Analysis of Selected Phenolic Compounds in Organic, Pesticide-Free, Conventional Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Using LC-ESI-MS/MS
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
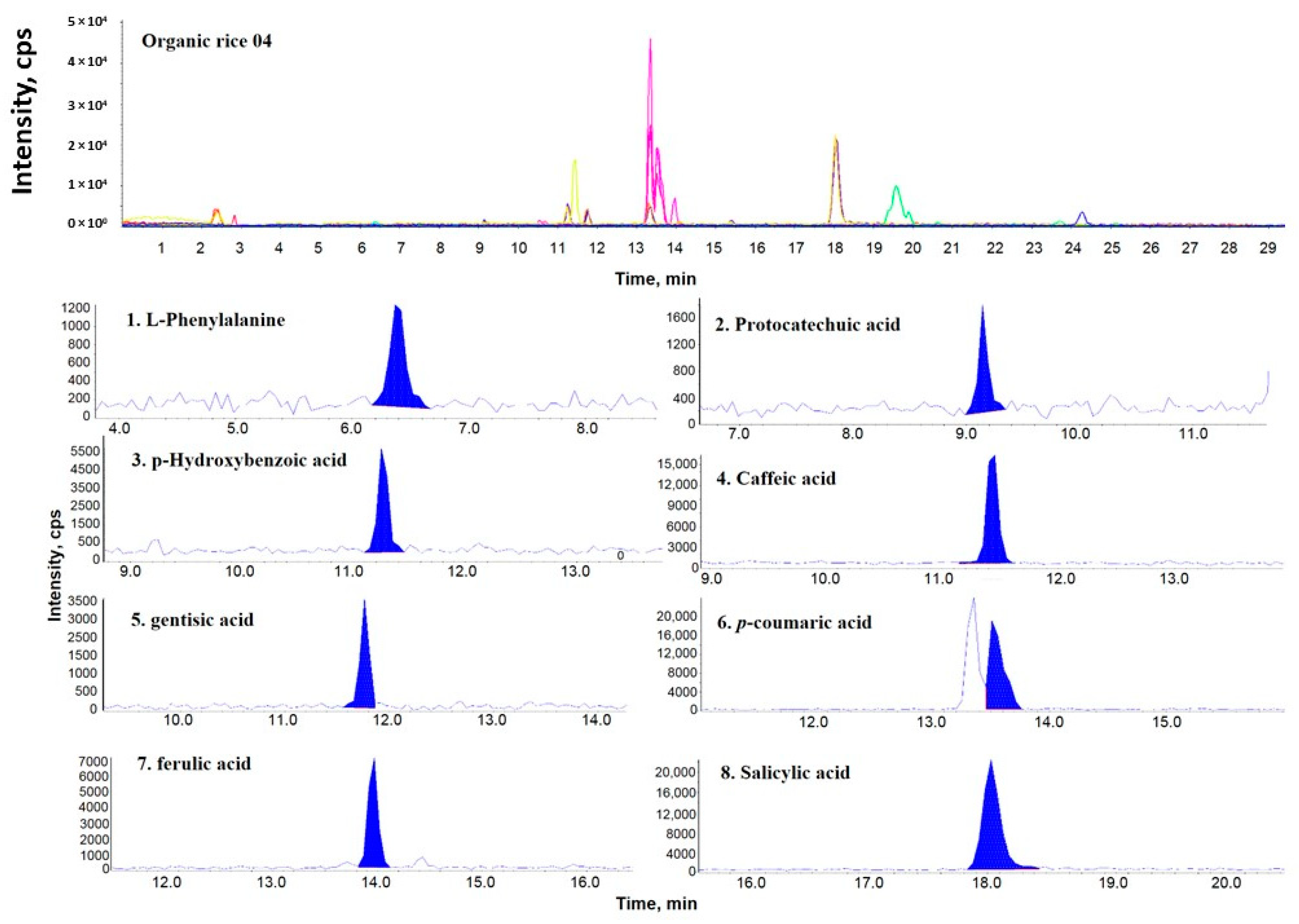
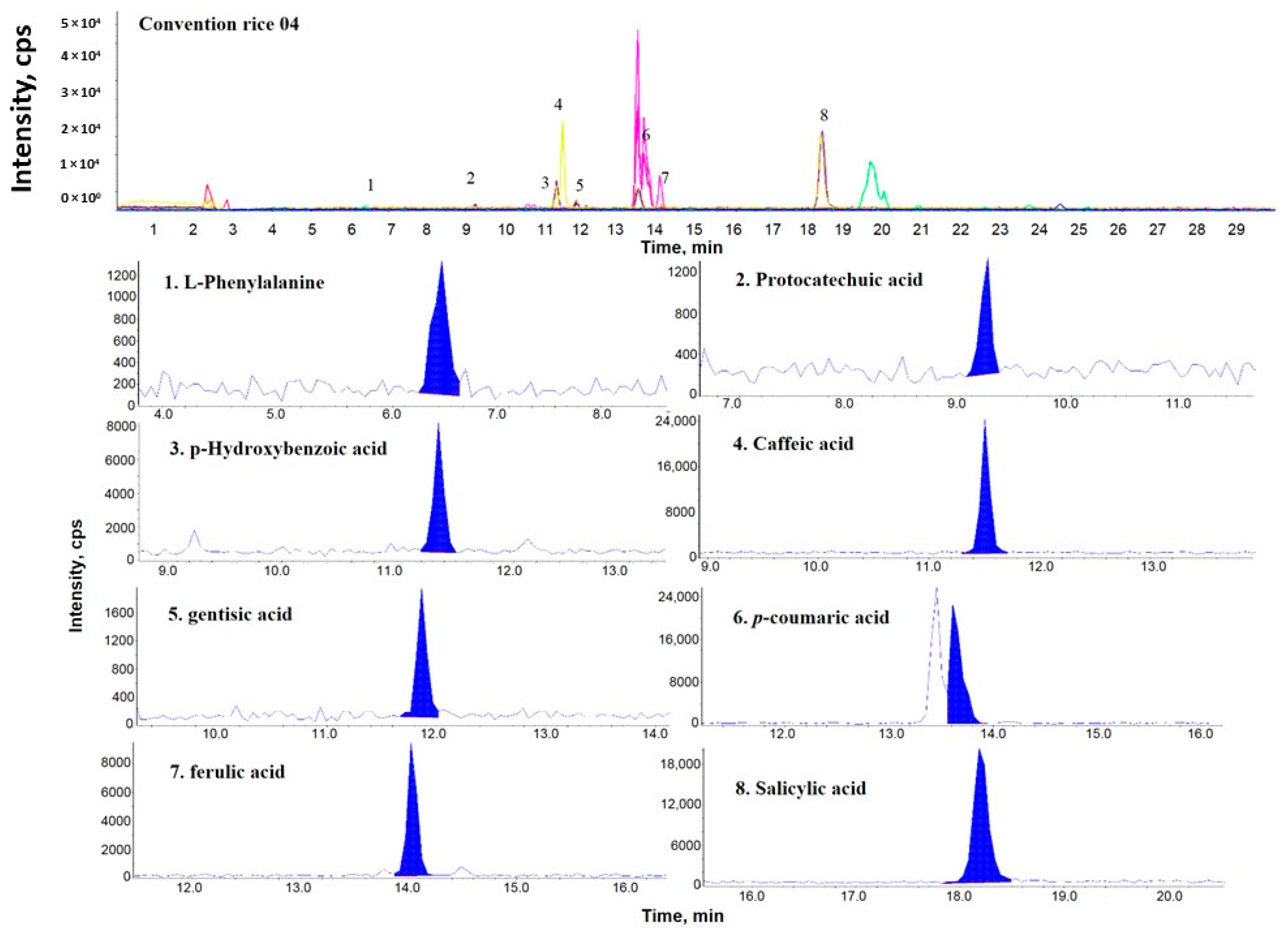
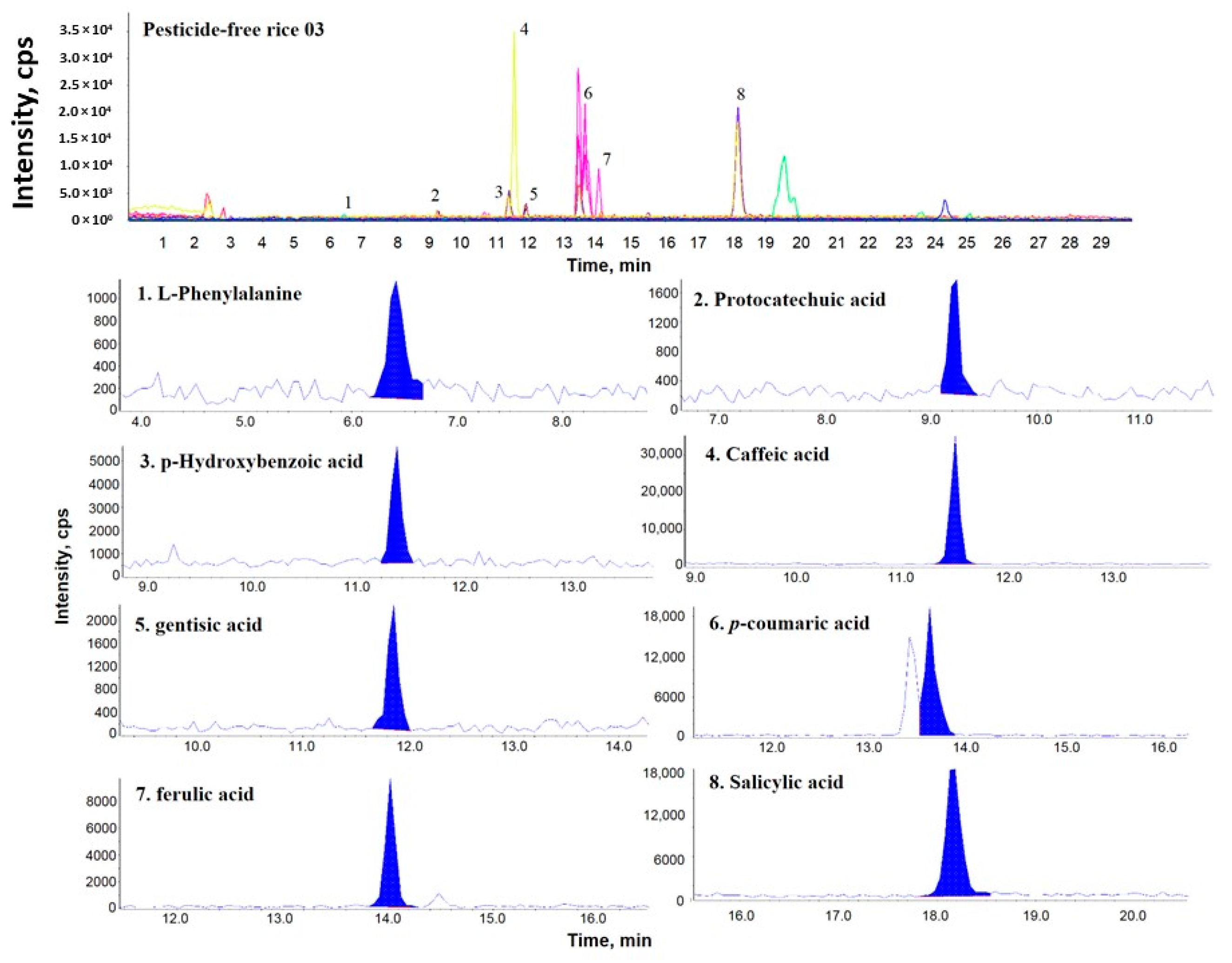
2.1. Comparison of the Phenolic Components Present in OR, PFR, and FR
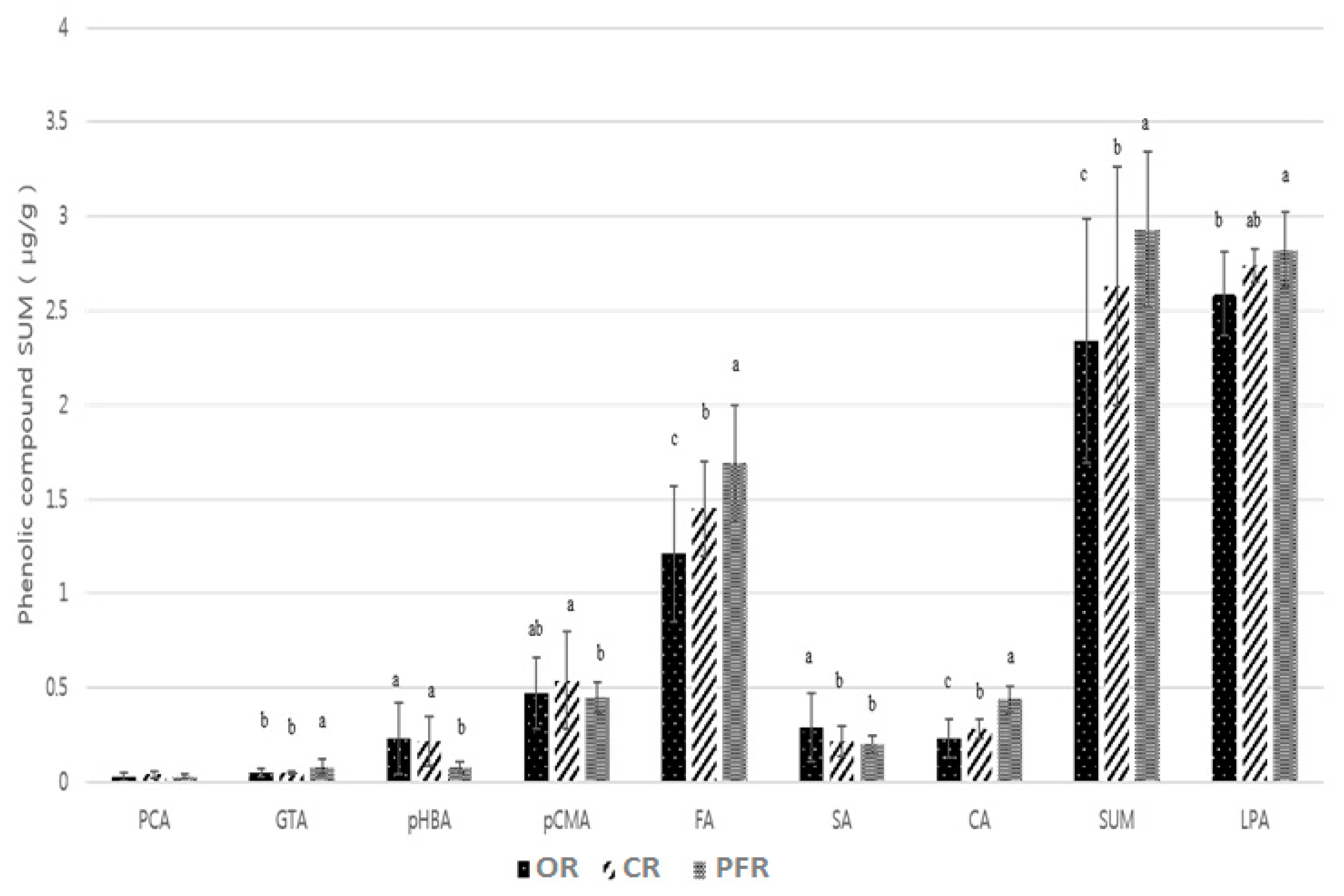
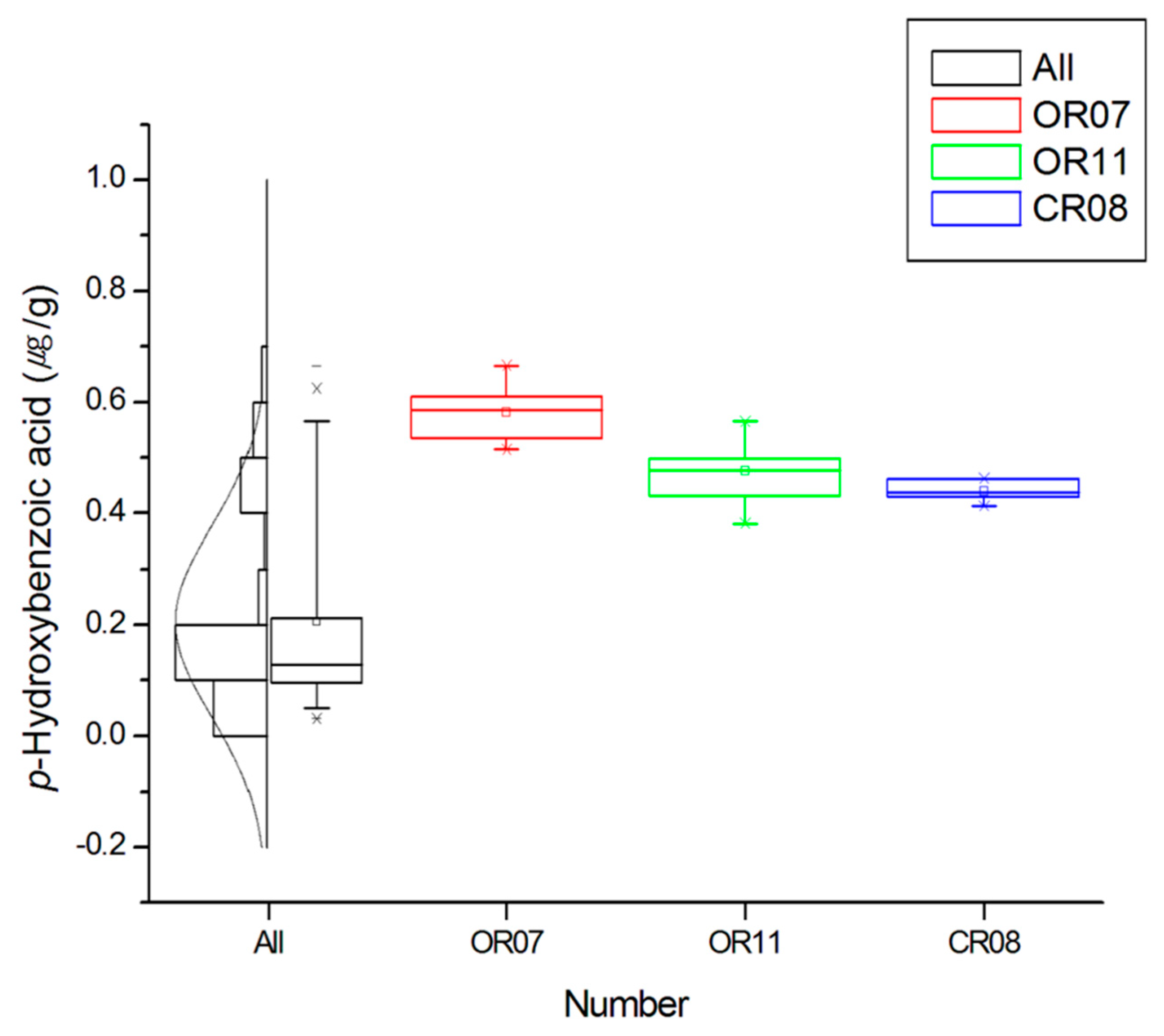
2.2. Comparison of the Phenolic Contents by Rice Samples
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Rice Samples and Preparation
3.2. Chemicals and Reagents
3.3. Extraction of Phenolic Compounds
3.4. Analysis of the Phenolic Compounds
3.5. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sabanis, D.; Tzia, C. Effect of rice, corn and soy flour addition on characteristics of bread produced from different wheat cultivars. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2009, 2, 68–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlachos, A.; Arvanitoyannis, I.S. A review of rice authenticity/adulteration methods and results. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2008, 48, 553–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartmann, T. From waste products to ecochemicals: Fifty years research of plant secondary metabolism. Phytochemistry 2007, 68, 2831–2846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oksana, S.; Marian, B.; Mahendra, R.; Bo, S.H. Plant phenolic compounds for food, pharmaceutical and cosmetiсs production. J. Med. Plants Res. 2012, 6, 2526–2539. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, G.F.; Xu, X.R.; Zhang, Y.; Li, D.; Gan, R.Y.; Li, H.B. Phenolic compounds and bioactivities of pigmented rice. