Abstract
In recent years, there has been increasing interest in dimeric molecules due to reports of their promising therapeutic value in the treatment of numerous diseases (such as cancer, HIV, Alzheimer’s and, malaria). Many reports in the literature have highlighted the ability of these molecules to interact not only with specific biologic receptors but also to induce a biological response that more than doubles the results of the corresponding monomeric counterpart. In this regard, flavonolignan dimers or simply bi-flavonolignans are an emerging class of dimeric compounds that unlike bi-flavonoids, which are very widespread in nature, consist of synthetic dimers of some flavonolignans isolated from the milk thistle Silybum marianum [L. Gaertn. (Asteraceae)]. This mini-review will discuss recent developments in the synthesis, characterization and antioxidant activity of new families of flavonolignan dimers, in light of emerging medicinal chemistry strategies.
1. Introduction
Flavonolignans are secondary metabolites present in a few plants (Asteraceae, Berberidaceae, Chenopodiaceae, Flacourtiaceae, Fabaceae, Poaceae, and the Scrophulariaceae species) commonly used in the human diet, of which consumption has increased considerably in recent years thanks to their beneficial biological activity [1]. Pelter and Haensel [2] first proposed the generic name "flavonolignan" for naturally occurring hybrid molecules that are biogenetically originated from ubiquitous flavonoids and monolignols (namely, p-coumaryl, coniferyl and, sinapyl alcohol) [3,4,5,6].
Flavonoid portions, the flavonolignans isolated from plants, may initially be divided into four types (Figure 1): flavanonol-, flavonol-, flavanone and flavone-type.
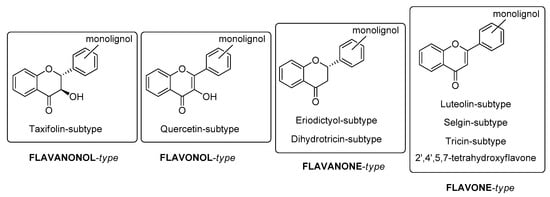
Figure 1.
Classification of naturally occurring flavonolignans.
Flavonolignans have a broad structural diversity as a consequence of the C-C or C-O linkage of the C6C3 unit (monolignol unit) to the flavonoid nucleus in different positions, affording dioxane, furan, cyclohexane rings or simple ether side chains. In general, these compounds contain several chiral centers, hence they usually occur in nature into stereoisomer forms. By 2016, over forty flavonolignans, containing eight different flavonoid counterparts, had been isolated from over twenty species of plants [1].
The main source of flavonolignans is the milk thistle Silybum marianum (L. Gaertn. (Asteraceae)). A crude extract of its seeds, industrially manufactured and named silymarin [7,8], contains several flavonolignans such as silibinin [9] (as pair stereoisomers silybin A and silybin B), [10], isosilybin A and isosilybin B, silychristin A, 2,3-dehydrosylibin (A and B) [11] and silydianin (Figure 2). S. marianum enjoyed a period of high esteem in folk medicine as a liver tonic [12]. Its extracts were used to improve liver function, protect against liver damage and accelerate the regeneration of damaged liver cells. Clinical studies have confirmed the usefulness of standardized milk thistle extracts in cases of liver intoxication, cirrhosis and other chronic liver diseases related to alcohol abuse. Several decades ago, silibinin and other components of the silymarin complex were discovered to be beneficial in treating liver damage resulting from the consumption of toxic fungi, such as Amanita phalloides [13]. It has been recently demonstrated that silymarin inhibits the production of leukotriene which explains its anti-inflammatory effect and antibiotic action. Clinical tests confirm the positive effects found in the experimental studies [14].
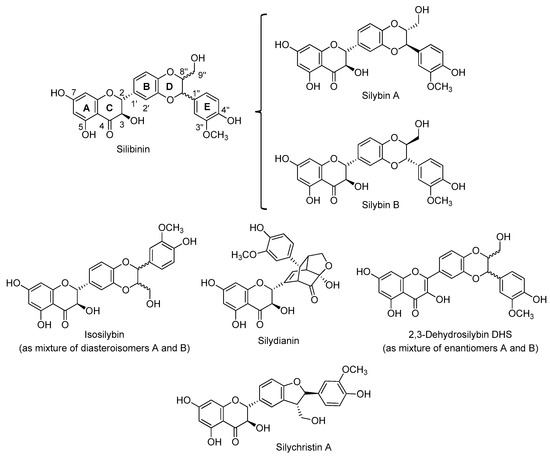
Figure 2.
