Analytical Methodology for Trace Determination of Propoxur and Fenitrothion Pesticide Residues by Decanoic Acid Modified Magnetic Nanoparticles
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussions
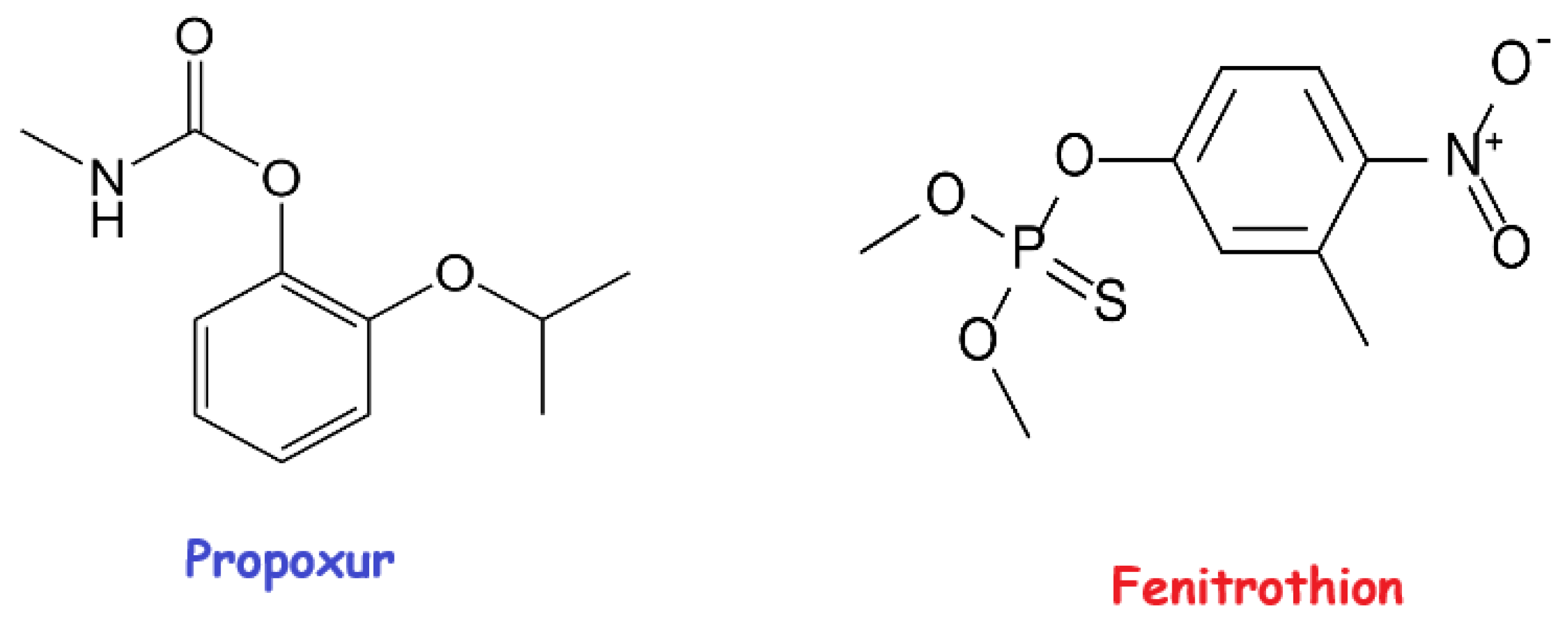
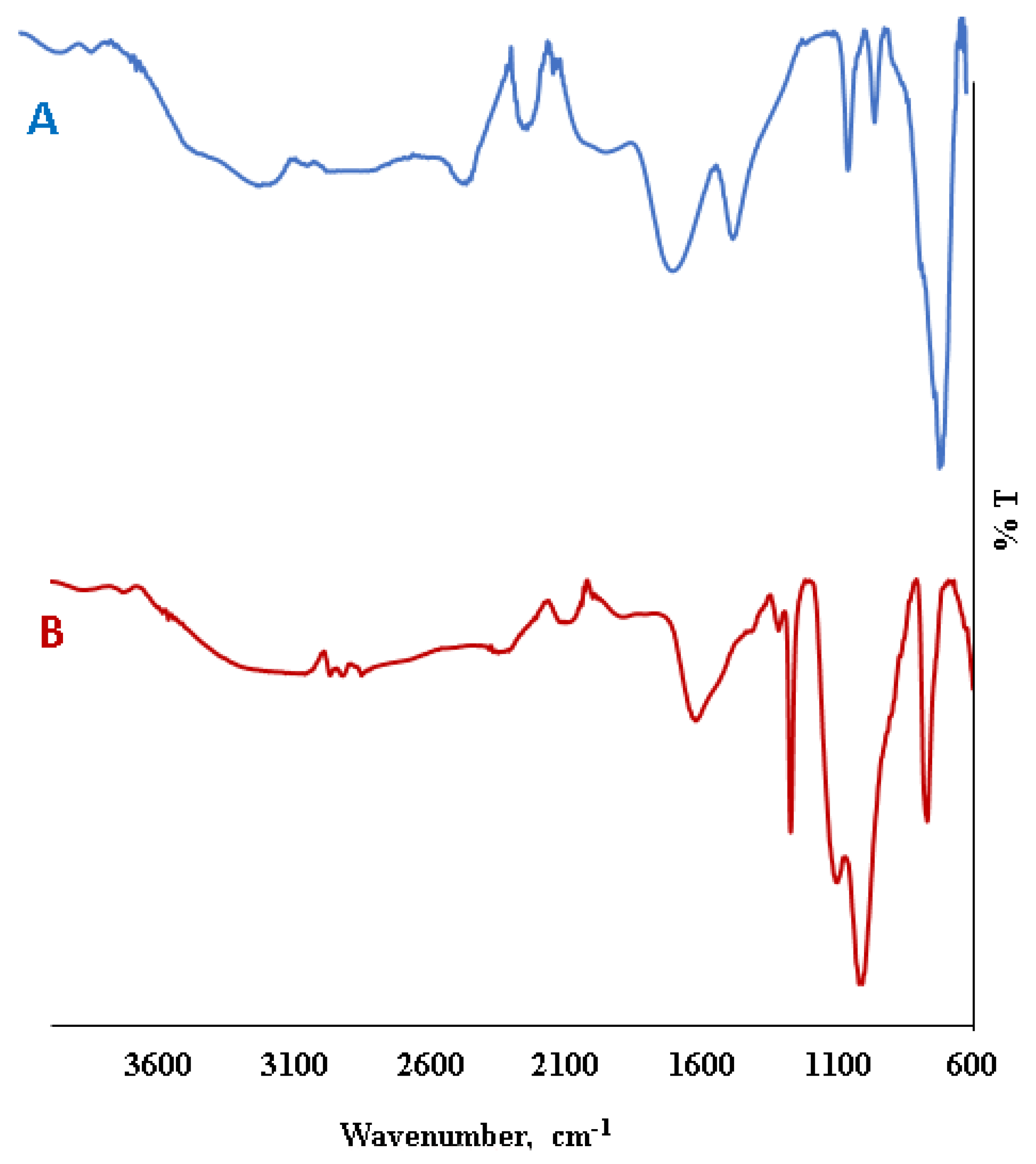
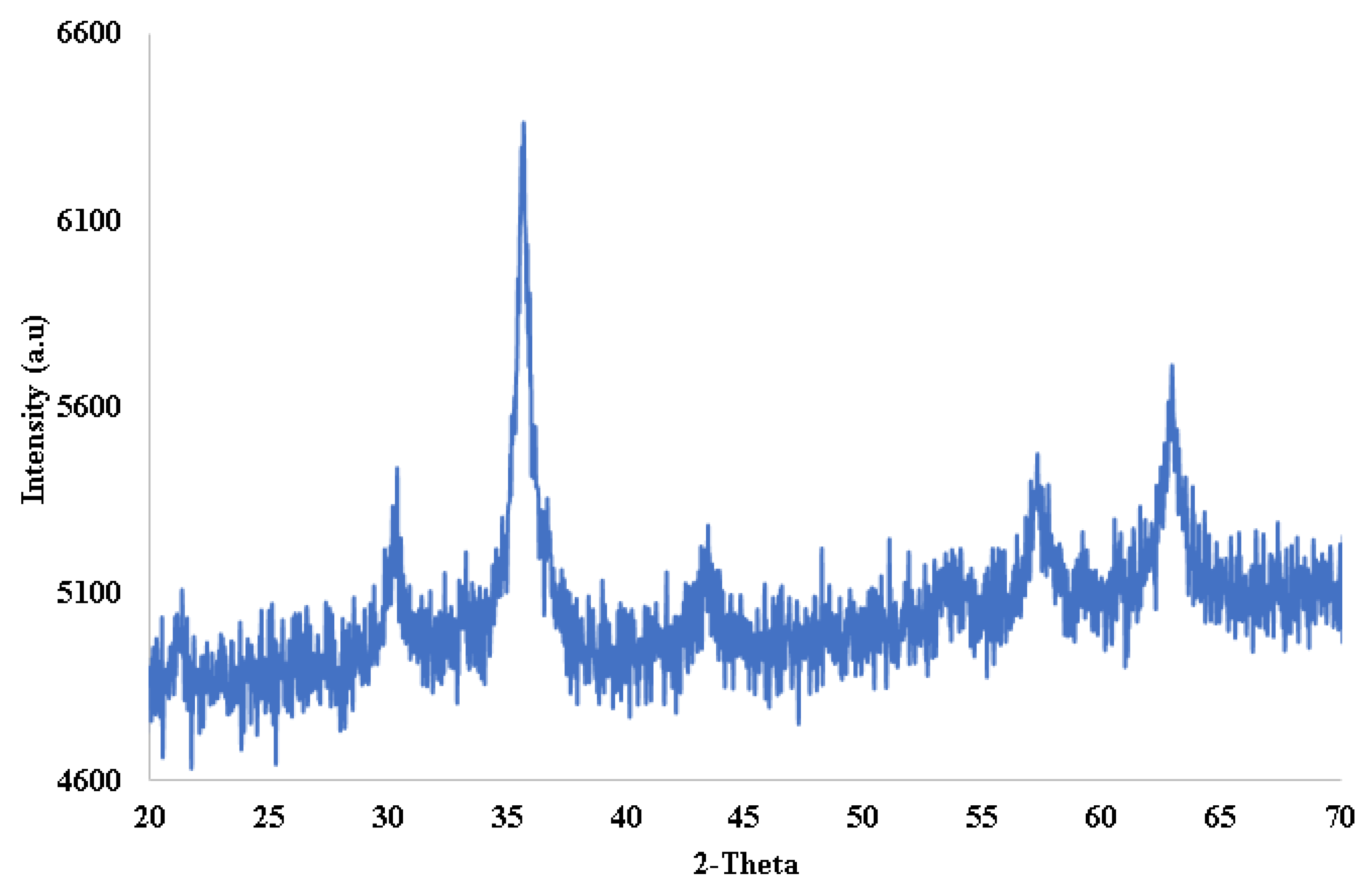
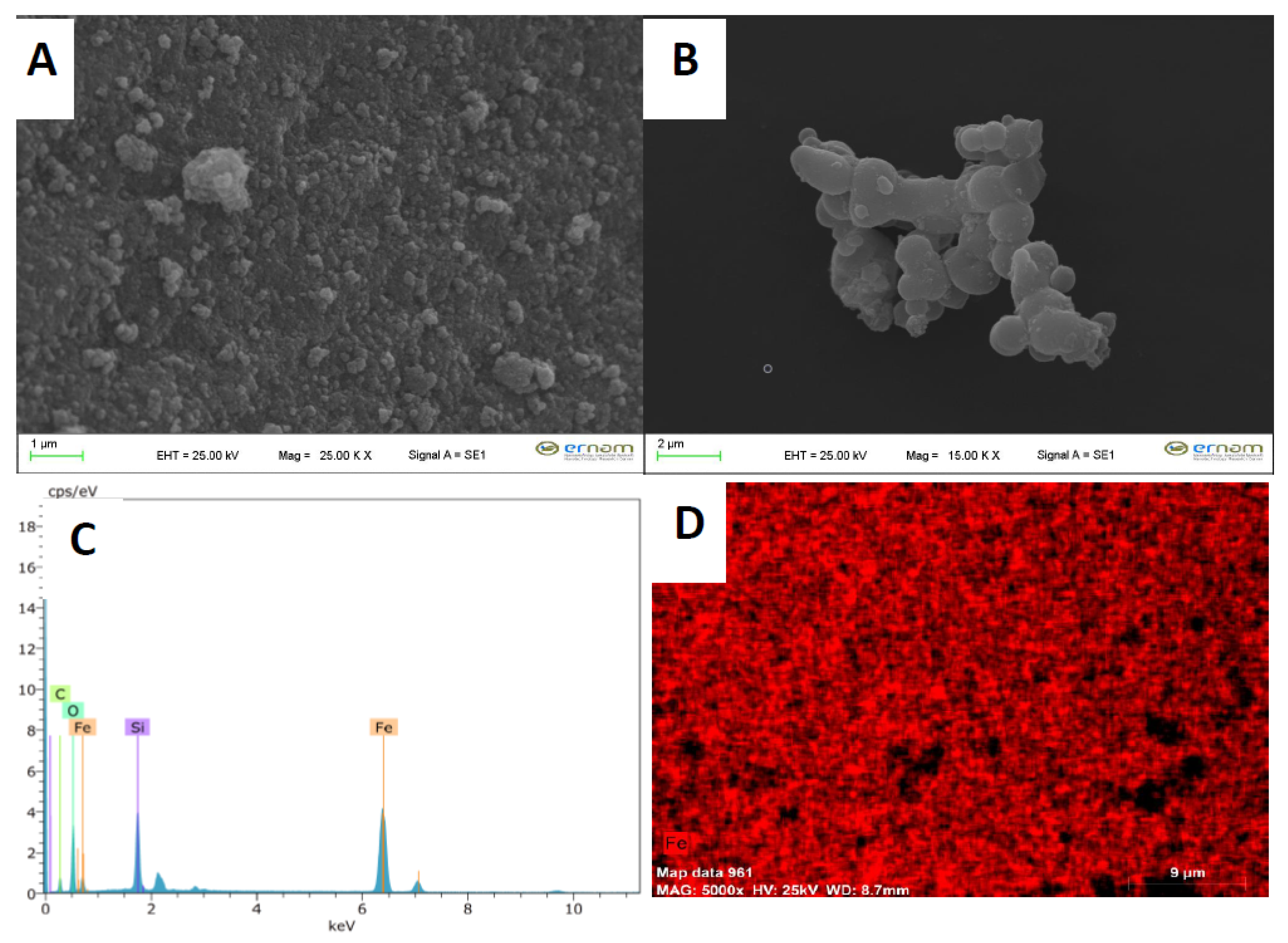
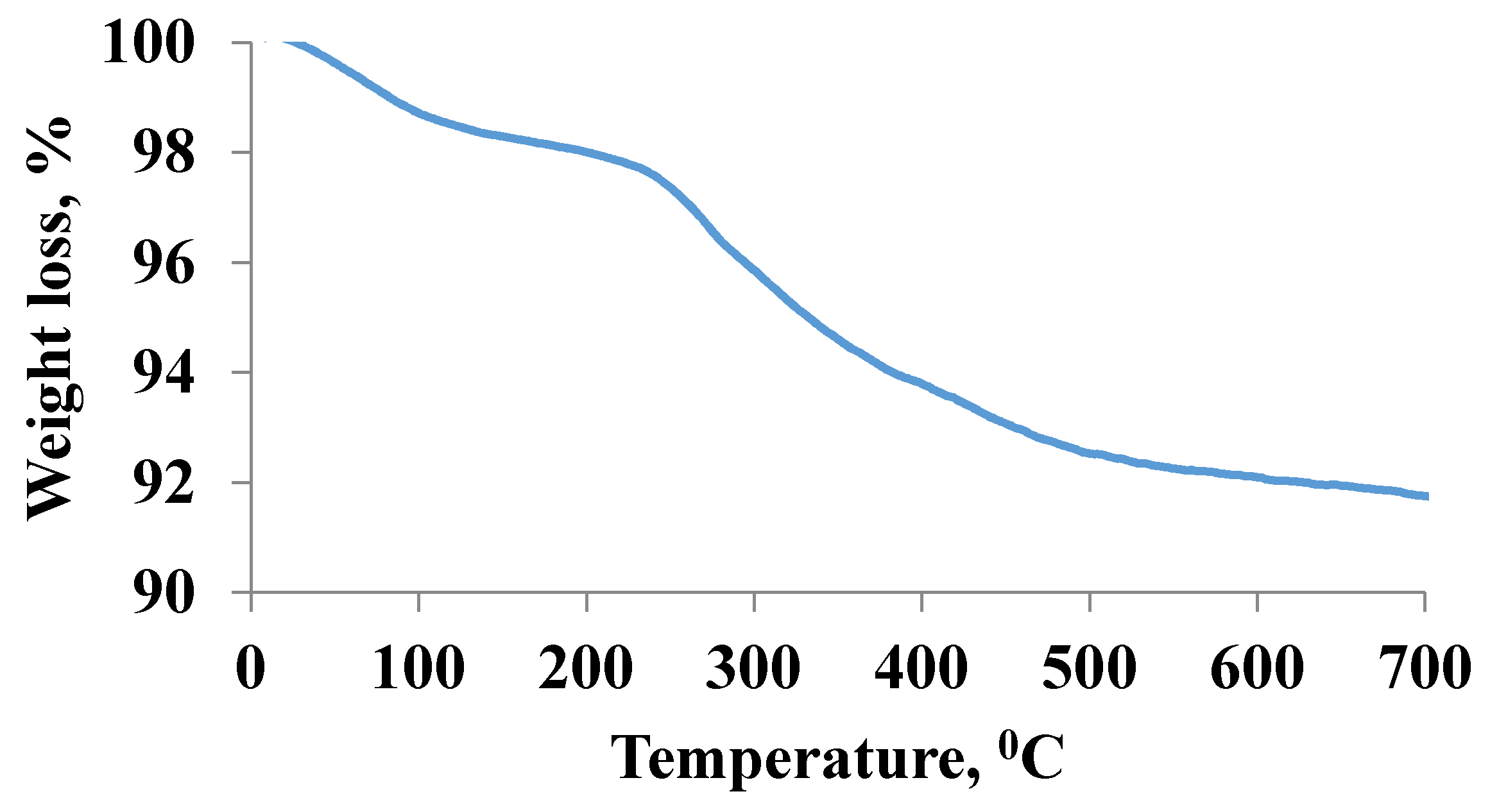
2.1. Characterization of Magnetic Nanoparticles
2.2. Optimization of Magnetic Solid-Phase Extraction Procedure
2.2.1. Effect of pH on Extraction Efficiency
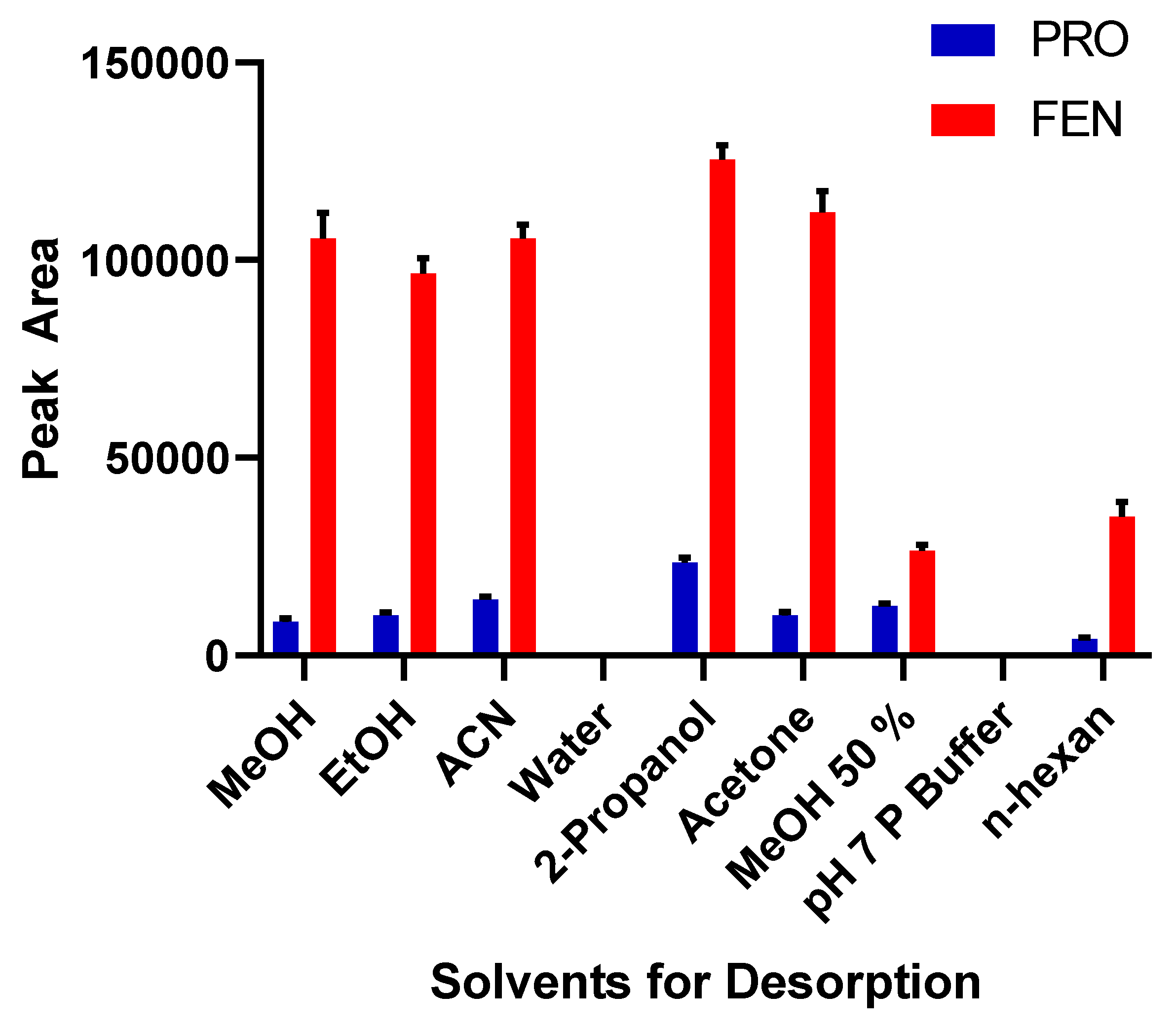
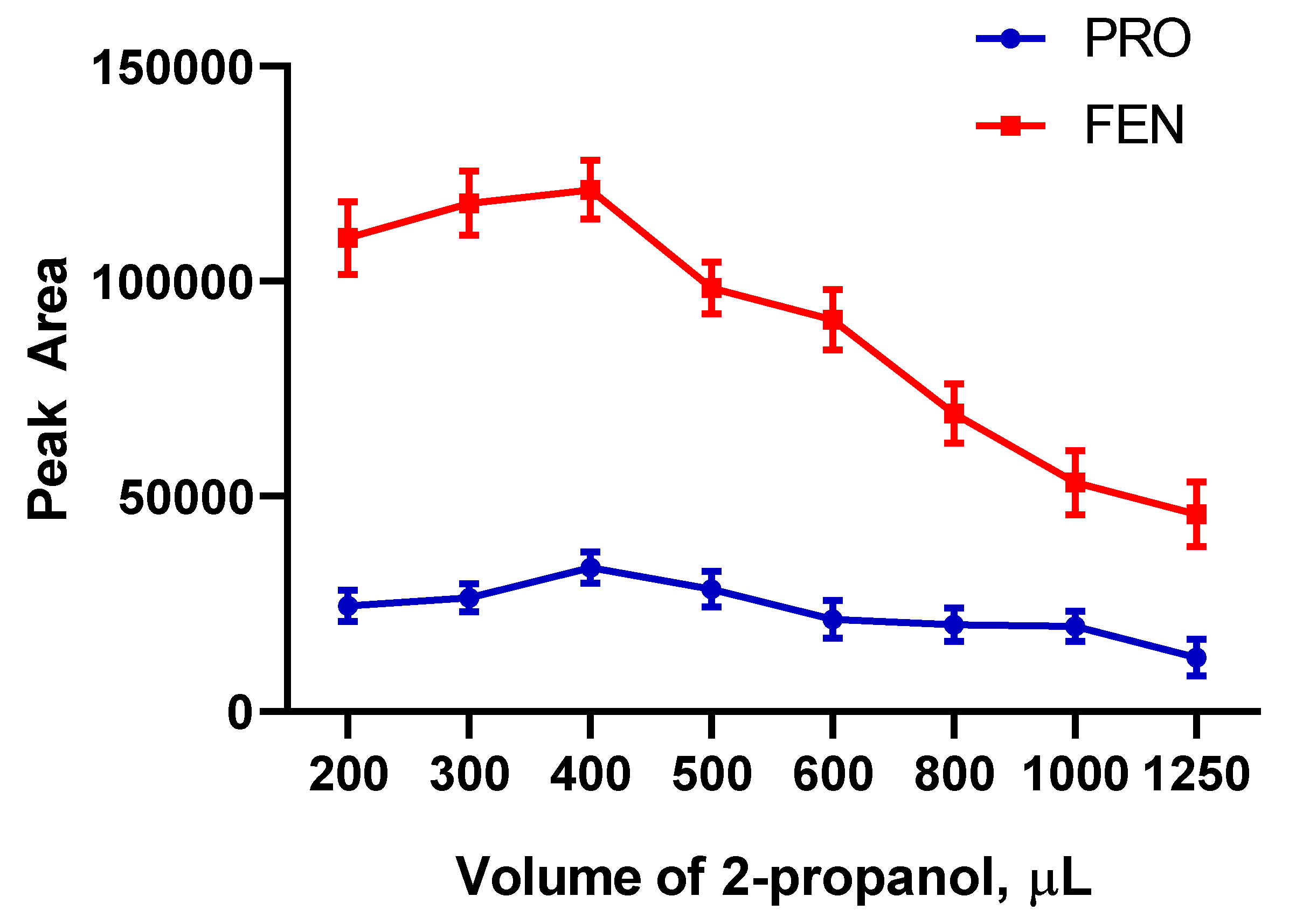
2.2.2. Selection of Desorption Solvent and Its Optimum Volume
2.2.3. Optimization of Shaking Time for Adsorption and Vortexing Time for Desorption
2.2.4. Reusability of Decanoic Acid Grafted Magnetic Particles
2.3. Method Validation
2.3.1. Linearity
2.3.2. Accuracy and Precision
2.3.3. Limits of Detection and Quantification
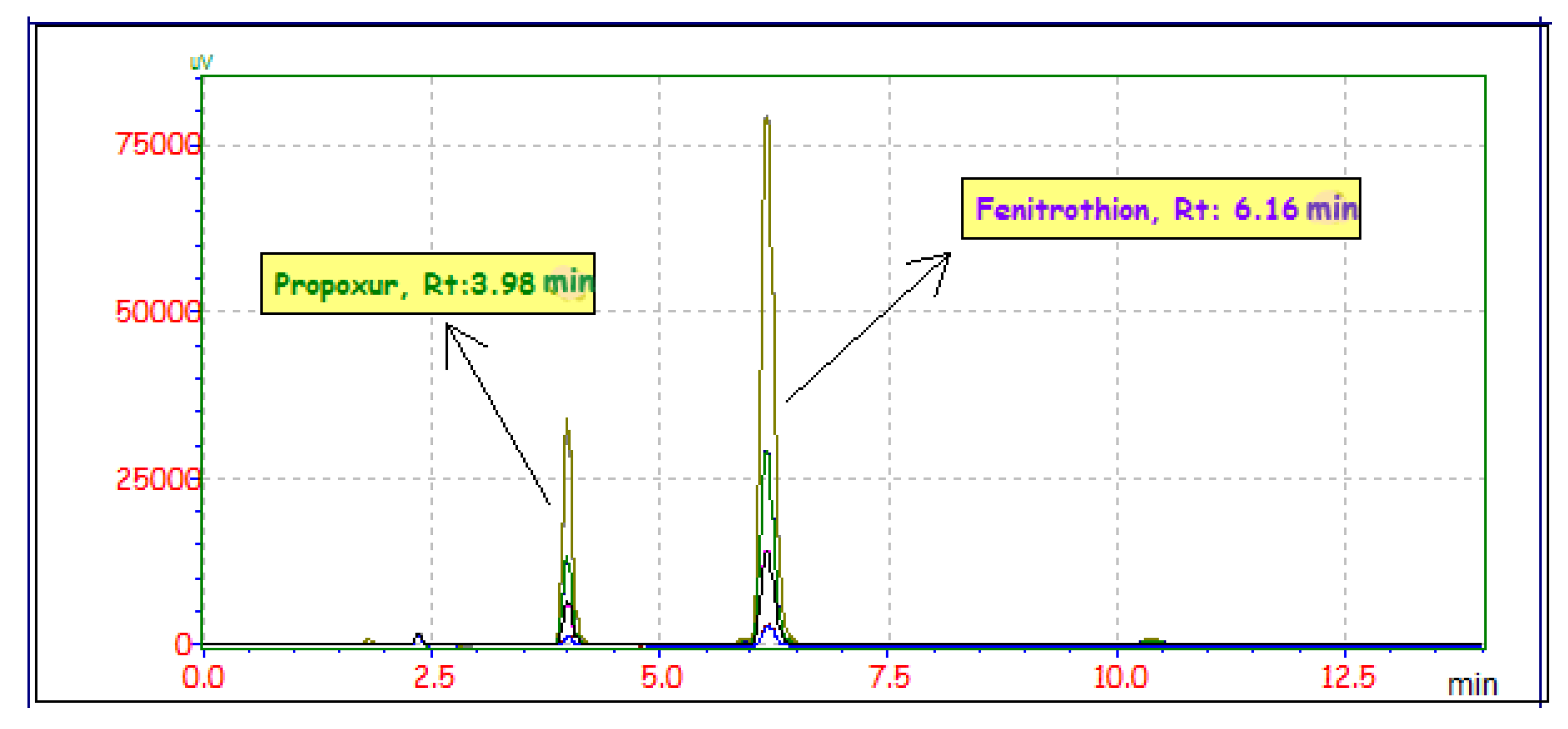
2.3.4. Selectivity
2.3.5. Robustness
2.3.6. Application in Real Sample
2.3.7. Performance Comparison between the Current and Other Reported Methods
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Reagents and Standard Solutions
3.2. Instrumentation
3.3. HPLC-PDA Operating Conditions
3.4. Synthesis of Magnetic Nanoparticles
3.5. The Proposed Method of Magnetic Solid-Phase Extraction
3.6. Preparation of Environmental Water Samples
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Narenderan, S.T.; Meyyanathan, S.N. Sample Treatment and Determination of Pesticide Residues in Potato Matrices: A Review. Potato Res. 2019, 62, 47–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidhu, G.K.; Singh, S.; Kumar, V.; Dhanjal, D.S.; Datta, S.; Singh, J. Toxicity, monitoring and biodegradation of organophosphate pesticides: A review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 49, 1135–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koc, F.; Yigit, Y.; Das, Y.K.; Gurel, Y.; Yarali, C. Determination of aldicarb, propoxur, carbofuran, carbaryl and methiocarb residues in honey by HPLC with post-column derivatization and fluorescence detection after elution from a florisil column. J. Food Drug Anal. 2008, 16, 39–45. [Google Scholar]