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2013, 53, 296–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vichapong, J.; Sookserm, M.; Srijesdaruk, V.; Swatsitang, P.; Srijaranai, S. High performance liquid chromatographic analysis of phenolic compounds and their antioxidant activities in rice varieties. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 43, 1325–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melini, V.; Acquistucci, R. Health-promoting compounds in pigmented Thai and wild rice. Foods 2017, 6, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves, G.H.; Paraginski, R.T.; Lamas, N.S.; Hoffmann, J.F.; Vanier, N.L.; de Oliveira, M. Effects of organic and conventional cropping systems on technological properties and phenolic compounds of freshly harvested and stored rice. J. Food Sci. 2017, 82, 2276–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Liu, Q.; Beta, T. Antioxidant properties of commercial wild rice and analysis of soluble and insoluble phenolic acids. Food Chem. 2010, 121, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, R.C.; Miller, N.; Paganga, G. Antioxidant properties of phenolic compounds. Trends Plant Sci. 1997, 2, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uttara, B.; Singh, A.S.; Zamboni, P.; Mahajan, R.T. Oxidative stress and neurodegenerative diseases: A review of upstream and downstream antioxidant therapeutic options. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2009, 7, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pham-Huy, L.A.; He, H.; Pham-Huy, C. Free Radicals, Antioxidants in Disease and Health. Int. J. Biomed. Sci. 2008, 4, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Randhir, R.; Shetty, K. Developmental stimulation of total phenolics and related antioxidant activity in light-and dark-germinated corn by natural elicitors. Process Biochem. 