Furocoumarin Content of Fennel—Below the Safety Threshold
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Material
4.2. Extraction
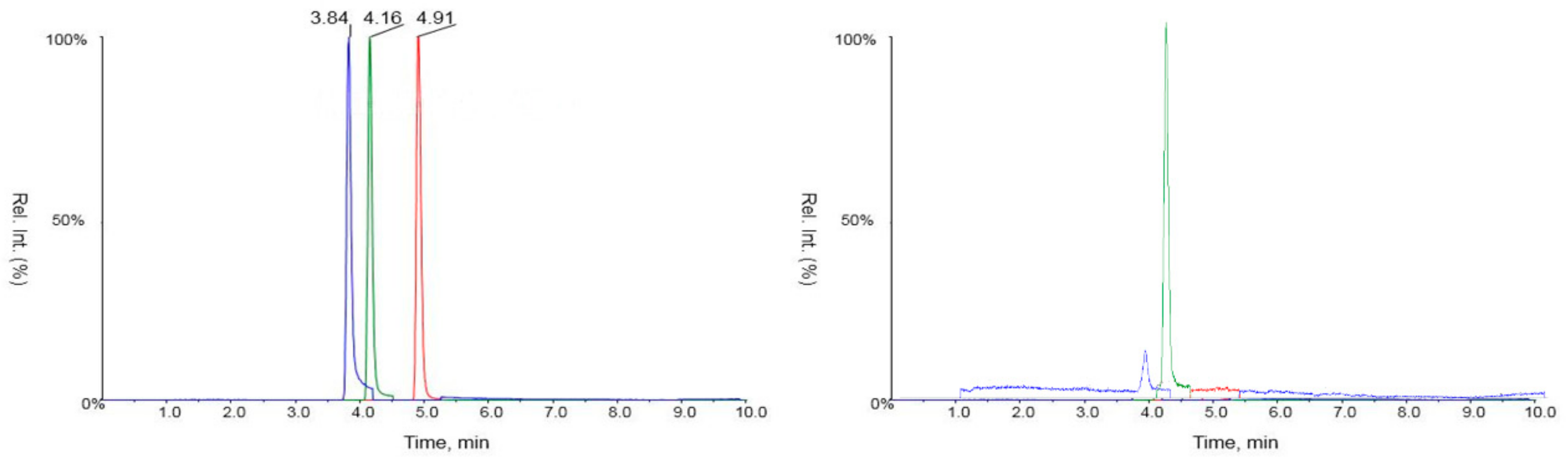
4.3. Determination and Quantification of Furocoumarins in Fennel Extracts by LC-MS
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- EMA. Community Herbal Monograph on Foeniculuum vulgare Miller subsp. vulgare var. dulce (Miller) Thellung, fructus; European Medicines Agency: London, UK, 2007; Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/herbal-monograph/final-community-herbal-monograph-foeniculum-vulgare-miller-subsp-vulgare-var-dulce-miller-thellung_en.pdf (accessed on 3 August 2019).
- EMA. Community Herbal Monograph on Foeniculum vulgare Miller subsp. vulgare var. vulgare, fructus; European Medicines Agency: London, UK, 2007; Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/herbal-monograph/final-community-herbal-monograph-foeniculum-vulgare-miller-subsp-vulgare-var-vulgare-fructus_en.pdf (accessed on 3 August 2019).