Main flavonolignans from S. marianum (L. Gaertn. (Asteraceae)).
The major component of silymarin is silibinin, which is an almost equimolar diasteromeric mixture of silybin A and silybin B, easily available due to its high proportion in silymarin (ca 30%). Isolation of both pure diastereomers in multigram quantities can be accomplished by a preparative HPLC method [10] or advanced chemo-enzymatic protocols [15,16]. In the past decade, the medicinal merits of silibinin have been extended to include the potential for preventing and treating various diseases, thanks to properties that include anti-cancer [17], neuroprotective [18,19], antiviral [20] and antifibrotic activities [21].
2. Bi-Flavonolignans: New Promising Synthetic Metabolite Dimers
Bi-flavonolignans are an emerging class of dimeric compounds that unlike bi-flavonoids, which are very widespread in nature, consists of synthetic dimers of some flavonolignans. Synthetic bi-flavonolignans have also been found to exhibit interesting antioxidant activities, at over twice the rate of their natural monomeric units. However, despite these attractive features, synthetic bi-flavonolignans represent a poorly explored compound family within drug discovery.
Even if the number of flavonolignan units available is naturally low, when coupled with the large number of possible permutations in the position and nature of inter-flavonolignan linkage, a considerable structural diversity within the bi-flavonolignan class could be provided. To date, there exist only a few different synthetic approaches and these typically generate compound collections that are based around a very limited range of structures.
Today the only bi-flavonolignans reported in the literature are characterized by two flavonolignan units conjoined through an alkyl, alkoxy or phosphodiester-based linker. The high structural diversity of the silymarin component (Figure 2) makes the design of chemical modifications a difficult but appealing challenge. Below, the synthesis of known bi-flavonolignans will be discussed, focusing on the molecular diversity and their resulting anti-oxidant properties.
2.1. Flavonolignan Dimers Linked by C-C and/or C-O Bridge
The first bi-flavonolignans were isolated only ten years ago from Gazek et al. [22,23]. In this paper, the authors reported that the oxidation of natural silibinin in the presence of a stable radical such as DPPH, prevents the evaluation of its radical scavenger mechanism of action due to the formation of complex mixtures of high molecular weight products that are very difficult to separate. In order to reduce the reactivity of natural silibinin, they studied methylated silibinin derivatives.
The methylation to hydroxyl at C-4′′ or C-7 (Figure 3) showed less reactivity than silibinin, about 30 and 80%, respectively. However, silibinin C-4′′ O-methylated only underwent a small slowdown of oxidative processes, giving a mixture of oligomers always too difficult to purify [23]. Instead, using silibinin O-methylated at C-7 and laccase-mediated oxidation with Trametes pubescens, bi-flavonolignans 1 and 2 (Figure 3) in a ratio of about 2:5 and with yields of 9% and 25%, respectively, were obtained [22]. The same products were obtained by an oxidation reaction based on K3Fe(CN)6 [23] with yields of 40 and 4%, respectively. It should be noted that the asymmetric products 1 and 2 were presumably a mixture of four diastereoisomeric products, while the symmetric product 3 was a mixture of three diasteroisomers. Interestingly, no significant results were obtained by applying the same catalyzed laccase reaction to the O-methylated at C-4′′ silibinin (overactive substrate). An extensive theoretical study [24] indicates that the site most susceptible to oxidative attack in the silibinin is the OH at C-4′′, which loses a hydrogen and give rise to a radical with high spin density on the oxygen O-4′′ and on the carbons C-1′′, C-3′′ and C-5′′. The dimerization process at ring E of the silibinin passes through the formation of a phenyl-phenyl link between the two radicals in the ketone-like form, which then undergoes tautomeric transformation to the enol form that is strongly favored by a thermodynamic point of view. The whole process is more facilitated in apolar solvents, since polar ones do not promote the formation of hydrogen bonds that stabilize the dimer form.