2005, 40, 1721–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Zhao, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Guo, R.; Gan, S.S.; Liu, C.J.; Zhang, K. S5H/DMR6 encodes a salicylic acid 5-hydroxylase that fine-tunes salicylic acid homeostasis. Plant Physiol. 2017, 175, 1082–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogt, T. Phenylpropanoid Biosynthesis. Mol. Plant 2010, 3, 2–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixon, R.A.; Paiva, N.L. Stress-induced phenylpropanoid metabolism. Plant Cell 1995, 7, 1085–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leon, J.; Yalpani, N.; Raskin, I.; Lawton, M.A. Induction of benzoic acid 2-hydroxylase in virus-inoculated tobacco. Plant Physiol. 1993, 103, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, R.A.; Achnine, L.; Kota, P.; Liu, C.J.; Reddy, M.; Wang, L. The phenylpropanoid pathway and plant defence-a genomics perspective. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2002, 3, 371–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, B.P.; Benbrook, C.M.; III, E.G.; Benbrook, K.L. Pesticide residues in conventional, integrated pest management (IPM)-grown and organic foods: Insights from three US data sets. Food Addit. Contam. 2002, 19, 427–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.J.; Choi, D.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, S.M.; Lee, Y.H.; Lee, B.M.; Kim, T.W. Long-term changes in soil chemical properties in organic arable farming systems in Korea. Korean J. Soil Sci. Fertil. 2004, 37, 228–234. [Google Scholar]
