Investigation of Lactones as Innovative Bio-Sourced Phase Change Materials for Latent Heat Storage
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
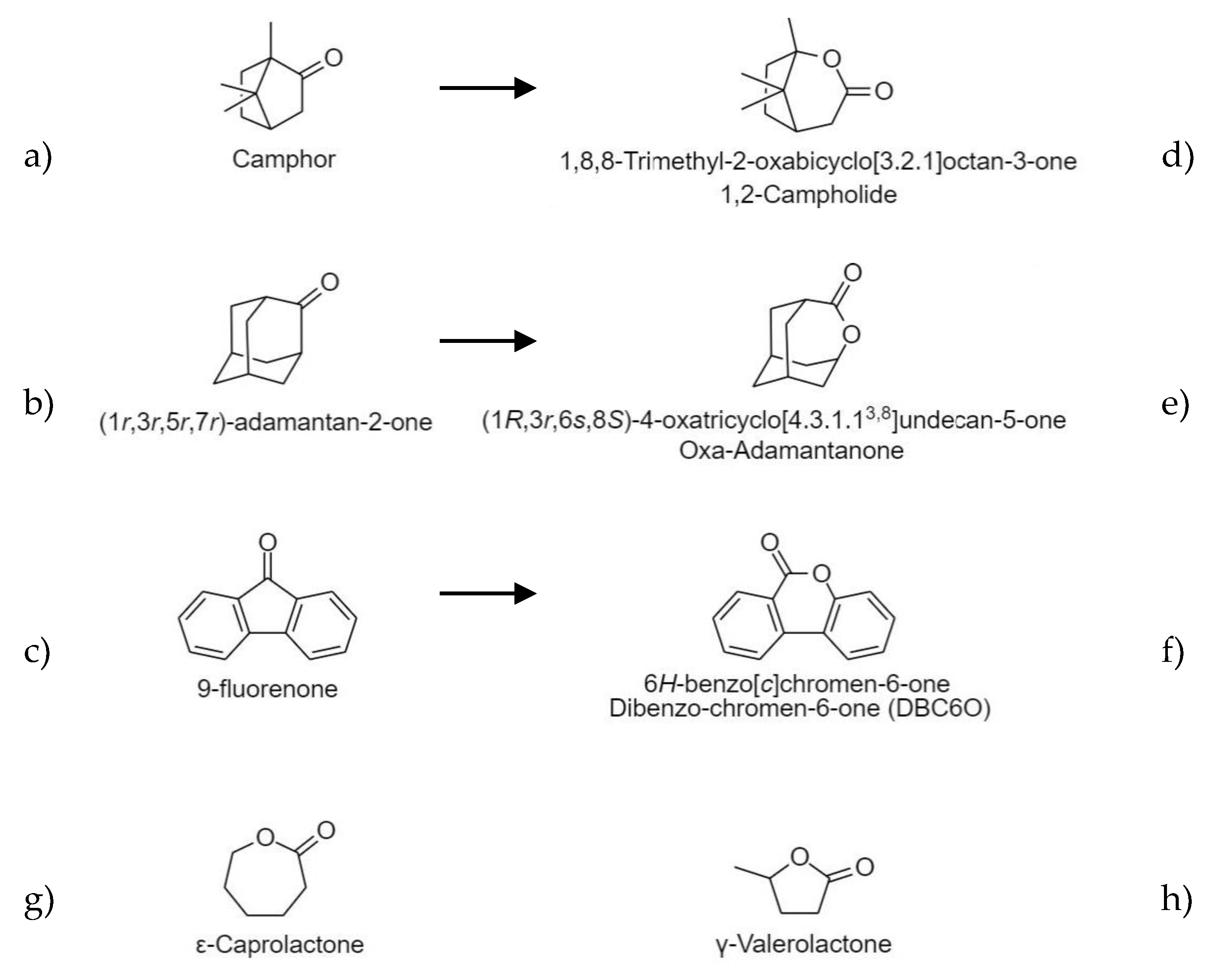
2.1. Structural Characterization of Lactones
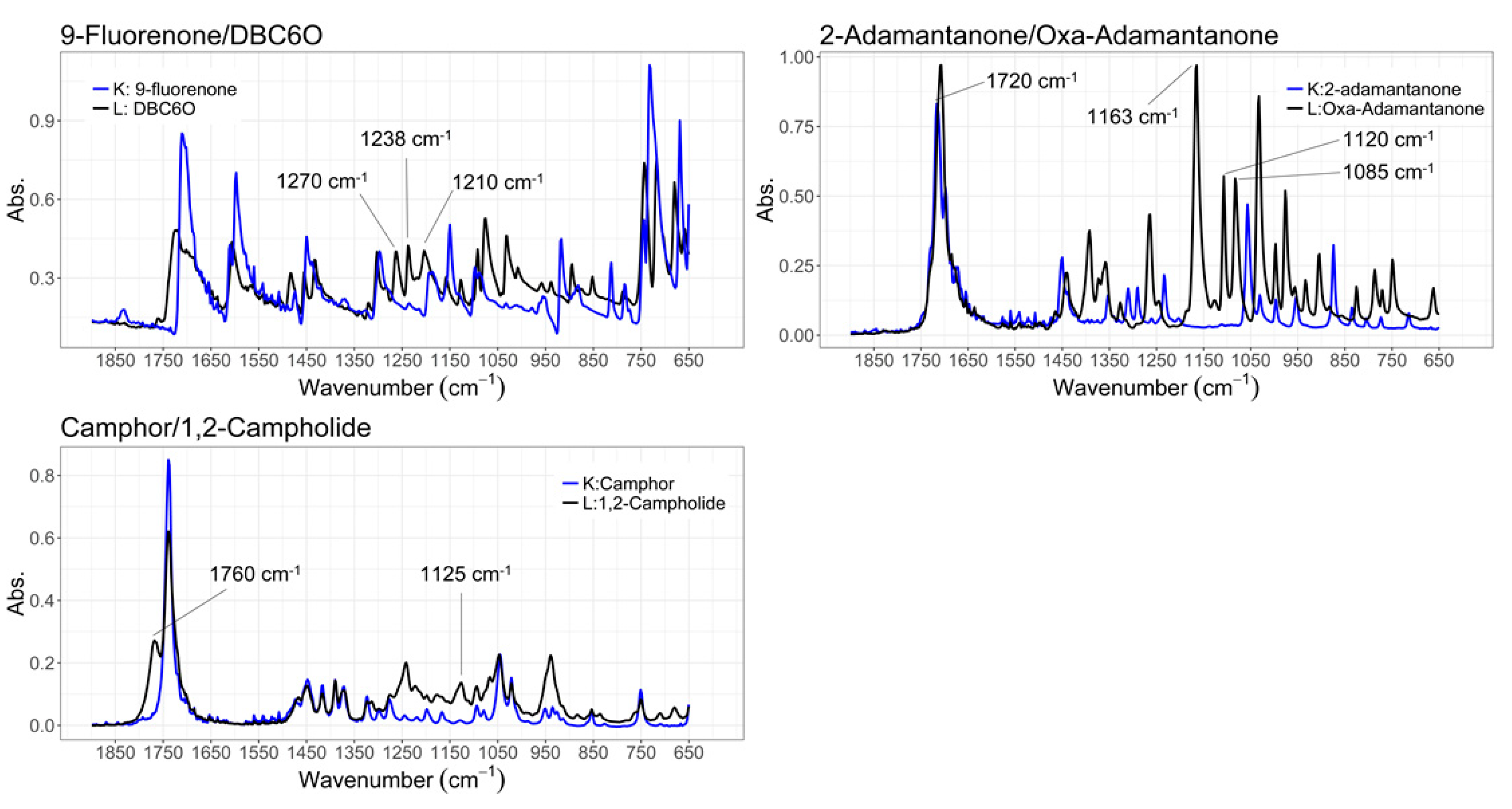
2.1.1. ATR-IR
2.1.2. GC-MS
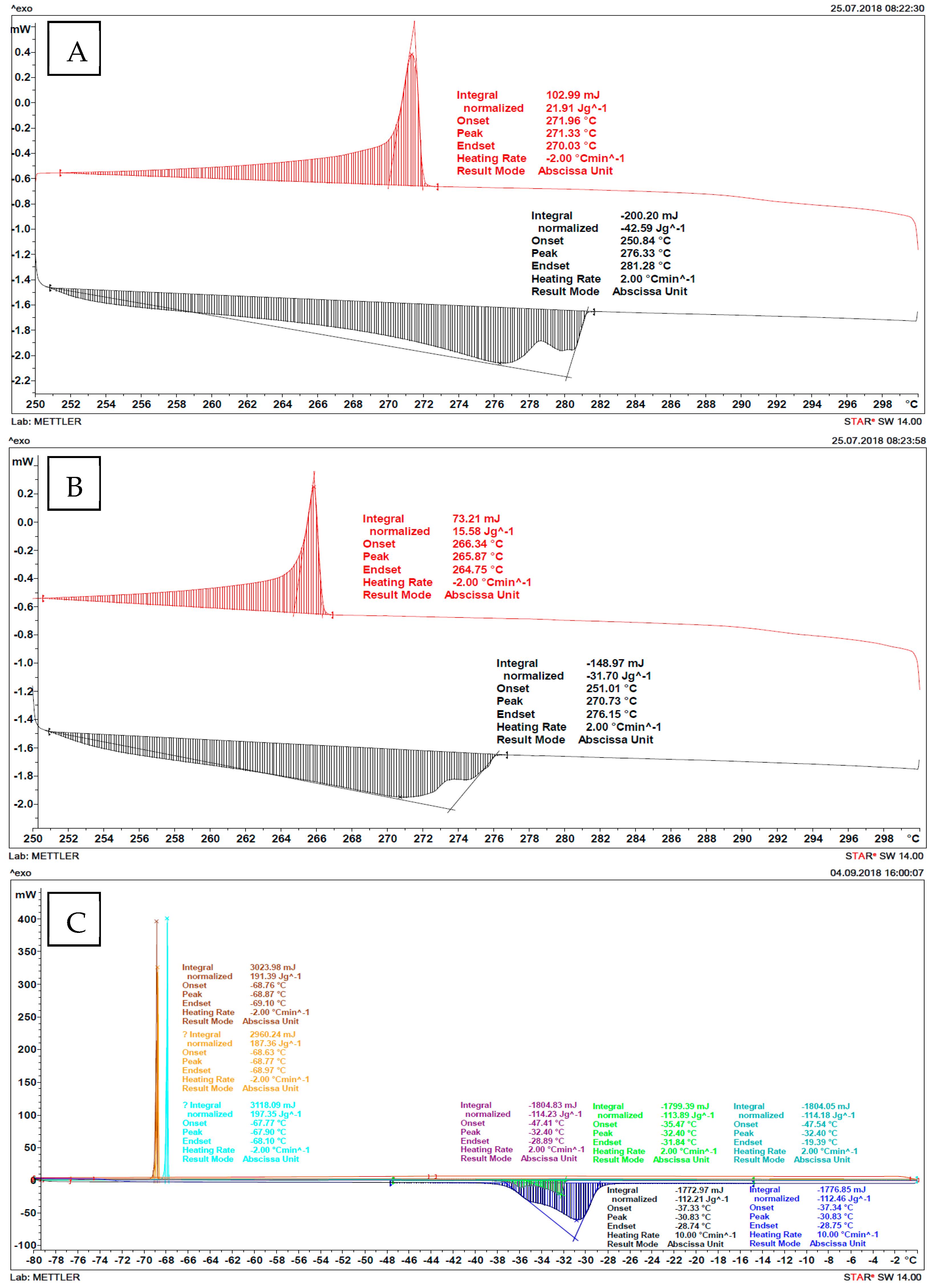
2.2. Analysis of Thermal Properties
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
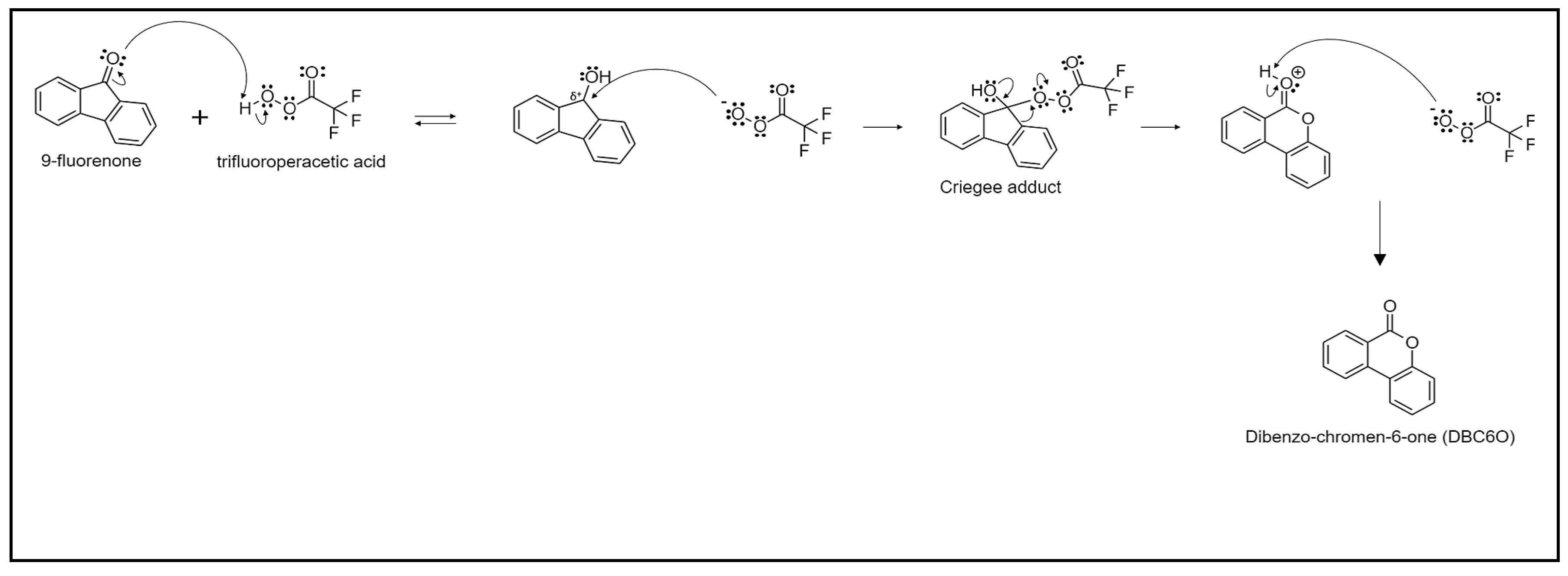
4.2. Synthesis of Lactones
4.3. Analytical Instruments and Methods
