Renoprotective Effect of Laminaria japonica Polysaccharide in Adenine-Induced Chronic Renal Failure
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
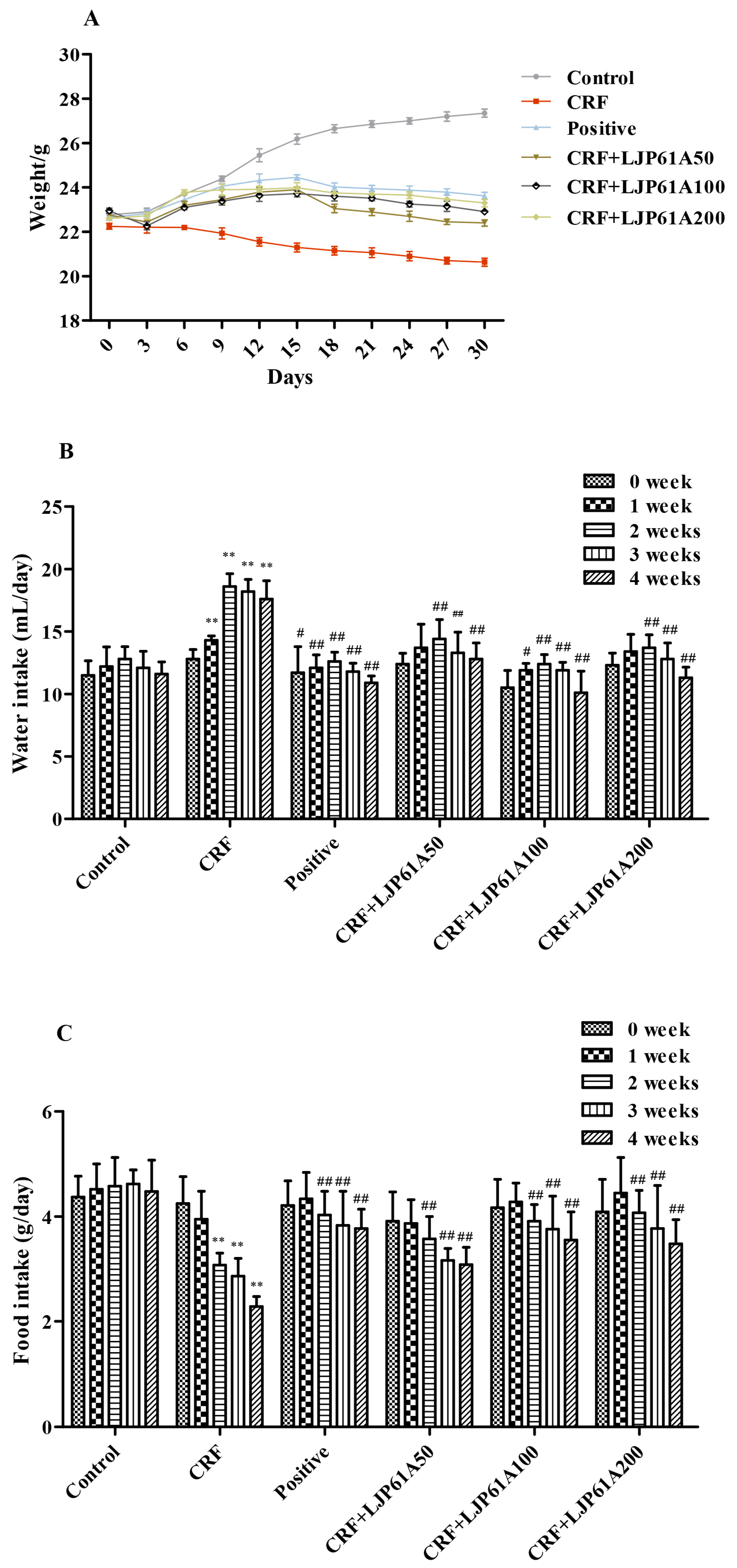
2.1. LJP61A Regulates Body Weight, Water and Food Intake of CRF Mice
2.2. LJP61A Ameliorates Kidney Injury of CRF Mice
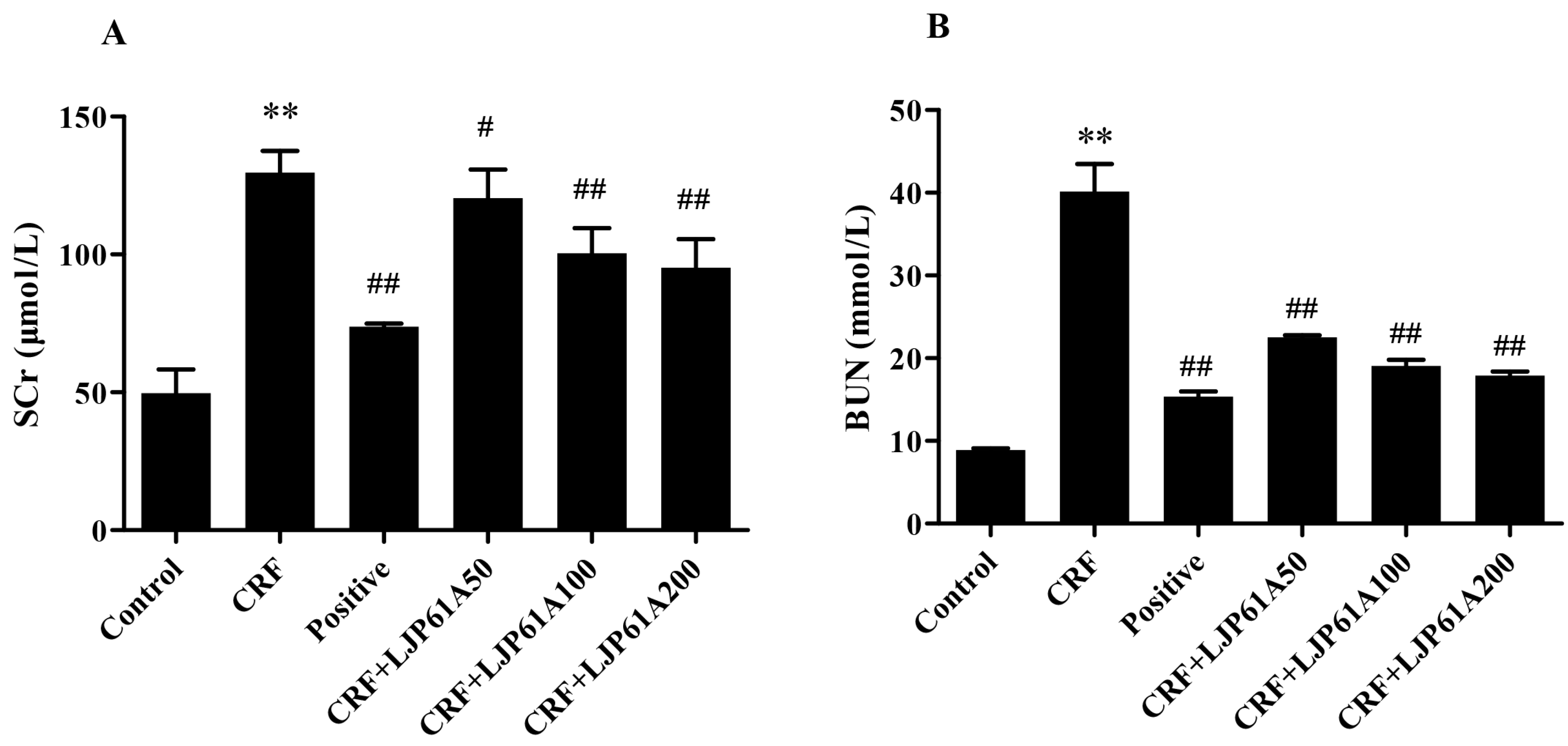
2.3. LJP61A Regulates the Blood Biochemical Index of CRF Mice
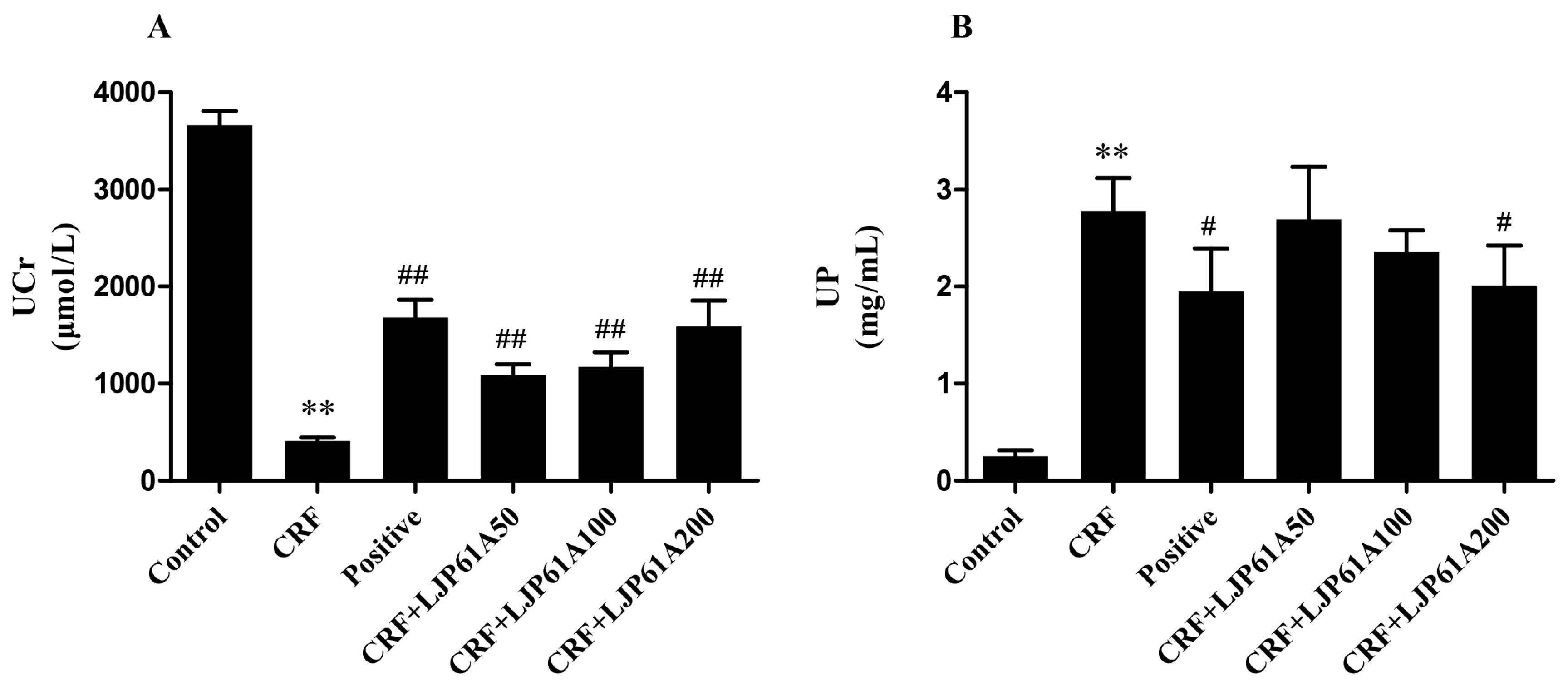
2.4. LJP61A Regulates the Urine Biochemical Index of CRF Mice
2.5. LJP61A Regulates the Electrolyte Disturbance of CRF Mice
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals
4.2. Animals
4.3. Experimental Procedure
4.4. Water and Food Intake
4.5. Kidney Pathological Examination
4.6. Serum Parameters
4.7. Urine Parameters
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zaki, M.R.; Ghazanfar, A.; Hussain, S.; Khan, F.A. Presentations, etiology and outcome of patients with Chronic Renal Failure admitted at Urology Department, Mayo Hospital Lahore-A retrospective analysis of 1257 patients over a period of 10 years. Ann. King Edw. Med. Univ. 2003, 9, 58–61. [Google Scholar]
- Khoury, T.; Tzukert, K.; Abel, R.; Rmeileh, A.A.; Levi, R.; Ilan, Y. The gut-kidney axis in chronic renal failure: A new potential target for therapy. Hemodial. Int. 2017, 21, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilbertson, D.T.; Liu, J.; Xue, J.L.; Louis, T.A.; Solid, C.A.; Ebben, J.P.; Collins, A.J. Projecting the number of patients with end-stage renal disease in the United States to the year 2015. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2005, 16, 3736–3741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.H. Nephrology in China. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2013, 9, 523–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eirin, A.; Lerman, L.O. Mesenchymal stem cell treatment for chronic renal failure. Stem. Cell. Res. Ther. 2014, 5, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toriihara, A.; Kitazume, Y.; Nishida, H.; Kubota, K.; Nakadate, M.; Tateishi, U. Comparison of FDG-PET/CT images between chronic renal failure patients on hemodialysis and controls. Am. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2015, 5, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Z. Antioxidant activity of sulfated polysaccharide fractions extracted from Laminaria japonica. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2008, 42, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patra, J.K.; Das, G.; Baek, K.H. Chemical Composition and Antioxidant and Antibacterial Activities of an Essential Oil Extracted from an Edible Seaweed, Laminaria japonica L. Molecules 2015, 20, 12093–12113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, C.; Zhou, S.; Zhu, L.; Ming, J.; Zeng, F.; Xu, R. Antitumor Effects of Laminaria Extract Fucoxanthin on Lung Cancer. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Liu, H.; Luo, P.; Li, Y. Production Inhibition and Excretion Promotion of Urate by Fucoidan from Laminaria japonica in Adenine-Induced Hyperuricemic Mice. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, X.Q.; Xiao, J.J.; Zhang, H.N.; Wang, J.H.; Pan, L.H.; Yang, X.F.; Luo, J.P. Polysaccharides in Laminaria japonica (LP): Extraction, physicochemical properties and their hypolipidemic activities in diet-induced mouse model of atherosclerosis. Food Chem. 2012, 134, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.H.; Kim, Y.W.; Kim, H.B.; Lee, B.J.; Lee, D.S. Anti-apoptotic activity of laminarin polysaccharides and their enzymatically hydrolyzed oligosaccharides from Laminaria japonica. Biotechnol. Lett. 2006, 28, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, X.Q.; Xue, L.; Zhang, H.L.; Asghar, M.N.; Pan, L.H.; Liu, J.; Luo, J.P. Molecular mechanism of a new Laminaria japonica polysaccharide on the suppression of macrophage foam cell formation via regulating cellular lipid metabolism and suppressing cellular