Organoselenium Compounds as Novel Adjuvants of Chemotherapy Drugs—A Promising Approach to Fight Cancer Drug Resistance
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemistry
3.2. Cell Lines
3.3. Checkerboard Combination Assay
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations:
| 5-FU | 5-fluorouracil |
| ABCB1 | ATP-binding cassette transporter subfamily B member 1 |
| CI | combination index |
| Cis | cisplatin |
| Cpm | cyclophosphamide |
| DMSO | dimethyl-sulfoxide |
| Dox | doxorubicin |
| EPI | efflux pump inhibitor |
| EU | European Union |
| FDA | Food and Drug Administration |
| IU | international units |
| IR | infrared spectroscopy |
| MDR | multidrug-resistant/multidrug resistance |
| MS | mass spectrometry |
| MTT | 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide |
| Mtx | methotrexate |
| NMR | nuclear magnetic resonance |
| OD | optical density |
| PAR | parental cell line |
| SDS | sodium dodecyl sulfate |
| QoL | Quality of Life |
| US | United States |
| Ver | verapamil |
| Vin | vincristine |
References
- McGuire, S. World Cancer Report 2014. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization, International Agency for Research on Cancer, WHO Press, 2015. Adv. Nutr. 2016, 7, 418–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munro, A.J. Comparative cancer survival in European countries. Br. Med. Bull. 2014, 110, 5–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermine, O.; Ramos, J.C.; Tobinai, K. A Review of New Findings in Adult T-cell Leukemia-Lymphoma: A Focus on Current and Emerging Treatment Strategies. Adv. Ther. 2018, 35, 135–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, R. NK/T Cell Lymphoma: Updates in Therapy. Curr. Hematol. Malig. Rep. 2018, 13, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siaghani, P.J.; Song, J.Y. Updates of Peripheral T Cell Lymphomas Based on the 2017 WHO Classification. Curr. Hematol. Malig. Rep. 2018, 13, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leonard, J.; Stock, W. Progress in adult ALL: Incorporation of new agents to frontline treatment. Hematol. Am. Soc. Hematol. Educ. Program 2017, 2017, 28–36. [Google Scholar]
- Lue, J.K.; Kress, A.; Amengual, J.E. Therapeutic Options for Aggressive T-Cell Lymphomas. Curr. Hematol. Malig. Rep. 2017, 12, 269–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subbiah, V.; Kurzrock, R. Challenging Standard-of-Care Paradigms in the Precision Oncology Era. Trends Cancer 2018, 4, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sumpio, C.; Knobf, M.T.; Jeon, S. Treatment complexity: A description