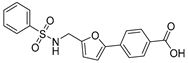
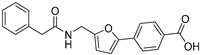
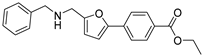
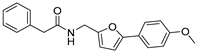
Abstract
Human sirtuin 2 (SIRT2), a member of the sirtuin family, has been considered as a promising drug target in cancer, neurodegenerative diseases, type II diabetes, and bacterial infections. Thus, SIRT2 inhibitors have been involved in effective treatment strategies for related diseases. Using previously established fluorescence-based assays for SIRT2 activity tests, the authors screened their in-house database and identified a compound, 4-(5-((3-(quinolin-5-yl)ureido)methyl)furan-2-yl)benzoic acid (20), which displayed 63 ± 5% and 35 ± 3% inhibition against SIRT2 at 100 μM and 10 μM, respectively. The structure-activity relationship (SAR) analyses of a series of synthesized (5-phenylfuran-2-yl)methanamine derivatives led to the identification of a potent compound 25 with an IC50 value of 2.47 μM, which is more potent than AGK2 (IC50 = 17.75 μM). Meanwhile, 25 likely possesses better water solubility (cLogP = 1.63 and cLogS = −3.63). Finally, the molecular docking analyses indicated that 25 fitted well with the induced hydrophobic pocket of SIRT2.
1. Introduction
Histone deacetylases (HDACs) are enzymes that catalyze the removal of acyl groups from ε-N-acyl-lysine amino groups on histones and non-histone substrates. These have been identified and grouped into four classes [1,2,3]: Classes I, II, and IV HDACs are Zn2+-dependent metalloproteases; class III HDACs, namely sirtuins (SIRTs), use NAD+ as a cofactor for catalysis [4,5,6]. There are seven isotypes of sirtuins (SIRT1–7), which differ in their catalytic activity and subcellular localization [7]. The isotype SIRT2, which is located in both cytoplasm and nucleus [8], mainly catalyzes deacetylation and defatty-acylation for a variety of protein substrates, including histones H3 and H4 [9,10], and nonhistone proteins α-tubulin [11], p53 [12], Foxo1 [13], p300 [14], NFκB [15], PAR3 and PRLR [16]. Thus, SIRT2 has been shown to be involved in cell cycle regulation [11,17,18], autophagy [19], peripheral myelination [20], and immune and inflammatory responses [21,22,23]. Recently, many studies revealed that the dysregulation of SIRT2 activity is a key factor contributing to the pathogenesis of cancer [24], neurodegenerative diseases [25,26], type II diabetes [27], and bacterial infections [21,23], which makes SIRT2 a promising target for pharmaceutical intervention.
To date, except for some substrate analogues [7], a number of small molecule inhibitors targeting SIRT2 have been reported. The representative inhibitors are shown in Figure 1: The moderate potency or non-specific inhibitors Sirtinol (46 μM) [28], EX-527 (46 μM) [29,30], AGK2 (3.5 μM) [31,32], AEM1(18.5 μM) [33], AK-7 (15.5 μM) [34], and AC-93253 (6 μM) [35], the highly potent but unselective inhibitors VII (0.048 μM) and VIII (0.001 μM) [36], and the potent and highly isotype-selective SIRT2 inhibitor SirReal2 (0.4 μM) [23,37]. However, there remains a shortage of novel SIRT2 inhibitors as lead candidates for drug discovery and development.
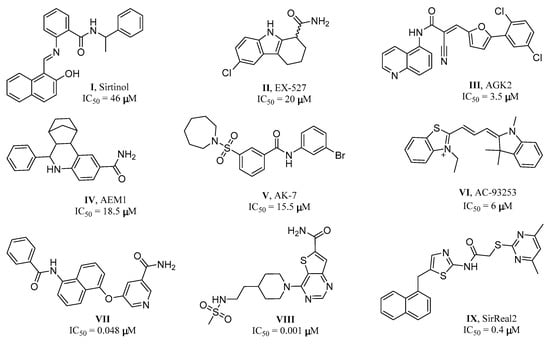
Figure 1.
Chemical structures and inhibition potencies of selected examples SIRT2 inhibitors.
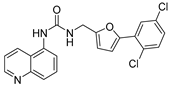
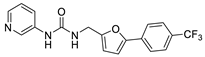
The authors previously established a fluorescence-based method for SIRT2 inhibition tests [38,39,40], and identified a series of N-(3-(phenoxymethyl)phenyl)acetamide derivatives as highly selective SIRT2 inhibitors [38,41], some of which showed inhibitory activities against SIRT2 highly-expressed human breast cancer cells and non-small cell lung cancer cells. Recently, the in-house compound collection using the fluorescence-based method was screened, and a new compound was identified, 4-(5-((3-(quinolin-5-yl)ureido)methyl)furan-2-yl)benzoic acid (20, Figure 2), which displayed 63 ± 5% and 35 ± 3% inhibition against SIRT2 at 100 μM and 10 μM, respectively (Table 1). The scaffold of compound 20 is novel for SIRT2 inhibitors, and 20 has a relatively low molecular weight (387 Da) with moderate physicochemical properties (cLogP = 3.05, cLogS = −4.04). Thus, in this study, the authors used 20 as a starting point for further structural modifications (Linker, A, B, Figure 2) to improve the inhibitory potency against SIRT2.

Figure 2.
Chemical structure of 20 and the focus of structural modifications.

Table 1.
The inhibitory activities and calculated clogP/clogS values of compounds 12, 20–22, 30, 32, 35–36, 39, 43–47 and 49–52 against human SIRT2.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Chemistry
This study synthesized a series of (5-phenylfuran-2-yl)methanamine derivatives using the synthetic routes outlined in Scheme 1, Scheme 2 and Scheme 3. Firstly, urea-based compounds 11–19 were acquired through the condensation reaction between the key intermediate 5a–5i with aromatic-amine compounds 6–10 in the presence of triphosgene, in 82–93% yields (Scheme 1). The intermediates 5a–5i were obtained by using Suzuki cross-coupling reaction between commercially available substituted iodobenzenes 1a–1i with (5-formylfuran-2-yl)boronic acid (2), respectively. Then, the condensation reaction and reduction reaction were performed in sequence to produce the intermediates 5a–5i. The carboxylic acid compounds 20–26 were subsequently produced through the hydrolysis reaction from the corresponding esters.

Scheme 1.
The preparation of target compounds 12, 17, 18 and 20–26. Reagents and conditions: (i) Pd(Pph3)2Cl2, Na2CO3, MeCN/H2O = 1:1, 60 °C, 1 h, 80–85% [42]; (ii) NH2OH·HCl, NaOAc, EtOH, Ref., 0.5 h, 100% [43]; (iii) Zn, HCl, EtOH, 80 °C; 62–83%; (iv) BTC, Et3N, DCM, RT., 0.5 h, 6 h, 82–93%; (v) NaOH, EtOH/H2O = 1:1, 80 °C, 2 h, 86–95%.
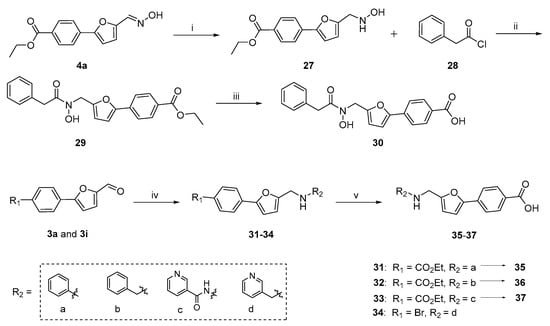
Scheme 2.
The preparation of target compounds 30 and 32–37. Reagents and conditions: (i) NaBH3CN, HCl, MeOH, 0–60 °C, 4 h, 54%; (ii) NaHCO3, diethyl ether, RT, 6 h, 78%; (iii) NaOH, EtOH/H2O = 1:1, 80 °C, 2 h, 89%; (iv) hantzschester, TFA, molecular sieve, DCM, 45 °C, 6–12 h, 56–95%; (v) NaOH, EtOH/H2O = 1:1, 80 °C, 2 h, 92–96%.
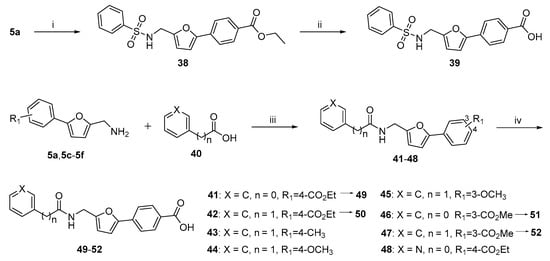
Scheme 3.
The preparation of target compounds 39, and 43–52. Reagents and conditions: (i) benzenesulfonyl chloride, Et3N, DCM, RT, 2 h, 91%; (ii) NaOH, EtOH/H2O = 1:1, 80 °C, 2 h, 90%; (iii) HOBT, EDCI, DIPEA, DCM, RT, 12 h, 73–91%; (iv) NaOH, EtOH/H2O = 1:1, 80 °C, 2 h, 90–95%.
