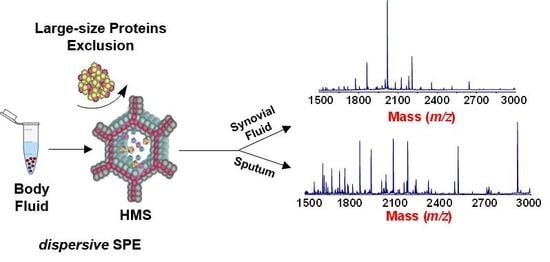
Hexagonal Mesoporous Silica as a Rapid, Efficient and Versatile Tool for MALDI-TOF MS Sample Preparation in Clinical Peptidomics Analysis: A Pilot Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Preparation of Serial Diluted Solutions and Preconcentration Experiments with HMS
2.3. Sputum Collection
2.4. Sputum Processing
2.5. Sputum Processing with HMS
2.6. SF Collection and Treatment with Hyaluronidase.
2.7. Ultrafiltration Procedure for SF and HSE-treated SF
2.8. SF Processing with HMS
2.9. Sputum and SF MALDI-TOF MS
2.10. Reproducibility
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Preconcentration of Extremely Diluted Solutions of Standard Peptides
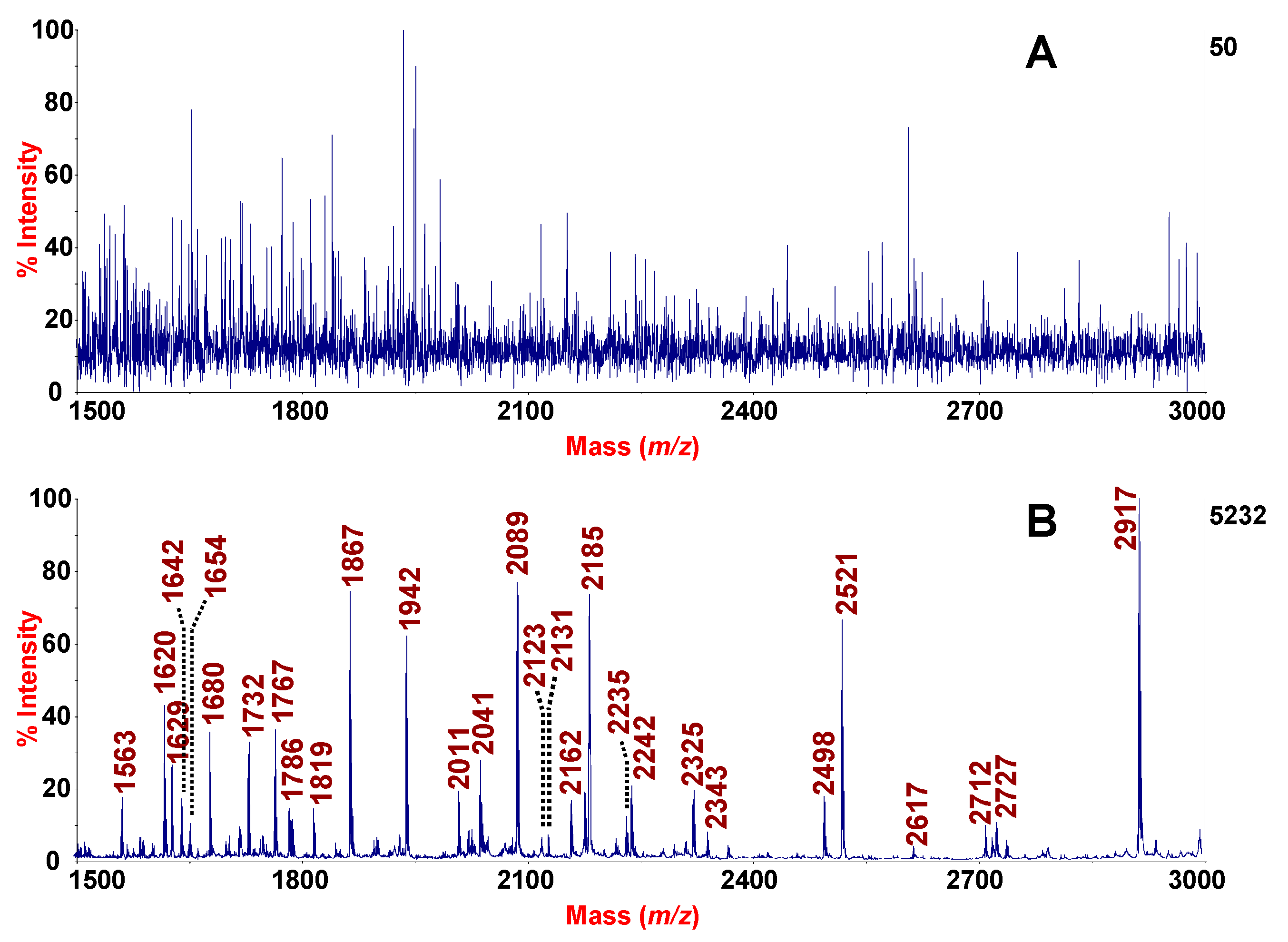
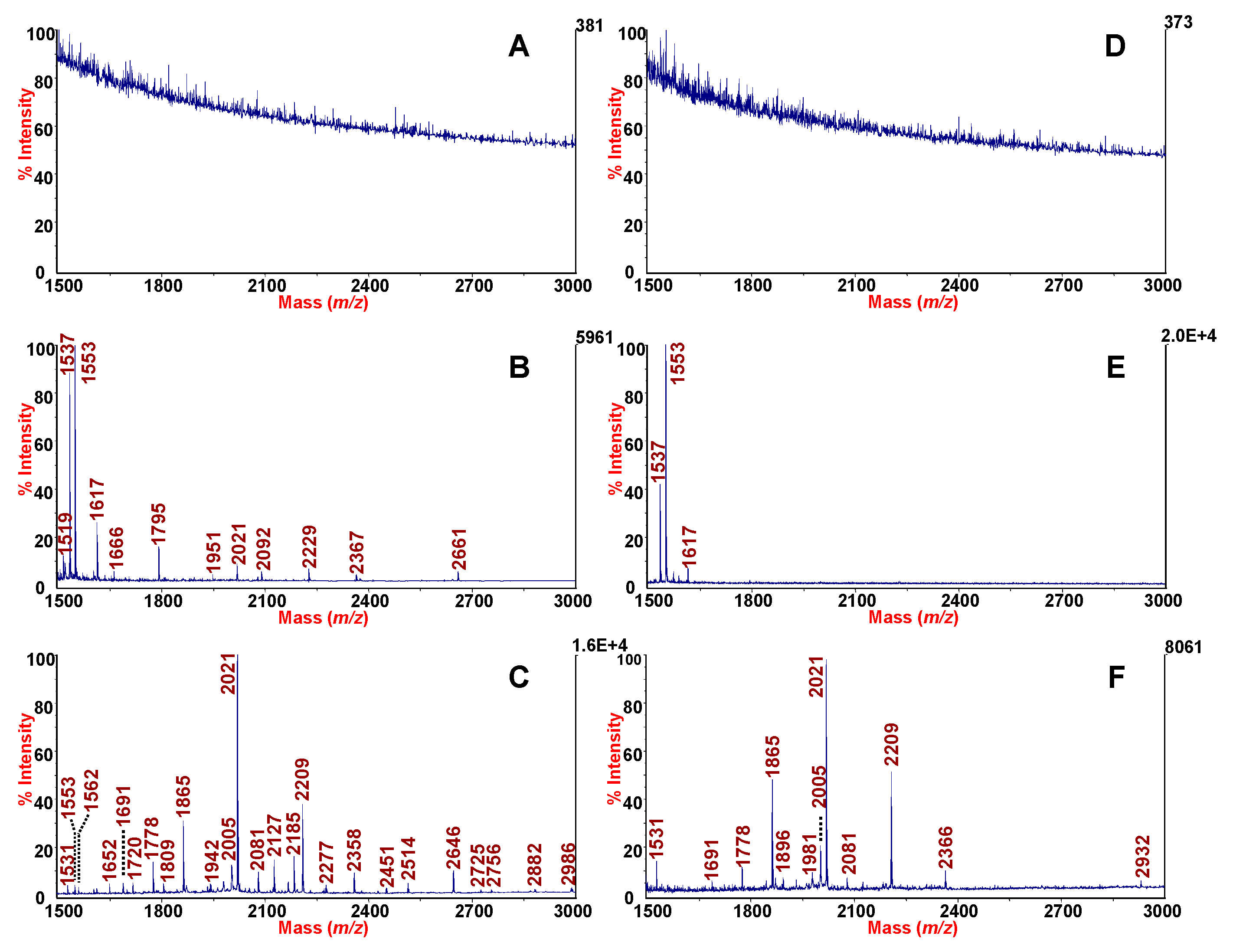
3.2. Analysis of Peptidic Profiles of Clinical Samples Sputum and SF
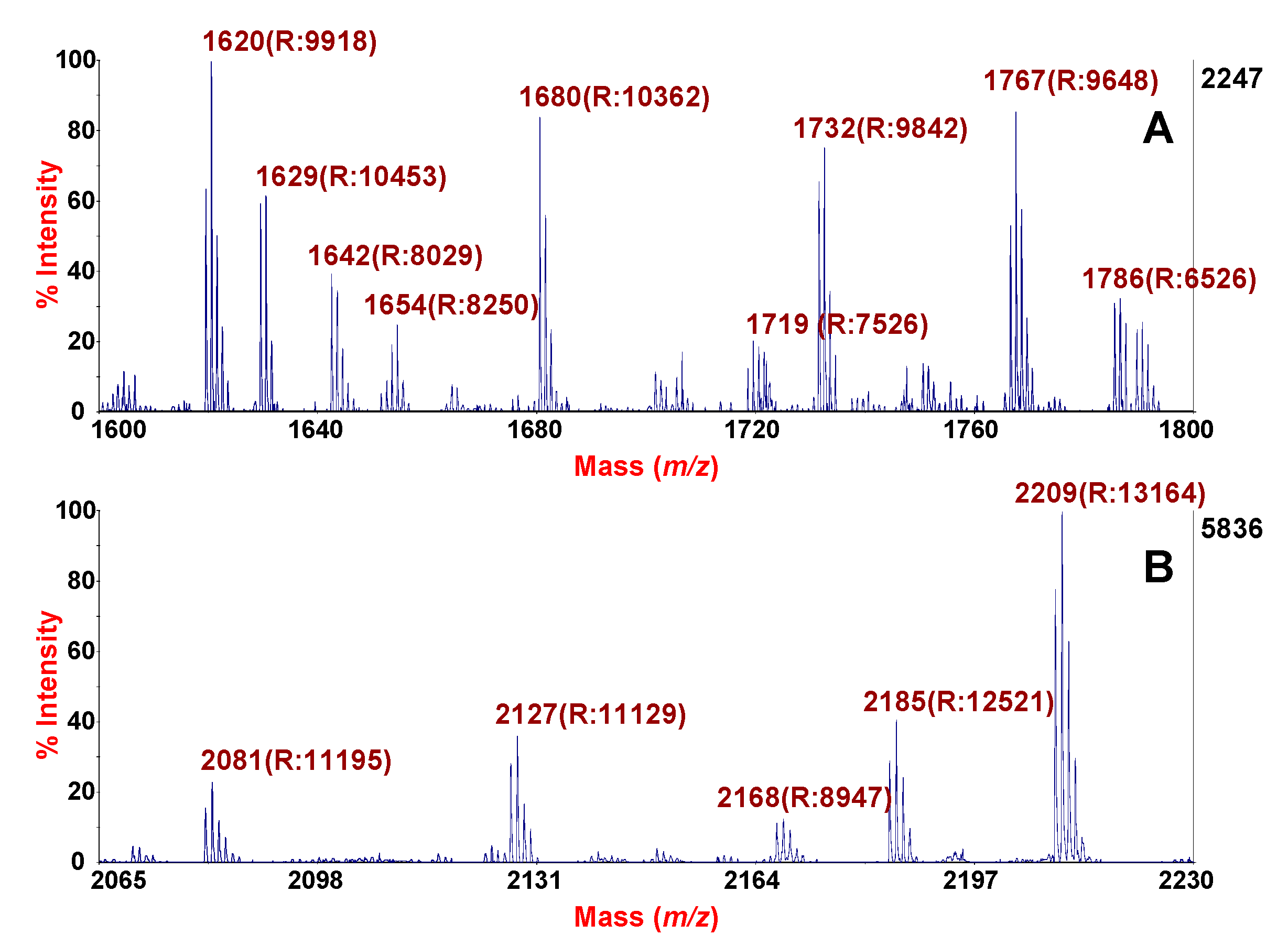
3.3. HMS-MALDI-TOF MS Sputum Profile
3.4. Enrichment of Naturally Occurring Peptides from SF
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lai, Z.W.; Petrera, A.; Schilling, O. The emerging role of the peptidome in biomarker discovery and degradome profiling. Biol. Chem. 2015, 396, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maes, E.; Oeyen, E.; Boonen, K.; Schildermans, K.; Mertens, I.; Pauwels, P.; Valkenborg, D.; Baggerman, G. The challenges of peptidomics in complementing proteomics in a clinical context. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baracat-Pereira, M.C.; de Oliveira Barbosa, M.; Magalhaes, M.J., Jr.; Carrijo, L.C.; Games, P.D.; Almeida, H.O.; Sena Netto, J.F.; Pereira, M.R.; de Barros, E.G. Separomics applied to the proteomics and peptidomics of low-abundance proteins: Choice of methods and challenges—A review. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2012, 35, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duncan, M.W.; Nedelkov, D.; Walsh, R.; Hattan, S.J. Applications of MALDI Mass Spectrometry in Clinical Chemistry. Clin. Chem. 2016, 62, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iles, R.K.; Shahpari, M.E.; Cuckle, H.; Butler, S.A. Direct and rapid mass spectral fingerprinting of maternal urine for the detection of Down syndrome pregnancy. Clin. Proteom. 2015, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savino, R.; Paduano, S.; Preianò, M.; Terracciano, R. The proteomics big challenge for biomarkers and new drug-targets discovery. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 13926–13948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magni, F.; Van Der Burgt, Y.E.; Chinello, C.; Mainini, V.; Gianazza, E.; Squeo, V.; Deelder, A.M.; Kienle, M.G. Biomarkers discovery by peptide and protein profiling in biological fluids based on functionalized magnetic beads purification and mass spectrometry. Blood Transfus. 2010, 8, s92–s97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, R.; Liu, H.; Liu, N.; Wang, Y. Ligand Fishing: A Remarkable Strategy for Discovering Bioactive Compounds from Complex Mixture of Natural Products. Molecules 2016, 21, 1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callesen, A.K.; Madsen, J.S.; Vach, W.; Kruse, T.A.; Mogensen, O.; Jensen, O.N. Serum protein profiling by solid phase extraction and mass spectrometry: A future diagnostics tool? Proteomics 2009, 9, 1428–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, K.; Wu, H.; Hu, T.Y.; Li, Y. Mesoporous silica chip: Enabled peptide profiling as an effective platform for controlling bio-sample quality and optimizing handling procedure. Clin. Proteom. 2016, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajduk, J.; Matysiak, J.; Kokot, Z.J. Challenges in biomarker discovery with MALDI-TOF MS. Clin. Chim. Acta 2016, 458, 84–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terracciano, R.; Casadonte, F.; Pasqua, L.; Candeloro, P.; Di Fabrizio, E.; Urbani, A.; Savino, R. Enhancing plasma peptide MALDI-TOF-MS profiling by mesoporous silica assisted crystallization. Talanta 2010, 80, 1532–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savino, R.; Terracciano, R. Mesopore-assisted profiling strategies in clinical proteomics for drug/target discovery. Drug Discov. Today 2012, 17, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasanzadeh, M.; Shadjou, N.; de la Guardia, M.; Eskandani, M.; Sheikhzadeh, P. Mesoporous silica-based materials for use in biosensors. Trends Anal. Chem. 2012, 33, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.E.; Ryoo, R.; Ahn, W.S.; Lee, C.W.; Chang, J.S. Nanotechnology in Mesostructured Materials, 1st ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Lombardo, N.; Preianò, M.; Maggisano, G.; Murfuni, M.S.; Messina, L.; Pelaia, G.; Savino, R.; Terracciano, R. A rapid differential display analysis of nasal