- Dangour, A.D.; Lock, K.; Hayter, A.; Aikenhead, A.; Allen, E.; Uauy, R. Nutrition-related health effects of organic foods: A systematic review. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 92, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harukaze, A.; Murata, M.; Homma, S. Analyses of free and bound phenolics in rice. Food Sci. Technol. Res. 1999, 5, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butsat, S.; Siriamornpun, S. Antioxidant capacities and phenolic compounds of the husk, bran and endosperm of Thai rice. Food Chem. 2010, 119, 606–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camm, E.L.; Towers, G.N. Phenylalanine ammonia lyase. Phytochemistry 1973, 12, 961–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morreel, K.; Ralph, J.; Lu, F.; Goeminne, G.; Busson, R.; Herdewijn, P.; Goeman, J.L.; Eycken, V.D.J.; Boerjan, W.; Messens, E. Phenolic profiling of caffeic acid O-methyltransferase-deficient poplar reveals novel benzodioxane oligolignols. Plant Physiol. 2004, 136, 4023–4036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chalabaev, S.; Turlin, E.; Bay, S.; Ganneau, C.; Brito-Fravallo, E.; Charles, J.F.; Danchin, A.; Biville, F. Cinnamic acid, an autoinducer of its own biosynthesis, is processed via hca enzymes in Photorhabdus luminescens. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 1717–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Widhalm, J.R.; Dudareva, N. A familiar ring to it: Biosynthesis of plant benzoic acids. Mol. Plant 2015, 8, 83–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anantharaju, P.G.; Gowda, P.C.; Vimalambike, M.G.; Madhunapantula, S.V. An overview on the role of dietary phenolics for the treatment of cancers. Nutr. J. 2016, 15, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas-Tah, A.; Martínez, L.M.; Hernández-Chávez, G.; Rocha, M.; Martínez, A.; Bolívar, F.; Gosset, G. Production of cinnamic and p-hydroxycinnamic acid from sugar mixtures with engineered Escherichia coli. Microb. Cell Fact. 