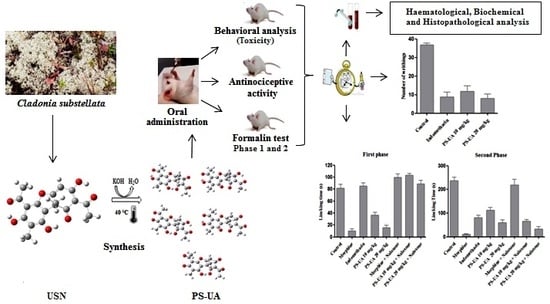
Usnic Acid Potassium Salt: Evaluation of the Acute Toxicity and Antinociceptive Effect in Murine Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
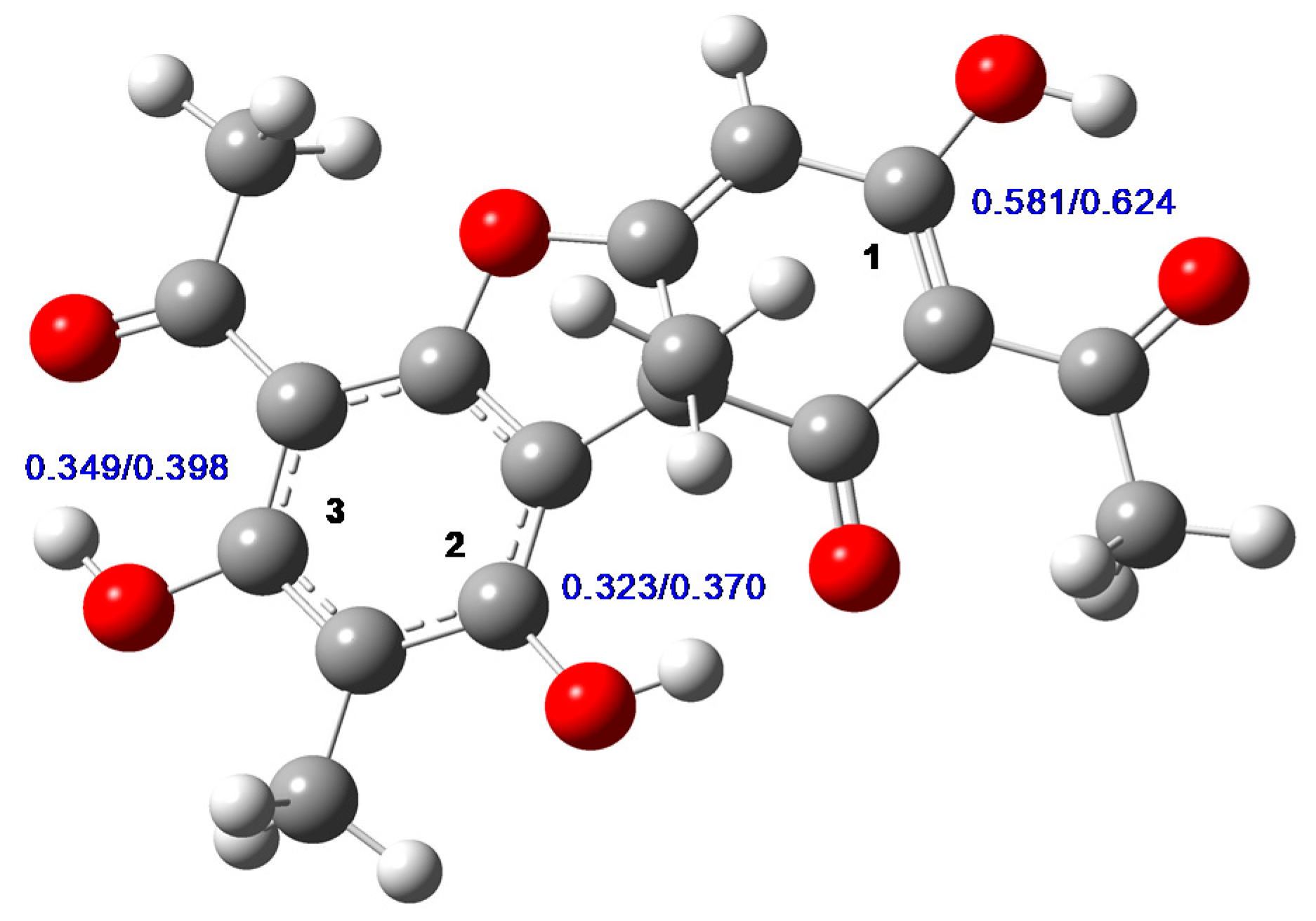
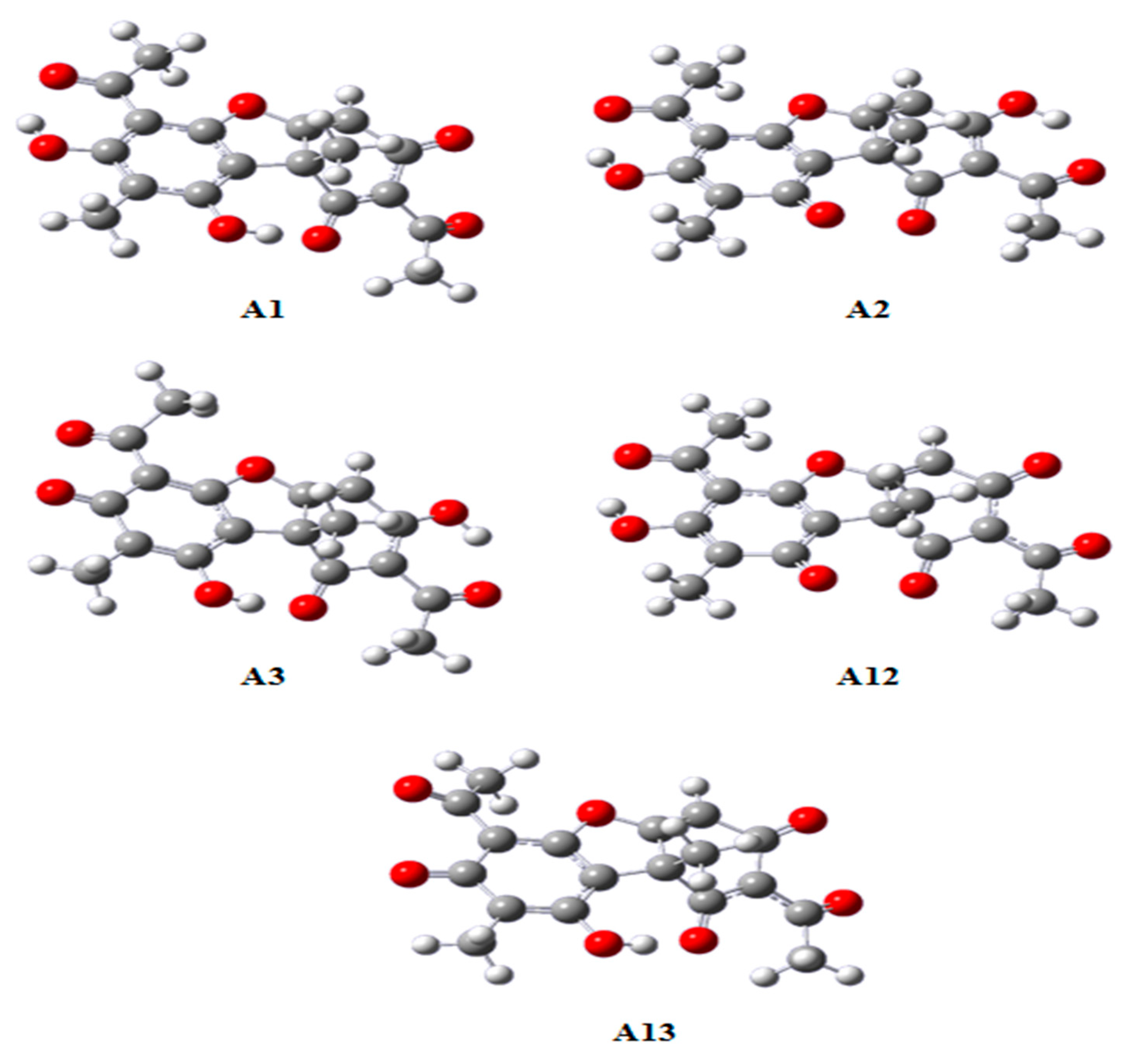
2.1. Chemical Analysis of UA and PS-UA
2.2. Signs of Toxicity and Behavioral Analysis of Mice after PS-UA Treatment
2.3. Haematological and Biochemical Analyses
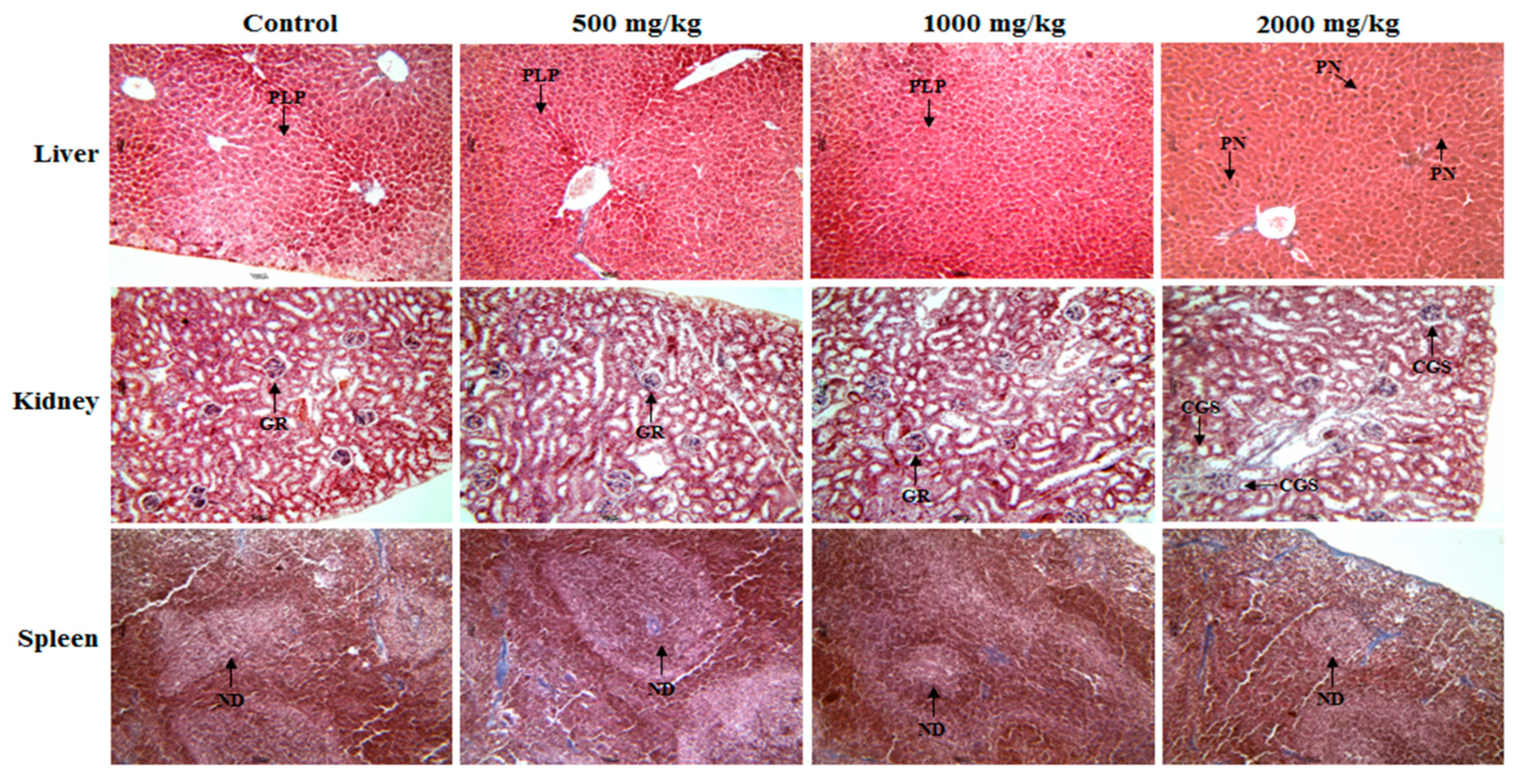
2.4. Histopathological Analyses of the PS-UA Treatments
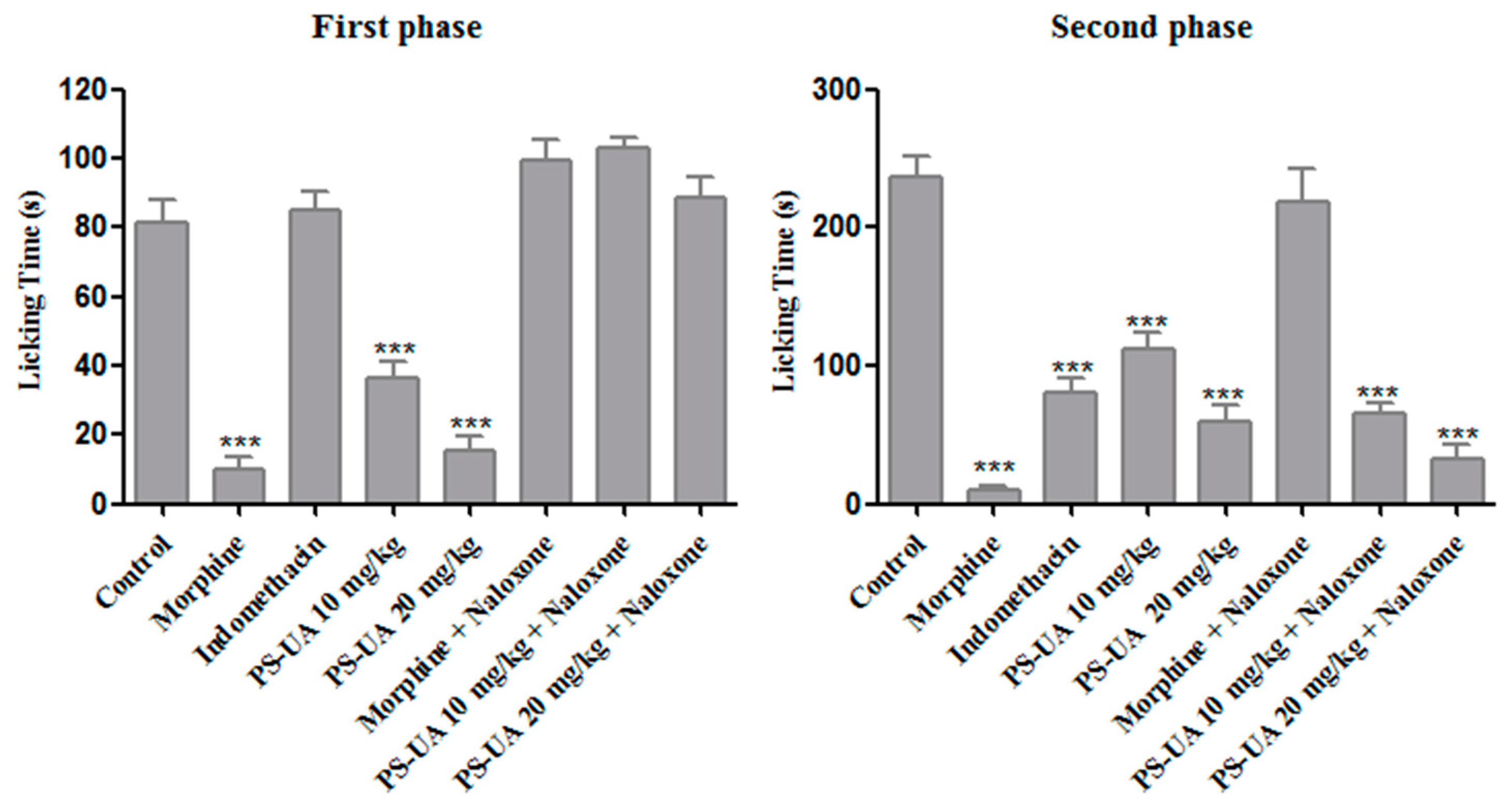
2.5. Antinociceptive Activity
3. Material and Methods
3.1. Lichen Collection
3.2. Extraction and Isolation of Usnic Acid and its Modification into Potassium Salt
3.3. Computational Methods
3.4. Acute Toxicity Evaluation
3.5. Haematological and Biochemical Analyses
3.6. Histopathological Analysis
3.7. Evaluation of Antinociceptive Activity
3.7.1. Acetic Acid-Induced Writhing Test
3.7.2. Formalin Test
3.8. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guo, L.; Shi, Q.; Fang, J.L.; Mei, N.; Ali, A.A.; Lewis, S.M.; Leakey, J.E.; Frankos, V.H. Review of usnic acid and Usnea barbata toxicity. J. Environ. Sci. Health. C Environ. Carcinog. Ecotoxicol. Rev. 2008, 26, 317–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yousuf, A.; Choudhary, M.I.; Atta-Ur-Rahman. Lichens: Chemistry and biological activities. Stud. Nat. Prod. Chem. 2014, 43, 223–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, K.; Joshi, P.G.; Rawat, M.S.M. Lichens as a potential natural source of bioactive compounds: A review. Phytochem. Rev. 2010, 9, 303–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balunas, M.J.; Kinghorn, A.D. Drug discovery from medicinal plants. Life Sci. 2005, 78, 431–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahti, T. Cladoniaceae, 1st ed.; The Organization for Flora Neotropica, New York Botanical Garden Press 78: New York, NY, USA, 2000; pp. 1–362. [Google Scholar]
- White, P.A.S.; Oliveira, R.C.M.; Oliveira, A.P.; Serafini, M.R.; Araújo, A.A.S.; Gelain, D.P.; Moreira, J.C.F.; Almeida, J.R.G.S.; Quintans, J.S.S.; Quintans-Junior, L.J.; et al. Antioxidant activity and mechanisms of action of natural compounds isolated from Lichens: A systematic review. Molecules 2014, 19, 14496–14527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araújo, A.A.S.; Melo, M.G.D.; Rabelo, T.K.; Nunes, P.S.; Santos, S.L.; Serafini, M.R.; Santosa, M.R.V.; Quintans-Júnior, L.J.; Gelain, D.P. Review of the biological properties and toxicity of usnic acid. Nat. Prod. Res. 2015, 29, 2167–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutchinson, M.R.; Shavit, Y.; Grace, P.M.; Rice, K.C.; Maier, S.F.; Watkins, L.R. Exploring the neuroimmunopharmacology of opioids: An integrative review of mechanisms of