Next, the desired target compound 30, a hydroxamic acid derivative, was prepared by a three-step sequence starting from the synthesized intermediate 4a (Scheme 2). Sodium cyanoborohydride (NaBH3CN)-mediated reduction reaction was firstly performed to reduce the aldoxime group of intermediate 4a to the hydroxylamine of intermediate 27 (54% yield), followed by condensation with 2-phenylacetyl chloride in the presence of NaHCO3 to give the compound 29. Further, hydrolysis of compound 29 using 3.0 equiv NaOH led to the white solid target compound 30. The synthesis of target compounds 32–37 are also depicted in Scheme 2. The reactions of commercially available amines (aniline, phenylmethanamine, and pyridin-3-ylmethanamine) or hydrazide (nicotinohydrazide) with intermediates 3a or 3i in the presence of hantzschester (1.2 equiv), catalytic amount of molecular sieve and trifluoroacetic acid, resulted in the reductive amination products 31–34. The resulting compounds 31–33 were subsequently hydrolyzed to give the desired compounds 35–37 in high yields.
Finally, Scheme 3 presents the synthetic routes for compounds 39 and 43–52, which contain a sulfonamide or amide linker. For sulfonamide linker compound 39, intermediate 5a was used to react with benzenesulfonyl chloride in the presence of Et3N at room temperature, and the resulting compound 38 underwent a hydrolysis reaction to give the desired target compound 39, in 80% yield for two steps. The synthetic access to structurally diverse amide linker compounds 41–48 was achieved using a condensation reaction of carboxylic acid (40) with amine (5a, 5c–5f) in the presence of 1-hydroxybenzotriazole (HOBT), 1-(3-(dimethylamino)propyl)-3-ethylcarbodiimide hydrochloride (EDCI), and N,N-diisopropylethylamine (DIPEA). The resulting ester-contained compounds 41, 42, 46 and 47 were subjected to hydrolyzation to afford the target compounds 49–52 in good yields.
2.2. SAR Studies with SIRT2
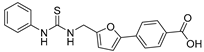
The enzyme activity assays were performed using a fluorogenic-based method [38,39,40], and Ac-Glu-Thr-Asp-Lys(Dec)-AMC, termed p2270, was used as the substrate. The SAR studies with all of the synthesized (5-phenylfuran-2-yl)methanamine derivatives (Table 1 and Table 2) were carried out. The compounds bearing various linkers or different substituents (A moiety) at 3- or 4-position of the phenyl of (5-phenylfuran-2-yl)methanamine scaffold (Table 1) were firstly investigated. Compared with the hit compound 20, compounds 12 and 21, containing a urea as linker, showed comparable or slightly lower SIRT2 inhibitory activities at 100 μM or 10 μM;.Carboxyl acid which contained compounds 20 and 21, appeared to have better clogP and clogS properties than 12 (with clogP of 5.14 and clogS of −4.43). Compound 22 (23 ± 3%), bearing a thiourea linker, displayed lower inhibitory activity to SIRT2 than the corresponding compound 21 (33 ± 3%) at 10μM. Further comparison of the different linkers, including hydroxamic acid (30), secondary amine (35, 36), sulfonamide (39) and amide (49, 50) revealed that urea linker derivatives were likely to have more potent SIRT2 inhibition than other linker derivatives. The additional compounds with the 4-ethyl formate (32), 4-methyl (43), 4-methoxy group (44) replaced the 4-carboxyl of the phenyl of (5-phenylfuran-2-yl)methanamine scaffold or changed to 3-position substituents (45–47, 51, and 52) did not show improved inhibitory activity against SIRT2. These results indicate that the urea linker and 4-carboxyl of the phenyl of (5-phenylfuran-2-yl)methanamine scaffold may be beneficial to fit with the binding pocket of SIRT2.

Table 2.
The inhibitory activities and calculated clogP/clogS values of compounds 17–18, 23–26, 33–34, 37 and 48 against human SIRT2.
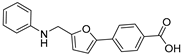
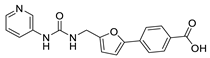
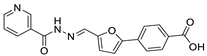
The authors next synthesized compounds 23–26, which contain a urea linker and 4-carboxyl of the phenyl of (5-phenylfuran-2-yl)methanamine. The tested inhibitory activities and calculated clogP and clogS values are shown in Table 2. Compounds 23, 24, and 26 appear to have moderate physiochemical properties, but compound 25, with the pyridine moiety, likely possesses better water solubility (cLogP = 1.63 and cLogS = −3.63). Notably, compound 25 (99 ± 2% @ 100 μM, 90 ± 3% @ 10 μM) shows potent inhibition against SIRT2, which is substantially more potent than the structurally similar compound AGK2 (80 ± 6% @ 100 μM, 30 ± 5% @ 10 μM). Considering the fact that the introduction of pyridine at the skeleton has improved SIRT2 inhibition, a series of pyridine-containing (5-phenylfuran-2-yl)methanamine derivatives (17, 18, 33, 34, 37 and 48) were further synthesized. Comparing with 25, only compounds 17 (50 ± 4% @ 100 μM, 37 ± 3% @ 10 μM) and 18 (40 ± 5% @ 100 μM, 23 ± 2% @ 10 μM), which both contained a urea linker, displayed low inhibition to SIRT2, whereas compounds 33, 34, 37 and 48 had almost no SIRT2 inhibitory activities (Table 2).
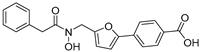
Collectively, the structural optimization and SAR studies led to the discovery of compound 25, which exhibited high potency against SIRT2, better than the hit compound 20 and positive control AGK2. Subsequently, the IC50 value of 25 was then measured against SIRT2, and the IC50 curve has been presented in Figure 3. The study observed that compound 25 inhibited SIRT2 via a dose dependent manner with an IC50 value of 2.47 μM, which is more potent than AGK2 (with an IC50 value of 17.75 μM). Molecular docking was then used to investigate the possible binding mode of 25 with SIRT2. The results indicated that 25 appeared to fit well with the induced hydrophobic pocket (Figure 4) [44,45]. The carboxyl acid group of 25 is likely positioned to make hydrogen-bonding interactions with the main chain of Asp170 and the side chain of Thr171 and Tyr139. The furan and pyridine moiety likely have hydrophobic contacts with hydrophobic residues Phe119, Phe234, Phe131, Leu138, and Ile169 (Figure 4). Notably, the pyridine appears to form edge-to-face aromatic interactions with Phe119, and fits well with the pocket around Phe119, Phe131, and Phe234, suggesting that introducing substituents on pyridine may result in a clash with these three residues. Together, these docking results may explain why the replacement of the carboxyl acid group or the introduction of substituents on pyridine leads to a decrease in SIRT2 inhibition, and indicates the possible inhibition mode for this series of compounds.
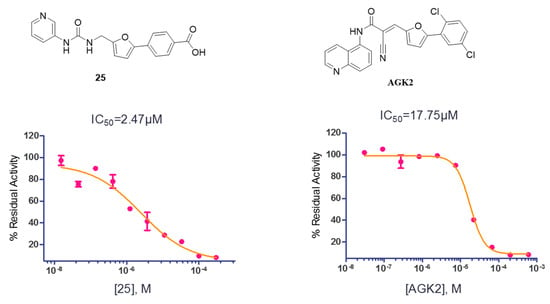
Figure 3.
The chemical structures and IC50 curves against SIRT2 of 25 and AGK2.

Figure 4.
The docking pose of the compound 25 in the substrate binding site of SIRT2.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Synthesis
As previously reported, proton (1H) and carbon (13C) NMR spectra were recorded on a Bruker AV-400 (Bruker Company, Billerica, Germany) instrument and are reported in ppm relative to tetramethylsilane (TMS) and referenced to the solvent in which the spectra were collected. Unless otherwise noted, all of the commercially available starting materials, reagents, and solvents and reagents were used without further purification. The analytical thin-layer chromatography (TLC) was run on Merck silica gel 60 F-254 (Qingdao Haiyang, Qingdao, China). The spots on the plates were visualized under UV light (λ = 254 nm). Purification was performed on silica gel chromatography with EtOAc—petroleum ether or CH2Cl2-MeOH solvent systems. The melting points were measured on an electrothermal melting point apparatus without correction (JIAHANG, Shanghai, China. ESI-MS was obtained on a Shimadzu-2010EV series liquid chromatograph mass spectrometer (Shimadzu, Tokyo, Japan). High-resolution mass spectra (HRMS) were determined using a SCIEX X500 QTOF mass spectrometer (Shanghai Sciex Analytical Instrument Trading Co., Shanghai, China). All target compounds were purified to >95% purity, as determined by the high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). The HPLC analysis was performed on a Waters 2695 HPLC system equipped with a Kromasil C18 column (4.6 mm × 250 mm, 5 μm, Waters, Milford, MA, USA).