inflammation. Mol. Nutr. Food. Res. 2015, 59, 2008–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zha, X.Q.; Zhang, W.N.; Peng, F.H.; Xue, L.; Liu, J.; Luo, J.P. Alleviating VLDL overproduction is an important mechanism for Laminaria japonica polysaccharide to inhibit atherosclerosis in LDLr−/− mice with diet-induced insulin resistance. Mol. Nutr. Food. Res. 2017, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Y.; Li, Q.M.; Fang, Q.; Zha, X.Q.; Pan, L.H.; Luo, J.P. Laminaria japonica polysaccharide inhibits vascular calcification via preventing osteoblastic differentiation of vascular smooth muscle cells. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2018, 66, 1821–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.J.; Wu, V.; Wu, P.C.; Wu, C.J. Meta-analysis of the associations of p-cresyl sulfate (PCS) and indoxyl sulfate (IS) with cardiovascular events and all-cause mortality in patients with chronic renal failure. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0132589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neven, E.; D’haese, P.C. Vascular calcification in chronic renal failure: What have we learned from animal studies? Circ. Res. 2011, 108, 249–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diwan, V.; Mistry, A.; Gobe, G.; Brown, L. Adenine-induced chronic kidney and cardiovascular damage in rats. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods 2013, 68, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guevara, M.; Ginès, P.; Bandi, J.C.; Gilabert, R.; Sort, P.; Jiménez, W.; Garcia-Pagan, J.C.; Bosch, J.; Arroyo, V.; Rodés, J. Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt in hepatorenal syndrome: Effects on renal function and vasoactive systems. Hepatology 1998, 28, 416–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrone, R.D.; Madias, N.E.; Levey, A.S. Serum creatinine as an index of renal function: New insights into old concepts. Clin. Chem. 1992, 38, 1933–1953. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ruggenenti, P.; Gaspari, F.; Perna, A.; Remuzzi, G. Cross sectional longitudinal study of spot morning urine protein: Creatinine ratio, 24 h urine protein excretion rate, glomerular filtration rate, and end stage renal failure in chronic renal disease in patients without diabetes. BMJ 1998, 316, 504–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosohata, K. Role of Oxidative Stress in Drug-Induced Kidney Injury. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bockenhauer, D.; Zieg, J. Electrolyte disorders. Clin. Perinatol. 2014, 41, 575–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, M.; Methven, S.; Gasparini, A.; Barany, P.; Birnie, K.; MacNeill, S.; May, M.T.; Caskey, F.J.; Carrero, J.-J. Cinacalcet use and the risk of cardiovascular events, fractures and mortality in chronic kidney disease patients with secondary hyperparathyroidism. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekercioglu, N.; Busse, J.W.; Sekercioglu, M.F.; Agarwal, A.; Shaikh, S.; Lopes, L.C.; Mustafa, R.A.; Guyatt, G.H.; Thabane, L. Cinacalcet versus standard treatment for chronic kidney disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ren. Fail. 2016, 38, 857–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Wang, F.; Yun, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Q. Effect and mechanism of fucoidan derivatives from Laminaria japonica in experimental adenine-induced chronic kidney disease. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2012, 139, 807–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claramunt, D.; Gil-Peña, H.; Fuente, R.; García-López, E.; Loredo, V.; Hernández-Frías, O.; Ordoñez, F.A.; Rodríguez-Suárez, J.; Santos, F. Chronic kidney disease induced by adenine: A suitable model of growth retardation in uremia. Am. J. Physiol Renal Physiol. 2015, 309, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moradi, H.; Yuan, J.; Ni, Z.; Norris, K.; Vaziri, N.D. Reverse cholesterol transport pathway in experimental chronic renal failure. Am. J. Nephrol. 