central immune signaling and their implications for opioid analgesia. Pharmacol. Rev. 2011, 63, 772–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okuyama, E.; Umeyama, K.; Yamazaki, M.; Kinoshita, Y.; Yamamoto, Y. Usnic acid and diffractaic acid as analgesic and antipyretic components of Usnea diffracta. Planta Med. 1995, 61, 113–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingólfsdóttir, K. Usnic acid. Phytochemistry 2002, 61, 729–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lira, M.C.B.; Ferraz, M.S.; Silva, D.G.V.C.; Cortes, M.E.; Teixeira, K.I.; Caetano, N.P.; Sinisterra, R.D.; Ponchel, G.; Santos-Magalhães, N.S. Inclusion complex of usnic acid with b-cyclodextrin: Characterization and nanoencapsulation into liposomes. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 2009, 64, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francolini, I.; Taresco, V.; Crisante, F.; Martinelli, A.; D’Ilario, L.; Piozzi, A. Water soluble usnic acid-polyacrylamide complexes with enhanced antimicrobial activity against Staphylococcus epidermidis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 7356–7369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, N.P.S.; Nascimento, S.C.; Wanderley, M.S.; Pontes-Filho, N.T.; Silva, J.F.; Castro, C.M.; Pereira, E.C.; Silva, N.H.; Honda, N.K.; Santos-Magalhães, N.S. Nanoencapsulation of usnic acid: An attempt to improve antitumour activity and reduce hepatotoxicity. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2006, 64, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro-Costa, R.M.; Alves, A.J.; Santos, N.P.; Nascimento, S.C.; Gonçalves, E.C.; Silva, N.H.; Honda, N.K.; Santos-Magalhães, N.S. In vitro and in vivo properties of usnic acid encapsulated into PLGA-microspheres. J. Microencapsul. 2004, 21, 371–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francolini, I.; Norris, P.; Piozzi, A.; Donelli, G.; Stoodley, P. Usnic acid, a natural antimicrobial agent able to inhibit bacterial biofilm formation on polymer surfaces. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2004, 48, 4360–4365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labib, M.E.; Brumlik, C.J.; Stoodley, P.; Dukhin, S.S.; Davidson, T.; Tabani, Y. The long-term release of antibiotics from monolithic nonporous polymer implants for use as tympanostomy tubes. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng. Asp. 2010, 5, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siqueira-Moura, M.P.; Lira, M.C.B.; Santos-Magalhães, N.S. Validação de método analítico espectrofotométrico UV para determinação de ácido úsnico em lipossomas. Rev. Bras. Cienc. Farm. 2008, 44, 621–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göke, K.; Lorenz, T.; Repanas, A.; Schneider, F.; Steiner, D.; Baumann, K.; Bunjes, H.; Dietzel, A.; Finke, J.H.; Glasmacher, B.; et al. Novel strategies for the formulation and processing of poorly watersoluble drugs. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2018, 126, 40–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poecheim, J.; Graeser, K.A.; Hoernschemeyer, J.; Becker, G.; Storch, K.; Printz, M. Development of stable liquid formulations for oligonucleotides. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2018, 129, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanolla, D.; Perissutti, B.; Passerini, N.; Chierotti, M.R.; Hasa, D.; Voinovich, D.; Gigli, L.; Demitri, N.; Geremia, S.; Keiser, J.; et al. A new soluble and bioactive polymorph of praziquantel. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2018, 127, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Bae, W.K.; Lee, J.Y.; Choi, Y.J.; Lee, K.H.; Park, M.S.; Yu, Y.H.; Park, S.Y.; Zhou, R.; Taş, İ.; et al. Potassium usnate, a water-soluble usnic acid salt, shows enhanced bioavailability and inhibits invasion and metastasis in colorectal cancer. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, M.C.B.; Silva, M.C.; Silva, L.R.S.; Lima, V.L.M.; Pereira, E.C.; Falcão, E.P.; Melo, A.M.M.A.; Silva, N.H. Usnic acid potassium salt: An alternative for the control of Biomphalaria glabrata (Say, 1818). PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e111102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, H.D.A.; Melo, A.M.M.A.; Siqueira, W.N.; Martins, M.C.B.; Aires, A.L.; Albuquerque, M.C.P.A.; Silva, N.H.; Lima, V.L.M. Potassium usnate toxicity against embryonic stages of the snail Biomphalaria glabrata and Schistosoma mansoni Cercariae. Acta Trop. 2018, 188, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araújo, H.D.A.; Silva, L.R.S.; Siqueira, W.N.; Fonseca, C.S.M.; Silva, N.H.; Melo, A.M.M.A.; Martins, M.C.B.; Lima, V.L.M. Toxicity of usnic acid from Cladonia substellata (Lichen) to embryos and adults of Biomphalaria glabrata. Acta Trop. 2018, 179, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, H.D.A.; Aires, A.L.; Soares, C.L.R.; Brito, T.G.S.; Nascimento, W.M.; Martins, M.C.B.; Silva, T.G.; Brayner, F.A.; Alves, L.C.; Silva, N.H.; et al. Usnic acid potassium salt from Cladonia substellata (Lichen): Synthesis, cytotoxicity and in vitro anthelmintic activity and ultrastructural analysis against adult worms of Schistosoma mansoni. Acta Trop. 2018, 192, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huneck, S.; Yoshimura, I. Identification of Lichen Substances, 1st ed.; Springer: Heidelberg/Berlin, Germany, 1996; pp. 1–449. [Google Scholar]