3.1.1. General Procedure for the Preparation of Key Intermediates 5a–5i
A mixture of substituted iodobenzenes (1a–1i, 15 mmol), (5-formylfuran-2-yl)boronic acid (2, 15 mmol), bis(triphenylphosphine)palladium(II) chloride (Pd(Pph3)2Cl2, 0.6 mmol) and sodium carbonate (Na2CO3, 30 mmol) in MeCN/H2O (10 mL /10 mL) was stirred for 1 h at 60 °C. Upon completion of the reaction as determined by TLC, MeCN was removed by a rotary evaporator under reduced pressure, and the residue was acidated with 1M HCl solution (pH 7) and filtered. Next, the filtrate was partitioned between water (60 mL) and ethyl acetate (3 × 50 mL). The organic layer was dried over magnesium sulfate anhydrous (MgSO4), filtered and concentrated in vacuo. The crude products were purified by column chromatography with appropriate eluents to give the coupling products 3a–3i, in 80–86% yields.
To a solution of the coupling products 3a–3i (12 mmol) in EtOH (25 mL), hydroxylamine hydrochloride (NH2OH.HCl, 14.4 mmol) and sodium acetate (NaOAc, 14.4 mmol) were added and the mixture was stirred at reflux for 0.5 h. When TLC indicated that the reaction was finished, the reaction solution was concentrated and the residue was partitioned between water (50) and ethyl acetate (3 × 50 mL). The combined organic layer was dried over MgSO4, filtered and concentrated in vacuo to give the crude products 4a–4i, which were used without further purification. Subsequently, to a stirring solution of condensation products, 4a–4i (12 mmol) in EtOH (25 mL) was added to zinc powder (Zn, 12 mmol) and 3 M hydrochloric acid (HCl, 8.0 mL) at ambient temperatures. The reaction mixture was heated to 80 °C for further 2 h. After completion (monitored by TLC), the solvent was removed in vacuo, the crude residue was treated with 100 mL of ice water, and the pH was adjusted to 7–8 with saturated NaHCO3. Then, the mixture was filtered by diatomite and extracted with ethyl acetate (3 × 80 mL). The combined extracts were dried, concentrated and purified by column chromatography with appropriate eluents with three ethylamine (Et3N, TEA) to afford the desired intermediates 5a–5i in high yields.
1-((5-(2,5-Dichlorophenyl)furan-2-yl)methyl)-3-(quinolin-5-yl)urea (12). A solution of quinolin-5-amine (7, 250 mg, 1.73 mmol) and TEA (200 μL, 2.03 mmol) dissolved in CH2Cl2 (DCM, 15 mL) was slowly dripped into a stirred solution of triphosgene (BTC, 256 mg, 0.85 mmol) in DCM (10 mL) by using a constant-pressure dropping funnel. Then, the mixture was stirred for another 0.5 h at room temperature (RT). After evaporation of the solvent, the residue was taken up in DCM (30 mL), and (5-(2,5-dichlorophenyl)furan-2-yl)methanamine (5b, 230 mg, 0.95 mmol) was added directly to the residue. The reaction mixture was stirred at RT for 6 h, and the solvent was subsequently removed in vacuo. The residue obtained was purified by column chromatography (V(PE):V(EA) = 1:1) to give the desired target compound 12 (343 mg, 0.84 mmol) in 88% yield. 96.8% HPLC purity. Mp: 245–246 °C. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.92 (s, 1H), 8.89 (dd, J = 4.0 Hz, J = 4.0 Hz, 1H), 8.54 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H), 8.06–8.04 (m, 1H), 7.86 (d, J = 2.8 Hz, 1H), 7.69 (s, 1H), 7.68 (d, J = 2.8 Hz, 1H), 7.60–7.53 (m, 2H), 7.39 (dd, J = 8.4 Hz, J = 2.4 Hz, 1H), 7.20 (d, J = 3.2 Hz, 2H), 6.53 (d, J = 3.2 Hz, 1H), 4.47 (d, J = 5.6 Hz, 2H) ppm. 13C-NMR (101 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 155.9, 154.7, 150.7, 148.7, 147.3, 135.8, 133.0, 132.7, 130.8, 130.3, 129.9, 128.6, 127.7, 126.9, 123.8, 121.3, 121.0, 117.4, 113.6, 109.5, 36.90 ppm. HRMS: m/z calcd for C21H16N3O2 [M + H]+ 412.0577, found 412.0573.
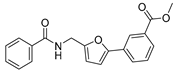
Ethyl 4-(5-((3-(pyridin-3-yl)ureido)methyl)furan-2-yl)benzoate (17). The title compound was prepared from pyridin-3-amine (9) and ethyl 4-(5-(aminomethyl)furan-2-yl)benzoate (5a) using the same method as compound 12, purified by column chromatography (V(DCM):V(MeOH) = 30:1). Yield: 82%. HPLC purity: 98.6%. Mp: 182–184 °C. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 9.45 (s, 1H), 8.59 (d, J = 2.4 Hz, 1H), 8.12 (dd, J = 4.4, 1.2 Hz, 1H), 7.99 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H), 7.93–7.88 (m, 1H), 7.82 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H), 7.26 (dd, J = 8.4, J = 4.4 Hz, 1H), 7.18 (s, 1H), 7.10 (d, J = 3.2 Hz, 1H), 6.46 (d, J = 3.2 Hz, 1H), 4.40 (d, J = 5.6 Hz, 2H), 4.32 (q, J = 7.2 Hz, 2H), 1.33 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 3H) ppm. 13C-NMR (101 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 165.8, 155.6, 155.0, 151.5, 142.6, 139.9, 137.5, 134.8, 130.3, 128.5, 124.8, 124.0, 123.6, 114.6, 109.8, 61.2, 45.8, 31.2 ppm. HRMS: m/z calcd for C20H20N3O4 [M + H]+ 366.1448 found 366.1444.
1-(Pyridin-3-yl)-3-((5-(4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)furan-2-yl)methyl)urea (18). The title compound was prepared from pyridin-3-amine (9) and ((5-(4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)furan-2-yl)methyl)-l2-azane (5h) using the same method as compound 12, purified by column chromatography (V(PE):V(EA) = 3:1). Yield: 83%. HPLC purity: 98.0%. Mp: 183–187 °C. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.87 (s, 1H), 8.58 (s, 1H), 8.14 (s, 1H), 7.91 (d, J = 12.8 Hz, 2H), 7.87 (s, 1H), 7.77 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H), 7.27 (dd, J = 12.8 Hz, J = 2.8 Hz, 1H), 7.11 (d, J = 3.2 Hz, 1H), 6.89 (t, J = 5.6 Hz, 1H), 6.46 (d, J = 3.2 Hz, 1H), 4.41 (d, J = 5.6 Hz, 2H) ppm. 13C-NMR (10 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 155.5, 154.9, 154.1, 151.0, 143.6, 142.1, 139.3, 137.9, 134.3, 130.0, 126.4, 126.3, 125.5, 124.0, 109.7, 45.8 ppm. HRMS: m/z calcd for C18H15N3O2 [M + H]+ 362.1061, found 362.1070.
4-(5-((3-(Quinolin-5-yl)ureido)methyl)furan-2-yl)benzoic Acid (20). A mixture of ethyl 4-(5-((3-(quinolin-5-yl)ureido)methyl)furan-2-yl)benzoate (11, 415 mg, 1.0 mmol), which was prepared from quinolin-5-amine (9) and ethyl 4-(5-(aminomethyl)furan-2-yl)benzoate (5a) using the same method as compound 12, and NaOH (127 mg, 3.0 mmol) reacted for 2 h in the solution of EtOH/H2O (10 mL/10 mL) at 80 °C. After evaporation of the organic solvent, the residue was treated with 50 mL of ice water, and the PH was adjusted to 6–7 with diluted HCl. Next, the mixture was extracted with ethyl acetate (3 × 50 mL). The combined extracts were washed with brine, dried, and concentrated. The residue obtained was purified by column chromatography (V(PE):V(EA) = 2:1) to give the final compound 20 (344 mg) in 89% yield. HPLC purity: 98.2%. Mp: 285–287 °C. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 9.84 (s, 1H), 9.01 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H), 8.86 (d, J = 4.0 Hz, 1H), 8.20 (t, J = 5.6 Hz, 1H), 8.14 (q, J = 5.6 Hz 1H), 7.94 (s, 1H), 7.92 (s, 1H), 7.68–7.62 (m, 4H), 7.50 (q, J = 4.0 Hz, 1H), 6.89 (d, J = 3.2 Hz, 1H), 6.45 (d, J = 3.2 Hz, 1H), 4.43 (d, J = 5.2 Hz, 1H) ppm. 13C-NMR (101 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 170.8, 156.2, 153.7, 152.8, 150.5, 148.7, 136.5, 131.6, 130.1, 129.9, 123.0, 122.7, 121.0, 120.7, 116.3, 107.2, 101.7, 99.6, 36.9 ppm. HRMS: m/z calcd for C22H18N3O4 [M + H]+ 388.1252, found 388.1254.
4-(5-((3-Phenylureido)methyl)furan-2-yl)benzoic Acid (21). The title compound was prepared from ethyl 4-(5-((3-phenylureido)methyl)furan-2-yl)benzoate (13) using the same method as compound 20, purified by column chromatography (V(PE):V(EA) = 2:1). Yield: 86%. HPLC purity: 97.6%. Mp: 285–288 °C. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 9.28 (s, 1H), 7.99 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H), 7.70 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H), 7.85 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H), 7.38 (s, 1H), 7.21 (t, J = 7.6 Hz, 2H), 6.95 (d, J = 3.2 Hz, 1H), 6.88 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 1H), 6.40 (d, J = 2.8 Hz, 1H), 4.37 (d, J = 5.2 Hz, 2H) ppm. 13C-NMR (101 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 168.9, 155.8, 154.6, 152.0, 141.2, 133.1, 130.3, 129.0, 123.1, 121.3, 118.0, 109.4, 108.5, 36.8 ppm. HRMS: m/z calcd for C19H16N2O4Na [M + Na]+ 359.0968, found 359.0965.