- Yildiz, Y.; Jan, A.; Yildiz, Y. Determination of 2-Isopropoxyphenyl Methyl Carbamate-Propoxur in Roach Control Peanut Butter by High Performance Liquid Chromatography. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2017, 4, 1000199. [Google Scholar]
- Suma, R.; Sarin, R.K.; Saiprakash, P.K.; Ramakrishna, S. Simple liquid chromatographic method for the rapid and simultaneous determination of propoxur and its major metabolite isopropoxy phenol in rat blood and urine using solid-phase extraction. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2005, 29, 728–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bazmandegan-Shamili, A.; Dadfarnia, S.; Haji Shabani, A.M.; Rohani Moghadam, M.; Saeidi, M. MultiSimplex optimization of the dispersive solid-phase microextraction and determination of fenitrothion by magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer and high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 2018, 15, 1181–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larki, A. A novel application of carbon dots for colorimetric determination of fenitrothion insecticide based on the microextraction method. Spectrochim. Acta—Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2017, 173, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidari, H.; Razmi, H. Multi-response optimization of magnetic solid phase extraction based on carbon coated Fe3O4 nanoparticles using desirability function approach for the determination of the organophosphorus pesticides in aquatic samples by HPLC-UV. Talanta 2012, 99, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Council Directive, Council of the European Union. On the quality of water intended for human consumption; Official Journal of the European Communities: Brussels, Belgium, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Stoytcheva, M.; Zlatev, R.; Montero, G.; Velkova, Z.; Gochev, V. A nanotechnological approach to biosensors sensitivity improvement: Application to organophosphorus pesticides determination. Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 2018, 32, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boeris, V.; Arancibia, J.A.; Olivieri, A.C. Determination of five pesticides in juice, fruit and vegetable samples by means of liquid chromatography combined with multivariate curve resolution. Anal. Chim. Acta 2014, 814, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuzimski, T.; Rejczak, T. Determination of pesticides in sunflower seeds by high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with a diode array detector. J. AOAC Int. 2014, 97, 1012–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malhat, F.; Boulangé, J.; Abdelraheem, E.; Abd Allah, O.; Abd El-Hamid, R.; Abd El-Salam, S. Validation of QuEChERS based method for determination of fenitrothion residues in tomatoes by gas chromatography–flame photometric detector: Decline pattern and risk assessment. Food Chem. 2017, 229, 814–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maddah, B.; Javadi, S.S.; Mirzaei, A.; Rahimi-Nasrabadi, M. Application of electrospun polystyrene nanofibers as solid phase extraction sorbent for the preconcentration of diazinon and fenitrothion in environmental waters. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2015, 38, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulusoy, H.I.; Gürkan, R.; Demir, Ö.; Ulusoy, S. Micelle-Mediated Extraction and Flame Atomic Absorption Spectrometric Method for Determination of Trace Cobalt Ions in Beverage Samples. Food Anal. Methods 2012, 5, 454–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Liu, Q.; Chen, Q.; Zhao, W.; Xiang, G.; He, L.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, S. Dicationic polymeric ionic-liquid-based magnetic material as an adsorbent for the magnetic solid-phase extraction of organophosphate pesticides and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. J. Sep. Sci. 2016, 39, 3221–3229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, E.; Alothman, Z.A.; Sumayli, H.M.T.; Ibrahim, M.; Soylak, M. Sorbent extraction of