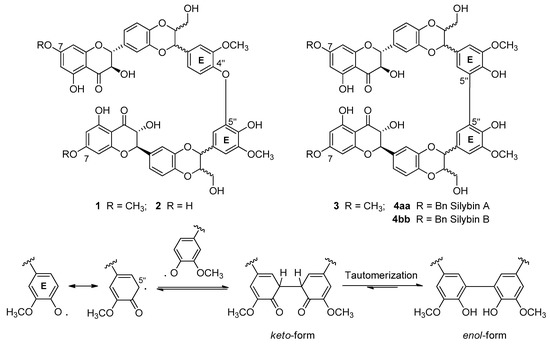
Figure 3.
First bi-flavonolignans from silibinin oxidation and the mechanism of 5′′-5′′ bond formation.
In the case of dehydrosilybin, both conformational and electronic point of views assumes that ring E is very similar to the corresponding ring of silibinin. The hydroxyl group at carbon C-3 is the site with the highest tendency to oxidation, with high spin density localized on O-3 and carbon C-3. If DHS is O-methylated at C-5, C-7, and C-4′′, the corresponding dimer 5 is obtained by DPPH treatment (Figure 4), the formation of which is thermodynamically favored in apolar solvents. It should be noted that the formation of the bond does not follow a tautomeric reorganization, but ring C of one of the two units, which loses flatness and has a simple bond between positions C-2 and C-3. Presumably, the reaction gives a mixture of diastereoisomers which differ in the configuration to the chiral centers C-2 and C-3 of the lower part, instead having configurations both R or both S at the C-7′′ and C-8′′ centers of the two flavonolignanic units (up to sixteen different compounds) [23].
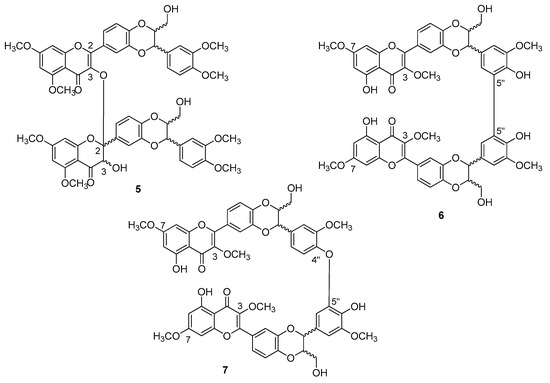
Figure 4.
Bi-flavonolignans from dehydro-silybin oxidation.
The dehydrosilybins methylated to the hydroxyl groups at C-3 and C-7, in the presence of an oxidant such as DPPH, leads to the formation of 6 (a mixture of the two enantiomers and the meso-isomer) and 7 dimers (a mixture of the two pairs of enantiomers), with low yields and dependent on the solvent used. If the hydroxyl groups at C-3 and C-7 are free, a more abundant mixture is obtained but difficult to purify. The formation of such dimers had been correctly predicted by the theoretical study. It is important to emphasize that the dimers are not stabilized by conjugation but by the formation of intramolecular hydrogen bonds, partly counteracted by steric repulsion.
Gavezzotti et al. [25] obtained the dimers 2 starting from silybin A and silybin B, selectively benzylated to the OH group at C-7 (Figure 4), in a reaction catalyzed by a laccase from Trametes versicolor. After de-O-benzylation the dimers 4aa and 4bb were obtained in 11% and 7% yields, respectively. By the same reaction, the silydianin dimer 8 (Figure 5) starting from the unprotected corresponding flavonolignan, and the benzylated silychristine dimer 9 were also obtained [25].
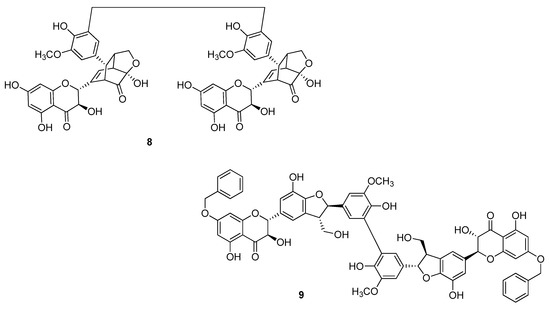
Figure 5.
