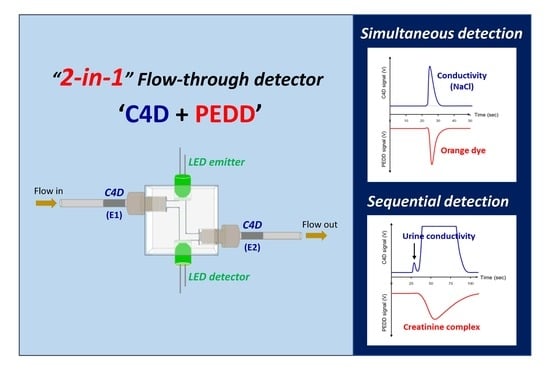
Dual-Purpose Photometric-Conductivity Detector for Simultaneous and Sequential Measurements in Flow Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
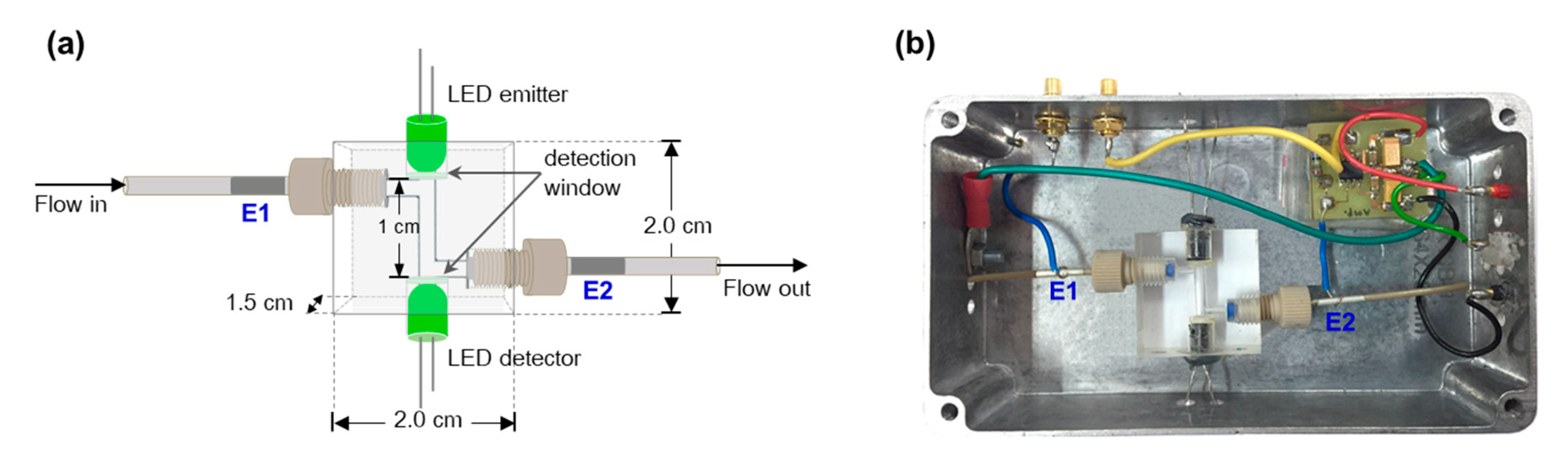
2.1. Design of the Detector
2.2. Optimization of Frequency and Voltage for the C4D
2.3. Quantification of Salts and Dye in ORS Samples
2.4. Determination of Creatinine and Measurement of Conductivity of Urine Samples
2.4.1. Zone Sequence and Signal Profiles
2.4.2. Analysis of Human Urine Samples
2.4.3. Analytical Features
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals, Reagents and Samples
3.1.1. Preparation of Standard Solutions and Oral Rehydration Salt Samples
3.1.2. Standard Solutions, Reagents and Samples for Urine Analysis
3.2. Flow Cell with Dual PEDD-C4D Detectors
3.3. Analysis by SIA with Dual-Detection Flow Cell
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Růžička, J.; Hansen, E.H. Flow injection analysis Part I. A new concept of fast continuous flow analysis. Anal. Chim. Acta 1975, 78, 145–157. [Google Scholar]
- Trojanowicz, M.; Kołacińska, K. Recent advances in flow injection analysis. Analyst 2016, 141, 2085–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruzicka, J.; Marshall, G.D. Sequential injection: A new concept for chemical sensors, process analysis and laboratory assays. Anal. Chim. Acta 1990, 237, 329–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Hansen, E.H. Sequential injection lab-on-valve: The third generation of flow injection analysis. Trends Anal. Chem. 2003, 22, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grudpan, K. Some recent developments on cost-effective flow-based analysis. Talanta 2004, 64, 1084–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itabashi, H.; Kawamoto, H.; Kawashima, T. A novel flow injection technique: All injection analysis. Anal. Sci. 2001, 17, 229–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teshima, N.; Noguchi, D.; Joichi, Y.; Lenghor, N.; Ohno, N.; Sakai, T.; Motomizu, S. Simultaneous injection-effective mixing analysis of palladium. Anal. Sci. 2010, 26, 143–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratanawimarnwong, N.; Ponhong, K.; Teshima, N.; Nacapricha, D.; Grudpan, K.; Sakai, T.; Motomizu, S. Simultaneous injection effective mixing flow analysis of urinary albumin using dye-binding reaction. Talanta 2012, 96, 50–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nacapricha, D.; Sastranurak, P.; Mantim, T.; Amornthammarong, N.; Uraisin, K.; Boonpanaid, C.; Chuyprasartwattana, C.; Wilairat, P. Cross injection analysis: Concept and operation for simultaneous injection of sample and reagents in flow analysis. Talanta 2013, 110, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choengchan, N.; Mantim, T.; Inpota, P.; Nacapricha, D.; Wilairat, P.; Jittangprasert, P.; Waiyawat, W.; Fucharoen, S.; Sirankpracha, P.; Phumala Morales, N. Tandem measurements of iron and creatinine by cross injection analysis with application to urine from thalassemic patients. Talanta 2015, 133, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, E.H.; Miró, M. How flow-injection analysis (FIA) over the past 25 years has changed our way of performing chemical analyses. Trends Anal. Chem. 2007, 26, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melchert, W.R.; Reis, B.F.; Rocha, F.R.P. Green chemistry and the evolution of flow analysis. A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 714, 8–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Worsfold, P.J.; Clough, R.; Lohan, M.C.; Monbet, P.; Ellis, P.S.; Quétel, C.R.; Floor, G.H.; McKelvie, I.D. Flow injection analysis as a tool for enhancing oceanographic nutrient measurements–A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 803, 15–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaftian, M.R.; Almeida, M.I.G.S.; Cattrall, R.W.; Kolev, S.D. Flow injection spectrophotometric determination of V(V) involving on-line separation using a poly(vinylidene fluoride-co-hexafluoropropylene)-based polymer inclusion membrane. Talanta 2018, 181, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Shu, H.; Yang, B.; Byrne, R.H.; Yuan, D. Spectrophotometric determination of pH and carbonate ion concentrations in seawater: Choices, constraints and consequences. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1081, 18–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sández, N.; Calvo-López, A.; Vidigal, S.S.M.P.; Rangel, A.O.S.S.; Alonso-Chamarro, J. Automated analytical microsystem for the spectrophotometric monitoring of titratable acidity in white, rosé and red wines. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1091, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalec, M.; Koncki, R.; Tymecki, Ł. Optoelectronic detectors for flow analysis systems manufactured by means of rapid prototyping technology. Talanta 2019, 198, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cecil, F.; Guijt, R.M.; Henderson, A.D.; Macka, M.; Breadmore, M.C. One step multi-material 3D printing for the fabrication of a photometric detector flow cell. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1097, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saetear, P.; Khamtau, K.; Ratanawimarnwong, N.; Sereenonchai, K.; Nacapricha, D. Sequential injection system for simultaneous determination of sucrose and phosphate in cola drinks using paired emitter-detector diode sensor. Talanta 2013, 115, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitanurak, J.; Inpota, P.; Mantim, T.; Ratanawimarnwong, N.; Wilairat, P.; Nacapricha, D. Simultaneous determination of iodide and creatinine in human urine by flow analysis with an on-line sample treatment column. Analyst 2015, 140, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaneam, S.; Kaewyai, K.; Mantim, T.; Chaisuksant, R.; Wilairat, P.; Nacapricha, D. Simultaneous and direct determination of urea and creatinine in human urine using a cost-effective flow injection system equipped with in house contactless conductivity detector and LED colorimeter. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1073, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bzura, J.; Fiedoruk-Pogrebniak, M.; Koncki, R. Photometric and fluorometric alkaline phosphatase assays using the simplest enzyme substrates. Talanta 2018, 190, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giakisikli, G.; Anthemidis, A.N. Automatic pressure-assisted dual-headspace gas-liquid microextraction. Lab-in-syringe platform for membraneless gas separation of ammonia coupled with fluorimetric sequential injection analysis. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1033, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inpota, P.; Strezelak, K.; Koncki, R.; Sripumkhai, W.; Jeamsaksri, W.; Ratanawimarnwong, N.; Wilairat, P.; Choengchan, N.; Chantiwas, R.; Nacapricha, D. Microfluidic analysis with front-face fluorometric detection for the determination of total inorganic iodine in drinking water. Anal. Sci. 2018, 34, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miró, M.; Estela, J.M.; Cerdà, V. Potentials of multisyringe flow injection analysis for chemiluminescence detection. Anal. Chim. Acta 2005, 541, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lara, F.J.; García-Campaña, A.M.; Aaron, J.-J. Analytical applications of photoinduced chemiluminescence in flow systems–A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2010, 679, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chailapakul, O.; Ngamukot, P.; Yoosamran, A.; Siangproh, W.; Wangfuengkanagul, N. Recent electrochemical and optical sensors in flow-based analysis. Sensors 2006, 6, 1383–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upan, J.; Reanpang, P.; Chailapakul, O.; Jakmunee, J. Flow injection amperometric sensor with a carbon nanotube modified screen printed electrode for determination of hydroquinone. Talanta 2016, 146, 766–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chailapakul, O.; Amatatongchai, M.; Wilairat, P.; Grudpan, K.; Nacapricha, D. Flow-injection determination of iodide ion in nuclear emergency tablets, using boron-doped diamond thin film electrode. Talanta 2004, 1253–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nontawong, N.; Amatatongchai, M.; Thimoonnee, S.; Laosing, S.; Jarujamrus, P.; Karuwan, C.; Chairam, S. Novel amperometric flow-injection analysis of creatinine using amolecularly-imprinted polymer coated copper oxidenanoparticle-modified carbon-paste-electrode. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2019, 175, 112770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danchana, K.; Clavijo, S.; Cerdà, V. Conductometric determination of sulfur dioxide in wine using a multipumping system coupled to a gas-diffusion cell. Anal. Lett. 2019, 52, 1363–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sereenonchai, K.; Teerasong, S.; Chan-Eam, S.; Saetear, P.; Choengchan, N.; Uraisin, K.; Amornthammarong, N.; Motomizu, S.; Nacapricha, D. A low-cost method for determination of calcium carbonate in cement by membraneless vaporization with capacitively coupled contactless conductivity detection. Talanta 2010, 81, 1040–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sereenonchai, K.; Saetear, P.; Amornthammarong, N.; Uraisin, K.; Wilairat, P.; Motomizu, S.; Nacapricha, D. Membraneless vaporization unit for direct analysis of solid sample. Anal. Chim. Acta 2007, 597, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaneam, S.; Inpota, P.; Saisarai, S.; Wilairat, P.; Ratanawimarnwong, N.; Uraisin, K.; Meesiri, W.; Nacapricha, D. Green analytical method for simultaneous determination of salinity, carbonate and ammoniacal nitrogen in waters using flow injection coupled dual-channel C4D. Talanta 2018, 189, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chantipmanee, N.; Alahmad, W.; Sonsa-ard, T.; Uraisin, K.; Ratanawimarnwong, N.; Mantim, T.; Nacapricha, D. Green analytical flow method for the determination of total sulfite in wine using membraneless gas-liquid separation with contactless conductivity detection. Anal. Methods 2017, 6107–6116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alahmad, W.; Pluangklang, T.; Mantim, T.; Cerdà, V.; Wilairat, P.; Ratanawimarnwong, N.; Nacapricha, D. Development of flow systems incorporating membraneless vaporization units and flow-through contactless conductivity detector for determination of dissolved ammonium and sulfide in canal water. Talanta 2018, 177, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraikaew, P.; Pluangklang, T.; Ratanawimarnwong, N.; Uraisin, K.; Wilairat, P.; Mantim, T.; Nacapricha, D. Simultaneous determination of ethanol and total sulfite in white wine using on-line cone reservoirs membraneless gas-liquid separation flow system. Microchem. J. 2019, 149, 104007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luque de Castro, M.D.; Valcàrcel Cases, M. Simultaneous determinations in flow injection analysis—A review. Analyst 1984, 109, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricci, A.; Teslic, N.; Petropolus, V.-I.; Parpinello, G.P.; Andrea, V. Fast analysis of total polyphenol content and antioxidant activity in wines and oenological tannins using a flow injection system with tandem diode array and electrochemical detections. Food Anal. Methods 2019, 12, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najib, F.M.; Othman, S. Simultaneous determination of Cl–, Br–, I– and F– with flow-injection/ion-selective electrode systems. Talanta 1992, 39, 1259–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, E.H.; Růžička, J.; Ghose, A.K. Flow injection analysis for calcium in serum, water and waste waters by spectrophotometry and by ion-selective electrode. Anal. Chim. Acta 1978, 100, 151–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mascini, M.; Palleshi, G. A flow-through detector for simultaneous determination of glucose and urea in serum samples. Anal. Chim. Acta 1983, 145, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsing, A.U.; Janata, J.; Růžička, J.; Levy, M. Miniaturization in analytical, chemistry—A combination of flow injection analysis and ion-sensitive field effect transistors for determination of pH, and potassium and calcium ions. Anal. Chim. Acta 1980, 118, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teerasong, S.; Chan-Eam, S.; Sereenonchai, K.; Amornthammarong, N.; Ratanawimarnwong, N.; Nacapricha, D. A reagent-free SIA module for monitoring of sugar, color and dissolved CO2 content in soft drinks. Anal. Chim. Acta 2010, 668, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tymecki, Ł.; Pokrzywnicka, M.; Koncki, R. Paired emitter detector diode (PEDD)-based photometry—An alternative approach. Analyst 2008, 133, 1501–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubáň, P.; Hauser, P.C. Contactless conductivity detection for analytical techniques—Developments from 2014 to 2016. Electrophoresis 2017, 38, 95–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubáň, P.; Hauser, P.C. Contactless conductivity detection for analytical techniques: Developments from 2016 to 2018. Electrophoresis 2019, 40, 124–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chvojka, T.; Jelínek, I.; Opekar, F.; Štulík, K. Dual photometric-contactless conductometric detector for capillary electrophoresis. Anal. Chim. Acta 2001, 433, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vochyánová, B.; Opekar, F.; Tůma, P. Simultaneous and rapid determination of caffeine and taurine in energy drinks by MEKC in a short capillary with dual contactless conductivity/photometry detection. Electrophoresis 2014, 35, 1660–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, F.; Yang, B.; Guan, Y. Simultaneous light emitting diode-induced fluorescence and contactless conductivity detection for capillary electrophoresis. Anal. Sci. 2005, 21, 583–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Shen, F.; Yu, Y.; Yang, M.; Kang, Q. Dual confocal laser-induced fluorescence/moveable contactless conductivity detector for capillary electrophoresis microchip. Microsyst. Technol. 2009, 15, 881–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Mo, Y.Y.; Chen, Z.G.; Li, X.; Li, O.L.; Zhou, X. Dual fluorescence/contactless conductivity detection for microfluidic chip. Anal. Chim. Acta 2008, 621, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryvolová, M.; Preisler, J.; Foret, F.; Hauser, P.C.; Krásenský, P.; Paull, B.; Macka, M. Combined contactless conductometric, photometric, and fluorimetric single point detector for capillary separation methods. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.L.; Li, W.L.; Zhang, J.B.; Tang, W.R.; Chen, X.F.; Cao, K.W.; Chu, Q.C.; Ye, J.N. Determination of unconjugated aromatic acids in urine by capillary electrophoresis with dual electrochemical detection—Potential application in fast diagnosis of phenylketonuria. Electrophoresis 2010, 31, 2989–2996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyaert, M.; Delanghe, J. Progress in Automated Urinalysis. Ann. Lab. Med. 2019, 39, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shirreffs, S.M.; Maughan, R.J. Urine osmolality and conductivity as indices of hydration status in athletes in the heat. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 1998, 30, 1598–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Luisa, F.; Abdala, S.; Dévora, S.; Benjumea, D.; Martín-Herrera, D. Electrical conductivity measurements of urine as a new simplified method to evaluate the diuretic activity of medicinal plants. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 151, 1019–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantim, T.; Saetear, P.; Teerasong, S.; Chan-Eam, S.; Sereenonchai, K.; Amornthammarong, N.; Ratanawimarnwong, N.; Wilairat, P.; Meesiri, W.; Uraisin, K.; et al. Reagent-free analytical flow methods for the soft drink industry: Efforts for environmentally friendly chemical analysis. Pure Appl. Chem. 2012, 84, 2015–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, A.C.B.; Borges, E.P.; Zagatto, E.A.G.; Worsfold, P.J. A critical examination of the components of the Schlieren effect in flow analysis. Talanta 2006, 68, 1076–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruzicka, J.; Hansen, E.H. Flow Injection Analysis, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1988; p. 27. [Google Scholar]