of chemotherapy and supportive care treatment visits in patients with advanced-stage cancer diagnoses. Support. Care Cancer 2016, 24, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chabner, B.A.; Roberts, T.G. Timeline: Chemotherapy and the war on cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2005, 5, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govender, J.; Loos, B.; Marais, E.; Engelbrecht, A.-M. Mitochondrial catastrophe during doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity: A review of the protective role of melatonin. J. Pineal Res. 2014, 57, 367–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ichikawa, Y.; Ghanefar, M.; Bayeva, M.; Wu, R.; Khechaduri, A.; Naga Prasad, S.V.; Mutharasan, R.K.; Naik, T.J.; Ardehali, H. Cardiotoxicity of doxorubicin is mediated through mitochondrial iron accumulation. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 617–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Octavia, Y.; Tocchetti, C.G.; Gabrielson, K.L.; Janssens, S.; Crijns, H.J.; Moens, A.L. Doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy: From molecular mechanisms to therapeutic strategies. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2012, 52, 1213–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, D.; Schulz, G.; Langley, R.; Donze, K.; Winchester, K.; Rodgers, C. Evidence-Based Practice Recommendations for Hydration in Children and Adolescents with Cancer Receiving Intravenous Cyclophosphamide. J. Pediatr. Oncol. Nurs. 2014, 31, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Au, W.; Sokova, O.I.; Kopnin, B.; Arrighi, F.E. Cytogenetic toxicity of cyclophosphamide and its metabolites in vitro. Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 1980, 26, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acton, E.M.; Narayanan, V.L.; Risbood, P.A.; Shoemaker, R.H.; Vistica, D.T.; Boyd, M.R. Anticancer specificity of some ellipticinium salts against human brain tumors in vitro. J. Med. Chem. 1994, 37, 2185–2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayat Mokhtari, R.; Homayouni, T.S.; Baluch, N.; Morgatskaya, E.; Kumar, S.; Das, B.; Yeger, H. Combination therapy in combating cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 38022–38043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccolo, M.T.; Menale, C.; Crispi, S. Combined anticancer therapies: An overview of the latest applications. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2015, 15, 408–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baguley, B.C. Multidrug resistance in cancer. Methods Mol. Biol. 2010, 596, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Yardley, D.A. Drug Resistance and the Role of Combination Chemotherapy in Improving Patient Outcomes. Int. J. Breast Cancer 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moitra, K.; Lou, H.; Dean, M. Multidrug efflux pumps and cancer stem cells: Insights into multidrug resistance and therapeutic development. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2011, 89, 491–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.-J.; Lei, Y.-H.; Yao, N.; Wang, C.-R.; Hu, N.; Ye, W.-C.; Zhang, D.-M.; Chen, Z.-S. Autophagy and multidrug resistance in cancer. Chin. J. Cancer 2017, 36, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teicher, B.A.; Herman, T.S.; Holden, S.A.; Wang, Y.Y.; Pfeffer, M.R.; Crawford, J.W.; Frei, E. Tumor resistance to alkylating agents conferred by mechanisms operative only in vivo. Science 1990, 247, 1457–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mecklenburg, S.; Shaaban, S.; Ba, L.A.; Burkholz, T.; Schneider, T.; Diesel, B.; Kiemer, A.K.; Röseler, A.; Becker, K.; Reichrath, J.; et al. Exploring synthetic avenues for the effective synthesis of selenium- and tellurium-containing multifunctional redox agents. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2009, 7, 4753–4762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamier, V.; Ba, L.A.; Jacob, C. Selenium- and tellurium-containing multifunctional redox agents as biochemical redox modulators with selective cytotoxicity. Chemistry 2010, 16, 10920–10928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanmartin, C.; Plano, D.; Font, M.; Palop, J.A. Selenium and clinical trials: New therapeutic evidence for multiple diseases. Curr. Med. Chem. 2011, 18, 4635–4650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plano, D.; Baquedano, Y.; Ibáñez, E.; Jiménez, I.; Palop, J.A.; Spallholz, J.E.; Sanmartín, C. Antioxidant-prooxidant properties of a new organoselenium compound library. Molecules 2010, 15, 7292–7312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartolini, D.; Sancineto, L.; Fabro de Bem, A.; Tew, K.D.; Santi, C.; Radi, R.; Toquato, P.; Galli, F. Selenocompounds in Cancer Therapy: An Overview. Adv. Cancer Res. 2017, 136, 259–302. [Google Scholar]