Pb(II), Cu(II), Ni(II), and Fe(III) Ions as 2-(5-Bromo-2-Pyridylazo)-5-diethylamino-phenol chelates on single-walled carbon nanotube disks prior to their flame atomic absorption spectrometric determinations in animal feeds and natura. J. AOAC Int. 2012, 95, 1205–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campone, L.; Piccinelli, A.L.; Celano, R.; Pagano, I.; Russo, M.; Rastrelli, L. Rapid and automated on-line solid phase extraction HPLC-MS/MS with peak focusing for the determination of ochratoxin A in wine samples. Food Chem. 2018, 244, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, C.; Wu, Q.; Wang, Z. Magnetic porous carbon-based solid-phase extraction of carbamates prior to HPLC analysis. Microchim. Acta 2016, 183, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabir, A.; Locatelli, M.; Ulusoy, H.İ. Recent Trends in Microextraction Techniques Employed in Analytical and Bioanalytical Sample Preparation. Separations 2017, 4, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulusoy, H.İ. Applications of Magnetic Nanoparticles for the Selective Extraction of Trace Species from a Complex Matrix, 1st ed.; Locatelli, M., Celia, C., Eds.; Nova Scientific Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ulusoy, H.İ.; Yılmaz, E.; Soylak, M. Magnetic solid phase extraction of trace paracetamol and caffeine in synthetic urine and wastewater samples by a using core shell hybrid material consisting of graphene oxide/multiwalled carbon nanotube/Fe3O4/SiO2. Microchem. J. 2019, 145, 843–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudr, J.; Haddad, Y.; Richtera, L.; Heger, Z.; Cernak, M.; Adam, V.; Zitka, O. Magnetic Nanoparticles: From Design and Synthesis to Real World Applications. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozcan, S.; Tor, A.; Aydin, M.E. Application of magnetic nanoparticles to residue analysis of organochlorine pesticides in water samples by GC/MS. J. AOAC Int. 2012, 95, 1343–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yilmaz, E.; Alosmanov, R.M.; Soylak, M. Magnetic solid phase extraction of lead(II) and cadmium(II) on a magnetic phosphorus-containing polymer (M-PhCP) for their microsampling flame atomic absorption spectrometric determinations. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 33801–33808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yılmaz, E.; Soylak, M. Preparation and characterization of magnetic carboxylated nanodiamonds for vortex-assisted magnetic solid-phase extraction of ziram in food and water samples. Talanta 2016, 158, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kılınç, E.; Çelik, K.S.; Bilgetekin, H. γ-Fe2O3magnetic nanoparticle functionalized with carboxylated multi walled carbon nanotube for magnetic solid phase extractions and determinations of Sudan dyes and Para Red in food samples. Food Chem. 2018, 242, 533–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barreto, I.S.; Andrade, S.I.E.; Cunha, F.A.S.; Lima, M.B.; Araujo, M.C.U.; Almeida, L.F. A robotic magnetic nanoparticle solid phase extraction system coupled to flow-batch analyzer and GFAAS for determination of trace cadmium in edible oils without external pretreatment. Talanta 2018, 178, 384–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, V.D.; Daharwal, S.J. Development and validation of multivariate calibration methods for simultaneous estimation of Paracetamol, Enalapril maleate and hydrochlorothiazide in pharmaceutical dosage form. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2017, 171, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Medicines Agency. ICH Topic Q2 (R1) Validation of Analytical Procedures: Text and Methodology. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/scientific-guideline/ich-q-2-r1-validation-analytical-procedures-text-methodology-step-5_en.pdf (accessed on 17 December 2019).
- Soo Lim, H.; Young Hwang, J.; Choi, E.A.; Lee, G.; Sun Yoon, S.; Kim, M.K. Development and validation of HPLC method for the determination of ferrocyanide ion in food grade salts. Food Chem. 2018, 239, 1167–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harshit, D.; Charmy, K.; Nrupesh, P. Organophosphorus pesticides determination by novel HPLC and spectrophotometric method. Food Chem. 2017, 230, 448–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, E.; Ulusoy, H.