- Badgujar, S.B.; Patel, V.V.; Bandivdekar, A.H. Foeniculum vulgare Mill: A review of its botany, phytochemistry, pharmacology, contemporary application, and toxicology. Biomed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 842674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aschenbeck, K.A.; Hylwa, S.A. Brushing Your Way to Allergic Contact Dermatitis. Dermatitis 2017, 28, 219–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blaschek, W.; Hilgenfeldt, U.; Holzgrabe, U.; Reichling, J.; Ruth, P. HagerROM 2015. Hagers Enzyklopädie der Arzneistooffe und Drogen; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Anonymous. SCF Opinion of the Scientific Committee on Food on Estragole (1-Allyl-4-methoxybenzene); European Commission: Brussells, Belgium, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- EFSA. Opinion of the Scientific Committee on a request from EFSA related to A Harmonised Approach for Risk Assessment of Substances Which are both Genotoxic and Carcinogenic. EFSA J. 2005, 3, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA. Statement on the applicability of the Margin of Exposure approach for the safety assessment of impurities which are both genotoxic and carcinogenic in substances added to food/feed. EFSA J. 2012, 10, 2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihats, D.; Pilsbacher, L.; Gabernig, R.; Routil, M.; Gutternigg, M.; Laenger, R. Levels of estragole in fennel teas marketed in Austria and assessment of dietary exposure. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 68, 569–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mullen, M.P.; Pathak, M.A.; West, J.D. Carcinogenic effects of monofunctional and bifunctional furocoumarins. Natl. Cancer Inst. Monogr. 1984, 66, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Cho, E.; Feskanich, D.; Li, W.-Q.; Sun, Q.; Han, J.; Qureshi, A.A. Citrus consumption and risk of basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma of the skin. Carcinogenesis 2015, 36, 1162–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wu, S.; Han, J.; Feskanich, D.; Cho, E.; Stampfer, M.J.; Willett, W.C.; Qureshi, A.A. Citrus consumption and risk of cutaneous malignant melanoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 2500–2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melough, M.M.; Chun, O.K. Dietary furocoumarins and skin cancer: A review of current biological evidence. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 122, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santana, L.; Uriarte, E.; Roleira, F.; Milhazes, N.; Borges, F. Furocoumarins in medicinal chemistry. Synthesis, natural occurrence and biological activity. Curr. Med. Chem. 2004, 11, 3239–3261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deans, A.J.; West, S.C. DNA interstrand crosslink repair and cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2011, 11, 467–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melough, M.M.; Cho, E.; Chun, O.K. Furocoumarins: A review of biochemical activities, dietary sources and intake, and potential health risks. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 113, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anonymous. DFG–SKLM Toxikologische Beurteilung von Furocumarinen in Lebensmitteln. In Lebensmittel und Gesundheit II. Sammlung der Beschlüsse und Stellungnahmen/Opinions (1997–2004); Eisenbrand, G., Ed.; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH: Weinheim, Germany, 2005; pp. 55–87. [Google Scholar]
- Messer, A.; Nieborowski, A.; Strasser, C.; Lohr, C.; Schrenk, D. Major furocoumarins in grapefruit juice I: Levels and urinary metabolite(s). Food Chem. Toxicol. 2011, 49, 3224–3231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EMA. Reflection Paper on the Risks Associated with Furocoumarins Contained in Preparations of Angelica archangelica L.; European Medicines Agency: London, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhary, S.; Ceska, O.; Têtu, C.; Warrington, P.; Ashwood-Smith, M.; Poulton, G. Oxypeucedanin, a Major Furocoumarin in Parsley, Petroselinum crispum. Planta Med. 1986, 52, 462–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beier, R.C.; Ivie, G.W.; Oertli, E.H.; Holt, D.L. HPLC analysis of linear furocoumarins (psoralens) in healthy celery (Apium graveolens). Food Chem. Toxicol. 1983, 21, 163–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceska, O.; Chaudhary, S.K.; Warrington, P.J.; Ashwood-Smith, M.J. Photoactive furocoumarins in fruits of some umbellifers. Phytochemistry 1986, 26, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceska, O.; Chaudhary, S.; Warrington, P.; Poulton, G.; Ashwood-Smith, M. Naturally-occurring crystals of photocarcinogenic furocoumarins on the surface of parsnip roots sold as food. Experientia 1986, 42, 1302–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Søborg, I.; Andersson, C.; Gry, J. Furocoumarins in Plant Foods: Exposure, Biological Properties, Risk Assessment and Recommendations; Nordic Council of Ministers [Nordiska ministerrådet]: Copenhagen, Denmark, 1996; ISBN 9291209430. [Google Scholar]
