Synthesis and In Vitro Evaluation of Novel Liver X Receptor Agonists Based on Naphthoquinone Derivatives
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
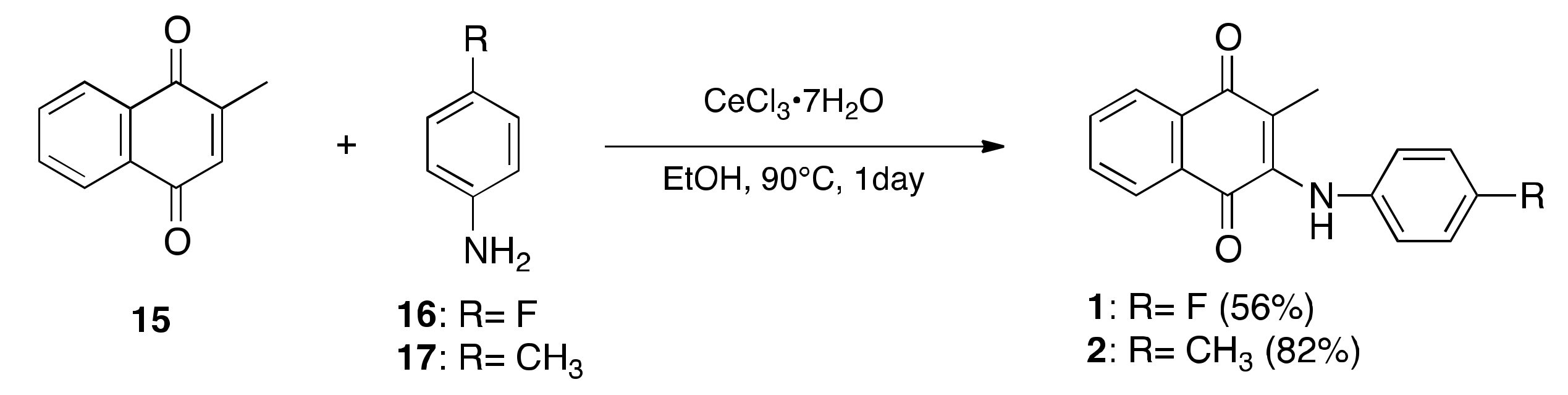
2.1. Synthesis of LXR Ligands
2.2. Transcriptional Activity of LXR Ligand
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Synthetic Method of Compounds
4.1.1. General Experimental Procedures
4.1.2. Preparation of 2-[(4-Fluorophenyl)amino]-3-methylnaphthalene-1,4-dione (1)
4.1.3. Preparation of 2-Methyl-3-[(4-methylphenyl)amino]naphthalene-1,4-dione (2)
4.1.4. Preparation of 2-chloro-3-[(4-fluorophenyl)amino]naphthalene-1,4-dione (20)
4.1.5. Preparation of 2-Chloro-3-[(4-methylphenyl)amino]naphthalene-1,4-dione (21)
4.1.6. Preparation of 2-Chloro-3-{[4-(1,1,1,3,3,3-hexafluoro-2-hydroxypropan-2-yl)phenyl]amino} naphthalene-1,4-dione (22)
4.1.7. Preparation of 2-[(4-Fluorophenyl)amino]-3-(piperidin-1-yl)naphthalene-1,4-dione (3)
4.1.8. Preparation of 2-[(4-Fluorophenyl)amino]-3-(p-tolylamino)naphthalene-1,4-dione (4)
4.1.9. Preparation of 2,3-Bis[(4-methylphenyl)amino]naphthalene-1,4-dione (5)
4.1.10. Preparation of 2[(4-Fluorophenyl)amino]-3-(piperidin-1-yl)naphthalene-1,4-dione (6)
4.1.11. Preparation of 2-(Piperidin-1-yl)-3-[(4-methylphenyl)amino]naphthalene-1,4-dione (7)
4.1.12. Preparation of 2-{[4-(1,1,1,3,3,3-Hexafluoro-2-hydroxypropan-2-yl)phenyl]amino}-3-(piperidin-1-yl)naphthalene- 1,4-dione (8)
4.1.13. Preparation of 2-[(4-Fluorophenyl)amino]-3-(pyrrolidin-1-yl)naphthalene-1,4-dione (9)
4.1.14. Preparation of 2-(Pyrrolidin-1-yl)-3-[(4-methylphenyl)amino]naphthalene-1,4-dione (10)
4.1.15. Preparation of 2-[(4-Fluorophenyl)amino]-3-morpholinonaphthalene-1,4-dione (11)
4.1.16. Preparation of 2-Morpholino-3-[(4-methylphenyl)amino]naphthalene-1,4-dione (12)
4.1.17. Preparation of 2-[(4-Fluorophenyl)amino]-3-(phenylthio)naphthalene-1,4-dione (13)
4.1.18. Preparation of 2-{[4-(1,1,1,3,3,3-Hexafluoro-2-hydroxypropan-2-yl)phenyl]amino}-3-(phenylthio)naphthalene-1,4-dione (14)
4.2. Cell Culture Conditions
4.3. Transient Transfection Assays
4.4. Computational Details
4.5. Molecular Docking Experiment
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schultz, J.R.; Tu, H.; Luk, A.; Repa, J.J.; Medina, J.C.; Li, L.; Schwendner, S.; Wang, S.; Thoolen, M.; Mangelsdorf, D.J.; et al. Role of LXRs in control of lipogenesis. Genes Dev. 2000, 14, 2831–2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkateswaran, A.; Laffitte, B.A.; Joseph, S.B.; Mak, P.A.; Wilpitz, D.C.; Edwards, P.A.; Tontonoz, P. Control of cellular cholesterol efflux by the nuclear oxysterol receptor LXR alpha. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 12097–12102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, M.A.; Venkateswaran, A.; Tarr, P.T.; Xenarios, I.; Kudoh, J.; Shimizu, N.; Edwards, P.A. Characterization of the human ABCG1 gene: Liver X receptor activates an internal promoter that produces a novel transcript encoding an alternative form of the protein. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 39438–39447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cramer, P.E.; Cirrito, J.R.; Wesson, D.W.; Lee, C.Y.; Karlo, J.C.; Zinn, A.E.; Casali, B.T.; Restivo, J.L.; Goebel, W.D.; James, M.J.; et al. ApoE-directed therapeutics rapidly clear β-amyloid and reverse deficits in AD mouse models. Science 2012, 335, 1503–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Namjoshi, D.R.; Martin, G.; Donkin, J.; Wilkinson, A.; Stukas, S.; Fan, J.; Carr, M.; Tabarestani, S.; Wuerth, K.; Hancock, R.E.; et al. The liver X receptor agonist GW3965 improves recovery from mild repetitive traumatic brain injury in mice partly through apolipoprotein E. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e53529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nomura, S.; Endo-Umeda, K.; Makishima, M.; Hashimoto, Y.; Ishikawa, M. Development of tetrachlorophthalimides as liver X receptor β (LXRβ)-selective agonists. ChemMedChem 2016, 11, 2347–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stachel, S.J.; Zerbinatti, C.; Rudd, M.T.; Cosden, M.; Suon, S.; Nanda, K.K.; Wessner, K.; DiMuzio, J.; Maxwell, J.; Wu, Z.; et al. Identification and in vivo evaluation of liver X receptor β-selective agonists for the potential treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 3489–3498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, C.; Hiipalla, R.A.; Liao, S. Selective activation of liver X receptor alpha by 6alpha-hydroxy bile acids and analogs. Steroids 2000, 65, 423–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honzumi, S.; Shima, A.; Hiroshima, A.; Koieyama, T.; Ubukata, N.; Terasaka, N. LXRalpha regulates human CETP expression in vitro and in transgenic mice. Atherosclerosis 2010, 212, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kick, E.K.; Busch, B.B.; Martin, R.; Stevens, W.C.; Bollu, V.; Xie, Y.; Boren, B.C.; Nyman, M.C.; Nanao, M.H.; Nguyen, L.; et al. Discovery of Highly Potent Liver X Receptor β Agonists. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 7, 1207–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swahn, B.M.; Macsari, I.; Viklund, J.; Öhberg, L.; Sjödin, J.; Neelissen, J.; Lindquist, J. Liver X receptor agonists with selectivity for LXRbeta; N-aryl-3,3,3-trifluoro-2-hydroxy-2-methylpropionamides. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19, 2009–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benites, J.; Valderrama, J.A.; Bettega, K.; Pedrosa, R.C.; Calderon, P.B.; Verrax, J. Biological evaluation of donor-acceptor aminonaphthoquinones as antitumor agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 45, 6052–6057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kongkathip, B.; Akkarasamiyo, S.; Hasitapan, K.; Sittikul, P.; Boonyalai, N.; Kongkathip, N. Synthesis of novel naphthoquinone aliphatic amides and esters and their anticancer evaluation. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 60, 271–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granot, Y.; Bittner, S. Pyrrolidino-1,4-naphthoquinone Deriviatives and Their Use for Treating Malignancies and Cardiovascular Diseases. U.S. Patent 8513437B2, 20 August 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda, T.; Miura, T.; Watanabe, Y. LXR Agonist. JP Patent 2007284367A, 1 November 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Tandon, V.K.; Maurya, H.K. ‘On water’: Unprecedented nucleophilic substitution and addition reactions with 1, 4-quinones in aqueous suspension. Tetrahedron Lett. 2009, 50, 