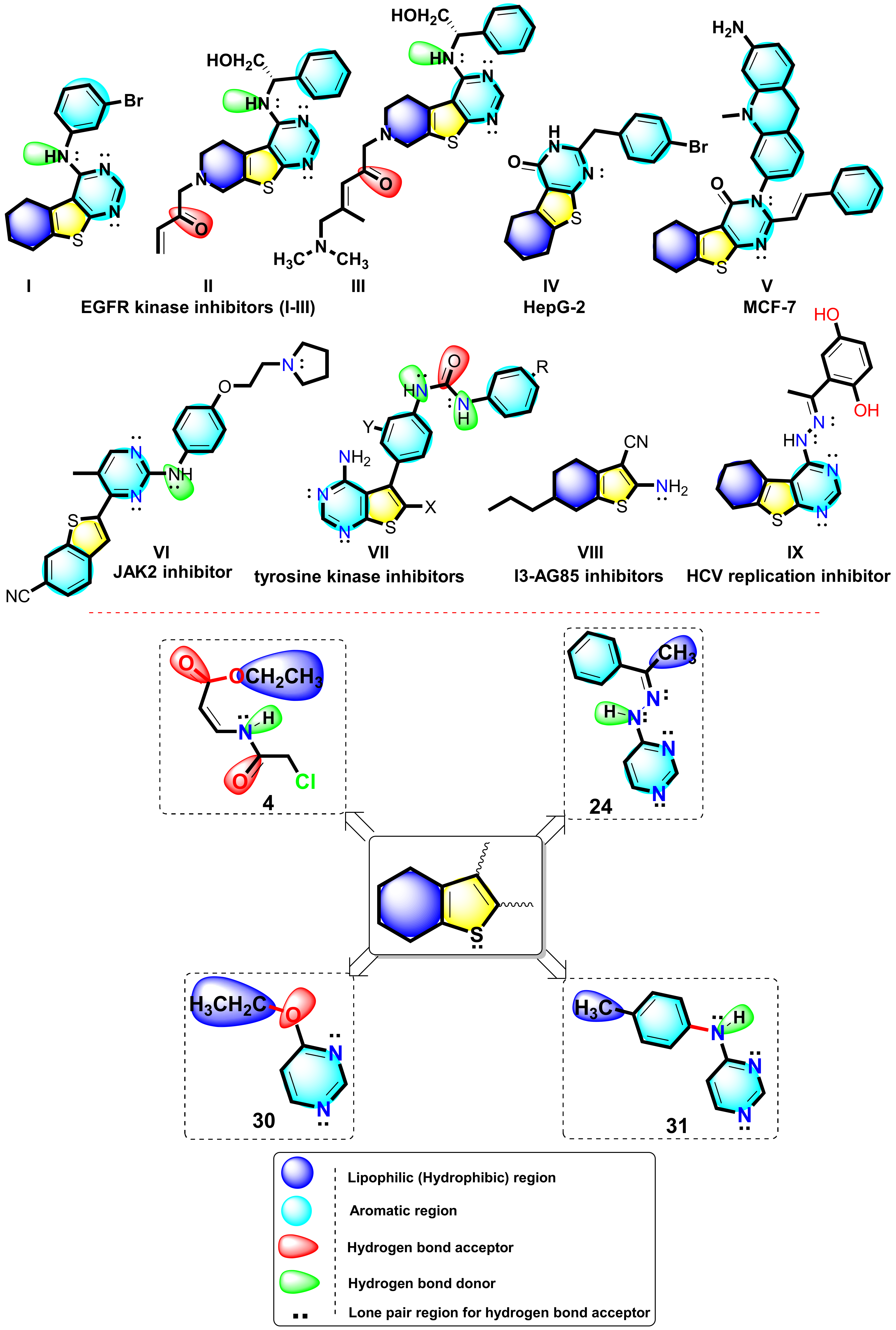
2.2.3. In Silico Molecular Docking Studies
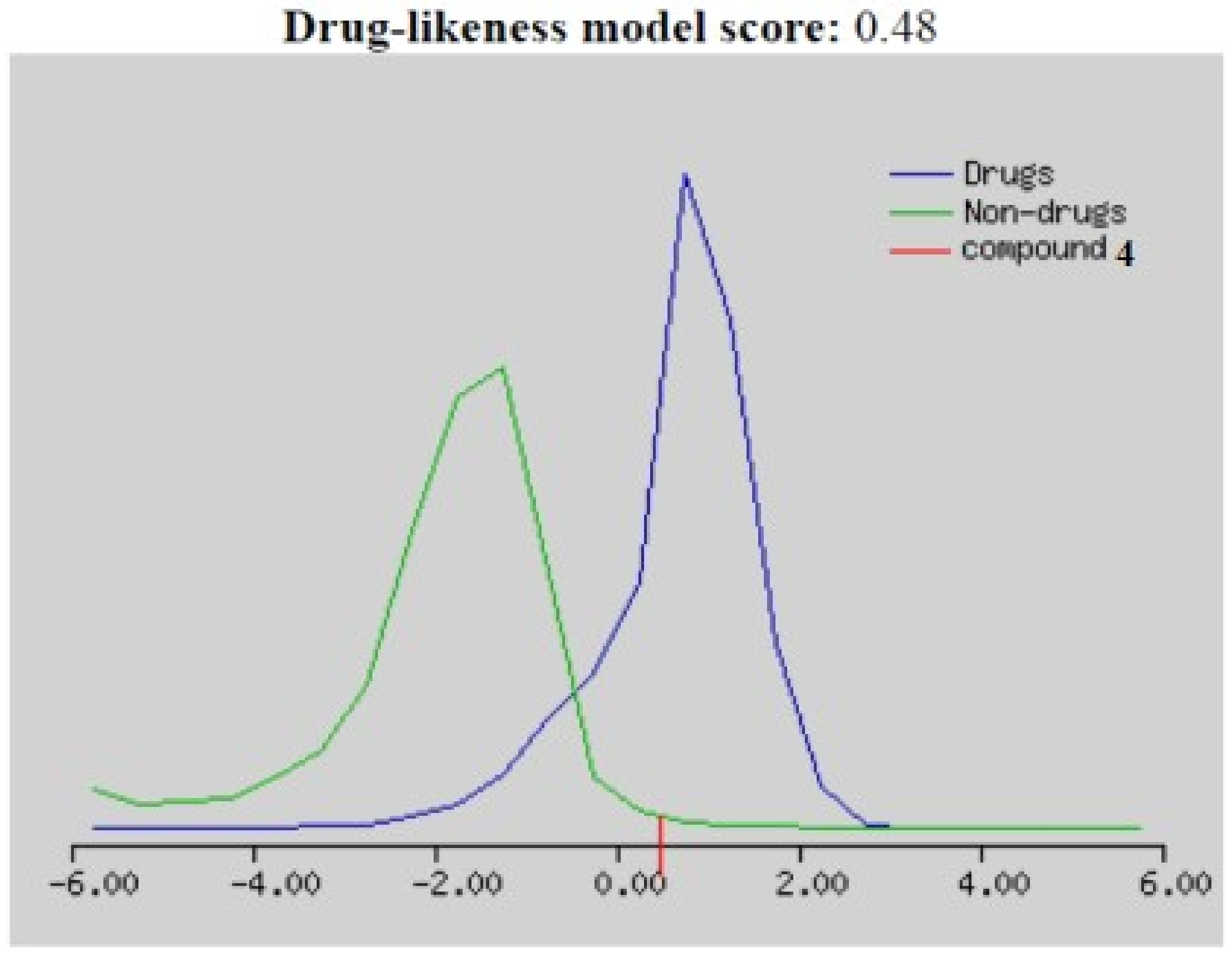
2.2.4. Bioinformatics Study
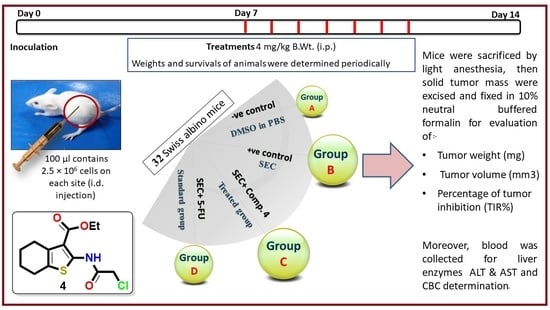
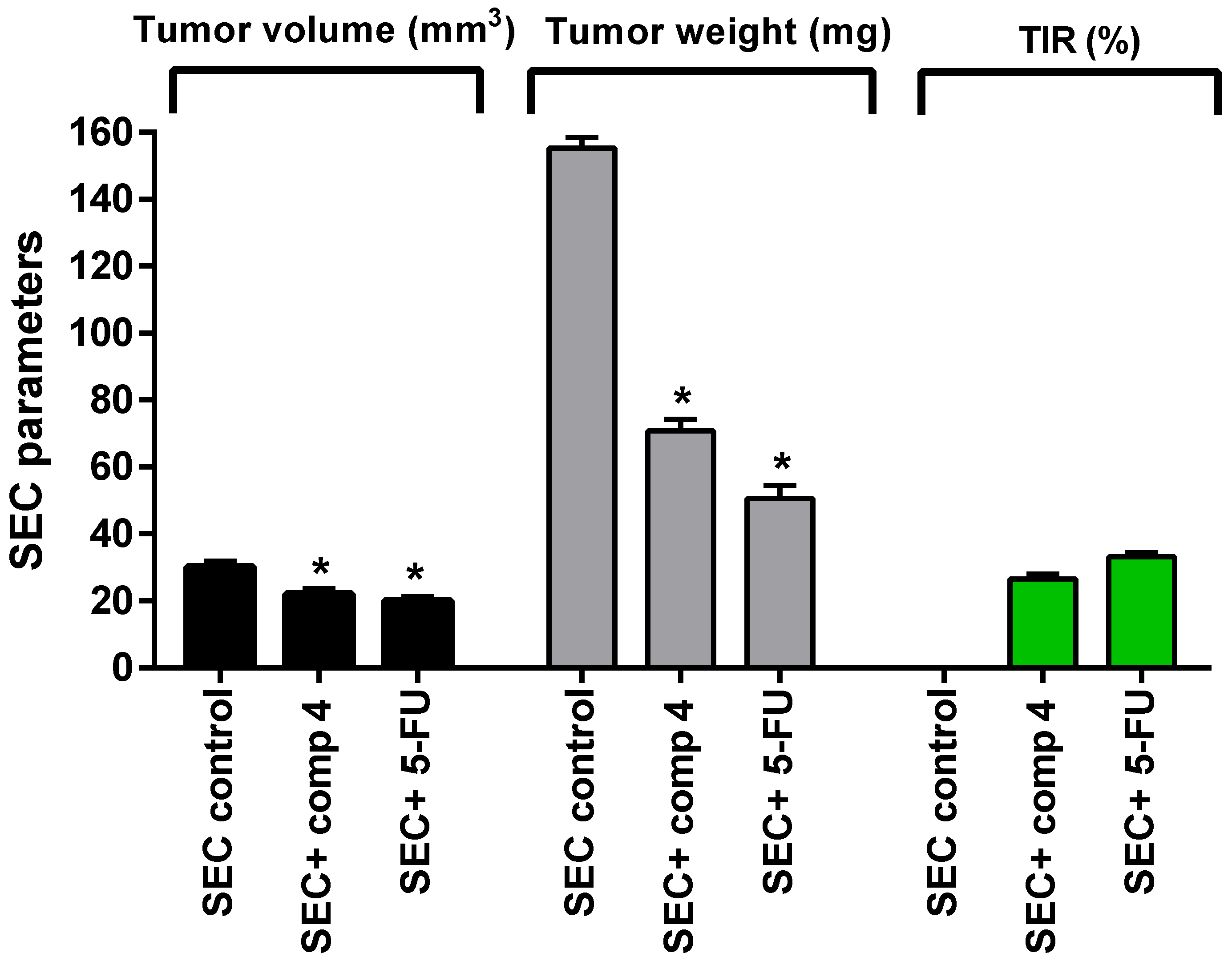
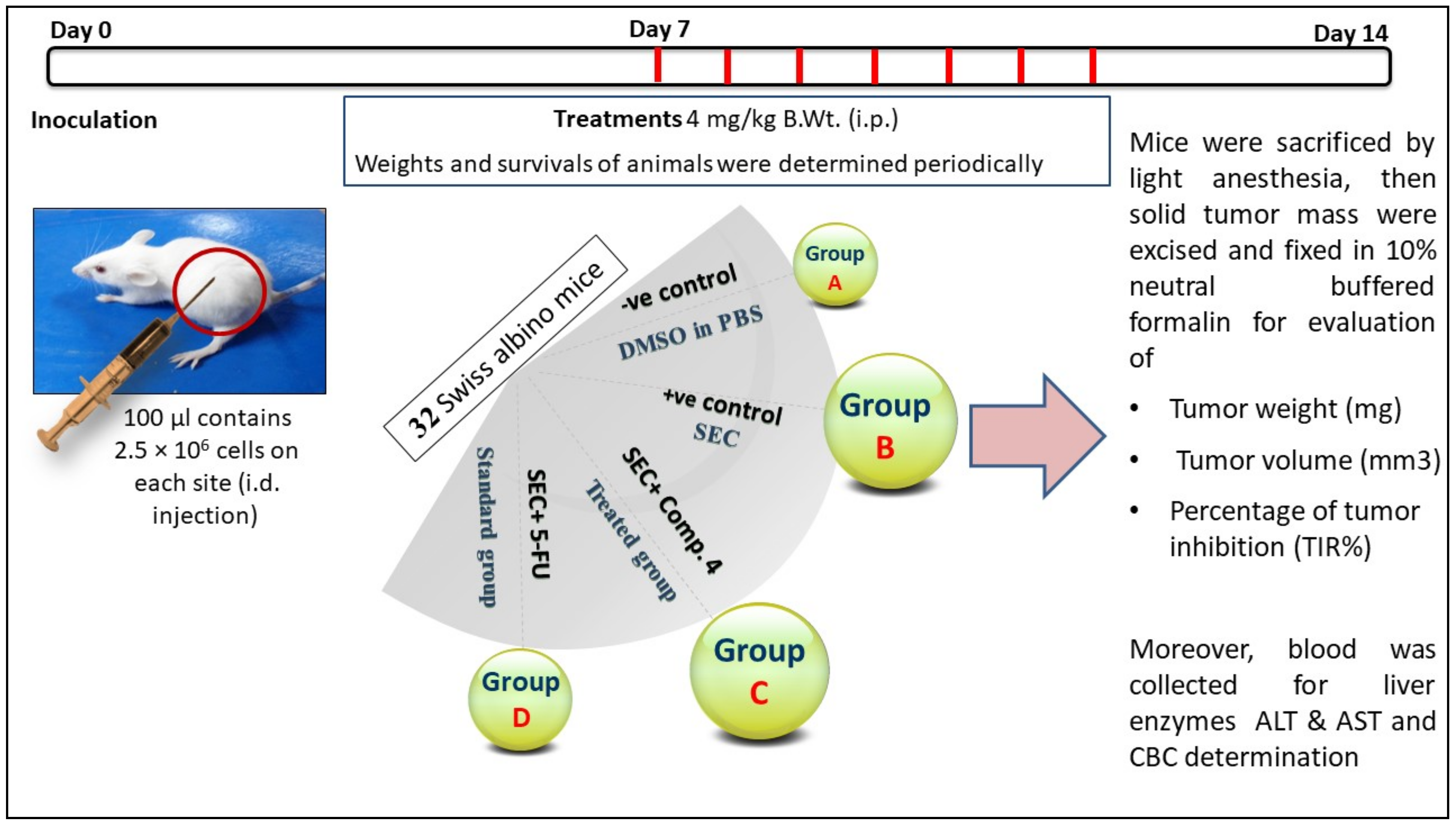
2.2.5. In Vivo Study
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Synthesis
3.2. Biological Experimental Assays (Full Protocols, see Supplementary Materials)
3.2.1. In Vitro
3.2.2. Flow Cytometry
3.2.3. In Silico Molecular Docking
3.2.4. Bioinformatics
3.2.5. In Vivo (SEC) Model
3.2.6. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ovaa, H.; Kuijl, C.; Neefjes, J. Recent and new targets for small molecule anti-cancer agents. Drug Discov. Today Technol. 2009, 6, e3–e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiss, R.; Sayeski, P.P.; Keserű, G.M. Recent developments on JAK2 inhibitors: A patent review. Expert Opin. Ther. Patents 2010, 20, 471–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, A.; Kambhampati, S.; Parmar, S.; Platanias, L.C. Jak family of kinases in cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2003, 22, 423–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinakaran, V.S.; Bomma, B.; Srinivasan, K.K. Fused pyrimidines: The heterocycle of diverse biological and pharmacological significance. Der Pharma Chem. 2012, 4, 255–265. [Google Scholar]
- Mavrova, A.T.; Dimov, S.; Yancheva, D.; Rangelov, M.; Wesselinova, D.; Tsenov, J.A. Synthesis, anticancer activity and photostability of novel 3-ethyl-2-mercapto-thieno[2,3- d ]pyrimidin-4( 3H )-ones. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 123, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rheault, T.R.; Caferro, T.R.; Dickerson, S.H.; Donaldson, K.H.; Gaul, M.D.; Goetz, A.S.; Mullin, R.J.; McDonald, O.B.; Petrov, K.G.; Rusnak, D.W.; et al. Thienopyrimidine-based dual EGFR/ErbB-2 inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19, 817–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bánhegyi, P.; Kéri, G.; Örfi, L.; Szekélyhidi, Z.; Wáczek, F. Vichem Chemie Kutato Kft, Tricyclic benzo [4, 5] thieno-[2, 3-d] pyrimidine-4-yl-amin Derivatives, Their Salts, Process for Producing the Compounds and Their Pharmaceutical Use. U.S. Patent 8,802,849, 12 August 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.