Bi-flavonolignans from silydianin (8) and silychristine (9) oxidation.
Whereas for the silibinin a behavioural profile has been postulated, including the role of the various hydroxyl groups [26], it is not easy to explain the antioxidant behaviour of dimers and their relative differences. These certainly can’t only depend on a greater number of hydroxy/phenolic groups, but are probably to be found in the three-dimensional structures. In all cases the DPPH test shown a radical scavenger capacity better than the corresponding monomers. Moreover, DHS dimers are always better than silibinin dimers thanks to a double bound at C-2/C-3 which allows a broad conjugation between the rings A, B and C. It is worth noting the property of dimer 2, which has an IC50 value almost five times higher than that of silibinin. Dimer 8 is active more than silydianin itself and almost as much as the Trolox®, a known reference antioxidant [25].
2.2. Flavonolignan Dimers Linked with Different Length Spacers
The first group of flavonolignan dimers, whose monomeric units are linked by a spacer between the monomeric units with different lengths and rigidity was proposed by Vavříková et al. in 2014 [27]. This paper reported the synthesis of bi-flavonolignans with dodecanediol acid esterified with hydroxyl groups at C-9′′ of the pure diastereoisomeric forms of silibinin, silybin A and silybin B (10aa, 10ab and 10bb, Figure 6) and dehydrosilybin 11.
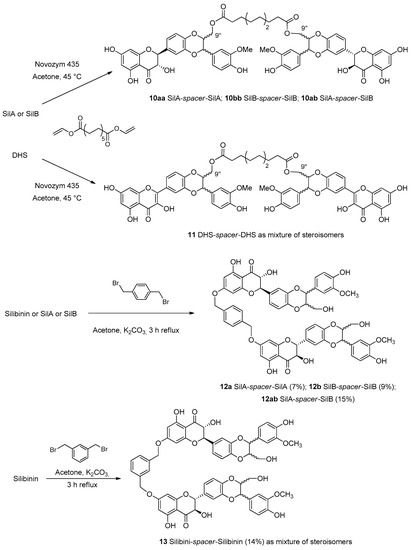
Figure 6.
Lipase-catalyzed synthesis of silybin and dehydro-silybin (DHS) dimers (10–11) and synthesis of silibinin dimers with ether spacer (12–13).
Products were obtained by a transesterification catalyzed by Novozym 435, a lipase B obtained from Candida antarctica immobilized on an acrylic resin. The length of the aliphatic linker between the two units of silybin was optimized: the short aliphatic chain did not allow the linkage of two monomeric units. On the other hand, by taking advantage of the significant higher reactivity of the OH group in the position C-7 through chemical synthesis, new dimers were prepared.
Classical reaction with p- or m-xylylene dibromide in the presence of K2CO3 was used to obtain dimers 12 and 13 with a more rigid xylenyl linker. Redox behavior and cytotoxicity on human umbilical vein endothelial cells, normal human adult keratinocytes, mouse fibroblasts (BALB/c 3T3) and human liver hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines (HepG2) were evaluated. In particular, the results obtained by DPPH and inhibition of microsomal lipoperoxidation assays reported that silybin dimers showed better activity than the monomers, on the contrary, the 2,3-dehydrosilybin dimer 11 presented weaker antioxidant/antilipoperoxidant activity than its monomer (DHS). Conversely, regarding the cytotoxicity aspect, the silybin dimers were more cytotoxic than the parent compound. Instead, the 2,3-dehydrosilybin dimer showed weaker cytotoxicity than the monomer [27].
Recently, a new family of flavonolignan dimers has been proposed by Romanucci et al. [28]: Phosphate-Linked Silibinin dimers (PLSd). Inspired by oligoflavonoid structures [29] and exploiting phosphoramidite chemistry [30,31,32,33], they reported an efficient synthetic strategy to obtain new silibinin dimers in which the monomeric units are linked through phosphodiester bonds (Figure 7).