4-(5-((3-Phenylthioureido)methyl)furan-2-yl)benzoic Acid (22). The title compound was prepared from ethyl 4-(5-((3-phenylthioureido)methyl)furan-2-yl)benzoate (14) using the same method as compound 20, purified by column chromatography (V(PE):V(EA) = 4:1). Yield: 87%. HPLC purity: 97.6%. Mp: 281–282 °C. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 11.04 (s, 1H), 9.44 (s, 1H), 7.95 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 3H), 7.70 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H), 7.64 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H), 7.30 (t, J = 4.0 Hz, 2H), 7.07 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H), 6.96 (d, J = 3.2 Hz, 1H), 6.48 (d, J = 3.2 Hz, 1H), 4.82 (d, J = 5.6 Hz, 2H) ppm. 13C-NMR (101 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 207.0, 181.4, 169.6 152.9, 152.4, 140.7, 132.7, 130.3, 128.7, 124.0, 123.1, 123.0, 110.1, 108.1, 31.2 ppm. HRMS: m/z calcd for C19H17N2O3S [M + H]+ 353.0954, found 353.0962.
4-(5-((3-(4-Cyano-3-fluorophenyl)ureido)methyl)furan-2-yl)benzoic Acid (23). The title compound was prepared from ethyl 4-(5-((3-(4-cyano-3-fluorophenyl)ureido)methyl)furan-2-yl)benzoate (15) using the same method as compound 20, purified by column chromatography (V(DCM):V(MeOH) = 30:1). Yield: 92%. HPLC purity: 97.2%. Mp: 192–193 °C. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 10.97 (s, 1H), 8.53 (s, 1H), 7.96 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H), 7.83 (dd, J = 12.8 Hz, J = 2.0 Hz 1H), 7.70 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 3H), 7.41 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H), 6.93 (d, J = 3.2 Hz, 1H), 6.41 (d, J = 3.2 Hz, 1H), 4.40 (d, J = 5.6 Hz, 2H) ppm. 13C-NMR (101 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 207.0, 169.6, 165.0, 162.5, 155.2, 153.6, 152.4, 148.45 134.3, 132.7, 130.3, 123.1, 115.4, 114.4, 109.6, 108.0, 45.9 ppm. HRMS: m/z calcd for C20H15FN3O4 [M + H]+ 380.1041, found 380.1040; C20H14FN3O4Na [M + Na]+ 402.0855, found 402.0857.
2-Hydroxy-4-(5-((3-phenylureido)methyl)furan-2-yl)benzoic Acid (24). The title compound was prepared from ethyl 2-hydroxy-4-(5-((3-phenylureido)methyl)furan-2-yl)benzoate (16) using the same method as compound 20, purified by column chromatography(V(DCM):V(MeOH) = 30:1). Yield: 86%. HPLC purity: 96.6%. Mp: 224–227 °C. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 12.05 (s br, 2H), 8.60 (s, 1H), 7.82 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 1H), 7.42 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H), 7.24 (d, J = 12.8 Hz, 4H), 7.10 (d, J = 3.2 Hz, 1H), 6.91 (s, 1H), 6.68 (s, 1H), 6.43 (d, J = 3.2 Hz, 1H), 4.38 (d, J = 5.6 Hz, 2H) ppm. 13C-NMR (101 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 172.1, 162.1, 155.5, 155.2, 151.2, 140.8, 137.0, 131.5, 129.2, 121.7, 118.3, 114.6, 111.9, 111.1, 110.2, 109.6, 36.9 ppm. HRMS: m/z calcd for C19H17N2O5 [M + H]+ 353.1132, found 353.1140.
4-(5-((3-(Pyridin-3-yl)ureido)methyl)furan-2-yl)benzoic Acid (25). The title compound was prepared from ethyl 4-(5-((3-(pyridin-3-yl)ureido)methyl)furan-2-yl)benzoate (17) using the same method ascompound 20, purified by column chromatography (V(PE):V(EA) = 3:1). Yield: 95%. HPLC purity: 98.6%. Mp: 218–220 °C. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 12.98 (s br, 1H), 8.84 (s, 1H), 8.58 (s, 1H), 8.14 (d, J = 4.0 Hz, 1H), 7.99 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H), 7.93 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H), 7.79 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H), 7.29 (q, J = 4.8 Hz, 1H), 7.08 (d, J = 3.2 Hz, 1H), 6.87 (t, J = 5.6 Hz, 1H), 6.45 (d, J = 3.2 Hz, 1H), 4.41 (d, J = 5.6 Hz, 2H) ppm. 13C-NMR (101 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 167.5, 155.4, 154.7, 151.6, 142.7, 140.1, 137.5, 134.5, 130.5, 129.5, 125.2, 124.1, 123.5, 109.8, 109.5, 31.2 ppm. HRMS: m/z calcd for C18H16N3O4 [M + H]+ 338.1135, found338.1138.
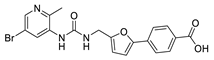
4-(5-((3-(5-Bromo-2-methylpyridin-3-yl)ureido)methyl)furan-2-yl)benzoic acid (26). The title compound was prepared from ethyl 4-(5-((3-(5-bromo-2-methylpyridin-3-yl)ureido)methyl)furan-2-yl)benzoate (19) using the same method as compound 20, purified by column chromatography (V(DCM):V(MeOH) = 10:1). Yield: 90%. HPLC purity: 97.6%. Mp: 250–254 °C. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 12.96 (s, 1H), 8.56 (d, J = 2.8 Hz, 1H), 8.35 (s, 1H), 8.14 (d, J = 2.8 Hz, 1H), 7.98 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H), 7.80 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H), 7.58 (s, 1H), 7.09 (d, J = 3.2 Hz, 1H), 6.49 (d, J = 3.2 Hz, 1H), 4.42 (d, J = 5.6 Hz, 2H), 2.40 (s, 3H) ppm. 13C-NMR (101 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 167.4, 155.4, 154.4, 151.8, 146.2, 142.0, 136.2, 134.4, 130.5, 129.6, 127.9, 123.5, 117.5, 110.0, 109.5, 36.8, 21.38 ppm. LCMS m/z: 428.0 [M − H]−.
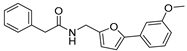
4-(5-((N-hydroxy-2-phenylacetamido)methyl)furan-2-yl)benzoic Acid Ethyl (30). To a solution of (E)-4-(5-((hydroxyimino)methyl)furan-2-yl)benzoate (4a, 610 mg, 2.35 mmol) in methyl alcohol (10 mL), sodium cyanoborohydride (440 mg, 1.5 mmol) and 12 M hydrochloric acid (780 μL, 9.4 mmol) were added at 0 °C. Then, the mixture was stirred at room temperature for 4 h. When TLC indicated that the reaction was finished, the reaction solution was concentrated and the residue was basified with 6 N sodium hydroxide solution (pH 8) and extracted several times with ethyl acetate. The combined organic extracts were dried (Na2SO4), and concentrated under reduced pressure to yield the reduction product ethyl 4-(5-((hydroxyamino)methyl)furan-2-yl)benzoate (27, 328 mg) in 54% yield. Next, 2-phenylacetyl chloride (28, 195 mg, 1.27 mmol) and NaHCO3 (106 mg, 1.27 mmol) were added to the solution of 27 (328 mg, 1.27 mmol) in diethyl ether (15 mL) and the reaction was stirred at room temperature for 6 h. Upon completion of the reaction as determined by TLC, the resulting solution was concentrated under reduced pressure to dryness and the residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography to give the light yellow compound 29 in 78% yield. The target compound 30 was gained from ethyl 4-(5-((N-hydroxy-2-phenylacetamido)methyl)furan-2-yl)benzoate (29) using the same method as compound 20, purified by column chromatography (V(PE):V(EA) = 3:1). Yield: 89%. HPLC purity: 97.0%. Mp: 162–163 °C. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 12.95 (s, 1H), 10.15 (s, 1H), 7.98 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 2H) 7.75 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H), 7.32–7.21 (m, 5H), 7.08 (d, J = 3.2 Hz, 1H), 6.49 (d, J = 3.2 Hz, 1H), 4.80 (s, 2H), 3.79 (s, 2H) ppm. 13C-NMR (101 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 171.9, 167.4, 152.0, 151.8, 136.1, 134.4, 130.5, 129.9, 129.6, 128.6, 126.8, 123.6, 111.7, 109.4, 45.07, 38.9 ppm. HRMS: m/z calcd for C20H16NO5 [M − H]− 350.1034, found 350.1066.