- Ribár, B.; Kapor, A.; Argay, G.; Engel, P.; Djarmati, Z.; Jankov, R.M. Crystal structure of usnic acid sodium salt 2 1/2 hydrate. J. Cryst. Spectr. Res. 1993, 23, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Montgomery, J.A.; Vreven, T.; Kudin, K.N.; Burant, J.C.; et al. Gaussian 03, Revision c.02; Gaussian Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Buemi, G.; Zuccarello, F. Molecular conformations, hydrogen-bond strengths and electronic structure of usnic acid: An AM1 and CNDO/S study. J. Mol. Struc. Theochem. 1990, 209, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galasso, V. Probing the molecular and electronic structure of the lichen metabolite usnic acid: A DFT study. Chem. Phys. 2010, 374, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouasla, A.; Bouasla, I. Ethnobotanical survey of medicinal plants in northeastern of Algeria. Phytomedicine 2017, 36, 68–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cechinel-Filho, V.; Yunes, R.A. Estratégias para a obtenção de compostos farmacologicamente ativos a partir de plantas medicinais: Conceitos sobre modificação estrutural para otimização da atividade. Quím. Nova. 1998, 21, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.; Lim, C.P.; Akowuah, G.A.; Ismail, N.N.; Hashim, M.A.; Hor, S.Y.; Ang, L.F.; Yam, M.F. Safety assessment of standardised methanol extract of Cinnamomum burmannii. Phytomedicine 2013, 20, 1124–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, D.K.; Souza, I.A.; Oliveira, A.F.; Barbosa, M.O.; Santana, M.A.; Pereira Júnior, D.F.; Lira, E.C.; Vieira, J.R. Phytochemical screening and acute toxicity of aqueous extract of leaves of Conocarpus erectus Linnaeus in swiss albino mice. An. Acad. Bras. Cienc. 2016, 88, 1431–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigma-Aldrich, Safety Data Sheet. Available online: https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/MSDS/MSDS/DisplayMSDSPage.do?country=BR&language=pt&productNumber=329967&brand=ALDRICH&PageToGoToURL=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.sigmaaldrich.com%2Fcatalog%2Fsearch%3Fterm%3D7562-610%26interface%3DCAS%2520No.%26N%3D0%26mode%3Dpartialmax%26lang%3Dpt%26region%3DBR%26focus%3Dproduct (accessed on 8 May 2018).
- OECD—Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development. Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals, OECD 423. Acute Oral Toxicity-Acute Toxic Class Method; Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development: Paris, French, 2001; pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Han, D.; Matsumaru, K.; Rettori, D.; Kaplowitz, N. Usnic acid-induced necrosis of cultured mouse hepatocytes: Inhibition of mitochondrial function and oxidative stress. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2004, 67, 439–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pramyothin, P.; Janthasoot, W.; Pongnimitprasert, N.; Phrukudom, S.; Ruangrungsi, N. Hepatotoxic effect of (+)usnic acid from Usnea siamensis Wainio in rats, isolated rat hepatocytes and isolated rat liver mitochondria. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2004, 90, 381–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, A.; Lee, T.; Moland, C.L.; Branham, W.S.; Fuscoe, J.C.; Leakey, J.E.A.; Allaben, W.T.; Lewis, S.M.; Ali, A.A.; Desai, V.G. Effect of (+)-usnic acid on mitochondrial functions as measured by mitochondria-specific oligonucleotide microarray in liver of B6C3F1 mice. Mitochondrion 2009, 9, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neff, G.W.; Reddy, K.R.; Durazo, F.A.; Meyer, D.; Marrero, R.; Kaplowitz, N. Severe hepatotoxicity associated with the use of weight loss diet supplements containing ma huang or usnic acid. J. Hepatol. 2004, 41, 1061–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez, W.; Maple, J.T.; Burgart, L.J.; Kamath, P.S. Severe hepatotoxicity associated with use of a dietary supplement containing usnic acid. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2006, 81, 541–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moura, M.R.L.; Reyes, F.G. Interação fármaco-nutriente: Uma revisão. Rev. Nutr. 2002, 15, 223–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radulovic, L.L.; Cilla, D.D.; Posvar, E.L.; Sedman, A.J.; Whitfield, L.R. Effect of food on the bioavailability of atorvastatin, an HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1995, 35, 990–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavelle, J.; Follansbee, S.; Trapnell, C.B.; Buhles, W.C.; Griffy, K.G.; Jung, D.; Dorr, A.; Connor, J. Effect of food on the relative bioavailability of oral ganciclovir. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1996, 36, 238–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, A.M.; Nascimento, M.F.; Ferreira, M.R.A.; Moura, D.F.; Souza, T.G.S.; Silva, G.C.; Ramos, E.H.S.; Paiva, P.M.G.; Medeiros, P.L.; Silva, T.G.; et al. Evaluation of acute toxicity, genotoxicity and inhibitory effect on acute inflammation of an ethanol extract of Morus alba L. (Moraceae) in mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 194, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, A.M.; Mesquista, M.S.; Silva, G.C.; Silva, E.O.; Medeiros, P.L.; Paiva, P.M.G.; Souza, I.A.; Napoleão, T.H. Evaluation of toxicity and antimicrobial activity of an ethanolic extract from leaves of Morus alba L. (Moraceae). Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2015, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, A.M.; Freire, M.O.L.; Silva, W.A.V.; Ferreira, M.R.A.; Paiva, P.M.G.; Soares, L.A.L.; Medeiros, P.L.; Carvalho, B.M.; Napoleão, T.H. Saline extract of Pilosocereus gounellei stem has antinociceptive effect in mice without showing acute toxicity and altering motor coordination. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2018, 95, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Abbas, A.K.; Fausto, N.; Aster, J.C. Robbins E Cotran, Bases Patológicas Das Doenças, 8th ed.; Elsevier: Rio de Janeiro, Brasil, 2010; pp. 1–1479. [Google Scholar]