swab fingerprints to distinguish allergic from non-allergic rhinitis subjects by mesoporous silica particles and MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry. Proteomics 2017, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terracciano, R.; Pasqua, L.; Casadonte, F.; Frascà, S.; Preianò, M.; Falcone, D.; Savino, R. Derivatized mesoporous silica beads for MALDI-TOF MS profiling of human plasma and urine. Bioconjug. Chem. 2009, 20, 913–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casadonte, F.; Pasqua, L.; Savino, R.; Terracciano, R. Smart trypsin adsorption into N-(2-aminoethyl)-3-aminopropyl-modified mesoporous silica for ultra fast protein digestion. Chemistry 2010, 16, 8998–9001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macquarrie, D.J.; Jackson, D.B.; Tailland, S.; Wilson, K.; Clark, J.H. New organically modified hexagonal mesoporous silicas: Preparation and applications in catalysis. Stud. Surf. Sci. Catal. 2000, 129, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercier, L.; Pinnavaia, T.J. Direct Synthesis of Hybrid Organic−Inorganic Nanoporous Silica by a Neutral Amine Assembly Route: Structure−Function Control by Stoichiometric Incorporation of Organosiloxane Molecules. Chem. Mater. 2000, 12, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanev, P.T.; Pinnavaia, T.J. Mesoporous Silica Molecular Sieves Prepared by Ionic and Neutral Surfactant Templating: A Comparison of Physical Properties. Chem. Mater. 1996, 8, 2068–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sierra, I.; Quintanilla, D.P. Heavy metal complexation on hybrid mesoporous silicas: An approach to analytical applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 3792–3807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casado, N.; Morante-Zarcero, S.; Perez-Quintanilla, D.; Câmara, J.S.; Sierra, I. Dispersive solid-phase extraction of polyphenols from juice and smoothie samples using hybrid mesostructured silica followed by ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography-ion-trap tandem mass spectrometry. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 67, 955–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preianò, M.; Pasqua, L.; Gallelli, L.; Galasso, O.; Gasparini, G.; Savino, R.; Terracciano, R. Simultaneous extraction and rapid visualization of peptidomic and lipidomic body fluids fingerprints using mesoporous aluminosilicate and MALDI-TOF MS. Proteomics 2012, 12, 3286–3294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corigliano, A.; Preianò, M.; Terracciano, R.; Savino, R.; De Gori, M.; Galasso, O.; Gasparini, G. C3f is a potential tool for the staging of osteoarthritis. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2017, 31, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Terracciano, R.; Preianò, M.; Palladino, G.P.; Carpagnano, G.E.; Foschino Barbaro, M.P.; Pelaia, G.; Savino, R.; Maselli, R. Peptidome profiling of induced sputum by mesoporous silica beads and MALDI-TOF MS for non-invasive biomarker discovery of chronic inflammatory lung diseases. Proteomics 2011, 11, 3402–3414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preianò, M.; Maggisano, G.; Murfuni, M.S.; Villella, C.; Colica, C.; Fregola, A.; Pelaia, C.; Lombardo, N.; Pelaia, G.; Savino, R.; et al. Rapid Detection and Identification of Antimicrobial Peptide Fingerprints of Nasal Fluid by Mesoporous Silica Particles and MALDI-TOF/TOF Mass Spectrometry: From the Analytical Approach to the Diagnostic Applicability in Precision Medicine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 4005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savino, R.; Casadonte, F.; Terracciano, R. In mesopore protein digestion: A new forthcoming strategy in proteomics. Molecules 2011, 16, 5938–5962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, M. Ordered Mesoporous Materials for Bioadsorption and Biocatalysis. Chem. Mat. 2005, 17, 4577–4593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanev, P.T.; Pinnavaia, T.J. A Neutral Templating Route to Mesoporous Molecular Sieves. Science 1995, 267, 865–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greco, V.; Piras, C.; Pieroni, L.; Ronci, M.; Putignani, L.; Roncada, P.; Urbani, A. Applications of MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry in clinical proteomics. Expert Rev. Proteom. 2018, 15, 683–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessler, R.; Partridge, M.R.; Miravitlles, M.; Cazzola, M.; Vogelmeier, C.; Leynaud, D.; Ostinelli, J. Symptom variability in patients with severe COPD: A pan-European cross-sectional study. Eur. Respir. J. 2011, 37, 37264–37272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gray, R.D.; MacGregor, G.; Noble, D.; Imrie, M.; Dewar, M.; Boyd, A.C.; Innes, J.A.; Porteous, D.J.; Greening, A.P. Sputum Proteomics in Inflammatory and Suppurative Respiratory Diseases. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2008, 178, 444–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, S.; Loo, J.A.; Wong, D.T. Human body fluid proteome analysis. Proteomics 2006, 6, 6326–6353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Romero, C.; Blanco, F.J. Proteomics role in the search for improved diagnosis, prognosis and treatment of osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2010, 18, 500–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mateos, J.; Lourido, L.; Fernández-Puente, P.; Calamia, V.; Fernández-López, C.; Oreiro, N.; Ruiz-Romero, C.; Blanco, F.J. Differential protein profiling of synovial fluid from rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis patients using LC–MALDI TOF/TOF. J. Proteom. 2012, 75, 2869–2878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, U.; Anwar, A.; Savage, R.S.; Costa, M.L.; Mackay, N.; Filer, A.; Raza, K.; Watts, R.A.; Winyard, P.G.; Tarr, J.; et al. Biomarkers of early stage osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis and musculoskeletal health. Sci. Rep. 2015, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, Y.; Pinnavaia, T.J. Optimizing Organic Functionality in Mesostructured Silica: Direct Assembly of Mercaptopropyl Groups in Wormhole Framework Structures. Chem. Mater. 2001, 13, 2173–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, S.; Brede, C.; Lescuyer, P.; Cocho, J.A.; Vialaret, J.; Bros, P.; Delatour, V.; Hirtz, C. Clinical mass spectrometry proteomics (cMSP) for medical laboratory: What does the future hold? Clin. Chim. Acta 2017, 467, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: All reagents used in this study are commercially available. Patients samples are not available from the authors. |

| Standard Peptides (m/z) | Serial Dilutions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1:100 | 1:400 | 1:800 | 1:8000 | 1:12000 | |
| des-Arg1-Bradykinin (905) | 7.26 nM (6.571 pg/µL) | 1.82 nM (1.642 pg/µL) | 0.90 nM (0.821 pg/µL) | 0.090 nM (0.082 pg/µL) | 0.060 nM (0.055 pg/µL) |
| Angiotensin I (1297) | 9.26 nM (12.015 pg/µL) | 2.32 nM (3.004 pg/µL) | 1.16 nM (1.502 pg/µL) | 0.116 nM (0.150 pg/µL) | 0.078 nM (0.100 pg/µL) |
| Glu1- Fibrinopeptide B (1571) | 9.29 nM (14.6 pg/µL) | 2.32 nM (3.65 pg/µL) | 1.16 nM (1.825 pg/µL) | 0.116 nM (0.183 pg/µL) | 0.078 nM (0.122 pg/µL) |