-H.; Coumar, M.S.; Chu, C.-Y.; Lin, W.-H.; Chen, Y.-R.; Chen, C.-T.; Shiao, H.-Y.; Rafi, S.; Wang, S.-Y.; Hsu, H.; et al. Design and Synthesis of Tetrahydropyridothieno[2,3-d]pyrimidine Scaffold Based Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) Kinase Inhibitors: The Role of Side Chain Chirality and Michael Acceptor Group for Maximal Potency. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 7316–7326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Chen, C.; Xu, S.; Cao, X. Synthesis and Bioevaluation of Thieno[2,3-d]pyrimidinone Derivatives as Potential Tumor Cell Growth Inhibitors. J. Chem. 2013, 2013, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, S.E.; Gawad, N.M.A.; George, R.F.; Akar, Y.A. Synthesis, antitumor and antibacterial activities of some novel tetrahydrobenzo[4,5]thieno[2,3-d]pyrimidine derivatives. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 65, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Guo, Y.; Frey, R.R.; Ji, Z.; Curtin, M.L.; Ahmed, A.A.; Albert, D.H.; Arnold, L.; Arries, S.S.; Barlozzari, T.; et al. Thienopyrimidine Ureas as Novel and Potent Multitargeted Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2005, 48, 6066–6083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noronha, G.; Mak, C.C.; Cao, J.; Chow, C.; Daneprovskaia, E.; Renick, J. Anilinopyrimidines as Jak Kinase Inhibitors. Patent WO2009046416A1, 9 April 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Ma, T.; Li, S.; Yang, Y.; Guo, J.; Kong, L.; Kong, L. Antagonizing STAT3 activation with benzo[b]thiophene 1, 1-dioxide based small molecules. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 125, 538–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Yang, Z.; Ding, C.; Xiong, A.; Wild, C.; Wang, L.; Ye, N.; Cai, G.; Flores, R.M.; Ding, Y.; et al. Discovery of potent anticancer agent HJC0416, an orally bioavailable small molecule inhibitor of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 82, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelrahman, S.; El-Gohary, N.S.; Elbendary, E.; El-Ashry, S.M.; Shaaban, M.I. Synthesis, antimicrobial, antiquorum-sensing, antitumor and cytotoxic activities of new series of cyclopenta(hepta)[ b ]thiophene and fused cyclohepta[ b ]thiophene analogs. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 140, 200–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ismail, M.M.; Kamel, M.M.; Mohamed, L.W.; Faggal, S.I.; Galal, M.A. Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Thiophene Derivatives as Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors. Molecules 2012, 17, 7217–7231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheich, C.; Puetter, V.; Schade, M. Novel small molecule inhibitors of MDR Mycobacterium tuberculosis by NMR fragment screening of antigen 85C. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 8362–8836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassetto, M.; Leyssen, P.; Neyts, J.; Yerukhimovich, M.M.; Frick, D.N.; Brancale, A. Computer-aided identification, synthesis and evaluation of substituted thienopyrimidines as novel inhibitors of HCV replication. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 123, 31–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashad, A.; Shamroukh, A.; Abdel-Megeid, R.E.; Mostafa, A.; El-Shesheny, R.; Kandeil, A.; Ali, M.A.; Banert, K. Synthesis and screening of some novel fused thiophene and thienopyrimidine derivatives for anti-avian influenza virus (H5N1) activity. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 45, 5251–5257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deka, S.; Mohan, S.; Saravanan, J.; Kakati, M.; Talukdar, A.; Sahariah, B.; Dey, B.; Sarma, R. Synthesis, characterization and in-vitro antiinflammatory activity of some novel thiophenes. J. Med. Sci. 2012, 5, 159–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuncha, M.; Shireesha, B.; Naidu, V.G.M.; Ramakrishna, S.; Narsaiah, B.; Rao, A.R.; Diwan, P.V. Anti-inflammatory potential of thienopyridines as possible alternative to NSAIDs. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 678, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mabkhot, Y.N.; Kheder, N.A.; Barakat, A.; Choudhary, M.I.; Yousuf, S.; Frey, W. Synthesis, Antimicrobial, Anti-Cancer and Molecular Docking of Two Novel Hitherto Unreported Thiophenes. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 63724–63729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewal, M.B.; Wani, A.S.; Vidaillac, C.; Oupicky, D.; Rybak, M.J.; Firestine, S.M. Thieno[2,3-d]pyrimidinedione derivatives as antibacterial agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 51, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Shangguan, S.; Qiu, N.; Hu, C.; Zhang, L.; Hu, Y. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of novel 3,4,5-trisubstituted aminothiophenes as inhibitors of p53-MDM2 interaction, Part 1. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2013, 21, 2879–2885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, C. Synthesis and antiviral/antitumor evaluation of 2-amino- and 2-carboxamido-3-arylsulfonylthiophenes and related compounds as a new class of diarylsulfones. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2001, 9, 1123–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titchenell, P.M.; Showalter, H.D.H.; Pons, J.-F.; Barber, A.J.; Jin, Y.; Antonetti, D.A. Synthesis and structure-activity relationships of 2-amino-3-carboxy-4-phenylthiophenes as novel atypical protein kinase C inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 3034–3038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Perspicace, E.; Jouan-Hureaux, V.; Ragno, R.; Ballante, F.; Sartini, S.; La Motta, C.; Da Settimo, F.; Chen, B.; Kirsch, G.; Schneider, S.; et al. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of new classes of thieno[3,2-d]pyrimidinone and thieno[1,2,3]triazine as inhibitor of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 (VEGFR-2). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 63, 765–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassab, A.E.; Gedawy, E.M. ChemInform Abstract: Synthesis and Anticancer Activity of Novel 2-Pyridyl Hexahydrocyclooctathieno[2,3-d]pyrimidine Derivatives. ChemInform 2013, 44, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kattan, S.W.; Nafie, M.S.; Elmgeed, G.A.; Alelwani, W.; Badar, M.; Tantawy, M.A. Molecular docking, anti-proliferative activity and induction of apoptosis in human liver cancer cells treated with androstane derivatives: Implication of PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. J. Steroid. Biochem. 2020, 198, 105604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipinski, C.A.; Lombardo, F.; Dominy, B.W.; Feeney, P.J. Experimental and computational approaches to estimate solubility and permeability in drug discovery and development settings. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 1997, 23, 3–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipinski, C. Lead- and drug-like compounds: The rule-of-five revolution. Drug Discov. Today Technol. 2004, 1, 337–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leeson, P.D.; Springthorpe, B. The influence of drug-like concepts on decision-making in medicinal chemistry. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2007, 6, 881–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, D.E.; Pickett, S.D. Computational methods for the prediction of ‘drug-likeness’. Drug Discov. Today 2000, 5, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghose, A.K.; Herbertz, T.; Hudkins, R.L.; Dorsey, B.D.; Mallamo, J.P. Knowledge-Based, Central Nervous System (CNS) Lead Selection and Lead Optimization for CNS Drug Discovery. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2011, 3, 50–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veber, D.F.; Johnson, S.R.; Cheng, H.-Y.; Smith, B.R.; Ward, K.W.; Kopple, K.D. Molecular Properties That Influence the Oral Bioavailability of Drug Candidates. J. Med. Chem. 2002, 45, 2615–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youssef, E.; El-Moneim, M.A.; Fathalla, W.; Nafie, M.S. Design, synthesis and antiproliferative activity of new amine, amino acid and dipeptide-coupled benzamides as potential sigma-1 receptor. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 2020, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosmann, T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: Application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J. Immunol. Methods 1983, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nafie, M.S.; Arafa, K.; Sedky, N.K.; Alakhdar, A.A.; Arafa, R.K. Triaryl dicationic DNA minor-groove binders with antioxidant activity display cytotoxicity and induce apoptosis in breast cancer. Interact Biol. Chem. 2020, 324, 109087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nafie, M.S.; Tantawy, M.A.; Elmgeed, G.A. Screening of different drug design tools to predict the mode of action of steroidal derivatives as anti-cancer agents. Steroids 2019, 152, 108485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, M.G.; Aziz, Y.M.A.; Elewa, M.; Elshihawy, H.A.; Said, M.M. Synthesis and molecular modeling of novel non-sulfonylureas as hypoglycemic agents and selective ALR2 inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2019, 27, 3383–3389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daina, A.; Michielin, O.; Zoete, V. SwissADME: A free web tool to evaluate pharmacokinetics, drug-likeness and medicinal chemistry friendliness of small molecules. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds 1–35 are available from the authors. |



| Entry | MCF-7 | HepG-2 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inhibition % | IC50 µg/mL | IC50 µM | Inhibition % | IC50 µg/mL | IC50 µM | |
| 2 | 27.12551 | ND | ND | 42.85714 | ND | ND |
| 3 | 46.93572 | ND | ND | 43.42105 | ND | ND |
| 4 | 80.625 | 7 | 23.2 | 78.63636 | 11.7 | 38.8 |
| 5 | 75.91912 | 19.3 | 52.9 | 76.41221 | 19.3 | 52.9 |
| 6 | 38.56502 | ND | ND | 45.17544 | ND | ND |
| 7 | 74.77941 | 48 | 131.3 | 73.58779 | 37 | 101.2 |
| 8 | 49.0284 | ND | ND | 52.41228 | ND | ND |
| 9 | 45.06726 | ND | ND | 81.79825 | 36.5 | 140.7 |
| 10 | 67.70833 | ND | ND | 78.18182 | 26.5 | 89.4 |
| 11 | 45.29148 | ND | ND | 72.98246 | 16.5 | 50.9 |
| 12 | 38.93871 | ND | ND | 73.07018 | 31 | 87.5 |