- Le Bars, D.; Gozariu, M.; Cadden, S.W. Animal models of nociception. Pharmacol. Rev. 2001, 53, 597–652. [Google Scholar]
- Rocha, A.P.; Kraychete, D.C.; Lemonica, L.; Carvalho, L.R.; Barros, G.A.; Garcia, J.B.; Sakata, R.K. Pain: Current aspects on peripheral and central sensitization. Rev. Bras. Anestesiol. 2007, 57, 94–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewanowitsch, T.; Miller, J.H.; Irvine, R.J. Reversal of morphine, methadone and heroin induced effects in mice by naloxone methiodide. Life Sci. 2006, 78, 682–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bershad, A.K.; Miller, M.A.; Norman, G.J.; Wit, H. Effects of opioid- and non-opioid analgesics on responses to psychosocial stress in humans. Horm. Behav. 2018, 102, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNamara, C.R.; Mandel-Brehm, J.; Bautista, D.M.; Siemens, J.; Deranian, K.L.; Zhao, M.; Hayward, N.J.; Chong, J.A.; Julius, D.; Moran, M.M.; et al. TRPA1 mediates formalin-induced pain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 13525–13530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, C.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Li, S.; Qiao, Y. Identification of natural compound carnosol as a novel TRPA1 receptor agonist. Molecules 2014, 19, 18733–18746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhai, C.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, L.; Li, S.; Qiao, Y. Cardamonin, a novel antagonist of hTRPA1 cation channel, reveals therapeutic mechanism of pathological pain. Molecules 2016, 21, 1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marenich, A.V.; Cramer, C.J.; Truhlar, D.G. Universal solvation model based on solute electron density and on a continuum model of the solvent defined by the bulk dielectric constant and atomic surface tensions. J. Phys. Chem. B 2009, 113, 6378–6396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breneman, C.M.; Wiberg, K.B. Determining atom-centered monopoles from molecular electrostatic potentials. The need for high sampling density in formamide conformational analysis. J. Comput. Chem. 1990, 11, 361–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malone, M.H. Pharmacological Approaches to Natural Product, Screening and Evaluation. New Natural Products and Plant Drugs with Pharmacological Biological or Therapeutical Activity, 1st ed.; Wagner, H., Wolf, P., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1977; pp. 23–53. [Google Scholar]
