Metal Organic Frameworks as Desulfurization Adsorbents of DBT and 4,6-DMDBT from Fuels
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Desulfurization Methods
3. Metal-Organic Frameworks (MOFs) as Efficient Adsorbents for Desulfurization
4. Desulfurization with MOFs
5. Functionalization of MOFs
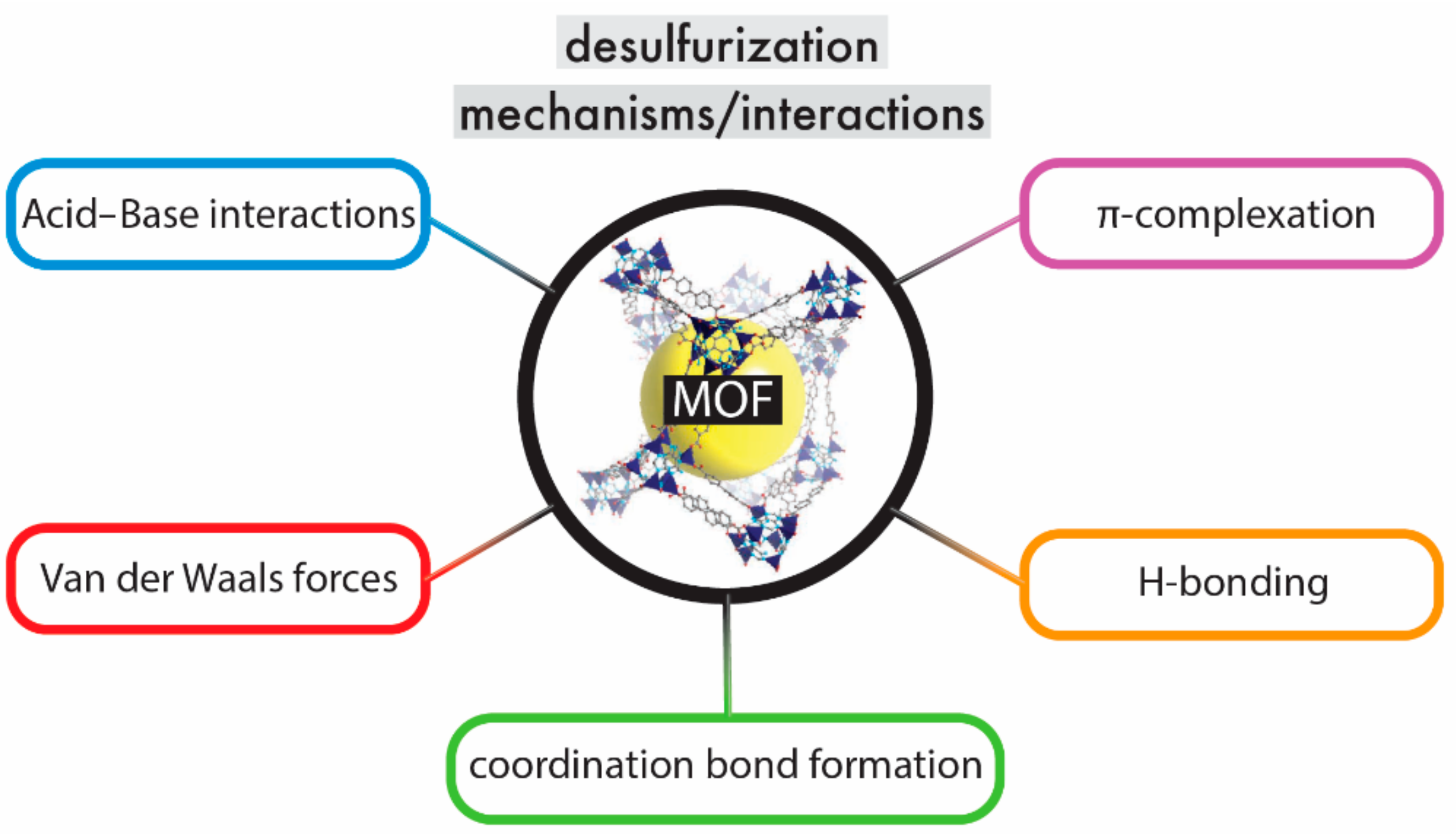
6. Mechanisms of Desulfurization
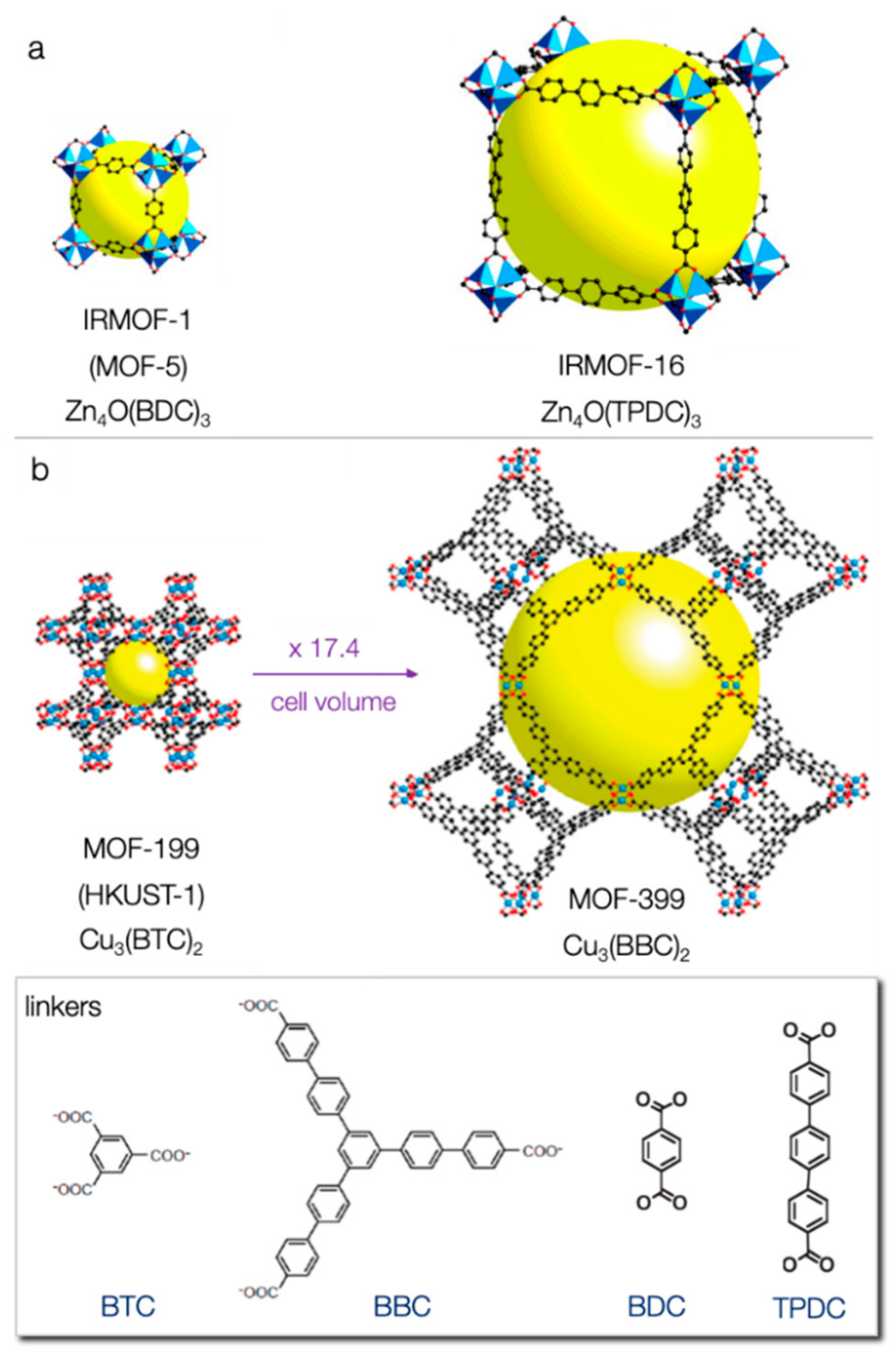
6.1. Effect of Porosity
6.2. Acid–Base Interactions
6.3. Coordination Bond Formation (Lewis Acid–Base Interaction)
6.4. π-Complexation
6.5. Van der Waals Forces
7. Drawbacks
8. Perspectives
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Colvile, R.N.; Hutchinson, E.J.; Mindell, J.S.; Warren, R.F. The transport sector as a source of air pollution. Atmos. Env. 2001, 35, 1537–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandy, R.F.; Benjamin, L.B.; Jonathan, L.M.; Robert, L.H.; Mohammad, N.S.; Tawfik, A.S.T. Enhanced oxidative desulfurization in a film-shear reactor. Fuel 2015, 156, 142–147. [Google Scholar]
- Air quality guidelines: Global update 2005: Particulate matter, ozone, nitrogen dioxide, and sulfur dioxide. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/69477 (accessed on 25 November 2019).
- Subramani, V. Hydrogen and syngas production and purification technologies. John Wiley & Sons Inc: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Samokhvalov, A.; Tatarchuk, B.J. Review of experimental characterization of active sites and determination of molecular mechanisms of adsorption, desorption and regeneration of the deep and ultra deep desulfurization sorbents for liquid fuels. Catal. Rev. Sci. Eng. 2010, 52, 381–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanislaus, A.; Marafi, A.; Rana, M.S. Recent advances in the science and technology of ultra low sulfur diesel (ULSD) production. Catal. Today 2010, 153, 1–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, R.G. Hard and soft acids and bases. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1963, 85, 3533–3539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global, BP Statistical Review of World Energy. Available online: http://www.usaee.org/usaee2013/submissions/presentations/SR%202013%20US%20events.pdf (accessed on 25 November 2019).
- Brieva, G.B.; Campos-Martin, J.M.; Al-zahrani, S.; Fierro, J.L.G. Removal of refractory organic sulfur compounds in fossil fuels using mof sorbents. Glob. Nest J. 2010, 12, 296–304. [Google Scholar]
- González-García, O.; Cedenõ-Caero, L. V-Mo based catalysts for oxidative desulfurization of diesel fuel. Catal. Today 2009, 148, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, P.S.; Afonso, C.A.M. Deep desulfurization of diesel fuel using ionic liquids: Current status and future challenges. Green Chem. 2010, 12, 1139–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capel-Sanchez, M.C.; Perez-Presas, P.; Campos-Martin, J.M.; Fierro, J.L.G. Highly efficient deep desulfurization of fuels by chemical oxidation. Catal. Today 2010, 157, 390–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos-Martin, J.M.; Capel-Sanchez, M.C.; Perez-Presas, P.; Fierro, J.L.G. Oxidative Processes of Desulfurization of Liquid Fuels. J. Chem. Tech. Biotech. 2010, 85, 879–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capel-Sanchez, M.C.; Campos-Martin, J.M.; Fierro, J.L.G. Removal of refractory organosulfur compounds via oxidation with hydrogen peroxide on amorphous Ti/SiO2 catalysts. Energy Env. Sci. 2010, 3, 328–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monticello, D.J. Riding the fossil fuel bio-desulfurization wave. Chem. Tech. 1998, 28, 38–45. [Google Scholar]
- Babich, I.V.; Moulijn, J.A. Science and technology of novel processes for deep desulfurization of oil refinery streams: A review. Fuel 2003, 82, 607–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.A.; Hasan, Z.; Jhung, S.H. Adsorption and removal of sulfur or nitrogen-containing compounds with metal-organic frameworks (MOFs). Adv. Porous Mater. 2013, 1, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruneta, S.; Meya, D.; Pérot, G.; Bouchy, C.; Diehl, F. On the hydrodesulfurization of FCC gasoline: A review. Appl. Catal. A: Gen. 2005, 278, 143–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.T.; Hernandez-Maldonaldo, A.J.; Yang, F.H. Desulfurization of transportation fuels with zeolites under ambient conditions. Science 2003, 301, 79–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, T.-H.; Cychosz, K.A.; Wong-Foy, A.G.; Dailly, A.; Matzger, A.J. Gas and liquid phase adsorption in isostructural Cu3[biaryltricarboxylate]2 microporous coordination polymers. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 1452–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Li, G.; Ning, G. Efficient oxidative desulfurization (ODS) of model fuel with H2O2 catalyzed by MoO3/-Al2O3 under mild and solvent free conditions. Fuel Process. Technol. 2011, 92, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhir, S.; Uppaluri, R.; Purkait, M.K. Oxidative desulfurization: Kinetic modeling. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 16, 1360–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, Z.; Jeon, J.; Jhung, S.H. Oxidative desulfurization of benzothiophene and thiophene with WO x/ZrO2 catalysts: Effect of calcination temperature of catalysts. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 205–206, 216–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almarri, M.; Ma, X.; Song, C. Role of surface oxygen-containing functional groups in liquid-phase adsorption of nitrogen compounds on carbon-basedadsorbents. Energy Fuels 2009, 23, 3940–3947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deliyanni, E.; Seredych, M.; Bandosz, T.J. Interactions of 4,6-dimethyldibenzothiophene with the surface of activated carbons. Langmuir 2009, 25, 9302–9312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, J.; Zhu, W.; Li, H.; Yang, L.; Chao, Y.; Wu, P.; Xun, S.; Jiang, W.; Zhang, M.; Li, H. Carbon-doped porous boron nitride: Metal-free adsorbents for sulfur removal from fuels. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 12738–12747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, A.; Ma, X.; Song, C. Liquid-phase adsorption of multi-ring thiophenic sulfur compounds on carbon materials with different surface properties. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 4699–4707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, H.J.; Ko, C.H.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, J.N. Removal of refractory sulfur compounds in diesel using activated carbon with controlled porosity. Energy Fuels 2009, 23, 2537–2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seredych, M.; Bandosz, T.J. Adsorption of dibenzothiophenes on nanoporous carbons: Identification of specific adsorption sites governing capacity and selectivity. Energy and Fuels 2010, 24, 3352–3360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seredych, M.; Bandosz, T.J. Investigation of the enhancing effects of sulfur and/or oxygen functional groups of nanoporous carbons on adsorption of dibenzothiophenes. Carbon 2011, 49, 1216–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seredych, M.; Bandosz, T.J. Removal of dibenzothiophenes from model diesel fuel on sulfur rich activated carbons. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2011, 106, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seredych, M.; Messali, L.; Bandosz, T.J. Analysis of factors affecting visible and UV enhanced oxidation of dibenzothiophenes on sulfur-doped activated carbons. Carbon 2013, 62, 356–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kampouraki, Z.C.; Giannakoudakis, D.A.; Triantafyllidis, K.S.; Deliyanni, E.A. Catalytic oxidative desulfurization of a 4,6-DMDBT containing model fuel by metal-free activated carbons: the key role of surface chemistry. Green Chem. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Gui, J.; Sun, Z. Adsorption structures of heterocyclic nitrogen compounds over Cu(I)Y zeolite: A first principle study on mechanism of the denitrogenation and the effect of nitrogen compounds on adsorptive desulfurization. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2008, 291, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Li, Z.; Liu, B.; Xia, Q.; Yu, M. Adsorption of benzothiophene and dibenzothiophene on ion-impregnated activated carbons and ion-exchanged Y zeolites. Energy Fuels 2008, 22, 3858–3863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Maldonado, A.J.; Qi, G.; Yang, R.T. Desulfurization of commercial fuels by π-complexation: Monolayer CuCl/γ-Al2O3. Appl. Catal. B Env. 2005, 61, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.Y.; Shi, T.B.; Jia, C.Z.; Ji, W.J.; Chen, Y.; He, M.Y. Adsorptive removal of aromatic organosulfur compounds over the modified Na-Y zeolites. Appl. Catal. B Env. 2008, 82, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Yan, Y.; Chen, W.; Kang, H.; Han, Y.; Zhang, W.; Fan, Y.; Li, Z. The high performance and mechanism of metal–organic frameworks and their composites in adsorptive desulfurization. Polyhedron 2018, 152, 202–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Maldonado, A.J.H.; Yang, R.T. Desulfurization of Transportation Fuels by Adsorption Desulfurization of Transportation Fuels. Catal. Rev. 2004, 46, 111–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, J.M.; Moon, J.H.; Bae, Y.S.; Lee, D.G.; Sohn, H.C.; Lee, C.H. Adsorptive desulfurization and denitrogenation of refinery fuels using mesoporous silica adsorbents. ChemSusChem 2008, 1, 307–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Barnes, J.C.; Bosoy, A.; Stoddart, J.F.; Zink, J.I. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles in biomedical applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 2590–2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinu, A.; Ariga, K. New ideas for mesoporous materials. Adv. Porous Mater. 2013, 1, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariga, K.; Ji, Q.; Mcshane, M.J.; Lvov, Y.M.; Vinu, A.; Hill, J.P. Inorganic nanoarchitectonics for biological applications. Chem. Mater. 2012, 24, 728–737. [Google Scholar]