İ.; Demir, Ö.; Soylak, M. A new magnetic nanodiamond/graphene oxide hybrid (Fe3O4@ND@GO) material for pre-concentration and sensitive determination of sildenafil in alleged herbal aphrodisiacs by HPLC-DAD system. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2018, 1084, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Lam, M.H.W.; Wu, R.S.S.; Jiang, B. Rapid magnetic-mediated solid-phase extraction and pre-concentration of selected endocrine disrupting chemicals in natural waters by poly(divinylbenzene-co-methacrylic acid) coated Fe3O4 core-shell magnetite microspheres for their liquid chromatography-ta. J. Chromatogr. A 2010, 1217, 1219–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maddah, B.; Shamsi, J. Extraction and preconcentration of trace amounts of diazinon and fenitrothion from environmental water by magnetite octadecylsilane nanoparticles. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1256, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Jiao, C.; Yang, X.; Wang, C.; Wu, Q.; Wang, Z. Solid phase extraction of carbamate pesticides with banana peel derived hierarchical porous carbon prior to high performance liquid chromatography. Anal. Methods 2017, 9, 593–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodadoust, S.; Talebianpoor, M.S.; Ghaedi, M. Application of an optimized dispersive nanomaterial ultrasound-assisted microextraction method for preconcentration of carbofuran and propoxur and their determination by high-performance liquid chromatography with UV detection. J. Sep. Sci. 2014, 37, 3117–3124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tankiewicz, M.; Biziuk, M. Fast, sensitive and reliable multi-residue method for routine determination of 34 pesticides from various chemical groups in water samples by using dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction coupled with gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 1533–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are available from the authors. |