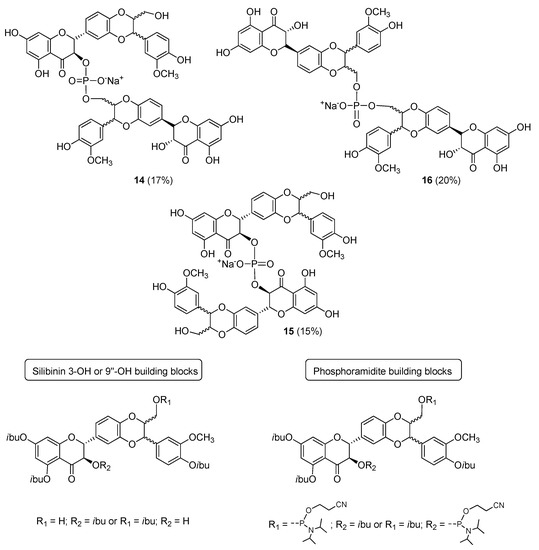
Figure 7.
Phosphate-Linked Silibinin dimers (PLSd) and building blocks useful for their synthesis.
Exploiting the selective protection of the hydroxyl groups of silibinin [34,35], the suitable building blocks (Figure 7) were synthesized in good yields. Silibinin 3-OH or 9′′-OH compounds were coupled with phosphoramidites building blocks in three different combinations, using 0.45 M DCI as the activator. After the oxidative treatment, deprotection from protecting groups and RP-18 HPLC analyses and purification, the products were converted into the corresponding sodium salts leading to the phosphodiester derivatives 14–16 (20%) in good yields (15–20%). PLSd have a good water solubility (more than 20 mgL−1) under circumneutral pH values, whereas the silibinin was found to be very poorly soluble (less than 0.4 mgL−1). Their antioxidant properties were evaluated by different approaches and preliminary antioxidant tests (DPPH test [36,37]) showed a pronounced increase in the activity of the dimers compared to to the silibinin. The anti-oxidant behavior of dimers 14–16 were also investigated towards two different ROS, 1O2 and OH radical. The ability to scavenge 1O2 in H2O was tested. Despite a similar reactivity for both dimers and silibinin, a higher reactivity towards the OH radical (about twice) was estimated for the dimers 14 and 16 with respect to the silibinin with a second order rate constant major than 1.5 × 1010 M−1·s−1. A value very similar to that reported for a known potent antioxidant as quercetin. The PLSd showed a very low toxicity towards HepG2 cells (even for long exposure times). The cytoprotective effect was evaluated on HepG2 cells and using the DCFH-DCF assay where the oxidative stress was carried out by Xanthine/Xanthine oxidase (X/XO) system. All the dimers showed a strong ability to scavenge most of the free radicals generated by X/XO on HepG2 cells and in all cases more efficiently than silibinin [29].
3. Conclusions
Dimer or oligomer molecules often exhibit enhanced biological activity relative to the simple monomer units and their pharmacokinetic parameters are improved [38,39]. Sometimes, an entirely new biological entity is created by dimerization or oligomerization of different building blocks [40,41,42,43,44]. Contrary to many flavonoids that exist naturally as dimer forms, the flavonolignan dimers are only synthetic. The source of flavonolignan monomeric units is the milk thistle Silybum marianum (L. Gaertn. (Asteraceae)), whose seed extract is named silymarin. In the last ten years, the synthetic approaches reported are different and range from chemical to enzymatic strategies. Initially, flavonolignan dimers have been observed in studies to understand the anti-oxidant (or pro-oxidant) activity of the different OH functions of flavonolignans as silibinin, silydianin or silychristin and theoretical studies have been conducted [22,23,24,25,26]. Starting from different O-alkylated (O-methyl or O-benzyl) flavonolignans, the reactivity profile of different OH groups was outlined. The focus of these studies was the reactivity of different OH groups in the presence of stable radical or enzymatic conditions and consequently, biological screening was not accomplished for dimers obtained.