2015, 14, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Kawai, S.; Mori, A.; Shiokawa, T.; Kajita, S.; Katayama, Y.; Morohoshi, N. Isolation and analysis of cinnamic acid 4-Hydroxylase homologous genes from a hybrid aspen, Populus kitakamiensist. Biosci. Biotech. Biochem. 1996, 60, 1586–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.; Nakamura, K.; Kayahara, H. Analysis of phenolic compounds in white rice, brown rice, and germinated brown rice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 4808–4813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riahi, A.; Hdider, C. Bioactive compounds and antioxidant activity of organically grown tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) cultivars as affected by fertilization. Sci. Hortic. 2013, 151, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.W.; Zhang, R.F.; Zhang, F.X.; Liu, R.H. Phenolic profiles and antioxidant activity of black rice bran of different commercially available varieties. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 7580–7587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, I.M.; Seo, S.H.; Ahn, J.K.; Kim, S.H. Effect of processing, fermentation, and aging treatment to content and profile of phenolic compounds in soybean seed, soy curd and soy paste. Food Chem. 2011, 127, 960–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.J.; Murphy, P.A. Mass balance study of isoflavones during soybean processing. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1996, 44, 2377–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabakaran, M.; Lee, J.-H.; Ahmad, A.; Kim, S.-H.; Woo, K.-S.; Kim, M.-J.; Chung, I.-M. Effect of storage time and temperature on phenolic compounds of soybean (Glycine max L.) Flour. Molecules 2018, 23, 2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: All samples of the compounds measured in this study are available from the authors. |