- Kamarudin, N.; Hisamuddin, N.; Ong, H.M.; Azmi, A.F.A.; Leong, S.W.; Abas, F.; Sulaiman, M.R.; Mossadeq, W.M.S. Analgesic effect of 5-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-3-hydroxy-1-(2-hydroxyphenyl)penta-2,4-dien-1-one in experimental animal models of nociception. Molecules 2018, 23, 2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ping, C.P.; Mohamad, T.A.S.T.; Akhtar, M.N.; Perimal, E.K.; Akira, A.; Israf Ali, D.A.I.; Sulaiman, M.R. Antinociceptive effects of cardamonin in mice: Possible involvement of TRPV1, glutamate, and opioid receptors. Molecules 2018, 23, 2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunskaar, S.; Hole, K. The formalin test in mice: Dissociation between inflammatory and non-inflammatory pain. Pain 1987, 30, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |

| Parameters | Treatments PS-UA (mg/kg) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 500 | 1000 | 2000 | |
| Stimulants | ||||
| Increased respiratory frequency | - | + | + | +++ |
| Piloerection | - | ++ | ++ | ++ |
| Stereotyped movement | - | - | + | ++ |
| Fine tremors | - | - | - | + |
| Lifting upper train | - | + | + | + |
| Depressant | ||||
| Prostration | - | +++ | +++ | +++ |
| Lowering hind quarters | - | - | - | ++ |
| Others | ||||
| Photophobia | - | - | - | + |
| Spasms | - | - | - | + |
| Fecal excretion | - | - | + | + |
| Abdominal distension | - | - | - | ++ |
| Change: Depression x Shake | ||||
| Death | - | - | - | ++ |
| Parameters | Treatments PS-UA (mg/kg) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 500 | 1000 | 2000 | |
| Water consumed (mL) | 38.75 ± 1.49 | 34.10 ± 2.29 | 27.30 ± 7.09 a | 19.40 ± 6.11 a |
| Food consumed (g) | 33.70 ± 1.29 | 30.20 ± 3.56 | 22.85 ± 3.40 a | 15.95 ± 7.59 a |
| Weight gain (g) | 32.40 ± 1.57 | 31.66 ± 1.50 | 31.60 ± 2.15 | 31.88 ± 1.84 |
| Parameters | Treatments PS-UA (mg/Kg) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 500 | 1000 | 2000 | |
| Erythrocytes (106/mm3) | 8.81 ± 0.81 | 8.88 ± 0.26 | 8.90 ± 0.41 | 9.16 ± 0.72 |
| Hematocrit (%) | 45.75 ± 3.97 | 45.55 ± 1.12 | 45.65 ± 2.65 | 47.05 ± 3.74 |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 15.81 ± 1.40 | 15.53 ± 0.36 | 15.37 ± 0.71 | 15.76 ± 1.01 |
| MCV (fL) | 51.90 ± 2.23 | 51.25 ± 1.46 | 52.10 ± 0.82 | 51.28 ± 1.89 |
| MCH (pg) | 17.90 ± 0.38 | 17.35 ± 0.54 | 17.23 ± 0.17 | 17.15 ± 0.41 |
| MCHC (%) | 34.25 ± 0.95 | 33.25 ± 0.50 | 33.25 ± 0.50 | 33.00 ± 0.81 |
| Leukocytes (103/mm3) | 2.21 ± 0.49 | 2.99 ± 0.52 | 3.65 ± 0.63 a | 4.52 ± 0.96 b |
| Segmented (%) | 40.75 ± 9.35 | 66.50 ± 21.75 | 75.75 ± 12.61a | 74.25 ± 8.53 a |
| Lymphocytes (%) | 21.03 ± 8.41 | 26.70 ± 4.67 | 28.65 ± 8.93 | 20.25 ± 2.14 |
| Monocytes (%) | 14.33 ± 4.93 | 12.33 ± 4.04 | 16.67 ± 2.88 | 14.83 ± 2.46 |
| Parameter | Treatments PS-UA (mg/kg) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 500 | 1000 | 2000 | |
