The Role of c-Met as a Biomarker and Player in Innate and Acquired Resistance in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Two New Mutations Warrant Further Studies
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
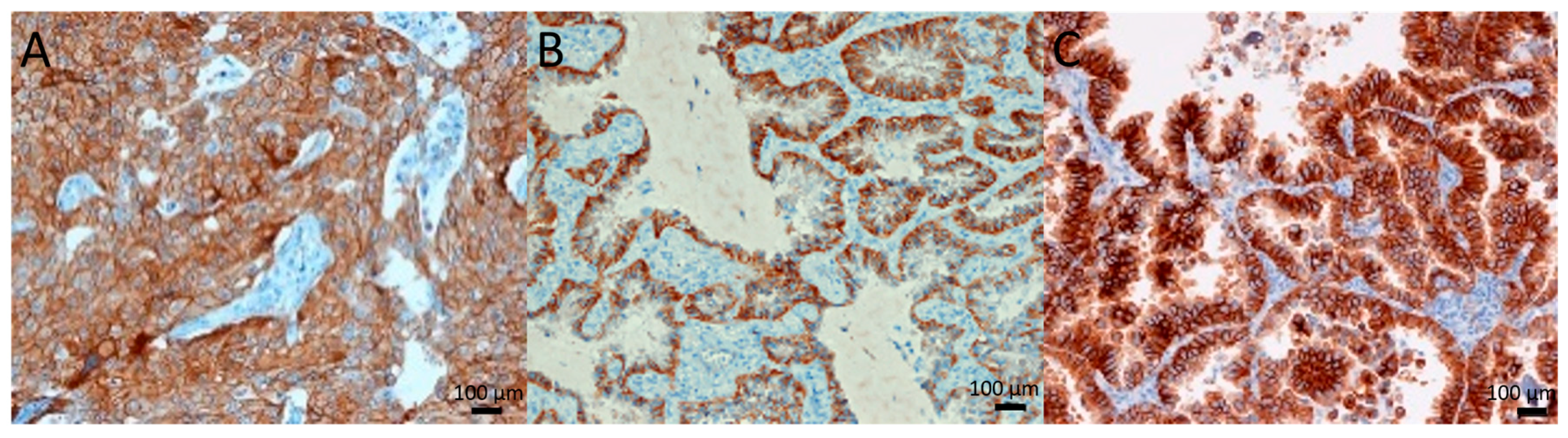
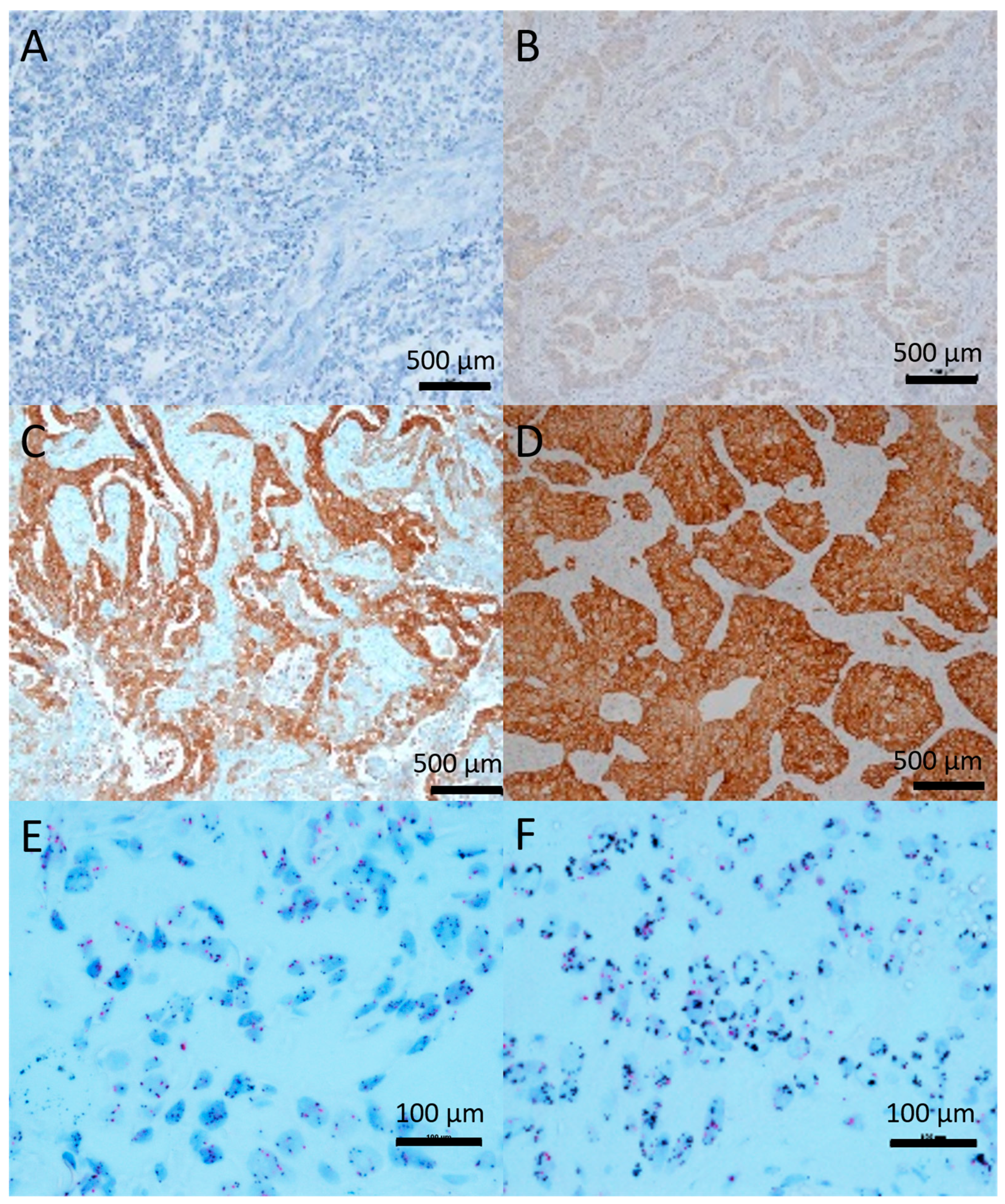
2.1. c-Met Expression and Gene Amplification
2.2. c-Met Primary Tumor Versus Metastasis
2.3. Correlation between c-Met and EGFR
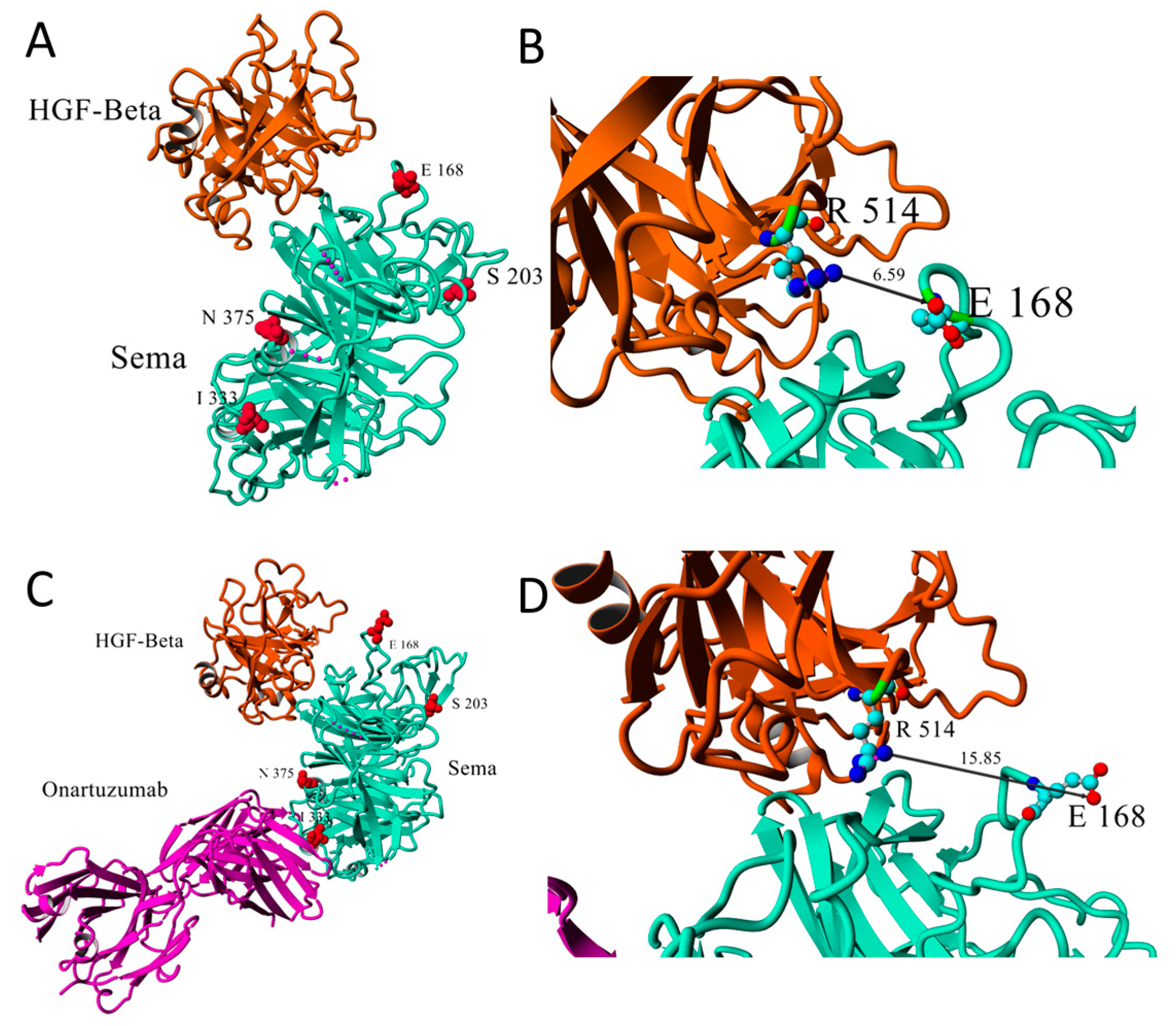
2.4. c-Met and TP53 Mutations
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patients
4.2. IHC and CISH
4.3. EGFR-Mutation Analysis
4.4. Next Generation Sequencing
4.5. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Van Der Steen, N.; Rolfo, C.; Pauwels, P.; Peters, G.J.; Giovannetti, E. New developments in the management of non- small-cell lung cancer, focus on rociletinib: What went wrong? Onco. Targets Ther. 2016, 9, 6065–6074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rosas, G.; Ruiz, R.; Araujo, J.M.; Pinto, J.A.; Mas, L. ALK rearrangements: Biology, detection and opportunities of therapy in non-small cell lung cancer. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2019, 136, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bean, J.; Brennan, C.; Shih, J.-Y.; Riely, G.; Viale, A.; Wang, L.; Chitale, D.; Motoi, N.; Szoke, J.; Broderick, S.; et al. MET amplification occurs with or without T790M mutations in EGFR mutant lung tumors with acquired resistance to gefitinib or erlotinib. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 20932–20937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cappuzzo, F.; Jänne, P.A.; Skokan, M.; Finocchiaro, G.; Rossi, E.; Ligorio, C.; Zucali, P.A.; Terracciano, L.; Toschi, L.; Roncalli, M.; et al. MET increased gene copy number and primary resistance to gefitinib therapy in non-small-cell lung cancer patients. Ann. Oncol. 2009, 20, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelman, J.A.; Zejnullahu, K.; Mitsudomi, T.; Song, Y.; Hyland, C.; Park, J.O.; Lindeman, N.; Gale, C.-M.M.; Zhao, X.; Christensen, J.; et al. MET amplification leads to gefitinib resistance in lung cancer by activating ERBB3 signaling. Science 2007, 316, 1039–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Steen, N.; Pauwels, P.; Gil-Bazo, I.; Castanon, E.; Raez, L.; Cappuzzo, F.; Rolfo, C. c-Met in NSCLC: Can we cut off the head of the Hydra? From the pathway to the resistance. Cancers 2015, 7, 556–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conrotto, P.; Corso, S.; Gamberini, S.; Comoglio, P.M.; Giordano, S. Interplay between scatter factor receptors and B plexins controls invasive growth. Oncogene 2004, 23, 5131–5137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kajiya, K.; Hirakawa, S.; Ma, B.; Drinnenberg, I.; Detmar, M. Hepatocyte growth factor promotes lymphatic vessel formation and function. EMBO J. 2005, 24, 2885–2895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bussolino, F.; Di Renzo, M.F.; Ziche, M.; Bocchietto, E.; Olivero, M.; Naldini, L.; Gaudino, G.; Tamagnone, L.; Coffer, A.; Comoglio, P.M. Hepatocyte growth factor is a