- Bae, Y.S.; Kim, M.B.; Lee, H.J.; Lee, C.H.; Ryu, J.W. Adsorptive denitrogenation of light gas oil by silica-zirconia cogel. Aiche J. 2006, 52, 510–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, C.H.; Park, J.G.; Park, J.C.; Song, H.; Han, S.S.; Kim, J.N. Surface status and size influences of nickel nanoparticles on sulfur compound adsorption. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2007, 253, 5864–5867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.L.; Favre-Reguillon, A.; Wang, X.X.; Fu, X.; Lemaire, M. Selective adsorption of neutral nitrogen compounds from fuel using ion-exchange resins. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2010, 55, 4849–4853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cronauer, D.C.; Young, D.C.; Solash, J.; Seshadrl, K.S.; Dannerx, D.A. Shale Oil Denitrogenation with Ion Exchange. 3. Characterization of Hydrotreated And Ion-Exchange Isolated Products. Ind. Eng. Chem. Process Des. Dev. 1986, 25, 756–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furukawa, H.; Cordova, K.E.; O’Keeffe, M.; Yaghi, O.M. The chemistry and applications of metal-organic frameworks. Science 2013, 341, 1230444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, S.; Xue, M.; Zhu, G. Metal-organic framework membranes: From synthesis to separation application. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 6116–6140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Chen, L.; Cui, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, L.; Su, C.Y. Applications of metal-organic frameworks in heterogeneous supramolecular catalysis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 6011–6061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Z.; Cao, D.; Lan, J.; Wang, W.; Broom, D.P. Multiscale simulation and modelling of adsorptive processes for energy gas storage and carbon dioxide capture in porous coordination frameworks. Energy Env. Sci. 2010, 3, 1469–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meek, S.T.; Greathouse, J.A.; Allendorf, M.D. Metal-organic frameworks: A rapidly growing class of versatile nanoporous materials. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 249–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.C.; Long, J.R.; Yaghi, O.M. Introduction to metal-organic frameworks. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 673–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.-R.; Sculley, J.; Zhou, H.-C. Metal–Organic Frameworks for Separations. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 869–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Férey, G. Hybrid porous solids: Past, present, future. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 191–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaghi, O.M.; Li, G.; Li, H. Selective binding and removal of guests in a microporous metal-organic framework. Nature 1995, 378, 703–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitagawa, S.; Kitaura, R.; Noro, S.I. Functional porous coordination polymers. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 2334–2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Zhou, H.C. A metal-organic framework with entatic metal centers exhibiting high gas adsorption affinity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 11734–11735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cychosz, K.A.; Wong-Foy, A.G.; Matzger, A.J. Liquid phase adsorption by microporous coordination polymers: Removal of organosulfur compounds. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 6938–6939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Kravtsov, V.C.; Larsen, R.; Eddaoudi, M. Molecular building blocks approach to the assembly of zeolite-like metal-organic frameworks (ZMOFs) with extra-large cavities. Chem. Commun. 2006, 14, 1488–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eddaoudi, M.; Kim, J.; Rosi, N.; Vodak, D.; Wachter, J.; O’Keeffe, M.; Yaghi, O.M. Systematic design of pore size and functionality in isoreticular MOFs and their application in methane storage. Science 2002, 295, 469–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumida, K.; Rogow, D.L.; Mason, J.A.; Mcdonald, T.M.; Bloch, E.D.; Herm, Z.R.; Bae, T.; Long, J.R. Carbon dioxide capture in metal-organic frameworks. Chem. Rev. 2012, 724–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.R.; Ma, Y.; McCarthy, M.C.; Sculley, J.; Yu, J.; Jeong, H.K.; Balbuena, P.B.; Zhou, H.C. Carbon dioxide capture-related gas adsorption and separation in metal-organic frameworks. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2011, 255, 1791–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, M.P.; Park, H.J.; Prasad, T.K.; Lim, D.-W. Hydrogen storage in metal-organic frameworks. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 782–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van De Voorde, B.; Bueken, B.; Denayer, J.; De Vos, D. Adsorptive separation on metal-organic frameworks in the liquid phase. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 5766–5788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.; Liu, D.; Zhong, C.; Li, J.R. Development of computational methodologies for metal-organic frameworks and their application in gas separations. Chem. Rev. 2013, 113, 8261–8323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhakshinamoorthy, A.; Garcia, H. Catalysis by metal nanoparticles embedded on metal-organic frameworks. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 5262–5284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horcajada, P.; Gref, R.; Baati, T.; Allan, P.K.; Maurin, G.; Couvreur, P.; Férey, G.; Morris, R.E.; Serre, C. Metal-organic frameworks in biomedicine. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 1232–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uemura, T.; Yanai, N.; Kitagawa, S. Polymerization reactions in porous coordination polymers. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 1228–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurmoo, M. Magnetic metal-organic frameworks. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 1353–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Deibert, B.J.; Li, J. Luminescent metal-organic frameworks for chemical sensing and explosive detection. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 5815–5840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannakoudakis, D.A.; Bandosz, T.J. Detoxification of Chemical Warfare Agents, 1st ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; ISBN 978-3-319-70759-4. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.R.; Kuppler, R.J.; Zhou, H.C. Selective gas adsorption and separation in metal-organic frameworks. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 1477–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.A.; Jhung, S.H. Effect of central metal ions of analogous metal-organic frameworks on the adsorptive removal of benzothiophene from a model fuel. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 260, 1050–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Gong, Q.; Olson, D.H.; Li, J. Commensurate adsorption of hydrocarbons and alcohols in microporous metal organic frameworks. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 836–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decoste, J.B.; Peterson, G.W. Metal−Organic Frameworks for Air Purification of Toxic Chemicals. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 5695–5727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peralta, D.; Chaplais, G.; Simon-Masseron, A.; Barthelet, K.; Pirngruber, G.D. Metal−Organic Framework Materials for Desulfurization by Adsorption. Energy Fuels 2012, 26, 4953–4960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, C.; Zhu, G.; Xia, D. A study of the distribution of sulfur compounds in gasoline fraction produced in China: Part 2. The distribution of sulfur compounds in full-range FCC and RFCC naphthas. Fuel Process Technol. 2002, 79, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Wang, G.; Xu, C.; Gao, J. Study on in Situ Sulfur Removal from Gasoline in Fluid Catalytic Cracking Process. J. Energy Fuels 2012, 26, 3201–3211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C. An overview of new approaches to deep desulfurization for ultra-clean gasoline, diesel fuel and jet fuel. Catal. Today 2003, 86, 211–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Dou, T.; Kang, S.; Li, Q.; Hu, Y. Deep desulfurization of gasoline using ion-exchange zeolites: Cu(I)- and Ag(I)-beta. Fuel Process. Technol. 2009, 90, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, M.; Shengui, J.U.; Feng, X.U.E. Selectivity adsorption of thiophene alkylated derivatives oveρ modified Cu+-13X zeolite. J. Rare Earths 2012, 30, 807–813. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.X.; Huang, H.L.; Li, C.X.; Meng, H.; Zhou Lu, Y.Z.; Zhong, C.L.; Liu, D.H.; Yang, Q.Y. Adsorption Behavior of Metal−Organic Frameworks for Thiophenic Sulfur from Diesel Oil. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 12449–12455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achmann, S.; Hagen, G.; Hämmerle, M.; Malkowsky, I.; Kiener, C.; Moos, R. Sulfur Removal from Low-Sulfur Gasoline and Diesel Fuel by Metal-Organic Frameworks. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2010, 33, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Cheng, Z.; Li, B.; Chen, T.; Zhang, W.; Chen, S.; Yang, Q.; Chang, L.; Che, G.; Ma, H. High-Efficiency Separation of Aromatic Sulfide from Liquid Hydrocarbon Fuel in Conjugated Porous Organic Framework with Polycarbazole Unit. Acs Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 43, 40970–40979. [Google Scholar]