| Albumin (g/dL) | 2.02 ± 0.28 | 1.90 ± 0.19 | 1.75 ± 0.09 | 1.80 ± 0.18 |
| ALT (U/L) | 39.46 ± 2.94 | 63.39 ± 20.7 | 86.78 ± 7.74 b | 207.6 ± 25.00 c |
| AST (U/L) | 115.8 ± 6.03 | 143.3 ± 22.5 | 229.44 ± 45.1 a | 306.4 ± 19.4 c |
| Total protein (g/dL) | 5.22 ± 0.05 | 5.27 ± 0.13 | 4.85 ± 0.24 b | 4.87 ± 0.12 b |
| Alkaline phosphatase (IU/L) | 15.04 ± 2.65 | 19.80 ± 4.55 | 31.00 ± 9.39 b | 33.65 ± 6.74 c |
| Urea (mg/dL) | 45.62 ± 2.54 | 46.56 ± 2.17 | 47.65 ± 1.27 | 46.43 ± 2.25 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 041.20 ± 0.06 | 041.60 ± 0.06 | 053.40 ± 0.02 | 064.60 ± 0.12 c |
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL) | 90.40 ± 11.95 | 92.60 ± 15.99 | 62.20 ± 14.45 b | 60.50 ± 3.10 b |
| Triglycerides (mg/dL) | 133.4 ± 27.36 | 112.8 ± 11.82 | 54.50 ± 7.55 c | 51.75 ± 8.13 c |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Douglas A. Araújo, H.; G. Silva Júnior, J.; R. Saturnino Oliveira, J.; Helena M. L. Ribeiro, M.; C. Barroso Martins, M.; A. Cavalcanti Bezerra, M.; Lima Aires, A.; C. P. Azevedo Albuquerque, M.; R. Melo-Júnior, M.; T. Pontes Filho, N.; et al. Usnic Acid Potassium Salt: Evaluation of the Acute Toxicity and Antinociceptive Effect in Murine Model. Molecules 2019, 24, 2042. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24112042
Douglas A. Araújo H, G. Silva Júnior J, R. Saturnino Oliveira J, Helena M. L. Ribeiro M, C. Barroso Martins M, A. Cavalcanti Bezerra M, Lima Aires A, C. P. Azevedo Albuquerque M, R. Melo-Júnior M, T. Pontes Filho N, et al. Usnic Acid Potassium Salt: Evaluation of the Acute Toxicity and Antinociceptive Effect in Murine Model. Molecules. 2019; 24(11):2042. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24112042
Chicago/Turabian StyleDouglas A. Araújo, Hallysson, José G. Silva Júnior, João R. Saturnino Oliveira, Maria Helena M. L. Ribeiro, Mônica C. Barroso Martins, Marcos A. Cavalcanti Bezerra, André Lima Aires, Mônica C. P. Azevedo Albuquerque, Mário R. Melo-Júnior, Nicodemos T. Pontes Filho, and et al. 2019. "Usnic Acid Potassium Salt: Evaluation of the Acute Toxicity and Antinociceptive Effect in Murine Model" Molecules 24, no. 11: 2042. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24112042
APA StyleDouglas A. Araújo, H., G. Silva Júnior, J., R. Saturnino Oliveira, J., Helena M. L. Ribeiro, M., C. Barroso Martins, M., A. Cavalcanti Bezerra, M., Lima Aires, A., C. P. Azevedo Albuquerque, M., R. Melo-Júnior, M., T. Pontes Filho, N., C. Pereira, E., J. Raposo Silva, D., V. dos Anjos, J., Peter S. Falcão, E., H. Silva, N., & L. Menezes Lima, V. (2019). Usnic Acid Potassium Salt: Evaluation of the Acute Toxicity and Antinociceptive Effect in Murine Model. Molecules, 24(11), 2042. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24112042