2009, 30, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eom, M.; Hudkins, K.L.; Alpers, C.E. Foam cells and the pathogenesis of kidney disease. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2015, 24, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagano, N.; Miyata, S.; Abe, M.; Kobayashi, N.; Wakita, S.; Yamashita, T.; Wada, M. Effect of manipulating serum phosphorus with phosphate binder on circulating PTH and FGF23 in renal failure rats. Kidney Int. 2006, 69, 531–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lezaic, V.; Tirmenstajn-Jankovic, B.; Bukvic, D.; Vujisic, B.; Perovic, M.; Novakovic, N.; Dopsaj, V.; Maric, I.; Djukanovic, L. Efficacy of hyperphosphatemia control in the progression of chronic renal failure and the prevalence of cardiovascular calcification. Clin. Nephrol. 2009, 71, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Zhang, S.; Ren, L.; Zhang, H.; Bai, X. Nephroprotective effects of Isaria felina in rats with adenine-induced chronic renal failure. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2013, 65, 1409–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, H.; Su, S.; Li, Y.; Zeng, H.; Zhu, Z.; Guo, J.; Zhu, Y.; Guo, S.; Yu, L.; Qian, D.; et al. Protective effects of Salvia miltiorrhiza on adenine-induced chronic renal failure by regulating the metabolic profiling and modulating the NADPH oxidase/ROS/ERK and TGF-β/Smad signaling pathways. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2018, 212, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are available from the authors. |


| Group | Serumk Calcium (mmol/L) | Serum Chlorine (mmol/L) | Serum Potassium (mmol/L) | Serum Magnesium (mmol/L) | Serum Sodium (mmol/L) | Serum Phosphorus (mmol/L) | Urine Calcium (mmol/L) | Urine Phosphorus (mmol/L) | Urine Magnesium (mmol/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 3.27 ± 0.12 | 85.29 ± 0.26 | 9.10 ± 0.21 | 1.88 ± 0.01 | 146.97 ± 0.39 | 3.52 ± 0.16 | 2.84 ± 0.68 | 14.37 ± 2.8 | 4.01 ± 0.52 |