| 13 | 56.65172 | ND | ND | 66.22807 | 27.5 | 94.0 |
| 14 | 61.13602 | 43 | 154.5 | 69.34211 | 33.6 | 120.7 |
| 15 | 60.46338 | 22 | 53.2 | 73.24561 | 22 | 53.2 |
| 16 | 66.66667 | ND | ND | 77.09091 | 25 | 68.2 |
| 17 | 67.70833 | ND | ND | 79.09091 | 42 | 110.4 |
| 19 | 68.41912 | ND | ND | 77.17557 | 38.5 | 334.42 |
| 20 | 34.90284 | ND | ND | 34.21053 | ND | ND |
| 21 | 60.38864 | 28 | 127.1 | 69.73684 | 13.6 | 61.7 |
| 22 | 31.98381 | ND | ND | 30.61224 | ND | ND |
| 23 | 1.00005 | ND | ND | 3.508772 | ND | ND |
| 24 | 72.39583 | 13 | 40.3 | 78.63636 | 10 | 31.0 |
| 25 | 38.7145 | ND | ND | 29.82456 | ND | ND |
| 26 | 70.67708 | 16.4 | 71.2 | 77.27273 | 29 | 125.9 |
| 27 | 79.0625 | 21.7 | 76.3 | 77.72727 | 32.6 | 114.6 |
| 28 | 70.40359 | 15.5 | 59.1 | 47.36842 | ND | ND |
| 29 | 80.20833 | 11 | 49.9 | 76.36364 | 14.5 | 65.8 |
| 30 | 72.91667 | 7.4 | 31.6 | 78.72727 | 8.8 | 37.6 |
| 31 | 76.04167 | 9.8 | 33.2 | 80.45455 | 17 | 57.5 |
| 32 | 47.36842 | ND | ND | 51.83673 | ND | ND |
| 33 | 71.875 | 31.2 | 95.9 | 81.36364 | 40 | 122.9 |
| 34 | 57.8125 | ND | ND | 77.63636 | ND | ND |
| Protein (PDB Code) | Binding Affinity (Kcal/mol) | Type of Interaction | Bond Length (Aº) | Interaction Moiety Involved | Amino Acid |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3ZMM | –14.32 | H-acceptor | 1.97 | C=O | Leu 932 |
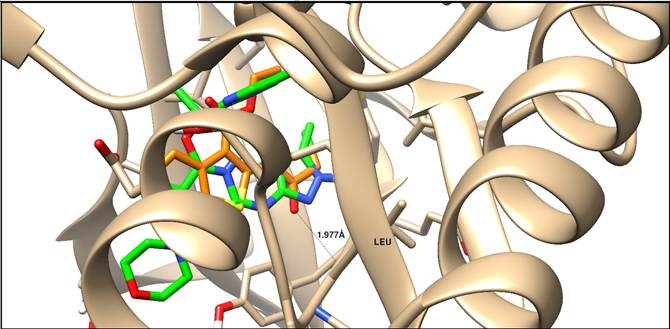 | |||||
| 4C62 | –13.39 | H-acceptor | 1.84 | C=O | Leu 932 |
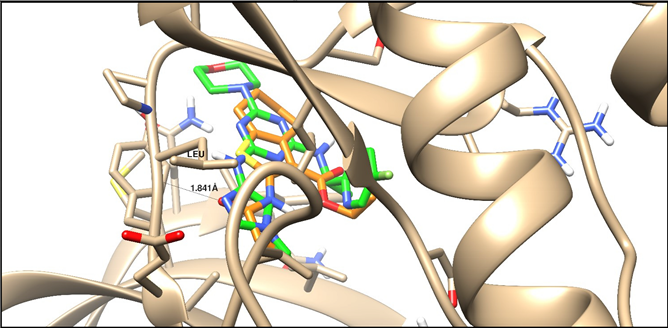 | |||||
| 5AEP | –11.38 | H-acceptor | 1.67 | C=O | Leu 932 |
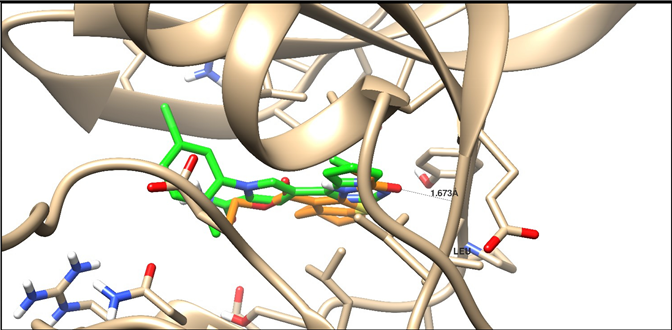 | |||||
| # | Molinspiration 2018.10 | MolSoft | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MWt (D) | MV (A3) | PSA (A2) | Log P | nrotb | nviolations | HBA | HBD | Solubility (mg/L) | Drug-Likeness Score | |
| 4 | 301.79 | 254.18 | 55.40 | 2.82 | 5 | 0 | 4 | 1 | 187.99 | 0.48 |
| 31 | 295.40 | 267.17 | 37.81 | 4.80 | 2 | 0 | 3 | 1 | 2.51 | 0.48 |
| 24 | 322.43 | 290.43 | 50.17 | 4.33 | 3 | 0 | 4 | 1 | 2.13 | 0.73 |
| 30 | 234.31 | 209.15 | 35.02 | 3.03 | 2 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 14.58 | 0.15 |