- Bonsnes, R.W.; Taussky, H.H. On the colorimetric determination of creatinine by the Jaffe reaction. J. Biol. Chem. 1945, 158, 581–591. [Google Scholar]
- Sakai, T.; Ohta, H.; Ohno, N.; Imai, J. Routine assay of creatinine in newborn baby urine by spectrophotometric flow-injection analysis. Anal. Chim. Acta 1995, 308, 446–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohira, S.-I.; Kirk, A.B.; Dasgupta, P.K. Automated measurement of urinary creatinine by multichannel kinetic spectrophotometry. Anal. Biochem. 2009, 384, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siangproh, W.; Teshima, N.; Sakai, T.; Katoh, S.; Chailapakul, O. Alternative method for measurement of albumin/creatinine ratio using spectrophotometric sequential injection analysis. Talanta 2009, 79, 1111–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kouri, T.T.; Kähkönen, U.; Malminiemi, K.; Vuento, R.; Rowan, R.M. Evaluation of sysmex UF-100 urine flow cytometer vs chamber counting of supravitally stained specimens and conventional bacterial cultures. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 1999, 112, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delanghe, J.R.; Kouri, T.T.; Huber, A.R.; Hannemann-Pohl, K.; Guder, W.G.; Lun, A.; Sinha, P.; Stamminger, G.; Beier, L. The role of automated urine particle flow cytometry in clinical practice. Clin. Chim. Acta 2000, 301, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanyanyiwa, J.; Galliker, B.; Schwarz, M.A.; Hauser, P. Improved capacitively coupled conductivity detector for capillary electrophoresis. Analyst 2002, 127, 214–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |




| Sample | Conductivity (mS cm−1) | Creatinine (mg L−1) * | |
|---|---|---|---|
| C4D Detector (n = 3) | PEDD Detector (n = 3) | Spectrophometer (n = 3) | |
| S1 | 19.18 ± 0.03 | (1.06 ± 0.02) × 103 | (1.08 ± 0.01) × 103 |
| S2 | 27.10 ± 0.12 | (1.40 ± 0.02) × 103 | (1.41 ± 0.03) × 103 |
| S3 | 26.57 ± 0.05 | (1.54 ± 0.01) × 103 | (1.56 ± 0.02) × 103 |
| S4 | 31.60 ± 0.01 | (1.17 ± 0.02) × 103 | (1.14 ± 0.02) × 103 |
| S5 | 12.42 ± 0.02 | (7.36 ± 0.05) × 102 | (7.13 ± 0.07) × 102 |
| S6 | 10.07 ± 0.02 | (5.60 ± 0.05) × 102 | (5.06 ± 0.05) × 102 |
| S7 | 4.99 ± 0.02 | (1.52 ± 0.04) × 102 | (1.22 ± 0.01) × 102 |
| S8 | 11.96 ± 0.06 | (4.39 ± 0.06) × 102 | (4.09 ± 0.06) × 102 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mantim, T.; Chaisiwamongkhol, K.; Uraisin, K.; Hauser, P.C.; Wilairat, P.; Nacapricha, D. Dual-Purpose Photometric-Conductivity Detector for Simultaneous and Sequential Measurements in Flow Analysis. Molecules 2020, 25, 2284. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25102284
Mantim T, Chaisiwamongkhol K, Uraisin K, Hauser PC, Wilairat P, Nacapricha D. Dual-Purpose Photometric-Conductivity Detector for Simultaneous and Sequential Measurements in Flow Analysis. Molecules. 2020; 25(10):2284. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25102284
Chicago/Turabian StyleMantim, Thitirat, Korbua Chaisiwamongkhol, Kanchana Uraisin, Peter C. Hauser, Prapin Wilairat, and Duangjai Nacapricha. 2020. "Dual-Purpose Photometric-Conductivity Detector for Simultaneous and Sequential Measurements in Flow Analysis" Molecules 25, no. 10: 2284. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25102284
APA StyleMantim, T., Chaisiwamongkhol, K., Uraisin, K., Hauser, P. C., Wilairat, P., & Nacapricha, D. (2020). Dual-Purpose Photometric-Conductivity Detector for Simultaneous and Sequential Measurements in Flow Analysis. Molecules, 25(10), 2284. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25102284