- Mueller, U.; Schubert, M.; Teich, F.; Puetter, H.; Schierle-Arndt, K.; Pastré, J. Metal-organic frameworks—Prospective industrial applications. J. Mater. Chem. 2006, 16, 626–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sano, Y.; Choi, K.H.; Korai, Y.; Mochida, I. Adsorptive removal of sulfur and nitrogen species from a straight run gas oil over activated carbons for its deep hydrodesulfurization. Appl. Catal. B Env. 2004, 49, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnobrich, J.K.; Lebel, O.; Cychosz, K.A.; Dailly, A.; Wong-Foy, A.G.; Matzger, A.J. Linker-directed vertex desymmetrization for the production of coordination polymers with high porosity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 13941–13948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, W.; Hu, J.; Zhou, L.; Li, S.; Hu, X.; Huang, H. Removal of dibenzothiophene with composite adsorbent MOF-5/Cu(I). Energy Fuels 2013, 27, 816–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.A.; Jhung, S.H. Low-temperature loading of Cu+ species over porous metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) and adsorptive desulfurization with Cu+-loaded MOFs. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cychosz, K.A.; Wong-Foy, A.G.; Matzger, A.J. Enabling cleaner fuels: Desulfurization by adsorption to microporous coordination polymers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 14538–14543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Xiao, J.; Wu, Y.; Xian, S.; Miao, G.; Wang, H.; Li, Z. A combined experimental/computational study on the adsorption of organosulfur compounds over metal-organic frameworks from fuels. Langmuir 2014, 30, 1080–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.L.; Lan, Y.Q.; Sakurai, H.; Xu, Q. Unusual regenerable porous metal-organic framework based on a new triple helical molecular necklace for separating organosulfur compounds. Chem. Eur. J. 2012, 18, 16303–16309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rui, J.; Liu, F.; Wang, R.; Lu, Y.; Yang, X. Adsorptive Desulfurization of Model Gasoline by Using Different Zn Sources Exchanged NaY Zeolites. Molecules 2017, 22, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.L.; Fan, H.L.; Tian, Z.; He, E.Y.; Li, Y.; Shangguan, J. Adsorptive removal of sulfur compounds using IRMOF-3 at ambient temperature. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 289, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, T.; Yang, Q.; Meng, C.; Xu, J.; Liu, H.; Hu, J.; Ling, H. Promoting desulfurization capacity and separation efficiency simultaneously by the novel magnetic Fe3O4@PAA@MOF-199. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 41902–41909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Chang, G.; Su, Y.; Xing, H.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, Y.; Ren, Q.; Bao, Z.; Chen, B. A metal-organic framework with immobilized Ag(i) for highly efficient desulfurization of liquid fuels. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 12205–12207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, H.S.; Ko, C.H.; Ahn, W.; Kim, B.J.; Croiset, E.; Chen, Z.; Nam, S.C. Selective dibenzothiophene adsorption on graphene prepared using different methods. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 10259–10264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.W.; Yang, G.S.; Tang, Y.J.; Li, S.L.; Zhang, S.R.; Su, Z.M.; Lan, Y.Q. Phenyl Groups Result in the Highest Benzene Storage and Most Efficient Desulfurization in a Series of Isostructural Metal-Organic Frameworks. Chem. Eur. J. 2015, 21, 9784–9789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullah, L.; Zhao, G.; Hedin, N.; Ding, X.; Zhang, S.; Yao, X.; Nie, Y.; Zhang, Y. Highly efficient adsorption of benzothiophene from model fuel on a metal-organic framework modified with dodeca-tungstophosphoric acid. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.A.; Bhadra, B.N.; Jhung, S.H. Heteropoly acid-loaded ionic liquid@metal-organic frameworks: Effective and reusable adsorbents for the desulfurization of a liquid model fuel. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 334, 2215–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Zuhra, Z.; Qin, L.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, L.; Tang, F.; Mu, C. Confinement of microporous MOF-74(Ni) within mesoporous γ-Al2O3 beads for excellent ultra-deep and selective adsorptive desulfurization performance. Fuel Process. Technol. 2018, 176, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.A.; Kim, C.M.; Jhung, S.H. Adsorptive desulfurization using Cu–Ce/metal–organic framework: Improved performance based on synergy between Cu and Ce. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 311, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.F.; Wang, Z.; Feng, Y.; Zhong, Y.; Liao, J.; Wang, Y.; Yao, J. Adsorptive desulfurization from the model fuels by functionalized UiO-66(Zr). Fuel 2018, 234, 256–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Li, X.; Dai, W.; Fang, Y.; Huang, H. Enhanced adsorption of dibenzothiophene with zinc/copper-based metal-organic frameworks. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 21044–21050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, Z.; Jhung, S.H. Facile Method to Disperse Nonporous Metal Organic Frameworks: Composite Formation with a Porous Metal Organic Framework and Application in Adsorptive Desulfurization. Acs Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 10429–10435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Xin, C.; Yin, Y.; Tian, X.; Li, Y.; Bian, W.; Lian, P. Metal organic framework as an adsorbent for desulphurization. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2012, 30, 483–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jhung, S.H.; Khan, N.A.; Hasan, Z. Analogous porous metal-organic frameworks: Synthesis, stability and application in adsorption. Cryst. Eng. Comm. 2012, 14, 7099–7109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit, C.; Bandosz, T.J. Exploring the coordination chemistry of MOF-graphite oxide composites and their applications as adsorbents. Dalt. Trans. 2012, 41, 4027–4035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, I.; Jhung, S.H. Adsorptive desulfurization and denitrogenation using metal-organic frameworks. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 301, 259–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furukawa, S.; Reboul, J.; Diring, S.; Sumida, K.; Kitagawa, S. Structuring of metal-organic frameworks at the mesoscopic/macroscopic scale. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 5700–5734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuhra, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Qin, L.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, L.; Ali, S.; Tang, F.; Ping, E. In situ formation of a multiporous MOF(Al)@γ-AlOOH composite material: A versatile adsorbent for both N- and S-heterocyclic fuel contaminants with high selectivity. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 360, 1623–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Peng, Y.; Chen, Q. Adsorption of N/S-Heteroaromatic Compounds from Fuels by Functionalized MIL-101(Cr) Metal-Organic Frameworks: The Impact of Surface Functional Groups. Energy Fuels 2016, 30, 5593–5600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.; Zhou, Y.; Li, D.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, Z.; Zuhra, Z.; Mu, C. Highly Dispersed HKUST-1 on Milimeter-Sized Mesoporous γ-Al2O3 Beads for Highly Effective Adsorptive Desulfurization. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 7249–7258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, I.; Khan, N.A.; Zubair Hasan, Z.; Sung Hwa Jhung, A.H. Adsorptive denitrogenation of model fuels with porous metal-organic framework (MOF) MIL-101 impregnated with phosphotungstic acid: Effect of acid site inclusion. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 250–251, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, N.A.; Jhung, S.H. Adsorptive removal of benzothiophene using porous copper- benzenetricarboxylate loaded with phosphotungstic acid. Fuel Process. Technol. 2012, 100, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, I.; Khan, N.A.; Jhung, S.H. Graphite oxide/metal-organic framework (MIL-101): Remarkable performance in the adsorptive denitrogenation of model fuels. Inorg. Chem. 2013, 52, 14155–14161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radwan, D.R.; Matloob, A.; Mikhail, S.; Saad, L.; Guirguis, D. Metal organic framework-graphene nano-composites for high adsorption removal of DBT as hazard material in liquid fuel. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 373, 447–458. [Google Scholar]
- Emam, H.E.; Ahmed, H.B.; El-Deib, H.R.; El-Dars, F.M.S.E.; Abdelhameed, R.M. Non-invasive route for desulfurization of fuel using infrared-assisted MIL-53(Al)-NH2 containing fabric. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 556, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasan, Z.; Jhung, S.H. Removal of hazardous organics from water using metal-organic frameworks (MOFs): Plausible mechanisms for selective adsorptions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 283, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, K.; Ni, J.; Cui, Y.; Han, H.; Xie, Y.; Liu, Y. Desulfurization by liquid phase adsorption: Role of exposed metal sites in metal-organic frameworks. J. Mol. Struct. 2019, 1184, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maes, M.; Trekels, M.; Boulhout, M.; Schouteden, S.; Vermoortele, F.; Alaerts, L.; Heurtaux, D.; Seo, Y.K.; Hwang, Y.K.; Chang, J.S.; et al. Selective removal of N-heterocyclic aromatic contaminants from fuels by lewis acidic metal-organic frameworks. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 4210–4214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grajciar, L.; Bludský, O.; Nachtigall, P. Water adsorption on coordinatively unsaturated sites in CuBTC MOF. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2010, 1, 3354–3359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietzel, P.D.C.; Besikiotis, V.; Blom, R. Application of metal-organic frameworks with coordinatively unsaturated metal sites in storage and separation of methane and carbon dioxide. J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 7362–7370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.W.; Seo, Y.K.; Hwang, Y.K.; Chang, J.S.; Leclerc, H.; Wuttke, S.; Bazin, P.; Vimont, A.; Daturi, M.; Bloch, E.; et al. Controlled reducibility of a metal-organic framework with coordinatively unsaturated sites for preferential gas sorption. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 5949–5952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, Y.K.; Hong, D.Y.; Chang, J.S.; Jhung, S.H.; Seo, Y.K.; Kim, J.; Vimont, A.; Daturi, M.; Serre, C.; Férey, G. Amine grafting on coordinatively unsaturated metal centers of MOFs: Consequences for catalysis and metal encapsulation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 4144–4148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, N.A.; Jhung, S.H. Adsorptive removal and separation of chemicals with metal-organic frameworks: Contribution of π-complexation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 325, 198–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furukawa, H.; Go, Y.B.; Ko, N.; Park, Y.K.; Uribe-Romo, F.J.; Kim, J.; O’Keeffe, M.; Yaghi, O.M. Isoreticular expansion of metal-organic frameworks with triangular and square building units and the lowest calculated density for porous crystals. Inorg. Chem. 2011, 50, 9147–9152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, Y.S.; Dubbeldam, D.; Nelson, A.; Walton, K.S.; Hupp, J.T.; Snurr, R.Q. Strategies for characterization of large-pore metal-organic frameworks by combined experimental and computational methods. Chem. Mater. 2009, 21, 4768–4777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, L.; Seow, J.Y.R.; Skinner, W.S.; Wang, Z.U.; Jiang, H.-L. Metal–organic frameworks: Structures and functional applications. Mater. Today 2019, 27, 43–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, M.; Liu, Y.; Schaffino, R.M.; Xiang, S.; Zhao, X.; Zhu, G.S.; Qiu, S.L.; Chen, B. New prototype isoreticular metal - Organic framework Zn4O(FMA)3 for gas storage. Inorg. Chem. 2009, 48, 4649–4651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farha, O.K.; Eryazici, I.; Jeong, N.C.; Hauser, B.G.; Wilmer, C.E.; Sarjeant, A.A.; Snurr, R.Q.; Nguyen, S.T.; Yazaydin, A.Ö.; Hupp, J.T. Metal-organic framework materials with ultrahigh surface areas: Is the sky the limit? J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 15016–15021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit, C.; Bandosz, T.J. Engineering the surface of a new class of adsorbents: Metal-organic framework/graphite oxide composites. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 447, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandosz, T.J.; Petit, C. MOF/graphite oxide hybrid materials: Exploring the new concept of adsorbents and catalysts. Adsorption 2011, 17, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit, C.; Bandosz, T.J. MOF-graphite oxide composites: Combining the uniqueness of graphene layers and metal-organic frameworks. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 4753–4757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahim, A.M.; Jagiello, J.; Bandosz, T.J. Enhanced reactive adsorption of H 2 S on Cu–BTC/ S- and N-doped GO composites. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 8194–8204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannakoudakis, D.A.; Bandosz, T.J. Graphite Oxide Nanocomposites for Air Stream Desulfurization. In Composite Nanoadsorbents; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Giannakoudakis, D.A.; Jiang, M.; Bandosz, T.J. Highly efficient air desulfurization on self-assembled bundles of copper hydroxide nanorods. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 31986–31994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Ding, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, N.; Yang, B.; Ma, L. Adsorptive desulfurization of thiophene from the model fuels onto graphite oxide/metal-organic framework composites. Pet. Sci. Technol. 2018, 36, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.; Chen, C.; Bedoya, F.E.; Kelsall, G.H.; O’Hare, D.; Petit, C. Carbon nitride nanosheet/metal–organic framework nanocomposites with synergistic photocatalytic activities. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2016, 6, 5042–5051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yuan, X.; Wu, Y.; Zeng, G.; Chen, X.; Leng, L.; Li, H. Synthesis and applications of novel graphitic carbon nitride/metal-organic frameworks mesoporous photocatalyst for dyes removal. Appl. Catal. B Env. 2015, 174–175, 445–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Zhang, X.; Song, H.; Chen, C.; Han, F.; Wen, C. Protonated graphitic carbon nitride coated metal-organic frameworks with enhanced visible-light photocatalytic activity for contaminants degradation; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Giannakoudakis, D.A.; Travlou, N.A.; Secor, J.; Bandosz, T.J. Oxidized g-C 3 N 4 Nanospheres as Catalytically Photoactive Linkers in MOF/g-C3N4 Composite of Hierarchical Pore Structure. Small 2017, 13, 1601758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannakoudakis, D.A.; Hu, Y.; Florent, M.; Bandosz, T.J. Smart textiles of MOF/g-C 3 N 4 nanospheres for the rapid detection/detoxification of chemical warfare agents. Nanoscale Horiz. 2017, 2, 356–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannakoudakis, D.A.; Bandosz, T.J. Defectous UiO-66 MOF Nanocomposites as Reactive Media of Superior Protection against Toxic Vapors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