5896–5902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tandon, V.K.; Maurya, H.K.; Verma, M.K.; Kumar, R.; Shukla, P.K. ‘On water’ assisted synthesis and biological evaluation of nitrogen and sulfur containing hetero-1, 4-naphthoquinones as potent antifungal and antibacterial agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 45, 2418–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.L.; Zheng, X.F.; Wang, L.; Reiner, J.; Xie, W.L.; Chang, J.B. [1,1’-bis(diphe-nylphosphino)ferrocene]dichloropalladium/ 1,1’-bis(di-phenylphosphino) ferrocene catalyzed synthesis of 2,3-diamino-1,4-naphthoquinones. Synthesis 2007, 7, 989–998. [Google Scholar]
- Satheshkumar, A.; Ganesh, K.; Elango, K.P. Charge transfer facilitated direct electrophilic substitution in phenylaminonaphthoquinones: Experimental, theoretical and electrochemical studies. N. J. Chem. 2014, 38, 993–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svensson, S.; Ostberg, T.; Jacobsson, M.; Norström, C.; Stefansson, K.; Hallén, D.; Johansson, I.C.; Zachrisson, K.; Ogg, D.; Jendeberg, L. Crystal structure of the heterodimeric complex of LXRalpha and RXRbeta ligand-binding domains in a fully agonistic conformation. EMBO J. 2003, 22, 4625–4633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molecular Operating Environment; Chemical Computing Group Inc.: Montreal, QC, Canada, 2019.
- Corbeil, C.R.; Willams, C.I.; Labute, P. Variability in docking success rates due to dataset preparation. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 2012, 26, 775–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Liu, M.; Yang, L.; Huang, F.; Lan, Y.; Li, H.; Wu, H.; Zhang, B.; Shi, H.; Wu, X. P-glycoprotein Inhibitor Tariquidar Potentiates Efficacy of Astragaloside IV in Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis Mice. Molecules 2019, 24, 561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |




© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nishioka, T.; Endo-Umeda, K.; Ito, Y.; Shimoda, A.; Takeuchi, A.; Tode, C.; Hirota, Y.; Osakabe, N.; Makishima, M.; Suhara, Y. Synthesis and In Vitro Evaluation of Novel Liver X Receptor Agonists Based on Naphthoquinone Derivatives. Molecules 2019, 24, 4316. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24234316
Nishioka T, Endo-Umeda K, Ito Y, Shimoda A, Takeuchi A, Tode C, Hirota Y, Osakabe N, Makishima M, Suhara Y. Synthesis and In Vitro Evaluation of Novel Liver X Receptor Agonists Based on Naphthoquinone Derivatives. Molecules. 2019; 24(23):4316. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24234316
Chicago/Turabian StyleNishioka, Tatsuma, Kaori Endo-Umeda, Yuki Ito, Akane Shimoda, Atsuko Takeuchi, Chisato Tode, Yoshihisa Hirota, Naomi Osakabe, Makoto Makishima, and Yoshitomo Suhara. 2019. "Synthesis and In Vitro Evaluation of Novel Liver X Receptor Agonists Based on Naphthoquinone Derivatives" Molecules 24, no. 23: 4316. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24234316
APA StyleNishioka, T., Endo-Umeda, K., Ito, Y., Shimoda, A., Takeuchi, A., Tode, C., Hirota, Y., Osakabe, N., Makishima, M., & Suhara, Y. (2019). Synthesis and In Vitro Evaluation of Novel Liver X Receptor Agonists Based on Naphthoquinone Derivatives. Molecules, 24(23), 4316. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24234316