| Sample Name | PCA | GTA | pHBA | SA | LPA | pCMA | CA | FA | Distribution Sum of Phenolic Compound |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR 01 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | 0.24 ± 0.03 | ND | 0.26 ± 0.08 | 0.14 ± 0.01 | 0.69 ± 0.10 | 1.33 ± 0.19 |
| OR 02 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | 0.13 ± 0.01 | ND | 0.27 ± 0.04 | 0.19 ± 0.01 | 0.61 ± 0.02 | 1.20 ± 0.04 |
| OR 03 | 0.02 ± 0.02 | 0.07 ± 0.00 | 0.09 ± 0.02 | 0.15 ± 0.01 | <LOD | 0.53 ± 0.03 | 0.18 ± 0.00 | 1.17 ± 0.04 | 2.21 ± 0.05 |
| OR 04 | 0.03 ± 0.01 | 0.09 ± 0.01 | 0.10 ± 0.02 | 0.22 ± 0.04 | 2.59 ± 0.22 | 0.42 ± 0.05 | 0.25 ± 0.01 | 1.26 ± 0.16 | 2.35 ± 0.28 |
| OR 05 | 0.03 ± 0.03 | 0.03 ± 0.00 | 0.13 ± 0.02 | 0.18 ± 0.01 | <LOD | 0.51 ± 0.07 | 0.26 ± 0.01 | 1.36 ± 0.08 | 2.50 ± 0.13 |
| OR 06 | 0.02 ± 0.01 | 0.03 ± 0.00 | <LOD | 0.24 ± 0.01 | <LOD | 0.43 ± 0.04 | 0.39 ± 0.01 | 1.76 ± 0.09 | 2.86 ± 0.10 |
| OR 07 | 0.03 ± 0.01 | <LOD | 0.58 ± 0.05 | 0.79 ± 0.03 | <LOD | 1.02 ± 0.04 | 0.07 ± 0.01 | 1.10 ± 0.08 | 3.59 ± 0.10 |
| OR 08 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | 0.22 ± 0.02 | ND | 0.31 ± 0.03 | 0.13 ± 0.01 | 1.16 ± 0.13 | 1.83 ± 0.15 |
| OR 09 | <LOD | 0.04 ± 0.00 | 0.18 ± 0.03 | 0.23 ± 0.01 | <LOD | 0.40 ± 0.03 | 0.12 ± 0.01 | 1.11 ± 0.09 | 2.08 ± 0.10 |
| OR 10 | 0.05 ± 0.01 | 0.04 ± 0.01 | 0.09 ± 0.01 | 0.23 ± 0.01 | ND | 0.47 ± 0.03 | 0.34 ± 0.02 | 1.46 ± 0.10 | 2.68 ± 0.09 |
| OR 11 | <LOD | <LOD | 0.48 ± 0.06 | 0.55 ± 0.04 | ND | 0.47 ± 0.05 | <LOD | 0.85 ± 0.10 | 2.35 ± 0.23 |
| OR 12 | 0.06 ± 0.02 | <LOD | <LOD | 0.32 ± 0.04 | ND | 0.52 ± 0.07 | 0.36 ± 0.03 | 1.78 ± 0.21 | 3.04 ± 0.30 |