potent angiogenic factor which stimulates endothelial cell motility and growth. J. Cell Biol. 1992, 119, 629–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell, J.; Kelly, C.; Rauch, J.; Kida, K.; Garc??a-Mu??oz, A.; Monsefi, N.; Turriziani, B.; Doherty, C.; Mehta, J.P.; Matallanas, D.; et al. HGF induces epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition by modulating the mammalian Hippo/MST2 and ISG15 pathways. J. Proteome Res. 2014, 13, 2874–2886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, A.; Villén, J.; Kornhauser, J.; Lee, K.A.; Stokes, M.P.; Rikova, K.; Possemato, A.; Nardone, J.; Innocenti, G.; Wetzel, R.; et al. Signaling networks assembled by oncogenic EGFR and c-Met. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 692–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Breindel, J.L.; Haskins, J.W.; Cowell, E.P.; Zhao, M.; Nguyen, D.X.; Stern, D.F. EGF receptor activates MET through MAPK to enhance non-small cell lung carcinoma invasion and brain metastasis. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 5053–5065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dulak, A.M.; Ph, D.; Gubish, C.T.; Stabile, L.P.; Siegfried, J.M. HGF-independent potentiation of EGFR action by c-Met. Oncogene 2011, 30, 3625–3635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tomasello, C.; Baldessari, C.; Napolitano, M.; Orsi, G.; Grizzi, G.; Bertolini, F.; Barbieri, F.; Cascinu, S. Resistance to EGFR inhibitors in non-small cell lung cancer: Clinical management and future perspectives. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2018, 123, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuta, K.; Kozu, Y.; Mimae, T.; Yoshida, A.; Kohno, T.; Sekine, I.; Tamura, T.; Asamura, H.; Furuta, K.; Tsuda, H. c-MET/phospho-MET protein expression and MET gene copy number in non-small cell lung carcinomas. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2012, 7, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, B.; Cen, H.; Tan, X.; Liu, W.; Ke, Q. Prognostic value of MET gene copy number and protein expression in patients with surgically resected non-small cell lung cancer: A meta-analysis of published literatures. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e99399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Steen, N.; Giovannetti, E.; Pauwels, P.; Peters, G.J.; Hong, D.S.; Cappuzzo, F.; Hirsch, F.R.; Rolfo, C. cMET exon 14 skipping: From the structure to the clinic. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2016, 11, 1423–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Camidge, D.R.; Ou, S.I.; Shapiro, G.I.; Otterson, G.A.; Villaruz, L.C.; Villalona-Calero, M.A.; Iafrate, A.J.; Varella-Garcia, M.; Dacic, S.; Cardarella, S.; et al. Efficacy and safety of crizotinib in patients with advanced c-MET-amplified non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 8001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peschard, P.; Fournier, T.M.; Lamorte, L.; Naujokas, M.A.; Band, H.; Langdon, W.Y.; Park, M. Mutation of the c-Cbl TKB domain binding site on the Met receptor tyrosine kinase converts it into a transforming protein. Mol. Cell 2001, 8, 995–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, P.C.; Kijima, T.; Maulik, G.; Fox, E.A.; Sattler, M.; Griffin, J.D.; Johnson, B.E.; Salgia, R. c-MET Mutational Analysis in Small Cell Lung Cancer: Novel Juxtamembrane Domain Mutations Regulating Cytoskeletal Functions c-MET Mutational Analysis in Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 6272–6281. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, P.C.; Jagadeeswaran, R.; Jagadeesh, S.; Tretiakova, M.S.; Nallasura, V.; Fox, E.A.; Hansen, M.; Schaefer, E.; Naoki, K.; Lader, A.; et al. Functional expression and mutations of c-Met and its therapeutic inhibition with SU11274 and small interfering RNA in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 1479–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cui, J.J.; Tran-Dubé, M.; Shen, H.; Nambu, M.; Kung, P.P.; Pairish, M.; Jia, L.; Meng, J.; Funk, L.; Botrous, I.; et al. Structure based drug design of crizotinib (PF-02341066), a potent and selective dual inhibitor of mesenchymal-epithelial transition factor (c-MET) kinase and anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK). J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 6342–6363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neal, J.W.; Dahlberg, S.E.; Wakelee, H.A.; Aisner, S.C.; Bowden, M.; Carbone, D.P.; Ramalingam, S.S. Cabozantinib (C), erlotinib (E) or the combination (E+C) as second- or third-line therapy in patients with EGFR wild-type (wt) non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): A randomized phase 2 trial of the ECOG-ACRIN Cancer Research Group (E1512). J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 8003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.-L.; Yang, J.C.-H.; Kim, D.-W.; Su, W.-C.; Ahn, M.-J.; Lee, D.H.; Vansteenkiste, J.F.; Zhang, L.; Felip, E.; Peng, B.; et al. Safety and efficacy of INC280 in combination with gefitinib (gef) in patients with EGFR-mutated (mut), MET-positive NSCLC: A single-arm phase lb/ll study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 8017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bladt, F.; Friese-Hamim, M.; Ihling, C.; Wilm, C.; Blaukat, A. The c-Met Inhibitor MSC2156119J Effectively Inhibits Tumor Growth in Liver Cancer Models. Cancers 2014, 6, 1736–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshioka, H.; Azuma, K.; Yamamoto, N.; Takahashi, T.; Nishio, M.; Katakami, N.; Ahn, M.J.; Hirashima, T.; Maemondo, M.; Kim, S.W.; et al. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase III trial of erlotinib with or without a c-Met inhibitor tivantinib (ARQ 197) in Asian patients with previously treated stage IIIB/IV nonsquamous nonsmall-cell lung cancer harboring wild-type epidermal growth factor receptor (ATTENTION study). Ann. Oncol. 2015, 26, 2066–2072. [Google Scholar]