- Moreno, E.; Plano, D.; Lamberto, I.; Font, M.; Encío, I.; Palop, J.A.; Sanmartín, C. Sulfur and selenium derivatives of quinazoline and pyrido[2,3-d]pyrimidine: Synthesis and study of their potential cytotoxic activity in vitro. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 47, 283–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plano, D.; Sanmartín, C.; Moreno, E.; Prior, C.; Calvo, A.; Palop, J.A. Novel potent organoselenium compounds as cytotoxic agents in prostate cancer cells. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2007, 17, 6853–6859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez-Pérez, M.; Ali, W.; Marć, M.A.; Handzlik, J.; Domínguez-Álvarez, E. Selenides and Diselenides: A Review of Their Anticancer and Chemopreventive Activity. Molecules 2018, 23, 628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gandin, V.; Khalkar, P.; Braude, J.; Fernandes, A.P. Organic selenium compounds as potential chemotherapeutic agents for improved cancer treatment. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cort, A.; Ozben, T.; Saso, L.; De Luca, C.; Korkina, L. Redox Control of Multidrug Resistance and Its Possible Modulation by Antioxidants. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 4251912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, X.; Gandhi, V. ROS-activated anticancer prodrugs: A new strategy for tumor-specific damage. Ther. Deliv. 2012, 3, 823–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.O.; Yoo, Y.B.; Kim, Y.H.; Baek, K.J.; Yang, J.-H.; Choi, P.C.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, K.R.; Park, K.S. Effects of combination therapy of docetaxel with selenium on the human breast cancer cell lines MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7. Ann. Surg. Treat. Res. 2015, 88, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumi-Diaka, J.; Merchant, K.; Haces, A.; Hormann, V.; Johnson, M. Genistein-selenium combination induces growth arrest in prostate cancer cells. J. Med. Food 2010, 13, 842–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, P.; Roy, S.S.; Bhattacharya, S. Molecular mechanism behind the synergistic activity of diphenylmethyl selenocyanate and Cisplatin against murine tumor model. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2015, 15, 501–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.; Wong, Y.-S. Selenocystine induces caspase-independent apoptosis in MCF-7 human breast carcinoma cells with involvement of p53 phosphorylation and reactive oxygen species generation. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2009, 41, 666–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, P.; Roy, S.S.; Basu, A.; Bhattacharya, S. Sensitization of cancer cells to cyclophosphamide therapy by an organoselenium compound through ROS-mediated apoptosis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2016, 84, 1992–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Fu, X.; Xiong, Z.; Zhang, H.; Hill, S.M.; Rowan, B.G.; Dong, Y. Methylseleninic acid enhances paclitaxel efficacy for the treatment of triple-negative breast cancer. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e31539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez-Álvarez, E.; Plano, D.; Font, M.; Calvo, A.; Prior, C.; Jacob, C.; Palop, J.A.; Sanmartín, C. Synthesis and antiproliferative activity of novel selenoester derivatives. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 73, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez-Álvarez, E.; Gajdács, M.; Spengler, G.; Palop, J.A.; Marć, M.A.; Kieć-Kononowicz, K.; Amaral, L.; Molnár, J.; Jacob, C.; Handzlik, J.; et al. Identification of selenocompounds with promising properties to reverse cancer multidrug resistance. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 26, 2821–2824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajdács, M.; Spengler, G.; Sanmartín, C.; Marć, M.A.; Handzlik, J.; Domínguez-Álvarez, E. Selenoesters and selenoanhydrides as novel multidrug resistance reversing agents: A confirmation study in a colon cancer MDR cell line. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 27, 797–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gajdács, M.; Handzlik, J.; Sanmartin, C.; Domínguez, E.; Spengler, G. [Organoselenium compounds as antitumor agents: In vitro evaluation on a colon cancer model system] (article in Hungarian). Acta Pharm. Hung. 2018, 88, 59–66. [Google Scholar]
- Gajdács, M.; Handzlik, J.; Sanmartín, C.; Domínguez-Álvarez, E.; Spengler, G. [Prediction of ADME properties for selenocompounds with anticancer and efflux pump inhibitory activity using preliminary computational methods] (article in Hungarian). Acta Pharm. Hung. 2018, 88, 67–74. [Google Scholar]
- Chou, T.-C. Preclinical versus clinical drug combination studies. Leuk. Lymphoma 2008, 49, 2059–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, T.-C. Theoretical basis, experimental design, and computerized simulation of synergism and antagonism in drug combination studies. Pharmacol. Rev. 2006, 58, 621–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, T.-C. Drug Combination Studies and Their Synergy Quantification Using the Chou-Talalay Method. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 440–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanmartín, C.; Plano, D.; Sharma, A.K.; Palop, J.A. Selenium Compounds, Apoptosis and Other Types of Cell Death: An Overview for Cancer Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 9649–9672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kathawala, R.J.; Gupta, P.; Ashby, C.R.; Chen, Z.