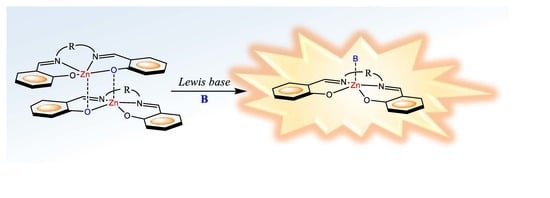
On the Aggregation and Sensing Properties of Zinc(II) Schiff-Base Complexes of Salen-Type Ligands
Abstract
1. Introduction
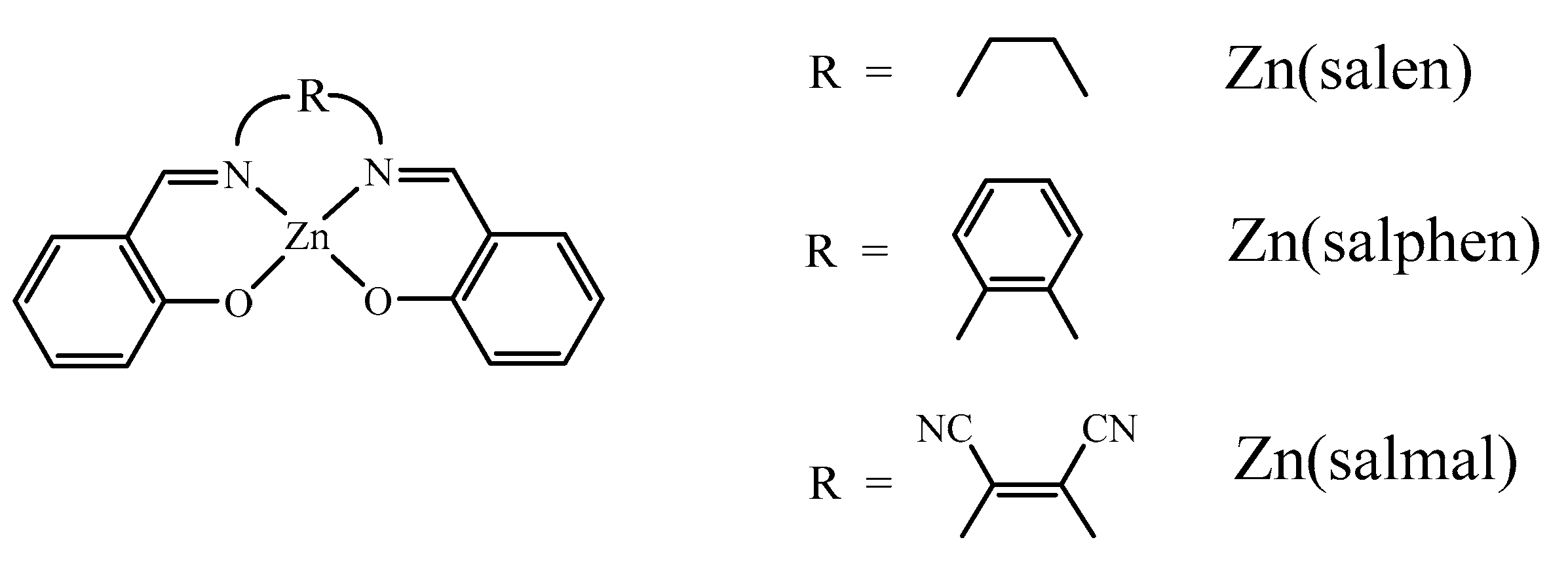
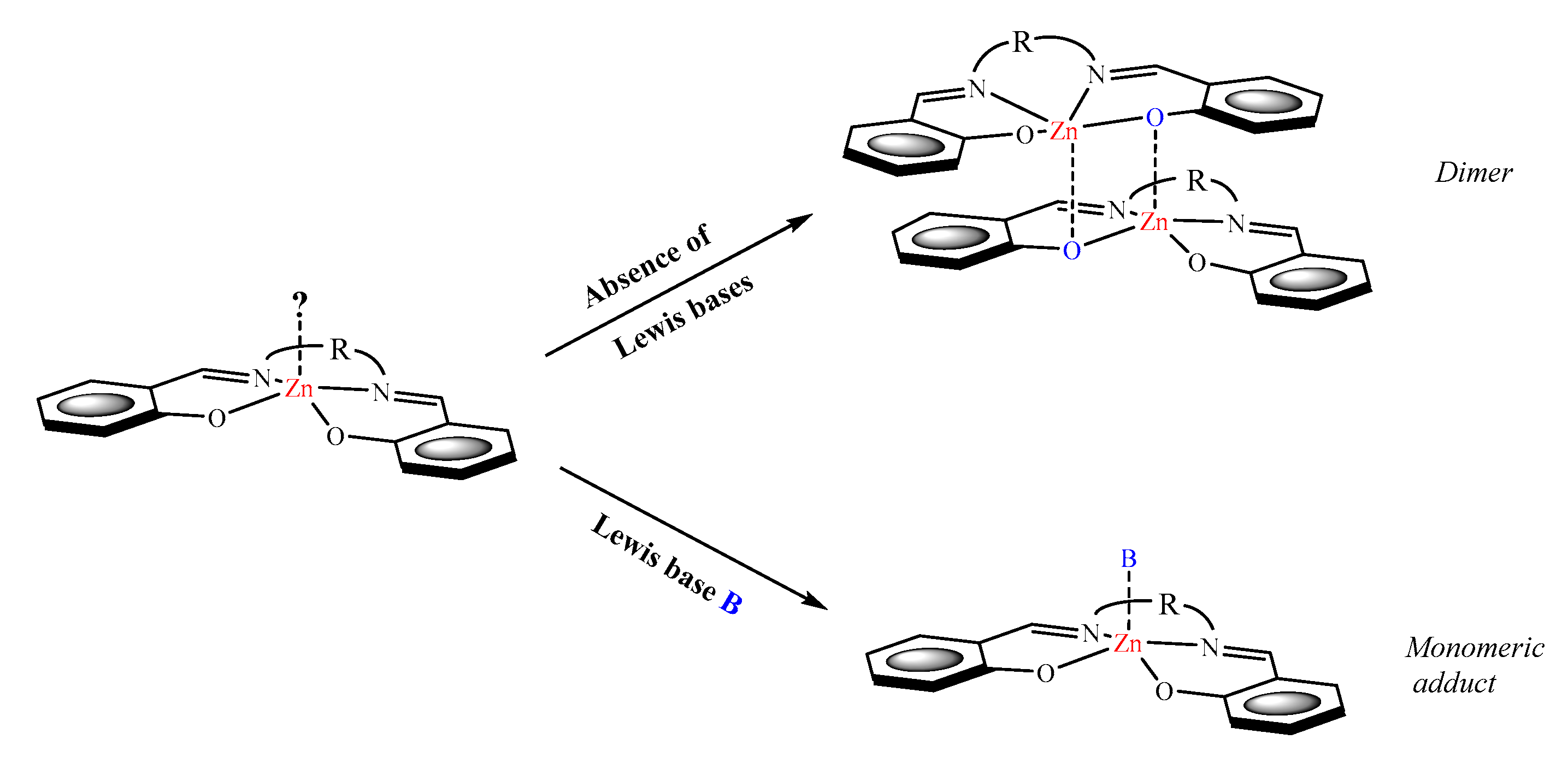
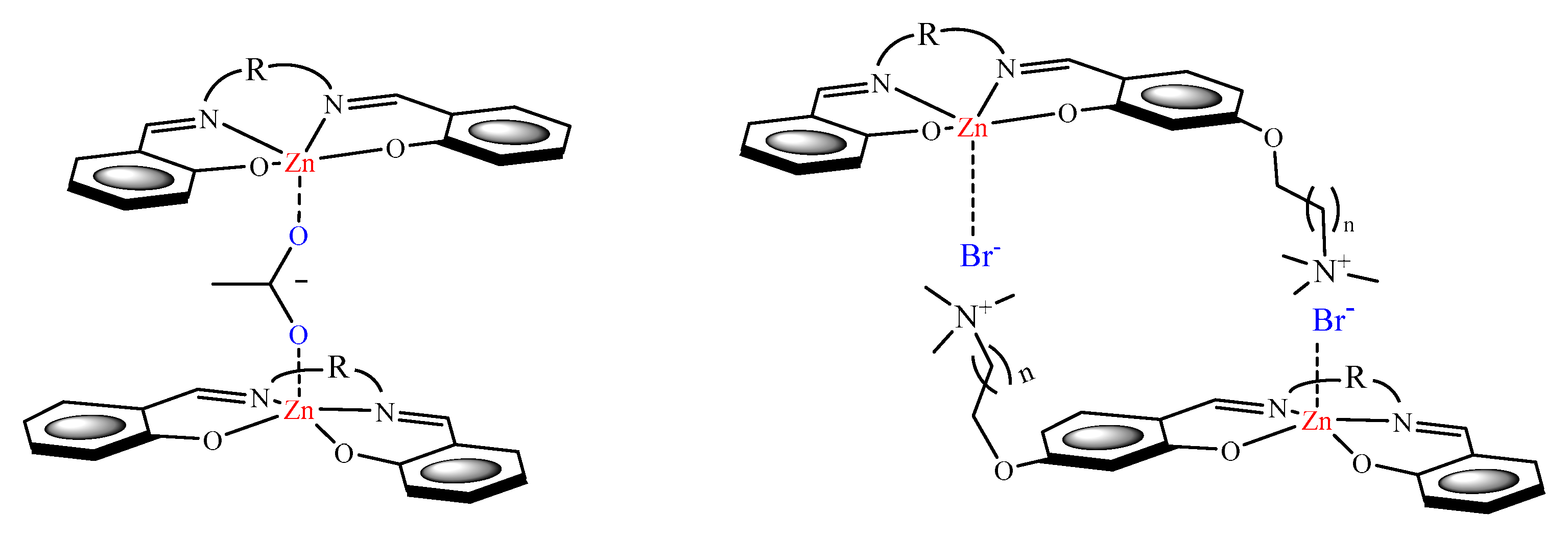
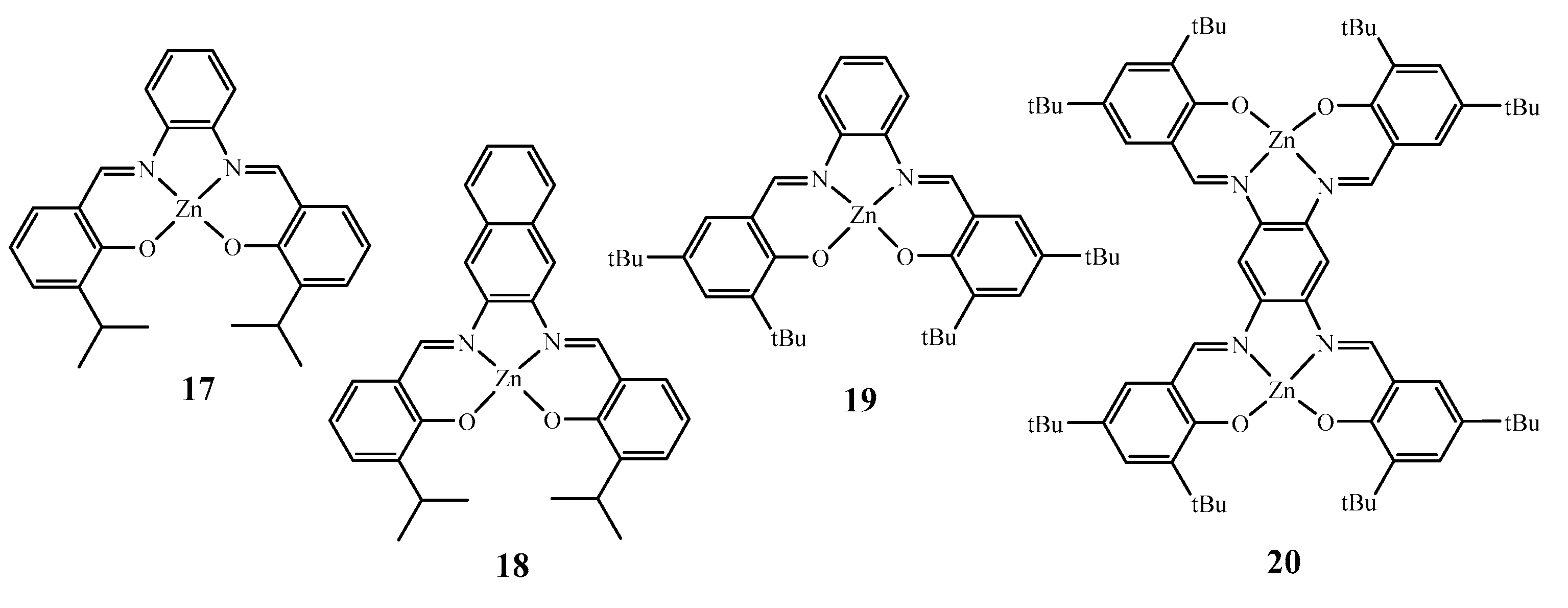
2. Lewis Acidic Properties of ZnL Complexes and Related Structures
3. Spectroscopic Properties of ZnL Complexes in Solution
3.1. 1H NMR Studies
3.2. 1H NMR Studies of Chiral Complexes
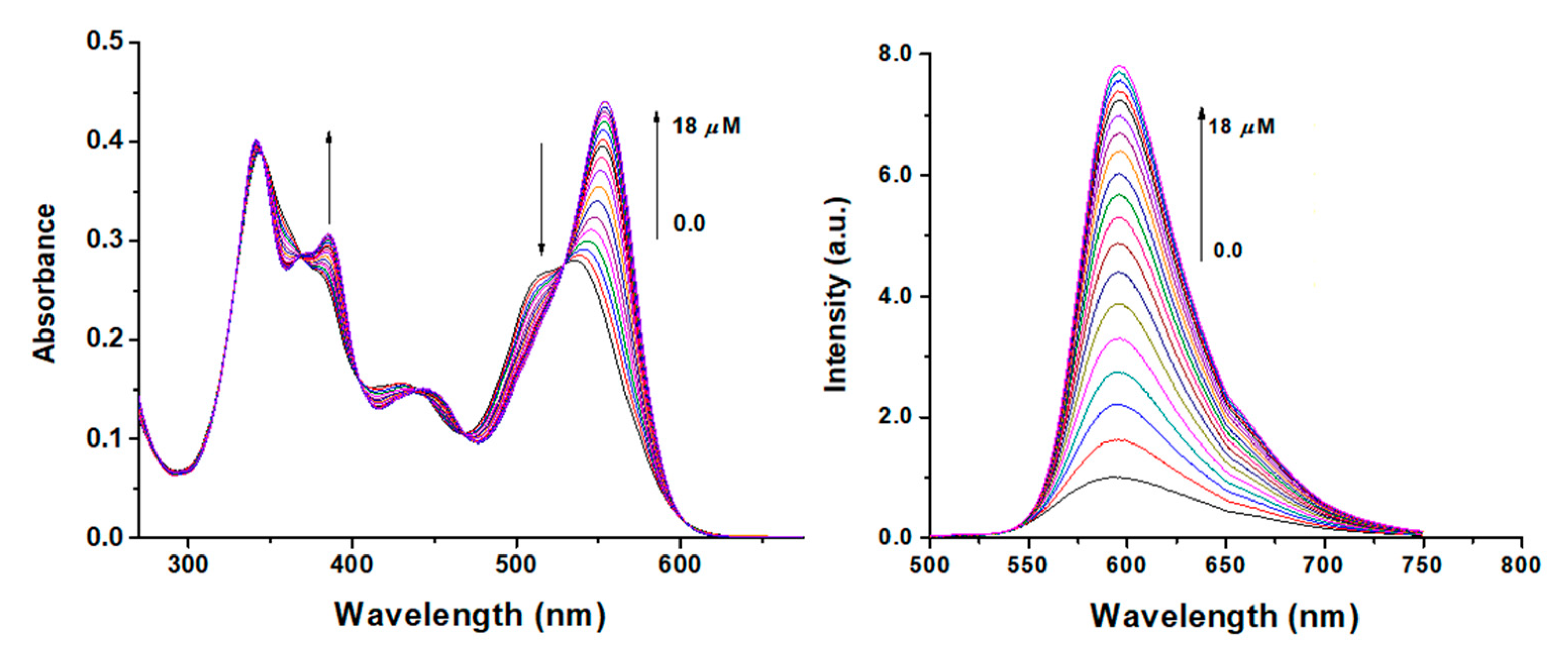
3.3. Optical Absorption and Fluorescence Studies
3.4. Deaggregation Studies
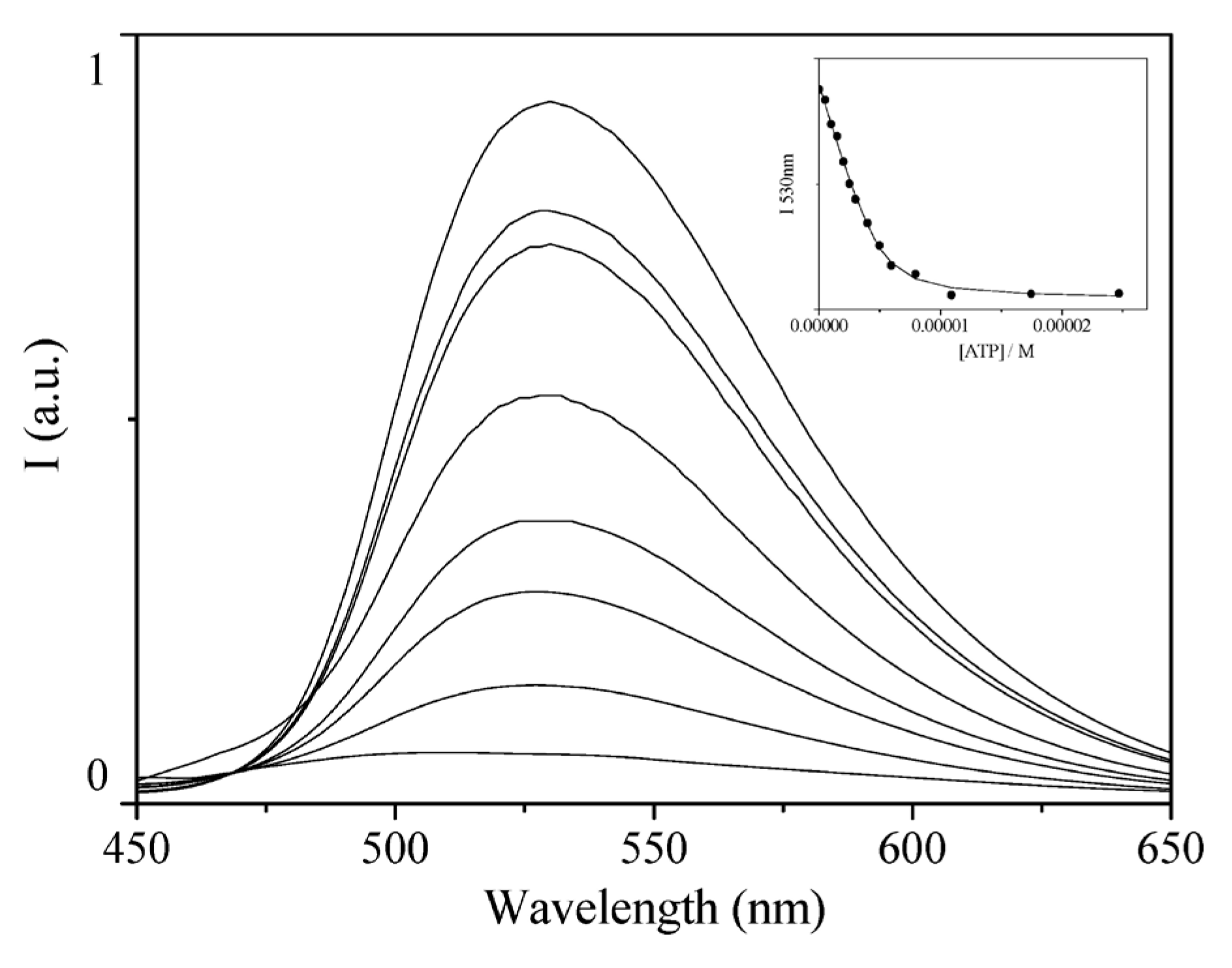
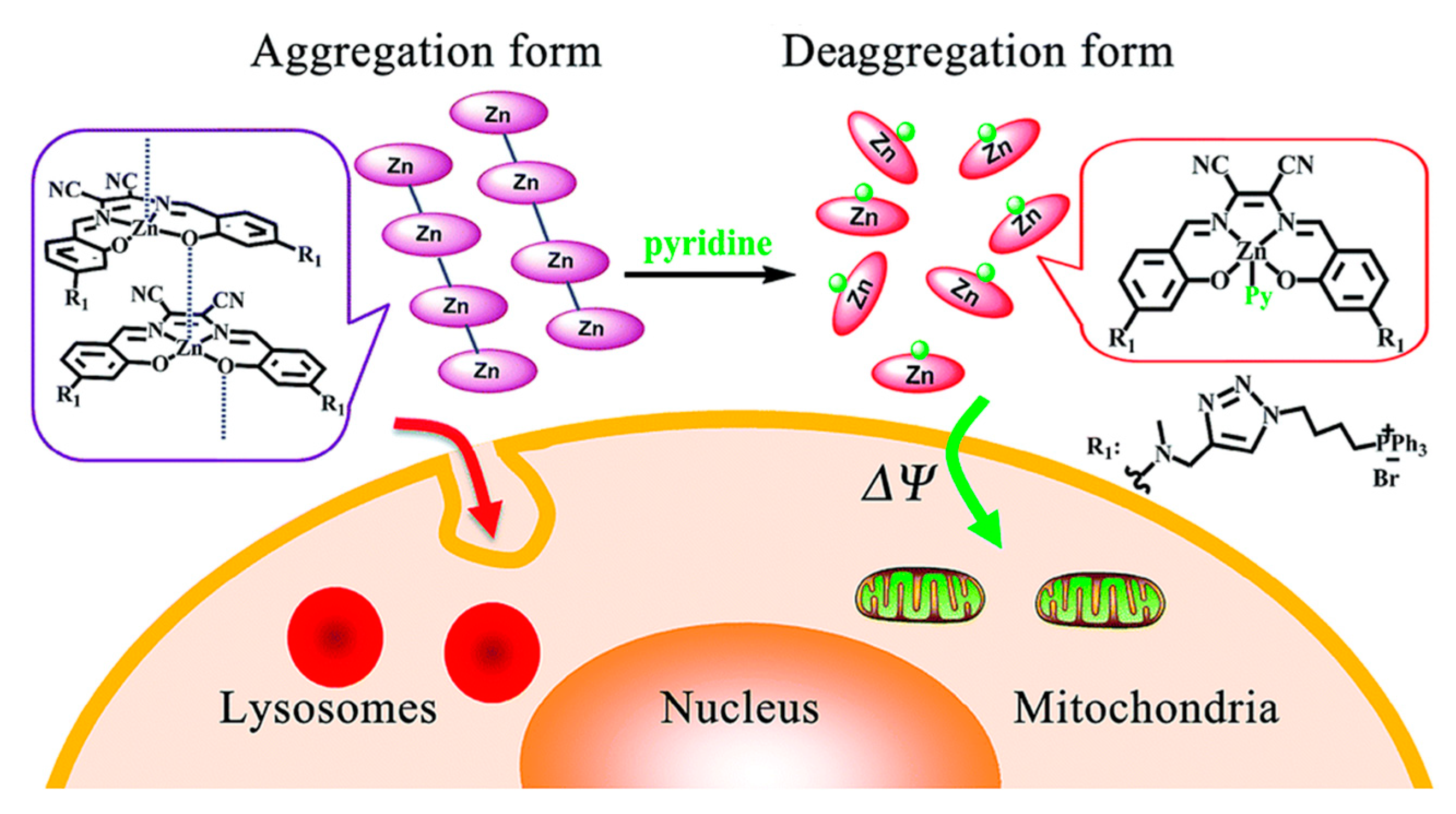
4. Sensing Properties of ZnL Complexes
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Steed, J.W.; Atwood, J.L. Supramolecular Chemistry, 2rd ed.; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 2009; ISBN 978-0-470-51233-3. [Google Scholar]
- Babu, S.S.; Praveen, V.K.; Ajayaghosh, A. Functional π-gelators and their applications. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 1973–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, K.M.-C.; Yam, W.-W. Self-assembly of luminescent alkynylplatinum(ii) terpyridyl complexes: modulation of photophysical properties through aggregation behavior. Acc. Chem. Res. 2011, 44, 424–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, Y.; Lam, J.W.Y.; Tang, B.Z. Aggregation-induced emission. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 5361–5388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elemans, J.A.A.W.; van Hameren, R.; Nolte, R.J.M.; Rowan, A.E. Molecular materials by self-assembly of porphyrins, phthalocyanines, and perylenes. Adv. Mater. 2006, 18, 1251–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowden, N.B.; Weck, M.; Choi, I.S.; Whitesides, G.M. Molecule-mimetic chemistry and mesoscale self-assembly. Acc. Chem. Res. 2001, 34, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escárcega-Bobadilla, M.V.; Zelada-Guillén, G.A.; Pyrlin, S.V.; Wegrzyn, M.; Ramos, M.M.; Giménez, E.; Stewart, A.; Maier, G.; Kleij, A.W. Nanorings and rods interconnected by self-assembly mimicking an artificial network of neurons. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Bella, S.; Colombo, A.; Dragonetti, C.; Righetto, S.; Roberto, D. Zinc(II) as a versatile template for efficient dipolar and octupolar second-order nonlinear optical molecular materials. Inorganics 2018, 6, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cozzi, P.G. Metal–Salen Schiff base complexes in catalysis: Practical aspects. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2004, 33, 410–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiteoak, C.J.; Salassa, G.; Kleij, A.W. Recent advances with π-conjugated salen systems. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 622–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, R.M.; Storr, T. The chemistry and applications of multimetallic salen complexes. Dalton Trans. 2014, 43, 9380–9391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleij, A.W. Nonsymmetrical salen ligands and their complexes: synthesis and applications. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2009, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wezenberg, S.J.; Kleij, A.W. Material applications for salen frameworks. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 2354–2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleij, A.W. New templating strategies with salen scaffolds (Salen=N,N’-Bis(salicylidene)ethylenediamine Dianion). Chem. Eur. J. 2008, 14, 10520–10529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleij, A.W. Zinc-centred salen complexes: Versatile and accessible supramolecular building motifs. Dalton Trans. 2009, 4635–4639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leoni, L.; Dalla Cort, A. The supramolecular attitude of metal–salophen and metal–salen complexes. Inorganics 2018, 6, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalla Cort, A.; De Bernardin, P.; Forte, G.; Yafteh Mihan, F. Metal–salophen-based receptors for anions. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 3863–3874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, H.