- Rolfo, C.; Van Der Steen, N.; Pauwels, P.; Cappuzzo, F. Onartuzumab in lung cancer: The fall of Icarus? Expert Rev. Anticancer Ther. 2015, 15, 487–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- David, R.S.; Edelman, M.J.; O’Byrne, K.; Paz-Ares, L.; Shames, D.S.; Yu, W.; Paton, V.E.; Mok, T. Onartuzumab plus erlotinib versus erlotinib in previously treated stage IIIb or IV NSCLC: Results from the pivotal phase 3 randomized, multicenter, placebo-controlled METLung (OAM4971g) global trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 8000. [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham, D.; Tebbutt, N.C.; Davidenko, I.; Murad, A.M.; Al-Batran, S.-E.; Ilson, D.H.; Tjulandin, S.; Gotovkin, E.; Karaszewska, B.; Bondarenko, I.; et al. Phase III, randomized, double-blind, multicenter, placebo (P)-controlled trial of rilotumumab (R) plus epirubicin, cisplatin and capecitabine (ECX) as first-line therapy in patients (pts) with advanced MET-positive (pos) gastric or gastroesophageal juncti. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 4000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mok, T.S.; Park, K.; Geater, S.L.; Agarwal, S.; Han, M.; Credi, M.; McKee, K.; Kuriyama, N.; Slichenmyer, W.; Tan, E.H. A randomized phase 2 study with exploratory biomarker analysis of ficlatuzumab a humanized hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) inhibitory monoclonal antibody, in combination with gefitinib versus gefitinib alone in Asian patients with lung adenocarcinoma. Ann. Oncol. 2012, 23, 1198P. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, H.A.; Planchard, D.; Lovly, C.M. Sequencing Therapy for Genetically Defined Subgroups of Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. Educ. Book 2018, 38, 726–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heymach, J.; Negrao, M.; Robichaux, J.; Carter, B.; Patel, A.; Altan, M.; Gibbons, D.; Fossella, F.; Simon, G.; Lam, V.; et al. A Phase II Trial of Poziotinib in EGFR and HER2 exon 20 Mutant Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC). J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018, 13, S323–S324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, T.; Wan, B.; Zhao, Y.; Li, C.; Liu, H.; Lv, T.; Zhan, P.; Song, Y. Treatment of uncommon EGFR mutations in non-small cell lung cancer: New evidence and treatment. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2019, 8, 302–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Yang, N.; Ou, Q.; Xiang, Y.; Jiang, T.; Wu, X.; Bao, H.; Tong, X.; Wang, X.; Shao, Y.W.; et al. Investigating novel resistance mechanisms to third-generation EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor osimertinib in non–small cell lung cancer patients. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 3097–3107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thress, K.S.; Paweletz, C.P.; Felip, E.; Cho, B.C.; Stetson, D.; Dougherty, B.; Lai, Z.; Markovets, A.; Vivancos, A.; Kuang, Y.; et al. Acquired EGFR C797S mutation mediates resistance to AZD9291 in non-small cell lung cancer harboring EGFR T790M. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 560–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, S.; Tsui, S.T.; Liu, C.; Song, Y.; Liu, D. EGFR C797S mutation mediates resistance to third-generation inhibitors in T790M-positive non-small cell lung cancer. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2016, 9, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Minari, R.; Bordi, P.; Tiseo, M. Third-generation epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitors in T790M-positive non-small cell lung cancer: Review on emerged mechanisms of resistance. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2016, 5, 695–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Song, Y.; Liu, D. EAI045: The fourth-generation EGFR inhibitor overcoming T790M and C797S resistance. Cancer Lett. 2017, 385, 51–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogi, A.; Kuwano, H. TP53 mutations in nonsmall cell lung cancer. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2011, 2011, 583929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Robles, A.I.; Jen, J.; Harris, C.C. Clinical outcomes of TP53 mutations in cancers. Perspect. Med. 2016, 6, a026294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hwang, C.-I.; Matoso, A.; Corney, D.C.; Flesken-Nikitin, A.; Körner, S.; Wang, W.; Boccaccio, C.; Thorgeirsson, S.S.; Comoglio, P.M.; Hermeking, H.; et al. Wild-type p53 controls cell motility and invasion by dual regulation of MET expression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 14240–14245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hwang, C.I.; Choi, J.; Zhou, Z.; Flesken-Nikitin, A.; Tarakhovsky, A.; Nikitin, A.Y. MET-dependent cancer invasion may be preprogrammed by early alterations of p53-regulated feedforward loop and triggered by stromal cell-derived HGF. Cell Cycle 2011, 10, 3834–3840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muller, P.A.J.; Trinidad, A.G.; Timpson, P.; Morton, J.P.; Zanivan, S.; van den Berghe, P.V.E.; Nixon, C.; Karim, S.A.; Caswell, P.T.; Noll, J.E.; et al. Mutant p53 enhances MET trafficking and signalling to drive cell scattering and invasion. Oncogene 2013, 32, 1252–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, Y.; Tong, X.; Yan, J.; Wu, X.; Shao, Y.W.; Fan, Y. Short-Term Responders of Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients to EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors Display High Prevalence of TP53 Mutations and Primary Resistance Mechanisms. Transl. Oncol. 2018, 11, 1364–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamos, J.; Lazarus, R.A.; Yao, X.; Kirchhofer, D.; Wiesmann, C. Crystal structure of the HGF beta-chain in complex with the Sema domain of the Met receptor. EMBO J. 2004, 23, 2325–2335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merchant, M.; Ma, X.; Maun, H.R.; Zheng, Z.; Peng, J.; Romero, M.; Huang, A.; Yang, N.; Nishimura, M.; Greve, J.; et al. Monovalent antibody design and mechanism of action of onartuzumab, a MET antagonist with anti-tumor activity as a therapeutic agent. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, E2987–E2996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krishnaswamy, S.; Kanteti, R.; Duke-cohan, J.S.; Loganathan, S.; Liu, W.; Ma, P.C.; Sattler, M.; Singleton, P.A.; Ramnath, N.; Innocenti, F.; et al. Ethnic differences and functional analysis of MET mutations in lung cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 5714–5723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shieh, J.M.; Tang, Y.A.; Yang, T.H.; Chen, C.Y.; Hsu, H.S.; Tan, Y.H.C.; Salgia, R.; Wang, Y.C. Lack of association of C-Met-N375S sequence variant with lung cancer susceptibility and prognosis. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2013, 10, 988–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bouaoun, L.; Sonkin, D.; Ardin, M.; Hollstein, M.; Byrnes, G.; Zavadil, J.; Olivier, M. TP53 Variations in Human Cancers: New Lessons from the IARC TP53 Database and Genomics Data. Hum. Mutat. 2016, 37, 865–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koeppen, H.; Yu, W.; Zha, J.; Pandita, A.; Penuel, E.; Rangell, L.; Raja, R.; Mohan, S.; Patel, R.; Desai, R.; et al. Biomarker Analyses from a Placebo-Controlled Phase II Study Evaluating Erlotinib {+/-} Onartuzumab in Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: MET Expression Levels Are Predictive of Patient Benefit. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 4488–4499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rafal, D.; Murry, W.; Wynes, P.; Shalini, S.; Bernadette, R.A.; James, R.-M.; Krzysztof, K.; Witold, R.; Barbara, S.; Jacek, J.; et al. Correlation between MET Gene Copy Number by Silver in Situ Hybridization and Protein Expression by Immunohistochemistry in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2012, 7, 997–1003. [Google Scholar]
- Weingertner, N.; Meyer, N.; Voegeli, A.-C.; Guenot, D.; Renaud, S.; Massard, G.; Falcoz, P.-E.; Olland, A.; Mennecier, B.; Gaub, M.-P.; et al. Correlation between MET protein expression and MET gene copy number in a Caucasian cohort of non-small cell lung cancers according to the new IASLC/ATS/ERS classification. Pathology 2015, 47, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Steen, N.; Giovannetti, E.; Carbone, D.; Leonetti, A.; Rolfo, C.D.; Peters, G.J. Resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor inhibition in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Drug Resist. 2018, 1, 230–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leonetti, A.; Sharma, S.; Minari, R.; Perego, P.; Giovannetti, E.; Tiseo, M. Resistance mechanisms to osimertinib in EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2019, 121, 725–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grugan, K.D.; Vega, M.E.; Wong, G.S.; Diehl, J.A.; Bass, A.J.; Wong, K.K.; Nakagawa, H.; Rustgi, A.K. A common p53 mutation (R175H) activates c-Met receptor tyrosine kinase to enhance tumor cell invasion. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2013, 14, 853–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakamura, T.; Matsumoto, K.; Kiritoshi, A.; Tano, Y.; Nakamura, T. Induction of hepatocyte growth factor in fibroblasts by tumor-derived factors affects invasive growth of Tumor Cells: In Vitro Analysis Interactions. Cancer Res. 1997, 57, 3305–3313. [Google Scholar]
- BE71030031000; Biobank@UZA, Belgian Virtual Tumourbank Funded by the National Cancer Plan. Available online: virtualtumourbank.kankerregister.org (accessed on 22 October 2014).