4.3.1. Attenuated Total Reflectance Infrared Spectroscopy (ATR-IR)
4.3.2. Gas Chromatography coupled with Mass Spectroscopy (GC-MS)
4.3.3. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
4.3.4. Thermal Gravimetric Analysis (TGA)
5. Conclusions and Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
List of Abbreviations
| ATR-IR | Attenuated Total Reflectance InfraRed Spectroscopy |
| DBC6O | Dibenzo-chromen-6-one |
| DSC | Differential Scanning Calorimetry |
| Et2O | Diethyl Ether |
| GC-MS | Gas-Chromatography coupled with Mass Spectrometry |
| H2O2 | Hydrogen Peroxide |
| LHS | Latent Heat Storage |
| Na2CO3 | Sodium Carbonate |
| Na2SO4 | Sodium sulfate |
| NIST | National Institute of Standards and Technology |
| PCL | Polycaprolactone |
| PCM | Phase Change Material |
| PFTBA | Perfluoroterbutylamine |
| SNSF | Swiss National Science Foundation |
| Tc | Crystallization Temperature |
| Tm | Melting Temperature |
| TFA | Trifluoroacetic acid |
| TFPAA | Trifluoroperoxyacetic acid |
| TGA | Thermogravimetric Analysis |
| ΔH | Enthalpy of fusion |
Appendix A
References
- International Energy Agency (IEA). Key World Energy Statistics 2017. Available online: https://www.iea.org/publications/freepublications/publication/KeyWorld2017.pdf (accessed on 15 August 2018).
- International Energy Agency Energy Conservation through Energy Saving (IEA-ECES) Programme, Annual Report 2017. Available online: https://www.irena.org/DocumentDownloads/Publications/IRENA-ETSAP%20Tech%20Brief%20E17%20Thermal%20Energy%20Storage.pdf (accessed on 15 August 2018).