3.1.2. Hantzsch-Involved Reductive Amination Used for Compounds 31–34
To a solution of substituted 5-phenylfuran-2-carbaldehydes (3a and 3i, 1.5 mmol), different amines (1.8 mmol) and diethyl 2,6-dimethyl- 1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate (hantzschester, 1.8 mmol) in DCM (25 mL), catalytic amount of molecular sieve and trifluoroacetic acid were added at room temperature, and the reaction was warmed to 45 °C and reacted for 6–12 h. After completion (monitored by TLC), the reaction was filtered, and the crude residue was obtained by concentrating the filtrate in vacuo. Finally, the crude residue was purified by column chromatography to give the desired compounds 31–34 in high yields.
Ethyl 4-(5-((Benzylamino)methyl)furan-2-yl)benzoate (32). Yield: 56%. HPLC purity: 98.1%. Mp: 250–251 °C. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 7.98 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H), 7.81 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H), 7.37–7.30 (m, 4H), 7.23 (t, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H), 7.08 (d, J = 3.2 Hz, 1H), 6.44 (d, J = 3.2 Hz, 1H), 4.31 (q, J = 7.2 Hz, 2H), 3.74 (s, 4H), 2.80 (s br, 1H), 1.33 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 3H) ppm. 13C-NMR (101 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 165.9, 156.4, 151.3, 140.9, 135.0, 130.3, 128.6, 128.5, 128.3, 127.1, 123.5, 110.0, 109.7, 61.2, 52.5, 45.3, 14.67 ppm. LCMS m/z: 335.2 [M + H]+.
Ethyl (E)-4-(5-((2-nicotinoylhydrazono)methyl)furan-2-yl)benzoate (33). Yield: 72%. HPLC purity: 97.5%. Mp: 201–204 °C. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 12.10 (s, 1H), 9.09 (d, J = 1.2 Hz, 1H),8.79 (d, J = 3.6 Hz, 1H), 8.41 (s, 1H), 8.28 (dt, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H), 8.05 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H), 7.94 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H), 7.62–7.58 (m, 1H), 7.36 (d, J = 3.6 Hz, 1H), 7.16 (d, J =3.6 Hz, 1H), 4.34 (q, J = 7.2 Hz, 2H), 1.35 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 3H) ppm. 13C-NMR (101 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 165.7, 162.2, 154.2, 152.9, 150.4, 149.0, 138.2, 136.0, 133.9, 130.4, 129.5, 129.4, 124.5, 124.1, 117.3, 111.3, 61.3, 14.7 ppm. HRMS: m/z calcd for C20H18N3O4 [M + H]+ 364.1260, found 364.1264.
1-(5-(4-Bromophenyl)furan-2-yl)-N-(pyridin-3-ylmethyl)methanamine (34). Yield: 95%. HPLC purity: 97.8%. Mp: 146–150 °C. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.53 (s, 1H), 8.44 (d, J = 3.6 Hz, 1H), 7.76 (d, J = 7.6 Hz, 1H), 7.64–7.58 (m, 5H), 7.35–7.32 (m, 1H), 6.93 (d, J = 3.2 Hz, 1H), 6.39 (d, J = 3.2 Hz, 1H), 3.75 (s, 2H), 3.72 (s, 2H), 1.23 (s, 1H) ppm. 13C-NMR (101 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 155.1, 151.3, 149.9, 148.4, 136.3, 136.2, 132.2, 130.1, 125.6, 123.8, 120.4, 109.8, 107.8, 49.9, 45.4 ppm. HRMS: m/z calcd for C17H15BrNO2 [M + H]+ 342.0368, found 343.0397 and 345.0387.
4-(5-((phenylamino)methyl)furan-2-yl)benzoic Acid (35). The title compound was prepared from ethyl 4-(5-((phenylamino)methyl)furan-2-yl)benzoate (31) using the same method ascompound 20, purified by column chromatography (V(PE):V(EA) = 2:1). Yield: 96%. HPLC purity: 98.3%. Mp: 207–210 °C. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 12.96 (s, 1H), 7.98 (d, J = 7.6 Hz, 2H), 7.78 (d, J = 7.6 Hz, 2H), 7.09 (t, J = 7.6 Hz, 2H), 7.05 (d, J = 3.2 Hz, 1H), 6.70 (d, J = 7.6 Hz, 2H), 6.57 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 1H), 6.47 (d, J = 3.2 Hz, 1H), 6.18 (s br, 1H), 4.34 (s, 2H) ppm. 13C-NMR (101 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 167.4, 155.2, 151.5, 148.7, 134.6, 130.5, 129.4, 129.3, 123.4, 116.7, 112.9, 110.1, 109.4, 40.5 ppm. LCMS m/z: 294.1 [M + H]+.
4-(5-((Benzylamino)methyl)furan-2-yl)benzoic Acid (36). The title compound was prepared from ethyl 4-(5-((benzylamino)methyl)furan-2-yl)benzoate (32) using the same method as compound 20, purified by column chromatography (V(PA):V(EA) = 2:1). Yield: 92%. HPLC purity: 98.0%. Mp: 248–250 °C. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 10.96 (s br, 1H), 8.00 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H), 7.88 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H), 7.60 (d, J = 6.4 Hz, 2H), 7.44–7.38 (m, 3H), 7.17 (d, J = 3.2 Hz, 1H), 6.81 (d, J = 3.2 Hz, 1H), 4.27 (s, 2H), 4.19 (s, 2H) ppm. 13C-NMR (101 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 167.4, 153.3, 147.3, 134.0, 132.5, 130.6, 130.5, 130.1, 129.3, 129.1, 124.0, 115.0, 109.5, 50.0, 42.6 ppm. HRMS: m/z calcd for C19H17NO3 [M + H]+ 308.1265, found 308.1260.
(E)-4-(5-((2-nicotinoylhydrazono)methyl)furan-2-yl)benzoic Acid (37). The title compound was prepared from ethyl (E)-4-(5-((2-nicotinoylhydrazono)methyl)furan-2-yl)benzoate (33) using the same method as compound 20, purified by column chromatography (V(PE):V(EA) = 2:1). Yield: 92%. HPLC purity: 97.2%. Mp: 237–240 °C. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 12.10 (s, 1H), 9.09 (s, 1H), 8.79 (d, J = 3.6 Hz, 1H), 8.41 (s, 1H), 8.28 (dt, J = 8.4 Hz, J = 2.0 Hz, 1H), 8.05 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H), 7.93 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H), 7.62–7.58 (m, 1H), 7.34 (d, J = 3.6 Hz, 1H), 7.16 (d, J = 3.6 Hz, 1H) ppm. 13C-NMR (101 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 164.7, 162.2, 154.6, 152.8, 150.9, 149.1, 138.4, 137.2, 136.0, 130.5, 129.6, 129.5, 124.2, 124.1, 117.1, 110.7 ppm. HRMS: m/z calcd for C18H14N3O4 [M + H]+ 336.0975, found 336.0952.
4-(5-(Phenylsulfonamidomethyl)furan-2-yl)benzoic Acid (39). The intermediate 5a (100 mg, 0.43 mmol) reacted with benzenesulfonyl chloride (90 mg, 0.05 mmol,) in the presence of Et3N (179 μL, 1.30 mmol) at room temperature, in DCM (15 mL). When TLC indicated that the reaction was finished, the reaction was concentrated in vacuo and the pH was adjusted to 7–8 with saturated NaHCO3. Then, the water solution was extracted with ethyl acetate (3 ×). The combined extracts were concentrated to give brown crude product ethyl 4-(5-(phenylsulfonamidomethyl)furan-2-yl)benzoate (38) in 91% yield, which was used to synthesize the target compound 39, in 90% yield. HPLC purity: 97.5%. Mp: 222–223 °C. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ13.00 (s, 1H), 8.36 (d, J = 6.0 Hz, 1H), 8.00 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H), 7.85 (d, J = 6.8 Hz, 2H), 7.69 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H), 7.62–7.55 (m, 3H), 6.98 (d, J = 3.6 Hz, 1H), 6.38 (d, J = 3.2 Hz, 1H) 4.19 (d, J = 6.0 Hz, 2H) ppm. 13C-NMR (101 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 167.4, 152.1, 152.0, 141.2, 134.2, 132.7, 130.4, 129.5, 129.5, 126.9, 123.6, 111.1, 109.1, 39.9 ppm. HRMS: m/z calcd for C18H16NO5S [M + H]+ 358.0671, found 358.0670.