- Kwon, Y.S.; Choi, W.G.; Kim, W.J.; Kim, W.K.; Kim, M.J.; Kang, W.H.; Kim, C.M. Antimicrobial constituents of foeniculum vulgare. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2002, 25, 154–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subehan; Zaidi, S.F.H.; Kadota, S.; Tezuka, Y. Inhibition on Human Liver Cytochrome P450 3A4 by Constituents of Fennel (Foeniculum vulgare): Identification and Characterization of a Mechanism-Based Inactivator. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 10162–10167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Lee, D.U.; Kim, Y.S.; Kim, H.P. 5-Lipoxygenase Inhibition of the Fructus of Foeniculum vulgare and Its Constituents. Biomol. Ther. (Seoul) 2012, 20, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilia, A.R.; Fumarola, M.; Gallori, S.; Mazzi, G.; Vincieri, F.F. Identification by HPLC–DAD and HPLC–MS Analyses and Quantification of Constituents of Fennel Teas and Decoctions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 4734–4738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EMA. Assessment Report on Foeniculuum vulgare Miller; European Medicines Agency: London, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
Sample Availability: Samples of the plant materials are available from the authors. |

| Sample | Recovery (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Psoralene | 5-Methoxypsoralene | Imperatorin | |
| Spiked before extraction | 101.34 | 105.81 | 84.56 |
| Spiked after extraction | 133.44 | 80.17 | 92.42 |
| Sample | μg/7.5 g Plant Material (± SD) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Psoralene | 5-Methoxypsoralene | Total | |
| 1 | 0.0551 ± 0.0015 | 0.6829 ± 0.0311 | 0.7380 |
| 2 | 0.0431 ± 0.0017 | 0.4830 ± 0.0172 | 0.5261 |
| 3 | 0.0504 ± 0.0011 | 0.6192 ± 0.0256 | 0.6696 |
| 4 | 0.0561 ± 0.0019 | 0.6419 ± 0.0301 | 0.6980 |
| 5 | 0.0646 ± 0.0031 | 0.6684 ± 0.0219 | 0.7330 |
| 6 | 0.0449 ± 0.0011 | 0.5239 ± 0.0092 | 0.5688 |
| 7 | 0.1072 ± 0.0050 | 1.1137 ± 0.0112 | 1.2209 |
| 8 | 0.0886 ± 0.0039 | 1.1052 ± 0.0216 | 1.1938 |
| 9 | 0.0938 ± 0.0045 | 1.0114 ± 0.0328 | 1.1052 |
| 10 | 0.0710 ± 0.0018 | 0.8730 ± 0.0178 | 0.9440 |
| 11 | 0.0175 ± 0.0006 | 0.1165 ± 0.0033 | 0.1340 |
| 12 | * | 0.0220 ± 0.0007 | 0.0220 |
| 13 | * | 0.0236 ± 0.0009 | 0.0236 |
| 14 | * | * | * |
| 15 | * | 0.0183 ± 0.0008 | 0.0183 |
| 16 | 0.0142 ± 0.0002 | 0.0618 ± 0.0021 | 0.0760 |
| 17 | * | * | * |
| 18 | * | * | * |
| 19 | * | * | * |
| 20 | 0.0193 ± 0.0007 | 0.2360 ± 0.0072 | 0.2553 |
| 21 | * | * | * |
| 22 | * | 0.0116 ± 0.0003 | 0.0116 |
| 23 | * | * | * |
| 24 | * | * | * |
| 25 | 0.0133 ± 0.0005 | 0.1184 ± 0.0039 | 0.1317 |
| 26 | 0.0078 ± 0.0002 | 0.0321 ± 0.0007 | 0.0399 |
| 27 | * | 0.0188 ± 0.0006 | 0.0188 |
| 28 | * | 0.0426 ± 0.0018 | 0.0426 |
| 29 | * | 0.0111 ± 0.0003 | 0.0111 |
| 30 | * | 0.1045 ± 0.0061 | 0.1045 |
| variety Berfena | * | 0.0634 ± 0.0028 | 0.0634 |
| variety Groβfrüchtig | * | 0.0099 ± 0.0002 | 0.0099 |
| variety Soroksár’ | * | 0.0745 ± 0.0011 | 0.0745 |
| caraway commercial sample | * | 0.1062 ± 0.0018 | 0.1062 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kerekes, D.; Csorba, A.; Gosztola, B.; Németh-Zámbori, É.; Kiss, T.; Csupor, D. Furocoumarin Content of Fennel—Below the Safety Threshold. Molecules 2019, 24, 2844. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24152844
Kerekes D, Csorba A, Gosztola B, Németh-Zámbori É, Kiss T, Csupor D. Furocoumarin Content of Fennel—Below the Safety Threshold. Molecules. 2019; 24(15):2844. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24152844
Chicago/Turabian StyleKerekes, Diána, Attila Csorba, Beáta Gosztola, Éva Németh-Zámbori, Tivadar Kiss, and Dezső Csupor. 2019. "Furocoumarin Content of Fennel—Below the Safety Threshold" Molecules 24, no. 15: 2844. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24152844
APA StyleKerekes, D., Csorba, A., Gosztola, B., Németh-Zámbori, É., Kiss, T., & Csupor, D. (2019). Furocoumarin Content of Fennel—Below the Safety Threshold. Molecules, 24(15), 2844. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24152844