Structural Evaluation and Electrophysiological Effects of Some Kynurenic Acid Analogs
Abstract
1. Introduction
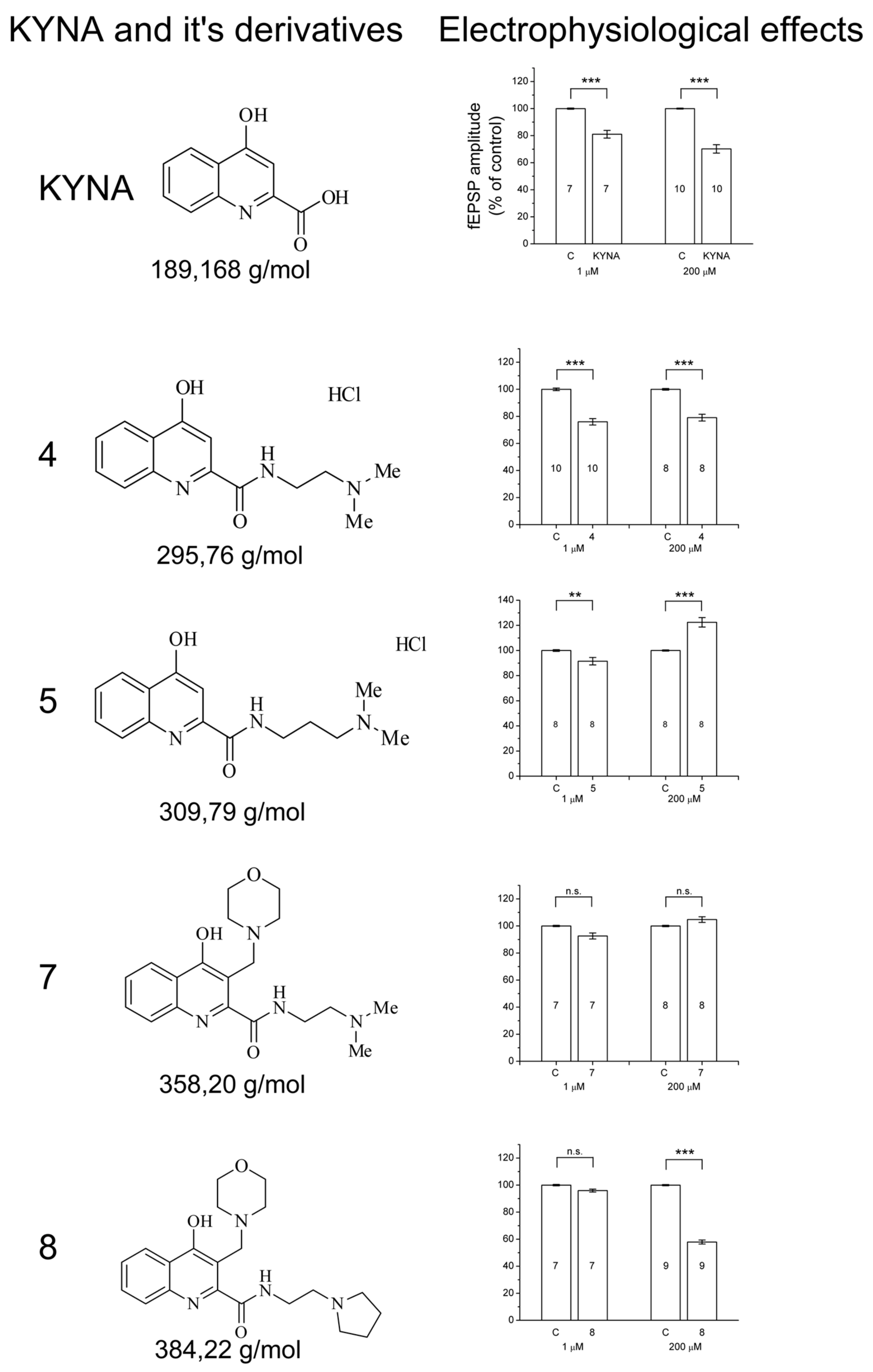
2. Results
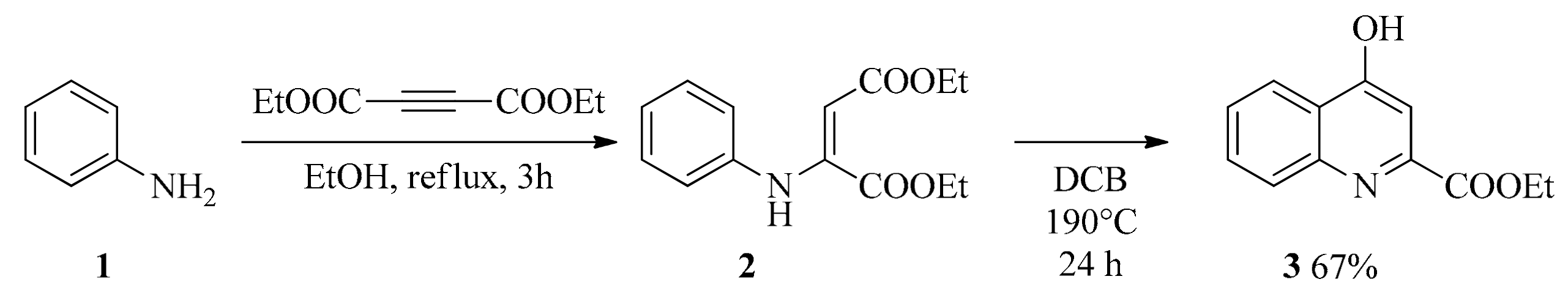
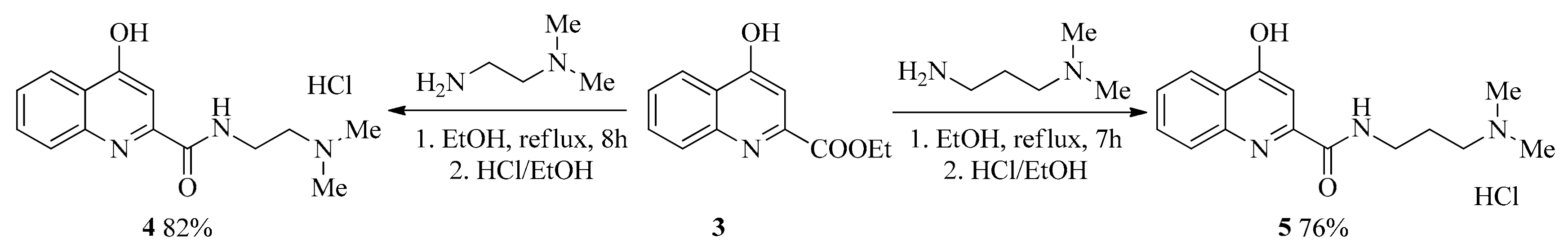
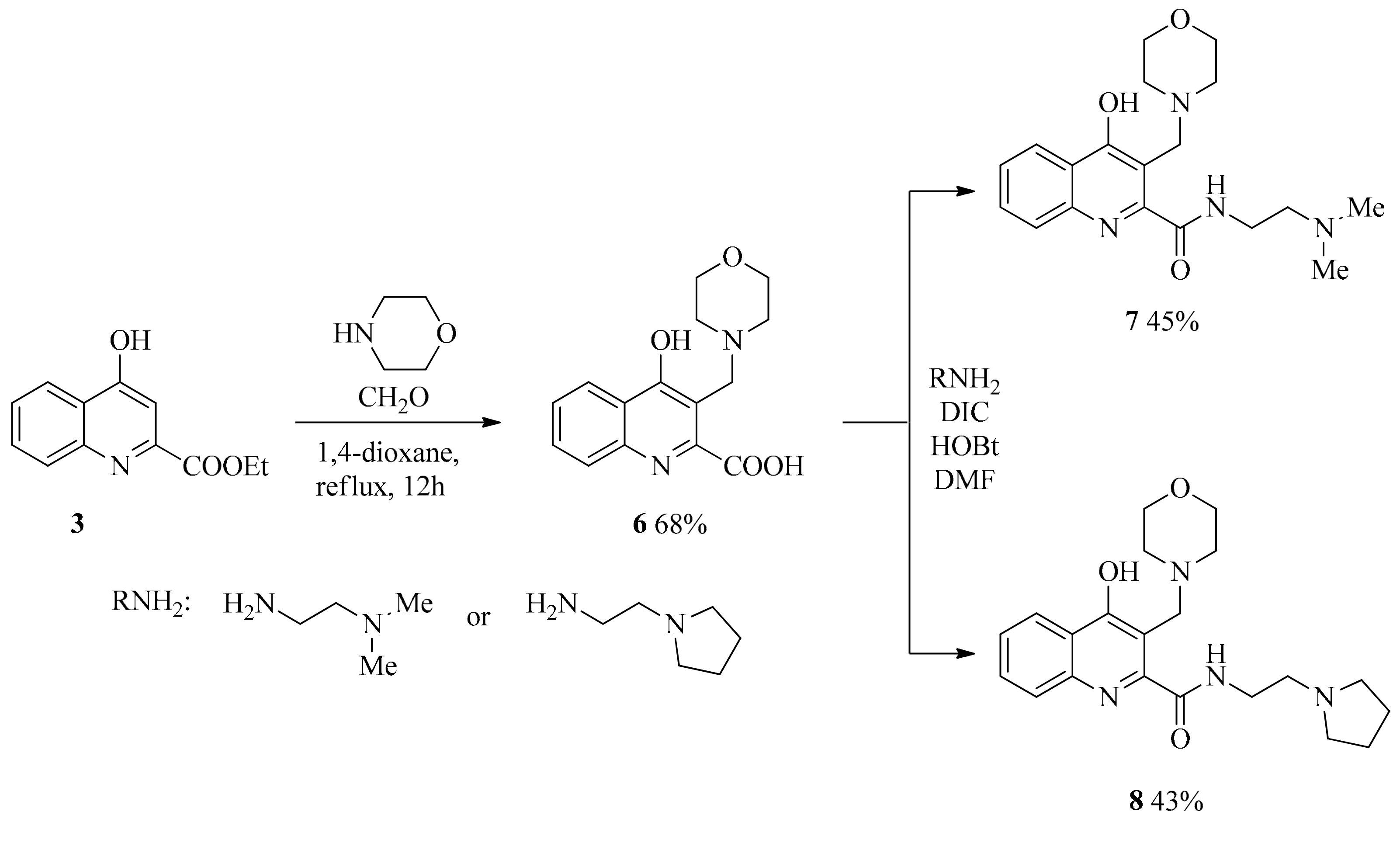
2.1. Design and Development of KYNA Derivatives
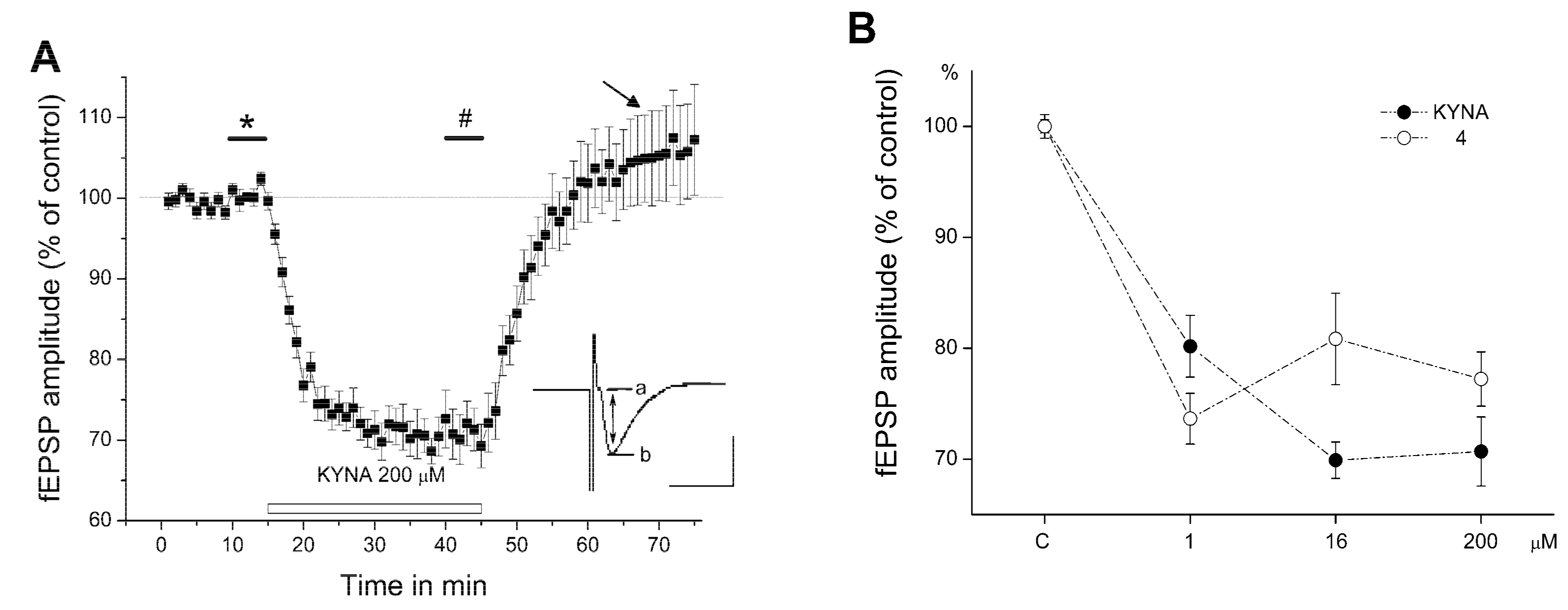
2.2. Electrophysiology
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Drugs
4.2. Synthesis
4.2.1. General Procedure for the Synthesis of Amides (4, 5)
4.2.2. General Procedure for the Syntheses of Aminoalkylated Amides 7, 8
4.3. Animals and Housing Conditions
4.4. Slice Preparation
4.5. Electrophysiology
5. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary File 1Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kostandy, B.B. The role of glutamate in neuronal ischemic injury: The role of spark in fire. Neurol. Sci. 2012, 33, 223–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, T.W.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.T. Excitotoxicity and stroke: Identifying novel targets for neuroprotection. Prog. Neurobiol. 2014, 115, 157–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Leary, R.A.; Nichol, A.D. Pathophysiology of severe traumatic brain injury overview. J. Neurosurg. Sci. 2018, 62, 542–548. [Google Scholar]
- Olloquequi, J.; Cornejo-Cordova, E.; Verdaguer, E.; Soriano, F.X.; Binvignat, O.; Auladell, C.; Camins, A. Excitotoxicity in the pathogenesis of neurological and psychiatric disorders: Therapeutic implications. J. Psychopharmacol. 2018, 32, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puyal, J.; Ginet, V.; Clarke, P.G. Multiple interacting cell death mechanisms in the mediation of excitotoxicity and ischemic brain damage: A challenge for neuroprotection. Prog. Neurobiol. 2013, 105, 24–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez, J.; Jurado-Coronel, J.C.; Avila, M.F.; Sabogal, A.; Capani, F.; Barreto, G.E. NMDARs in neurological diseases: A potential therapeutic target. Int. J. Neurosci. 2015, 125, 315–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsuki, H.; Nonaka, M.; Shirakawa, H.; Kume, T.; Akaike, A. Endogenous D-serine is involved in induction of neuronal death by N-methyl-D-aspartate and simulated ischemia in rat cerebrocortical slices. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2004, 311, 836–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manning, S.M.; Talos, D.M.; Zhou, C.; Selip, D.B.; Park, H.K.; Park, C.J.; Volpe, J.J.; Jensen, F.E. NMDA receptor blockade with memantine attenuates white matter injury in a rat model of periventricular leukomalacia. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 6670–6678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mothet, J.P.; Parent, A.T.; Wolosker, H.; Brady, R.O., Jr.; Linden, D.J.; Ferris, C.D.; Rogawski, M.A.; Snyder, S.H. D-serine is an endogenous ligand for the glycine site of the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 4926–4931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sas, K.; Robotka, H.; Rozsa, E.; Agoston, M.; Szenasi, G.; Gigler, G.; Marosi, M.; Kis, Z.; Farkas, T.; Vecsei, L.; et al. Kynurenine diminishes the ischemia-induced histological and electrophysiological deficits in the rat hippocampus. Neurobiol. Dis. 2008, 32, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Criddle, M.W.; Godfrey, D.A.; Kaltenbach, J.A. Attenuation of noise-induced hyperactivity in the dorsal cochlear nucleus by pre-treatment with MK-801. Brain Res. 2018, 1682, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Tang, X.; Guan, T.; Li, Y.; Sun, H. Neuroprotection by Combined Administration with Maslinic Acid, a Natural Product from Olea europaea, and MK-801 in the Cerebral Ischemia Model. Molecules 2016, 21, 1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muir, K.W.; Lees, K.R. Clinical experience with excitatory amino acid antagonist drugs. Stroke 1995, 26, 503–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contreras, P.C. D-serine antagonized phencyclidine- and MK-801-induced stereotyped behavior and ataxia. Neuropharmacology 1990, 29, 291–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krystal, J.H.; D’Souza, D.C.; Petrakis, I.L.; Belger, A.; Berman, R.M.; Charney, D.S.; Abi-Saab, W.; Madonick, S. NMDA agonists and antagonists as probes of glutamatergic dysfunction and pharmacotherapies in