- Heideman, D.A.M.; Thunnissen, F.B.; Doeleman, M.; Kramer, D.; Verheul, H.M.; Smit, E.F.; Postmus, P.E.; Meijer, C.J.L.M.; Meijer, G.A.; Snijders, P.J.F. A panel of high resolution melting (HRM) technology-based assays with direct sequencing possibility for effective mutation screening of EGFR and K-ras genes. Cell. Oncol. 2009, 31, 329–333. [Google Scholar]
- Vandeweyer, G.; Van Laer, L.; Loeys, B.; Van den Bulcke, T.; Kooy, R.F. VariantDB: A flexible annotation and filtering portal for next generation sequencing data. Genome Med. 2014, 6, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Mutation | RefSNP | Allelic Balance (%) | MAF | Reads on Position | c-Met-IHC | Histology |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N375S | rs33917957 | 61 | 2.3% | 10230 | 1+ | Adeno |
| E168D | rs55985569 | 50 | 0.5% | 4659 | 3+ | Adeno |
| S203T | rs200861145 | 12 | 0.1% | 2093 | 2+ | Squamous |
| S203T | rs200861145 | 11 | 0.1% | 2709 | 2+ | Adeno |
| S203T | rs200861145 | 15 | 0.1% | 5209 | 1+ | Squamous |
| S203T | rs200861145 | 14 | 0.1% | 4590 | 2+ | Squamous |
| S203T | rs200861145 | 20 | 0.1% | 1816 | 2+ | Adeno |
| E168D | rs55985569 | 43 | 0.5% | 9341 | 3+ | Adeno |
| I333T | NA | 8 | NA | 7765 | 3+ | Squamous |
| G783E | NA | 11 | NA | 1061 | 3+ | Squamous |
| S203T | rs200861145 | 45 | 0.1% | 6009 | 2+ | Adeno |
| C3082+1G>T | rs869320707 | 12 | 0% | 1353 | 2+ | Adeno |
| C2942−1G>A | NA | 39 | NA | 1180 | 3+ | Adeno |
| Sample ID | WT Codon | Mutant Codon | p.Mutant | c.Mutant | Functionality | c-Met | EGFR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8 | TGC | TTC | p.C242F | c.725G>T | Partial function Non-functional | 3+ | WT |
| 9 | GGG | TGG | p.G334W | c.1000G>T | Partial function | 1+ | WT |
| 10 | CGC | CTC | p.R337L | c.1010G>T | Non-functional | 2+ | WT |
| 17 | AGG | ATG | p.R249M | c.746G>T | Non-functional | 3+ | WT |
| 18 | CCT | TCT | p.P278S | c.832C>T | Non-functional | 2+ | L858R |
| 19 | GTC | GAC | p.V157D | c.470T>A | Non-functional | 2+ | WT |
| 58 | GAA | CAA | p.E258Q | c.772G>C | Partial function | 1+ | NA |
| 59 | AGG | ACG | p.R249T | c.746G>C | Non-functional | 2+ | NA |
| 72 | CGC | CTC | p.R175L | c.524G>T | Partial function | 0 | NA |
| 74 | CGA | TGA | p.R342X | c.1024C>T | NA | 2+ | NA |
| 75 | AGA | GGA | p.R280G | c.838A>G | Partial function Non-functional | 1+ | NA |
| 79 | GAC | CAC | p.D281H | c.841G>C | Non-functional | 0 | WT |
| 80 | GAG | AAG | p.E285K | c.853G>A | Non-functional | 2+ | NA |
| 81 | GCC | CCC | p.A276P | c.826G>C | Non-functional | 2+ | NA |
| 85 | GGG | GTG | p.G334V | c.1001G>T | Partial function | 3+ | NA |
| 92 | CGC | CAC | p.R158H | c.473G>A | Non-functional | 3+ | NA |
| 94 | CGT | CTT | p.R273L | c.818G>T | Non-functional | 1+ | NA |
| 97 | AGA | GGA | p.R280G | c.838A>G | Non-functional | 2+ | L858R |
| 97 | GGA | GTA | p.G266V | c.797G>T | Non-functional | 2+ | L858R |
| 97 | GGC | TGC | p.G245C | c.733G>T | Non-functional | 2+ | L858R |
| 101 | CGG | CAG | p.R267Q | c.800G>A | Partial function | 0 | NA |
| 101 | CCT | TCT | p.P190S | c.568C>T | Partial function | 0 | NA |
| 103 | GGT | GTT | p.G262V | c.785G>T | Non-functional | 1+ | NA |