In 2014, Vavříková et al. [27] reported the chemo-enzymatic synthesis of silibinin, silybin A and/or silybin B and 2,3-dehydro-silybin linked by different length spacers. This was one of the first syntheses starting from the two diastereoisomers, silybin A and silybin B [35]. Redox behavior and cytotoxicity on different line cells were evaluated and, in general, silibinin dimers showed better activity than the monomers, although the 2,3-dehydrosilybin dimer showed weaker antioxidant activity than its monomer. Conversely, the silibinin dimers were more cytotoxic than the parent compound. Instead, the 2,3-dehydrosilybin dimer showed weaker cytotoxicity than the monomer. It was recently reported that using inspiration from oligoflavonoid structures and the exploitation of phosphoramidite chemistry, resulted in an efficient synthetic strategy to obtain new silibinin dimers in which the monomeric units are linked through phosphodiester bonds: the Phosphate-Linked Silibinin dimers (PLSd) [28]. New dimers (PLSd) presented a good water solubility (more than 20 mg·L−1) under circumneutral pH values, whereas the silibinin was found to be poorly soluble (less than 0.4 mg·L−1). All dimers showed a strong ability to scavenge most of the radicals more efficiently than silibinin as well as a very low toxicity towards HepG2 cells (even for long exposure times). The combination of high antioxidant activity with low toxicity as well as their good water solubility, make the PLSd promising synthetic metabolites in the large class of polyphenols.
These last two strategies offer the possibility to design dimers with a high molecular diversity, both in the nature of the building blocks and the length of the spacer.
Funding
We acknowledge AIPRAS Onlus (Associazione Italiana per la Promozione delle Ricerche sull’Ambiente e la Salute umana) for grants in support of this investigation.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
References
- Vue, B.; Chen, Q.H. The potential of flavonolignans in prostate cancer management. Curr. Med. Chem. 2016, 23, 3925–3950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelter, A.; Haensel, R. The structure of silybin (Silybum substance E6), the first flavonolignan. Tetrahedron Lett. 1968, 25, 2911–2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della Greca, M.; Mancino, A.; Previtera, L.; Zarrelli, A.; Zuppolini, S. Lignans from Phillyrea angustifolia L. Phytochem. Lett. 2011, 4, 118–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorentino, A.; DellaGreca, M.; D’Abrosca, B.; Oriano, P.; Golino, A.; Izzo, A.; Zarrelli, A.; Monaco, P. Lignans, neolignans and sesquilignans from Cestrum parqui l’Her. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2007, 35, 392–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutillo, F.; DellaGreca, M.; Gionti, M.; Previtera, L.; Zarrelli, A. Phenols and lignans from Chenopodium album. Phytochem. Anal. 2006, 17, 344–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Della Greca, M.; Previtera, L.; Purcaro, R.; Zarrelli, A. Cinnamic acid amides and lignanamides from Aptenia cordifolia. Tetrahedron 2006, 62, 2877–2882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gažák, R.; Walterová, D.; Křen, V. Silybin and Silymarin - New and Emerging Applications in Medicine. Curr. Med. Chem. 2007, 14, 315–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Csupor, D.; Csorba, A.; Hohmann, J. Recent advances in the analysis of flavonolignans of Silybum marianum. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2016, 130, 301–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bijak, M. Silybin, a Major Bioactive Component of Milk Thistle (Silybum marianum L. Gaernt.)—Chemistry, Bioavailability and Metabolism. Molecules 2017, 22, 1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Fabio, G.; Romanucci, V.; Di Marino, C.; De Napoli, L.; Zarrelli, A. A Rapid and simple chromatographic separation of diastereomers of silibinin and their oxidation to produce 2,3-dehydrosilybin enantiomers in an optically pure form. Planta Med. 2013, 79, 1077–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Fabio, G.; Romanucci, V.; De Nisco, M.; Pedatella, S.; Di Marino, C.; Zarrelli, A. Microwave-assisted oxidation of silibinin: A simple and preparative method for the synthesis of improved radical scavengers. Tetrahedron Lett. 2013, 54, 6279–6282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abenavoli, L.; Capasso, R.; Milic, N.; Capasso, F. Milk thistle in liver diseases: Past, present, future. Phytother. Res. 2010, 24, 1423–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahin, A.; Arici, M.A.; Yilmaz, Y.; Kalkan, S.; Durmus, N.; Ergur, B.U.; Yakut, A.; Atabey, N.; Tuncok, Y. A Comparison of the Effectiveness of Silibinin and Resveratrol in Preventing Alpha-amanitin-induced Hepatotoxicity. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2018, 122, 633–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rakelly de Oliveira, D.; Relison Tintino, S.; Morais Braga, M.F.B.; Boligon, A.A.; Linde Athayde, M.; Douglas Melo Coutinho, H.; Alencar de Menezes, I.R.; Fachinetto, R. In vitro antimicrobial and modulatory activity of the natural products silymarin and silibinin. BioMed. Res. Int. 2015, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monti, D.; Gažák, R.; Marhol, P.; Biedermann, D.; Purchartová, K.; Fedrigo, M.; Riva, S.; Křen, V. Enzymatic Kinetic Resolution of Silybin Diastereoisomers. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 613–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gažák, R.; Marhol, P.; Purchartová, K.; Monti, D.; Biedermann, D.; Riva, S.; Cvak, L.; Křen, V. Large-scale separation of silybin diastereoisomers using lipases. Process Biochem. 2010, 45, 1657–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deep, G.; Agarwal, R. Antimetastatic efficacy of silibinin: Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic potential against cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2010, 29, 447–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.H.; Kim, S.H.; Yang, W.M. Mechanisms of action of phytochemicals from medicinal herbs in the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Planta Med. 2014, 80, 1249–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sciacca, M.F.M.; Romanucci, V.; Zarrelli, A.; Monaco, I.; Lolicato, F.; Spinella, N.; Galati, C.; Grasso, G.; D’Urso, L.; Romeo, M.; et al. Inhibition of Aβ Amyloid growth and toxicity by silybins: The crucial role of stereochemistry. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2017, 16, 1767–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McClure, J.; Lovelace, E.S.; Elahi, S.; Maurice, N.J.; Wagoner, J.; Dragavon, J.; Mittler, J.E.; Kraft, Z.; Stamatatos, L.; Horton, H.; et al. Silibinin inhibits HIV-1 infection by reducing cellular activation and proliferation. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e41832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loguercio, C.; Festi, D. Silybin and the liver: From basic research to clinical practice. World J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 17, 2288–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gažák, R.; Sedmera, P.; Marzorati, M.; Riva, S.; Křen, V. Laccase-mediated dimerization of the flavonolignan silybin. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2008, 50, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gažák, R.; Sedmera, P.; Vrbacký, M.; Vostálová, J.; Drahota, Z.; Marhol, P.; Valterova, D.; Křen, V. Molecular mechanisms of silybin and 2,3-dehydrosilybin antiradical activity-role of individual hydroxyl groups. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2009, 46, 745–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Košinová, P.; Gažák, R.; Duroux, J.L.; Lazzaroni, R.; Křen, V.; Assfeld, X.; Trouillas, P. Dimerisation Process of Silybin-Type Flavonolignans: Insights from Theory. ChemPhysChem 2011, 12, 1135–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gavezzotti, P.; Vavříková, E.; Valentová, K.; Fronza, G.; Kudanga, T.; Kuzma, M.; Riva, S.; Biedermann, D.; Křen, V. Enzymatic oxidative dimerization of silymarin flavonolignans. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2014, 109, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trouillas, P.; Marsal, P.; Svobodová, A.; Vostálová, J.; Gažák, R.; Hrbáč, J.; Sedmera, P.; Křen, V.; Lazzaroni, R.; Duroux, J.; Walterová, D. Mechanism of the Antioxidant Action of Silybin and 2,3-Dehydrosilybin Flavonolignans: A Joint Experimental and Theoretical Study. J. Phys. Chem. A 2008, 112, 1054–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vavříková, E.; Vacek, J.; Valentová, K.; Marhol, P.; Ulrichová, J.; Kuzma, M.; Křen, V. Chemo-enzymatic synthesis of silybin and 2,3-dehydrosilybin dimers. Molecules 2014, 19, 4115–4134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanucci, V.; Gravante, R.; Cimafonte, M.; Marino, C.D.; Mailhot, G.; Brigante, M.; Zarrelli, A.; Di Fabio, G. Phosphate-Linked Silibinin Dimers (PLSd): New Promising Modified Metabolites. Molecules 2017, 22, 1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quideau, S.; Deffieux, D.; Douat-Casassus, C.; Pouységu, L. Plant