-Y.; Tang, J.; Zhang, J.-L. Introducing metallosalens to biological studies: the renaissance of traditional coordination complexes. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2017, 5085–5093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enamullah, M.; Vasylyeva, V.; Janiak, C. Chirality and diastereoselection of Δ/Λ-configured tetrahedral zinc(II) complexes with enantiopure or racemic Schiff base ligands. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2013, 408, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamayou, A.-C.; Lüdeke, S.; Brecht, V.; Freedman, T.B.; Nafie, L.A.; Janiak, C. Chirality and diastereoselection of Δ/Λ-configured tetrahedral zinc complexes through enantiopure schiff base complexes: combined vibrational circular dichroism, density functional theory, 1H NMR, and X-ray structural studies. Inorg. Chem. 2011, 50, 11363–11374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onodera, T.; Akitsu, T. Tuning of the optical properties of chiral Schiff base Zn(II) complexes by substituents. Polyhedron 2013, 59, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, C.; Luneau, D. New Schiff base zinc(II) complexes exhibiting second harmonic generation. Dalton Trans. 2002, 83–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forte, G.; Oliveri, I.P.; Consiglio, G.; Failla, S.; Di Bella, S. On the Lewis acidic character of bis(salicylaldiminato)zinc(II) Schiff-base complexes: A computational and experimental investigation on a series of compounds varying the bridging diimine. Dalton Trans. 2017, 46, 4571–4581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamine, W.; Boughdiri, S.; Christ, L.; Morell, C.; Chermette, H. Coordination chemistry of Zn2+ with sal(ph)en ligands: Tetrahedral coordination or penta-coordination? A DFT analysis. J. Comput. Chem. 2019, 40, 717–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groizard, T.; Kahlal, S.; Dorcet, V.; Roisnel, T.; Bruneau, C.; Halet, J.-F.; Gramage-Doria, R. Nonconventional supramolecular self-assemblies of Zinc(II)-salphen building blocks. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2016, 5143–5151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallant, A.J.; Chong, J.H.; MacLachlan, M.J. Heptametallic bowl-shaped complexes derived from conjugated schiff-base macrocycles: synthesis, characterization, and x-ray crystal structures. Inorg. Chem. 2006, 45, 5248–5250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Consiglio, G.; Oliveri, I.P.; Punzo, F.; Thompson, A.L.; Di Bella, S.; Failla, S. Structure and aggregation properties of a schiff-base Zinc(II) complex derived from cis-1,2-diaminocyclohexane. Dalton Trans. 2015, 44, 13040–13048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, Q.; Zhou, P.; Song, F.; Wang, Y.; Liu, G.; Li, H. Controlled fluorescent properties of Zn(II) salen-type complex based on ligand design. CrystEngComm 2013, 15, 2786–2790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez Belmonte, M.; Wezenberg, S.J.; Haak, R.M.; Anselmo, D.; Escudero-Adán, E.C.; Benet-Buchholz, J.; Kleij, A.W. Self-assembly of Zn(salphen) complexes: Steric regulation, stability studies and crystallographic analysis revealing an unexpected dimeric 3,3′-t-Bu-substituted Zn(salphen) complex. Dalton Trans. 2010, 39, 4541–4550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleij, A.W.; Kuil, M.; Lutz, M.; Tooke, D.M.; Spek, A.L.; Kamer, P.C.J.; van Leeuwen, P.W.N.M.; Reek, J.N.H. Supramolecular zinc(II)salphen motifs: Reversible dimerization and templated dimeric structures. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2006, 359, 1807–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odoko, M.; Tsuchida, N.; Okabe, N. Bis{µ-2,2′-[ethane-1,3-diylbis(nitrilomethylidyne)]diphenolato} dizinc(II). Acta Cryst. 2006, E62, m708–m709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, S.; Mondal, P.; Prasad, S.K.; Rao, D.S.S.; Bhattacharjee, C.R. Zinc(II)-salphen complexes bearing long alkoxy side arms: Synthesis, solvent dependent aggregation, and spacer group substituent effect on mesomorphism and photophysical property. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 246, 290–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, S.; Mondal, P.; Prasad, S.K.; Rao, D.S.S.; Bhattacharjee, C.R. Induction of mesomorphism through supramolecular assembly in metal coordination compounds of “salphen”-type schiff bases: Photoluminescence and solvatochromism. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2016, 4604–4614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, S.; Bhattacharjee, C.R.; Mondal, P.; Prasad, S.K.; Rao, D.S.S. Synthesis and aggregation behaviour of luminescent mesomorphic zinc(II) complexes with ‘salen’ type asymmetric Schiff base ligands. Dalton Trans. 2015, 44, 7477–7488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharjee, C.R.; Das, G.; Mondal, P.; Prasad, S.K.; Rao, D.S.S. Novel green light emitting nondiscoid liquid crystalline Zinc(II) schiff-base complexes. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2011, 1418–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelada-Guillén, G.A.; Escárcega-Bobadilla, M.V.; Wegrzyn, M.; Giménez, E.; Maier, G.; Kleij, A.W. Enhanced conductivity for carbon nanotube based materials through supramolecular hierarchical self-assembly. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 5, 1701585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyrlin, S.V.; Hine, N.D.M.; Kleij, A.W.; Ramos, M.M.D. Self-assembly of bis-salphen compounds: From semiflexible chains to webs of nanorings. Soft Matter 2018, 14, 1181–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveri, I.P.; Malandrino, G.; Di Bella, S. Self-assembled nanostructures of amphiphilic Zinc(II) salophen complexes: Role of the solvent on their structure and morphology. Dalton Trans. 2014, 43, 10208–10214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveri, I.P.; Failla, S.; Malandrino, G.; Di Bella, S. Controlling the molecular self-assembly into nanofibers of amphiphilic Zinc(II) salophen complexes. J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 15335–15341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salassa, G.; Coenen, M.J.J.; Wezenberg, S.J.; Hendriksen, B.L.M.; Speller, S.; Elemans, J.A.A.W.; Kleij, A.W. Extremely strong self-assembly of a bimetallic salen complex visualized at the single-molecule level. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 7186–7192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, J.K.-H.; MacLachlan, M.J. Fibrous aggregates from dinuclear Zinc(II) salphen complexes. Dalton Trans. 2010, 39, 7310–7319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elemans, J.A.A.W.; Wezenberg, S.J.; Coenen, M.J.J.; Escudero-Adán, E.C.; Benet-Buchholz, J.; den Boer, D.; Speller, S.; Kleij, A.W.; De Feyter, S. Axial ligand control over monolayer and bilayer formation of metal-salophens at the liquid−solid interface. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 2548–2550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, J.K.-H.; MacLachlan, M.G. Metal-containing nanofibers via coordination chemistry. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2010, 254, 2363–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, J.K.-H.; Yu, Z.; Mirfakhrai, T.; MacLachlan, M.J. Supramolecular assembly of carbohydrate-functionalized salphen−metal complexes. Chem. Eur. J. 2009, 15, 13456–13465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, S.; Oh, M. Monitoring shape transformation from nanowires to nanocubes and size-controlled formation of coordination polymer particles. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 2049–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hui, J.K.-H.; Yu, Z.; MacLachlan, M.J. Supramolecular assembly of zinc salphen complexes: access to metal-containing gels and nanofibers. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 7980–7983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salassa, G.; Ryan, J.W.; Escudero-Adána, E.C.; Kleij, A.W. Spectroscopic properties of Zn(salphenazine) complexes and their application in small molecule organic solar cells. Dalton Trans. 2014, 43, 210–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escárcega-Bobadilla, M.V.; Anselmo, D.; Wezenberg, S.J.; Escudero-Adán, E.C.; Martínez Belmonte, M.; Martina, E.; Kleij, A.W. Metal-directed assembly of chiral bis-Zn(II) Schiff base structures. Dalton Trans. 