| 104 | CGT | CCT | p.R273P | c.818G>C | Non-functional | 3+ | L858R |
| 105 | AAG | AGG | p.K132R | c.395A>G | Partial function Non-functional | 1+ | NA |
| 117 | GGA | GTA | p.G266V | c.797G>T | Non-functional | 1+ | NA |
| 118 | GAG | TAG | p.E294X | c.880G>T | NA | 0 | NA |
| 121 | CCT | ACT | p.P278T | c.832C>A | Non-functional | 1+ | NA |
| 128 | GTG | GGG | p.V216G | c.647T>G | Non-functional | 2+ | NA |
| 131 | CGA | TGA | p.R196X | c.586C>T | NA | 0 | NA |
| 133 | CCC | TCC | p.P151S | c.451C>T | Non-functional | 0 | NA |
| 136 | GAG | TAG | p.E298X | c.892G>T | NA | 2+ | NA |
| 137 | CAT | CGT | p.H179R | c.536A>G | Partial function Non-functional | 2+ | NA |
| 141 | CAT | CGT | p.H214R | c.641A>G | Non-functional | 2+ | WT |
| 149 | CGT | CTT | p.R273L | c.818G>T | Non-functional | 3+ | WT |
| 153 | CAG | TAG | p.Q192X | c.574C>T | NA | 2+ | L858R |
| 160 | AGA | GGA | p.R280G | c.838A>G | Partial function Non-functional | 2+ | WT |
| Age | Range: 36–78 Years (Mean: 62) | N |
|---|---|---|
| Histology | Adenocarcinoma | 104 |
| Squamous carcinoma | 38 | |
| Large cell (or not otherwise specified, NOS) | 11 | |
| Differentiation | Well | 32 |
| Moderate | 63 | |
| Poor | 26 | |
| Invasiveness | Non-invasive | 49 |
| Invasive | 102 | |
| Gender | Male | 109 |
| Female | 44 | |
| Smoking | Non-smoker | 61 |
| Smoker | 92 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Van Der Steen, N.; Zwaenepoel, K.; Mazzaschi, G.; A. Luirink, R.; P. Geerke, D.; Op de Beeck, K.; Hermans, C.; Tiseo, M.; Van Schil, P.; Lardon, F.; et al. The Role of c-Met as a Biomarker and Player in Innate and Acquired Resistance in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Two New Mutations Warrant Further Studies. Molecules 2019, 24, 4443. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24244443
Van Der Steen N, Zwaenepoel K, Mazzaschi G, A. Luirink R, P. Geerke D, Op de Beeck K, Hermans C, Tiseo M, Van Schil P, Lardon F, et al. The Role of c-Met as a Biomarker and Player in Innate and Acquired Resistance in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Two New Mutations Warrant Further Studies. Molecules. 2019; 24(24):4443. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24244443
Chicago/Turabian StyleVan Der Steen, Nele, Karen Zwaenepoel, Giulia Mazzaschi, Rosa A. Luirink, Daan P. Geerke, Ken Op de Beeck, Christophe Hermans, Marcello Tiseo, Paul Van Schil, Filip Lardon, and et al. 2019. "The Role of c-Met as a Biomarker and Player in Innate and Acquired Resistance in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Two New Mutations Warrant Further Studies" Molecules 24, no. 24: 4443. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24244443
APA StyleVan Der Steen, N., Zwaenepoel, K., Mazzaschi, G., A. Luirink, R., P. Geerke, D., Op de Beeck, K., Hermans, C., Tiseo, M., Van Schil, P., Lardon, F., Germonpré, P., Rolfo, C., Giovannetti, E., J. Peters, G., & Pauwels, P. (2019). The Role of c-Met as a Biomarker and Player in Innate and Acquired Resistance in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Two New Mutations Warrant Further Studies. Molecules, 24(24), 4443. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24244443