| Treatments | Positive Control | SEC Control | SEC + Comp 4 | SEC + 5-FU |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALT *# (I/U) | 43.53 ± 1.06 | 84.65 ± 2.1 | 64.28 ± 1.64 | 51.31 ± 1.41 |
| AST *# (I/U) | 45.75 ± 0.97 | 97.64 ± 1.75 | 59.89 ± 1.85 | 50.64 ± 0.97 |
| Hb *# (g/dL) | 7.9 ± 0.86 | 3.99 ± 0.21 | 5.99 ± 0.49 | 7.02 ± 0.83 |
| RBCs count *# (× 106/μL) | 5.14 ± 0.65 | 3.28 ± 0.73 | 4.43 ± 0.47 | 4.98 ± 021 |
| WBCs count *# (× 103/μL) | 3.69 ± 0.53 | 4.89 ± 0.49 | 4.21 ± 0.43 | 3.98 ± 0.32 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gad, E.M.; Nafie, M.S.; Eltamany, E.H.; Hammad, M.S.A.G.; Barakat, A.; Boraei, A.T.A. Discovery of New Apoptosis-Inducing Agents for Breast Cancer Based on Ethyl 2-Amino-4,5,6,7-Tetra Hydrobenzo[b]Thiophene-3-Carboxylate: Synthesis, In Vitro, and In Vivo Activity Evaluation. Molecules 2020, 25, 2523. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25112523
Gad EM, Nafie MS, Eltamany EH, Hammad MSAG, Barakat A, Boraei ATA. Discovery of New Apoptosis-Inducing Agents for Breast Cancer Based on Ethyl 2-Amino-4,5,6,7-Tetra Hydrobenzo[b]Thiophene-3-Carboxylate: Synthesis, In Vitro, and In Vivo Activity Evaluation. Molecules. 2020; 25(11):2523. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25112523
Chicago/Turabian StyleGad, Emad M., Mohamed S. Nafie, Elsayed H. Eltamany, Magdy S. A. G. Hammad, Assem Barakat, and Ahmed T. A. Boraei. 2020. "Discovery of New Apoptosis-Inducing Agents for Breast Cancer Based on Ethyl 2-Amino-4,5,6,7-Tetra Hydrobenzo[b]Thiophene-3-Carboxylate: Synthesis, In Vitro, and In Vivo Activity Evaluation" Molecules 25, no. 11: 2523. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25112523
APA StyleGad, E. M., Nafie, M. S., Eltamany, E. H., Hammad, M. S. A. G., Barakat, A., & Boraei, A. T. A. (2020). Discovery of New Apoptosis-Inducing Agents for Breast Cancer Based on Ethyl 2-Amino-4,5,6,7-Tetra Hydrobenzo[b]Thiophene-3-Carboxylate: Synthesis, In Vitro, and In Vivo Activity Evaluation. Molecules, 25(11), 2523. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25112523