2012, 41, 9766–9772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouari, K.; Ourari, A.; Weiss, J. Synthesis and characterization of a novel unsymmetrical tetradentate schiff base complex of Zinc(II) derived from N,N′-bis(5-bromosalicylidene) 2,3-diaminopyridine (H2L): Crystal structure of [Zn(II)L] pyridine. J. Chem. Crystallogr. 2010, 40, 831–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liuzzo, V.; Oberhauser, W.; Pucci, A. Synthesis of new red photoluminescent Zn(II)-salicylaldiminato complex. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2010, 13, 686–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, G.A.; Zhou, H.; Stern, C.L.; Nguyen, S.T. A General high-yield route to bis(salicylaldimine) Zinc(II) complexes: Application to the synthesis of pyridine-modified salen-type Zinc(II) complexes. Inorg. Chem. 2001, 40, 3222–3227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, A.L.; Atwood, D.A. Five-coordinate Salen(tBu) complexes of zinc. Inorg. Chim. Acta 1998, 277, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleij, A.W.; Kuil, M.; Tooke, D.M.; Spek, A.L.; Reek, J.N.H. Metal-directed self-assembly of a ZnII-salpyr complex into a supramolecular vase structure. Inorg. Chem. 2007, 46, 5829–5831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, W.-S.; Lee, K.Y.; Ryu, E.-H.; Gu, J.-M.; Kim, Y.; Lee, S.J.; Huh, S. Catalytic transesterifications by a Zn–BisSalen MOF containing open pyridyl groups inside 1D channels. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2013, 4228–4233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, E.; Martínez Belmonte, M.; Escudero-Adán, E.C.; Kleij, A.W. Exploring the building-block potential of readily accessible chiral [Zn(salen)] complexes. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2014, 4632–4641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleij, A.W.; Kuil, M.; Tooke, D.M.; Lutz, M.; Spek, A.L.; Reek, J.N.H. ZnII-salphen complexes as versatile building blocks for the construction of supramolecular box assemblies. Chem. Eur. J. 2005, 11, 4743–4750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wezenberg, S.J.; Escudero-Adán, E.C.; Benet-Buchholz, J.; Kleij, A.W. Anion-templated formation of supramolecular multinuclear assemblies. Chem. Eur. J. 2009, 15, 5695–5700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveri, I.P.; Failla, S.; Colombo, A.; Dragonetti, C.; Righetto, S.; Di Bella, S. Synthesis, characterization, optical absorption/fluorescence spectroscopy, and second-order nonlinear optical properties of aggregate molecular architectures of unsymmetrical schiff-base Zinc(II) complexes. Dalton Trans. 2014, 43, 2168–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveri, I.P.; Failla, S.; Malandrino, G.; Di Bella, S. New molecular architectures by aggregation of tailored Zinc(II) schiff-base complexes. New J. Chem. 2011, 35, 2826–2831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Consiglio, G.; Failla, S.; Finocchiaro, P.; Oliveri, I.P.; Di Bella, S. An Unprecedented structural interconversion in solution of aggregate Zinc(II) salen schiff-base complexes. Inorg. Chem. 2012, 51, 8409–8418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Consiglio, G.; Failla, S.; Finocchiaro, P.; Oliveri, I.P.; Di Bella, S. Aggregation properties of bis(salicylaldiminato)Zinc(II) schiff-base complexes and their lewis acidic character. Dalton Trans. 2012, 41, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Consiglio, G.; Failla, S.; Finocchiaro, P.; Oliveri, I.P.; Purrello, R.; Di Bella, S. Supramolecular aggregation/deaggregation in amphiphilic dipolar schiff-base Zinc(II) complexes. Inorg. Chem. 2010, 49, 5134–5142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Consiglio, G.; Failla, S.; Oliveri, I.P.; Purrello, R.; Di Bella, S. Controlling the molecular aggregation. an amphiphilic schiff-base Zinc(II) complex as supramolecular fluorescent probe. Dalton Trans. 2009, 10426–10428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, C.T.L.; MacLachlan, M.J. Supramolecular assembly and coordination-assisted deaggregation of multimetallic macrocycles. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 4178–4182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salassa, G.; Castilla, A.M.; Kleij, A.J. Cooperative self-assembly of a macrocyclic Schiff base complex. Dalton Trans. 2011, 40, 5236–5243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Consiglio, G.; Oliveri, I.P.; Failla, S.; Di Bella, S. Supramolecular aggregates of defined stereochemical scaffolds: aggregation/deaggregation in schiff-base Zinc(II) complexes derived from enantiopure trans-1,2-diaminocyclohexane. Inorg. Chem. 2016, 55, 10320–10328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Consiglio, G.; Oliveri, I.P.; Failla, S.; Di Bella, S. Supramolecular Aggregation of a new substituted bis(salicylaldiminato)zinc(II) schiff-base complex derived from trans-1,2-diaminocyclohexane. Inorganics 2018, 6, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveri, I.P.; Forte, G.; Consiglio, G.; Failla, S.; Di Bella, S. Aggregates of defined stereochemical scaffolds: A study in solution of a Zinc(II) schiff base complex derived from the enantiopure trans-1,2-cyclopentanediamine. Inorg. Chem. 2017, 56, 14206–14213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Fu, H.; Shen, F.; Sheng, X.; Peng, A.; Gu, Z.; Ma, H.; Ma, J.S.; Yao, J. Distinct M and P helical complexes of H2O and metal ions NiII, CuII, and ZnII with enantiomerically pure chiral bis(pyrrol-2-ylmethyleneamine)cyclohexane ligands: Crystal structures and circular dichroism properties. Inorg. Chem. 2007, 46, 3548–3556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Li, Q.; Proni, G. One-pot diastereoselective assembly of helicates based on a chiral salen scaffold. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2014, 40, 47–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Consiglio, G.; Failla, S.; Fortuna, C.G.; D’Urso, L.; Forte, G. Aggregation of a Zn(II)-salen complex: Theoretical study of structure and spectra. Comput. Theor. Chem. 2015, 1067, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vladimirova, K.G.; Freidzon, A.Y.; Kotova, O.V.; Vaschenko, A.A.; Lepnev, L.S.; Bagatur’yants, A.A.; Vitukhnovskiy, A.G.; Stepanov, N.F.; Alfimov, M.V. Theoretical study of structure and electronic absorption spectra of some schiff bases and their zinc complexes. Inorg. Chem. 2009, 48, 11123–11130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cozzi, P.G.; Dolci, L.S.; Garelli, A.; Montalti, M.; Prodi, L.; Zaccheroni, N. Photophysical properties of Schiff-base metal complexes. New J. Chem. 2003, 27, 692–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumur, F.; Contal, E.; Wantz, G.; Gigmes, D. Photoluminescence of Zinc complexes: Easily tunable optical properties by variation of the bridge between the imido groups of schiff base ligands. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2014, 4186–4198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.-J.; Hao, L.; Chen, C.-Y.; Qiu, Q.-M.; Wang, K.; Song, J.-B.; Li, H. Red-shift in fluorescence emission of D-A type asymmetrical Zn(II) complexes by extending the π-π stacking interaction. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 20488–20493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barboza, C.A.; Germino, J.C.; Martinez Santana, A.; Quites, F.J.; Muniz Vazquez, P.A.; Zambon Atvars, T.D. Structural correlations between luminescent properties and excited state internal proton transfer in some Zinc(II) N,N′-bis(salicylidenes). J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 6152–6163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccinno, M.; Aragay, G.; Yafteh Mihan, F.; Ballester, P.; Dalla Cort, A. Unexpected emission properties of a 1,8-naphthalimide unit covalently appended to a Zn–salophen. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2015, 2664–2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Su, H.; Wang, P.; Wang, W.; Li, H. The enhancement of the D–A effect of an asymmetric Schiff base by introducing acetyl groups into diaminomaleonitrile: Synthesis, red fluorescence and crystal structure. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 14268–14275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minei, P.; Fanizza, E.; Rodríguez, A.M.; Muñoz-García, A.B.; Cimino, P.; Pavone, M.; Pucci, A. Cost-effective solar concentrators based on red fluorescent Zn(II)-salicylaldiminato complex. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 17474–17482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Bella, S.; Consiglio, G.; La Spina, G.; Oliva, C.; Cricenti, A. Nanoscale uniform self-assembled monolayers of fluorescent zinc(II) complexes on the Si(100) surface. J. Chem. Phys. 2008, 129, 114704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Bella, S.; Leonardi, N.; Consiglio, G.; Sortino, S.; Fragalà, I. fluorescent self-assembled monolayers of bis(salicylaldiminato)zinc(II) schiff-base complexes. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2004, 4561–4565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Bella, S.; Consiglio, G.; Sortino, S.; Giancane, G.; Valli, L. Langmuir–Schäfer films of functional amphiphilic nickel(ii) and Zinc(II) schiff base complexes. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2008, 5228–5234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, M.K.; Singh, Y.D.; Singh, N.B.; Sarkar, U. Emissive bis-salicylaldiminato schiff base ligands and their zinc(II)complexes: Synthesis, photophysical properties, mesomorphism and DFT studies. J. Mol. Struct. 2015, 1081, 316–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjee, C.H.; Das, G.; Mondal, P.; Rao, N.V.S. Novel photoluminescent hemi-disclike liquid crystalline Zn(II) complexes of [N2O2] donor 4-alkoxy substituted salicyldimine Schiff base with aromatic spacer. Polyhedron 2010, 29, 3089–3096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Gou, F.; Fang, R.; Jing, H.; Zhu, Z. SalenZn-bridged D-π-A dyes for dye-sensitized solar cells. Chin. J. Chem. 2014, 32, 513–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Yu, H.; Yan, X.; Zhang, Y.; Miao, Y.; Ye, K.; Wang, Y. A luminescent benzothiadiazole-bridging bis(salicylaldiminato)zinc(II) complex with mechanochromic and organogelation properties. Dalton Trans. 2018, 47, 6146–6155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, A.C.W.; MacLachlan, M.J. Poly(salphenyleneethynylene)s: Soluble, conjugated metallopolymers that exhibit unique supramolecular crosslinking behavior. J. Mater. Chem. 2007, 17, 1923–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Bella, S.; Oliveri, I.P.; Colombo, A.; Dragonetti, C.; Righetto, S.; Roberto, D. An unprecedented switching of the second-order nonlinear optical response in aggregate bis(salicylaldiminato)Zinc(II) schiff-base complexes. Dalton Trans. 2012, 41, 7013–7016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.-B.; Zhan, J.; Hai, Y.; Zhang, J.-L. Molecular assembly directed by metal–aromatic interactions: Control of the aggregation and photophysical properties of Zn–salen complexes by aromatic mercuration. Chem. Eur. J. 2012, 18, 4242–4249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalla Cort, A.; Mandolini, L.; Pasquini, C.; Rissanen, K.; Russo, L.; Schiaffino, L. Zinc–salophen complexes as selective receptors for tertiary amines. New J. Chem. 2007, 31, 1633–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escudero-Adán, E.C.; Benet-Buchholz, J.; Kleij, A.W. Supramolecular adsorption of alkaloids by metallosalphen complexes. Inorg. Chem. 2008, 47, 4256–4263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wezenberg, S.J.; Escudero-Adán, E.C.; Benet-Buchholz, J.; Kleij, A.W. Colorimetric discrimination between important alkaloid nuclei mediated by a bis-salphen chromophore. Org. Lett. 2008, 10, 3311–3314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveri, I.P.; Di Bella, S. Sensitive fluorescent detection and lewis basicity of aliphatic amines. J. Phys. Chem. A 2011, 115, 14325–14330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveri, I.P.; Di Bella, S. Highly sensitive fluorescent probe for detection of alkaloids. Tetrahedron 2011, 67, 9446–9449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveri, I.P.; Maccarrone, G.; Di Bella, S. A lewis basicity scale in dichloromethane for amines and common nonprotogenic solvents using a Zinc(II) schiff-base complex as reference lewis acid. J. Org. Chem. 2011, 76, 8879–8884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveri, I.P.; Di Bella, S. Lewis basicity of relevant monoanions in a non-protogenic organic solvent using a zinc(II) Schiff-base complex as reference Lewis acid. Dalton Trans. 