| Parameter | Before MSPE | After MSPE | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fenitrothion | Propoxur | Fenitrothion | Propoxur | |
| Linear range | 2.0–20.0 μg mL−1 | 2.0–20.0 μg mL−1 | 5.0–800.0 ng mL−1 | 10.0–800.0 ng mL−1 |
| LOD | 0.57 μg mL−1 | 0.57 μg mL−1 | 1.43 ng mL−1 | 3.15 ng mL−1 |
| LOQ | 1.88 μg mL−1 | 1.88 μg mL−1 | 4.93 ng mL−1 | 9.86 ng mL−1 |
| RSD (%) | 3.8 | 3.6 | 2.9 | 3.2 |
| Slope | 10.218 | 1.473 | 1348.8 | 173.76 |
| (R2) | 0.9972 | 0.9985 | 0.9954 | 0.9908 |
| Preconcentration Factor a | - | - | 125 | 125 |
| Enhancement Factor b | - | - | 132 | 118 |
| Sample | Added ng mL−1 | Found a ng mL−1 | RSD % | Recovery % | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Propoxur | Fenitrothion | Propoxur | Fenitrothion | Propoxur | Fenitrothion | ||
| River water I | - | <LOD | <LOD | - | - | - | - |
| 100.0 | 94.2 ± 2.7 | 103.2 ± 3.4 | 2.8 | 3.3 | 94.2 | 103.2 | |
| 200.0 | 206.1 ± 13.5 | 202.4 ± 8.4 | 6.5 | 4.1 | 103.5 | 101.2 | |
| Lake water II | - | <LOD | <LOD | - | - | - | - |
| 100.0 | 97.9 ± 3.8 | 99.5 ± 2.9 | 3.9 | 2.9 | 97.9 | 99.5 | |
| 200.0 | 192.1 ± 10.5 | 203.7 ± 9.8 | 5.5 | 4.8 | 96.1 | 101.8 | |
| Pond water | - | <LOD | <LOD | - | - | - | - |
| 100.0 | 107.4 ± 3.6 | 95.8 ± 3.9 | 3.4 | 4.0 | 107.4 | 95.8 | |
| 200.0 | 193.4 ± 8.9 | 205.8 ± 8.5 | 4.6 | 4.1 | 96.7 | 102.9 | |
| Preconcentration Method | Determination Method | Target Molecule | LOD | Linear Range | Applications | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quenchers based method | Gas chromatography-flame photometric detector | Fenitrothion | 0.005 μg mL−1 | 0.005–5.0 μg mL−1 | Tomatoes | [13] |
| Dispersive solid-phase microextraction | HPLC-UV | Fenitrothion | 0.1 μg L−1 | 0.3–50.0 μg L−1 | Water and fruit samples | [6] |
| Electrospun polystyrene nanofibers as solid-phase extraction sorbent | HPLC-DAD | Fenitrothion | 0.07 ng mL−1 | 0.5–50.0 ng mL−1 | Environmental waters | [14] |
| Magnetite octadecylsilane nanoparticles | HPLC-UV | Fenitrothion | 0.014 ng mL−1 | 0.03–30 ng mL−1 | Environmental water | [35] |