2-Phenyl-N-((5-(p-tolyl)furan-2-yl)methyl)acetamide (43). (5-(p-tolyl)furan-2-yl)methanamine (5c, 378 mg, 1.49 mmol) reacted with 2-phenylacetic acid (200 mg, 1.47 mmol) in the presence of 1-hydroxybenzotriazole (HOBT, 214 mg, 1.47 mmol), 1-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-3-ethylcarbodiimide hydrochloride (EDCI, 282 mg, 1.47 mmol), and N,N-diisopropylethylamine (DIPEA, 0.21 mL, 4.3 mmol) in DCM (20 mL). The mixture was stirred at room temperature for 12 h. Then, the mixture was concentrated and partitioned between water (60 mL) and ethyl acetate (3 × 60 mL). The organic layer was dried over MgSO4, filtered, concentrated and purified by column chromatography (V(PE):V(EA) = 6:1) to give the target compound 43 (327 mg) in 73% yield. HPLC purity: 99.2%. Mp: 193–194 °C. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.60 (t, J = 5.6 Hz, 1H), 7.54 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H), 7.30 (d, J = 4.4 Hz, 4H), 7.24–7.21 (m, 3H), 6.78 (d, J = 3.2 Hz, 1H), 6.30 (d, J = 3.2 Hz, 1H), 4.33 (d, J = 5.6 Hz, 2H), 3.48 (s, 2H), 2.32 (s, 2H) ppm. 13C-NMR (101 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ170.5, 152.8, 152.2, 137.1, 136.8, 129.9, 129.4, 128.7, 128.2, 126.8, 123.7, 109.4, 106.1, 42.7, 36.3, 21.3 ppm. HRMS: m/z calcd for C20H19NO2 Na [M + Na]+ 328.1231, found 328.1228.
N-((5-(4-methoxyphenyl)furan-2-yl)methyl)-2-phenylacetamide (44). The title compound was prepared from intermediate 5d using the same method as compound 43, purified by column chromatography (V(PA):V(EA) = 7:1). Yield: 86%. HPLC purity: 98.2%. Mp: 196–197 °C. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.59 (t, J = 5.6 Hz, 1H), 7.58 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 7.30 (d, J = 4.4 Hz, 4H), 7.25–7.21 (m, 1H), 6.99 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 6.69 (d, J = 3.2 Hz, 1H), 6.28 (d, J = 3.2 Hz, 1H), 4.33 (d, J = 5.6 Hz, 2H), 3.79 (s, 3H), 3.49 (s, 2H) ppm. 13C-NMR (101 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 170.5, 159.1, 152.8, 151.8, 136.8, 129.4, 128.7, 126.8, 125.2, 123.8, 114.8, 109.4, 105.1, 55.6, 42.7, 36.3 ppm. HRMS: m/z calcd for C20H19NO2 Na [M + Na]+ 344.1170, found 344.1175.
N-((5-(3-methoxyphenyl)furan-2-yl)methyl)-2-phenylacetamide (45). The title compound was prepared from intermediate 5e using the same method as compound 43, purified by column chromatography (V(PE):V(EA) = 7:1). Yield: 91%. HPLC purity: 97.8%. Mp: 182–184 °C. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.61 (t, J = 5.6 Hz, 1H), 7.35–7.29 (m, 5H), 7.25–7.23 (m, 2H), 7.21–7.20 (m, 1H), 6.89 (d, J = 3.2 Hz, 1H), 6.86 (dd, J = 8.0 Hz, J = 3.2 Hz, 1H), 6.32 (d, J = 3.6 Hz, 1H), 4.34 (d, J = 5.6 Hz, 2H), 3.80 (s, 3H), 3.50 (s, 2H) ppm. 13C-NMR (101 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 170.6, 160.1, 152.7, 152.5, 136.8, 132.1, 130.5, 129.4, 128.7, 126.8, 116.2, 113.4, 109.5, 109.1, 107.4, 55.6, 42.7, 36.3 ppm. HRMS: m/z calcd for C20H19NO2 Na [M + Na]+ 344.1170, found 344.1174.
Methyl 3-(5-(benzamidomethyl)furan-2-yl)benzoate (46). The title compound was prepared from intermediate 5f and benzoic acid using the same method as compound 43, purified by column chromatography (V(PE):V(EA) = 8:1). Yield: 90%. HPLC purity: 97.9%. Mp: 197–198 °C. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 9.09 (t, J = 6.4 Hz, 1H), 8.22 (s, 1H), 7.95 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H), 7.91 (d, J = 7.6 Hz, 2H), 7.85 (d, J = 7.6 Hz, 1H), 7.59–7.53 (m, 2H), 7.50–7.46 (m, 2H), 7.03 (d, J = 3.2 Hz, 1H), 6.44 (d, J = 3.2 Hz, 1H), 4.57 (q, J = 5.6 Hz, 2H), 3.89 (s, 3H) ppm. 13C-NMR (101 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ166.7, 166.5, 153.6, 151.4, 134.6, 131.8, 131.3, 130.8, 130.0, 128.8, 128.3, 128.2, 127.8, 123.8, 109.9, 108.3, 52.8, 36.8 ppm. HRMS: m/z calcd for C20H17NO4 [M + H]+ 336.1210, found 336.1211; C20H16NO4Na [M + Na]+ 358.1010, found 358.1015.
Methyl 3-(5-((2-Phenylacetamido)methyl)furan-2-yl)benzoate (47). The title compound was prepared from intermediate 5f and phenylacetic acid using the same method as compound 43, purified by column chromatography (V(PE):V(EA) = 8:1). Yield: 90%. HPLC purity: 97.2%. Mp: 183–184 °C. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.66 (t, J = 5.6 Hz, 1H), 8.21 (s, 1H), 7.92 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H), 7.86 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H), 7.57 (t, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H), 7.30 (d, J = 4.4 Hz, 4H), 7.25–7.20 (m, 1H), 7.01 (d, J = 3.2 Hz, 1H), 6.36 (d, J = 3.2 Hz, 1H), 4.37 (d, J = 5.6 Hz, 2H), 3.89 (s, 3H), 3.49 (s, 2H) ppm. 13C-NMR (101 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 170.6, 166.5, 153.4, 151.5, 136.8, 131.2, 130.8, 129.9, 129.4, 128.7, 128.3, 126.8, 123.8, 109.8, 108.2, 52.8, 42.7, 36.2 ppm. HRMS: m/z calcd for C21H19NO4Na [M + Na]+ 372.1171, found 372.1177.
Ethyl 4-(5-(Nicotinamidomethyl)furan-2-yl)benzoate (48). The title compound was prepared from intermediate 5a and nicotinic acid using the same method as compound 43, purified by column chromatography (V(PE):V(EA) = 6:1). Yield: 78%. HPLC purity: 97.8%. Mp: 182–183 °C. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 9.30 (t, J = 2.0 Hz, 1H), 9.07 (d, J = 1.6 Hz, 1H), 8.73 (d, J = 6.0 Hz, 1H), 8.25 (t, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H), 8.00 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H), 7.81 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H), 7.53 (d, J = 6.4 Hz, 1H), 7.11 (d, J = 3.6 Hz, 1H), 6.52 (d, J = 3.2 Hz, 1H), 4.61 (d, J = 5.6 Hz, 2H), 4.31 (q, J = 7.2 Hz, 2H), 1.34 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 3H) ppm. 13C-NMR (101 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 165.8, 165.4, 153.9, 152.5, 151.6, 149.0, 135.6, 134.8, 130.3, 130.1, 128.6, 124.0, 123.6, 110.3, 109.8, 61.2, 36.8, 14.7 ppm. LCMS m/z: 351.1 [M + H]+.
4-(5-(Benzamidomethyl)furan-2-yl)benzoic Acid (49). Using the intermediate 5a and benzoic acid, the title compound 49 was synthesized via condensation reaction (87% yield), and hydrolysis reaction (92% yield) in turn. HPLC purity: 97.0%. Mp: 183–186 °C. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 9.09 (t, J = 5.6 Hz, 1H), 7.98 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H), 7.90 (d, J = 1.6 Hz, 2H), 7.79 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 7.77–7.49 (m, 3H), 7.08 (d, J = 2.4 Hz, 1H), 6.47 (d, J = 3.2 Hz, 1H), 4.58 (d, J = 5.6 Hz, 2H) ppm. 13C-NMR (101 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 167.5, 166.7, 154.2, 151.6, 134.5, 134.5, 131.9, 130.5, 129.5, 128.8, 127.8, 123.5, 110.1, 109.5, 36.8 ppm. LCMS m/z: 320.1 [M − H]−.
4-(5-((2-Phenylacetamido)methyl)furan-2-yl)benzoic Acid (50). Using the intermediate 5a and phenylacetic acid, the title compound 49 was synthesized via condensation reaction (82% yield), and hydrolysis reaction (95% yield) in turn. HPLC purity: 97.1%. Mp: 228–230 °C. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 12.98 (s, 1H), 8.65 (t, J = 5.4 Hz, 1H), 7.98 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 7.75 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H), 7.30 (d, J = 4.4 Hz, 4H), 7.26–7.22 (m, 1H), 7.05 (d, J = 3.2 Hz, 1H), 6.38, (d, J = 3.2 Hz, 1H), 4.37 (d, J = 5.6 Hz, 2H), 3.49 (s, 2H) ppm. 13C-NMR (101 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ170.6, 167.4, 154.0, 151.7, 136.8, 134.5, 130.5, 129.5, 129.5, 128.7, 126.9, 123.5, 109.9, 109.4, 42.7, 36.3 ppm. HRMS: m/z calcd for C20H17NO4Na [M + Na]+ 358.1026, found 358.1015.