| OR 13 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | 0.24 ± 0.02 | ND | 0.42 ± 0.04 | 0.32 ± 0.02 | 1.42 ± 0.11 | 2.40 ± 0.14 |
| Group Mean | 0.03 ± 0.02 | 0.05 ± 0.02 b | 0.23 ± 0.19 a | 0.29 ± 0.18 a | 2.59 ± 0.22 b | 0.47 ± 0.19 ab | 0.23 ± 0.1 c | 1.21 ± 0.36 c | 2.34 ± 0.65 c |
| CR 01 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | 0.23 ± 0.01 | ND | 0.40 ± 0.05 | 0.35 ± 0.01 | 1.44 ± 0.11 | 2.43 ± 0.16 |
| CR 02 | <LOD | 0.05 ± 0.01 | <LOD | 0.12 ± 0.00 | <LOD | 0.29 ± 0.06 | 0.23 ± 0.02 | 1.11 ± 0.11 | 1.79 ± 0.15 |
| CR 03 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | 0.21 ± 0.01 | ND | 0.36 ± 0.03 | 0.33 ± 0.01 | 1.52 ± 0.18 | 2.42 ± 0.20 |
| CR 04 | 0.03 ± 0.02 | 0.06 ± 0.01 | 0.19 ± 0.03 | 0.21 ± 0.01 | 2.74 ± 0.09 | 0.56 ± 0.08 | 0.30 ± 0.01 | 1.59 ± 0.12 | 2.94 ± 0.15 |
| CR 05 | <LOD | 0.05 ± 0.01 | 0.14 ± 0.01 | 0.16 ± 0.01 | <LOD | 0.68 ± 0.10 | 0.27 ± 0.01 | 1.66 ± 0.13 | 2.95 ± 0.21 |
| CR 06 | <LOD | <LOD | 0.12 ± 0.02 | 0.28 ± 0.01 | ND | 0.55 ± 0.03 | 0.31 ± 0.01 | 1.71 ± 0.11 | 2.97 ± 0.11 |
| CR 07 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | 0.15 ± 0.00 | <LOD | 0.40 ± 0.03 | 0.24 ± 0.02 | 1.07 ± 0.07 | 1.85 ± 0.07 |
| CR 08 | 0.05 ± 0.01 | 0.06 ± 0.00 | 0.44 ± 0.02 | 0.37 ± 0.04 | <LOD | 1.11 ± 0.09 | 0.22 ± 0.01 | 1.47 ± 0.10 | 3.73 ± 0.18 |
| Group Mean | 0.04 ± 0.02 | 0.05 ± 0.01 b | 0.22 ± 0.13 a | 0.22 ± 0.08 b | 2.74 ± 0.09 ab | 0.54 ± 0.26 a | 0.28 ± 0.05 b | 1.45 ± 0.25 b | 2.63 ± 0.63 b |
| PFR 01 | <LOD | 0.14 ± 0.01 | 0.06 ± 0.02 | 0.25 ± 0.01 | 2.91 ± 0.14 | 0.51 ± 0.05 | 0.40 ± 0.04 | 2.01 ± 0.19 | 3.38 ± 0.29 |
| PFR 02 | 0.04 ± 0.01 | 0.04 ± 0.01 | <LOD | 0.14 ± 0.01 | 2.87 ± 0.08 | 0.48 ± 0.03 | 0.41 ± 0.02 | 1.49 ± 0.09 | 2.6 ± 0.09 |
| PFR 03 | 0.02 ± 0.01 | 0.08 ± 0.01 | 0.09 ± 0.04 | 0.21 ± 0.02 | 2.67 ± 0.25 | 0.37 ± 0.06 | 0.49 ± 0.09 | 1.56 ± 0.30 | 2.82 ± 0.28 |