| Neurotensin (1674) | 0.34 nM (0.569 pg/µL) | 0.085 nM (0.140 pg/µL) | 0.043 nM (0.071 pg/µL) | 0.004 nM (0.007 pg/µL) | 0.003 nM (0.005 pg/µL) |
| Sample | Bead Type | Average a) Number of Peaks S/N > 20 | Average a) Number of Peaks S/N > 30 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sputum | N/A b) | 25 ± 2 | 13 ± 2 |
| Sputum | HMS | 741 ± 27 | 498 ± 35 |
| MPS | Pore Size Diameter (nm) | Pore Volume (cm3/g) | BET Surface Area (m2/g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| HMS | 2–4 | 1–2 | 800–1000 |
| MPAS | 3.0 | 0.90 | 937 |
| Sample | Bead Type | Average a) Number of Peaks S/N > 20 | Average a) Number of Peaks S/N > 30 |
|---|---|---|---|
| SF | N/A ) | 0 ± 0 | 0 ± 0 |
| SF | Amicon Centrifugal filter-C18 | 480 ± 31 | 303 ± 34 |
| SF | HMS | 765 ± 15 | 582 ± 11 |
| HSE-SF | N/Ab) | 12 ± 1 | 2 ± 1 |
| HSE-SF | Amicon Centrifugal filter-C18 | 488 ± 9 | 345 ± 11 |
| HSE-SF | HMS | 967 ± 39 | 681 ± 6 |
| SF | MPAS | 668 ± 84 | 367 ± 55 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Terracciano, R.; Preianò, M.; Maggisano, G.; Pelaia, C.; Savino, R. Hexagonal Mesoporous Silica as a Rapid, Efficient and Versatile Tool for MALDI-TOF MS Sample Preparation in Clinical Peptidomics Analysis: A Pilot Study. Molecules 2019, 24, 2311. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24122311
Terracciano R, Preianò M, Maggisano G, Pelaia C, Savino R. Hexagonal Mesoporous Silica as a Rapid, Efficient and Versatile Tool for MALDI-TOF MS Sample Preparation in Clinical Peptidomics Analysis: A Pilot Study. Molecules. 2019; 24(12):2311. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24122311
Chicago/Turabian StyleTerracciano, Rosa, Mariaimmacolata Preianò, Giuseppina Maggisano, Corrado Pelaia, and Rocco Savino. 2019. "Hexagonal Mesoporous Silica as a Rapid, Efficient and Versatile Tool for MALDI-TOF MS Sample Preparation in Clinical Peptidomics Analysis: A Pilot Study" Molecules 24, no. 12: 2311. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24122311
APA StyleTerracciano, R., Preianò, M., Maggisano, G., Pelaia, C., & Savino, R. (2019). Hexagonal Mesoporous Silica as a Rapid, Efficient and Versatile Tool for MALDI-TOF MS Sample Preparation in Clinical Peptidomics Analysis: A Pilot Study. Molecules, 24(12), 2311. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24122311