| Magnetic solid-phase extraction | Spectrophotometry | Fenitrothion | 0.5 ng mL−1 | 2–230 ng mL−1 | Environmental and biological samples | [34] |
| Magnetic solid-phase extraction | Gas chromatographic determination | Fenitrothion | 3.9 ng mL−1 | 10–50000 ng mL−1 | Fruit juices | [33] |
| Magnetic solid-phase extraction | HPLC-UV | Fenitrothion | 0.2–0.8 μg L−1 | 1–100 μg L−1 | Water samples | [16] |
| Magnetic solid-phase extraction | HPLC-UV | Propoxur | 0.2 ng g−1 | 1.0 –100.0 ng g−1 | Apple sample | [19] |
| Solid-phase extraction | HPLC-UV | Propoxur | 0.05 ng g−1 | 0.2–80.0 ng g−1 | Cucumber and watermelon samples | [36] |
| Magnetic solid-phase extraction | HPLC-PDA | Propoxur Fenitrothion | 1.43 ng mL−1 | 5–800 ng mL−1 | Environmental waters | This Study |
| 3.15 ng mL−1 | 10–800 ng mL−1 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Canlı, A.G.; Sürücü, B.; Ulusoy, H.İ.; Yılmaz, E.; Kabir, A.; Locatelli, M. Analytical Methodology for Trace Determination of Propoxur and Fenitrothion Pesticide Residues by Decanoic Acid Modified Magnetic Nanoparticles. Molecules 2019, 24, 4621. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24244621
Canlı AG, Sürücü B, Ulusoy Hİ, Yılmaz E, Kabir A, Locatelli M. Analytical Methodology for Trace Determination of Propoxur and Fenitrothion Pesticide Residues by Decanoic Acid Modified Magnetic Nanoparticles. Molecules. 2019; 24(24):4621. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24244621
Chicago/Turabian StyleCanlı, Amine Gizem, Bilge Sürücü, Halil İbrahim Ulusoy, Erkan Yılmaz, Abuzar Kabir, and Marcello Locatelli. 2019. "Analytical Methodology for Trace Determination of Propoxur and Fenitrothion Pesticide Residues by Decanoic Acid Modified Magnetic Nanoparticles" Molecules 24, no. 24: 4621. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24244621
APA StyleCanlı, A. G., Sürücü, B., Ulusoy, H. İ., Yılmaz, E., Kabir, A., & Locatelli, M. (2019). Analytical Methodology for Trace Determination of Propoxur and Fenitrothion Pesticide Residues by Decanoic Acid Modified Magnetic Nanoparticles. Molecules, 24(24), 4621. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24244621