| Group Mean | 0.03 ± 0.01 | 0.08 ± 0.04 a | 0.08 ± 0.03 b | 0.2 ± 0.05 b | 2.82 ± 0.2 a | 0.45 ± 0.08 b | 0.44 ± 0.07 a | 1.69 ± 0.31 a | 2.93 ± 0.41 a |
| LSD | 0.0113 | 0.0125 | 0.0822 | 0.0551 | 0.1575 | 0.08 | 0.033 | 0.1263 | 0.2423 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Prabakaran, M.; Chung, I.-M.; Son, N.-Y.; Chi, H.-Y.; Kim, S.-Y.; Yang, Y.-J.; Kwon, C.; An, Y.-J.; Ahmad, A.; Kim, S.-H. Analysis of Selected Phenolic Compounds in Organic, Pesticide-Free, Conventional Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Using LC-ESI-MS/MS. Molecules 2019, 24, 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24010067
Prabakaran M, Chung I-M, Son N-Y, Chi H-Y, Kim S-Y, Yang Y-J, Kwon C, An Y-J, Ahmad A, Kim S-H. Analysis of Selected Phenolic Compounds in Organic, Pesticide-Free, Conventional Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Using LC-ESI-MS/MS. Molecules. 2019; 24(1):67. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24010067
Chicago/Turabian StylePrabakaran, Mayakrishnan, Ill-Min Chung, Na-Young Son, Hee-Youn Chi, So-Yeon Kim, Yu-Jin Yang, Chang Kwon, Yeon-Ju An, Ateeque Ahmad, and Seung-Hyun Kim. 2019. "Analysis of Selected Phenolic Compounds in Organic, Pesticide-Free, Conventional Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Using LC-ESI-MS/MS" Molecules 24, no. 1: 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24010067
APA StylePrabakaran, M., Chung, I.-M., Son, N.-Y., Chi, H.-Y., Kim, S.-Y., Yang, Y.-J., Kwon, C., An, Y.-J., Ahmad, A., & Kim, S.-H. (2019). Analysis of Selected Phenolic Compounds in Organic, Pesticide-Free, Conventional Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Using LC-ESI-MS/MS. Molecules, 24(1), 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24010067