- International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA). Thermal Energy Storage, Technology Brief E17 January 2013. Available online: https://www.irena.org/DocumentDownloads/Publications/IRENA-ETSAP%20Tech%20Brief%20E17%20Thermal%20Energy%20Storage.pdf (accessed on 20 August 2018).
- International Energy Agency (IEA). Technology Roadmap. Energy-efficient Buildings: Heating and Cooling Equipment. Available online: https://www.iea.org/publications/freepublications/publication/buildings_roadmap.pdf (accessed on 20 August 2018).
- Mehling, H.; Cabeza, L.F. Heat and Cold Storage with PCM. An up to Date Introduction into Basics and Applications; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2008; ISBN 978-3-540-68556-2. [Google Scholar]
- Pielichowska, K.; Pielichowski, K. Phase change materials for thermal energy storage. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2014, 65, 67–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nkwetta, D.N.; Haghighat, F. Thermal energy storage with phase change material—A state-of-the-art review. Sust. Cities Soc. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Jeong, S.-G.; Chung, O.; Kim, S. Bio-based PCM/carbon nanomaterials composites with enhanced thermal conductivity. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2014, 120 (Pt B), 549–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravotti, R.; Fellmann, O.; Lardon, N.; Fischer, L.J.; Stamatiou, A.; Wortlischek, J. Synthesis and Investigation of Thermal Properties of Highly Pure Carboxylic Fatty Esters to Be Used as PCM. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravotti, R.; Fellmann, O.; Lardon, N.; Fischer, L.J.; Stamatiou, A.; Wortlischek, J. Analysis of Bio-Based Fatty Esters PCM’s Thermal Properties and Investigation of Trends in Relation to Chemical Structures. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamatiou, A.; Obermeyer, M.; Fischer, L.J.; Schuetz, P.; Wortlischek, J. Investigation of unbranched, saturated, Carboxylic Esters as phase change materials. Renew. Energy 2017, 108, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sari, A.; Karaipekli, A.; Kaygusuz, K. Capric acid and Stearic Acid mixture impregnated with gypsum wallboard for low-temperature latent heat thermal energy storage. Int. J. Energy Res. 2008, 32, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PCM Products official website www.pcmproducts.net. Global PCM based Building Services Application Examples. Available online: http://www.pcmproducts.net/files/PCM%20Global%20Application%20Examples.pdf (accessed on 10 September 2018).
- Li, G.; Hwang, Y.; Radermacher, R.; Chun, H.H. Review of cold storage materials for subzero applications. Energy 2013, 51, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gin, B.; Farid, M.M.; Bansal, P.K. Effect of door opening and defrost cycle on a freezer with phase change panels. Energy Convers. Manag. 2010, 51, 2698–2706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, K.; Calautit, J.; Wang, Z.; Wu, Y.; Liu, H. A review of the applications of phase change materials in cooling, heating and power generation in different temperature ranges. Appl. Energy 2018, 220, 242–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abhat, A. Low Temperature Latent Heat Thermal Energy Storage: Heat Storage Materials. Sol. Energy 1983, 30, 313–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baeyer, A.; Villiger, V. Einwirkung des Caro’schen Reagens auf Ketone. Ber. Dtsch. Chem. Ges. 1899, 32, 3625–3633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, R.G. Flavours and Fragrances Chemistry, Bioprocessing and Sustainability; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2007; ISBN 978-3-540-49339-6. [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez, A.R.; Contreras, O.C.; Acevedo, J.C.; Moreno, L.G.N. Poly(ε-Caprolactone) Degradation Under Acidic and Alkaline Conditions. Am. J. Polym. Sci. 2013, 3, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Project “Key Issues for Renewable Heat in Europe” (K4RES-H), EIE/04/204/S07.38607. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/energy/intelligent/projects/sites/iee-projects/files/projects/documents/k4res-h_applications_of_renewable_heating_and_cooling.pdf (accessed on 20 August 2018).
- U.S. Energy Information Administration | International Energy Outlook 2016. Available online: https://www.eia.gov/outlooks/ieo/pdf/0484(2016).pdf (accessed on 6 August 2018).