| CRF | 2.55 ± 0.05 ** | 105.97 ± 0.52 ** | 11.83 ± 0.12 ** | 2.43 ± 0.07 ** | 162.07 ± 1.76 ** | 5.82 ± 0.11 ** | 1.69 ± 0.30 * | 8.75 ± 1.6 * | 2.67 ± 1.78 * |
| Positive | 3.13 ± 0.10 ▲▲ | 101.69 ± 0.61 | 9.60 ± 0.47 ▲▲ | 2.18 ± 0.04 ▲▲ | 148.15 ± 0.85 | 3.93 ± 0.25 ▲▲ | 2.56 ± 0.22 ▲▲ | 10.30 ± 3.5 ▲▲ | 3.10 ± 1.25 ▲▲ |
| CRF+LJP61A50 | 2.56 ± 0.11 | 105.30 ± 0.27 | 10.43 ± 0.42 ▲▲ | 2.11 ± 0.12 ▲▲ | 158.73 ± 1.66 | 5.22 ± 0.12 ▲▲ | 1.91 ± 0.12 ▲ | 10.26 ± 2.1 ▲▲ | 2.89 ± 2.01 ▲▲ |
| CRF+LJP61A100 | 2.78 ± 0.11 ▲▲ | 104.13 ± 0.66 | 10.07 ± 0.50 ▲▲ | 1.97 ± 0.07 ▲▲ | 152.66 ± 0.22 | 4.79 ± 0.13 ▲▲ | 1.89 ± 0.45 ▲ | 11.35 ± 1.9 ▲▲ | 2.92 ± 1.34 ▲▲ |
| CRF+LJP61A200 | 2.98 ± 0.12 ▲▲ | 102.00 ± 0.90 | 9.97 ± 0.22 ▲▲ | 1.89 ± 0.06 ▲▲ | 150.73 ± 0.55 | 3.72 ± 0.22 ▲▲ | 2.49 ± 0.27 ▲▲ | 11.84 ± 3.0 ▲▲ | 3.05 ± 2.70 ▲▲ |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Long, M.; Li, Q.-M.; Fang, Q.; Pan, L.-H.; Zha, X.-Q.; Luo, J.-P. Renoprotective Effect of Laminaria japonica Polysaccharide in Adenine-Induced Chronic Renal Failure. Molecules 2019, 24, 1491. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24081491
Long M, Li Q-M, Fang Q, Pan L-H, Zha X-Q, Luo J-P. Renoprotective Effect of Laminaria japonica Polysaccharide in Adenine-Induced Chronic Renal Failure. Molecules. 2019; 24(8):1491. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24081491
Chicago/Turabian StyleLong, Miao, Qiang-Ming Li, Qing Fang, Li-Hua Pan, Xue-Qiang Zha, and Jian-Ping Luo. 2019. "Renoprotective Effect of Laminaria japonica Polysaccharide in Adenine-Induced Chronic Renal Failure" Molecules 24, no. 8: 1491. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24081491
APA StyleLong, M., Li, Q.-M., Fang, Q., Pan, L.-H., Zha, X.-Q., & Luo, J.-P. (2019). Renoprotective Effect of Laminaria japonica Polysaccharide in Adenine-Induced Chronic Renal Failure. Molecules, 24(8), 1491. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24081491