3-(5-(Benzamidomethyl)furan-2-yl)benzoic Acid (51). The title compound was prepared from compound 46 via hydrolysis reaction (90% yield), purified by column chromatography (V(PE):V(EA) = 3:1). HPLC purity: 97.0%. Mp: 190–191 °C. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 13.15 (s br, 1H), 9.20 (t, J = 6.4 Hz, 1H), 8.22 (s, 1H), 7.94–7.91 (m, 3H), 7.83 (d, J = 7.6 Hz, 1H), 7.54 (t, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H), 7.47 (t, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H), 7.00 (d, J = 3.2 Hz, 1H), 6.42 (d, J = 3.2 Hz, 1H), 4.55 (d, J = 5.6 Hz, 2H) ppm. 13C-NMR (101 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 167.5, 166.7, 153.5, 151.5, 134.5, 132.0, 131.8, 131.1, 129.8, 128.8, 128.4, 127.8, 124.1, 109.8, 108.1, 36.7 ppm. HRMS: m/z calcd for C19H15NO4 [M + Na]+ 344.0852, found 344.0855.
3-(5-((2-Phenylacetamido)methyl)furan-2-yl)benzoic Acid (52). The title compound was prepared from compound 47 via hydrolysis reaction (91% yield), purified by column chromatography (V(PE):V(EA) = 3:1). HPLC purity: 97.2%. Mp: 220–221 °C. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.85 (t, J = 5.6 Hz, 1H), 8.27 (s, 1H), 7.91 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H), 7.58 (t, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H), 7.36–7.34 (m, 4H), 7.29–7.25 (m, 1H), 7.02 (d, J = 3.2 Hz, 1H), 6.40 (d, J = 3.2 Hz, 1H), 4.41 (d, J = 5.6 Hz, 2H), 3.55 (s, 2H) ppm. 13C-NMR (101 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 170.7, 167.8, 153.2, 151.8, 136.8, 131.0, 129.6, 129.5, 128.7, 128.4, 127.6, 126.8, 124.1, 109.7, 107.8, 42.7, 36.2 ppm. HRMS: m/z calcd for C20H17NO4Na [M + Na]+ 358.1011, found 358.105.
3.2. Inhibition Assays
This study tested the inhibitory activities of the synthesized compounds against recombinant human SIRT2 proteins using a fluorogenic substrate p2270(Ac-Glu-Thr-Asp-Lys(Dec)-AMC)-coupled trypsin assay. The assay buffer is 25 mM Tris–HCl pH 8.0, 150 mM NaCl, and 10% glycerol. The test compounds were added to 60 μL of reaction mixture containing SIRT2 enzymes (0.2 μM), and each compound was prepared in a 3-fold dilution series (300 μM–15 nM) with the final DMSO concentration < 1%. After incubation at 25 °C for 30 min, the reaction started by the addition of the substrate p2270 (10 mM) and NAD+(400 mM) at 25 °C. After 2 h, 50 μL 3~4 U/μL trypsin and 4 mM nicotinamide were added to terminate the reaction, followed by further incubation for 30 min at 25 °C. The fluorescence intensity was measured using a microplate reader (λex = 380 nm, λem = 460 nm). All determinations were performed in triplicate. The IC50 values were obtained using GraphPad Prism software as described previously.
3.3. Molecular Docking Assays
All the docking simulations were performed using AutoDock Vina. The crystal structure of SIRT2 complexed with an N-(3-(phenoxymethyl)phenyl)acetamide derivative (24a) (PDB ID: 5YQO) and was used as the docking template. All the water and solvant molecules, as well as 24a were removed, and clean protein structure coordinates were obtained. AutoDockTools was used to assign Gasteiger-Marsili charges to the protein structure model, and merge non-polar hydrogens onto their respective heavy atoms of the protein structure (saved as pdbqt format). The 3D coordinates of the compound structures were prepared using the Discovery Studio viewer, followed by assigning atom types and partial charges using AutoDockTools (saved as pdbqt format). The binding site was defined as a rectangular grid, with the grid center coordinates of [x, y, z = −13.5, −10.1, −18.4] and the grid size of [25, 25, 25], to encompass the entire binding site. The number of possible docking poses were set as 10, and the other docking parameters were set as default. The docking results were inspected using PyMOL.
4. Conclusions
In this study, a series of (5-phenylfuran-2-yl)methanamine derivatives were synthesized. The SAR analyses of these compounds with SIRT2 led to the identification of compound 25 with 99 ± 2% @ 100 μM and 90 ± 3 % @ 10 μM inhibition against SIRT2. Meanwhile, 25 likely possesses better water solubility (cLogP = 1.63 and cLogS = −3.63). The IC50 measurements revealed that 25 had considerable potency against SIRT2 with an IC50 value of 2.47 μM, which is more potent than AGK2. The molecular docking analyses indicated that 25 fits well with the induced hydrophobic pocket of SIRT2. This study will aid future investigations to discover new potent and selective SIRT2 inhibitors to provide potential treatments for relevant diseases.
Author Contributions
L.W., C.L., C.S. and X.Z. designed and synthesized the target compounds. W.C., F.Y., C.W. and Y.Z. performed the biological evaluation. S.Q. performed the molecular docking. Z.W. and L.Y. interpreted the data and wrote the paper. All authors have approved the final manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Science and Technology Benefiting People National Natural Science Foundation (No. 81703355), Project of Chengdu (No. 2015-HM01-00335-SF), Sichuan Education Department (No. 18TD0023), Science and Technology Department of Sichuan Province (No. 2016HH0075), Chun-Hui Project from Ministry of Education of China (No.172507), Open research Subject of Key Laboratory of Food Biotechnology of Sichuan province of China (No. szj2016-021), and the Center of Comprehensive Health Management (No. szj2017-043). The APC was funded by Young Scholars Reserve Talents program of Xihua University (No. 0220170305).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Bhalla, K.N. Epigenetic and Chromatin Modifiers as Targeted Therapy of Hematologic Malignancies. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 3971–3993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blander, G.; Guarente, L. The Sir2 Family of Protein Deacetylases. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2004, 73, 417–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Ji, S.; Yu, Z.-J.; Wang, H.-L.; Cheng, X.; Li, W.-J.; Jing, L.; Yu, Y.; Chen, Q.; Yang, L.-L.; et al. Structure-based discovery of new selective small-molecule sirtuin 5 inhibitors. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2018, 91, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirschey, M.D. Old Enzymes, New Tricks: Sirtuins Are NAD+-Dependent De-acylases. Cell Metab. 2011, 14, 718–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, H.; Lin, H. Sirtuins in Epigenetic Regulation. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 2350–2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Ma, X.; He, Y.; Yuan, C.; Chen, Q.; Li, G.; Chen, X. Sirtuin 5: A review of structure, known inhibitors and clues for developing new inhibitors. Sci. China Life Sci. 2016, 60, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamagata, K.; Goto, Y.; Nishimasu, H.; Morimoto, J.; Ishitani, R.; Dohmae, N.; Takeda, N.; Nagai, R.; Komuro, I.; Suga, H.; et al. Structural basis for potent inhibition of SIRT2 deacetylase by a macrocyclic peptide inducing dynamic structural change. Structure 2014, 22, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; He, J.; Liao, M.; Hu, M.; Li, W.; Ouyang, H.; Wang, X.; Ye, T.; Zhang, Y.; Ouyang, L. An overview of Sirtuins as potential therapeutic target: Structure, function and modulators. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 161, 48–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, C.; Lucia, M.S.; Hansen, K.C.; Tyler, J.K. CBP/p300-mediated acetylation of histone H3 on lysine 56. Nature 2009, 459, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaquero, A.; Scher, M.B.; Lee, D.H.; Sutton, A.; Cheng, H.L.; Alt, F.W.; Serrano, L.; Sternglanz, R.; Reinberg, D. SirT2 is a histone deacetylase with preference for histone H4 Lys 16 during mitosis. Genes Dev. 2006, 20, 1256–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- North, B.J.; Marshall, B.L.; Borra, M.T.; Denu, J.M.; Verdin, E. The Human Sir2 Ortholog, SIRT2, Is an NAD+-Dependent Tubulin Deacetylase. Mol. Cell 2003, 11, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peck, B.; Chen, C.-Y.; Ho, K.-K.; Di Fruscia, P.; Myatt, S.S.; Coombes, R.C.; Fuchter, M.J.; Hsiao, C.-D.; Lam, E.W.-F. SIRT Inhibitors Induce Cell Death and p53 Acetylation through Targeting Both SIRT1 and SIRT2. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2010, 9, 844–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, E.; Gesta, S.; Kahn, C.R. SIRT2 Regulates Adipocyte Differentiation through FoxO1 Acetylation/Deacetylation. Cell Metab. 2007, 6, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Matsumori, H.; Nakayama, Y.; Osaki, M.; Kojima, H.; Kurimasa, A.; Ito, H.; Mori, S.; Katoh, M.; Oshimura, M.; et al. SIRT2 down-regulation in HeLa can induce p53 accumulation via p38 MAPK activation-dependent p300 decrease, eventually leading to apoptosis. Genes Cells 2011, 16, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothgiesser, K.M.; Erener, S.; Waibel, S.; Luscher, B.; Hottiger, M.O. Correction: SIRT2 regulates NF-kappaB-dependent gene expression through deacetylation of p65 Lys310. J. Cell Sci. 2019, 132, 4251–4258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.; Song, C.; Wang, X.; Zhang, G.