- Olah, A.G.; Wang, Q.; Trivedi, N.J.; Prakash, S. Baeyer-Villiger Oxidation of Ketones to Esters with Sodium Percarbonate/Trifluoroacetic Acid. Synthesis 1991, 9, 739–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.; Dudley, E.; Song, Q.; Plummer, S.; Tang, J.; Newton, R.P.; Brenton, A.G. Mass Spectrometry analysis of terpene lactones in Ginkgo Biloba. Rapid. Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2008, 22, 766–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kjonaas, R.A.; Clemons, A.E. The Baeyer-Villiger oxidation with trifluoroacetic acid and household sodium percarbonate. J. Chem. Educ. 2008, 85, 827–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Idaboy, J.R.; Reyes, L.; Mora-Diez, N. The mechanism of the Baeyer-Villiger rearrangement: quantum chemistry and TST study supported by experimental kinetic data. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2007, 5, 3682–3689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krow, G.R. The Baeyer-Villiger Oxidation of Ketones and Aldehydes. Org. React. 1993, 43, 251–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Not available. |


| Compound | Retention Time (min) | Fragmentation Peaks, m/z with Relative Intensities (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Oxa-adamantanone | 9.27 | 122 (9), 94 (9), 80 (100), 67 (10), 55 (4) |
| 1,2-Campholide | 5.87 | 168 (5), 125 (83), 111 (78), 97 (6), 86 (5), 71 (5), 55 (100) |
| DBC6O | 12.81 | 196 (100), 168 (27), 139 (23), 113 (2), 98 (2), 84 (2), 70 (9), 55 (1) |
| Compound | Tc (Peak, °C) | Tm (peak, °C) | Tc (Onset, °C) | Tm (onset, °C) | ΔH (J/g) | T (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oxa-adamantanone | 283.36 ± 7.97 | 287.69 ± 7.27 | 284.31 ± 7.95 | 281.82 ± 11.46 | 25.93 * ± 5.27 | 150 ± 10–250 ± 10 |
| 1,2-Campholide | 91.71 ± N.A. | 95.43 ± N.A. | 93.25 ± N.A. | 80.49 ± N.A. | 8.54 *± N.A. | 93 ± 6–225 ± 13 |
| DBC6O | 49.80 ± 5.20 | 92.83 ± 0.30 | 51.05 ± 4.94 | 89.90 ± 1.34 | 62.60 ± 1.46 | 175 ± 5–307 ± 21 |
| ε-Caprolactone | −29.63 ± 1.50 | −1.55 ± 1.77 | −28.36 ± 1.66 | −6.99 ± 1.28 | 121.7 ± 5.04 | 105 ± 7–205 ± 7 |
| γ-Valerolactone | −69.03 ± 0.74 | −32.13 ± 0.50 | −68.91 ± 0.73 | −40.32 ± 0.99 | 109.8 ± 5.03 | 93 ± 4–188 ± 4 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ravotti, R.; Fellmann, O.; Lardon, N.; Fischer, L.J.; Stamatiou, A.; Worlitschek, J. Investigation of Lactones as Innovative Bio-Sourced Phase Change Materials for Latent Heat Storage. Molecules 2019, 24, 1300. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24071300
Ravotti R, Fellmann O, Lardon N, Fischer LJ, Stamatiou A, Worlitschek J. Investigation of Lactones as Innovative Bio-Sourced Phase Change Materials for Latent Heat Storage. Molecules. 2019; 24(7):1300. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24071300
Chicago/Turabian StyleRavotti, Rebecca, Oliver Fellmann, Nicolas Lardon, Ludger J. Fischer, Anastasia Stamatiou, and Jörg Worlitschek. 2019. "Investigation of Lactones as Innovative Bio-Sourced Phase Change Materials for Latent Heat Storage" Molecules 24, no. 7: 1300. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24071300
APA StyleRavotti, R., Fellmann, O., Lardon, N., Fischer, L. J., Stamatiou, A., & Worlitschek, J. (2019). Investigation of Lactones as Innovative Bio-Sourced Phase Change Materials for Latent Heat Storage. Molecules, 24(7), 1300. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24071300