neuropsychiatric disorders. Harv. Rev. Psychiatry 1999, 7, 125–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scorza, M.C.; Castane, A.; Bortolozzi, A.; Artigas, F. Clozapine does not require 5-HT1A receptors to block the locomotor hyperactivity induced by MK-801 Clz and MK-801 in KO1A mice. Neuropharmacology 2010, 59, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muir, K.W. Glutamate-based therapeutic approaches: Clinical trials with NMDA antagonists. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2006, 6, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarcz, R. The kynurenine pathway of tryptophan degradation as a drug target. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2004, 4, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vécsei, L. Kynurenines Int He Brain: From Experiments to Clinics; Nova Biomedical Books: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Kessler, M.; Terramani, T.; Lynch, G.; Baudry, M. A glycine site associated with N-methyl-D-aspartic acid receptors: Characterization and identification of a new class of antagonists. J. Neurochem. 1989, 52, 1319–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilmas, C.; Pereira, E.F.; Alkondon, M.; Rassoulpour, A.; Schwarcz, R.; Albuquerque, E.X. The brain metabolite kynurenic acid inhibits alpha7 nicotinic receptor activity and increases non-alpha7 nicotinic receptor expression: Physiopathological implications. J. Neurosci. 2001, 21, 7463–7473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenedo, R.; Pittaluga, A.; Cozzi, A.; Attucci, S.; Galli, A.; Raiteri, M.; Moroni, F. Presynaptic kynurenate-sensitive receptors inhibit glutamate release. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2001, 13, 2141–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Simonavicius, N.; Wu, X.; Swaminath, G.; Reagan, J.; Tian, H.; Ling, L. Kynurenic acid as a ligand for orphan G protein-coupled receptor GPR35. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 22021–22028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiNatale, B.C.; Murray, I.A.; Schroeder, J.C.; Flaveny, C.A.; Lahoti, T.S.; Laurenzana, E.M.; Omiecinski, C.J.; Perdew, G.H. Kynurenic acid is a potent endogenous aryl hydrocarbon receptor ligand that synergistically induces interleukin-6 in the presence of inflammatory signaling. Toxicol. Sci. 2010, 115, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szalardy, L.; Klivenyi, P.; Zadori, D.; Fulop, F.; Toldi, J.; Vecsei, L. Mitochondrial disturbances, tryptophan metabolites and neurodegeneration: Medicinal chemistry aspects. Curr. Med. Chem. 2012, 19, 1899–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gellert, L.; Knapp, L.; Nemeth, K.; Heredi, J.; Varga, D.; Olah, G.; Kocsis, K.; Menyhart, A.; Kis, Z.; Farkas, T.; et al. Post-ischemic treatment with L-kynurenine sulfate exacerbates neuronal damage after transient middle cerebral artery occlusion. Neuroscience 2013, 247, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangas, A.; Yajeya, J.; Gonzalez, N.; Ruiz, I.; Duleu, S.; Geffard, M.; Covenas, R. Overexpression of kynurenic acid in stroke: An endogenous neuroprotector? Ann. Anat. 2017, 211, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vecsei, L.; Szalardy, L.; Fulop, F.; Toldi, J. Kynurenines in the CNS: Recent advances and new questions. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2013, 12, 64–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulop, F.; Szatmari, I.; Vamos, E.; Zadori, D.; Toldi, J.; Vecsei, L. Syntheses, transformations and pharmaceutical applications of kynurenic acid derivatives. Curr. Med. Chem. 2009, 16, 4828–4842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, K.; Plangar, I.; Tuka, B.; Gellert, L.; Varga, D.; Demeter, I.; Farkas, T.; Kis, Z.; Marosi, M.; Zadori, D.; et al. Synthesis and biological effects of some kynurenic acid analogs. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2011, 19, 7590–7596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marosi, M.; Nagy, D.; Farkas, T.; Kis, Z.; Rozsa, E.; Robotka, H.; Fulop, F.; Vecsei, L.; Toldi, J. A novel kynurenic acid analogue: A comparison with kynurenic acid. An in vitro electrophysiological study. J. Neural Transm. 2010, 117, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadori, D.; Nyiri, G.; Szonyi, A.; Szatmari, I.; Fulop, F.; Toldi, J.; Freund, T.F.; Vecsei, L.; Klivenyi, P. Neuroprotective effects of a novel kynurenic acid analogue in a transgenic mouse model of Huntington’s disease. J. Neural Transm. 