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, X.; Sun, Q.; Huang, L.; Xiang, R.; Hu, Y.; et al. Discovery of New SIRT2 Inhibitors by Utilizing a Consensus Docking/Scoring Strategy and Structure–Activity Relationship Analysis. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2017, 57, 669–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dryden, S.C.; Nahhas, F.A.; Nowak, J.E.; Goustin, A.-S.; Tainsky, M.A. Role for Human SIRT2 NAD-Dependent Deacetylase Activity in Control of Mitotic Exit in the Cell Cycle. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2003, 23, 3173–3185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, T.; Hiratsuka, M.; Osaki, M.; Oshimura, M. The Molecular Biology of Mammalian SIRT Proteins: SIRT2 Functions on Cell Cycle Regulation. Cell Cycle 2007, 6, 1011–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado de Oliveira, R.; Sarkander, J.; Kazantsev, A.; Outeiro, T. SIRT2 as a Therapeutic Target for Age-Related Disorders. Front. Pharmacol. 2012, 3, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beirowski, B.; Gustin, J.; Armour, S.M.; Yamamoto, H.; Viader, A.; North, B.J.; Michán, S.; Baloh, R.H.; Golden, J.P.; Schmidt, R.E.; et al. Sir-two-homolog 2 (Sirt2) modulates peripheral myelination through polarity protein Par-3/atypical protein kinase C (aPKC) signaling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, E952–E961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskandarian, H.A.; Impens, F.; Nahori, M.-A.; Soubigou, G.; Coppée, J.-Y.; Cossart, P.; Hamon, M.A. A Role for SIRT2-Dependent Histone H3K18 Deacetylation in Bacterial Infection. Science 2013, 341, 1238858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pais, T.F.; Szegő, É.M.; Marques, O.; Miller-Fleming, L.; Antas, P.; Guerreiro, P.; de Oliveira, R.M.; Kasapoglu, B.; Outeiro, T.F. The NAD-dependent deacetylase sirtuin 2 is a suppressor of microglial activation and brain inflammation. EMBO J. 2013, 32, 2603–2616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, T.; Alam, H.B.; Liu, B.; Bronson, R.T.; Nikolian, V.C.; Wu, E.; Chong, W.; Li, Y. Selective Inhibition of SIRT2 Improves Outcomes in a Lethal Septic Model. Curr. Mol. Med. 2015, 15, 634–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.-S.; Vassilopoulos, A.; Wang, R.-H.; Lahusen, T.; Xiao, Z.; Xu, X.; Li, C.; Veenstra, T.D.; Li, B.; Yu, H.; et al. SIRT2 Maintains Genome Integrity and Suppresses Tumorigenesis through Regulating APC/C Activity. Cancer Cell 2011, 20, 487–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donmez, G.; Outeiro, T.F. SIRT1 and SIRT2: Emerging targets in neurodegeneration. EMBO Mol. Med. 2013, 5, 344–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luthi-Carter, R.; Taylor, D.M.; Pallos, J.; Lambert, E.; Amore, A.; Parker, A.; Moffitt, H.; Smith, D.L.; Runne, H.; Gokce, O.; et al. SIRT2 inhibition achieves neuroprotection by decreasing sterol biosynthesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 7927–7932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.H.; Zhu, Y.M.; Ozden, O.; Kim, H.S.; Jiang, H.Y.; Deng, C.X.; Gius, D.; Vassilopoulos, A. SIRT2 is a tumor suppressor that connects aging, acetylome, cell cycle signaling, and carcinogenesis. Transl. Cancer Res. 2012, 1, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Grozinger, C.M.; Chao, E.D.; Blackwell, H.E.; Moazed, D.; Schreiber, S.L. Identification of a class of small molecule inhibitors of the sirtuin family of NAD-dependent deacetylases by phenotypic screening. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 38837–38843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gertz, M.; Fischer, F.; Nguyen, G.T.; Lakshminarasimhan, M.; Schutkowski, M.; Weyand, M.; Steegborn, C. Ex-527 inhibits Sirtuins by exploiting their unique NAD+-dependent deacetylation mechanism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, E2772–E2781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Cui, H.; Yu, X.; Peng, T.; Wang, G.; Wen, X.; Sun, Y.; Liu, S.; Zhang, S.; Hu, L.; et al. Synthesis and Evaluation of Novel Benzofuran Derivatives as Selective SIRT2 Inhibitors. Molecules 2017, 22, 1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Outeiro, T.F.; Kontopoulos, E.; Altmann, S.M.; Kufareva, I.; Strathearn, K.E.; Amore, A.M.; Volk, C.B.; Maxwell, M.M.; Rochet, J.C.; McLean, P.J.; et al. Sirtuin 2 inhibitors rescue alpha-synuclein-mediated toxicity in models of Parkinson’s disease. Science 2007, 317, 516–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirrie, L.; McCarthy, A.R.; Major, L.L.; Morkūnaitė, V.; Zubrienė, A.; Matulis, D.; Lain, S.; Lebl, T.; Westwood, N.J. Discovery and Validation of SIRT2 Inhibitors Based on Tenovin-6: Use of a 1H-NMR Method to Assess Deacetylase Activity. Molecules 2012, 17, 12206–12224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, G.; Breitenbucher, F.; Schuler, M.; Ehrenhofer-Murray, A.E. A Novel Sirtuin 2 (SIRT2) Inhibitor with p53-dependent Pro-apoptotic Activity in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 5208–5216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, D.M.; Balabadra, U.; Xiang, Z.; Woodman, B.; Meade, S.; Amore, A.; Maxwell, M.M.; Reeves, S.; Bates, G.P.; Luthi-Carter, R.; et al. A Brain-Permeable Small Molecule Reduces Neuronal Cholesterol by Inhibiting Activity of Sirtuin 2 Deacetylase. ACS Chem. Biol. 2011, 6, 540–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.Y.; Xu, N.; Malyukova, A.; Scarlett, C.J.; Sun, Y.T.; Zhang, X.D.; Ling, D.; Su, S.P.; Nelson, C.; Chang, D.K.; et al. The histone deacetylase SIRT2 stabilizes Myc oncoproteins. Cell Death Differ. 2012, 20, 503–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, H.; Kamal, Z.; Ai, T.; Xu, Y.; More, S.S.; Wilson, D.J.; Chen, L. Discovery of Potent and Selective Sirtuin 2 (SIRT2) Inhibitors Using a Fragment-Based Approach. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 8340–8357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiedel, M.; Rumpf, T.; Karaman, B.; Lehotzky, A.; Gerhardt, S.; Ovádi, J.; Sippl, W.; Einsle, O.; Jung, M. Structure-Based Development of an Affinity Probe for Sirtuin2. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 2252–2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.-L.; Wang, H.-L.; Zhong, L.; Yuan, C.; Liu, S.-Y.; Yu, Z.-J.; Liu, S.; Yan, Y.-H.; Wu, C.; Wang, Y.; et al. X-ray crystal structure guided discovery of new selective, substrate-mimicking sirtuin 2 inhibitors that exhibit activities against non-small cell lung cancer cells. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 155, 806–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.-L.; Xu, W.; Yan, J.; Su, H.-L.; Yuan, C.; Li, C.; Zhang, X.; Yu, Z.-J.; Yan, Y.-H.; Yu, Y.; et al. Crystallographic and SAR analyses reveal the high requirements needed to selectively and potently inhibit SIRT2 deacetylase and decanoylase. MedChemComm 2019, 10, 164–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galleano, I.; Schiedel, M.; Jung, M.; Madsen, A.; Olsen, C. A Continuous, Fluorogenic Sirtuin 2 Deacylase Assay: Substrate Screening and Inhibitor Evaluation. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 1021–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Ma, X.; Yuan, C.; He, Y.; Li, L.; Fang, S.; Xia, W.; He, T.; Qian, S.; Xu, Z.; et al. Discovery of 2-((4,6-dimethylpyrimidin-2-yl)thio)-N-phenylacetamide derivatives as new potent and selective human sirtuin 2 inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 134, 230–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, D.; Robinson, E.; Hom, K.; Yu, W.; Nguyen, N.; Li, Y.; Zong, Q.; Wilks, A.; Xue, F. Structure-based design and biological evaluation of inhibitors of the pseudomonas aeruginosa heme oxygenase (pa-HemO). Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2018, 28, 1024–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yano, J.K.; Denton, T.T.; Cerny, M.A.; Zhang, X.; Johnson, E.F.; Cashman, J.R. Synthetic Inhibitors of Cytochrome P-450 2A6: Inhibitory Activity, Difference Spectra, Mechanism of Inhibition, and Protein Cocrystallization. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 6987–7001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finnin, M.S.; Donigian, J.R.; Pavletich, N.P. Structure of the histone deacetylase SIRT2. Nat. Struct. Biol. 2001, 8, 621–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rumpf, T.; Schiedel, M.; Karaman, B.; Roessler, C.; North, B.J.; Lehotzky, A.; Oláh, J.; Ladwein, K.I.; Schmidtkunz, K.; Gajer, M.; et al. Selective Sirt2 inhibition by ligand-induced rearrangement of the active site. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of all the compounds are available from the authors. |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).