2017, 46, 11608–11614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Germain, M.E.; Vargo, T.R.; Khalifah, P.G.; Knapp, M.J. Fluorescent detection of nitroaromatics and 2,3-dimethyl-2,3-dinitrobutane (DMNB) by a Zinc complex: (salophen)Zn. Inorg. Chem. 2007, 46, 4422–4429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Germain, M.E.; Knapp, M.J. Discrimination of nitroaromatics and explosives mimics by a fluorescent Zn(salicylaldimine) sensor array. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 5422–5423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cano, M.; Rodríguez, L.; Lima, J.C.; Pina, F.; Dalla Cort, A.; Pasquini, C.; Schiaffino, L. Specific supramolecular interactions between Zn2+-salophen complexes and biologically relevant anions. Inorg. Chem. 2009, 48, 6229–6235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabaté, F.; Giannicchi, I.; Acóna, L.; Dalla Cort, A.; Rodríguez, L. Anion selectivity of Zn-salophen receptors: Influence of ligand substituents. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2015, 434, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strianese, M.; Milione, S.; Maranzana, A.; Grassi, A.; Pellecchia, C. Selective detection of ATP and ADP in aqueous solution by using a fluorescent zinc receptor. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 11419–11421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurček, O.; Cametti, M.; Pontini, M.; Kolehmainena, E.; Rissanen, K. A Zinc-salophen/bile-acid conjugate receptor solubilized by CTABr micelles binds phosphate in water. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2013, 11, 4585–4590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wezenberg, S.J.; Anselmo, D.; Escudero-Adán, E.C.; Benet-Buchholz, J.; Kleij, A.W. Dimetallic activation of dihydrogen phosphate by Zn(salphen) chromophores. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2010, 4611–4616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, N.; Zelder, F. Detecting biologically relevant phosphates with locked salicylaldehyde probes in water. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 17170–17173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.; Gou, F.; Zhang, X.; Shen, G.; Zhou, X.; Xiang, H. A class of multiresponsive colorimetric and fluorescent pH probes via three different reaction mechanisms of salen complexes: A selective and accurate ph measurement. Inorg. Chem. 2016, 55, 9221–9229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalla Cort, A.; Bernardin, P.; Schiaffino, L. A new water soluble Zn-salophen derivative as a receptor for α-aminoacids: Unexpected chiral discrimination. Chirality 2009, 21, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puglisi, R.; Ballistreri, F.P.; Gangemi, C.M.A.; Toscano, R.M.; Tomaselli, G.A.; Pappalardo, A.; Trusso Sfrazzetto, G. Chiral Zn–salen complexes: A new class of fluorescent receptors for enantiodiscrimination of chiral amines. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 911–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Rodríguez, L.; Bandeira, N.A.G.; Bo, C.; Kleij, A.W. Highly efficient chirality transfer from diamines encapsulated within a self-assembled calixarene-salen host. Chem. Eur. J. 2015, 21, 7144–7150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escárcega-Bobadilla, M.V.; Salassa, G.; Martínez Belmonte, M.; Escudero-Adán, E.C.; Kleij, A.W. Versatile switching in substrate topicity: Supramolecular chirality induction in Di- and trinuclear host complexes. Chem. Eur. J. 2012, 18, 6805–6810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hai, Y.; Chen, J.-J.; Zhao, P.; Lv, H.; Yu, Y.; Xu, P.; Zhang, J.-L. Luminescent zinc salen complexes as single and two-photon fluorescence subcellular imaging probes. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 2435–2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Cai, Y.-B.; Jing, J.; Zhang, J.