2011, 118, 865–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demeter, I.; Nagy, K.; Farkas, T.; Kis, Z.; Kocsis, K.; Knapp, L.; Gellert, L.; Fulop, F.; Vecsei, L.; Toldi, J. Paradox effects of kynurenines on LTP induction in the Wistar rat. An in vivo study. Neurosci. Lett. 2013, 553, 138–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassai, F.; Kedves, R.; Gyertyan, I.; Tuka, B.; Fulop, F.; Toldi, J.; Lendvai, B.; Vecsei, L. Effect of a kynurenic acid analog on home-cage activity and body temperature in rats. Pharmacol. Rep. 2015, 67, 1188–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knyihar-Csillik, E.; Mihaly, A.; Krisztin-Peva, B.; Robotka, H.; Szatmari, I.; Fulop, F.; Toldi, J.; Csillik, B.; Vecsei, L. The kynurenate analog SZR-72 prevents the nitroglycerol-induced increase of c-fos immunoreactivity in the rat caudal trigeminal nucleus: Comparative studies of the effects of SZR-72 and kynurenic acid. Neurosci. Res. 2008, 61, 429–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukacs, M.; Warfvinge, K.; Kruse, L.S.; Tajti, J.; Fulop, F.; Toldi, J.; Vecsei, L.; Edvinsson, L. KYNA analogue SZR72 modifies CFA-induced dural inflammation-regarding expression of pERK1/2 and IL-1beta in the rat trigeminal ganglion. J. Headache Pain 2016, 17, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, W.; Liu, Y.; Zeng, L.; Su, W.; Zhou, M. Substituent effect of ancillary ligands on the luminescence of bis [4,6-(di-fluorophenyl)-pyridinato-N,C2’]iridium(III) complexes. Dalton Trans. 2012, 41, 9373–9381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulop, F.; Szatmari, I.; Toldi, J.; Vecsei, L. Novel Types of C-3 Substituted Kynurenic Acid Derivatives with Improved Neuroprotective Activity. U.S. Patent 16/082,099, 11 April 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Nozaki, K.; Beal, M.F. Neuroprotective effects of L-kynurenine on hypoxia-ischemia and NMDA lesions in neonatal rats. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 1992, 12, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, T.W. Development and therapeutic potential of kynurenic acid and kynurenine derivatives for neuroprotection. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2000, 21, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.Q.; Lee, S.C.; Scharfman, H.E.; Schwarcz, R. L-4-chlorokynurenine attenuates kainate-induced seizures and lesions in the rat. Exp. Neurol. 2002, 177, 222–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozsa, E.; Robotka, H.; Nagy, D.; Farkas, T.; Sas, K.; Vecsei, L.; Toldi, J. The pentylenetetrazole-induced activity in the hippocampus can be inhibited by the conversion of L-kynurenine to kynurenic acid: An in vitro study. Brain Res. Bull. 2008, 76, 474–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vamos, E.; Pardutz, A.; Varga, H.; Bohar, Z.; Tajti, J.; Fulop, F.; Toldi, J.; Vecsei, L. l-kynurenine combined with probenecid and the novel synthetic kynurenic acid derivative attenuate nitroglycerin-induced nNOS in the rat caudal trigeminal nucleus. Neuropharmacology 2009, 57, 425–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gigler, G.; Szenasi, G.; Simo, A.; Levay, G.; Harsing, L.G., Jr.; Sas, K.; Vecsei, L.; Toldi, J. Neuroprotective effect of L-kynurenine sulfate administered before focal cerebral ischemia in mice and global cerebral ischemia in gerbils. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2007, 564, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robotka, H.; Sas, K.; Agoston, M.; Rozsa, E.; Szenasi, G.; Gigler, G.; Vecsei, L.; Toldi, J. Neuroprotection achieved in the ischaemic rat cortex with L-kynurenine sulphate. Life Sci. 2008, 82, 915–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulop, F.; Szatmari, I.; Toldi, J.; Vecsei, L. Modifications on the carboxylic function of kynurenic acid. J. Neural Transm. 2012, 119, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrigoni, E.; Greene, R.W. Schaffer collateral and perforant path inputs activate different subtypes of NMDA receptors on the same CA1 pyramidal cell. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2004, 142, 317–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Kawakami, R.; Shinohara, Y.; Fukaya, M.; Sakimura, K.; Mishina, M.; Watanabe, M.; Ito, I.; Shigemoto, R. Target-cell-specific left-right asymmetry of NMDA receptor content in schaffer collateral synapses in epsilon1/NR2A knock-out mice. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 9213–9226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prescott, C.; Weeks, A.M.; Staley, K.J.; Partin, K.M. Kynurenic acid has a dual action on AMPA receptor responses. Neurosci. Lett. 2006, 402, 108–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozsa, E.; Robotka, H.; Vecsei, L.; Toldi, J. The Janus-face kynurenic acid. J. Neural Transm. 2008, 115, 1087–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vamos, E.; Fejes, A.; Koch, J.; Tajti, J.; Fulop, F.; Toldi, J.; Pardutz, A.; Vecsei, L. Kynurenate derivative attenuates the nitroglycerin-induced CamKIIalpha and CGRP expression changes. Headache 2010, 50, 834–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardingham, G.E.; Bading, H. Synaptic versus extrasynaptic NMDA receptor signalling: Implications for neurodegenerative disorders. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2010, 11, 682–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papouin, T.; Oliet, S.H. Organization, control and function of extrasynaptic NMDA receptors. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2014, 369, 20130601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petralia, R.S.; Wang, Y.X.; Hua, F.; Yi, Z.; Zhou, A.; Ge, L.; Stephenson, F.A.; Wenthold, R.J. Organization of NMDA receptors at extrasynaptic locations. Neuroscience 2010, 167, 68–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szapiro, G.; Barbour, B. Parasynaptic signalling by fast neurotransmitters: The cerebellar cortex. Neuroscience 2009, 162, 644–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paoletti, P.; Bellone, C.; Zhou, Q. NMDA receptor subunit diversity: Impact on receptor properties, synaptic plasticity and disease. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2013, 14, 383–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, B. Involvement of extrasynaptic glutamate in physiological and pathophysiological changes of neuronal excitability. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2018, 75, 2917–2949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borza, I.; Kolok, S.; Galgoczy, K.; Gere, A.; Horvath, C.; Farkas, S.; Greiner, I.; Domany, G. Kynurenic acid amides as novel NR2B selective NMDA receptor antagonists. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2007, 17, 406–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocsis, K.; Knapp, L.; Gellert, L.; Olah, G.; Kis, Z.; Takakuwa, H.; Iwamori, N.; Ono, E.; Toldi, J.; Farkas, T. Acetyl-L-carnitine normalizes the impaired long-term potentiation and spine density in a rat model of global ischemia. Neuroscience 2014, 269, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marosi, M.; Fuzik, J.; Nagy, D.; Rakos, G.; Kis, Z.; Vecsei, L.; Toldi, J.; Ruban-Matuzani, A.; Teichberg, V.I.; Farkas, T. Oxaloacetate restores the long-term potentiation impaired in rat hippocampus CA1 region by 2-vessel occlusion. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 604, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available. |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fehér, E.; Szatmári, I.; Dudás, T.; Zalatnai, A.; Farkas, T.; Lőrinczi, B.; Fülöp, F.; Vécsei, L.; Toldi, J. Structural Evaluation and Electrophysiological Effects of Some Kynurenic Acid Analogs. Molecules 2019, 24, 3502. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24193502
Fehér E, Szatmári I, Dudás T, Zalatnai A, Farkas T, Lőrinczi B, Fülöp F, Vécsei L, Toldi J. Structural Evaluation and Electrophysiological Effects of Some Kynurenic Acid Analogs. Molecules. 2019; 24(19):3502. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24193502
Chicago/Turabian StyleFehér, Evelin, István Szatmári, Tamás Dudás, Anna Zalatnai, Tamás Farkas, Bálint Lőrinczi, Ferenc Fülöp, László Vécsei, and József Toldi. 2019. "Structural Evaluation and Electrophysiological Effects of Some Kynurenic Acid Analogs" Molecules 24, no. 19: 3502. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24193502
APA StyleFehér, E., Szatmári, I., Dudás, T., Zalatnai, A., Farkas, T., Lőrinczi, B., Fülöp, F., Vécsei, L., & Toldi, J. (2019). Structural Evaluation and Electrophysiological Effects of Some Kynurenic Acid Analogs. Molecules, 24(19), 3502. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24193502