-S. The modulation of ABC transporter-mediated multidrug resistance in cancer: A review of the past decade. Drug Resist. Updat. 2015, 18, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, J.I.; Haber, M.; Henderson, M.J.; Norris, M.D. ABC transporters in cancer: More than just drug efflux pumps. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2010, 10, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spengler, G.; Evaristo, M.; Handzlik, J.; Serly, J.; Molnár, J.; Viveiros, M.; Kiéc-Kononowicz, K.; Amaral, L. Biological activity of hydantoin derivatives on P-glycoprotein (ABCB1) of mouse lymphoma cells. Anticancer Res. 2010, 30, 4867–4871. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Joyce, H.; McCann, A.; Clynes, M.; Larkin, A. Influence of multidrug resistance and drug transport proteins on chemotherapy drug metabolism. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2015, 11, 795–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobori, T.; Harada, S.; Nakamoto, K.; Tokuyama, S. Mechanisms of P-glycoprotein alteration during anticancer treatment: Role in the pharmacokinetic and pharmacological effects of various substrate drugs. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2014, 125, 242–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molavian, H.R.; Goldman, A.; Phipps, C.J.; Kohandel, M.; Wouters, B.G.; Sengupta, S.; Sivaloganathan, S. Drug-induced reactive oxygen species (ROS) rely on cell membrane properties to exert anticancer effects. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 27439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokoyama, C.; Sueyoshi, Y.; Ema, M.; Mori, Y.; Takaishi, K.; Hisatomi, H. Induction of oxidative stress by anticancer drugs in the presence and absence of cells. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 14, 6066–6070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briehl, M.M.; Tome, M.E.; Wilkinson, S.T.; Jaramillo, M.C.; Lee, K. Mitochondria and redox homeostasis as chemotherapeutic targets. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2014, 42, 939–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graczyk-Jarzynka, A.; Zagozdzon, R.; Muchowicz, A.; Siernicka, M.; Juszczynski, P.; Firczuk, M. New insights into redox homeostasis as a therapeutic target in B-cell malignancies. Curr. Opin. Hematol. 2017, 24, 393–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornwell, M.M.; Pastan, I.; Gottesman, M.M. Certain calcium channel blockers bind specifically to multidrug-resistant human KB carcinoma membrane vesicles and inhibit drug binding to P-glycoprotein. J. Biol. Chem. 1987, 262, 2166–2170. [Google Scholar]