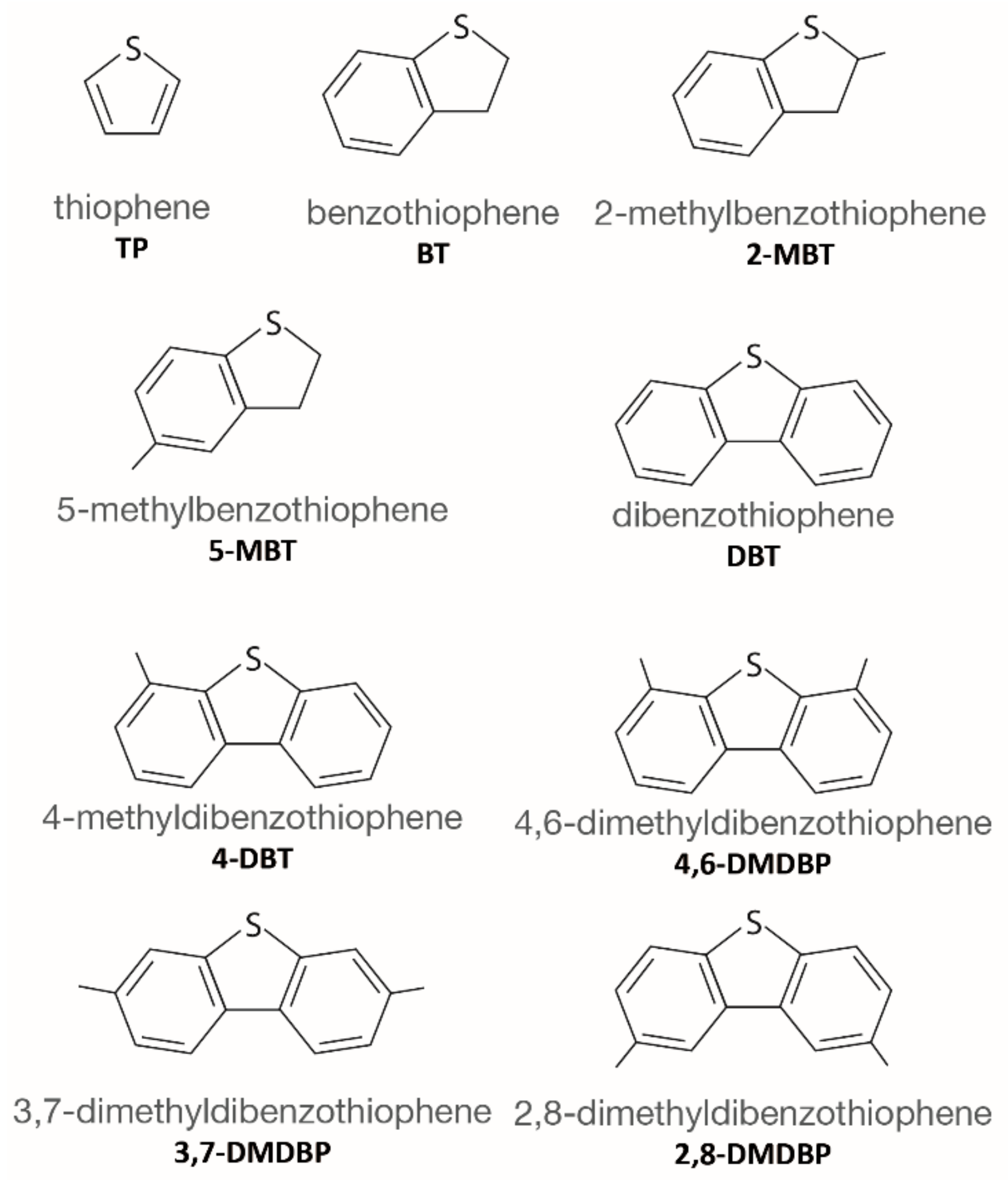




| Adsorbent | Conditions or Remarks | Adsorption Capacity (mmol/g) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| MIL-53(Cr) | n-Octane solvent, 298 K | 0.60 | [89] |
| MIL-53(Al) | 0.26 | [89] | |
| MIL-47(V) | 1.6 | [89] | |
| NENU-511 | i-Octane solvent, 298 K | 2.2 | [99] |
| NENU-512 | n-octane | 1.4 | [99] |
| NENU-513 | 1.1 | [99] | |
| NENU-514 | 1.0 | [99] | |
| Zr(BTC) | liquid fuel | 290 mg/g | [100] |
| ZIF-8 | n-octane | 45 | [101] |
| MIL-100(Fe) | 114 | [101] | |
| MIL-101(Cr) | 35.77% | [92] | |
| MIL-100(Fe) | 20.76% | [92] | |
| MOF-74(Ni) MIL-101 | 76.97 36.4 | [102] [103] | |
| UiO-66 | 19.83 | [104] | |
| HKUST-1 | 18.2 | [92] |
| Adsorbent | Conditions or Remarks Solvent, Temperature (K) | Adsorption Capacity | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| NENU-511 | i-Octane | 2.6 mmol/g | [99] |
| NENU-512 | 2.2 mmol/g | [99] | |
| NENU-513 | 2.0 mmol/g | [99] | |
| NENU-514 | 1.9 mmol/g | [99] | |
| HKUST-1 | 7.7 mgS/g | [92] | |
| MIL-101(Cr) | n-octane | 32.5 mgS/g | [92] |
| ZIF-8 | 45 mgS/g | [101] | |
| MIL-100(Fe) | 114 mgS/g | [101] | |
| MOF-101 | 52.4 mg/g | [101] | |
| MIL-100(Fe) | 35.77% | [101] | |
| MIL-101(Cr) | 20.76% | [101] | |
| MOF-74(Ni) | 85.05% | [102] | |
| MOF-505 | 39.2% | [91] | |
| MOF-199 | dodecane | 90% | [105] |
| Adsorbent | Adsorbate (SCC) | Conditions or Remarks Solvent, Temperature (K) | Adsorption Capacity (mmol/g) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| UMCM-152 | DBT/DMDBT | i-Octane, 298 K | 1.8, 2.6 | [38] |
| UMCM-153 | 2.8, 1.2 | [38] | ||
| MIL-101(Cr) | Octane, 298 K | 0.20/0.17 | [65] | |
| MIL-100(Fe) | 0.20/0.25 | [65] | ||
| HKUST-1 | 0.57/0.28 | [65] | ||
| MOF-505 | BT/DBT/DMDBT | i-Octane, 298 K | 0.38/0.21/0.13 | [91] |
| UMCM-150 | 0.30/0.45/0.19 | [65] | ||
| HKUST-1 | 0.19/0.24/0.08 | [65] |
| Adsorbent | Functionalizing Group | Adsorbate (SCC) | Solvent | Adsorption Capacity (mgS/g) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIL-53(Al) | Al | BD | n-octane | 8.3 | [112,113] |
| MIL-53(Cr) | Cr | 23.6 | [112,113] | ||
| IL/MIL-101(Cr) | Cr | 0.65 | [112,113] | ||
| MIL-101 | - | 36.4 | [102] | ||
| Cu/MIL-101 | Cu | 52.0 | [102] | ||
| Ce/MIL-101 | Ce | 45.6 | [102] | ||
| Cu-Ce/MIL-101 | Cu-Ce | 62.1 | [102] | ||
| Cu-MIL-100-Fe | Cu | - | [101] | ||
| Cu2O/MIL-100(Fe) | Cu2O | 1.1 | [101] | ||
| CuCl/MIL-47(V) | CuCl | 2.3 | [74] | ||
| MOF-74(Ni)@γ-Al2O3 | γ-Al2O3 | 87.77 | [102] | ||
| UiO-66-NH2 | –NH2 | - | [104] | ||
| UiO-66-COOH | –COOH | 22.6 | [104] | ||
| HPA/IL@ZIF-8 | HPA | 68 | [101] | ||
| HPA/IL@MIL-100(Fe) | HPA | 167 | [101] | ||
| PWA/HKUST-1 | PWA | 1.1 | [110] | ||
| HPW(1.5)/Zr(BTC) | HPW | liquid fuel | 238 | [100] | |
| Al(OH)(1,4-NDC)@γ-AlOOH | γ-AlOOH | - | [112] | ||
| MIL-101(Cr)-SO3H | –SO3H | BT, DBT | n-octane | 9.95, 2.14 | [92] |
| MIL-101(Cr)- SO3Ag | –SO3Ag | 28.8, 31 | [92] | ||
| MIL-101(Cr)-NH2 | –NH2 | 2.6, 5.6 | [97] | ||
| MIL-101(Cr)-NO2 | –NO2 | 1.2, 2.1 | [97] | ||
| Ag+/MOF-101(L) | Ag+ | DBT | 50.9 | [92] | |
| Ag+/MOF-101(M) | Ag+ | 47.8 | [92] | ||
| Ag+/MOF-101(H) | Ag+ | 42.7 | [92] | ||
| Cu-BTC/Gr | 46.2 | [105] | |||
| CuCl/MOF-5 | CuCl | 3.4 | [105] | ||
| MOF-74(Ni)@-γAl2O3 | γ-Al2O3 | 76.97% | [114,115] | ||
| MOF-74(Ni)@γ-Al2O3 | γ-Al2O3 | 93.43% | [114,115] | ||
| HPA/IL@MIL-100(Fe) | HPA | 167 | [101] | ||
| HPA/IL@ZIF-8 | HPA | 65 | [101] | ||
| PTA@MIL-101(Cr) | PTA | 136.5 | [116,117] | ||
| PWA/MIL-101(Cr) | PWA | 0.35 | [65] |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kampouraki, Z.-C.; Giannakoudakis, D.A.; Nair, V.; Hosseini-Bandegharaei, A.; Colmenares, J.C.; Deliyanni, E.A. Metal Organic Frameworks as Desulfurization Adsorbents of DBT and 4,6-DMDBT from Fuels. Molecules 2019, 24, 4525. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24244525
Kampouraki Z-C, Giannakoudakis DA, Nair V, Hosseini-Bandegharaei A, Colmenares JC, Deliyanni EA. Metal Organic Frameworks as Desulfurization Adsorbents of DBT and 4,6-DMDBT from Fuels. Molecules. 2019; 24(24):4525. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24244525
Chicago/Turabian StyleKampouraki, Zoi-Christina, Dimitrios A. Giannakoudakis, Vaishakh Nair, Ahmad Hosseini-Bandegharaei, Juan Carlos Colmenares, and Eleni A. Deliyanni. 2019. "Metal Organic Frameworks as Desulfurization Adsorbents of DBT and 4,6-DMDBT from Fuels" Molecules 24, no. 24: 4525. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24244525
APA StyleKampouraki, Z.-C., Giannakoudakis, D. A., Nair, V., Hosseini-Bandegharaei, A., Colmenares, J. C., & Deliyanni, E. A. (2019). Metal Organic Frameworks as Desulfurization Adsorbents of DBT and 4,6-DMDBT from Fuels. Molecules, 24(24), 4525. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24244525