-L. Unravelling the correlation between metal induced aggregation and cellular uptake/subcellular localization of znsalen: An overlooked rule for design of luminescent metal probes. Chem. Sci. 2015, 6, 2389–2397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brissos, R.; Ramos, D.; Lima, J.C.; Yafteh Mihan, F.; Borràs, M.; de Lapuente, J.; Dalla Cort, A.; Rodríguez, L. Luminescent Zinc salophen derivatives: Cytotoxicity assessment and action mechanism studies. New J. Chem. 2013, 37, 1046–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannicchi, I.; Brissos, R.; Ramos, D.; de Lapuente, J.; Lima, G.C.; Dalla Cort, A.; Rodríguez, L. Substituent Effects on the biological properties of Zn-salophen complexes. Inorg. Chem. 2013, 52, 9245–9253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveri, I.P.; Malandrino, G.; Di Bella, S. Phase transition and vapochromism in molecular assemblies of a polymorphic Zinc(II) schiff-base complex. Inorg. Chem. 2014, 53, 9771–9777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirabella, S.; Oliveri, I.P.; Ruffino, F.; Maccarrone, G.; Di Bella, S. Low-cost chemiresistive sensor for volatile amines based on a 2D network of a zinc(II) Schiff-base complex. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2016, 109, 143108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveri, I.P.; Malandrino, G.; Mirabella, S.; Di Bella, S. Vapochromic and chemiresistive characteristics of a nanostructured molecular material composed of a zinc(II)-salophen complex. Dalton Trans. 2018, 47, 15977–15982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piccinno, M.; Angulo-Pachón, C.A.; Ballester, P.; Escuder, B.; Dalla Cort, A. Rational design of a supramolecular gel based on a Zn(II)-salophen bis-dipeptide derivative. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 57306–57309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

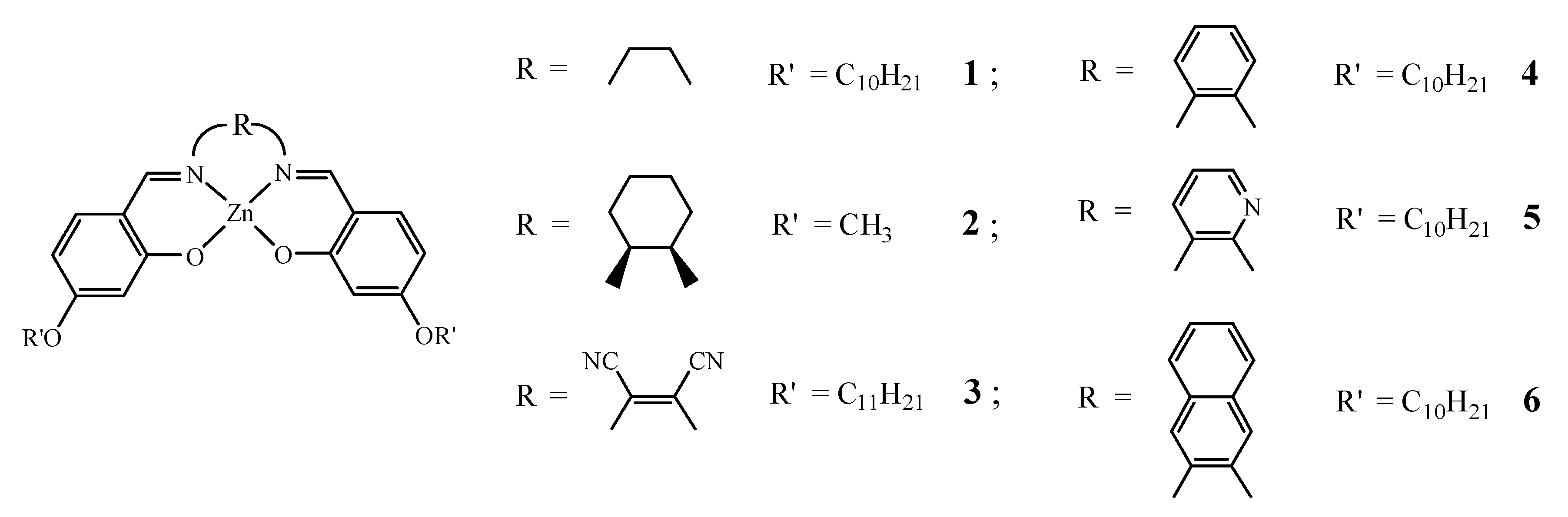
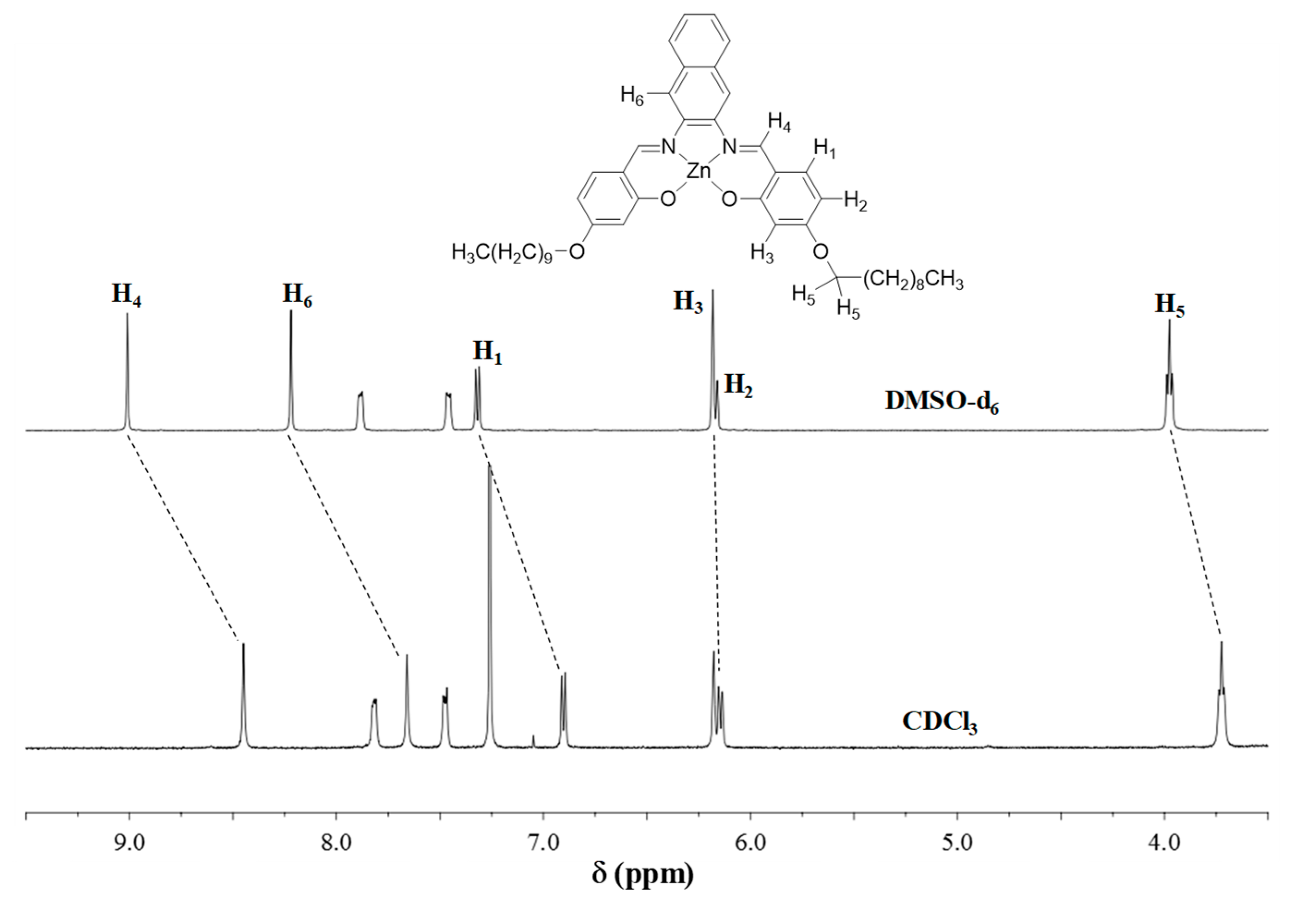
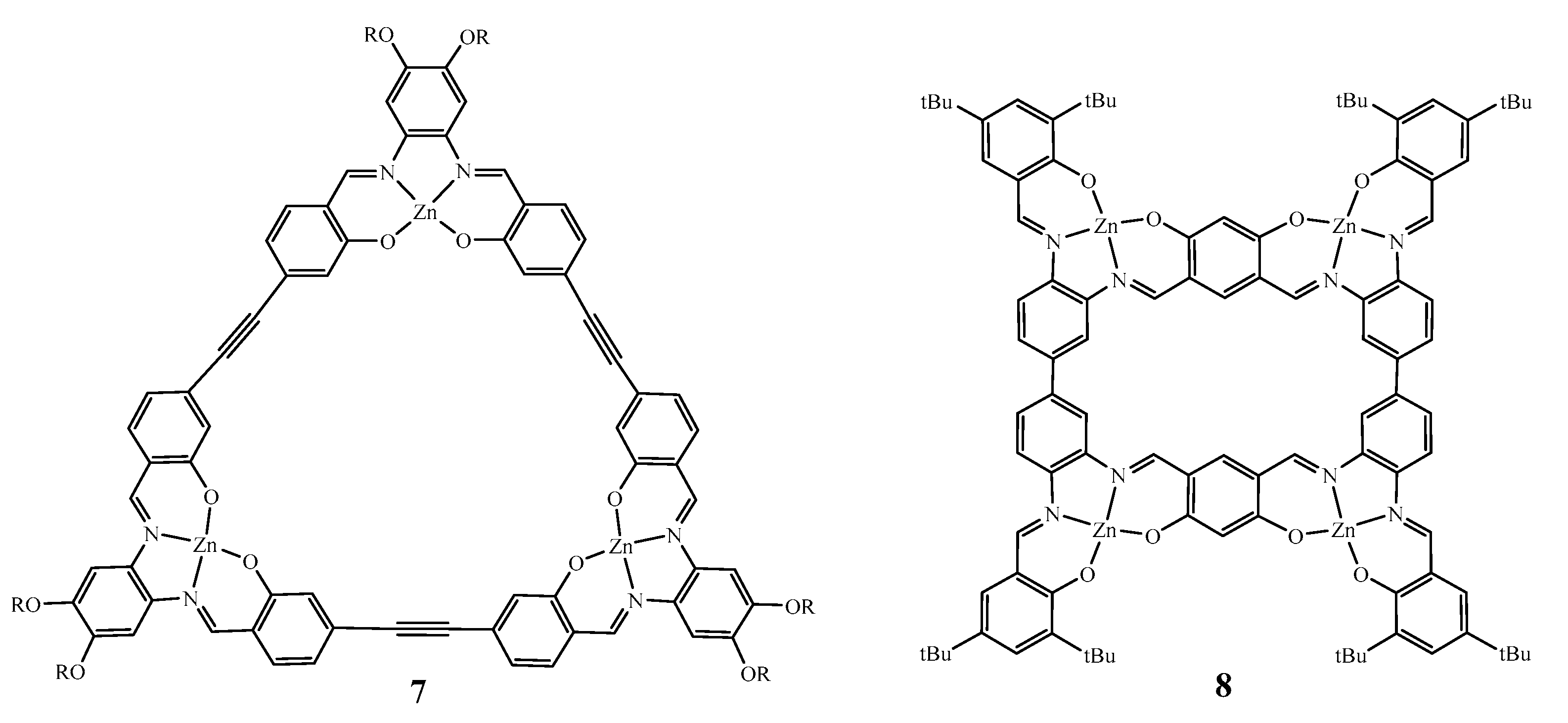
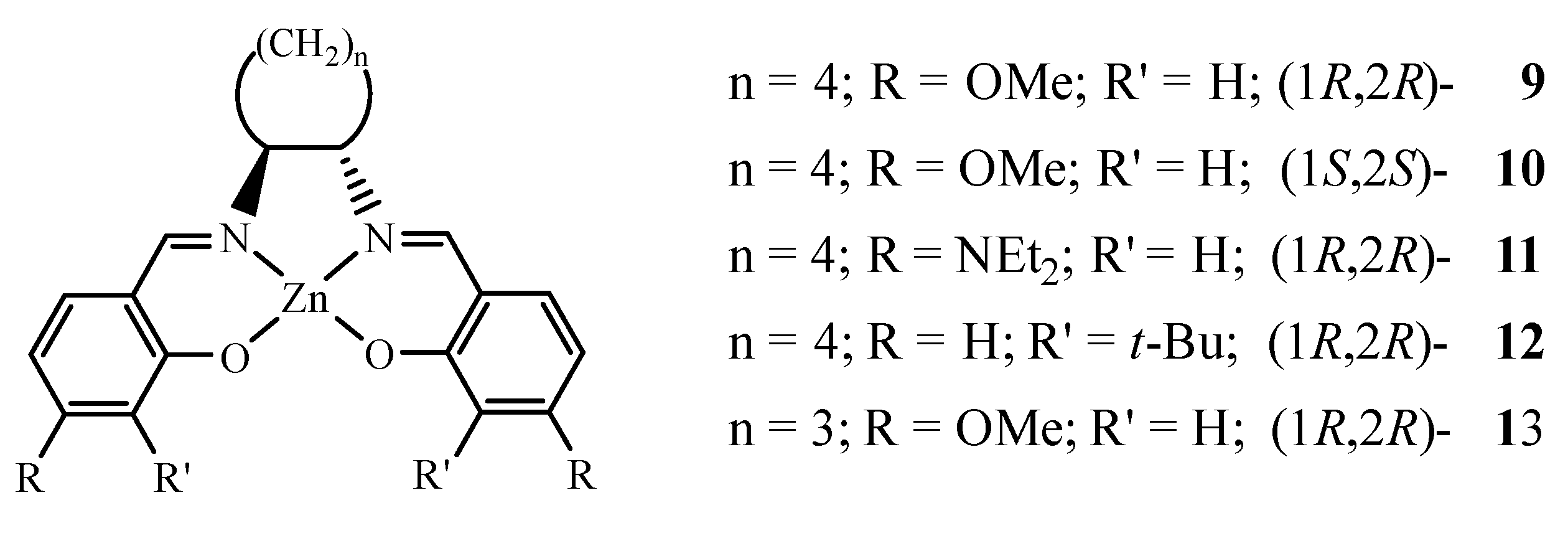


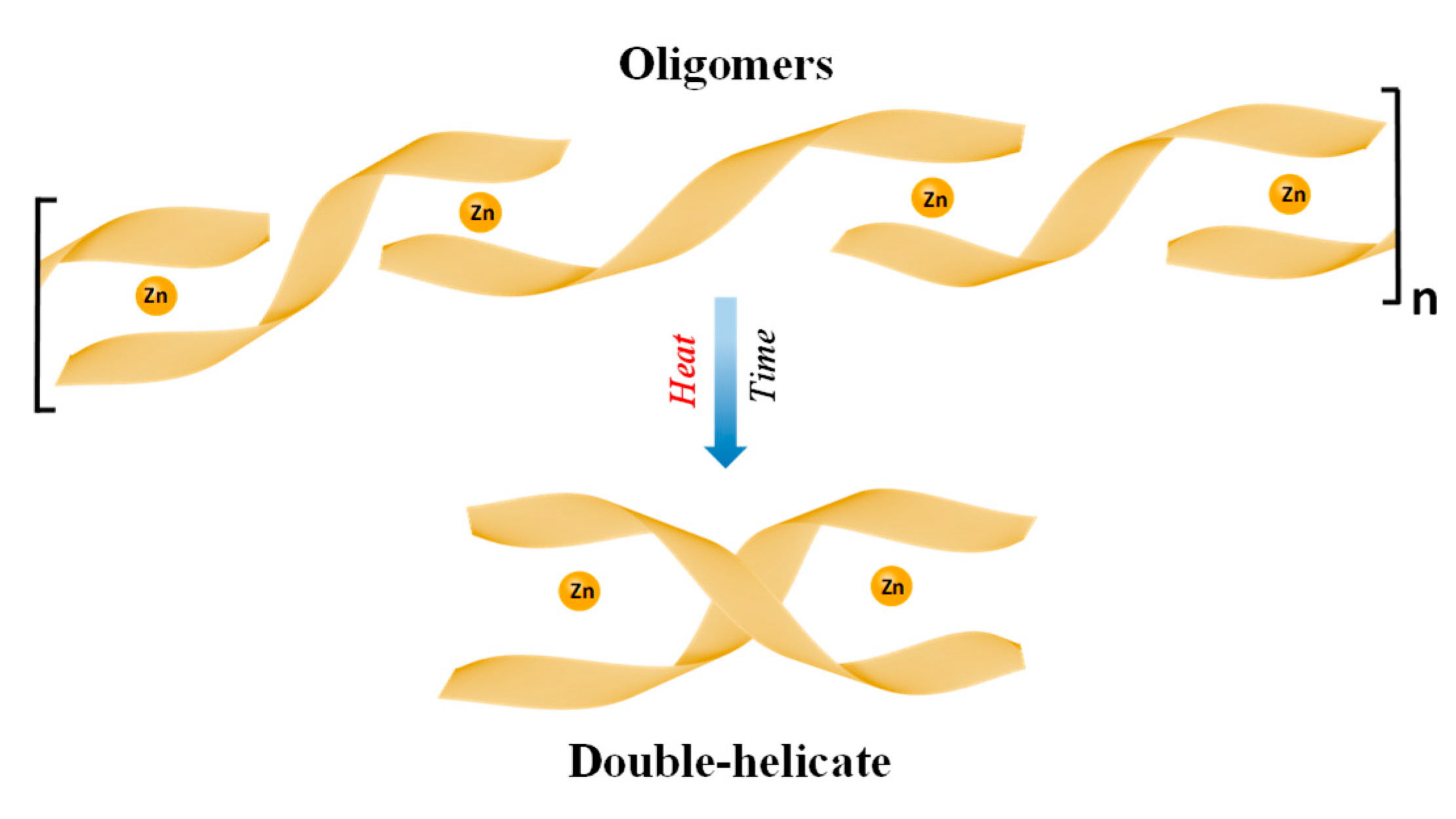
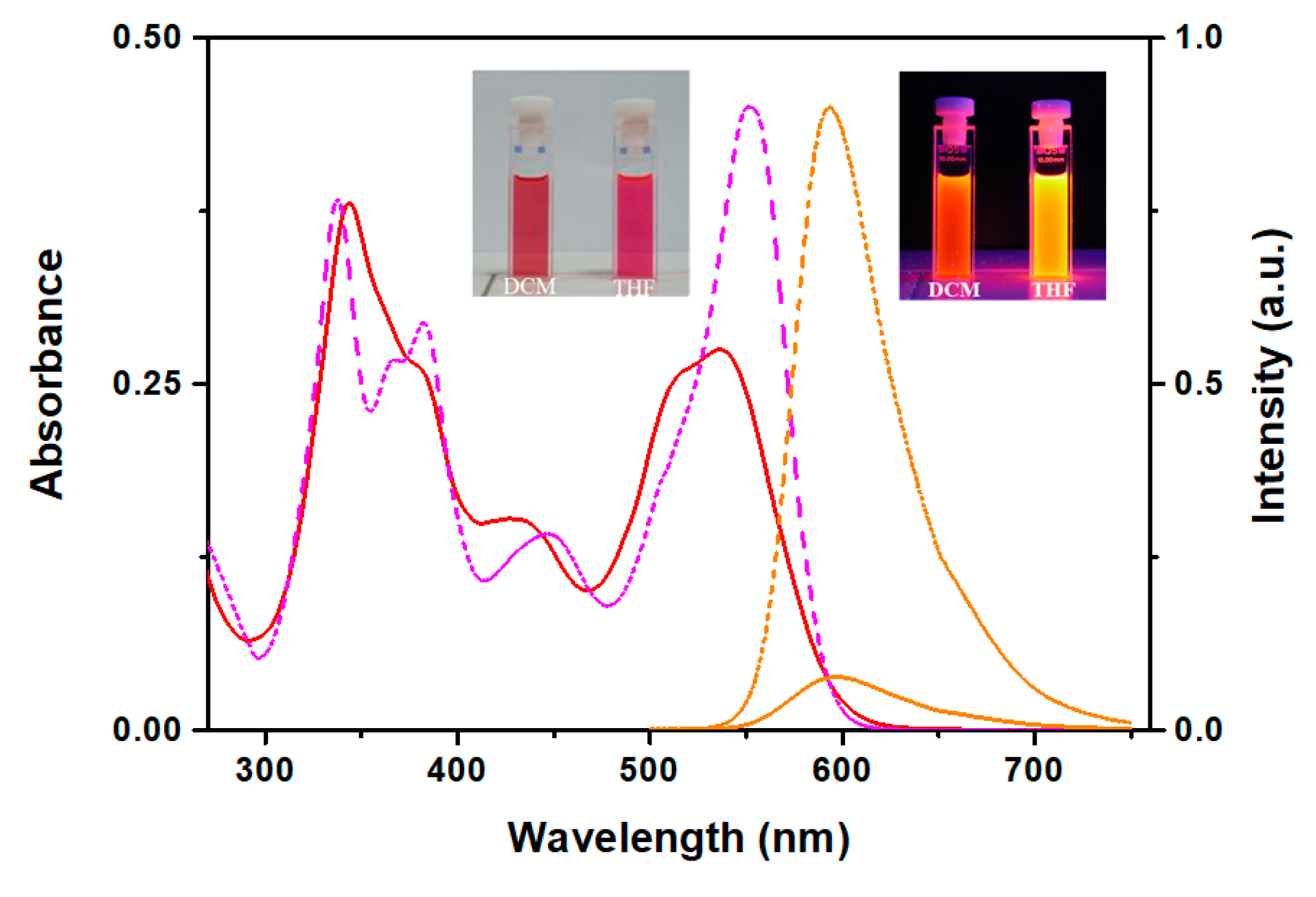
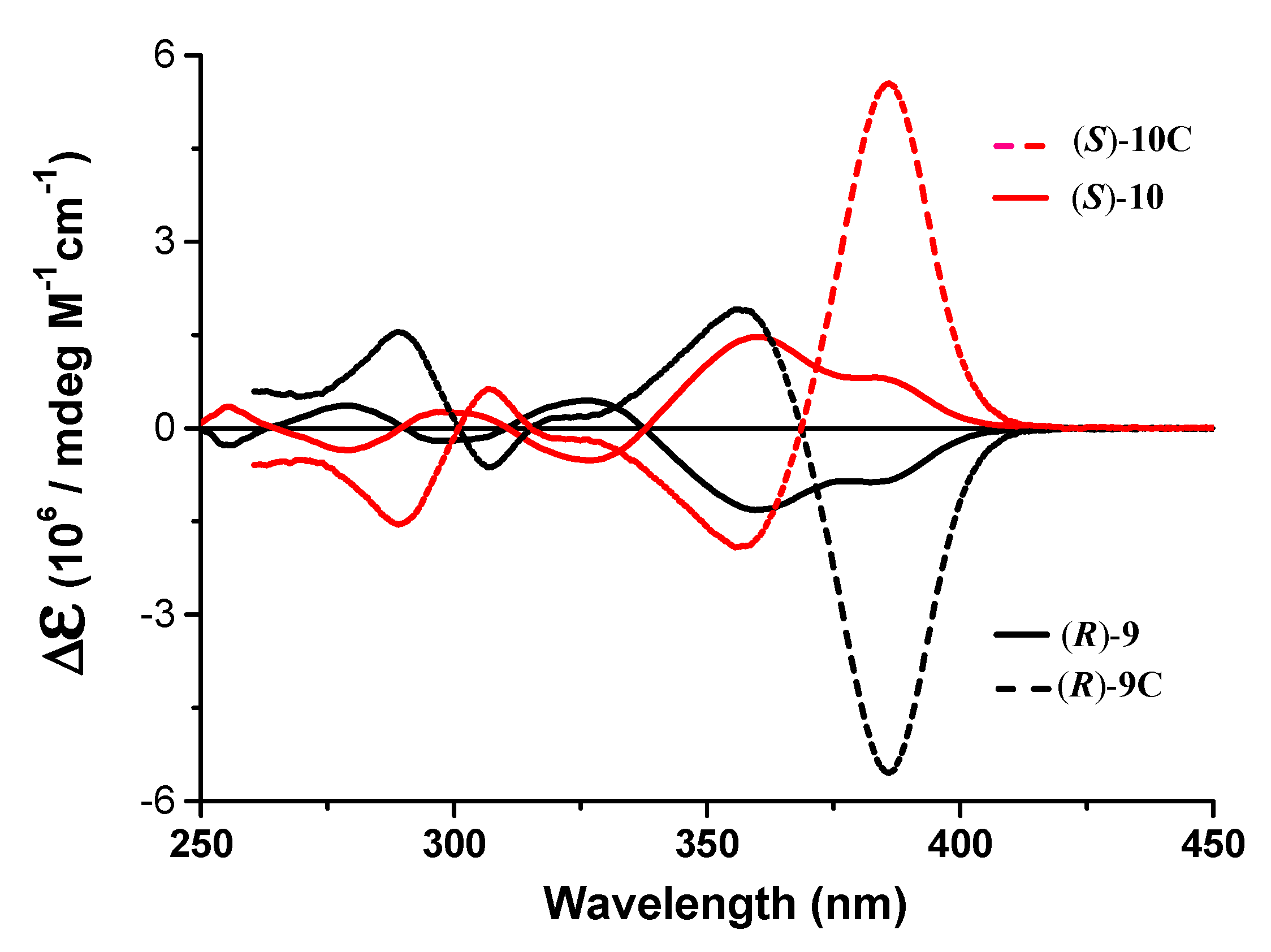
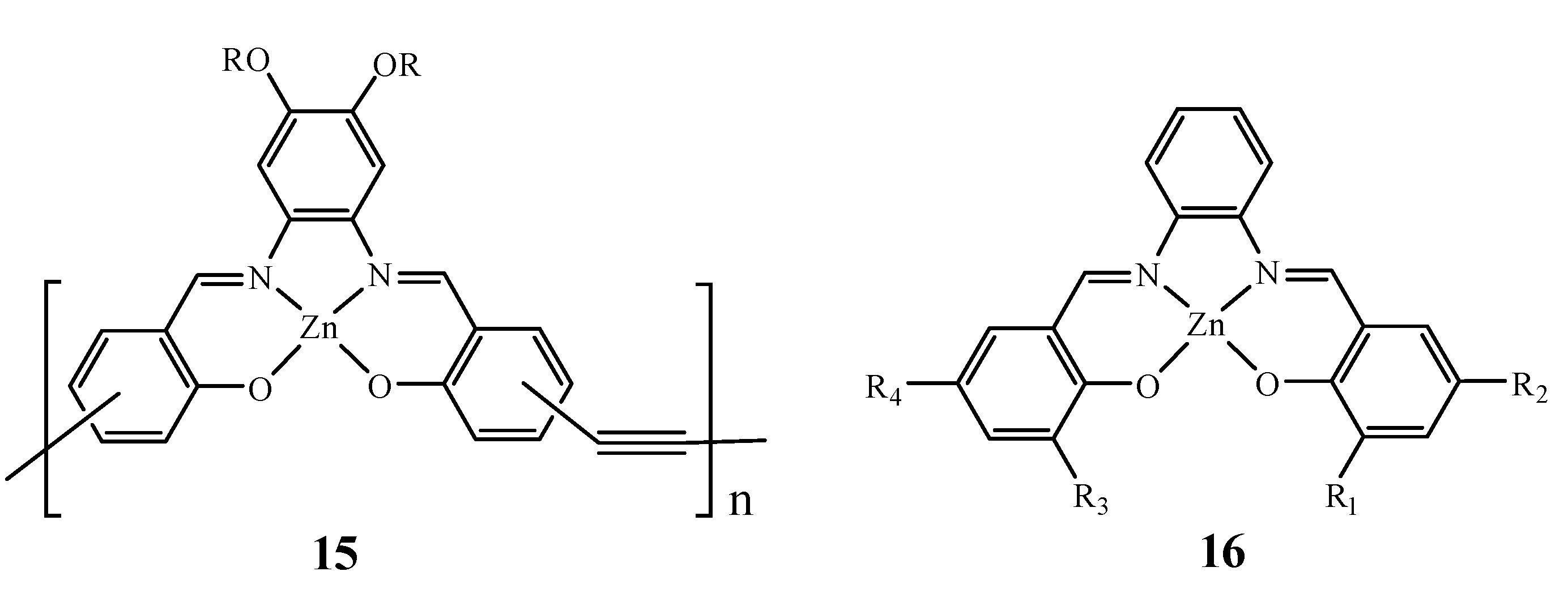



| Compound | H1 | H2 | H3 | H4 | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.12 | <0.1 | 0.2 | 0.16 | 60 |
| 2 | 0.11 | −0.16; −0.12 | −0.43; <0.1 | <0.1; 0.22 | 27 |
| 3 | 0.38 | <0.1 | 0.63 | 0.05 | 62 |
| 4 | 0.22 | <0.1 | <0.1 | 0.39 | 61 |
| 5 | 0.38; 0.31 | <0.1 | 0.26 | 0.51; 0.12 | 61 |
| 6 | 0.41 | <0.1 | <0.1 | 0.55 | 61 |
| Compound | Diamino Bridge | δ, ppm | Zn(II) Coordination | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | cis-cyclohexane-1,2-diamine | 8.08; 8.33 | penta | 27 a |
| 3 | 2,3-diamino-maleonitrile | 8.35 | penta | 62, 28 a |
| 4 | benzene-1,2-diamine | 8.47 | penta | 61, 30 a |
| 9C | trans-cyclohexane-1,2-diamine | 7.35 | tetra | 66 |
| 11-h | trans-cyclohexane-1,2-diamine | 7.22 | tetra | 67 |
| 12 | trans-cyclohexane-1,2-diamine | 7.45 | tetra | 66, 70 a |
| 13 | trans-cyclopentane-1,2-diamine | 7.50 | tetra | 68 |
| 14 | trans-cyclohexane-1,2-diamine | 7.30 | tetra | 69 a |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ∆G (kcal/mol) | −2.75 | −3.87 | −8.38 | −6.11 | −6.63 | −6.37 |
| Calc Log K | 2.02 | 2.84 | 6.14 | 4.48 | 4.86 | 4.67 |
| Exptl Log K | 1.95 | 2.93 | 6.18 | 4.28 | 4.70 | 4.47 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Consiglio, G.; Oliveri, I.P.; Failla, S.; Di Bella, S. On the Aggregation and Sensing Properties of Zinc(II) Schiff-Base Complexes of Salen-Type Ligands. Molecules 2019, 24, 2514. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24132514
Consiglio G, Oliveri IP, Failla S, Di Bella S. On the Aggregation and Sensing Properties of Zinc(II) Schiff-Base Complexes of Salen-Type Ligands. Molecules. 2019; 24(13):2514. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24132514
Chicago/Turabian StyleConsiglio, Giuseppe, Ivan Pietro Oliveri, Salvatore Failla, and Santo Di Bella. 2019. "On the Aggregation and Sensing Properties of Zinc(II) Schiff-Base Complexes of Salen-Type Ligands" Molecules 24, no. 13: 2514. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24132514
APA StyleConsiglio, G., Oliveri, I. P., Failla, S., & Di Bella, S. (2019). On the Aggregation and Sensing Properties of Zinc(II) Schiff-Base Complexes of Salen-Type Ligands. Molecules, 24(13), 2514. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24132514