- Takács, D.; Csonka, Á.; Horváth, Á.; Windt, T.; Gajdács, M.; Riedl, Z.; Hajós, G.; Amaral, L.; Molnár, J.; Spengler, G. Reversal of ABCB1-related Multidrug Resistance of Colonic Adenocarcinoma Cells by Phenothiazines. Anticancer Res. 2015, 35, 3245–3251. [Google Scholar]
- Chou, T.; Martin, N. CompuSyn for Drug Combinations: PC Software and User’s Guide: A Computer Program for Quantitation of Synergism and Antagonism in Drug Combinations, and the Determination of IC50 and ED50 and LD50 Values; ComboSyn Inc.: Paramus, NJ, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |
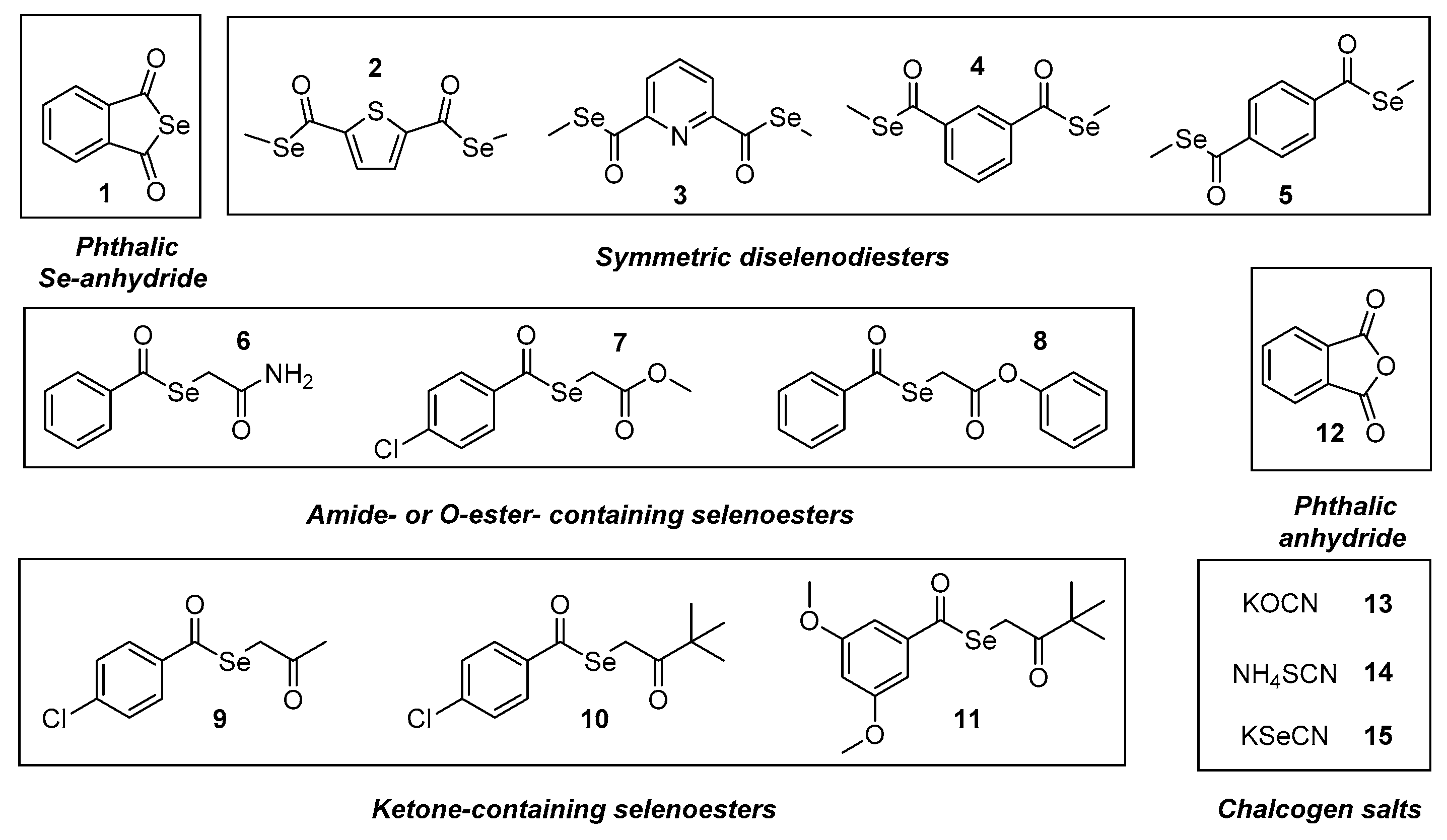
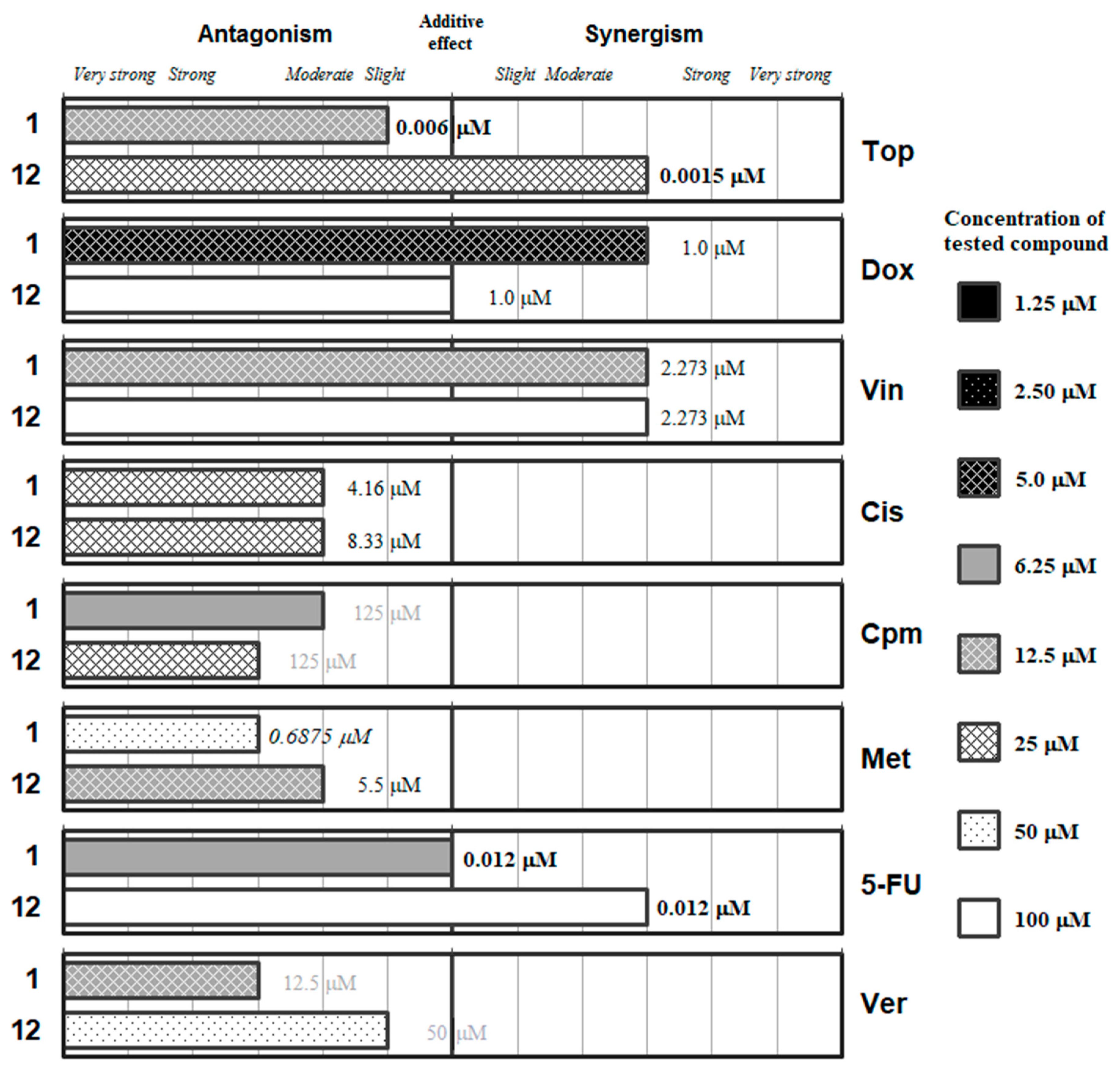
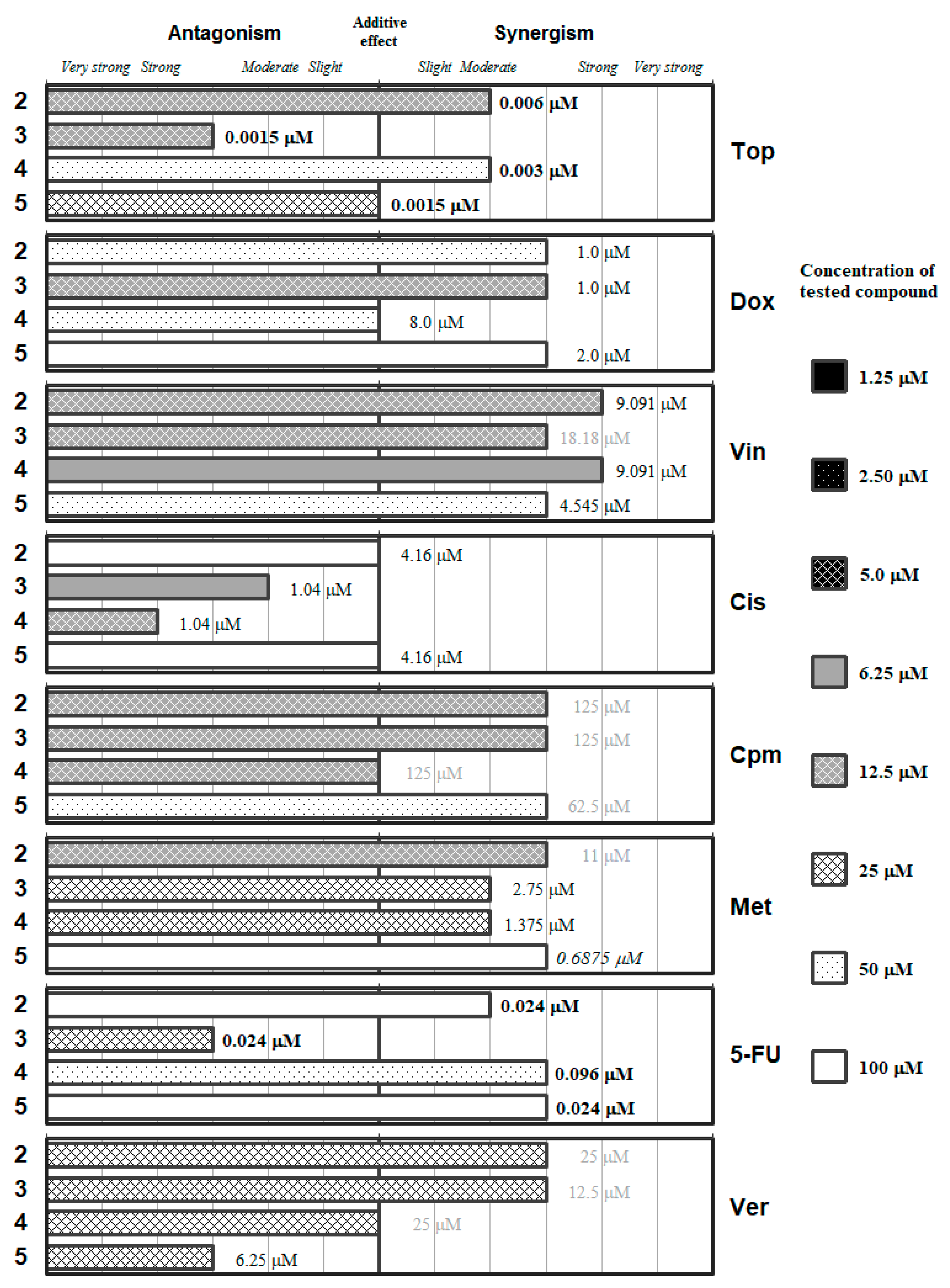



| Combination Index (CI) | Type of Interaction | Combination Index (CI) | Type of Interaction |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0–0.1 | very strong synergism | 0.9–1.1 | additive effect |
| 0.1–0.3 | strong synergism | 1.1–1.2 | slight antagonism |
| 0.3–0.7 | synergism | 1.2–1.45 | moderate antagonism |
| 1.45–3.3 | antagonism | ||
| 0.7–0.85 | moderate synergism | 3.3–10 | strong antagonism |
| 0.85–0.9 | slight synergism | >10 | very strong antagonism |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Spengler, G.; Gajdács, M.; Marć, M.A.; Domínguez-Álvarez, E.; Sanmartín, C. Organoselenium Compounds as Novel Adjuvants of Chemotherapy Drugs—A Promising Approach to Fight Cancer Drug Resistance. Molecules 2019, 24, 336. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24020336
Spengler G, Gajdács M, Marć MA, Domínguez-Álvarez E, Sanmartín C. Organoselenium Compounds as Novel Adjuvants of Chemotherapy Drugs—A Promising Approach to Fight Cancer Drug Resistance. Molecules. 2019; 24(2):336. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24020336
Chicago/Turabian StyleSpengler, Gabriella, Márió Gajdács, Małgorzata Anna Marć, Enrique Domínguez-Álvarez, and Carmen Sanmartín. 2019. "Organoselenium Compounds as Novel Adjuvants of Chemotherapy Drugs—A Promising Approach to Fight Cancer Drug Resistance" Molecules 24, no. 2: 336. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24020336
APA StyleSpengler, G., Gajdács, M., Marć, M. A., Domínguez-Álvarez, E., & Sanmartín, C. (2019). Organoselenium Compounds as Novel Adjuvants of Chemotherapy Drugs—A Promising Approach to Fight Cancer Drug Resistance. Molecules, 24(2), 336. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24020336