polyphenols: Chemical properties, biological activities, and synthesis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 586–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanucci, V.; Zarrelli, A.; Guaragna, A.; Di Marino, C.; Di Fabio, G. New phosphorylating reagents for deoxyribonucleosides and oligonucleotides. Tetrahedron Lett. 2017, 58, 1227–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarrelli, A.; Romanucci, V.; Della Greca, M.; De Napoli, L.; Previtera, L.; Di Fabio, G. New silybin scaffold for chemical diversification: Synthesis of novel 23-phosphodiester silybin conjugates. Synlett 2013, 24, 45–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanucci, V.; Agarwal, C.; Agarwal, R.; Pannecouque, C.; Iuliano, M.; De Tommaso, G.; Caruso, T.; Di Fabio, G.; Zarrelli, A. Silibinin phosphodiester glyco-conjugates: Synthesis, redox behaviour and biological investigations. Bioorg. Chem. 2018, 77, 349–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarrelli, A.; Romanucci, V.; Tuccillo, C.; Federico, A.; Loguercio, C.; Gravante, R.; Di Fabio, G. New silibinin glyco-conjugates: Synthesis and evaluation of antioxidant properties. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 24, 5147–5149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarrelli, A.; Sgambato, A.; Petito, V.; De Napoli, L.; Previtera, L.; Di Fabio, G. New C-23 modified of silybin and 2,3-dehydrosilybin: Synthesis and preliminary evaluation of antioxidant properties. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2011, 21, 4389–4392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarrelli, A.; Romanucci, V.; De Napoli, L.; Previtera, L.; Di Fabio, G. Synthesis of new silybin derivatives and evaluation of their antioxidant properties. Helv. Chim. Acta 2015, 98, 399–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barontini, M.; Bernini, R.; Carastro, R.; Gentili, P.; Romani, A. Synthesis and DPPH radical scavenging activity of novel compounds obtained from tyrosol and cinnamic acid derivatives. New J. Chem. 2014, 38, 809–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernini, R.; Montani, M.S.; Merendino, N.; Romani, A.; Velotti, F. Hydroxytyrosol-derived compounds: A basis for the creation of new pharmacological agents for cancer prevention and therapy. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 9089–9107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berube, G. Natural and synthetic biologically active dimeric molecules: Anticancer agents, anti-Hiv agents, steroid derivatives and opioid antagonists. Curr. Med. Chem. 2006, 13, 131–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mott, B.T.; Tripathi, A.; Siegler, M.A.; Moore, C.D.; Sullivan, D.J.; Posner, G.H. Synthesis and antimalarial efficacy of two-carbon-linked, artemisinin-derived trioxane dimers in combination with known antimalarial drugs. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 2630–2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenett-Siems, K.; Kohler, I.; Kraft, C.; Pertz, H.H.; Kren, V.; Fiserova, A.; Kuzma, M.; Ulrichova, J.; Bienzle, U.; Eich, E. In vitro antiplasmodial activities of semisynthetic N,N′-spacer-linked oligomeric ergolines. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2004, 12, 817–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, K.F.; Zhao, Y.Z.; Burkett, B.A.; Wong, I.L.K.; Chow, L.M.C.; Chan, T.H. Flavonoid dimers as bivalent modulators for P-glycoprotein-based multidrug resistance: Synthetic apigenin homodimers linked with defined-length poly(ethylene glycol) spacers increase drug retention and enhance chemosensitivity in resistant cancer cells. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 6742–6759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Arnatt, C.K.; Li, G.; Haney, K.M.; Ding, D.; Jacob, J.C.; Selley, D.E.; Zhang, Y. Design and synthesis of a bivalent ligand to explore the putative heterodimerization of the mu opioid receptor and the chemokine receptor CCR5. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2012, 10, 2633–2646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nimczick, M.; Decker, M. New approaches in the design and development of cannabinoid receptor ligands: multifunctional and bivalent compounds. ChemMedChem. 2015, 10, 773–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dvoracsko, S.; Stefanucci, A.; Novellino, E.; Mollica, A. The design of multitarget ligands for chronic and neuropathic pain. Future Med. Chem. 2015, 7, 2469–2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).